The Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Function Is Modulated by HIV-1 Accessory Proteins
Abstract
:1. Natural Killer Cells Control Virus Production
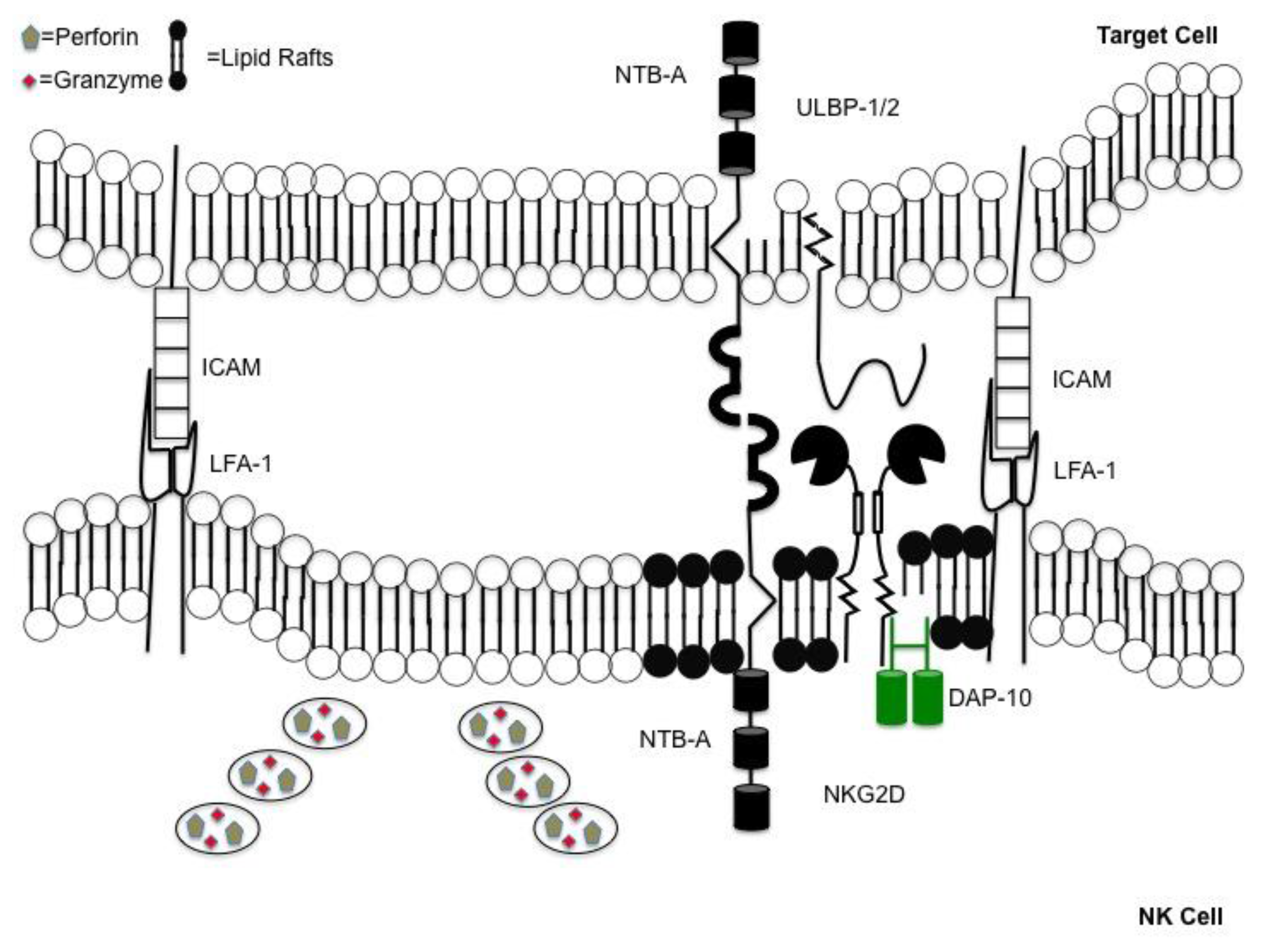
2. Polarization of Lytic Granules in NK Cells Requires Stable Interactions with Target Cells
3. Degranulation Follows Engagement of NK Cell Activating Receptors
4. Phospholipase C-γ is the Key Mediator for NK Cell Degranulation
5. Inhibitory Receptors Regulate Cytoskeleton Rearrangement and Synapse Formation
6. HIV-1 Alters NK Cell Degranulation by Modulating Ligands to NK Cell Receptors
6.1. HIV-1 Vpr Induces Expression of Ligands for the NK Cell Activating Receptor NKG2D
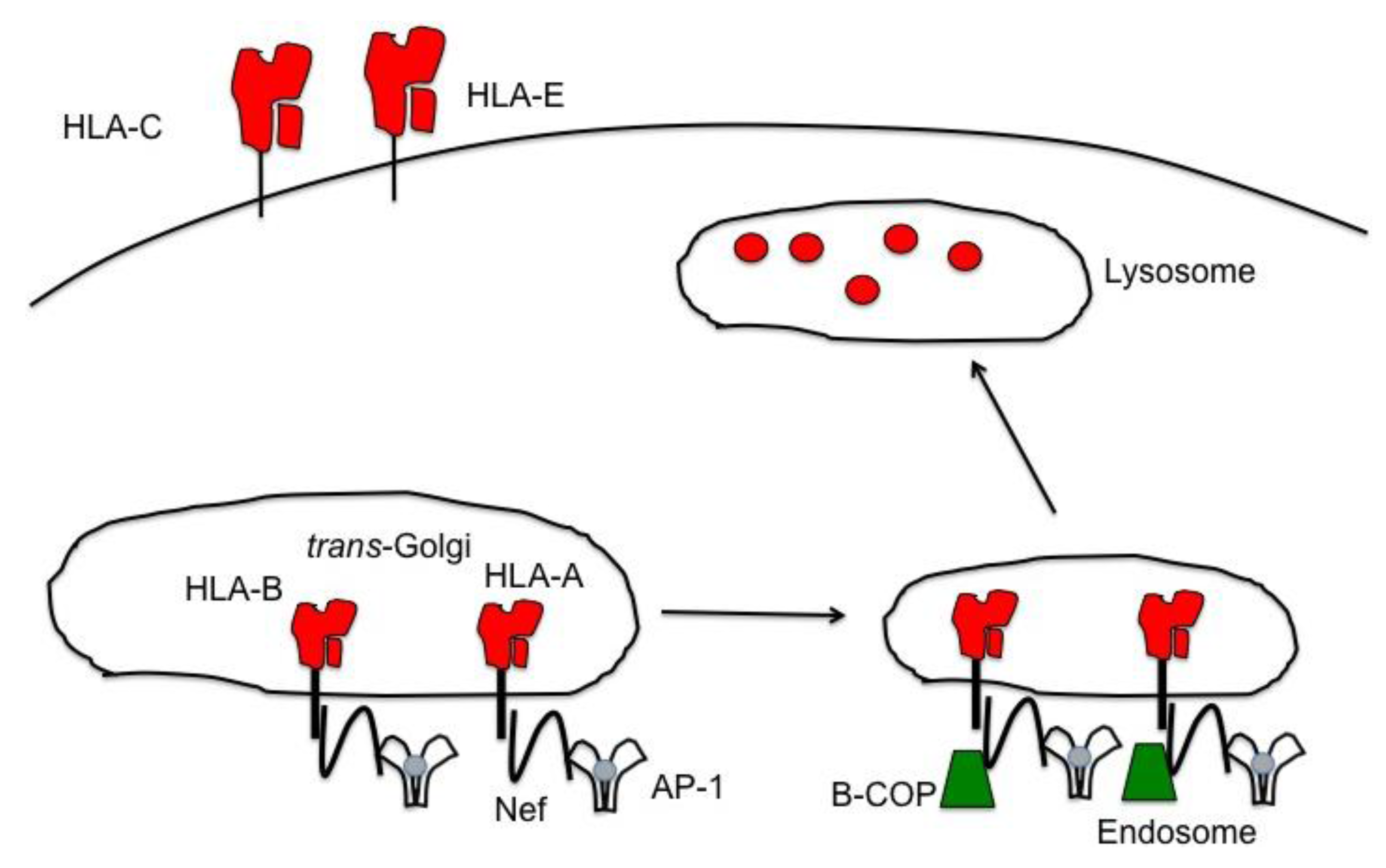
6.2. Nef down Modulates Ligands for Inhibitory Receptors on NK Cells
6.3. NK Cell Degranulation is Hindered by Down Modulation of NTB-A on HIV-1 Infected Cells by Vpu
7. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- Bukowski, J.F.; Woda, B.A.; Habu, S.; Okumura, K.; Welsh, R.M. Natural killer cell depletion enhances virus synthesis and virus-induced hepatitis in vivo. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habu, S.; Akamatsu, K.; Tamaoki, N.; Okumura, K. In vivo significance of NK cell on resistance against virus (HSV-1) infections in mice. J. Immunol. 1984, 133, 2743–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein-Streilein, J.; Guffee, J.; Fan, W. Locally and systemically derived natural killer cells participate in defense against intranasally inoculated influenza virus. Reg. Immunol. 1988, 1, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biron, C.A.; Byron, K.S.; Sullivan, J.L. Severe herpesvirus infections in an adolescent without natural killer cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joncas, J.; Monczak, Y.; Ghibu, F.; Alfieri, C.; Bonin, A.; Ahronheim, G.; Rivard, G. Brief report: killer cell defect and persistent immunological abnormalities in two patients with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 1989, 28, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalloul, A.; Oksenhendler, E.; Chosidow, O.; Ribaud, P.; Carcelain, G.; Louvet, S.; Massip, P.; Lebon, P.; Autran, B. Severe herpes virus (HSV-2) infection in two patients with myelodysplasia and undetectable NK cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the blood. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 30, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoukaty, A.; Lee, I.F.; Wu, J.; Tan, R. Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection associated with low expression of leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor-1 (LAIR-1) on natural killer cells. J. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 23, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzioni, A.; Eidenschenk, C.; Katz, R.; Beck, R.; Casanova, J.L.; Pollack, S. Fatal varicella associated with selective natural killer cell deficiency. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotta, S.; Stilla, A.; Wack, A.; D’Andrea, A.; Nuti, S.; D’Oro, U.; Mosca, M.; Filliponi, F.; Brunetto, R.M.; Bonino, F.; et al. Inhibition of natural killer cells through engagement of CD81 by the major hepatitis C virus envelope protein. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, M.R.; Ashiru, O.; Reeves, M.B.; Okecha, G.; Trowsdale, J.; Tomasec, P.; Wilkinson, G.W.; Sinclair, J.; Sissons, J.G. Human cytomegalovirus encodes an MHC class I-like molecule (UL142) that functions to inhibit NK cell lysis. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7457–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Bresnahan, W.; Taylor, R.T.; Stastny, P. Effect of human cytomegalovirus on expression of MHC class I-related chains A. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinis, M.; Simova, J.; Indrova, M.; Bieblova, J.; Pribylova, H.; Moravcova, S.; Jandlova, T.; Bubenik, J. Immunization with MHC class I-negative but not -positive HPV16-associated tumour cells inhibits growth of MHC class I-negative tumours. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 30, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, T.; Djeu, J.Y.; Dougherty, S.F.; Oppenheim, J.J. Capacity of human large granular lymphocytes (LGL) to produce multiple lymphokines: interleukin 2, interferon, and colony stimulating factor. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arase, H.; Arase, N.; Saito, T. Fas-mediated cytotoxicity by freshly isolated natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluman, E.M.; Bartynski, K.J.; Avalos, B.R.; Caligiuri, M.A. Human natural killer cells produce abundant macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha in response to monocyte-derived cytokines. J. Clin. Invest. 