Lysogenic Conversion and Phage Resistance Development in Phage Exposed Escherichia coli Biofilms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Lysogenic Conversion of a Mature E. coli Biofilm with an Stx-Encoding Phage
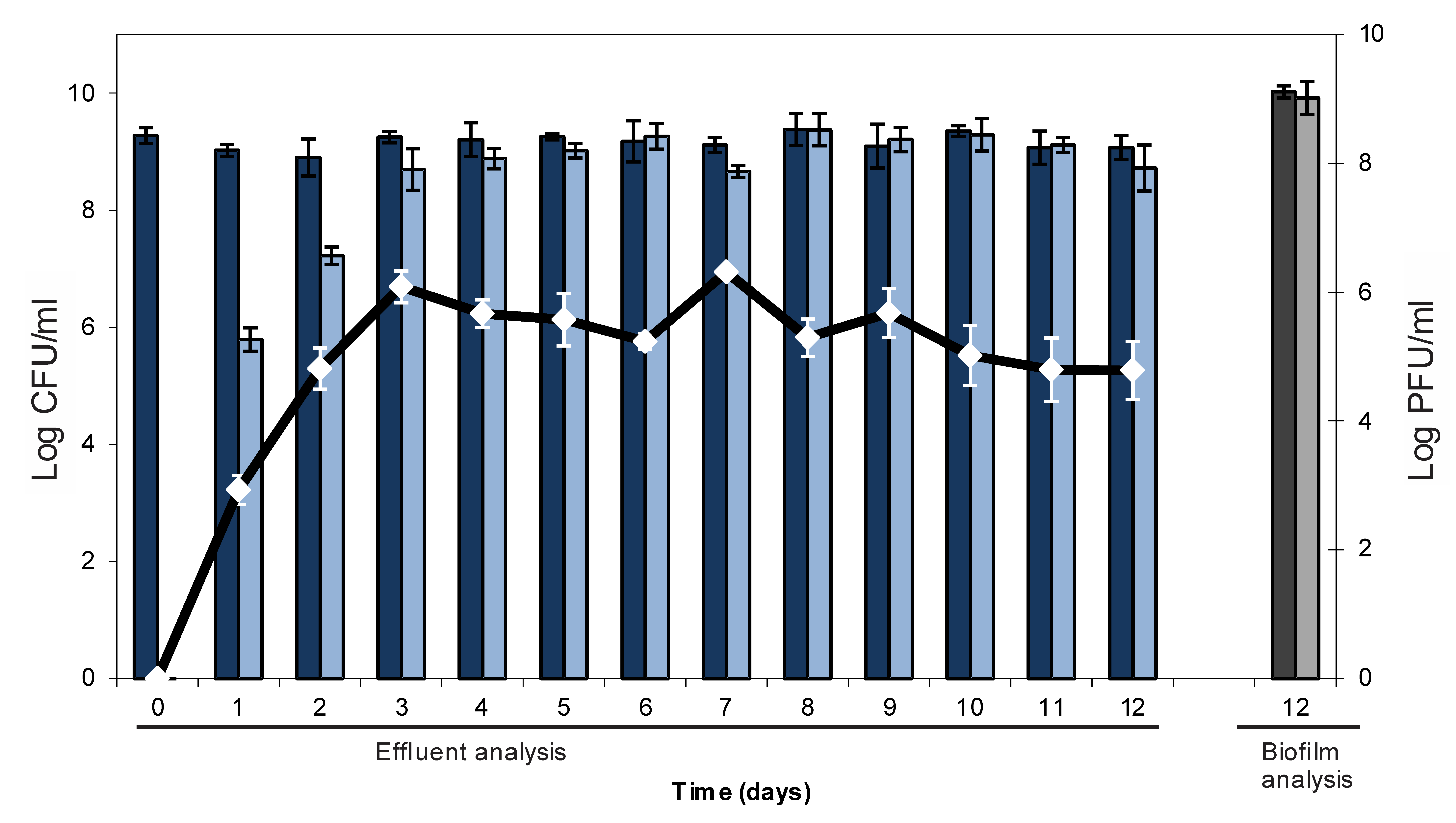
2.2. Resistance Development of E. coli biofilms Against a Lytic Phage
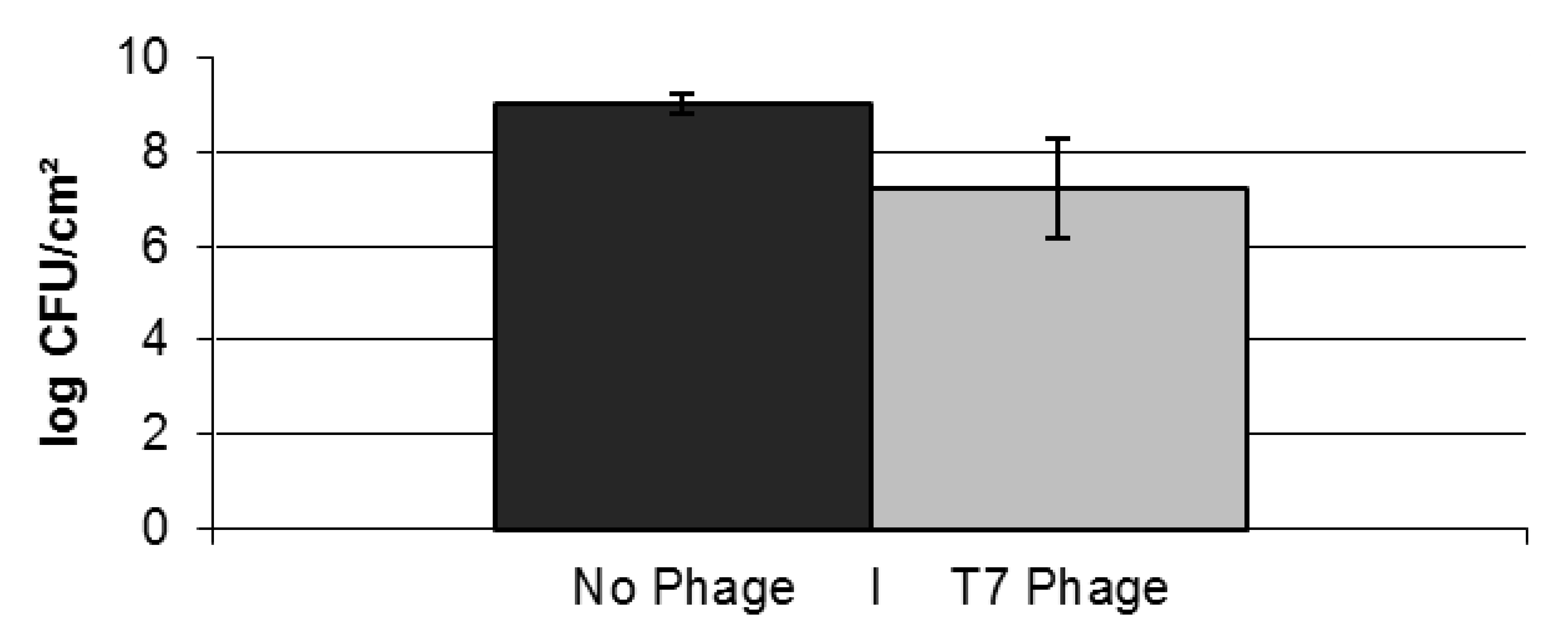
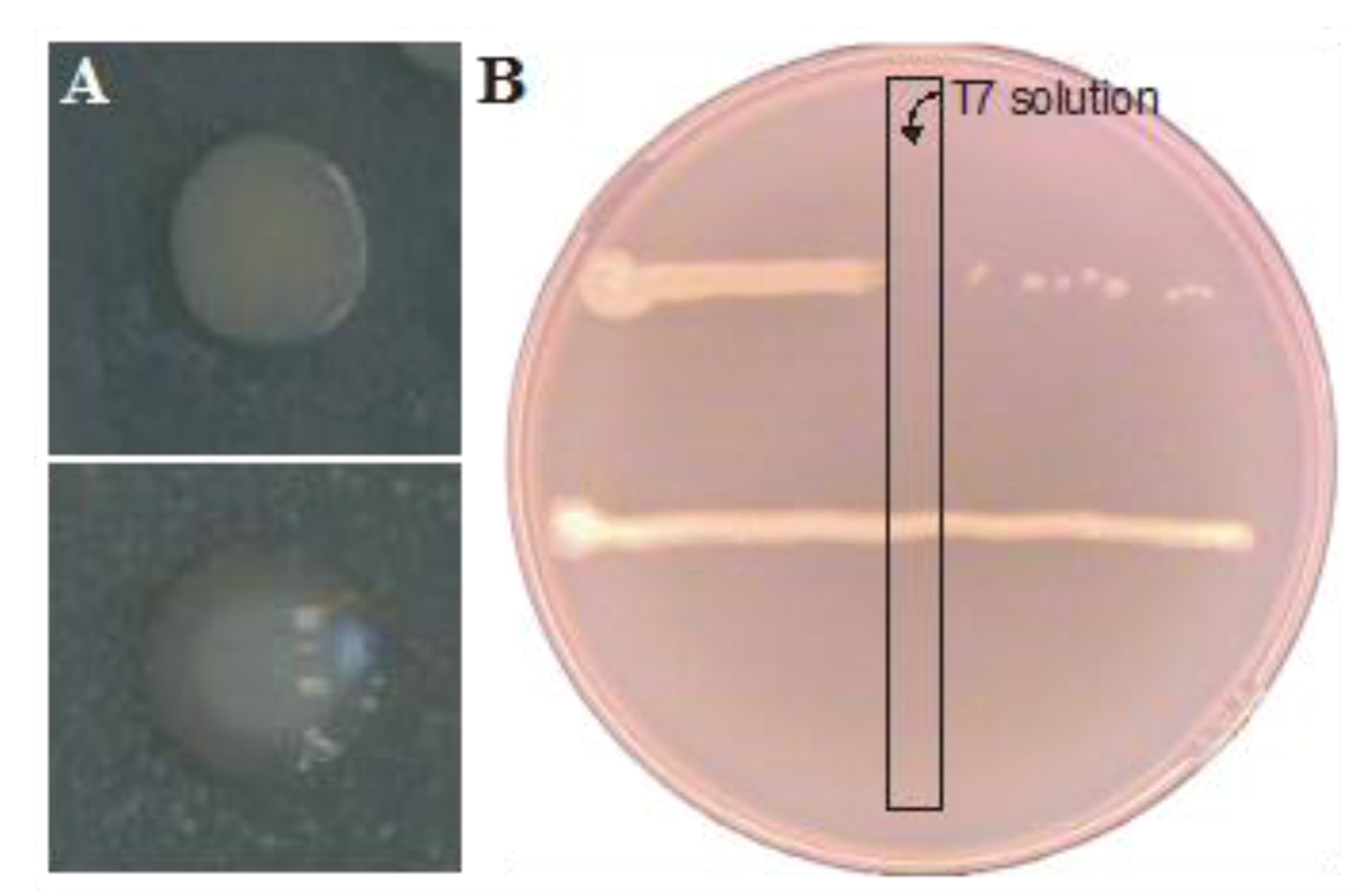
| Cell counts (log CFU/cm²) | Biofilm 1 | Biofilm 2 | Biofilm 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total cell count | 7.31 | 5.82 | 7.91 |
| T7 resistant cells | 6.76 | 2.49 | 7.05 |
| T7 sensitive cells | 7.17 | 5.82 | 7.85 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Strains, Standard Culture Conditions and Chemicals
3.2. Analysis of H-19B::Tn10
3.3. Setup for Biofilm Formation
3.4. Analysis of Biofilms
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, P.; Michiels, C.W.; Aertsen, A. Bacterial interactions in biofilms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Johansen, H.K.; Song, Z.J.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T. The clinical impact of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francolini, I.; Donelli, G. Prevention and control of biofilm-based medical-device-related infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Stoodley, P.; Kathju, S.; Høiby, N.; Moser, C.; Costerton, J.W.; Moter, A.; Bjarnsholt, T. Towards diagnostic guidelines for biofilm-associated infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloin, C.; Roux, A.; Ghigo, J.M. Escherichia coli biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 249–289. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, D.G.; Koopmans, M.; Verhoef, L.; Duizer, E.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Sprong, H.; Opsteegh, M.; Langelaar, M.; Threfall, J.; Scheutz, F.; et al. Food-borne diseases—The challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Akóva, M.; Carmeli, Y.; Giske, C.G.; Glupczynski, Y.; Gniadkowski, M.; Livermore, D.M.; Miriagou, V.; Naas, T.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. Rapid evolution and spread of carbapenemases among Enterobacteriaceae in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.M.; Stickler, D.J.; Mobley, H.L.; Shirtliff, M.E. Complicated catheter-associated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 26–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.R.; Henderson, I.R. The evolution of the Escherichia coli phylogeny. