Resistance Patterns Associated with HCV NS5A Inhibitors Provide Limited Insight into Drug Binding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure and Function of NS5A
3. Possible Mechanisms of NS5A Inhibitors
4. Resistance to HCV NS5A Inhibitors in vitro and in vivo
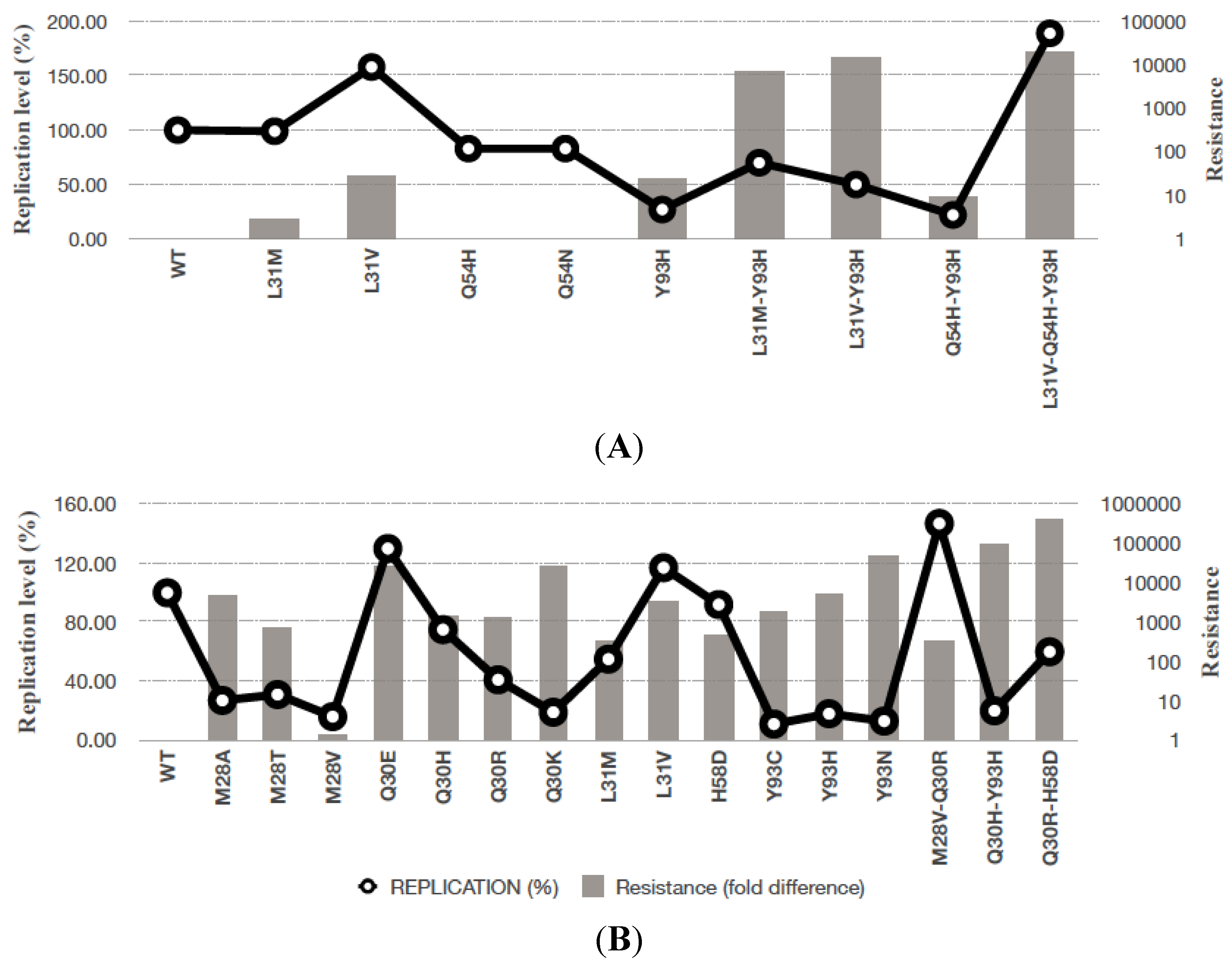
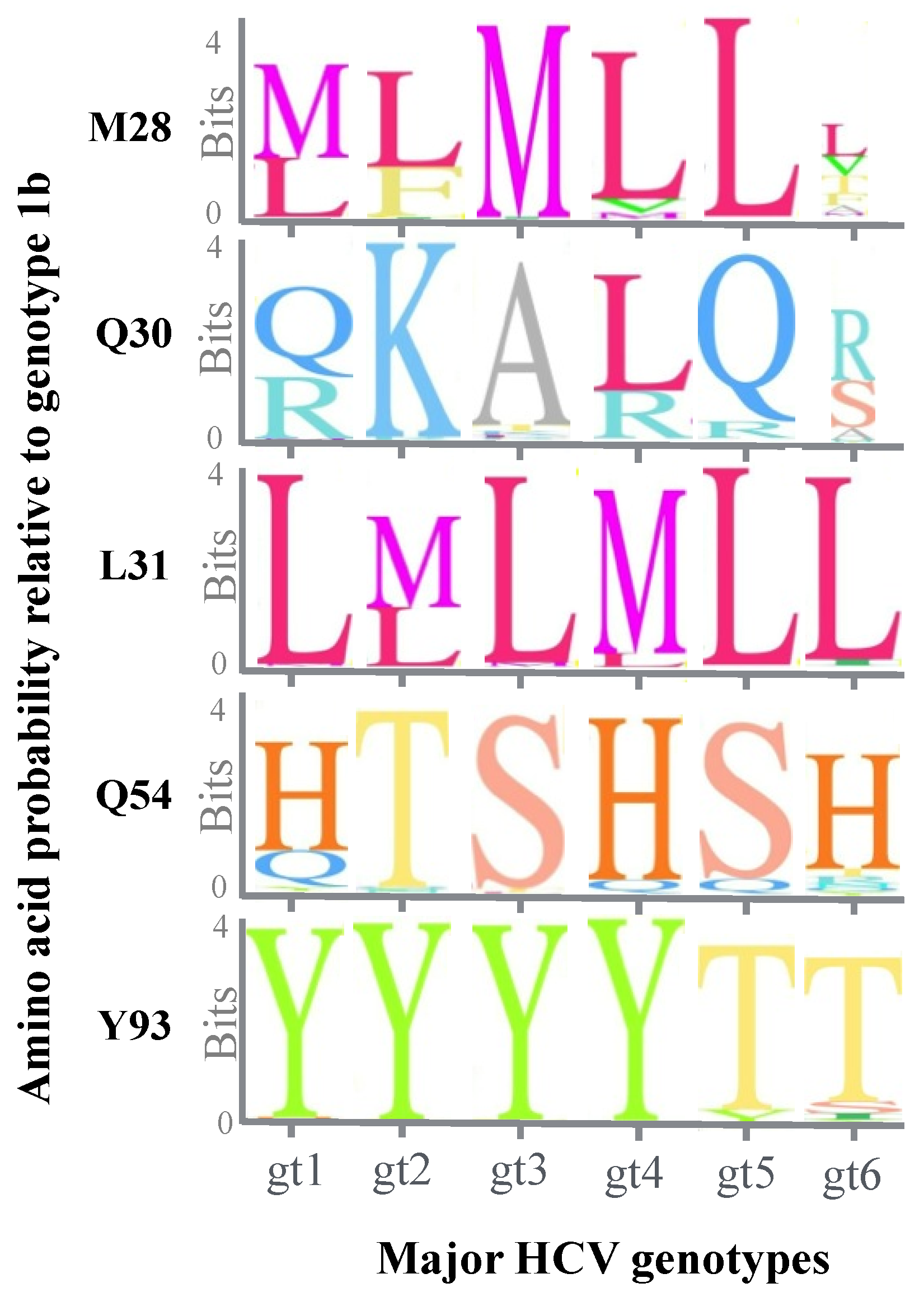
5. Effect of Genotypic Variation on the Efficacy of NS5A Inhibitors
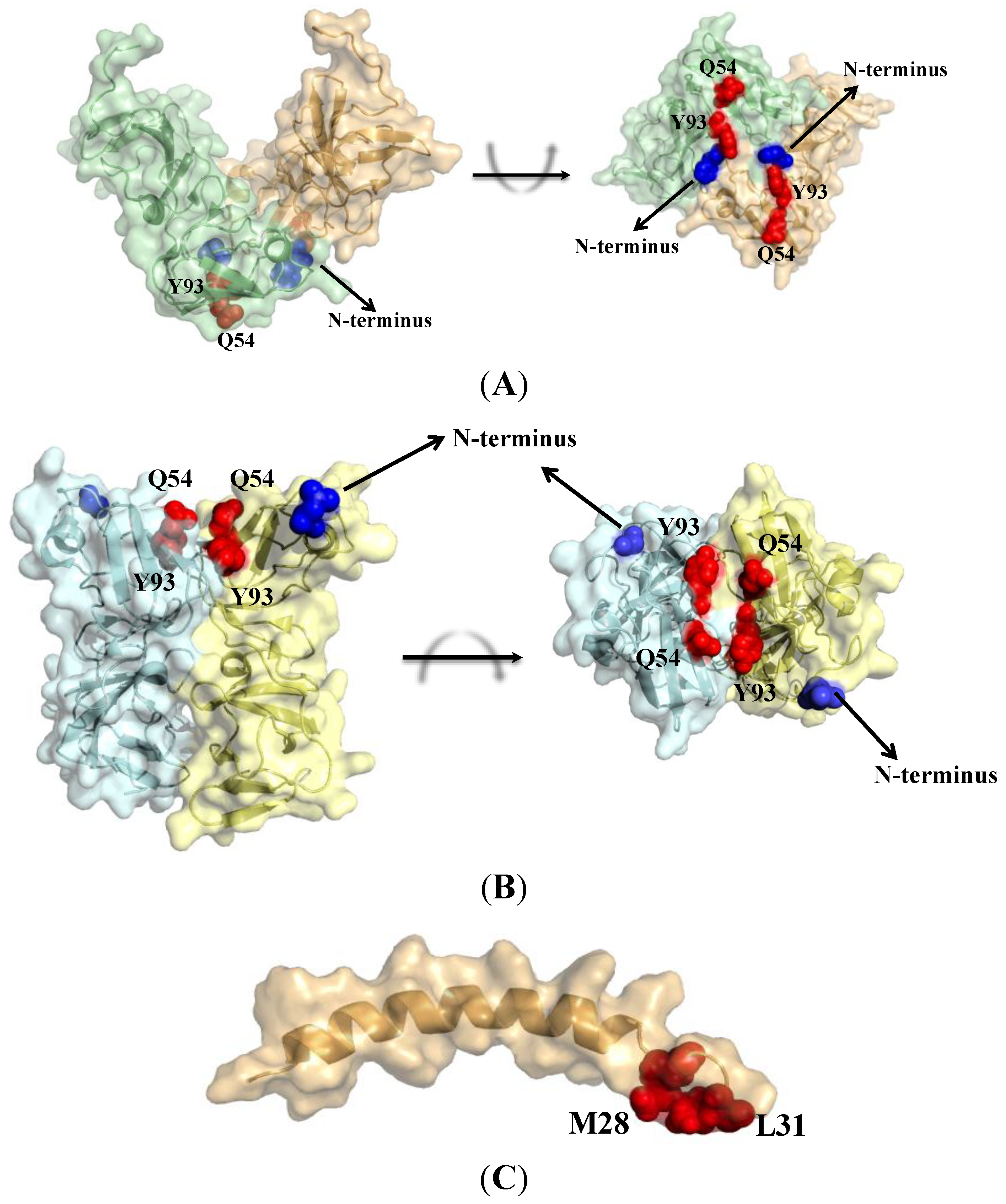
6. Resistance Mutations Define Binding
7. Barriers to the Selection of Drug Resistance
8. Conclusions
| NS5A Inhibitor | Clinical Trial | Drug Combination | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daclatasvir (BMS-790052) | Phase III completed | +Asunaprevir | Submitted for FDA approval [59,60] |
| +polymerase inhibitor (Sofosbuvir or VX-135) ± Protease inhibitor ± Ribavirin | Genotypes 1, 3, 4 Under investigation for use in HCV-HIV co-infected cohorts [61,62,63,64,65] | ||
| Ledipasvir (GS-5885) | Phase III completed | +Sofosbuvir | Approved by FDA for genotype 1 [66,67] |
| GS-5816 | Phase III | +Sofosbuvir | Genotypes 1,2,3,4,5,6 [68,69] |
| ACH-3102 | Phase II completed | +Sofosbuvir | Genotype 1 (≤8 weeks treatment) [70] |
| Samatasvir (IDX-719) | Phase II | +Simeprevir (protease inhibitor) ± TMC647055 (polymerase inhibitor) | Genotype 1, 4, 6 [71] |
| GSK2336805 | Phase II | + Simeprevir + PEG-IFN + Ribavirin | Genotype 1 or 4 [72] |
| PPI-668 | Phase II | + Faldeprevir (protease inhibitor) + B1207127 (polymerase inhibitor) | [73] |
| PPI-461 | Phase Ib completed | - | Genotype 1 [74] |
| TD-6450 | Phase I | - | Potent against genotype 1a [75,76] |
| JNJ-47910382 | Phase I | - | Asian genotype-1 [77] |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- World Health Organization. WHO hepatitis c fact sheet no 164. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/ (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Flores, A.; Marrero, J.A. Emerging trends in hepatocellular carcinoma: Focus on diagnosis and therapeutics. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2014, 8, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.P.; Krajden, M.; Bilodeau, M.; Kaita, K.; Marotta, P.; Peltekian, K.; Ramji, A.; Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Sherman, M. Burden of disease and cost of chronic hepatitis c infection in canada. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 28, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, B.A.; Liu, R.; Lahser, F.; Agrawal, S.; Belanger, B.; Butkiewicz, N.; Chase, R.; Gheyas, F.; Hart, A.; Hesk, D.; et al. Sch 503034, a mechanism-based inhibitor of hepatitis c virus ns3 protease, suppresses polyprotein maturation and enhances the antiviral activity of alpha interferon in replicon cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H.; Hayashi, N.; Izumi, N.; Okanoue, T.; Tsubouchi, H.