Co-circulation of Four Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Illnesses in 2004
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Detection of HCoVs and RT-rtPCRs
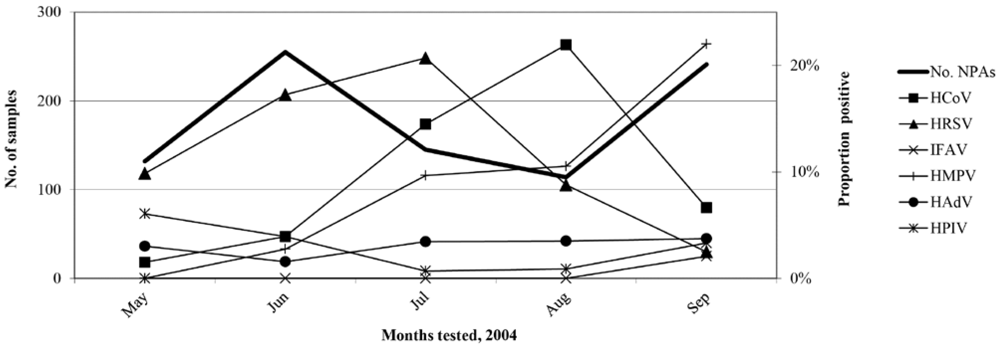
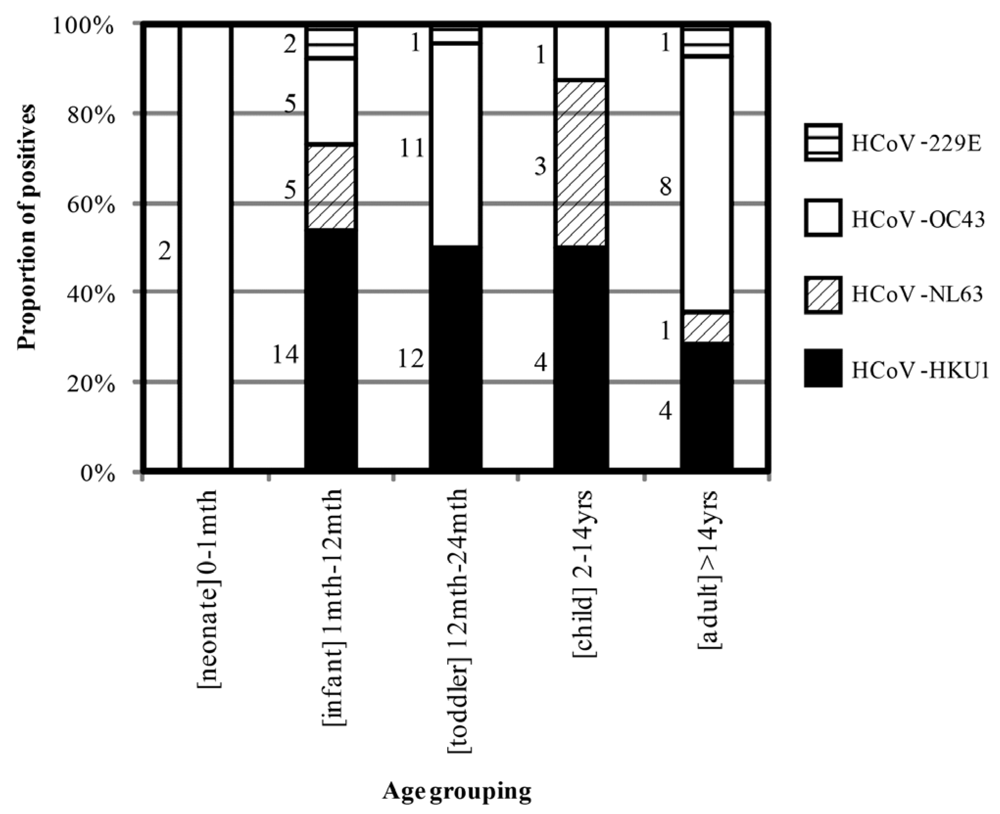
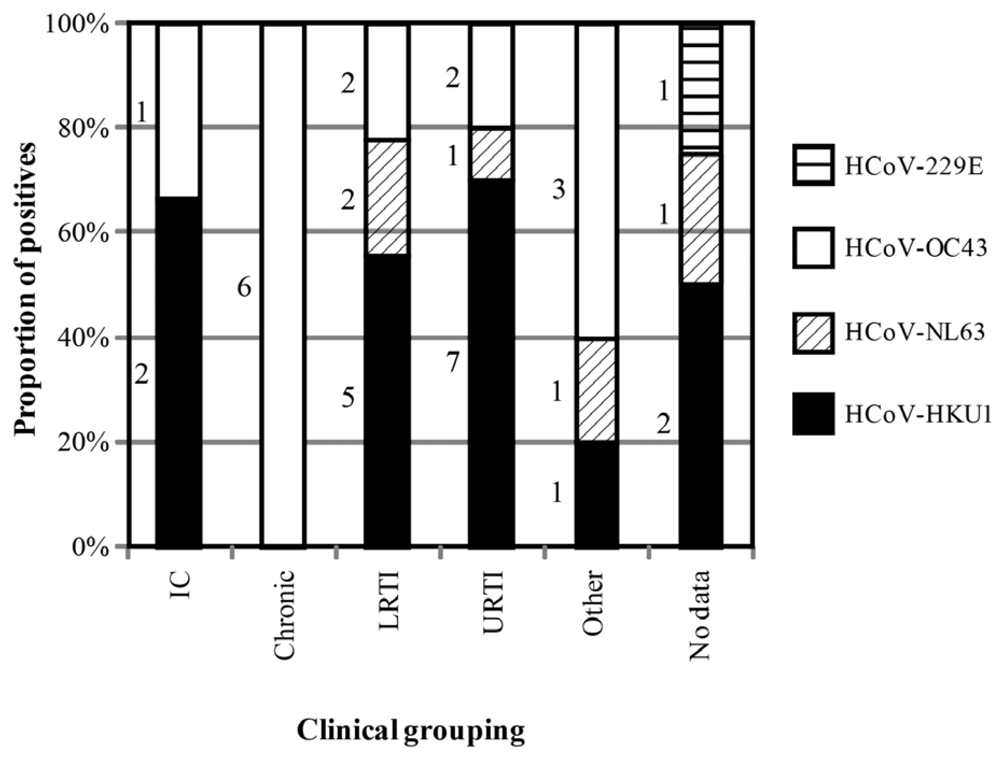
2.2. Epidemiology and Clinical Features of HCoV-positive Individuals During Winter 2004
| Oligonucleotide Name (gene target) | Oligonucleotide Sequence |
|---|---|
| 229E 01.4 (N) | ACAACGTGGTCGTCAGGGT |
| 229E 02.6 (N) | GCAACCCAGACGACACCT |
| 229E_MGB | FAM-CATCTTTATGGGGTCCTG -MGBNFQ |
| 229E 01.3 T7 | AAAATAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGAACCACAACGTGGTCGTCAGGGT |
| 229E 02.5 T7 | GGTTCTGAATTCTTGCGCCTAA |
| HKU1 01.2 (1b) | GTTGGGACGATATGTTACGTCATCTT |
| HKU1 02.2 (1b) | TGCTAGTACCACCAGGCTTAACATA |
| HKU1_MGB | FAM-CAACCGCCACACATAA-MGBNFQ |
| HKU1 01.2 T7 | AAAATAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGTTGGGACGATATGTTACGTCATCTT |
| HKU1 02.2 T7 | TGCTAGTACCACCAGGCTTAACATA |
| OC43 01.3 (N) | GAAGGTCTGCTCCTAATTCCAGAT |
| OC43 02.4 (N) | TTTGGCAGTATGCTTAGTTACTT |
| OC43_TM | ROX-TGCCAAGTTTTGCCAGAACAAGACTAGC-BHQ2 |
| OC43 01.2 T7 | AAAATAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGATGAGGCTATTCCGACTAGGT |
| OC43 02.4 T7 | ACCAGATGCCGACATAAGGTTCATTCT |
| NL63_N_01.13 (N) | GAGTTCGAGGATCGCTCTAATA |
| NL63_N_02.8 (N) | TGAATCCCCCATATTGTGATTAAA |
| NL63_TM5 | CY5-AAAATGTTATTCAGTGCTTTGGTCCTCGTGA-BHQ1 |
| NL63 01.6 T7 | AAAATAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGTCTTGGTAATCGCAAACGTAATC |
| NL63 02.6 T7 | TATCAAAGAATAACGCAGCCTGATTA |
| 229E | NL63 | OC43 | HKU1 | Total population (n = 888) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (%) | 2 (50.0) | 91 (100) | 12 (44.4) | 19 (55.9) | 514 (57.9) |
| Detections | 4 | 9 | 272 | 342 | 2903 (32.7) |
| Co-detections (%) | 3 (75.0) | 2 (22.2) | 6 (18.5) | 11 (23.5) | 294 (10.5) |
| Mean age, years | 4.9 | 3.9 | 18.6 | 4.9 | 7.9 |
| Peak month | July | August | July | August | June |
| Average severity score (single/co-detection) | ND/2.5 | 2.0/4.5 | 2.9/2.0 | 1.6/1.5 | - |
| HCoV detected | Average Score 1 | Detections | Fever | Vomit | Cough | Diarrhoea | Rash | AOM 2 | IC 3 (n = 4) | chronic (n = 9) | LRTI (n = 18) | URTI (n = 17) | other (n = 9) | no data (n = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HKU1 single | 1.63 | 17 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 2 |
| HKU1 dual | 1.54 | 14 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
| NL63 single | 2.00 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| NL63 dual | 4.50 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OC43 single | 2.85 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| OC43 dual | 2.00 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 229E single | ND | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 229E dual | 2.50 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 62 | 8 | 7 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 19 | 17 | 9 | 4 | ||
| SoDe HCoV | 5 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 4 | ||
| 8.1% | 6.5% | 9.7% | 0.0% | 3.2% | 3.2% | 4.8% | 9.7% | 14.5% | 16.1% | 8.1% | 6.5% | |||
| CoDe HCoV | 3 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 0 | ||
