Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus: A Model of NF-κB-Associated Tumorigenesis
Abstract
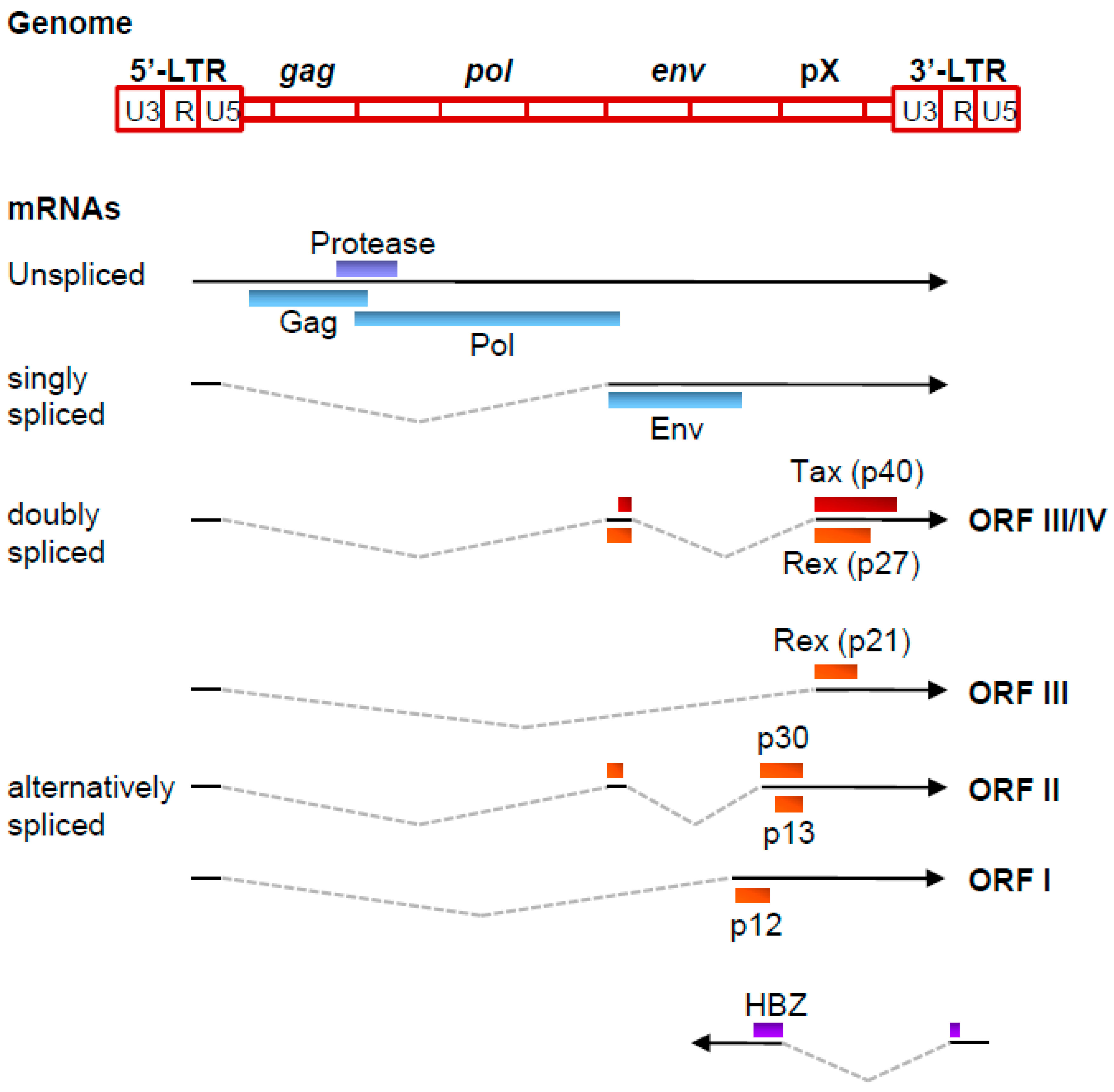
1. Introduction
2. NF-κB Signaling Pathways
2.1. The NF-κB Family
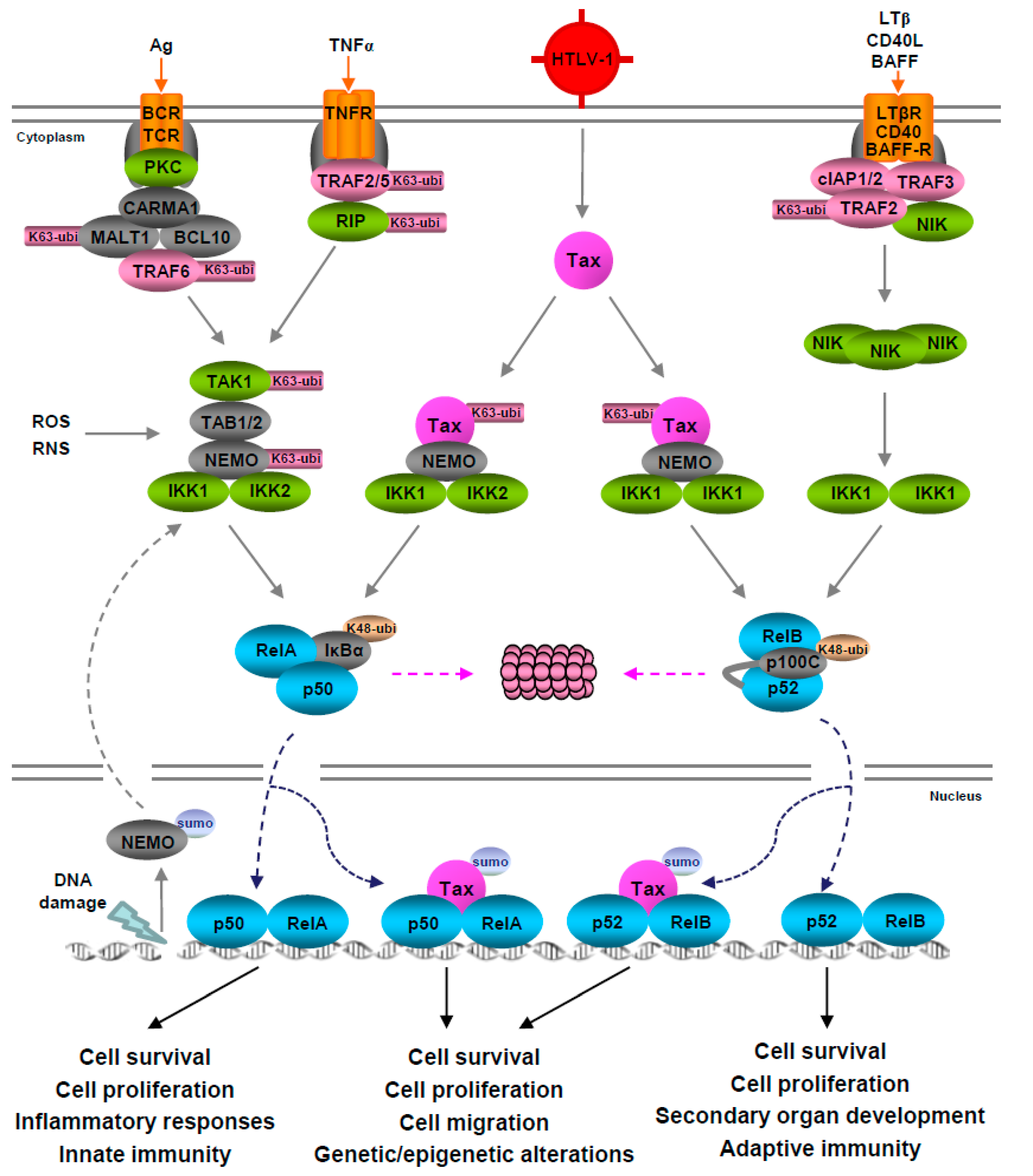
2.2. Pathways Leading to NF-κB Activation
2.3. Termination of NF-κB Activation
3. HTLV-1 Deregulation of NF-κB
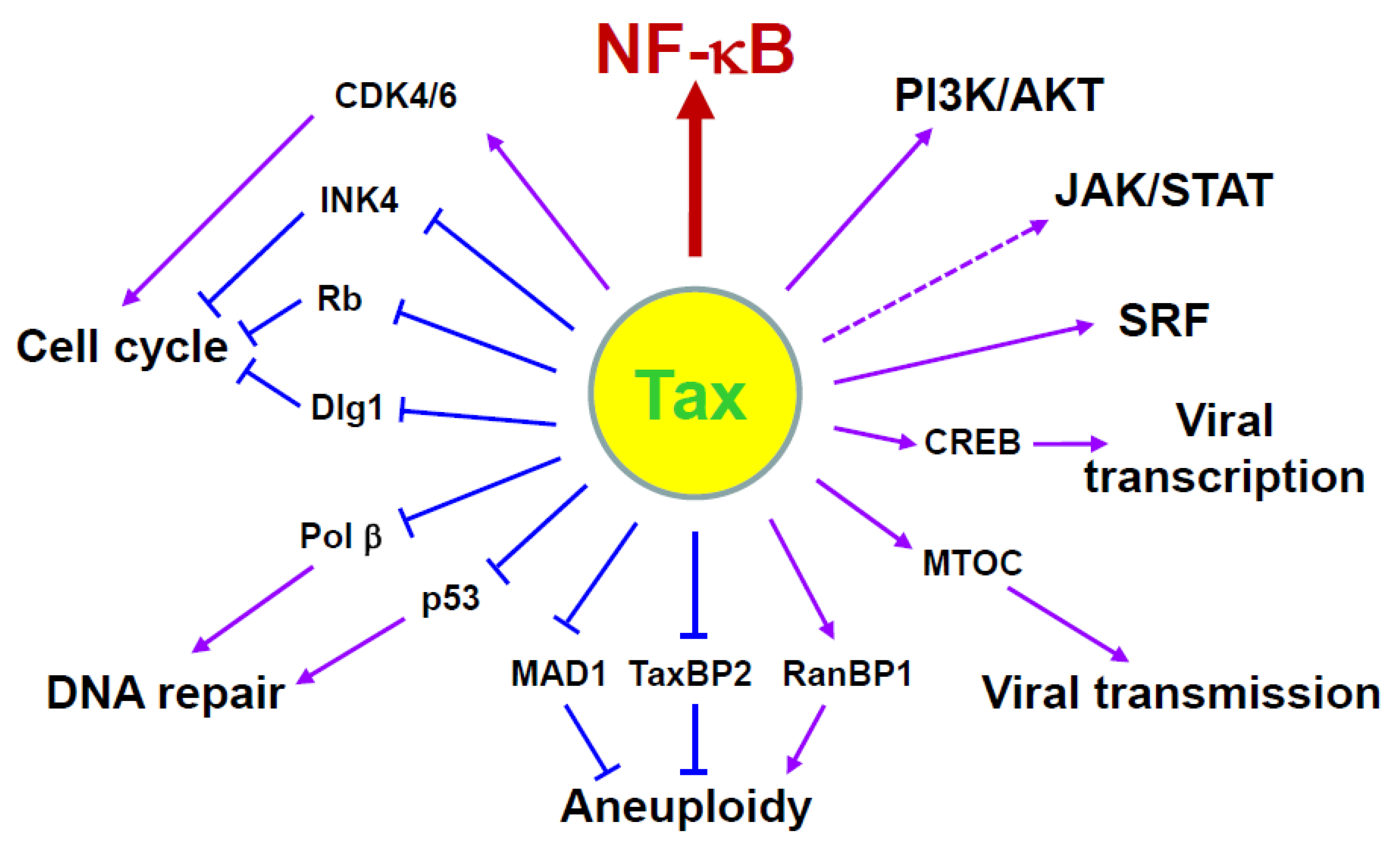
3.1. Tax-Mediated NF-κB Activation
3.2. Tax-Independent NF-κB Activation
3.3. Persistent NF-κB Activation by HTLV-1
3.4. Differences between Tax-Dependent and Tax-Independent NF-κB Activation by HTLV-1
4. NF-κB in ATL Leukemogenesis
4.1. Significance of NF-κB in Tax-Mediated Cellular Transformation and ATL Leukemogenesis
4.2. Functional Role of NF-κB in Tax-Mediated Cellular Transformation and ATL Leukemogenesis
5. Negative Regulation of Tax
5.1. Repression of Tax by Viral Genes
5.2. Repression of Tax by Cellular Genes
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Gallo, R. History of the discoveries of the first human retroviruses: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5926–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuer, G.; Green, P.L. Comparative biology of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5996–56004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, U.; Jacobson, S. Treatment of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Toward rational targeted therapy. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukasaki, K.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A.; Ratner, L.; Ramos, J.C.; Harrington, W., Jr.; O’Mahony, D.; Janik, J.E.; Bittencourt, A.L.; Taylor, G.P.; et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A proposal from an international consensus meeting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, D.U.; Proietti, F.A.; Ribas, J.G.; Araujo, M.G.; Pinheiro, S.R.; Guedes, A.C.; Carneiro-Proietti, A.B. Epidemiology, treatment, and prevention of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, T. Oncogenic retroviruses in animals and humans. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C.; Yamaoka, S. Activation of NF-kappaB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5952–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Jeang, K.T. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Fujii, M. Distinct functions of HTLV-1 Tax1 from HTLV-2 Tax2 contribute key roles to viral pathogenesis. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzatti, R.; Vogel, J.; Jay, G. The human T-lymphotropic virus type I tax gene can cooperate with the ras oncogene to induce neoplastic transformation of cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Grassmann, R.; Berchtold, S.; Radant, I.; Alt, M.; Fleckenstein, B.; Sodroski, J.G.; Haseltine, W.A.; Ramstedt, U. Role of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 X region proteins in immortalization of primary human lymphocytes in culture. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4570–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Shimotohno, K. Proliferative response of Tax1-transduced primary human T cells to anti-CD3 antibody stimulation by an interleukin-2-independent pathway. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Takahashi, C.; Yamaoka, S.; Nosaka, T.; Maki, M.; Hatanaka, M. Oncogenic transformation by the tax gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1990, 87, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Shiku, H. Differences in sensitivity to induction of apoptosis among rat fibroblast cells transformed by HTLV-I tax gene or cellular nuclear oncogenes. Oncogene 1995, 11, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, T.; Sonobe, H.; Iwata, J.; Kubonishi, I.; Satoh, H.; Takata, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Tateno, M.; Tozawa, H.; Mori, S.; et al. Phenotypic progression of a rat lymphoid cell line immortalized by human T-lymphotropic virus type I to induce lymphoma/leukemia-like disease in rats. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6686–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, S.; Tobe, T.; Hatanaka, M. Tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype. Oncogene 1992, 7, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Nerenberg, M.; Hinrichs, S.H.; Reynolds, R.K.; Khoury, G.; Jay, G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science 1987, 237, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, S.H.; Nerenberg, M.; Reynolds, R.K.; Khoury, G.; Jay, G. A transgenic mouse model for human neurofibromatosis. Science 1987, 237, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, R.S.; Maliszewski, C.R.; Sato, T.A.; Hanley-Hyde, J.; Maroulakou, I.G.; Hunziker, R.; Schneck, J.P.; Green, J.E. Abnormal B-cell function in HTLV-I-tax transgenic mice. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, W.J.; Kimata, J.T.; Wong, F.H.; Zutter, M.; Ley, T.J.; Ratner, L. Development of leukemia in mice transgenic for the tax gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1995, 92, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Tosu, M.; Yoshida, E.; Saijo, S.; Nakayama-Yamada, J.; Itagaki, K.; Asano, M.; Siomi, H.; Hatanaka, M.; Takeda, T.; et al. Augmentation of c-fos and c-jun expression in transgenic mice carrying the human T-cell leukemia virus type-I tax gene. Virus Genes 1995, 9, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.P.; Irvine, J.; Blyth, K.; Cameron, E.R.; Onions, D.E.; Campbell, M.E. Tumours derived from HTLV-I tax transgenic mice are characterized by enhanced levels of apoptosis and oncogene expression. J. Pathol. 