Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and Regulatory T Cells in HTLV-1-Associated Neuroinflammatory Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
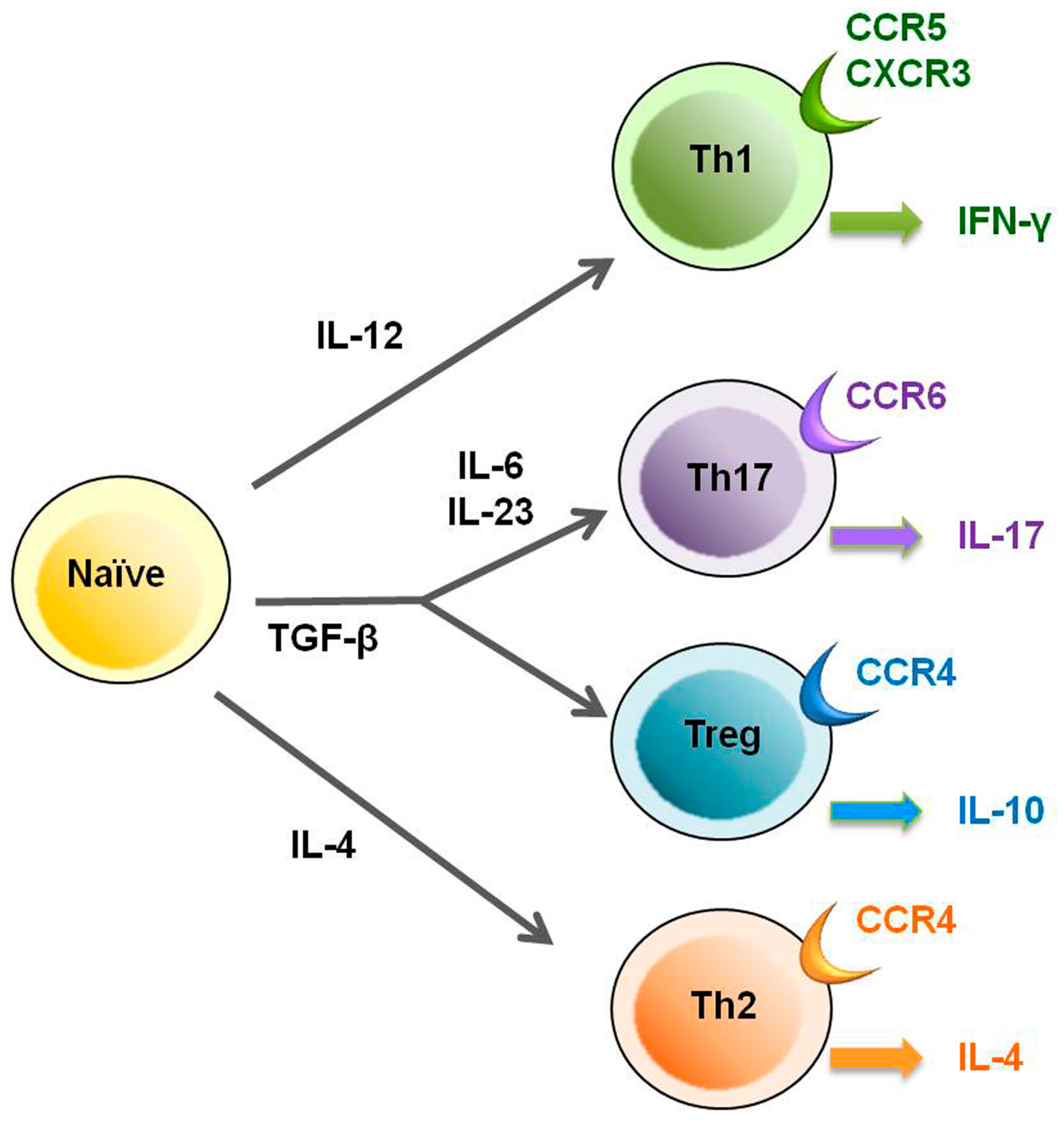
2. HTLV-1 and Regulatory T Cells
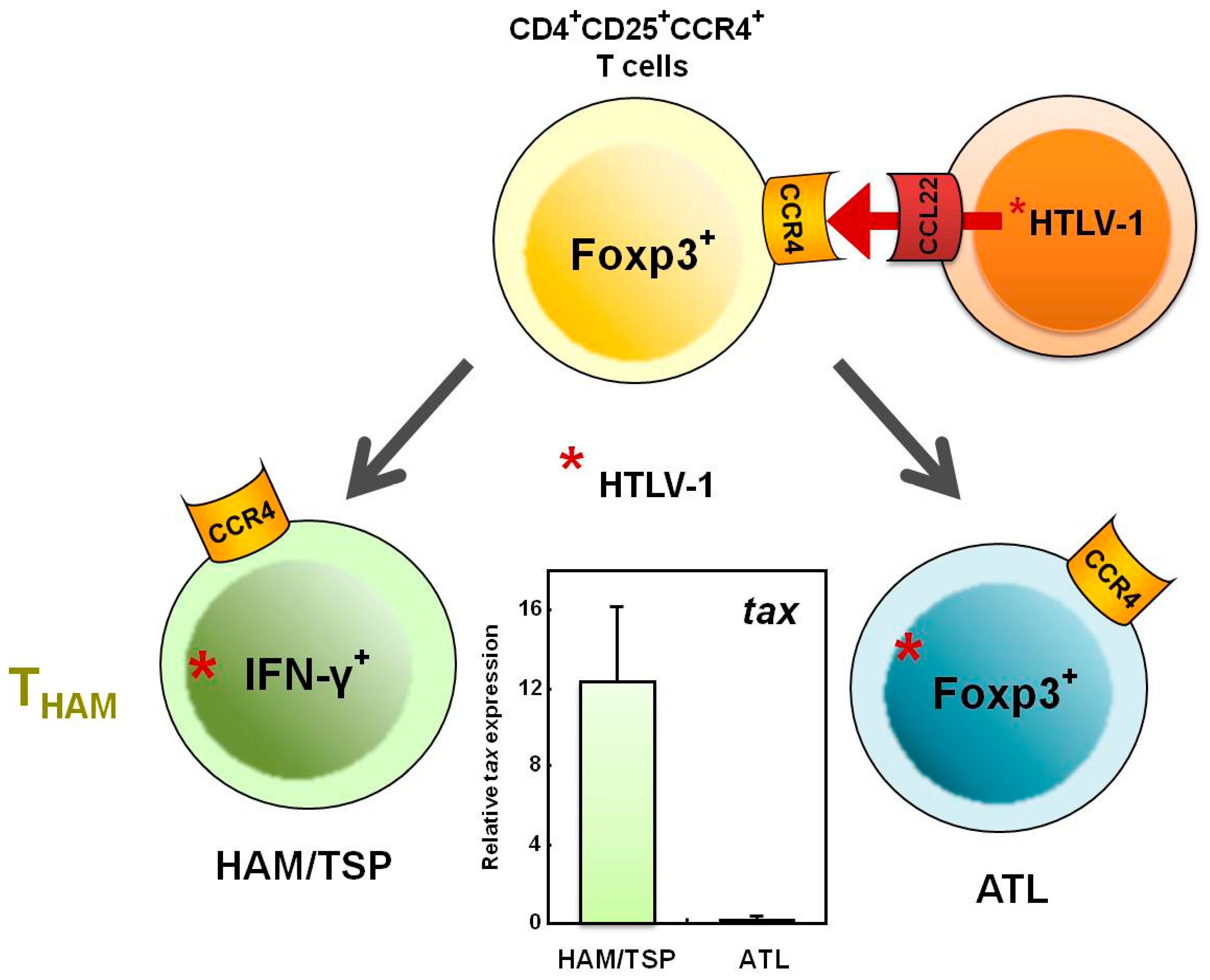
3. HTLV-1 and CD4+CD25+CCR4+ T Cells
4. HTLV-1 and Foxp3–CD4+CD25+CCR4+ T Cells
5. Increased Numbers of CD4+Foxp3+ Cells in HAM/TSP Patients
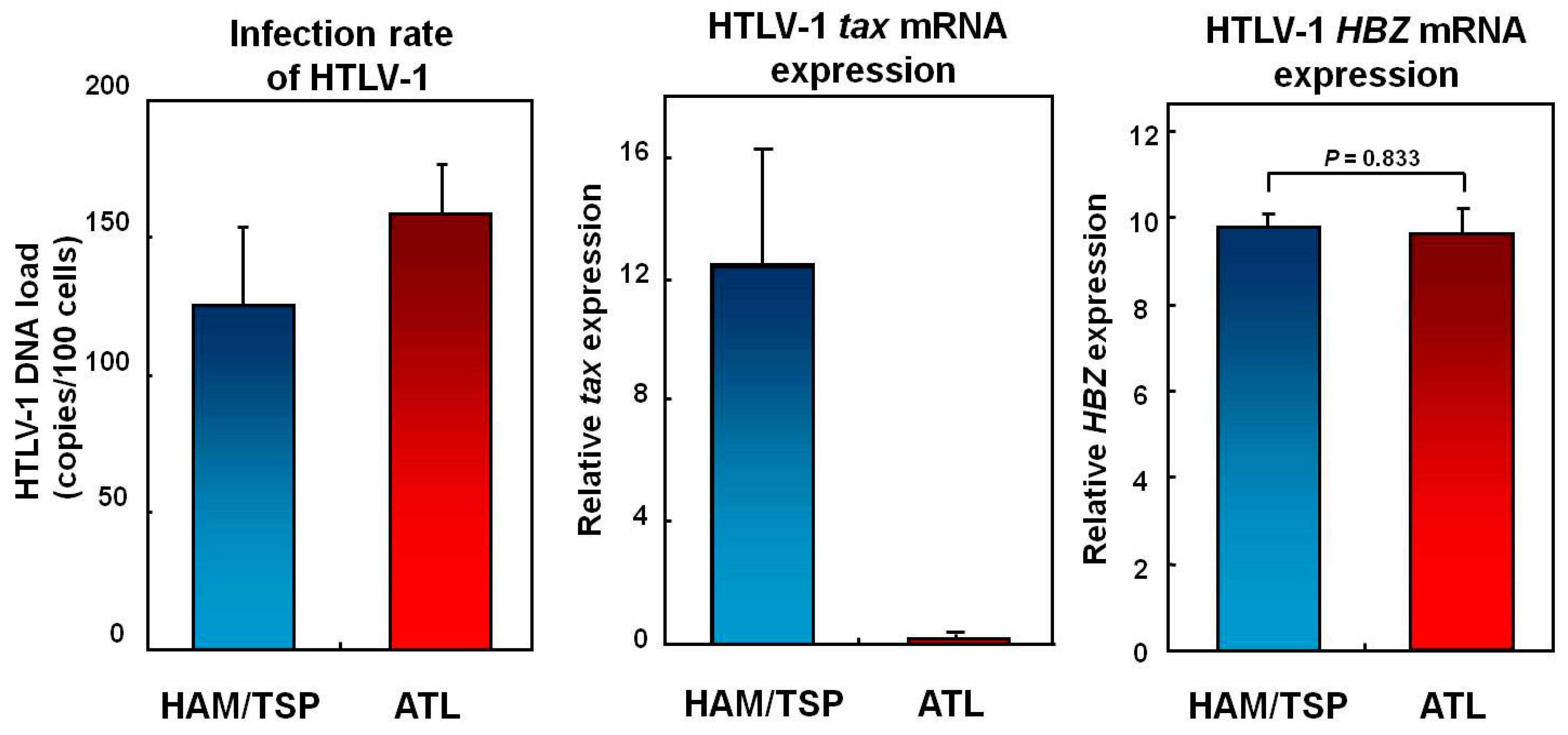
6. Does the THAM Cell Population Include exFoxp3+ Cells?
7. Mechanisms Underlying Increased HTLV-1 Tax Expression in HAM/TSP Patients
8. Conclusion
Conflict of interest
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Birmann, B.M.; Breen, E.C.; Stuver, S.; Cranston, B.; Martinez-Maza, O.; Falk, K.I.; Okayama, A.; Hanchard, B.; Mueller, N.; Hisada, M. Population differences in immune marker profiles associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection in Japan and Jamaica. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, T.; Yodoi, J.; Sagawa, K.; Takatsuki, K.; Uchino, H. Adult T-cell leukemia: Clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood 1977, 50, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; de The, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, N.; Amitani, H.; Igata, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Tara, M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Nakashima, S.; Shirao, M.; Araki, S.; Takatsuki, K.; Mori, S.; Miyata, N. Uveitis associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1992, 114, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Matsuoka, N.; Ida, H.; Nakashima, M.; Sakai, M.; Sakito, S.; Kawakami, A.; Terada, K.; Shimada, H.; Kawabe, Y.; et al. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome with antibodies to HTLV-I: Clinical and laboratory features. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1992, 51, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K.; Maruyama, I.; Sato, K.; Kitajima, I.; Nakajima, Y.; Osame, M. Chronic inflammatory arthropathy associated with HTLV-I. Lancet 1989, 1, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, O.S.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Mora, C.; Char, G. HTLV-1 and polymyositis in Jamaica. Lancet 1989, 2, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, S.; Kubota, H.; Arimura, K.; Kawabata, M.; Osame, M. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: Analysis of 213 patients based on clinical features and laboratory findings. J. Neurovirol. 1995, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Usuku, K.; Matsumoto, W.; Kodama, D.; Takenouchi, N.; Moritoyo, T.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ichinose, M.; Bangham, C.R.; Izumo, S.; et al. Analysis of HTLV-I proviral load in 202 HAM/TSP patients and 243 asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers: High proviral load strongly predisposes to HAM/TSP. J. Neurovirol. 