Identification and Characterization of a Novel Alpaca Respiratory Coronavirus Most Closely Related to the Human Coronavirus 229E
Abstract
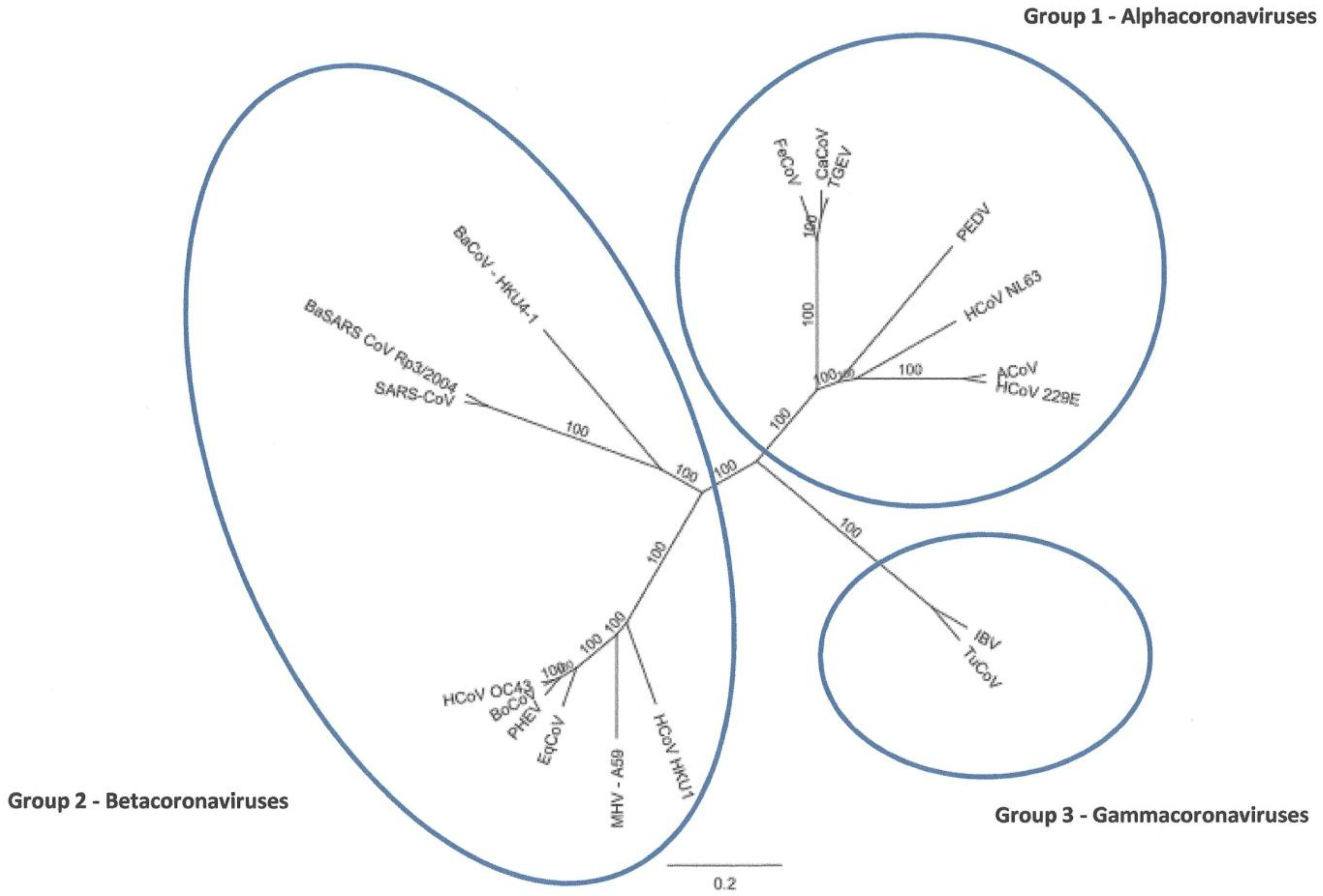
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of ACoV Genome
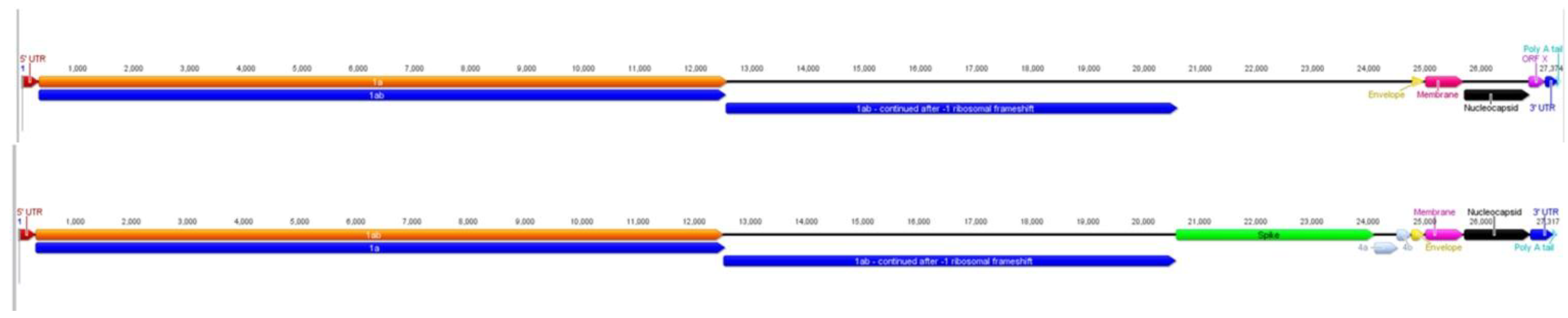
2.3. Comparison of ACoV and HCoV-229E Genes/Proteins
| Gene | Nucleotide (%) a | Amino acid (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| Pol 1a | 92.5 | 93.2 |
| Pol 1ab | 92.9 | 95.0 |
| Spike | 94.2 | 94.2 |
| Envelope | 87.2 | 91.0 |
| Membrane | 89.0 | 91.2 |
| Nucleocapsid | 86.7 | 87.1 |
2.4. Characteristics of the ACoV Spike Gene/Protein and Comparison with HCoV 229 E Spike Gene/Protein
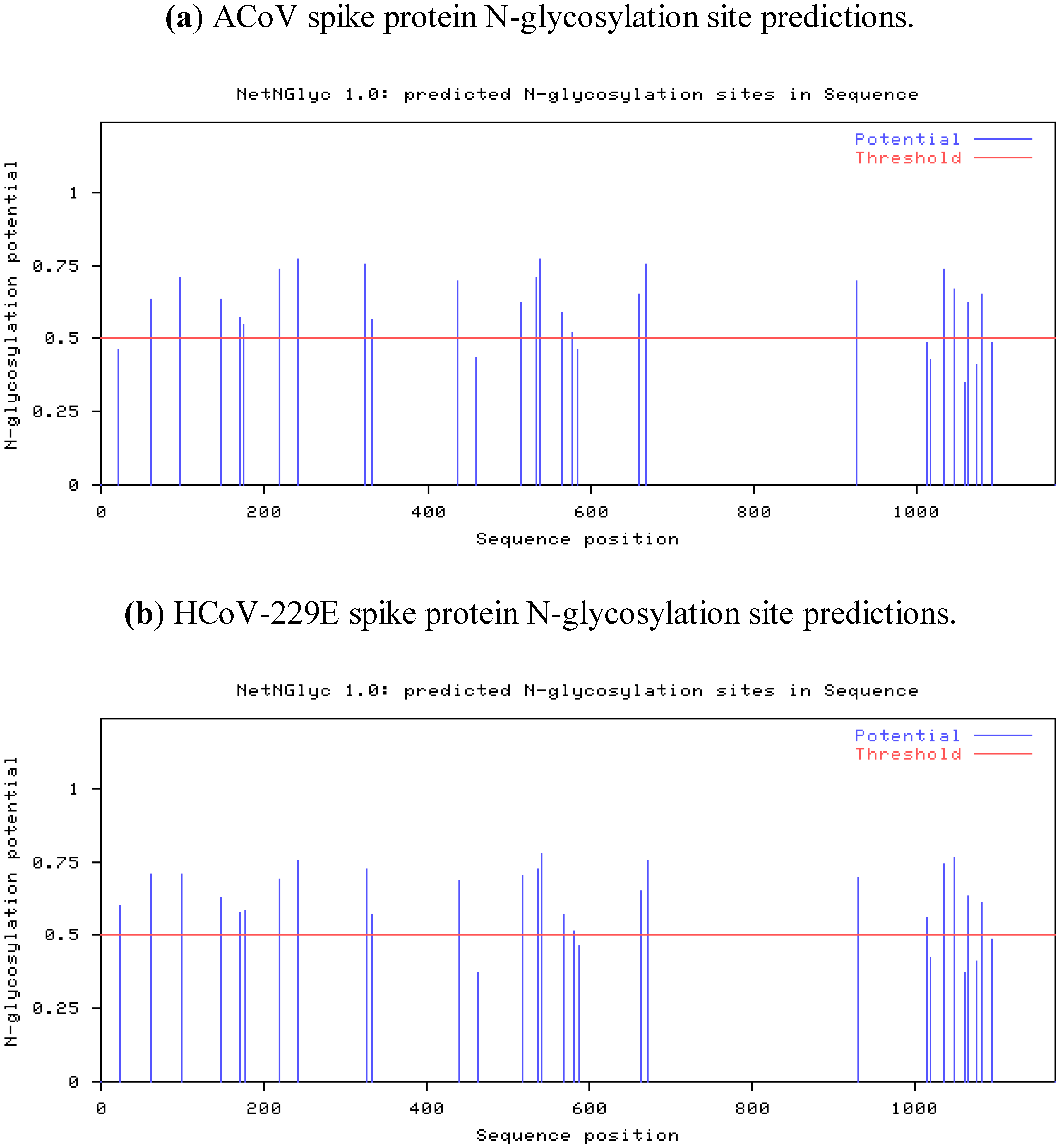
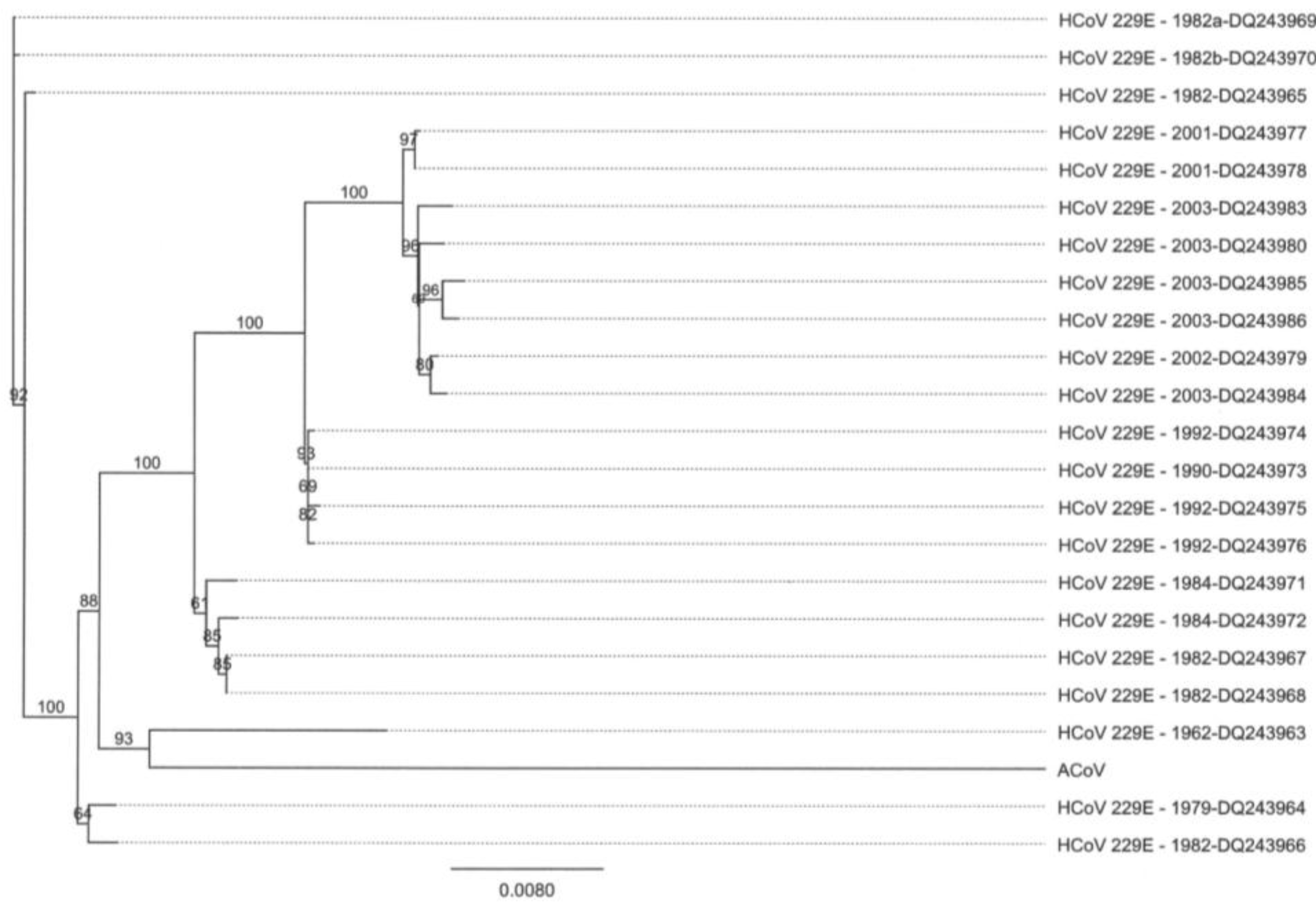

2.5. Characteristics of the ACoV Nucleocapsid Gene/Protein and Comparison with HCoV 229 E Nucleocapsid Gene/Protein
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cells and Viruses
3.2. Viral RNA Preparation
3.3. RT-PCR Amplification
3.4. 5' RACE and 3' RACE
3.5. Primers
3.6. TOPO TA Cloning
3.7. DNA Sequencing and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Crossley, B.M.; Barr, B.C.; Magdesian, K.G.; Ing, M.; Mora, D.; Jensen, D.; Loretti, A.P.; McConnell, T.; Mock, R. Identification of a novel coronavirus possibly associated with acute respiratory syndrome in alpacas (Vicugna pacos) in California, 2007. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2010, 22, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Cebra, C.K.; Baker, R.J.; Mattson, D.E.; Cohen, S.A.; Alvarado, D.E.; Rohrmann, G.F. Analysis of the genome sequence of an alpaca coronavirus. Virology 2007, 365, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, C.B.; Beaudette, F.R. Infection of the Cloaca with the virus of infectious bronchitis. Science 1932, 76, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, N.C. Virologic and immunologic aspects of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1987, 218, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, E.R. Infectious Diseases and Pathology of Reptiles; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 3487–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkman, R.; van der Hoek, L. Human coronaviruses 229E and NL63: Close yet still so far. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2009, 108, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Huang, Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouzard, S.; Millet, J.K.; Licitra, B.N.; Whittaker, G.R. Mechanisms of coronavirus cell entry mediated by the viral spike protein. Viruses 2012, 4, 1011–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; Smeenk, I.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J.; de Groot, R.J. Feline coronavirus type II strains 79–1683 and 79–1146 originate from a double recombination between feline coronavirus type I and canine coronavirus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4508–4514. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.M.; Cavanagh, D. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 1997, 48, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlough, J.E.; Johnson-Lussenburg, C.M.; Stoddart, C.A.; Jacobson, R.H.; Scott, F.W. Experimental inoculation of cats with human coronavirus 229E and subsequent challenge with feline infectious peritonitis virus. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1985, 49, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Barlough, J.E.; Stoddart, C.A.; Sorresso, G.P.; Jacobson, R.H.; Scott, F.W. Experimental inoculation of cats with canine coronavirus and subsequent challenge with feline infectious peritonitis virus. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1984, 34, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Tusell, S.M.; Schittone, S.A.; Holmes, K.V. Mutational analysis of aminopeptidase N, a receptor for several group 1 coronaviruses, identifies key determinants of viral host range. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.D.; Wesley, R.D. Seroconversion of pigs in contact with dogs exposed to canine coronavirus. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 56, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkman, R.; Mulder, H.L.; Rumping, L.; Kraaijvanger, I.; Deijs, M.; Jebbink, M.F.; Verschoor, E.J.; van der Hoek, L. Seroconversion to HCoV-NL63 in rhesus macaques. Viruses 2009, 1, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, P.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Monroe, S.S.; Nix, W.A.; Campagnoli, R.; Icenogle, J.P.; Penaranda, S.; Bankamp, B.; Maher, K.; Chen, M.H.; et al. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science 2003, 300, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, J.; Raabe, T.; Siddell, S.G. Characterization of the human coronavirus 229E (HCV 229E) gene 1. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1993, 342, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Marle, G.; Luytjes, W.; van der Most, R.G.; van der Straaten, T.; Spaan, W.J. Regulation of coronavirus mRNA transcription. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7851–7856. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Berkhout, B.; van der Hoek, L. Genome structure and transcriptional regulation of human coronavirus NL63. Virol. J. 2004, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, B.J.; van der Zee, R.; de Haan, C.A.; Rottier, P.J. The coronavirus spike protein is a class I virus fusion protein: Structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8801–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NetNGlyc 1.0 Server. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNGlyc/ (accessed on 27 August 2010).
