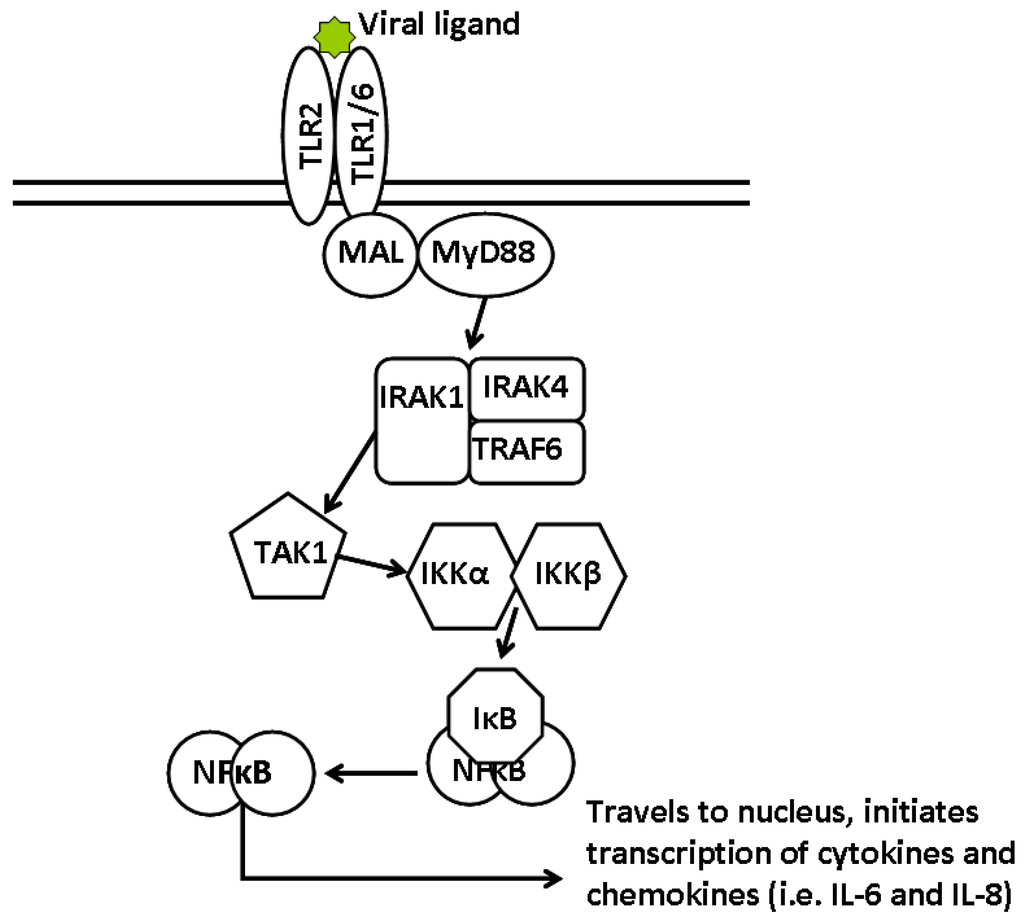
Abstract
The innate response to infection by an Old World arenavirus is initiated and mediated by extracellular and intracellular receptors, and effector molecules. In response, the invading virus has evolved to inhibit these responses and create the best environment possible for replication and spread. Here, we will discuss both the host’s response to infection with data from human infection and lessons learned from animal models, as well as the multitude of ways the virus combats the resulting immune response. Finally, we will highlight recent work identifying TLR2 as an innate sensor for arenaviruses and how the TLR2-dependent response differs depending on the pathogenicity of the strain.
1. Introduction
Old World arenaviruses cause a wide spectrum of disease in humans, determined by the strain of virus and the immune status of the patient. Lassa virus (LASV) affects an estimated 2 million people each year, causing mild, flu-like illness to severe multisystem disease. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) generally causes a mild, self-limiting illness in the immunocompetent person with rare progression to severe or fatal encephalitis, but can cause a hemorrhagic fever-like disease in patients in which the virus was acquired through solid organ transplantation, and are thus immunocompromised.