1998, 4, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, Y.; Nagai, M.; Brennan, M.; Mora, C.A.; Soldan, S.S.; Tomaru, U.; Takenouchi, N.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M.; Jacobson, S. Correlation of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) mRNA with proviral DNA load, virus-specific CD8(+) T cells, and disease severity in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Blood 2002, 99, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Yamano, Y.; Brennan, M.B.; Mora, C.A.; Jacobson, S. Increased HTLV-I proviral load and preferential expansion of HTLV-I Tax-specific CD8+ T cells in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with HAM/TSP. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Kubota, R.; Greten, T.F.; Schneck, J.P.; Leist, T.P.; Jacobson, S. Increased activated human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) Tax11-19-specific memory and effector CD8+ cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Correlation with HTLV-I provirus load. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.; Shida, H.; McFarlin, D.E.; Fauci, A.S.; Koenig, S. Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-I pX in patients with HTLV-I associated neurological disease. Nature 1990, 348, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, R.; Kawanishi, T.; Matsubara, H.; Manns, A.; Jacobson, S. HTLV-I specific IFN-gamma+ CD8+ lymphocytes correlate with the proviral load in peripheral blood of infected individuals. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 102, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanon, E.; Goon, P.; Taylor, G.P.; Hasegawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Weber, J.N.; Bangham, C.R. High production of interferon gamma but not interleukin-2 by human T-lymphotropic virus type I-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Blood 2001, 98, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vine, A.M.; Heaps, A.G.; Kaftantzi, L.; Mosley, A.; Asquith, B.; Witkover, A.; Thompson, G.; Saito, M.; Goon, P.K.; Carr, L.; et al. The role of CTLs in persistent viral infection: Cytolytic gene expression in CD8+ lymphocytes distinguishes between individuals with a high or low proviral load of human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Tosu, M.; Yoshida, E.; Takiguchi, M.; Sato, K.; Kitajima, I.; Nishioka, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Takeda, T.; Hatanaka, M.; et al. Induction of inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in mice transgenic for HTLV-I. Science 1991, 253, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamaru, Y.; Ishizu, A.; Ikeda, H.; Sugaya, T.; Fugo, K.; Higuchi, M.; Yamazaki, H.; Yoshiki, T. Immunological hyperresponsiveness in HTLV-I LTR-env-pX transgenic rats: A prototype animal model for collagen vascular