| 4.8% | 4.8% | 6.5% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 8.1% | 1.6% | 4.8% | 16.1% | 11.3% | 6.5% | 0.0% |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Study Population
3.2. HCoV RT-PCR Testing
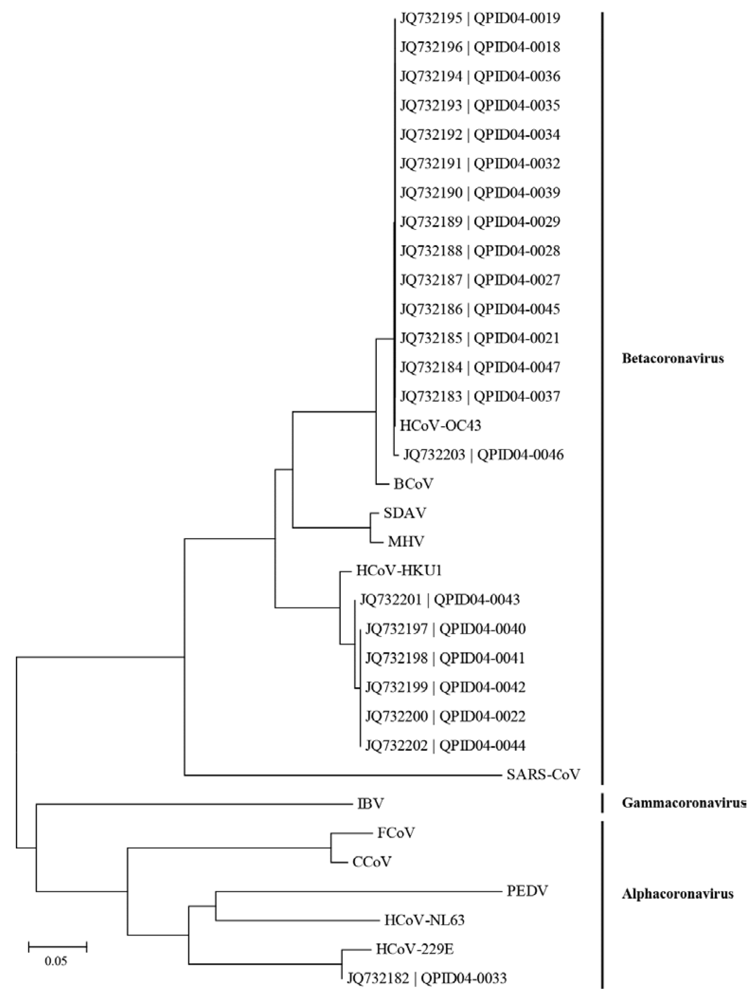
3.3. Nucleotide Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Clinical Data Collection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Heikkinen, T.; Järvinen, A. The common cold. Lancet 2003, 361, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Klig, J.E.; Shah, N.B. Office pediatrics: current issues in lower respiratory infections in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2005, 17, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, F.G. Rhinovirus and the lower respiratory tract. Rev. Med. Virol. 2004, 14, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Kuiken, T.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Newer respiratory virus infections: human metapneumovirus, avian influenza virus, and human coronaviruse. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 18, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoek, L.; Sure, K.; Ihorst, G.; Stang, A.; Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Petersen, G.; Forster, J.; Berkhout, B.; Überla, K. Croup is associated with the novel coronavirus NL63. PloS Med. 2005, 2, e240. [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn, B.J. The epidemiology of acute respiratory tract infection in young children: Comparison of findings from several developing countries. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, S870–S888. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.B. Respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Syrmis, M.W.; Whiley, D.M.; Thomas, M.; Mackay, I.M.; Williamson, J.; Siebert, D.J.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P. A sensitive, specific and cost-effective multiplex reverse-transcriptase-PCR assay for the detection of seven common respiratory viruses in respiratory samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 2004, 6, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, K.G.; Kent, J.; Hammersley, V.; Cancio, E. Acute viral infections of upper respiratory tract in elderly people living in the community: comparative, prospective, population based study of disease burden. Br. Med. J. 1997, 315, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Ireland, D.C.; Kent, J.; Nicholson, K.G. Improved detection of rhinoviruses in nasal and throat swabs by seminested RT-PCR. J. Med. Virol. 1993, 40, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kuiken, T.; Fouchier, R.; Rimmelzwaan, G.; Osterhaus, A. Emerging viral infections in a rapidly changing world. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Hamre, D.; Kindig, D.A.; Mann, J. Growth and intracellular development of a new respiratory virus. J. Virol. 1967, 1, 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell, D.A.J.; Bynoe, M.L. Cultivation of a novel type of common-cold virus in organ cultures. Br. Med. J. 1965, 1, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Gorse, G.J.; O'Connor, T.Z.; Hall, S.L.; Vitale, J.N.; Nichol, K.L. Human coronavirus and acute respiratory illness in older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 847–857. [Google Scholar]