1998, 186, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sawa, H.; Lewis, M.J.; Orba, Y.; Sheehy, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ichinohe, T.; Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Y.; Katano, H.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Thymus-derived leukemia-lymphoma in mice transgenic for the Tax gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Tripp, A.; Lairmore, M.D.; Crawford, L.; Sieburg, M.; Ramos, J.C.; Harrington, W., Jr.; Beilke, M.A.; Feuer, G. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma development in HTLV-1-infected humanized SCID mice. Blood 2010, 115, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Ono, H.; Shimotohno, K. Characterization of T cells immortalized by Tax1 of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Blood 1995, 86, 4243–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Rabson, A.B.; Young, W.; Qing, G.; Qu, Z. Alternative pathways of NF-kappaB activation: a double-edged sword in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Fu, J. NF-kappaB and Cancer: A Paradigm of Yin-Yang. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 192–221. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, N.R.; MacKichan, M.L.; Israel, A. The precursor of NF-kappa B p50 has I kappa B-like functions. Cell 1992, 71, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, F.; DiDonato, J.A.; Rosette, C.; Karin, M. p105 and p98 precursor proteins play an active role in NF-kappa B-mediated signal transduction. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heissmeyer, V.; Krappmann, D.; Hatada, E.N.; Scheidereit, C. Shared pathways of IkappaB kinase-induced SCF(betaTrCP)-mediated ubiquitination and degradation for the NF-kappaB precursor p105 and IkappaBalpha. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriskantharajah, S.; Belich, M.P.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Janzen, J.; Tybulewicz, V.; Seddon, B.; Ley, S.C. Proteolysis of NF-kappaB1 p105 is essential for T cell antigen receptor-induced proliferation. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, G.; Qu, Z.; Xiao, G. Regulation of NF-kappa B2 p100 processing by its cis-acting domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitin signalling in the NF-kappaB pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuerzberger-Davis, S.M.; Miyamoto, S. TAK-ling IKK activation: "Ub" the judge. Sci. Signal 2010, 3, pe3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, A. The IKK complex, a central regulator of NF-kappaB activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; May, M.J.; Jimi, E.; Ghosh, S. The phosphorylation status of nuclear NF-kappaB determines its association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, B.P.; Westerheide, S.D.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The p65 (RelA) subunit of NF-kappaB interacts with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressors HDAC1 and HDAC2 to negatively regulate gene expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 7065–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, A.; Suizu, F.; Yoshida, Y.; Perrem, K.; Liou, Y.C.; Wulf, G.; Rottapel, R.; Yamaoka, S.; Lu, K.P. Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Fischle, W.; Verdin, E.; Greene, W.C. Duration of nuclear NF-kappaB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science 2001, 293, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Qu, Z.; Xiao, G. Stabilization of basally translated NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) protein functions as a molecular switch of processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40578–40582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Zhang, M.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. Regulation of the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26243–26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C.; Ley, S.C. New insights into NF-kappaB regulation and function. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Sun. S.C. Negative regulation of the nuclear factor kappa B-inducing kinase by a cis-acting domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 19, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Gardam, S.; Sierro, F.; Basten, A.; Mackay, F.; Brink, R. TRAF2 and TRAF3 signal adapters act cooperatively to control the maturation and survival signals delivered to B cells by the BAFF receptor. Immunity 2008, 28, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, A.P.; Amesbury, M.; Chan, T.; Gardam, S.; Basten, A.; Brink, R. TRAF2 differentially regulates the canonical and noncanonical pathways of NF-kappaB activation in mature B cells. Immunity 2004, 21, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Q.; Zarnegar, B.; Oganesyan, G.; Saha, S.K.; Yamazaki, S.; Doyle, S.E.; Dempsey, P.W.; Cheng, G. Rescue of TRAF3-null mice by p100 NF-kappa B deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.R.; Bishop, G.A. Differential regulation of CD40-mediated TNF receptor-associated factor degradation in B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3780–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Blankenship, J.W.; Wayson, S.M.; Fedorova, A.V.; Kayagaki, N.; Garg, P.; Zobel, K.; Dynek, J.N.; Elliott, L.O.; Wallweber, H.J.; et al. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007, 131, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vince, J.E.; Wong, W.W.; Khan, N.; Feltham, R.; Chau, D.; Ahmed, A.U.; Benetatos, C.A.; Chunduru, S.K.; Condon, S.M.; McKinlay, M.; et al. IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007, 131, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. Genetic evidence for the essential role of beta-transducin repeat-containing protein in the inducible processing of NF-kappa B2/p100. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22111–22114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senftleben, U.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, G.; Greten, F.R.; Krahn, G.; Bonizzi, G.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C.; Karin, M. Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science 2001, 293, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. Induction of p100 processing by NF-kappaB-inducing kinase involves docking IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) to p100 and IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30099–30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnegar, B.; Yamazaki, S.; He, J.Q.; Cheng, G. Control of canonical NF-kappaB activation through the NIK-IKK complex pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 3503–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhase, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Chen, Y.; Karin, M. Positive and negative regulation of IkappaB kinase activity through IKKbeta subunit phosphorylation. Science 1999, 284, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razani, B.; Zarnegar, B.; Ytterberg, A.J.; Shiba, T.; Dempsey, P.W.; Ware, C.F.; Loo, J.A.; Cheng, G. Negative feedback in noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation. Sci. Signal 2010, 3, pe41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, I.E.; O’Rourke, K.M.; Zhou, H.; Eby, M.; Aravind, L.; Seshagiri, S.; Wu, P.; Wiesmann, C.; Baker, R.; Boone, D.L.; et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 2004, 430, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikos, A.; Laherty, C.D.; Dixit, V.M. Transcriptional activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducible zinc finger protein, A20, is mediated by kappa B elements. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17971–17976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shembade, N.; Ma, A.; Harhaj, E.W. Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 2010, 327, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, D.L.; Turer, E.E.; Lee, E.G.; Ahmad, R.C.; Wheeler, M.T.; Tsui, C.; Hurley, P.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Hitotsumatsu, O.; et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Kovalenko, A.; Cantarella, G.; Wallach, D. Recruitment of the IKK signalosome to the p55 TNF receptor: RIP and A20 bind to NEMO (IKKgamma) upon receptor stimulation. Immunity 2000, 12, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, C.; Pacifico, F.; Lavorgna, A.; Mellone, S.; Iannetti, A.; Acquaviva, R.; Formisano, S.; Vito, P.; Leonardi, A. ABIN-1 binds to NEMO/IKKgamma and co-operates with A20 in inhibiting NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18482–18488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutti, J.E.; Turk, B.E.; Asara, J.M.; Ma, A.; Cantley, L.C.; Abbott, D.W. IkappaB kinase beta phosphorylates the K63 deubiquitinase A20 to cause feedback inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 7451–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. CYLD: a tumor suppressor deubiquitinase regulating NF-kappaB activation and diverse biological processes. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummelkamp, T.R.; Nijman, S.M.; Dirac, A.M.; Bernards, R. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature 2003, 424, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, A.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Cantarella, G.; Israel, A.; Wallach, D.; Courtois, G. The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-kappaB signalling by deubiquitination. Nature 2003, 424, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompouki, E.; Hatzivassiliou, E.; Tsichritzis, T.; Farmer, H.; Ashworth, A.; Mosialos, G. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 2003, 424, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, J.; Biswas, S.; Shreeram, S.; Humaidi, M.; Wong, E.T.; Dhillion, M.K.; Teo, H.; Hazra, A.; Fang, C.C.; López-Collazo, E.; et al. WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Berman, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Dorf, M.E. RNAi screen in mouse astrocytes identifies phosphatases that regulate NF-kappaB signaling. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fang, G.H.; Wadzinski, B.E.; Sakurai, H.; Richmond, A. Protein phosphatase 2A interacts with and directly dephosphorylates RelA. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47828–47833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg. J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xu, L.G.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. SINK is a p65-interacting negative regulator of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27072–27079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šošić, D.; Richardson, J.A.; Yu, K.; Ornitz, D.M.; Olson, E.N. Twist regulates cytokine gene expression through a negative feedback loop that represses NF-kappaB activity. Cell 2003, 112, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Hori, M.; Sanda, T.; Okamoto, T. Identification of a novel inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB, RelA-associated inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15662–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C.; Ganchi, P.A.; Ballard, D.W.; Greene, W.C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science 1993, 259, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccani, S.; Marazzi, I.; Beg, A.A.; Natoli, G. Degradation of promoter-bound p65/RelA is essential for the prompt termination of the nuclear factor kappaB response. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Grusby, M.J.; Kaisho, T. PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-kappaB activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yan, P.; Li, S.; Qu, Z.; Xiao, G. Molecular determinants of PDLIM2 in suppressing HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6499–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Ohsuqi, T.; Shoda, M.; Ishida, T.; Aizawa, S.; Maruyama-Nagai, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; Koga, S.; Yamada, Y.; Kamihira, S.; et al. Dual targeting of transformed and untransformed HTLV-1-infected T cells by DHMEQ, a potent and selective inhibitor of NF-kappaB, as a strategy for chemoprevention and therapy of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, D.W.; Böhnlein, E.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Wano, Y.; Franza, B.R.; Greene, W.C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science 1988, 241, 1652–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhnlein, E.; Siekevitz, M.; Ballard, D.W.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Rimsky, L.; Bogérd, H.; Hoffman, J.; Wano, Y.; Franza, B.R.; Greene, W.C. Stimulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax gene product involves the action of inducible cellular proteins. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.; Nabel, G.L. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature 1988, 333, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruben, S.; Poteat, H.; Tan, T.H.; Kawakami, K.; Roeder, R.; Haseltine, W.; Rosen, C.A. Cellular transcription factors and regulation of IL-2 receptor gene expression by HTLV-I tax gene product. Science 1988, 241, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.L.; Shin, Y.A.; Yang, J.M.; DiDonato, J.A.; Ballard, D.W. IKKgamma mediates the interaction of cellular IkappaB kinases with the tax transforming protein of human T cell leukemia virus type 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15297–15300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. IKKgamma serves as a docking subunit of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) and mediates interaction of IKK with the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22911–22914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.Y.; Giordano, V.; Kibler, K.V.; Nakano, H.; Jeang, K.T. Role of adapter function in oncoprotein-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax interacts directly with IkappaB kinase gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17402–17405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. Domain-specific interaction with the I kappa B kinase (IKK)regulatory subunit IKK gamma is an essential step in tax-mediated activation of IKK. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34060–34067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, A.M.; Montanp, M.; Van Beneden, K.; Chen, L.F.; Greene, W.C. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 tax induction of biologically Active NF-kappaB requires IkappaB kinase-1-mediated phosphorylation of RelA/p65. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18137–18145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmes, O.J.; Jeang, K.T. Localization of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax to subnuclear compartments that overlap with interchromatin speckles. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6347–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, F.; McDowall, A.; Burny, A.; Gaynor, R. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 transactivator protein Tax colocalizes in unique nuclear structures with NF-kappaB proteins. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3484–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.Y.; Jeang, K.T. HTLV-I Tax self-association in optimal trans-activation function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, F.; Adya, N.; Greene, W.C.; Giam, C.Z. Interaction of the human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax dimer with CREB and the viral 21-base-pair repeat. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8368–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Sun, S.C. Activation of IKKalpha and IKKbeta through their fusion with HTLV-I tax protein. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5198–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Minoda. Y.; Yoshida, R.; Yoshida, H.; Iha, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Takaesu, G. HTLV-1 Tax-mediated TAK1 activation involves TAB2 adapter protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlik, M.; Good, L.; Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Zandi, E.; Karin, M.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and IkappaB kinase participate in human T-cell leukemia virus I Tax-mediated NF-kappaB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 21132–21136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.J.; Christerson, L.B.