and HTLV-I-related inflammatory diseases. Pathobiology 2001, 69, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aono, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Hasunuma, T.; Marriott, S.J.; Nishioka, K. Extracellular human T cell leukemia virus type I tax protein stimulates the proliferation of human synovial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekevitz, M.; Feinberg, M.B.; Holbrook, N.; Wong-Staal, F.; Greene, W.C. Activation of interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor (Tac) promoter expression by the trans-activator (tat) gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus, type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1987, 84, 5389–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, S.L.; Feinberg, M.B.; Wolf, J.B.; Holbrook, N.J.; Wong-Staal, F.; Leonard, W.J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: Activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell 1987, 49, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, N.; Brown, K.; Bamford, R.N.; Tagaya, Y.; Siebenlist, U.; Waldmann, T.A. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I Tax protein trans-activates interleukin 15 gene transcription through an NF-kappaB site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1998, 95, 2452–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariner, J.M.; Lantz, V.; Waldmann, T.A.; Azimi, N. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I Tax activates IL-15R alpha gene expression through an NF-kappa B site. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, T.A. The biology of interleukin-2 and interleukin-15: Implications for cancer therapy and vaccine design. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Sakaguchi, N.; Asano, M.; Itoh, M.; Toda, M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, S.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 2003, 299, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ono, M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008, 133, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, Y.; Cohen, C.J.; Takenouchi, N.; Yao, K.; Tomaru, U.; Li, H.C.; Reiter, Y.; Jacobson, S. Increased expression of human T lymphocyte virus type I (HTLV-I) Tax11-19 peptide-human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen A*201 complexes on CD4+ CD25+ T Cells detected by peptide-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted antibodies in patients with HTLV-I-associated neurologic disease. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Yamano, Y.; Takenouchi, N.; Li, H.C.; Tomaru, U.; Yao, K.; Grant, C.W.; Maric, D.A.; Jacobson, S. Virus-induced dysfunction of CD4+CD25+ T cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated neuroimmunological disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, U.; Grant, C.; Griffith, C.; Fugo, K.; Takenouchi, N.; Jacobson, S. Reduced Foxp3 protein expression is associated with inflammatory disease during human t lymphotropic virus type 1 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelsson, J.; Barbosa, H.M.; Jordan, K.A.; Chapman, J.M.; Brunialti, M.K.; Neto, W.K.; Nukui, Y.; Sabino, E.C.; Chieia, M.A.; Oliveira, A.S.; et al. The frequency of CD127low expressing CD4+CD25high T regulatory cells is inversely correlated with human T lymphotrophic virus type-1 (HTLV-1) proviral load in HTLV-1-infection and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. BMC Immunol. 2008, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, D.; Kubota, R.; Takenouchi, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Hirano, R.; Takashima, H.; Osame, M.; Izumo, S.; Arimura, K. Reduced Foxp3 expression with increased cytomegalovirus-specific CTL in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 200, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.M.; Brembilla, B.N.; Sorg, O.; Chicheportiche, R.; Matthes, T.; Dayer, J.M.; Saurat, J.H.; Roosnek, E.; Chizzolini, C. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor reveals distinct requirements for IL-22 and IL-17 production by human T helper cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Oh, U.; Yao, K.; Yamano, Y.; Jacobson, S. Dysregulation of TGF-beta signaling and regulatory and effector T-cell function in virus-induced neuroinflammatory disease. Blood 2008, 111, 5601–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsugi, E.; KUmasaka, T. Low CD4/CD8 T-cell ratio associated with inflammatory arthropathy in human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Saito, K.; Arimura, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Ohara, Y. In vivo expression of the HBZ gene of HTLV-1 correlates with proviral load, inflammatory markers and disease severity in HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Retrovirology 2009, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Zhao, T.; Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, P.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohshima, K.; Green, P.L.; Ohkura, N.; et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces T-cell lymphoma and systemic inflammation in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, K.; Ohshima, K.; Tsuchiya, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kawano, R.; Suzumiya, J.; Utsunomiya, A.; Harada, M.; Kikuchi, M. Expression of FoxP3, a key molecule in CD4CD25 regulatory T cells, in adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncador, G.; Garcia, J.F.; Maestre, L.; Lucas, E.; Menarguez, J.; Ohshima, K.; Nakamura, S.; Banham, A.H.; Piris, M.A. FOXP3, a selective marker for a subset of adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Yamada, Y.; Akamatsu, N.; Kamihira, S.; Imaizumi, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Matsuyama, T. Possible origin of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells from human T lymphotropic virus type-1-infected regulatory T cells. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ishii, N.; Ine, S.; Ikeda, S.; Fujimura, T.; Ndhlovu, L.C.; Soroosh, P.; Tada, K.; Harigae, H.; Kameoka, J.; et al. Regulatory T cell-like activity of Foxp3+ adult T cell leukemia cells. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubar, Y.; Hori, T.; Morita, R.; Sakaguchi, S.; Uchiyama, T. Delineation of immunoregulatory properties of adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2006, 84, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimauchi, T.; Kabashima, K.; Tokura, Y. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells from blood and skin tumors express cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 and Foxp3 but lack suppressor activity toward autologous CD8+ T cells. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, Y.; Itoyama, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Takamatsu, K.; Kira, J.; Iwamasa, T.; Goto, I.; Yamamoto, N. In vivo infection of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in non-T cells. Virology 1993, 196, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Brennan, M.B.; Sakai, J.A.; Mora, C.A.; Jacobson, S. CD8(+) T cells are an in vivo reservoir for human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Blood 2001, 98, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.S.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Huang, Y.K.; Bertolette, D.C.; Ruscetti, F.W. Cell-free HTLV-1 infects dendritic cells leading to transmission and transformation of CD4(+) T cells. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enose-Akahata, Y.; Oh, U.; Grant, C.; Jacobson, S. Retrovirally induced CTL degranulation mediated by IL-15 expression and infection of mononuclear phagocytes in patients with HTLV-I-associated neurologic disease. Blood 2008, 112, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azakami, K.; Sato, T.; Araya, N.; Utsunomiya, A.; Kubota, R.; Suzuki, K.; Hasegawa, D.; Izumi, T.; Fujita, H.; Aratani, S.; et al. Severe loss of invariant NKT cells exhibiting anti-HTLV-1 activity in patients with HTLV-1-associated disorders. Blood 2009, 114, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.H.; Edwards, A.J.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Rudge, P.; Dalgleish, A.G. In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 5682–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshie, O.; Fujisawa, R.; Nakayama, T.; Harasawa, H.; Tago, H.; Izawa, D.; Hieshima, K.; Tatsumi, Y.; Matsushima, K.