- de Haan, C.A.; Haijema, B.J.; Schellen, P.; Schreur, P.W.; te Lintelo, E.; Vennema, H.; Rottier, P.J. Cleavage of group 1 coronavirus spike proteins: How furin cleavage is traded off against heparan sulfate binding upon cell culture adaptation. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6078–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelle, B.; Karl, N.; Ludewig, B.; Siddell, S.G.; Thiel, V. Selective replication of coronavirus genomes that express nucleocapsid protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6620–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.M.C.; Perlman, S.; Anderson, L.J. Coronaviridae. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Williams: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1305–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Integrated DNATechnologies, Inc. Available online: http://www.idtdna.com (accessed on 11 February 2009).
- Hamre, D.; Procknow, J.J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 121, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Farsani, S.M.; Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Goossens, H.; Ieven, M.; Deijs, M.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Hoek, L. The first complete genome sequences of clinical isolates of human coronavirus 229E. Virus Genes 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferle, S.; Oppong, S.; Drexler, J.F.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Ipsen, A.; Seebens, A.; Muller, M.A.; Annan, A.; Vallo, P.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; et al. Distant relatives of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and close relatives of human coronavirus 229E in bats, Ghana. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S.R.; Navas-Martin, S. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandell, R.A.; Fabricant, C.G.; Nelson-Rees, W.A. Development, characterization, and viral susceptibility of a feline (Felis catus) renal cell line (CRFK). In Vitro 1973, 9, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegmann-Wessels, C.; Herrler, G. Sialic acids as receptor determinants for coronaviruses. Glycoconj. J. 2006, 23, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingley, S.T.; Gombold, J.L.; Lavi, E.; Weiss, S.R. MHV-A59 fusion mutants are attenuated and display altered hepatotropism. Virology 1994, 200, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, T.; Casais, R.; Dove, B.; Britton, P.; Cavanagh, D. Recombinant infectious bronchitis coronavirus Beaudette with the spike protein gene of the pathogenic M41 strain remains attenuated but induces protective immunity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13804–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leparc-Goffart, I.; Hingley, S.T.; Chua, M.M.; Phillips, J.; Lavi, E.; Weiss, S.R. Targeted recombination within the spike gene of murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus-A59: Q159 is a determinant of hepatotropism. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9628–9636. [Google Scholar]
- Chibo, D.; Birch, C. Analysis of human coronavirus 229E spike and nucleoprotein genes demonstrates genetic drift between chronologically distinct strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, J.P.; Myint, S.H. PCR sequencing of the spike genes of geographically and chronologically distinct human coronaviruses 229E. J. Virol. Methods 1998, 75, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilani, M.; Balboni, A.; Bassani, M.; Scagliarini, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Prosperi, S. Sequence analysis of the nucleocapsid gene of feline coronaviruses circulating in Italy. New Microbiol. 2010, 33, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Wilbrink, B.; Pyrc, K.; Zaaijer, H.L.; Minor, P.D.; Franklin, S.; Berkhout, B.; Thiel, V.; van der Hoek, L. Human coronavirus 229E encodes a single ORF4 protein between the spike and the envelope genes. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Crossley, B.M.; Mock, R.E.; Callison, S.A.; Hietala, S.K. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Alpaca Respiratory Coronavirus Most Closely Related to the Human Coronavirus 229E. Viruses 2012, 4, 3689-3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4123689
Crossley BM, Mock RE, Callison SA, Hietala SK. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Alpaca Respiratory Coronavirus Most Closely Related to the Human Coronavirus 229E. Viruses. 2012; 4(12):3689-3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4123689
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrossley, Beate M., Richard E. Mock, Scott A. Callison, and Sharon K. Hietala. 2012. "Identification and Characterization of a Novel Alpaca Respiratory Coronavirus Most Closely Related to the Human Coronavirus 229E" Viruses 4, no. 12: 3689-3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4123689
APA StyleCrossley, B. M., Mock, R. E., Callison, S. A., & Hietala, S. K. (2012). Identification and Characterization of a Novel Alpaca Respiratory Coronavirus Most Closely Related to the Human Coronavirus 229E. Viruses, 4(12), 3689-3700. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4123689