1996, 97, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratke, K.; Kuepper, M.; Bade, B.; Virchow, J.C., Jr.; Luttmann, W. Differential expression of human granzymes A, B, and K in natural killer cells and during CD8+ T cell differentiation in peripheral blood. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 2608–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, E.; Gil-Parrado, S.; Jenne, D.E.; Kurschus, F.C. Natural killer cell-derived human granzyme H induces an alternative, caspase-independent cell-death program. Blood 2007, 110, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocikat, R.; Braumuller, H.; Gumy, A.; Egeter, O.; Ziegler, H.; Reusch, U.; Bubeck, A.; Louis, J.; Mailhammer, R.; Riethmuller, G.; et al. Natural killer cells activated by MHC class I(low) targets prime dendritic cells to induce protective CD8 T cell responses. Immunity 2003, 19, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Lindstrom, J.M.; Anderson, C.G.; Dennert, G. Cytotoxic granules from killer cells: specificity of granules and insertion of channels of defined size into target membranes. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 4245–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, D.; Shi, L.; Feske, S.; Massol, R.; Navarro, F.; Kirchhausen, T.; Lieberman, J. Perforin triggers a plasma membrane-repair response that facilitates CTL induction of apoptosis. Immunity 2005, 23, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A.; Fehniger, T.A.; Caligiuri, M.A. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Cantoni, C.; Mingari, M.C.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, L. Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretta, L.; Moretta, A. Unravelling natural killer cell function: triggering and inhibitory human NK receptors. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L. NK cell recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 225–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, L.L. Up on the tightrope: Natural killer cell activation and inhibition. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; March, M.E.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Long, E.O. Activation, coactivation, and costimulation of resting human natural killer cells. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 214, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.S.; Altin, J.G.; Waldron, J.C.; Kinnear, B.F.; Parish, C.R. A carbohydrate structure associated with CD15 (Lewis x) on myeloid cells is a novel ligand for human CD2. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 2866–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higai, K.; Ichikawa, A.; Matsumoto, K. Binding of sialyl Lewis X antigen to lectin-like receptors on NK cells induces cytotoxicity and tyrosine phosphorylation of a 17-kDa protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugie, K.; Nakamura, K.; Teshigawara, K.; Diamond, M.S.; Springer, T.A.; Nakamura, Y.; Leonard, W.J.; Uchida, A.; Yodoi, J. Activation of natural killer cells by the mAb YTA-1 that recognizes leukocyte function-associated antigen-1. Int. Immunol. 1995, 7, 763–769. [Google Scholar]
- Orange, J.S. Formation and function of the lytic NK-cell immunological synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davignon, D.; Martz, E.; Reynolds, T.; Kurzinger, K.; Springer, T.A. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1): A surface antigen distinct from Lyt-2,3 that participates in T lymphocyte-mediated killing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1981, 78, 4535–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Kawashima, H.; Lowe, J.B.; Lanier, L.L.; Fukuda, M. Suppression of tumor formation in lymph nodes by L-selectin-mediated natural killer cell recruitment. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lollo, B.A.; Chan, K.W.; Hanson, E.M.; Moy, V.T.; Brian, A.A. Direct evidence for two affinity states for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 on activated T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 21693–21700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Long, E.O. Minimal requirement for induction of natural cytotoxicity and intersection of activation signals by inhibitory receptors. Blood 2009, 114, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.F.; Faure, M.; Long, E.O. LFA-1 contributes an early signal for NK cell cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentlik, A.N.; Sanborn, K.B.; Holzbaur, E.L.; Orange, J.S. Rapid lytic granule convergence to the MTOC in natural killer cells is dependent on dynein but not cytolytic commitment. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 2241–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.M.; Chiu, I.; Fassett, M.; Cohen, G.B.; Mandelboim, O.; Strominger, J.L. The human natural killer cell immune synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 15062–15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riteau, B.; Barber, D.F.; Long, E.O. Vav1 phosphorylation is induced by beta2 integrin engagement on natural killer cells upstream of actin cytoskeleton and lipid raft reorganization. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.B.; Cella, M.; Giurisato, E.; Fujikawa, K.; Miletic, A.V.; Kloeppel, T.; Brim, K.; Takai, T.; Shaw, A.S.; Colonna, M.; et al. Vav1 controls DAP10-mediated natural cytotoxicity by regulating actin and microtubule dynamics. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfing, C.; Purtic, B.; Klem, J.; Schatzle, J.D. Stepwise cytoskeletal polarization as a series of checkpoints in innate but not adaptive cytolytic killing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 7767–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; March, M.E.; Barber, D.F.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Long, E.O. Cytolytic granule polarization and degranulation controlled by different receptors in resting NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryceson, Y.T.; March, M.E.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Long, E.O. Synergy among receptors on resting NK cells for the activation of natural cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion. Blood 2006, 107, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottino, C.; Castriconi, R.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A. Cellular ligands of activating NK receptors. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretta, A.; Sivori, S.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Morelli, L.; Augugliaro, R.; Bottino, C.; Moretta, L. Existence of both inhibitory (p58) and activatory (p50) receptors for HLA-C molecules in human natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohring, C.; Scheidegger, D.; Samaridis, J.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. A human killer inhibitory receptor specific for HLA-A1,2. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 3098–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessino, A.; Sivori, S.; Bottino, C.; Malaspina, A.; Morelli, L.; Moretta, L.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, A. Molecular cloning of NKp46: a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily involved in triggering of natural cytotoxicity. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Parolini, S.; Pessino, A.; Sivori, S.; Augugliaro, R.; Morelli, L.; Marcenaro, E.; Accame, L.; Malaspina, A.; Biassoni, R.; et al. Identification and molecular characterization of NKp30, a novel triggering receptor involved in natural cytotoxicity mediated by human natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, S.; Mingueneau, M.; Fuseri, N.; Malissen, B.; Raulet, D.H.; Malissen, M.; Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E. Multiplicity and plasticity of natural killer cell signaling pathways. Blood 2006, 107, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, A.W., 4th; Campbell, K.S. Signal transduction in natural killer cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 298, 23–57. [Google Scholar]
- Colucci, F.; Schweighoffer, E.; Tomasello, E.; Turner, M.; Ortaldo, J.R.; Vivier, E.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Di Santo, J.P. Natural cytotoxicity uncoupled from the Syk and ZAP-70 intracellular kinases. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Dietrich, J.; Harpur, A.G.; Lindquist, J.A.; Haude, A.; Loke, Y.W.; King, A.; Colonna, M.; Trowsdale, J.; Wilson, M.J. Cutting edge: KAP10, a novel transmembrane adapter protein genetically linked to DAP12 but with unique signaling properties. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 4651–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upshaw, J.L.; Arneson, L.N.; Schoon, R.A.; Dick, C.J.; Billadeau, D.D.; Leibson, P.J. NKG2D-mediated signaling requires a DAP10-bound Grb2-Vav1 intermediate and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in human natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tybulewicz, V.L. Vav-family proteins in T-cell signalling. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, G.; Ji, Q. Phospholipase C-gamma as a signal-transducing element. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 253, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Das, A.; Gross, C.C.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Long, E.O. Synergistic signals for natural cytotoxicity are required to overcome inhibition by c-Cbl ubiquitin ligase. Immunity 2010, 32, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menager, M.M.; Menasche, G.; Romao, M.; Knapnougel, P.; Ho, C.H.; Garfa, M.; Raposo, G.; Feldmann, J.; Fischer, A.; de Saint Basile, G. Secretory cytotoxic granule maturation and exocytosis require the effector protein hMunc13-4. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.M.; Meeths, M.; Chiang, S.C.; Bechensteen, A.G.; Boelens, J.J.; Heilmann, C.; Horiuchi, H.; Rosthoj, S.; Rutynowska, O.; Winiarski, J.; et al. Different NK cell-activating receptors preferentially recruit Rab27a or Munc13-4 to perforin-containing granules for cytotoxicity. Blood 2009, 114, 4117–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; McBride, S.; Mak, D.O.; Vardi, N.; Palczewski, K.; Haeseleer, F.; Foskett, J.K. Identification of a family of calcium sensors as protein ligands of inositol trisphosphate receptor Ca(2+) release channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002, 99, 7711–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul-Pavicic, A.; Chiang, S.C.; Rensing-Ehl, A.; Jessen, B.; Fauriat, C.; Wood, S.M.; Sjoqvist, S.; Hufnagel, M.; Schulze, I.; Bass, T.; et al. ORAI1-mediated calcium influx is required for human cytotoxic lymphocyte degranulation and target cell lysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 108, 3324–3329. [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.H.; Boles, K.; van der Merwe, P.A.; Kumar, V.; Mathew, P.A.; Barclay, A.N. 2B4, the natural killer and T cell immunoglobulin superfamily surface protein, is a ligand for CD48. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, P.R.; Lai, W.C.; Chuang, S.S.; Bennett, M.; Mathew, P.A. CS1, a novel member of the CD2 family, is homophilic and regulates NK cell function. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, M.; Marcenaro, E.; Romeo, E.; Bellora, F.; Marras, D.; Vely, F.; Ferracci, G.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A.; Bottino, C. Homophilic interaction of NTBA, a member of the CD2 molecular family: induction of cytotoxicity and cytokine release in human NK cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayos, J.; Wu, C.; Morra, M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Allen, D.; van Schaik, S.; Notarangelo, L.; Geha, R.; Roncarolo, M.G.; et al. The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. Nature 1998, 395, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Relouzat, F.; Roncagalli, R.; Aoukaty, A.; Tan, R.; Latour, S.; Veillette, A. Molecular dissection of 2B4 signaling: implications for signal transduction by SLAM-related receptors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5144–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissmann, P.; Beauchamp, L.; Wooters, J.; Tilton, J.C.; Long, E.O.; Watzl, C. Molecular basis for positive and negative signaling by the natural killer cell receptor 2B4 (CD244). Blood 2005, 105, 4722–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archuleta, M.M.; Schieven, G.L.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Deanin, G.G.; Burchiel, S.W. 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene activates protein-tyrosine kinases Fyn and Lck in the HPB-ALL human T-cell line and increases tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1, formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, and mobilization of intracellular calcium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1993, 90, 6105–6109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.; Lanyi, A.; Song, H.K.; Griesbach, J.; Simarro-Grande, M.; Poy, F.; Howie, D.; Sumegi, J.; Terhorst, C.; Eck, M.J. SAP couples Fyn to SLAM immune receptors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdener, F.; Dangelmaier, C.; Ashby, B.; Kunapuli, S.P.; Daniel, J.L. Activation of phospholipase Cgamma2 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binstadt, B.A.; Brumbaugh, K.M.; Dick, C.J.; Scharenberg, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Colonna, M.; Lanier, L.L.; Kinet, J.P.; Abraham, R.T.; Leibson, P.J. Sequential involvement of Lck and SHP-1 with MHC-recognizing receptors on NK cells inhibits FcR-initiated tyrosine kinase activation. Immunity 1996, 5, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burshtyn, D.N.; Scharenberg, A.M.; Wagtmann, N.; Rajagopalan, S.; Berrada, K.; Yi, T.; Kinet, J.P.; Long, E.O. Recruitment of tyrosine phosphatase HCP by the killer cell inhibitor receptor. Immunity 1996, 4, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.S.; Schoon, R.A.; Robertson, M.J.; Leibson, P.J. Inhibition of selective signaling events in natural killer cells recognizing major histocompatibility complex class I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1995, 92, 6484–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiante, N.M.