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Frequent expression of CCR4 in adult T-cell leukemia and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-transformed T cells. Blood 2002, 99, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Nagira, M.; Takagi, S.; Kakizaki, M.; Nishimura, M.; Wang, J.; Gray, P.W.; Matsushima, K.; Yoshie, O. Selective recruitment of CCR4-bearing Th2 cells toward antigen-presenting cells by the CC chemokines thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and macrophage-derived chemokine. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iellem, A.; Mariani, M.; Lang, R.; Recalde, H.; Panina-Bordignon, P.; Sinigaglia, F.; D’Ambrosio, D. Unique chemotactic response profile and specific expression of chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, Y.; Araya, N.; Sato, T.; Utsunomiya, A.; Azakami, K.; Hasegawa, D.; Izumi, T.; Fujita, H.; Aratani, S.; Yagishita, N.; et al. Abnormally high levels of virus-infected IFN-gamma+ CCR4+ CD4+ CD25+ T cells in a retrovirus-associated neuroinflammatory disorder. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyara, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kitoh, A.; Shima, T.; Wing, K.; Niwa, A.; Parizot, C.; Taflin, C.; Heike, T.; Valeyre, D.; et al. Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity 2009, 30, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshie, O. Expression of CCR4 in adult T-cell leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2005, 46, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannagi, M. Immunologic control of human T-cell leukemia virus type I and adult T-cell leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) infection and the onset of adult T-cell leukemia (ATL). Retrovirology 2005, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, R.; Nagai, M.; Kawanishi, T.; Osame, M.; Jacobson, S. Increased HTLV type 1 tax specific CD8+ cells in HTLV type 1-asociated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Correlation with HTLV type 1 proviral load. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2000, 16, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, T.; Nakamura, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Nakane, S.; Kambara, C.; Shirabe, S.; Hamasaki, S.; Motomura, M.; Eguchi, K. Elevated levels of interleukin-12 and interferon-gamma in patients with human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 95, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulza, F.; Heaps, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. High frequency of CD4+FoxP3+ cells in HTLV-1 infection: Inverse correlation with HTLV-1-specific CTL response. Blood 2008, 111, 5047–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Bailey-Bucktrout, S.L.; Jeker, L.T.; Penaranda, C.; Martinez-Llordella, M.; Ashby, M.; Nakayama, M.; Rosenthal, W.; Bluestone, J.A. Instability of the transcription factor Foxp3 leads to the generation of pathogenic memory T cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, M.; Komatsu, N.; Kawamoto, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kanagawa, O.; Honjo, T.; Hori, S.; Fagarasan, S. Preferential generation of follicular B helper T cells from Foxp3+ T cells in gut Peyer’s patches. Science 2009, 323, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, B.; Mosley, A.J.; Heaps, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; McLean, A.R.; Bangham, C.R. Quantification of the virus-host interaction in human T lymphotropic virus I infection. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, B.; Zhang, Y.; Mosley, A.J.; de Lara, C.M.; Wallace, D.L.; Worth, A.; Kaftantzi, L.; Meekings, K.; Griffin, G.E.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. In vivo T lymphocyte dynamics in humans and the impact of human T-lymphotropic virus 1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 8035–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, B.; Bangham, C.R. How does HTLV-I persist despite a strong cell-mediated immune response? Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derse, D.; Crise, B.; Li, Y.; Princler, G.; Lum, N.; Stewart, C.; McGrath, C.F.; Hughes, S.H.; Munroe, D.J.; Wu, X. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 integration target sites in the human genome: Comparison with those of other retroviruses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6731–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meekings, K.N.; Leipzig, J.; Bushman, F.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. HTLV-1 integration into transcriptionally active genomic regions is associated with proviral expression and with HAM/TSP. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2011 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Araya, N.; Sato, T.; Yagishita, N.; Ando, H.; Utsunomiya, A.; Jacobson, S.; Yamano, Y. Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and Regulatory T Cells in HTLV-1-Associated Neuroinflammatory Disease. Viruses 2011, 3, 1532-1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3091532
Araya N, Sato T, Yagishita N, Ando H, Utsunomiya A, Jacobson S, Yamano Y. Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and Regulatory T Cells in HTLV-1-Associated Neuroinflammatory Disease. Viruses. 2011; 3(9):1532-1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3091532
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraya, Natsumi, Tomoo Sato, Naoko Yagishita, Hitoshi Ando, Atae Utsunomiya, Steven Jacobson, and Yoshihisa Yamano. 2011. "Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and Regulatory T Cells in HTLV-1-Associated Neuroinflammatory Disease" Viruses 3, no. 9: 1532-1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3091532
APA StyleAraya, N., Sato, T., Yagishita, N., Ando, H., Utsunomiya, A., Jacobson, S., & Yamano, Y. (2011). Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and Regulatory T Cells in HTLV-1-Associated Neuroinflammatory Disease. Viruses, 3(9), 1532-1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3091532