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Kato, M.; Rito, K.; Komada, Y.; Seto, C.; et al. Simeprevir (tmc435) once daily with peginterferon-alpha-2b and ribavirin in patients with genotype 1 hepatitis c virus infection: The concerto-4 study. Hepatol. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves new treatment for hepatitis c virus. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm376449.htm (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Approval of sovaldi (sofosbuvir) tablets for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/forconsumers/byaudience/forpatientadvocates/ucm377920.htm (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Gane, E.J.; Stedman, C.A.; Hyland, R.H.; Ding, X.; Svarovskaia, E.; Symonds, W.T.; Hindes, R.G.; Berrey, M.M. Nucleotide polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for hepatitis c. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Nettles, R.E.; Belema, M.; Snyder, L.B.; Nguyen, V.N.; Fridell, R.A.; Serrano-Wu, M.H.; Langley, D.R.; Sun, J.H.; O’Boyle, D.R., 2nd; et al. Chemical genetics strategy identifies an hcv ns5a inhibitor with a potent clinical effect. Nature 2010, 465, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Huang, L.; Cordek, D.G.; Vaughan, R.; Reynolds, S.L.; Kihara, G.; Raney, K.D.; Kao, C.C.; Cameron, C.E. Hepatitis c virus nonstructural protein 5a: Biochemical characterization of a novel structural class of RNA-binding proteins. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12480–12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanji, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Satoh, S.; Shimotohno, K. Phosphorylation of hepatitis c virus-encoded nonstructural protein ns5a. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3980–3986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordek, D.G.; Croom-Perez, T.J.; Hwang, J.; Hargittai, M.R.; Subba-Reddy, C.V.; Han, Q.; Lodeiro, M.F.; Ning, G.; McCrory, T.S.; Arnold, J.J.; et al. Expanding the proteome of an RNA virus by phosphorylation of an intrinsically disordered viral protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24397–24416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Staschke, K.; De Francesco, R.; Tan, S.L. Phosphorylation of hepatitis c virus ns5a nonstructural protein: A new paradigm for phosphorylation-dependent viral RNA replication? Virology 2007, 364, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, S.; Harak, C.; Romero-Brey, I.; Radujkovic, D.; Klein, R.; Ruggieri, A.; Rebhan, I.; Bartenschlager, R.; Lohmann, V. The lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol-4 kinase iii alpha regulates the phosphorylation status of hepatitis c virus ns5a. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penin, F.; Brass, V.; Appel, N.; Ramboarina, S.; Montserret, R.; Ficheux, D.; Blum, H.E.; Bartenschlager, R.; Moradpour, D. Structure and function of the membrane anchor domain of hepatitis c virus nonstructural protein 5a. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40835–40843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Rice, C.M. The ns5a protein of hepatitis c virus is a zinc metalloprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48576–48587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.M.; Langley, D.R.; Garnett, J.A.; Angell, R.; Hedgethorne, K.; Meanwell, N.A.; Matthews, S.J. The crystal structure of ns5a domain 1 from genotype 1a reveals new clues to the mechanism of action for dimeric HCV inhibitors. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, R.A.; Brodsky, O.; Hickey, M.J.; Wells, P.A.; Cronin, C.N. Crystal structure of a novel dimeric form of ns5a domain i protein from hepatitis c virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4395–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Rice, C.M. Structure of the zinc-binding domain of an essential component of the hepatitis c virus replicase. Nature 2005, 435, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanoulle, X.; Badillo, A.; Verdegem, D.; Penin, F.; Lippens, G. The domain 2 of the hcv ns5a protein is intrinsically unstructured. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanoulle, X.; Verdegem, D.; Badillo, A.; Wieruszeski, J.M.; Penin, F.; Lippens, G. Domain 3 of non-structural protein 5a from hepatitis c virus is natively unfolded. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, A.; Harris, M. Hepatitis c virus ns5a: Tales of a promiscuous protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2485–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordek, D.G.; Bechtel, J.T.; Maynard, A.T.; Kazmierski, W.M.; Cameron, C.E. Targeting the ns5a protein of hcv: An emerging option. Drugs Futur. 2011, 36, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chassey, B.; Navratil, V.; Tafforeau, L.; Hiet, M.S.; Aublin-Gex, A.; Agaugue, S.; Meiffren, G.; Pradezynski, F.; Faria, B.F.; Chantier, T.; et al. Hepatitis c virus infection protein network. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosnoblet, C.; Fritzinger, B.; Legrand, D.; Launay, H.; Wieruszeski, J.M.; Lippens, G.; Hanoulle, X. Hepatitis c virus ns5b and host cyclophilin a share a common binding site on ns5a. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44249–44260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelmont, L.; Hanoulle, X.; Chatterji, U.; Berger, C.; Snoeck, J.; Bobardt, M.; Lim, P.; Vliegen, I.; Paeshuyse, J.; Vuagniaux, G.; et al. Deb025 (alisporivir) inhibits hepatitis c virus replication by preventing a cyclophilin a induced cis-trans isomerisation in domain ii of ns5a. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Boyle Ii, D.R.; Sun, J.H.; Nower, P.T.; Lemm, J.A.; Fridell, R.A.; Wang, C.; Romine, J.L.; Belema, M.; Nguyen, V.N.; Laurent, D.R.; et al. Characterizations of HCV NS5a replication complex inhibitors. Virology 2013, 444, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascher, D.B.; Wielens, J.; Nero, T.L.; Doughty, L.; Morton, C.J.; Parker, M.W. Potent hepatitis c inhibitors bind directly to NS5a and reduce its affinity for RNA. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Lemm, J.A.; O’Boyle, D.R., 2nd; Sun, J.H.; Nower, P.T.; Nguyen, V.; Hamann, L.G.; Snyder, L.B.; Deon, D.H.; Ruediger, E.; et al. The effects of NS5a inhibitors on NS5a phosphorylation, polyprotein processing and localization. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Romero-Brey, I.; Radujkovic, D.; Terreux, R.; Zayas, M.; Paul, D.; Harak, C.; Hoppe, S.; Gao, M.; Penin, F.; et al. Daclatasvir-like inhibitors of NS5a block early biogenesis of hepatitis c virus-induced membranous replication factories, independent of RNA replication. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1094–1105.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGivern, D.R.; Masaki, T.; Williford, S.; Ingravallo, P.; Feng, Z.; Lahser, F.; Asante-Appiah, E.; Neddermann, P.; De Francesco, R.; Howe, A.Y.; et al. Kinetic analyses reveal potent and early blockade of hepatitis c virus assembly by NS5a inhibitors. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 453–462.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahari, H.; Cotler, S.J.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. Understanding triphasic HCV decline during treatment in the era of il28b polymorphisms and direct acting antiviral agents via mathematical modeling. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedj, J.; Dahari, H.; Rong, L.; Sansone, N.D.; Nettles, R.E.; Cotler, S.J.; Layden, T.J.; Uprichard, S.L.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling shows that the NS5a inhibitor daclatasvir has two modes of action and yields a shorter estimate of the hepatitis c virus half-life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3991–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridell, R.A.