- Principi, N.; Bosis, S.; Esposito, S. Effects of coronavirus infections in children. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 15, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoek, L.; Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Vermeulen-Oost, W.; Berkhout, R.J.M.; Wolthers, K.C.; Wertheim-van DIllen, P.M.E.; Kaandorp, J.; Spaargaren, J.; Berkhout, B. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Chu, C.-M.; Chan, K.-H.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Huang, Y.; Wong, B.H.L.; Poon, R.W.S.; Cai, J.J.; Luk, W.-K.; et al. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 884–895. [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and clinical presentations of the four human coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 detected over 3 years using a novel multiplex real-time PCR method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Gaunt, E.; Rossen, J.W.; Templeton, K.E.; Kuijpers, T.W. The dominance of human coronavirus OC43 and NL63 infections in infants. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Severance, E.G.; Bossis, I.; Dickerson, F.B.; Stallings, C.R.; Origoni, A.E.; Sullens, A.; Yolken, R.H.; Viscidi, R.P. Development of a nucleocapsid-based human coronavirus immunoassay and estimates of individuals exposed to coronavirus in a U.S. metropolitan population. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar]
- van Elden, L.J.R.; van Kraaij, M.G.J.; Nijhuis, M.; Hendricksen, K.A.W.; Dekker, A.d.W.; Rozenberg-Arksa, M.; van Loon, A.M. Polymerase chain reaction is more sensitive than viral culture and antigen testing for the detection of respiratory viruses in adults with hematological cancer and pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Vabret, A.; Mourez, T.; Gouarin, S.; Petitjean, J.; Freymuth, F. An outbreak of coronavirus OC43 respiratory infection in Normandy, France. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 985–989. [Google Scholar]
- van Elden, L.J.R.; van Loon, A.M.; van Alphen, F.; Hendriksen, K.A.W.; Hoepelman, A.I.M.; van Kraaij, M.G.J.; Oosterheert, J.-J.; Schipper, P.; Schuurman, R.; Nijhuis, M. Frequent detection of human coronaviruses in clinical specimens from patients with respiratory tract infection by use of a novel real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 652–657. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Tse, H.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Lee, P.; Tang, B.S.F.; Cheung, C.H.Y.; Lee, R.A.; So, L.-Y.; Lau, Y.-L.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Coronavirus HKU1 and other coronavirus infections in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, S.R.; Robinson, C.C.; Holmes, K.V. Detection of four human coronaviruses in respiratory infections in children: a one-year study in Colorado. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Xu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Vernet, G.; Paranhos-Baccala, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Prevalence of human coronaviruses in adults with acute respiratory tract infections in Beijing, China. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers, J.; Martin, E.T.; Heugel, J.; Wright, N.; Morrow, R.; Englund, J.A. Clinical disease in children associated with newly described coronavirus subtypes. Pediatrics 2007, 119, e70–e76. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, M.; Lassauniere, R.; Kresfelder, T.L.; Westerberg, Y.; Visser, A. Contribution of common and recently described respiratory viruses to annual hospitalizations in children in South Africa. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, H.K.; Crowe, J.E., Jr; Edwards, K.M.; Griffin, M.R.; Zhu, Y.; Weinberg, G.A.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Hall, C.B.; Podsiad, A.B.; Iwane, M.; Williams, J.V. Coronavirus infection and hospitalizations for acute respiratory illness in young children. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 853–856. [Google Scholar]
- Milano, F.; Campbell, A.P.; Guthrie, K.A.; Kuypers, J.; Englund, J.A.; Corey, L.; Boeckh, M. Human rhinovirus and coronavirus detection among allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Blood 2010, 115, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Hamre, D.; Beem, M. Virologic studies of acute respiratory disease in young adults. V. Coronavirus 229E infections during six years of surveillance. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1972, 96, 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hamre, D.; Procknow, J.J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 121, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Pene, F.; Merlat, A.; Vabret, A.; Rozenberg, F.; Buzyn, A.; Dreyfus, F.; Cariou, A.; Freymuth, F.; Lebon, P. Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 929–932. [Google Scholar]
- Folz, R.J.; Elkordy, M.A. Coronavirus pneumonia following autologous bone marrow transplantation for breast cancer. Chest 1999, 115, 901–905. [Google Scholar]
- Forgie, S.; Marrie, T.J. Healthcare-associated atypical pneumonia. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 30, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, C.J.; Clothier, H.J.; Seccull, A.; Tran, T.; Catton, M.C.; Lambert, S.B.; Druce, J.D. Human coronavirus OC43 causes influenza-like illness in residents and staff of aged-care facilities in Melbourne, Australia. Epidemiol. Infect. 2004, 133, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- McKean, M.C.; Leech, M.; Lambert, P.C.; Hewitt, C.; Myint, S.; Silverman, M. A model of viral wheeze in nonasthmatic adults: symptoms and physiology. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Enserink, M. Calling all coronavirologists. Science 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gagneur, A.; Sizun, J.; Vallet, S.; Legrand, M.C.; Picard, B.; Talbot, P.J. Coronavirus-related nosocomial viral respiratory infections in a neonatal and paediatric intensive care unit: a prospective study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 51, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sizun, J.; Gagneur, A.; Legrand, C.; Baron, M.R. Respiratory coronavirus infections in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2001, 20, 555–556. [Google Scholar]
