Sialic Acid Binding Properties of Soluble Coronavirus Spike (S1) Proteins: Differences between Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and expression of soluble spike proteins

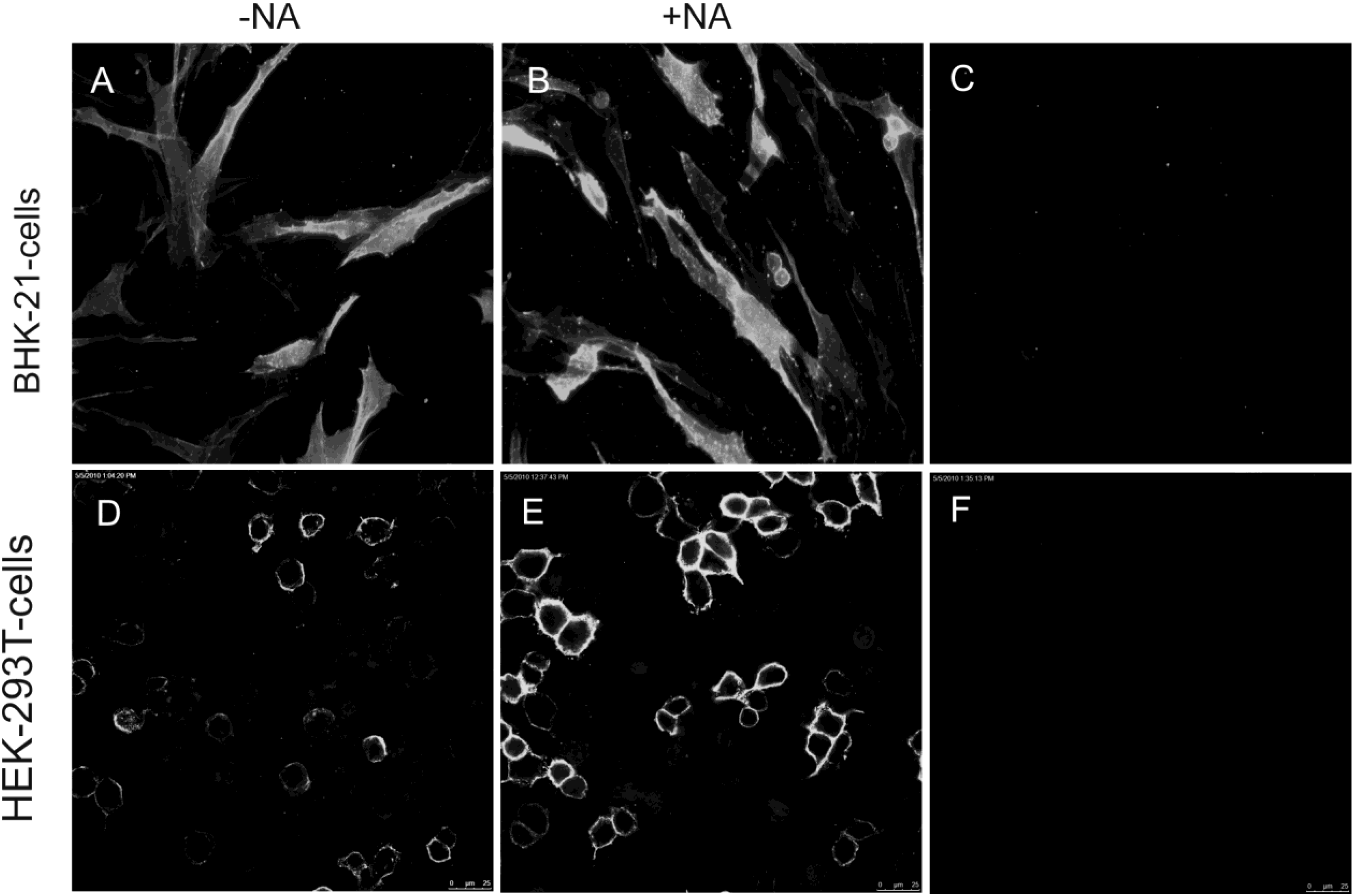
2.2. Soluble TGEV Spike protein binds to cells expressing APN
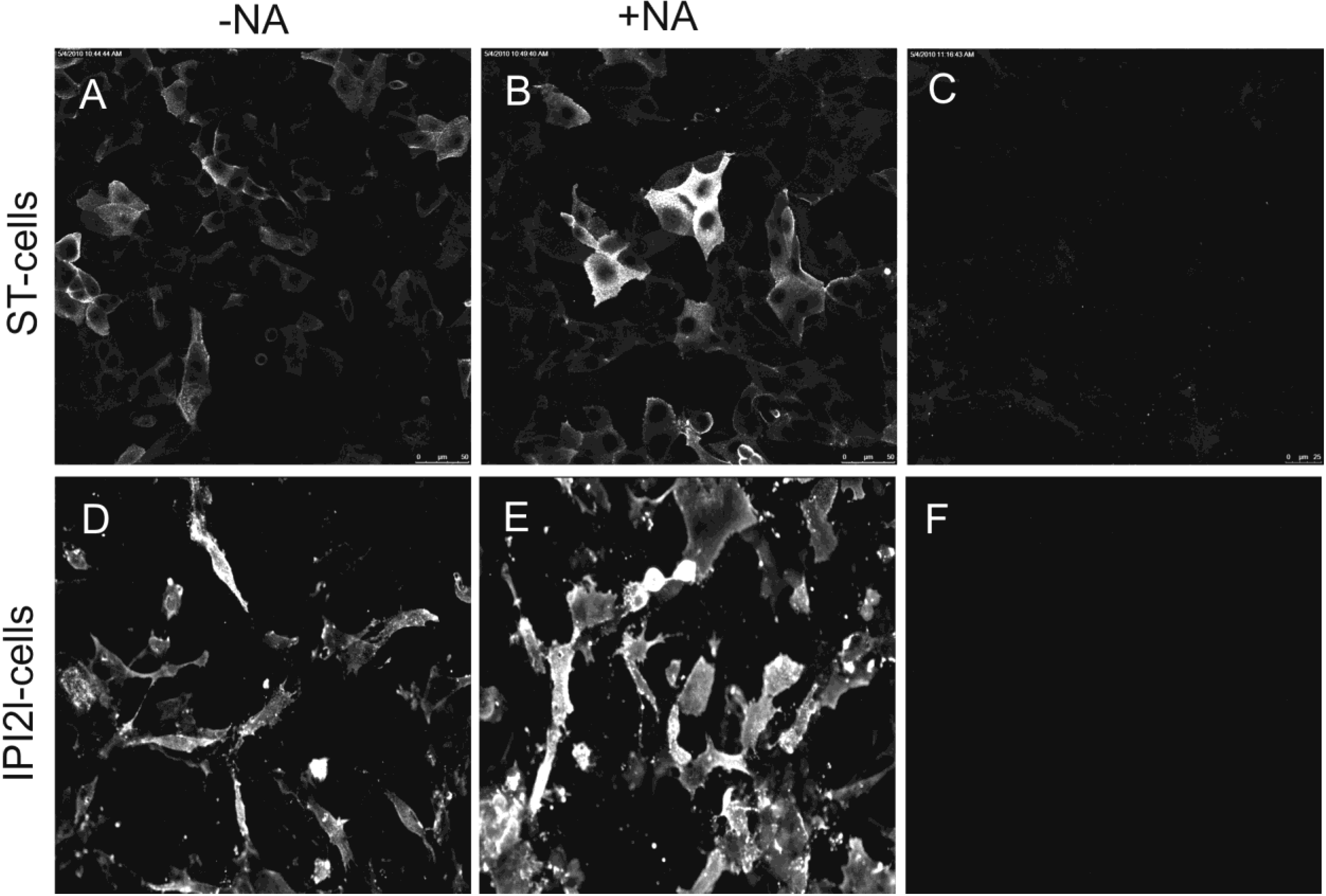
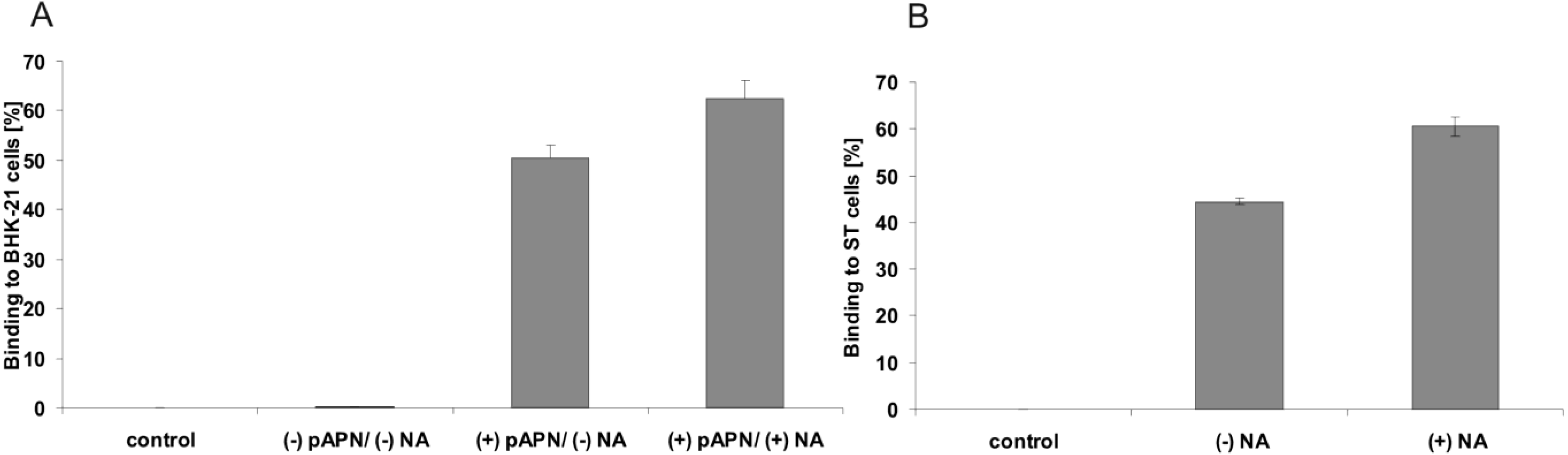
2.3. Binding of soluble TGEV spike is not decreased after neuraminidase treatment of intestinal cells
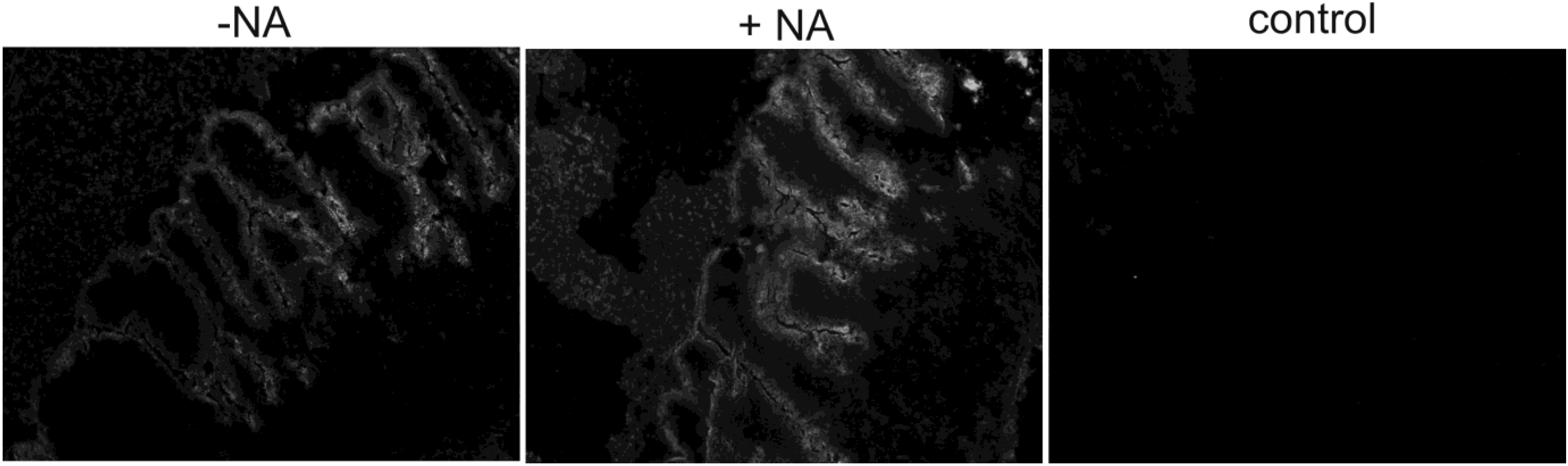
2.4. Soluble IBV Spike binds to chicken host cells in a sialic acid dependent manner
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cells:
3.2. Cloning of soluble proteins:
3.3. Preparation of soluble proteins:
3.4. Binding tests:
3.5. FACS analysis:
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Delmas, B.; Gelfi, J.; L'Haridon, R.; Vogel, L.K.; Sjostrom, H.; Noren, O.; Laude, H. Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero–pathogenic coronavirus TGEV. Nature 1992, 357, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krempl, C.; Schultze, B.; Laude, H.; Herrler, G. Point mutations in the S protein connect the sialic acid binding activity with the enteropathogenicity of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3285–3287. [Google Scholar]