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Nolan, L.K. Pathogenomics of the virulence plasmids of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 750–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfan, M.J.; Torres, A.G. Molecular mechanisms that mediate colonization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werber, D.; Krause, G.; Frank, C.; Fruth, A.; Flieger, A.; Mielke, M.; Schaade, L.; Stark, K. Outbreaks of virulent diarrheagenic Escherichia coli—are we in control? BMC Med. 2012, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton-Celsa, A.; Mohawk, K.; Teel, L.; O'Brien, A. Pathogenesis of Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 357, 67–103. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H. Shiga-toxin-converting bacteriophages. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, S.; Karch, H.; Schmidt, H. Shiga toxin-encoding bacteriophages—genomes in motion. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 294, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minot, S.; Sinha, R.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Wu, G.D.; Lewis, J.D.; Bushman, F.D. The human gut virome: Inter-individual variation and dynamic response to diet. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M. Preventing biofilms of clinically relevant organisms using bacteriophage. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc-Carrillo, C.; Abedon, S.T. Pros and cons of phage therapy. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.M.; Gorman, S.P.; Donnelly, R.F.; Gilmore, B.F. Recent advances in bacteriophage therapy: how delivery routes, formulation, concentration and timing influence the success of phage therapy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Azeredo, J.; Sutherland, I.W. The use of phages for the removal of infectious biofilms. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2008, 9, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Martínez, B.; Donovan, D.M.; Rodríguez, A.; García, P. Bacteriophage virion-associated peptidoglycan hydrolases: potential new enzybiotics. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.A.; Sutherland, I.W.; Jones, M.V. Biofilm susceptibility to bacteriophage attack: The role of phage-borne polysaccharide depolymerase. Microbiology 1998, 144, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, M.; García, E.; Moscoso, M. In vitro destruction of Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilms with bacterial and phage peptidoglycan hydrolases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4144–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.A.; Tan, C.H.; Mikkelsen, P.J.; Kung, V.; Woo, J.; Tay, M.; Hauser, A.; McDougald, D.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S. The biofilm life cycle and virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are dependent on a filamentous prophage. ISME J. 2009, 3, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Shi, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Sun, J.; Yan, Y. Application of a bacteriophagelysin to disrupt biofilms formed by the animal pathogen Streptococcus suis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8272–8279. [Google Scholar]