- Vallet, S.; Gagneur, A.; Talbot, P.J.; Legrand, M.-C.; Sizun, J.; Picard, B. Detection of human coronavirus 229E in nasal specimens in large scale studies using an RT-PCR hybridization assay. Mol. Cell. Probe. 2004, 18, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sloots, T.P.; McErlean, P.; Speicher, D.J.; Arden, K.E.; Nissen, M.D.; Mackay, I.M. Evidence of human coronavirus HKU1 and human bocavirus in Australian children. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 35, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, S.S.; Chan, K.H.; Chu, K.W.; Kwan, S.W.; Guan, Y.; Poon, L.L.M.; Peiris, J.S.M. Human coronavirus NL63 infection and other coronavirus infections in children hospitalized with acute respiratory disease in Hong Kong, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Yuen, K.Y. Clinical features and molecular epidemiology of coronavirus-HKU1–associated community-acquired pneumonia. Hong Kong Med. J. 2009, 15, 546–547. [Google Scholar]
- Arden, K.E.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. New human coronavirus, HCoV-NL63, associated with severe lower respiratory tract disease in Australia. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 75, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.T.; Arden, K.E.; Greer, R.M.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. A novel duplex real-time PCR for HPIV-4 detects co-circulation of both viral subtypes among ill children during 2008. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 54, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- McErlean, P.; Shackelton, L.A.; Lambert, S.B.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. Characterisation of a newly identified human rhinovirus, HRV-QPM, discovered in infants with bronchiolitis. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 39, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McErlean, P.; Shackelton, L.A.; Andrewes, E.; Webster, D.R.; Lambert, S.B.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. Distinguishing Molecular Features and Clinical Characteristics of a Putative New Rhinovirus Species, Human Rhinovirus C (HRV C). PLoS One 2008, 3, e1847. [Google Scholar]
- Arden, K.E.; Faux, C.E.; O'Neill, N.T.; McErlean, P.; Nitsche, A.; Lambert, S.B.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. Molecular characterization and distinguishing features of a novel human rhinovirus (HRV) C, HRVC-QCE, detected in children with fever, cough and wheeze during 2003. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Maertzdorf, J.; Wang, C.K.; Brown, J.B.; Quinto, J.D.; Chu, M.; de Graaf, M.; van den Hoogen, B.G.; Spaete, R.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assay for detection of human metapneumoviruses from all known genetic lineages. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 981–986. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Holloway, B.; Dare, R.K.; Kuypers, J.; Yagi, S.; Williams, J.V.; Hall, C.B.; Erdman, D.D. Real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay for comprehensive detection of human rhinoviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Arden, K.E.; Mackay, I.M. Newly identified human rhinoviruses: molecular methods heat up the cold viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20, 156–176. [Google Scholar]