- Schultze, B.; Krempl, C.; Ballesteros, M.L.; Shaw, L.; Schauer, R.; Enjuanes, L.; Herrler, G. Transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus, but not the related porcine respiratory coronavirus, has a sialic acid (N–glycolylneuraminic acid) binding activity. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5634–5637. [Google Scholar]
- Sestak, K.; Lanza, I.; Park, S.K.; Weilnau, P.A.; Saif, L.J. Contribution of passive immunity to porcine respiratory coronavirus to protection against transmissible gastroenteritis virus challenge exposure in suckling pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 57, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Krempl, C.; Schultze, B.; Herrler, G. Analysis of cellular receptors for human coronavirus OC43. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1995, 380, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Xu, L.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, L.; Pasquarella, J.R.; Holmes, K.V.; Li, F. Crystal structure of bovine coronavirus spike protein lectin domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 41931–41938. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, C.; Schwegmann–Wessels, C.; Cavanagh, D.; Neumann, U.; Herrler, G. Sialic acid is a receptor determinant for infection of cells by avian Infectious bronchitis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegmann–Wessels, C.; Bauer, S.; Winter, C.; Enjuanes, L.; Laude, H.; Herrler, G. The sialic acid binding activity of the S protein facilitates infection by porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madu, I.G.; Chu, V.C.; Lee, H.; Regan, A.D.; Bauman, B.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Heparan sulfate is a selective attachment factor for the avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus Beaudette. Avian. Dis. 2007, 51, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of coronavirus spike protein receptor–binding subunits. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2856–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, J.; Santiago, C.; Mudgal, G.; Ordono, D.; Enjuanes, L.; Casasnovas, J.M. Structural bases of coronavirus attachment to host aminopeptidase N and its inhibition by neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, I.N.; de Vries, R.P.; Grone, A.; de Haan, C.A.; Verheije, M.H. Binding of avian coronavirus spike proteins to host factors reflects virus tropism and pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8903–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Herrler, G.; Neumann, U. Infection of the tracheal epithelium by infectious bronchitis virus is sialic acid dependent. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahwan, K.; Hesse, M.; Mork, A.-K.; Herrler, G.; Winter, C. Sialic Acid Binding Properties of Soluble Coronavirus Spike (S1) Proteins: Differences between Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus. Viruses 2013, 5, 1924-1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5081924
Shahwan K, Hesse M, Mork A-K, Herrler G, Winter C. Sialic Acid Binding Properties of Soluble Coronavirus Spike (S1) Proteins: Differences between Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus. Viruses. 2013; 5(8):1924-1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5081924
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahwan, Katarina, Martina Hesse, Ann-Kathrin Mork, Georg Herrler, and Christine Winter. 2013. "Sialic Acid Binding Properties of Soluble Coronavirus Spike (S1) Proteins: Differences between Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus" Viruses 5, no. 8: 1924-1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5081924
APA StyleShahwan, K., Hesse, M., Mork, A.-K., Herrler, G., & Winter, C. (2013). Sialic Acid Binding Properties of Soluble Coronavirus Spike (S1) Proteins: Differences between Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus. Viruses, 5(8), 1924-1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5081924