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.H.; O’Boyle, D.R., 2nd; Nower, P.; Valera, L.; Qiu, D.; Roberts, S.; Huang, X.; Kienzle, B.; et al. Genotypic and phenotypic analysis of variants resistant to hepatitis c virus nonstructural protein 5a replication complex inhibitor bms-790052 in humans: In vitro and in vivo correlations. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, J.H.; O’Boyle, D.R., 2nd; Nower, P.; Valera, L.; Roberts, S.; Fridell, R.A.; Gao, M. Persistence of resistant variants in hepatitis c virus-infected patients treated with the NS5a replication complex inhibitor daclatasvir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridell, R.A.; Qiu, D.; Wang, C.; Valera, L.; Gao, M. Resistance analysis of the hepatitis c virus NS5a inhibitor bms-790052 in an in vitro replicon system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3641–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemm, J.A.; O’Boyle, D., 2nd; Liu, M.; Nower, P.T.; Colonno, R.; Deshpande, M.S.; Snyder, L.B.; Martin, S.W.; St Laurent, D.R.; Serrano-Wu, M.H.; et al. Identification of hepatitis c virus NS5a inhibitors. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, J.J.; Nettles, J.H.; Amblard, F.; Hurwitz, S.J.; Bassit, L.; Stanton, R.A.; Ehteshami, M.; Schinazi, R.F. Approaches to hepatitis c treatment and cure using NS5a inhibitors. Infect. Drug Resist. 2014, 7, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.J.; Gallay, P.A. Hepatitis c NS5a protein: Two drug targets within the same protein with different mechanisms of resistance. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8C, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, U.; Garcia-Rivera, J.A.; Baugh, J.; Gawlik, K.; Wong, K.A.; Zhong, W.; Brass, C.A.; Naoumov, N.V.; Gallay, P.A. The combination of alisporivir plus an NS5a inhibitor provides additive to synergistic anti-hepatitis c virus activity without detectable cross-resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallay, P.A.; Lin, K. Profile of alisporivir and its potential in the treatment of hepatitis c. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevaliez, S.; Hezode, C. Il28b polymorphisms and chronic hepatitis c. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2010, 34, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pageaux, G.P.; Hilleret, M.N.; Garrigues, V.; Bismuth, M.; Audin-Mamlouk, H.; Zarski, J.P.; Mourad, G. Pegylated interferon-alpha-based treatment for chronic hepatitis c in renal transplant recipients: An open pilot study. Transpl. Int. 2009, 22, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnock-Jones, K. Boceprevir: A review of its use in the