Because of strict regulations, studies involving LASV can be quite cumbersome. Since the earliest symptoms of LASV infection are non-specific, patient data is unreliable and incomplete. In order to understand the immune responses that contribute to LASV pathogenesis, or lack thereof, the use of surrogate arenaviruses, both Old and New World, in cell culture and animal model experiments helps to build a better picture of how Old World arenaviruses can cause severe disease.
3. Immune Evasion
Severe LASV infection is characterized by unchecked viremia, functional liver damage, and immunosuppression [29,30]. Viremia is strongly linked to disease manifestation and fatal outcomes. Viral evasion of immune mechanisms that would limit replication and spread would be beneficial to the virus. Inhibition of the antiviral state in infected cells as well as undiscovered infection by innate immune effector cells would allow efficient replication and dissemination. A lack of cytokine induction has been documented with pathogenic LASV and LCMV, strain WE [14,31,32]. In patients succumbing to LASV infection, the absence of IL-8 and IP-10, among a few other cytokines, was highly correlated to fatal outcome [12]. Exposure of PBMC from healthy donors to LASV demonstrated that IFN-related and apoptotic genes, as well as NFκB and coagulation pathways were the most highly affected in gene expression analysis [33]. However, treatment with IFN-I, but not IFN-γ, only limited arenavirus replication 10-fold in DC, and 10-100 fold in macrophages [34]. In accordance with the minimal effect of IFN-I on viral replication, it has been well documented that the nucleoprotein of all arenaviruses, with the exception of Tacaribe (TACV), functions as an IFN-I antagonist [35,36,37]. It is possible that the regulation of IFN-I by NP provides for chronic infection of the virus in its natural host as both virulent and non-virulent arenaviruses antagonized IFN-I in a dose-dependent manner [36].
Additionally, arenaviruses have a specific tropism for APCs, in which they are able to infect without activating these cells [7,38,39]. In human DC:T-cell co-cultures, LASV induced only weak memory phenotype markers, while MOPV strongly stimulated CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, activation markers, proliferative responses, and cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) activities [38]. We can speculate that TLR2-mediated production of cytokines in MOPV-infected cells [14] contributes to maturation of APC and thus strong adaptive immune responses. With 99% of the host cellular receptor, α-dystroglycan (DG), being expressed in the spleen, the virus is able to infect large numbers of APCs without initiating hallmark activation signals [34,39,40]. Infected DCs do not undergo migration or upregulation of costimulatory molecules thus allowing for efficient viral replication. These infected DCs may provide a reservoir of virus particles that can hide from immune surveillance. Infected macrophages lack phagocytic abilities and do not upregulate cytokines or chemokines that would recruit additional effector cells.
Collectively, the absence of cytokine production and the delayed maturation of APC potentially contributes to defective adaptive immune responses. The reduced expression of co-stimulatory molecules, CD40, CD80 and CD86, as well as down regulation of MHC class I and II molecules likely contributes to the observed lack of activated CD8+ and CD4+ T cells during infection in non-human primates and hence, an absence of cytotoxic function in mice [40,41,42,43,44]. However, while APCs fail to mature during arenavirus activation, they are still able to respond to external stimuli. Cytokines and costimulatory markers were upregulated even in infected cells when treated with LPS or poly:IC. Such treatment even inhibited viral replication, indicating that the cellular anti-viral mechanisms were not irreversibly damaged during infection [34].
Whether the inhibited induction of cytokines is a direct or indirect outcome of virulent virus infection, the lack of innate stimulation likely positions the host to have a delayed adaptive immune response that would effectively clear the infection. Suppression of cytokine responses, whether IFN-I or proinflammatory, might be necessary, but insufficient contributions to manifestation of disease. Pathogenesis may rely on other factors, such as viral replication, though replication of pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains was equivalent in vitro [14].