- Arden, K.E.; McErlean, P.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. Frequent detection of human rhinoviruses, paramyxoviruses, coronaviruses, and bocavirus during acute respiratory tract infections. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.; Smith, I.; Harrower, B.; Warrilow, D.; Bletchly, C. A simple method for preparing synthetic controls for conventional and real-time PCR for the identification of endemic and exotic disease agents. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 135, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. Bioedit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlateva, K.T.; Crusio, K.M.; Leontovich, A.M.; Lauber, C.; Claas, E.; Kravchenko, A.A.; Spaan, W.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Design and validation of consensus-degenerate hybrid oligonucleotide primers for broad and sensitive detection of corona- and toroviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 177, 174s–183s. [Google Scholar]
- Dare, R.K.; Fry, A.M.; Chittaganpitch, M.; Sawanpanyalert, P.; Olsen, S.J.; Erdman, D.D. Human coronavirus infections in rural Thailand: a comprehensive study using real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Prill, M.M.; Iwane, M.K.; Edwards, K.M.; Williams, J.V.; Weinberg, G.A.; Staat, M.A.; Willby, M.J.; Talbot, H.K.; Hall, C.B.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Griffin, M.R.; Curns, A.T.; Erdman, D.D. Human coronavirus in young children hospitalized for acute respiratory illness and asymptomatic controls. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Loeffelholz, M.J.; Pong, D.L.; Pyles, R.B.; Xiong, Y.; Miller, A.L.; Bufton, K.K.; Chonmaitree, T. Comparison of the FilmArray respiratory panel and Prodesse real-time PCR assays for the detection of respiratory pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4083–4088. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, S.; Bosis, S.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Tremolati, E.; Begliatti, E.; Rognoni, A.; Tagliabue, C.; Principi, N.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Impact of human coronavirus infections in otherwise healthy children who attended an emergency department. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Esper, F.; Ou, Z.; Huang, Y.T. Human coronaviruses are uncommon in patients with gastrointestinal illness. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 131–133. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E.; Speicher, D.J.; O’Neil, N.T.; McErlean, P.K.; Greer, R.M.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P. Co-circulation of Four Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Illnesses in 2004. Viruses 2012, 4, 637-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040637
Mackay IM, Arden KE, Speicher DJ, O’Neil NT, McErlean PK, Greer RM, Nissen MD, Sloots TP. Co-circulation of Four Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Illnesses in 2004. Viruses. 2012; 4(4):637-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040637
Chicago/Turabian StyleMackay, Ian M., Katherine E. Arden, David J. Speicher, Nicholas T. O’Neil, Peter K. McErlean, Ristan M. Greer, Michael D. Nissen, and Theo P. Sloots. 2012. "Co-circulation of Four Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Illnesses in 2004" Viruses 4, no. 4: 637-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040637
APA StyleMackay, I. M., Arden, K. E., Speicher, D. J., O’Neil, N. T., McErlean, P. K., Greer, R. M., Nissen, M. D., & Sloots, T. P. (2012). Co-circulation of Four Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Illnesses in 2004. Viruses, 4(4), 637-653. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4040637