management of genotype 1 chronic hepatitis c. Drugs 2012, 72, 2431–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.M. Telaprevir: A review of its use in the management of genotype 1 chronic hepatitis c. Drugs 2012, 72, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheel, T.K.; Gottwein, J.M.; Mikkelsen, L.S.; Jensen, T.B.; Bukh, J. Recombinant HCV variants with NS5a from genotypes 1-7 have different sensitivities to an NS5a inhibitor but not interferon-alpha. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jia, L.; O’Boyle, D.R., 2nd; Sun, J.H.; Rigat, K.; Valera, L.; Nower, P.; Huang, X.; Kienzle, B.; Roberts, S.; et al. Comparison of daclatasvir resistance barrier on NS5a from HCV genotypes 1–6: Implications for cross-genotype activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5155–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridell, R.A.; Qiu, D.; Valera, L.; Wang, C.; Rose, R.E.; Gao, M. Distinct functions of NS5a in hepatitis c virus RNA replication uncovered by studies with the NS5a inhibitor bms-790052. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7312–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Valera, L.; Jia, L.; Kirk, M.J.; Gao, M.; Fridell, R.A. In vitro activity of daclatasvir on hepatitis c virus genotype 3 NS5a. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jia, L.; Huang, H.; Qiu, D.; Valera, L.; Huang, X.; Sun, J.H.; Nower, P.T.; O’Boyle, D.R., 2nd; Gao, M.; et al. In vitro activity of bms-790052 on hepatitis c virus genotype 4 NS5a. ns5a. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1588–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Geneious Basic, version 5.5.8; Biomatters Ltd: Auckland, New Zealand, 2012.
- Coburn, C.A.; Meinke, P.T.; Chang, W.; Fandozzi, C.M.; Graham, D.J.; Hu, B.; Huang, Q.; Kargman, S.; Kozlowski, J.; Liu, R.; et al. Discovery of mk-8742: An HCV NS5a inhibitor with broad genotype activity. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, K.H.; Anwar-Mohamed, A.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Robins, M.J.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Houghton, M. A refined model of the HCV NS5a protein bound to daclatasvir explains drug-resistant mutations and activity against divergent genotypes. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Olson, C.A.; Wu, N.C.; Ke, R.; Loverdo, C.; Chu, V.; Truong, S.; Remenyi, R.; Chen, Z.; Du, Y.; et al. A quantitative high-resolution genetic profile rapidly identifies sequence determinants of hepatitis c viral fitness and drug sensitivity. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotte, M. The distinct contributions of fitness and genetic barrier to the development of antiviral drug resistance. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powdrill, M.H.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Kozak, R.A.; Russell, R.S.; Martin, R.; Svarovskaia, E.S.; Mo, H.; Kouyos, R.D.; Gotte, M. Contribution of a mutational bias in hepatitis c virus replication to the genetic barrier in the development of drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20509–20513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everson, G.T.; Sims, K.D.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Hezode, C.; Lawitz, E.; Bourliere, M.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Rustgi, V.; Schwartz, H.; Tatum, H.; et al. Efficacy of an interferon- and ribavirin-free regimen of daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and bms-791325 in treatment-naive patients with HCV genotype 1 infection. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulkowski, M.S.; Gardiner, D.F.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Reddy, K.R.; Hassanein, T.; Jacobson, I.; Lawitz, E.; Lok, A.S.; Hinestrosa, F.; Thuluvath, P.J.; et al. Daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir for previously treated or untreated chronic HCV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bristol-myers squibb submits ndas for daclatasvir and asunaprevir to US FDA for the treatment of hepatitis c. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. A phase 3 study with asunaprevir and daclatasvir (dual) for null or partial responders to peginterferon alfa and ribavirin (p/r),intolerant or ineligible to p/r subjects and treatment-naive subjects with chronic hepatitis c genotype 1b infection. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT01581203 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. A phase 3 evaluation of daclatasvir and sofosbuvir in treatment naive and treatment experienced subjects with genotype 3 chronic hepatitis c infection. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02032901 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. A phase 3 evaluation of daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir in treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced chronic hepatitis c (genotype 1,2,3,4,5,or 6) subjects coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02032888 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. A phase 3 evaluation of daclatasvir, sofosbuvir, and ribavirin in genotype 1-6 chronic hepatitis c infection subjects with cirrhosis who may require future liver transplant and subjects post-liver transplant. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02032875 (accessed on 20 August 2014).