While a robust cell mediated immune response is observed ex vivo from patients surviving LASV infection, lack of efficient maturation of APCs and initiation of the adaptive CTL response may contribute to fatal LASV infections. Early responses to LASV infection are likely key to establishing a successful immune response. Given that IFN-I is poorly induced by LASV and that, with the exception of TACV, all arenaviruses encode an IFN-I antagonist, the proinflammatory immune response is likely necessary for establishing the ideal environment to combat arenavirus infection and limit viral replication. TLR2 is necessary for the proinflammatory response to LCMV in vitro and in vivo, however, the induction of proinflammatory responses by arenaviruses of different pathogenic potential has not been thoroughly examined.
5. Future Directions
Two important questions remain: how does TLR2 signaling contribute to resistance/recovery from arenavirus infection and how could the virus inhibit TLR2 signaling? To determine the importance of TLR2 signaling in protection against arenavirus infection, the correct animal model must be used. Mouse models of arenavirus infection rely on IFN-I rather than inflammatory cytokines and cytotoxic T cell responses. These mouse models provide more information for chronic infections rather than severe acute infections, such as those caused by LASV in humans. The non-human primate model most closely resembles the disease progression seen in humans. However, methods to decipher the contribution of TLR2 are more difficult to pursue in such models. The use of function-blocking antibody treatment may provide some insight. Studies could then be directed toward the activation of APC, T cells, or viral load, in the absence or reduction of TLR2 signaling. These types of studies could help elucidate the contribution of TLR2 signaling in the model presented below (Figure 3), in which pathogenic arenavirus fails to create an antiviral environment during the early stages of infection broadly affecting the ability to elicit an efficient adaptive immune response.
Along with the global effects of TLR2 signaling in arenavirus infection, it is still necessary to determine how arenaviruses stimulate the TLR2-dependent response and how this is inhibited during pathogenic arenavirus infection (Figure 4). We have demonstrated the requirement for live replicating virus and the differential activation of NFκB. From these results, we hypothesize that stimulation of TLR2 occurs during the replication cycle of the virus, whether via a viral component such as a protein-derived ligand or through viral RNA recognition. It is also possible that during the replicative cycle of the virus, the stress induced on the host cell results in release of danger signals that could then stimulate TLR2 [51]. One possible method to determine the contribution of intracellular TLR2 signaling would be the use of intrabodies directed towards TLR2. Intrabodies are intracellular antibodies that are expressed and retained in the endoplasmic reticulum [52]. Recently, an intrabody directed towards TLR2 was reported that was derived from a monoclonal antibody antagonistic to human and murine TLR2. This intrabody was able to retain TLR2 from the plasma membrane effectively and prevent NFκB activation from the cell surface. Additionally, the use of cross-linking studies and molecular imaging would also be useful in determining how arenaviruses are stimulating TLR2.
Ideally, one would like to singly express protein components of arenaviruses to determine if they stimulate TLR2. However, the requirement for live replicating virus confounds these efforts. The use of virus replicon particles (VRP) in which a replication defective virus particle encodes a gene under a separate promoter may help shed some light on this issue. VRPs could be used to express a particular gene of interest from either pathogenic or non-pathogenic arenaviruses. Additionally, using reverse genetics, proteins of pathogenic arenaviruses could be interchanged with the non-pathogenic protein, providing the replication necessary while singly expressing the pathogenic component.