- Siringan, P.; Connerton, P.L.; Payne, R.J.; Connerton, I.F. Bacteriophage-Mediated dispersal of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3320–3632. [Google Scholar]
- Neely, M.N.; Friedman, D.I. Functional and genetic analysis of regulatory regions of coliphage H-19B: Location of shiga-like toxin and lysis genes suggest a role for phage functions in toxin release. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleckner, N.; Bender, J.; Gottesman, S. Uses of transposons with emphasis on Tn10. Meth. Enzymol. 1991, 204, 139–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Moreno, R.; Acosta, S.; Hernalsteens, J.P.; Jofre, J.; Muniesa, M. Use of the lambda Red recombinase system to produce recombinant prophages carrying antibiotic resistance genes. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson, D.W.; Reidl, J.; Zhang, X.; Keusch, G.T.; Mekalanos, J.J.; Waldor, M.K. In vivo transduction with shiga toxin 1-encoding phage. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4496–4498. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Skarina, T.; Yee, A.; Jobin, M.C.; Dileo, R.; Semesi, A.; Fares, C.; Lemak, A.; Coombes, B.K.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; et al. NleG Type 3 effectors from enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli are U-Box E3 ubiquitin ligases. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Ooka, T.; Iguchi, A.; Toh, H.; Asadulghani, M.; Oshima, K.; Kodama, T.; Abe, H.; Nakayama, K.; Kurokawa, K.; et al. Comparative genomics reveal the mechanism of the parallel evolution of O157 and non-O157 enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17939–17944. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.L.; Rooks, D.J.; Fogg, P.C.; Darby, A.C.; Thomson, N.R.; McCarthy, A.J.; Allison, H.E. Comparative genomics of Shiga toxin encoding bacteriophages. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 311. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, K.L.; Siegel, E.C. Mutation preventing capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12 and its effect on bacteriophage resistance. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 106, 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Scholl, D.; Adhya, S.; Merril, C. Escherichia coli K1's capsule is a barrier to bacteriophage T7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4872–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyer, M.S.; Reed, R.R.; Steitz, J.A.; Low, K.B. Identification of a sex-factor-affinity site in E. coli as gamma delta. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1981, 45, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, P.; Van Houdt, R.; Aertsen, A.; Vanoirbeek, K.; Engelborghs, Y.; Michiels, C.W. Role of quorum sensing and antimicrobial component production by Serratia. plymuthica in formation of biofilms, including mixed biofilms with Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7294–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aertsen, A.; Faster, D.; Michiels, C.W. Induction of Shiga toxin-converting prophage in Escherichia coli by high hydrostatic pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.J.; Studier, F.W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 166, 477–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.B.; Sternberg, C.; Andersen, J.B.; Palmer, R.J.; Nielsen, A.T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S. Molecular tools for study of biofilm physiology. Meth. Enzymol. 1999, 310, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, P.C.; Saunders, J.R.; McCarthy, A.J.; Allison, H.E. Cumulative effect of prophage burden on Shiga toxin production in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2012, 158, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.E.; Stanley, K.N.; Allison, H.E.; Flint, H.J.; Stewart, C.S.; Sharp, R.J.; Saunders, J.R.; McCarthy, A.J. Lytic and lysogenic infection of diverse Escherichia coli and Shigella. strains with a verocytotoxigenic bacteriophage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4335–4337. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, S.D.; Strasser, J.E.; Chalk, C.L.; Weiss, A.A. Nonpathogenic Escherichia coli can contribute to the production of Shiga toxin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, I.; Schmidt, H.; Dow, M.; Malik, A.; Oswald, E.; Nagy, B. Transduction of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a derivative of a shiga toxin 2-encoding bacteriophage in a porcine ligatedileal loop system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 7242–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, N.A.; Helgerson, A.F.; Mai, V.; Ritchie, J.M.; Acheson, D.W. In vivo transduction of anStx-encoding phage in ruminants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5086–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, P.J.; Rosenberg, S.M.; Slack, A. Antibiotic-induced lateral transfer of antibiotic resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; McDaniel, A.D.; Wolf, L.E.; Keusch, G.T.; Waldor, M.K.; Acheson, D.W. Quinolone antibiotics induce Shiga toxin-encoding bacteriophages, toxin production, and death in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aertsen, A.; Van Houdt, R.; Michiels, C.W. Construction and use of an stx1 transcriptional fusion to gfp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 245, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, L.