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. Short duration combination therapy with daclatasvir, asunaprevir, BMS-791325 and sofosbuvir in subjects infected with chronic hepatitis-c (FOURWARD study). Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02175966 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Janssen Research & Development, LLC. A phase 2 open-label study to investigate the efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of 12 weeks of treatment with simeprevir, daclatasvir and sofosbuvir, followed by a 5-year post-treatment long-term follow-up, in treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced subjects with chronic hepatitis c virus genotype 1 or 4 infection and decompensated liver disease. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02262728 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first combination pill to treat hepatitis c. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm418365.htm (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Afdhal, N.; Zeuzem, S.; Kwo, P.; Chojkier, M.; Gitlin, N.; Puoti, M.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zarski, J.P.; Agarwal, K.; Buggisch, P.; et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilead Sciences. A phase 2, multicenter, randomized, open-label study to investigate the safety and efficacy of sofosbuvir + gs-5816 for 12 weeks in treatment-naive subjects with chronic HCV infection. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01858766 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Gilead Sciences. A phase 2, multicenter, randomized, open-label study to investigate the safety and efficacy of sofosbuvir + gs-5816 for 12 weeks in treatment-experienced subjects with chronic HCV infection. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01909804 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Achillion Pharmaceuticals. Achillion reports HCV pipeline progress and outlines 2014 HCV milestones. 2014. Available online: http://ir.achillion.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=818759 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Idenix Pharmaceuticals. A randomized study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of idx719 in combinations with simeprevir and/or tmc647055/ritonavir with or without ribavirin for 12 weeks in subjects with chronic hepatitis c infection. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01852604 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- GlaxoSmithKline. Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to assess safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics (pk) of gsk2336805 in combination with peginterferon and ribavirin in treatment-naive chronic hepatitis c subjects with hepatitis c virus genotypes 1 or 4. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01439373 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Presidio Pharmaceuticals Inc. A phase 2a study of ppi-668 in combination with bi 207127 and faldaprevir, with and without ribavirin, in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis c (HCV genotype 1a). Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01859962 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Presidio Pharmaceuticals Inc. A phase 1b study to assess the safety, antiviral efficacy and pharmacokinetics of ppi-461 in patients with HCV genotype-1 infection. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01247194 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Theravance Biopharma Antibiotics Inc. Theravance Biopharma R & D, I. A double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic, and antiviral activity of td-6450, a NS5a inhibitor, in treatment naïve subjects with genotype 1, 2 or 3 chronic hepatitis c virus (HCV). Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02116543 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Budman, J.; Waltman, C.E.; Krey-Epstein, W.; Chang, R.; Smith, S.; Amrite, A.; Mammen, M.; McKinnell, M. Td-6450, a heterodimeric HCV NS5a inhibitor with a high barrier to resistance and pan-genotypic potency. In Proceedings of HEPDART 2013: Frontiers in Drug Development for Viral Hepatitis, Conference Reports for NATAP, Big Island, HI, USA, 8–12 December 2013.
- Janssen R&D Ireland. A phase ib, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in asian genotype 1 chronic HCV-infected subjects to determine the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and antiviral activity of repeated doses of jnj-47910382 given in different doses and dose regimens. Available online: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01586325 (accessed on 3 November 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Issur, M.; Götte, M. Resistance Patterns Associated with HCV NS5A Inhibitors Provide Limited Insight into Drug Binding. Viruses 2014, 6, 4227-4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114227
Issur M, Götte M. Resistance Patterns Associated with HCV NS5A Inhibitors Provide Limited Insight into Drug Binding. Viruses. 2014; 6(11):4227-4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114227
Chicago/Turabian StyleIssur, Moheshwarnath, and Matthias Götte. 2014. "Resistance Patterns Associated with HCV NS5A Inhibitors Provide Limited Insight into Drug Binding" Viruses 6, no. 11: 4227-4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114227
APA StyleIssur, M., & Götte, M. (2014). Resistance Patterns Associated with HCV NS5A Inhibitors Provide Limited Insight into Drug Binding. Viruses, 6(11), 4227-4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6114227