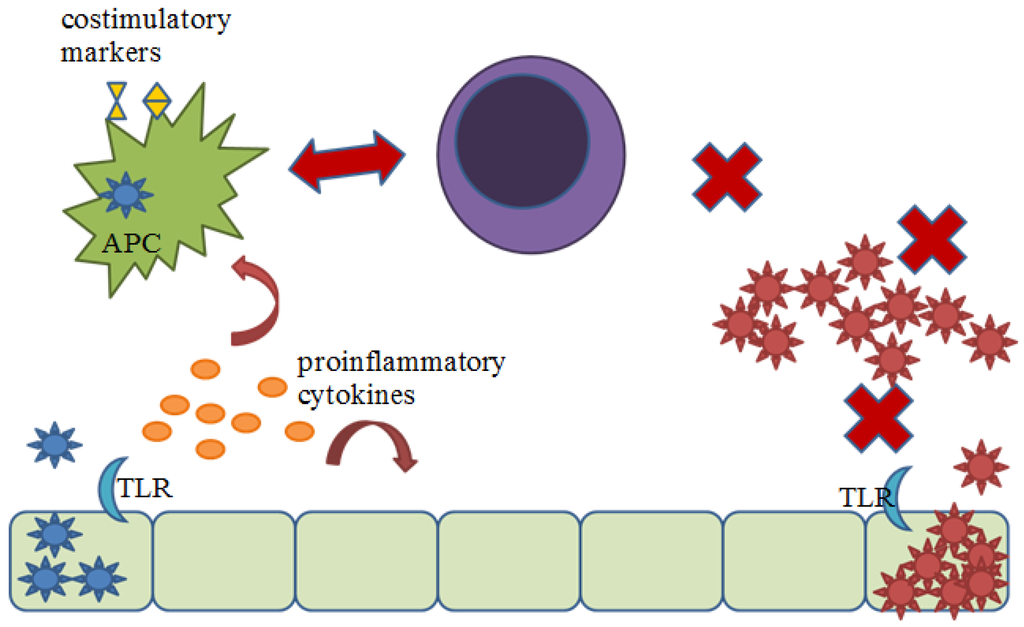
Figure 3.
Proposed model for contribution of TLR2 signaling to protection against arenavirus infection. Non-pathogenic arenavirus (blue) infects host cells and begins to replicate, stimulating TLR2. TLR2-dependent signaling induced the production of cytokines creating an anti-viral environment, recruiting innate effector cells, and inducing the activation of APC. APC are then able to efficiently activate an adaptive cytotoxic T cell response, by presenting viral antigen and upregulating costimulatory molecules, which is able to clear the infection. Pathogenic arenaviruses (red) fail to stimulate TLR2, allowing for unrecognized infection and uncontrolled replication. APCs are not activated towards maturation and cannot effectively activate an adaptive cytotoxic response.
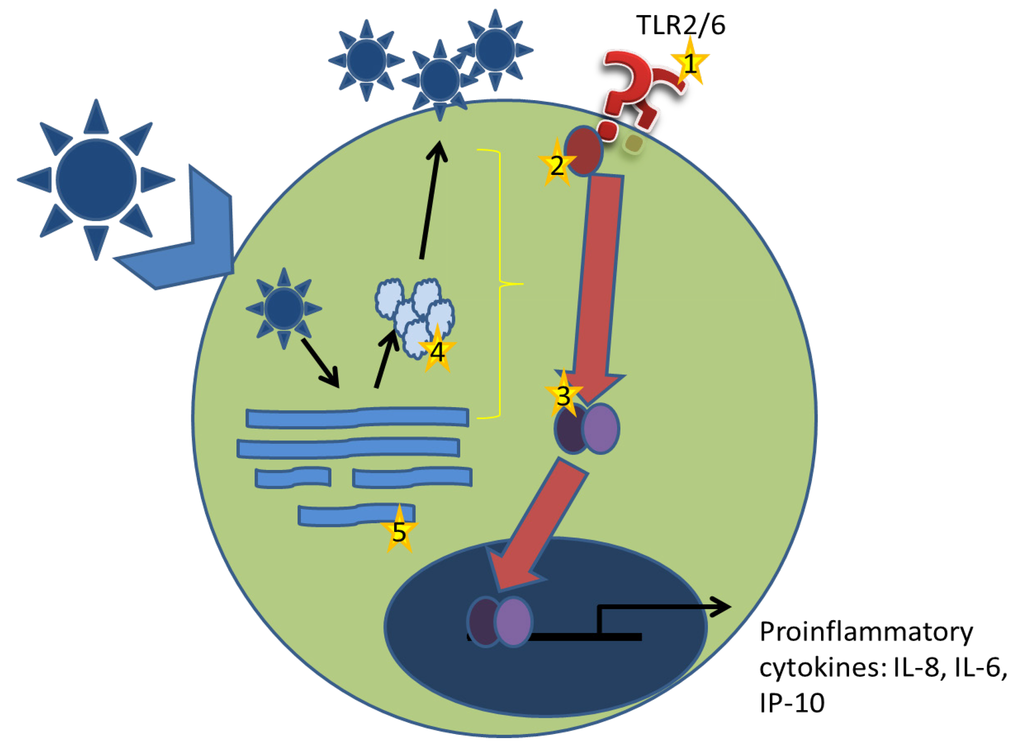
Figure 4.