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. The use of lyticbacteriophages in the prevention and eradication of biofilms of Proteus mirabilis and Escherichia coli. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- Chibeu, A.; Lingohr, E.J.; Masson, L.; Manges, A.; Harel, J.; Ackermann, H.W.; Kropinski, A.M.; Boerlin, P. Bacteriophages with the ability to degrade uropathogenic Escherichia coli biofilms. Viruses 2012, 4, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, B.D.; McLean, R.J.; Aron, G.M. Bacteriophage T4 multiplication in a glucose-limited Escherichia coli biofilm. Can. J. Microbiol. 2001, 47, 680–684. [Google Scholar]
- Buckling, A.; Rainey, P.B. Antagonistic coevolution between a bacterium and a bacteriophage. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, A.; Yomo, T. Ongoing phenotypic and genomic changes in experimental coevolution of RNA bacteriophage Qβ and Escherichia coli. PLoSGenet. 2011, 7, e1002188. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.K.; Collins, J.J. Engineered bacteriophage targeting gene networks as adjuvants for antibiotic therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4629–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.M.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Donnelly, R.F.; Gilmore, B.F. Synergistic phage-antibiotic combinations for the control of Escherichia coli biofilms in vitro. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Moons, P.; Faster, D.; Aertsen, A. Lysogenic Conversion and Phage Resistance Development in Phage Exposed Escherichia coli Biofilms. Viruses 2013, 5, 150-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5010150
Moons P, Faster D, Aertsen A. Lysogenic Conversion and Phage Resistance Development in Phage Exposed Escherichia coli Biofilms. Viruses. 2013; 5(1):150-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoons, Pieter, David Faster, and Abram Aertsen. 2013. "Lysogenic Conversion and Phage Resistance Development in Phage Exposed Escherichia coli Biofilms" Viruses 5, no. 1: 150-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5010150
APA StyleMoons, P., Faster, D., & Aertsen, A. (2013). Lysogenic Conversion and Phage Resistance Development in Phage Exposed Escherichia coli Biofilms. Viruses, 5(1), 150-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/v5010150