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; Parham, P. Killer cell inhibitory receptor recognition of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I blocks formation of a pp36/PLC-gamma signaling complex in human natural killer (NK) cells. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbins, C.C.; Watzl, C.; Billadeau, D.D.; Leibson, P.J.; Burshtyn, D.N.; Long, E.O. Vav1 dephosphorylation by the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 as a mechanism for inhibition of cellular cytotoxicity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 6291–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.E.; Long, E.O. Inhibitory receptor signaling via tyrosine phosphorylation of the adaptor Crk. Immunity 2008, 29, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccone, E.; Pende, D.; Viale, O.; Than, A.; Di Donato, C.; Orengo, A.M.; Biassoni, R.; Verdiani, S.; Amoroso, A.; Moretta, A.; et al. Involvement of HLA class I alleles in natural killer (NK) cell-specific functions: expression of HLA-Cw3 confers selective protection from lysis by alloreactive NK clones displaying a defined specificity (specificity 2). J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Biassoni, R.; Bottino, C.; Pende, D.; Vitale, M.; Poggi, A.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L. Major histocompatibility complex class I-specific receptors on human natural killer and T lymphocytes. Immunol. Rev. 1997, 155, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.; Dimasi, N.; Wang, J.; Mariuzza, R.A.; Margulies, D.H. Structure and function of natural killer cell receptors: Multiple molecular solutions to self, nonself discrimination. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 853–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.L.; Chen, B.K.; Kalams, S.A.; Walker, B.D.; Baltimore, D. HIV-1 Nef protein protects infected primary cells against killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature 1998, 391, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, L.; Johansson, S.; Michaelsson, J.; Tomasello, E.; Vivier, E.; Karre, K.; Hoglund, P. Loss or mismatch of MHC class I is sufficient to trigger NK cell-mediated rejection of resting lymphocytes in vivo—Role of KARAP/DAP12-dependent and -independent pathways. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscetti, F.W.; Mikovits, J.A.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Overton, R.; Stevenson, H.; Stromberg, K.; Herberman, R.B.; Farrar, W.L.; Ortaldo, J.R. Analysis of effector mechanisms against HTLV-I- and HTLV-III/LAV-infected lymphoid cells. J. Immunol. 1986, 136, 3619–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zucker-Franklin, D. Apparent ineffectiveness of natural killer cells vis-a-vis retrovirus-infected targets. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 3679–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaparte, M.I.; Barker, E. Inability of natural killer cells to destroy autologous HIV-infected T lymphocytes. AIDS 2003, 17, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houchins, J.P.; Yabe, T.; McSherry, C.; Bach, F.H. DNA sequence analysis of NKG2, a family of related cDNA clones encoding type II integral membrane proteins on human natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Song, Y.; Bakker, A.B.; Bauer, S.; Spies, T.; Lanier, L.L.; Phillips, J.H. An activating immunoreceptor complex formed by NKG2D and DAP10. Science 1999, 285, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Groh, V.; Wu, J.; Steinle, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; Spies, T. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 1999, 285, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosman, D.; Mullberg, J.; Sutherland, C.L.; Chin, W.; Armitage, R.; Fanslow, W.; Kubin, M.; Chalupny, N.J. ULBPs, novel MHC class I-related molecules, bind to CMV glycoprotein UL16 and stimulate NK cytotoxicity through the NKG2D receptor. Immunity 2001, 14, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, S.; Orsulic, S.; Brown, E.J.; Raulet, D.H. The DNA damage pathway regulates innate immune system ligands of the NKG2D receptor. Nature 2005, 436, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R.T. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2177–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.C.; Haber, J.E. Surviving the breakup: The DNA damage checkpoint. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2006, 40, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.L.; Le Rouzic, E.; Planelles, V. HIV-1 Vpr: Mechanisms of G2 arrest and apoptosis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2008, 85, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshal, M.; Kim, B.; Zhu, Y.; Nghiem, P.; Planelles, V. Activation of the ATR-mediated DNA damage response by the HIV-1 viral protein R. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25879–25886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, W.C.; Rogel, M.E.; Kinsey, C.M.; Michael, S.F.; Fultz, P.N.; Nowak, M.A.; Hahn, B.H.; Emerman, M. HIV-1 Vpr increases viral expression by manipulation of the cell cycle: A mechanism for selection of Vpr in vivo. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrimech, M.; Yao, X.J.; Bachand, F.; Rougeau, N.; Cohen, E.A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Vpr functions as an immediate-early protein during HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4101–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, E.S.; Chen, J.; Andersen, J.L.; Ardon, O.; Dehart, J.L.; Blackett, J.; Choudhary, S.K.; Camerini, D.; Nghiem, P.; Planelles, V. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr-mediated G2 arrest requires Rad17 and Hus1 and induces nuclear BRCA1 and gamma-H2AX focus formation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 9286–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Wang, L.; Mukherjee, S.; Narayan, O. Biochemical mechanism of HIV-1 Vpr function. Oligomerization mediated by the N-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 32131–32137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rouzic, E.; Belaidouni, N.; Estrabaud, E.; Morel, M.; Rain, J.C.; Transy, C.; Margottin-Goguet, F. HIV1 Vpr Arrests the Cell Cycle by Recruiting DCAF1/VprBP, a Receptor of the Cul4-DDB1 Ubiquitin Ligase. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHart, J.L.; Zimmerman, E.S.; Ardon, O.; Monteiro-Filho, C.M.; Arganaraz, E.R.; Planelles, V. HIV-1 Vpr activates the G2 checkpoint through manipulation of the ubiquitin proteasome system. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHart, J.L.; Planelles, V. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpr links proteasomal degradation and checkpoint activation. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Davis, Z.; DeHart, J.; Zimmerman, E.; Bosque, A.; Brunetta, E.; Mavilio, D.; Planelles, V.; Barker, E. HIV-1 Vpr triggers natural killer cell-mediated lysis of infected cells through activation of the ATR-mediated DNA damage response. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.; Sindhu, S.; Pham, T.N.; Belzile, J.P.; Cohen, E.A. HIV-1 Vpr up-regulates expression of ligands for the activating NKG2D receptor and promotes NK cell-mediated killing. Blood 115, 1354–1363. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Soto, A.; Quinones-Lombrana, A.; Lopez-Arbesu, R.; Lopez-Larrea, C.; Gonzalez, S. Transcriptional regulation of ULBP1, a human ligand of the NKG2D receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 30419–30430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerboni, C.; Neri, F.; Casartelli, N.; Zingoni, A.; Cosman, D.; Rossi, P.; Santoni, A.; Doria, M. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Nef protein downmodulates the ligands of the activating receptor NKG2D and inhibits natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkau, T.; Schmitt-Landgraf, R.; Schimpl, A.; Wecker, E. Downregulation of HLA class I antigens in HIV-1-infected cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1989, 5, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, O.; Marechal, V.; Le Gall, S.; Lemonnier, F.; Heard, J.M. Endocytosis of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules is induced by the HIV-1 Nef protein. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.B.; Gandhi, R.T.; Davis, D.M.; Mandelboim, O.; Chen, B.K.; Strominger, J.L.; Baltimore, D. The selective downregulation of class I major histocompatibility complex proteins by HIV-1 protects HIV-infected cells from NK cells. Immunity 1999, 10, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Roeth, J.F.; Kasper, M.R.; Fleis, R.I.; Przybycin, C.G.; Collins, K.L. Direct binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef to the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) cytoplasmic tail disrupts MHC-I trafficking. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12173–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, S.; Buseyne, F.; Trocha, A.; Walker, B.D.; Heard, J.M.; Schwartz, O. Distinct trafficking pathways mediate Nef-induced and clathrin-dependent major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9256–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, S.; Erdtmann, L.; Benichou, S.; Berlioz-Torrent, C.; Liu, L.; Benarous, R.; Heard, J.M.; Schwartz, O. Nef interacts with the mu subunit of clathrin adaptor complexes and reveals a cryptic sorting signal in MHC I molecules. Immunity 1998, 8, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.M.; Benichou, S.; Guatelli, J.C. Cooperative binding of the class I major histocompatibility complex cytoplasmic domain and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef to the endosomal AP-1 complex via its mu subunit. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonderlich, E.R.; Williams, M.; Collins, K.L. The tyrosine binding pocket in the adaptor protein 1 (AP-1) mu1 subunit is necessary for Nef to recruit AP-1 to the major histocompatibility complex class I cytoplasmic tail. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3011–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duden, R.; Griffiths, G.; Frank, R.; Argos, P.; Kreis, T.E. Beta-COP, a 110 kd protein associated with non-clathrin-coated vesicles and the Golgi complex, shows homology to beta-adaptin. Cell 1991, 64, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.R.; Wonderlich, E.R.; Roeth, J.F.; Leonard, J.A.; Collins, K.L. HIV-1 Nef targets MHC-I and CD4 for degradation via a final common beta-COP-dependent pathway in T cells. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piguet, V.; Wan, L.; Borel, C.; Mangasarian, A.; Demaurex, N.; Thomas, G.; Trono, D. HIV-1 Nef protein binds to the cellular protein PACS-1 to downregulate class I major histocompatibility complexes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.E.; Iafrate, A.J.; Skowronski, J. The SH3 domain-binding surface and an acidic motif in HIV-1 Nef regulate trafficking of class I MHC complexes. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2777–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, M.R.; Collins, K.L. Nef-mediated disruption of HLA-A2 transport to the cell surface in T cells. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubben, N.B.; Sahlender, D.A.; Motley, A.M.; Lehner, P.J.; Benaroch, P.; Robinson, M.S. HIV-1 Nef-induced down-regulation of MHC class I requires AP-1 and clathrin but not PACS-1 and is impeded by AP-2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 3351–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaparte, M.I.; Barker, E. Killing of human immunodeficiency virus-infected primary T-cell blasts by autologous natural killer cells is dependent on the ability of the virus to alter the expression of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Blood 2004, 104, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Sowrirajan, B.; Davis, Z.B.; Ward, J.P.; Campbell, E.M.; Planelles, V.; Barker, E. Degranulation of natural killer cells following interaction with HIV-1-infected cells is hindered by downmodulation of NTB-A by Vpu. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, C.; Falco, M.; Parolini, S.; Marcenaro, E.; Augugliaro, R.; Sivori, S.; Landi, E.; Biassoni, R.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Moretta, L.; et al. NTB-A [correction of GNTB-A], a novel SH2D1A-associated surface molecule contributing to the inability of natural killer cells to kill Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Bonaparte, M.; Sacks, J.; Guterman, J.; Fogli, M.; Mavilio, D.; Barker, E. HIV modulates the expression of ligands important in triggering natural killer cell cytotoxic responses on infected primary T-cell blasts. Blood 2007, 110, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogli, M.; Mavilio, D.; Brunetta, E.; Varchetta, S.; Ata, K.; Roby, G.; Kovacs, C.; Follmann, D.; Pende, D.; Ward, J.; et al. Lysis of endogenously infected CD4+ T cell blasts by rIL-2 activated autologous natural killer cells from HIV-infected viremic individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, R.M.; Stark, S.; Watzl, C. Cutting edge: NTB-A activates NK cells via homophilic interaction. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6524–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinke, S.; Watzl, C. Functions of NTB-A’s adaptor proteins. University Heidelberg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Claus, M.; Meinke, S.; Bhat, R.; Watzl, C. Regulation of NK cell activity by 2B4, NTB-A and CRACC. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowrirajan, B.; Cambell, E.; Barker, E. HIV-1 Vpu Sequesters NTB-A in the trans-Golgi Network. Rush University Medical Center, Stritch School of Medicine, Loyola University Chicago: Maywood, IL, USA, 2011; unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, U.; Schneider, T.; Henklein, P.; Hoffmann, K.; Berthold, E.; Hauser, H.; Pauli, G.; Porstmann, T. Human-immunodeficiency-virus-type-1-encoded Vpu protein is phosphorylated by casein kinase II. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 204, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, R.L.; Maldarelli, F.; Martin, M.A.; Strebel, K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein induces rapid degradation of CD4. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, U.; Anton, L.C.; Bacik, I.; Cox, J.H.; Bour, S.; Bennink, J.R.; Orlowski, M.; Strebel, K.; Yewdell, J.W. CD4 glycoprotein degradation induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein requires the function of proteasomes and the ubiquitin-conjugating pathway. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margottin, F.; Bour, S.P.; Durand, H.; Selig, L.; Benichou, S.; Richard, V.; Thomas, D.; Strebel, K.; Benarous, R. A novel human WD protein, h-beta TrCp, that interacts with HIV-1 Vpu connects CD4 to the ER degradation pathway through an F-box motif. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.S.; Katsura, C.; Skasko, M.A.; Fitzpatrick, K.; Lau, D.; Ruiz, A.; Stephens, E.B.; Margottin-Goguet, F.; Benarous, R.; Guatelli, J.C. Vpu antagonizes BST-2-mediated restriction of HIV-1 release via beta-TrCP and endo-lysosomal trafficking. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.L.; Viswanathan, K.; McCarroll, M.N.; Gustin, J.K.; Fruh, K.; Moses, A.V. Vpu directs the degradation of the human immunodeficiency virus restriction factor BST-2/Tetherin via a {beta}TrCP-dependent mechanism. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7931–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffinet, C.; Homann, S.; Ambiel, I.; Tibroni, N.; Rupp, D.; Keppler, O.T.; Fackler, O.T. Antagonism of CD317 restriction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) particle release and depletion of CD317 are separable activities of HIV-1 Vpu. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Barker, E. HIV-1 increases cell surface levels of ICAMs. Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA. 2008, unpublished work.



| Name | Ligand | Adaptor Protein |
|---|---|---|
| NKp30 | Unknown | FcεRIγCD3ζ |
| NKp44 | Unknown | DAP12 |
| NKp46 | Unknown | FcεRIγCD3ζ |
| CD158h/KIR2DS1 | HLA-C | DAP12 |
| CD158i/KIR2DS4 | HLA-Cw4 | DAP12 |
| CD158e2/KIR3DS1 | Unknown | DAP12 |
| CD158j/KIR2DS2 | Unknown | DAP12 |
| NKG2D | ULBP-1-6, MIC-A,-B | DAP10 |
| CD16 | IgG | FcεRIγCD3ζ |
| Name | Ligand | Adaptor Protein |
|---|---|---|
| NTB-A | NTB-A | SAP/EAT-2 |
| DNAM-1 | CD155/CD112 | Protein Kinase C |
| CRACC | CRACC | EAT-2 |
| 2B4 | CD48 | SAP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2011 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sowrirajan, B.; Barker, E. The Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Function Is Modulated by HIV-1 Accessory Proteins. Viruses 2011, 3, 1091-1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3071091
Sowrirajan B, Barker E. The Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Function Is Modulated by HIV-1 Accessory Proteins. Viruses. 2011; 3(7):1091-1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3071091
Chicago/Turabian StyleSowrirajan, Bharatwaj, and Edward Barker. 2011. "The Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Function Is Modulated by HIV-1 Accessory Proteins" Viruses 3, no. 7: 1091-1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3071091
APA StyleSowrirajan, B., & Barker, E. (2011). The Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Function Is Modulated by HIV-1 Accessory Proteins. Viruses, 3(7), 1091-1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3071091