Working model for arenavirus induced TLR2 signaling. Arenaviruses bind the host cellular receptor and enter a host cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Through a unique pathway, arenaviruses enter the endosomal sorting complex and have released their genomic contents within 20 minutes. Replication of genomic and mRNAs as well as protein production begins. Virus particles are assembled at the plasma membrane and are released by budding. (1) In arenavirus-TLR2 stimulation, it is unlikely that the virus stimulated TLR2 from the plasma membrane as replication defective virus particles were unable to elicit a TLR2-dependent response. (2) Disruption of the signaling pathway could be achieved by preventing association of Mal with TLR2 TIR domain. During replication, the Glycoprotein complex inserts itself into the plasma membrane and has the potential to block association. (3) NFκB is differentially activated during infection with pathogenic and non-pathogenic arenaviruses. This indicates that the inhibition observed with LCMV-WE infection occurs upstream of NFκB activation. Given that viral replication was necessary for both induction of TLR2-dependent responses and inhibition, it is possible that a viral protein (4), or viral RNA (5) is exerting these effects. It is equally possible that viral replication induces a cellular stress response that stimulates TLR2.
By comparing the differences in TLR2-dependent responses during infection by arenaviruses of differing pathogenic potential for humans and non-human primates in vitro, we have provided a possible explanation for the development of severe disease in LASV infection. Further work in this area could entail looking for differences in TLR2 stimulation, TLR2 mutations, and TLR2-related SNPs to determine why some, but not all infected patients, succumb to LASV infection. Additionally, having identified the differences in TLR2-dependent cytokine responses between pathogenic and non-pathogenic virus infection, this work provides an avenue for development of therapeutics. With limited treatments available to use against LASV infection, use of TLR2 agonists may provide activation of the type of immune response necessary to clear virus more effectively and increase chances for survival. It is not clear whether activation of TLR2 signaling should be taken into account in vaccine design for arenaviruses. The ideal vaccine candidate for Old World arenaviruses would stimulate an efficient cytotoxic response and generate long lasting memory. Knowing the role of TLR2/Mal/MyD88 signaling in generating specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses, and taking into consideration the inability of LASV to induce memory markers in T cells, it remains paradoxical that ML29, containing a small genomic segment from Lassa virus, has impaired induction of IL6 and IL8, yet is an excellent attenuated vaccine in non-human primates. Further reverse genetic and systems studies will be necessary to assess the role of the proinflammatory response in pathogenesis and protection.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Files
References
- Biron, C.A.; Nguyen, K.B.; Pien, G.C. Innate immune responses to LCMV infections: Natural killer cells and cytokines. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 263, 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Merigan, T.C.; Oldstone, M.B.; Welsh, R.M. Interferon production during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of nude and normal mice. Nature 1977, 268, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djavani, M.M.; Crasta, O.R.; Zapata, J.C.; Fei, Z.; Folkerts, O.; Sobral, B.; Swindells, M.; Bryant, J.; Davis, H.; Pauza, C.D.; et al. Early blood profiles of virus infection in a monkey model for lassa fever. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7960–7973. [Google Scholar]
- Rodas, J.D.; Cairo, C.; Djavani, M.; Zapata, J.C.; Ruckwardt, T.; Bryant, J.; Pauza, C.D.; Lukashevich, I.S.; Salvato, M.S. Circulating natural killer and gammadelta t cells decrease soon after infection of rhesus macaques with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo. Cruz. 2009, 104, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asper, M.; Sternsdorf, T.; Hass, M.; Drosten, C.; Rhode, A.; Schmitz, H.; Gunther, S. Inhibition of different lassa virus strains by alpha and gamma interferons and comparison with a less pathogenic arenavirus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3162–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habjan, M.; Andersson, I.; Klingstrom, J.; Schumann, M.; Martin, A.; Zimmermann, P.; Wagner, V.; Pichlmair, A.; Schneider, U.; Muhlberger, E.; et al. Processing of genome 5' termini as a strategy of negative-strand rna viruses to avoid rig-i-dependent interferon induction. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2032. [Google Scholar]
- Pannetier, D.; Faure, C.; Georges-Courbot, M.C.; Deubel, V.; Baize, S. Human macrophages, but not dendritic cells, are activated and produce alpha/beta interferons in response to mopeia virus infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10516–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, T.; Noda, T.; Urata, S.; Kawaoka, Y.; Yasuda, J. Inhibition of lassa and marburg virus production by tetherin. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2382–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Cerny, A.M.; Zacharia, A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Induction and inhibition of type i interferon responses by distinct components of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9452–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, A.; Kato, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Lymphocytoid choriomeningitis virus activates plasmacytoid dendritic cells and induces a cytotoxic t-cell response via myd88. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, G.S.; Qui, X.; Bente, D.A.; Strong, U.C.; Jones, S.M. Resistance to a Lassa virus infection is interferon-dependent, but not B or T cell-mediated in mice. Abstracts for the 28th Meeting of the American Society for Virology 2009, W7-7, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Mahanty, S.; Bausch, D.G.; Thomas, R.L.; Goba, A.; Bah, A.; Peters, C.J.; Rollin, P.E. Low levels of interleukin-8 and interferon-inducible protein-10 in serum are associated with fatal infections in acute lassa fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Baruch, A.; Michiel, D.F.; Oppenheim, J.J. Signals and receptors involved in recruitment of inflammatory cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11703–11706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Maryankova, R.; Vladyko, A.S.; Nashkevich, N.; Koleda, S.; Djavani, M.; Horejsh, D.; Voitenok, N.N.; Salvato, M.S. Lassa and mopeia virus replication in human monocytes/macrophages and in endothelial cells: Different effects on il-8 and tnf-alpha gene expression. J. Med. Virol. 1999, 59, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennewald, S.M.; Aronson, J.F.; Zhang, L.; Herzog, N.K. Alterations in nf-kappab and rbp-jkappa by arenavirus infection of macrophages in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennewald, S.M.; Scott, E.P.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Aronson, J.F.; Gorenstein, D.G.; Luxon, B.A.; Shope, R.E.; Beasley, D.W.; Barrett, A.D.; et al. Thioaptamer decoy targeting of ap-1 proteins influences cytokine expression and the outcome of arenavirus infections. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Mandell, L.; Cerny, A.; Chan, M.; Golenbock, D.T.; Finberg, R.W. Myd88 is critical for the development of innate and adaptive immunity during acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalat, R.; Lau, L.; Locksley, R.M.; Barton, G.M. Toll-like receptor 2 on inflammatory monocytes induces type i interferon in response to viral but not bacterial ligands. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Halle, A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Cerny, A.M.; Porpiglia, E.; Rogers, M.; Golenbock, D.T.; Finberg, R.W. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection of cns glial cells results in tlr2-myd88/mal-dependent inflammatory responses. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 194, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.W.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Nunneley, J.; Medvedev, A.E.; Salvato, M.S.; Lukashevich, I.S. Pathogenic old world arenaviruses inhibit tlr2/mal-dependent proinflammatory cytokines in vitro. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7216–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; McCormick, J.B. Towards a human lassa fever vaccine. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Meulen, J.; Badusche, M.; Kuhnt, K.; Doetze, A.; Satoguina, J.; Marti, T.; Loeliger, C.; Koulemou, K.; Koivogui, L.; Schmitz, H.; et al. Characterization of human cd4(+) t-cell clones recognizing conserved and variable epitopes of the lassa virus nucleoprotein. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulen, J.; Badusche, M.; Satoguina, J.; Strecker, T.; Lenz, O.; Loeliger, C.; Sakho, M.; Koulemou, K.; Koivogui, L.; Hoerauf, A. Old and new world arenaviruses share a highly conserved epitope in the fusion domain of the glycoprotein 2, which is recognized by lassa virus-specific human cd4+ t-cell clones. Virology 2004, 321, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Cerny, A.M.; Chan, M.; Bronson, R.T.; Finberg, R.W. Myd88 intrinsically regulates cd4 t-cell responses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholdy, C.; Christensen, J.E.; Grujic, M.; Christensen, J.P.; Thomsen, A.R. T-cell intrinsic expression of myd88 is required for sustained expansion of the virus-specific cd8+ t-cell population in lcmv-infected mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.H.; Cui, W.; Larosa, D.F.; Taylor, D.K.; Zhang, J.; Goldstein, D.R.; Wherry, E.J.; Kaech, S.M.; Turka, L.A. Myd88 plays a critical t cell-intrinsic role in supporting cd8 t cell expansion during acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3804–3810. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.H.; Zhang, R.; Blosser, C.D.; Hou, B.; Defranco, A.L.; Maltzman, J.S.; Wherry, E.J.; Turka, L.A. Antiviral memory cd8 t-cell differentiation, maintenance, and secondary expansion occur independently of myd8. Blood 2011, 117, 3123–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.M.; McCormick, J.B.; Webb, P.A.; Smith, E.S.; Elliott, L.H.; King, I.J. Clinical virology of lassa fever in hospitalized patients. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.B.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P. Lassa fever. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 262, 75–109. [Google Scholar]
- Moraz, M.L.; Kunz, S. Pathogenesis of arenavirus hemorrhagic fevers. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Tikhonov, I.; Rodas, J.D.; Zapata, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Djavani, M.; Salvato, M.S. Arenavirus-mediated liver pathology: Acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of rhesus macaques is characterized by high-level interleukin-6 expression and hepatocyte proliferation. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Rodas, J.D.; Tikhonov, II; Zapata, J.C.; Yang, Y.; Djavani, M.; Salvato, M.S. Lcmv-mediated hepatitis in rhesus macaques: We but not arm strain activates hepatocytes and induces liver regeneration. Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 2319–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.; While, D.; Poonia, B.; Mani, S.; Jett, M.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Crasta, O.; Zhang, Y.; Salvato, M.; Lukashevich, I. Expression of coagulation factor thrombomodulin is increased in cells exposed to lassa virus. In Proceedings of The 29th ASV Meeting, Bozeman, Montana, USA, July 17, 2010.
- Baize, S.; Pannetier, D.; Faure, C.; Marianneau, P.; Marendat, I.; Georges-Courbot, M.C.; Deubel, V. Role of interferons in the control of lassa virus replication in human dendritic cells and macrophages. Microbes. Infect. 2006, 8, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Emonet, S.; Giannakas, P.; Cubitt, B.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; de la Torre, J.C. Identification of amino acid residues critical for the anti-interferon activity of the nucleoprotein of the prototypic arenavirus lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11330–11340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Giannakas, P.; Cubitt, B.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; de la Torre, J.C. Differential inhibition of type i interferon induction by arenavirus nucleoproteins. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12696–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Zuniga, E.I.; Rosario, D.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; de la Torre, J.C. Inhibition of the type i interferon response by the nucleoprotein of the prototypic arenavirus lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9192–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannetier, D.; Reynard, S.; Russier, M.; Journeaux, A.; Tordo, N.; Deubel, V.; Baize, S. Human dendritic cells infected with the nonpathogenic mopeia virus induce stronger t-cell responses than those infected with lassa virus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8293–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baize, S.; Kaplon, J.; Faure, C.; Pannetier, D.; Georges-Courbot, M.C.; Deubel, V. Lassa virus infection of human dendritic cells and macrophages is productive but fails to activate cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla, N.; Kunz, S.; Holz, A.; Lewicki, H.; Homann, D.; Yamada, H.; Campbell, K.P.; de La Torre, J.C.; Oldstone, M.B. Immunosuppression and resultant viral persistence by specific viral targeting of dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baize, S.; Marianneau, P.; Loth, P.; Reynard, S.; Journeaux, A.; Chevallier, M.; Tordo, N.; Deubel, V.; Contamin, H. Early and strong immune responses are associated with control of viral replication and recovery in lassa virus-infected cynomolgus monkeys. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5890–5903. [Google Scholar]
- Borrow, P.; Evans, C.F.; Oldstone, M.B. Virus-induced immunosuppression: Immune system-mediated destruction of virus-infected dendritic cells results in generalized immune suppression. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla, N.; McGavern, D.B.; Teng, C.; Kunz, S.; Oldstone, M.B. Viral targeting of hematopoietic progenitors and inhibition of dc maturation as a dual strategy for immune subversion. J. Clin. Inv. 2004, 113, 737–745. [Google Scholar]
- Mahanty, S.; Hutchinson, K.; Agarwal, S.; McRae, M.; Rollin, P.E.; Pulendran, B. Cutting edge: Impairment of dendritic cells and adaptive immunity by ebola and lassa viruses. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, C.D.; Lavanya, M.; Wang, E.; Ross, S.R. Junin virus infects mouse cells and induces innate immune responses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11058–11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groseth, A.; Hoenen, T.; Weber, M.; Wolff, S.; Herwig, A.; Kaufmann, A.; Becker, S. Tacaribe virus but not junin virus infection induces cytokine release from primary human monocytes and macrophages. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieback, K.; Lien, E.; Klagge, I.M.; Avota, E.; Schneider-Schaulies, J.; Duprex, W.P.; Wagner, H.; Kirschning, C.J.; Ter Meulen, V.; Schneider-Schaulies, S. Hemagglutinin protein of wild-type measles virus activates toll-like receptor 2 signaling. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8729–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, K.W.; Guerrero, M.; Compton, T. Human cytomegalovirus envelope glycoproteins b and h are necessary for tlr2 activation in permissive cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7094–7102. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Dolganiuc, A.; Szabo, G. Toll-like receptors 1 and 6 are involved in tlr2-mediated macrophage activation by hepatitis c virus core and ns3 proteins. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganiuc, A.; Oak, S.; Kodys, K.; Golenbock, D.T.; Finberg, R.W.; Kurt-Jones, E.; Szabo, G. Hepatitis c core and nonstructural 3 proteins trigger toll-like receptor 2-mediated pathways and inflammatory activation. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisinha, S. Insight into the mechanisms regulating immune homeostasis in health and disease. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschning, C.J.; Dreher, S.; Maass, B.; Fichte, S.; Schade, J.; Koster, M.; Noack, A.; Lindenmaier, W.; Wagner, H.; Boldicke, T. Generation of anti-tlr2 intrabody mediating inhibition of macrophage surface tlr2 expression and tlr2-driven cell activation. BMC Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).