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kwak, Y.T.; Xu, S.; Mercurio, F.; Barbosa, M.; Cobb, M.H.; Gaynor, R.B. HTLV-I Tax protein binds to MEKK1 to stimulate IkappaB kinase activity and NF-kappaB activation. Cell 1998, 93, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, G.; Waterfield, M.; Chang, M.; Wu, X.; Sun, S.C. Deregulated activation of oncoprotein kinase Tpl2/Cot in HTLV-I-transformed T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14041–14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Singhirunnusorn, P.; Mori, A.; Yamaoka, S.; Kitajima, I.; Saiki, I.; Sakurai, H. Constitutive activation of TAK1 by HTLV-1 tax-dependent overexpression of TAB2 induces activation of JNK-ATF2 but not IKK-NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 25177–25181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohda, J.; Irisawa, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Sato, S.; Ohtani, K.; Fujisawa, J.; Inoue, J. HTLV-1 Tax-induced NFkappaB activation is independent of Lys-63-linked-type polyubiquitination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Zhou, Y.; Refaat, A.; Takasaki, I.; Koizumi, K.; Yamaoka, S.; Tabuchi, Y.; Saiki, I.; Sakurai, H. Human T cell lymphotropic virus 1 manipulates interferon regulatory signals by controlling the TAK1-IRF3 and IRF4 pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4441–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, Y.; Nasr, R.; Favre-Bonvin, A.; El-Sabban, M.; Renault, N.; Giron, M.L.; Setterblad, N.; Hajj, H.E.; Chiari, E.; Mikati, A.G.; et al. Ubiquitylated Tax targets and binds the IKK signalosome at the centrosome. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harhaj, N.S.; Sun, S.C.; Harhaj, E.W. Activation of NF-kappa B by the human T cell leukemia virus type I Tax oncoprotein is associated with ubiquitin-dependent relocalization of I kappa B kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 4185–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Journo, C.; Filipe, J.; About, F.; Chevalier, S.A.; Afonso, P.V.; Brady, J.N.; Flynn, D.; Tangy, F.; Israël, A.; Vidalain, P.O.; et al. NRP/Optineurin Cooperates with TAX1BP1 to potentiate the activation of NF-kappaB by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 tax protein. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avesani, F.; Romanelli, M.G.; Turci, M.; Di Gennaro, G.; Sampaio, C.; Bidoia, C.; Bertazzoni, U.; Bex, F. Association of HTLV Tax proteins with TAK1-binding protein 2 and RelA in calreticulin-containing cytoplasmic structures participates in Tax-mediated NF-κB activation. Virology 2010, 408, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ren, T.; Guan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, H. HTLV-1 Tax is a critical lipid raft modulator that hijacks IkappaB kinases to the microdomains for persistent activation of NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6208–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsoul, I.; Lodewick, J.; Lebrun, S.; Brasseur, R.; Burny, A.; Gaynor, R.B.; Bex, F. Exclusive ubiquitination and sumoylation on overlapping lysine residues mediate NF-kappaB activation by the human T-cell leukemia virus tax oncoprotein. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 10391–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, R.; Chiari, E.; El-Sabban, M.; Mahieux, R.; Kfoury, Y.; Abdulhay, M.; Yazbeck, V.; Hermine, O.; de Thé, H.; Pique, C.; Bazarbachi, A. Tax ubiquitylation and sumoylation control critical cytoplasmic and nuclear steps of NF-kappaB activation. Blood 2006, 107, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shembade, N.; Harhaj, N.S.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Harhaj, E.W. The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein requires the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 for NF-kappaB activation. J. Virol. 2003, 81, 13735–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, Y.; Setterblad, N.; El-Sabban, M.; Zamborlini, A.; Dassouki, Z.; El Hajj, H.; Hermine, O.; Pique, C.; de Thé, H.; Saïb, A.; Bazarbachi, A. Tax ubiquitylation and SUMOylation control the dynamic shuttling of Tax and NEMO between Ubc9 nuclear bodies and the centrosome. Blood 2011, 117, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S. Nuclear initiated NF-kappa B signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Wuerzberger-Davis, S.M.; Wu, Z.H.; Miyamoto, S. Sequential modification of NEMO/IKKgamma by SUMO-1 and ubiquitin mediates NF-kappaB activation by genotoxic stress. Cell 2003, 115, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, U.N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Prajapati, S.; Gaynor, R.B. Nuclear role of I kappa B Kinase-gamma/NF-kappa B essential modulator (IKK gamma/NEMO) in NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 3509–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, F.; Murphy, K.; Wattiez, R.; Burny, A.; Gaynor, R.B. Phosphorylation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 transactivator tax on adjacent serine residues is critical for tax activation. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewick, J.; Lamsoul, I.; Polania, A.; Lebrun, S.; Burny, A.; Ratner, L.; Bex, F. Acetylation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein by p300 promotes activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Virology 2009, 386, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkin, S.S.; Ward, M.D.; Fryrear, K.A.; Semmes, O.J. Site-specific phosphorylation differentiates active from inactive forms of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31705–31712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peloponese, J.M., Jr.; Yasunaga, J.; Kinjo, T.; Watashi, K.; Jeang, K.T. Peptidylproline cis-trans-isomerase Pin1 interacts with human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax and modulates its activation of NF-kappaB. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3238–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Rya, A.; Yamamoto, N. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 stabilizes the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax oncoprotein and promotes malignant transformation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Fan, Y.; Gupta, N.; Matsuura, I.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P.; Gélinas, C. Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 markedly enhances the oncogenic activity of the rel proteins in the nuclear factor-kappaB family. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4589–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Cvijic, M.E.; Fong, A.; Harhaj, E.W.; Uhlik, M.T.; Waterfield, M.; Sun, S.C. Retroviral oncoprotein Tax induces processing of NF-kappaB2/p100 in T cells: Evidence for the involvement of IKKalpha. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6805–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harhaj, E.W.; Good, L.; Xiao, G.; Uhlik, M.; Cvijic, M.E.; Rivera-Walsh, I.; Sun, S.C. Somatic mutagenesis studies of NF-kappa B signaling in human T cells: evidence for an essential role of IKK gamma in NF-kappa B activation by T-cell costimulatory signals and HTLV-I Tax protein. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, S.; Courtois, G.; Bessia, C.; Whiteside, S.T.; Weil, R.; Agou, F.; Kirk, H.E.; Kay, R.J.; Israël, A. Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the IkappaB kinase complex essential for NF-kappaB activation. Cell 1998, 93, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Qing, G.; Rabson, A.B.; Xiao, G. Tax deregulation of NF-kappaB2 p100 processing involves both beta-TrCP-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44563–44572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, Y.; Kubota, R.; Tara, M.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M. Existence of escape mutant in HTLV-I tax during the development of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Osame, M.; Kubota, R.; Tara, M.; Yoshida, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1) Tax is expressed at the same level in infected cells of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy or tropical spastic paraparesis patients as in asymptomatic carriers but at a lower level in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 1995, 85, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koiwa, T.; Hamano-Usami, A.; Ishida, T.; Okayama, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kamihira, S.; Watanabe, T. 5’-long terminal repeat-selective CpG methylation of latent human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2001, 76, 9389–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Maeda, M.; Morikawa, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Nosaka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsuoka, M. Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of tax gene in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Maeda, M.; Mueller, N.; Okayama, A.; Matsuoka, M. Silencing of human T-cell leukemia virus type I gene transcription by epigenetic mechanisms. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiya, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Etoh, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kamihira, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki. K. Two types of defective human T-lymphotropic virus type I provirus in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 1996, 88, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hironaka, N.; Mochida, K.; Mori, N.; Maeda, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamaoka, S. Tax-independent constitutive IkappaB kinase activation in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Fujii, M.; Ikeda, S.; Yamada, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Ballard, D.W.; Yamamoto, N. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB in primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 1999, 93, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Qing, G.; Qu, Z.; Wu, C.C.; Rabson, A.B.; Xiao, G. Targeting autophagic regulation of NFkappaB in HTLV-I transformed cells by geldanamycin: Implications for therapeutic interventions. Autophagy 2007, 3, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, I.K.; Gu, H. Negative regulation of TCR signaling and T-cell activation by selective protein degradation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Delrow, J.; Drawid, A.; Sengupta, A.M.; Fan, G.; Gélinas, C. Repression of B-cell linker (BLNK) and B-cell adaptor for phosphoinositide 3-kinase (BCAP) is important for lymphocyte transformation by rel proteins. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harhaj, E.W.; Good, L.; Xiao, G.; Sun, S.C. Gene expression profiles in HTLV-I-immortalized T cells: deregulated expression of genes involved in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 1999, 18, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Oh-Hori, N.; Sato, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Kimura, G.; Nomoto, K. Absence of transcription of lck (lymphocyte specific protein tyrosine kinase) message in IL-2-independent, HTLV-I-transformed T cell lines. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 4493–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yssel, H.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Duc Dodon, M.D.; Blanchard, D.; Gazzolo, L.; de Vries, J.E.; Spits, H. Human T cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I infection of a CD4+ proliferative/cytotoxic T cell clone progresses in at least two distinct phases based on changes in function and phenotype of the infected cells. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waal Malefyt, R.; Yssel, H.; Spits, H.; de Vries, J.E.; Sancho, J.; Terhorst, C.; Alarcon, B. Human T cell leukemia virus type I prevents cell surface expression of the T cell receptor through down-regulation of the CD3-gamma, -delta, -epsilon, and -zeta genes. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 2297–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.; Levraud, J.; Dodon, M.D.; Bessia, C.; Hazan, U.; Kourilsky, P.; Israël, A. Altered expression of tyrosine kinases of the Src and Syk families in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected T-cell lines. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harhaj, E.W.; Harhaj, N.S.; Grant, C.; Mostoller, K.; Alefantis, T.; Sun, S.C.; Wigdahl, B. Human T cell leukemia virus type I Tax activates CD40 gene expression via the NF-kappaB pathway. Virology 2005, 333, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Matsuda, T.; Mori, N.; Yamada, Y.; Horie, R.; Watanabe, T.; Takahashi, M.; Oie, M.; Fujii, M. Elevated expression of CD30 in adult T-cell leukemia cell lines: possible role in constitutive NF-kappaB activation. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, E.P.; Alexander, R.K.; Daniel, S.; Kashanchi, F.; Brady, J.N. Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha in human neuronal cells by extracellular human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6982–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Sharma, N.; Nyborg, J.K. The proto-oncogene Bcl3, induced by Tax, represses Tax-mediated transcription via p300 displacement from the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 promoter. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11939–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coope, H.J.; Atkinson, P.; Huhse, B.; Belich, M.; Janzen, J.; Holman, M.J.; Klaus, G.G.; Johnston, L.H.; Ley, S.C. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100 to p52. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5375–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.W.; Rumble, J.M.; Duckett, C.S. CD30 activates both the canonical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways in anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, s10252–s10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, R.; Higashihara, M.; Watanabe, T. Hodgkin’s lymphoma and CD30 signal transduction. Int. J. Hematol. 2003, 77, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, S.J.; Semmes, O.J. Impact of HTLV-I Tax on cell cycle progression and the cellular DNA damage repair response. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5986–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlichlia, K.; Khazaie, K. HTLV-1 Tax: Linking transformation, DNA damage and apoptotic T-cell death. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogawa, M.; Higuchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Oie, M.; Mori, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Aoyagi, Y.; Fujii, M. Rearranged NF-kappa B2 gene in an adult T-cell leukemia cell line. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Dewan, M.Z.; Sugimoto, H.; Martinez Bruyn, V.J.; Iwasaki. Y.; Matsubara, K.; Qi, X.; Saitoh, T.; Imoto, I.; et al. Overexpressed NF-kappaB-inducing kinase contributes to the tumorigenesis of adult T-cell leukemia and Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood 2008, 111, 5118–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ito, T.; Shimizu, T.; Ishida, T.; Semba, K.; Watanabe, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Inoue, J. Epigenetic alteration of the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) gene is involved in enhanced NIK expression in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Qu, Z.; Xiao, G. Endoproteolytic processing of C-terminally truncated NF-kappaB2 precursors at kappaB-containing promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 5324–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Xiao, G. Essential role of IkappaB kinase alpha in the constitutive processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9765–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Muramatsu, M.; Hirai, H.; Suzuki, T.; Fujisawa, J.; Yoshida, M.; Arai, K.; Arai, N. HTLV-I encoded Tax in association with NF-kappa B precursor p105 enhances nuclear localization of NF-kappa B p50 and p65 in transfected cells. Oncogene 1992, 8, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Brockman, J.A.; Scherer, D.C.; Al-Murrani, S.W.; Green, P.L.; Ballard, D.W. Inactivation of IkappaBbeta by the tax protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: a potential mechanism for constitutive induction of NF-kappaB. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, L.; Sun, S.C. Persistent activation of NF-kappa B/Rel by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax involves degradation of I kappa B beta. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2730–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggirwar, S.B.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. Activation of NF-kappa B/Rel by Tax involves degradation of I kappa B alpha and is blocked by a proteasome inhibitor. Oncogene 1995, 11, 993–998. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.C.; Xiao, G. Deregulation of NF-kappaB and its upstream kinases in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Fujisawa, J.; Suzuki, T.; Ueda, K.; Muramatsu, M.; Tsuboi, A.; Arai, N.; Yoshida, M. Transcriptional activator Tax of HTLV-1 binds to the NF-kappa B precursor p105. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Hirai, H.; Fujisawa, J.; Fujita, T.; Yoshida, M. A trans-activator Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 binds to NF-kappa B p50 and serum response factor (SRF) and associates with enhancer DNAs of the NF-kappa B site and CArG box. Oncogene 1993, 8, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Hirai, H.; Yoshida, M. Tax protein of HTLV-1 interacts with the Rel homology domain of NF-kappa B p65 and c-Rel proteins bound to the NF-kappa B binding site and activates transcription. Oncogene 1994, 9, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, T.; Hirai, H.; Suzuki, T.; Fujisawa, J.; Yoshida, M. HTLV-1 Tax enhances NF-kappa B2 expression and binds to the products p52 and p100, but does not suppress the inhibitory function of p100. Virology 1995, 206, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Hirai, H.; Murakami, T.; Yoshida, M. Tax protein of HTLV-1 destabilizes the complexes of NF-kappa B and I kappa B-alpha and induces nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B for transcriptional activation. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos, L.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 tax protein increases NF-kappa B dimer formation and antagonizes the inhibitory activity of the I kappa B alpha regulatory protein. Virology 1996, 225, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraud, C.; Sun, S.C.; Ganchi, P.; Ballard, D.W.; Greene, W.C. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax associates with and is negatively regulated by the NF-kappa B2 p100 gene product: implications for viral latency. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lacoste, J.; Lanoix, J.; Pepin, N.; Hiscott, J. Interactions between HTLV-I Tax and NF-kappa B/Rel proteins in T cells. Leukemia 1994, 8, S71–S76. [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix, J.; Lacoste, J.; Pepin, N.; Rice, N.; Hiscott, J. Overproduction of NFKB2 (lyt-10) and c-Rel: a mechanism for HTLV-I Tax-mediated trans-activation via the NF-kappa B signalling pathway. Oncogene 1994, 9, 841–852. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Fu, J.; Qu, Z.; Li, S.; Tanaka, T.; Grusby, M.J.; Xiao, G. PDLIM2 suppresses human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis by targeting Tax into the nuclear matrix for proteasomal degradation. Blood 2009, 113, 4370–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, N.; Molitor, J.A.; Smith, M.R.; Kim, J.H.; Daitoku, Y.; Greene, W.C. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax induces expression of the Rel-related family of kappa B enhancer-binding proteins: evidence for a pretranslational component of regulation. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 6892–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K.; Yoshida, M. Characterization of mRNA expression of IkappaB alpha and NF-kappaB subfamilies in primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Rice, N.R.; Chen, E.; Yang, N.S.; Mikovits, J.; Longo, D.L. Differential expression of Rel family members in human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected cells: transcriptional activation of c-rel by Tax protein. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Qu, Z.; Yan, P.; Ishikawa, C.; Aqeilan, R.; Rabson, A.B.; Xiao, G. The tumor suppressor gene wwox links the canonical and non-canonical NF-kappaB pathways in HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Blood 2011, 117, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.J.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Radonovich, M.F.; Park, H.U.; Brady, J.N. Activated AKT regulates NF-kappaB activation, p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6719–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, R.I.; Tsuchiya, K.; Suzuki, K.; Itoh, K.; Fujita, J.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tsuji, T. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax down-regulates the expression of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate inositol phosphatases via the NF-kappaB pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 2680–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köntgen, F.; Grumont, R.J.; Strasser, A.; Metcalf, D.; Li, R.; Tarlinton, D.; Gerondakis, S. Mice lacking the c-rel proto-oncogene exhibit defects in lymphocyte proliferation, humoral immunity, and interleukin-2 expression. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, H.C.; Jin, Z.; Tumang, J.; Andjelic, S.; Smith, K.A.; Liou, M.L. c-Rel is crucial for lymphocyte proliferation but dispensable for T cell effector function. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, C.; Nakachi, S.; Senba, M.; Sugai, M.; Mori, N. Activation of AID by human T-cell leukemia virus Tax oncoprotein and the possible role of its constitutive expression in ATL genesis. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Greene, W.C. Identification of HTLV-I tax trans-activator mutants exhibiting novel transcriptional phenotypes. Genes Dev. 1990, 4, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmes, O.J.; Jeang, K.T. Mutational analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax: regions necessary for function determined with 47 mutant proteins. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, S.; Inoue, H.; Sakurai, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Hazama, M.; Yamada, T.; Hatanaka, M. Constitutive activation of NF-kappa B is essential for transformation of rat fibroblasts by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Greene, W.C. Type I human T cell leukemia virus tax protein transforms rat fibroblasts through the cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein/activating transcription factor pathway. J. Clin. Invest. 1991, 88, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Shibata, H.; Fujisawa, J.I.; Inoue, H.; Hakura, A.; Tsukahara, T.; Fujii, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein transforms rat fibroblasts via two distinct pathways. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4445–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, O.; Koch, C.; Schmitt, I.; Semmes, O.J.; Jeang, K.T.; Grassmann, R. A human T-cell leukemia virus Tax variant incapable of activating NF-kappaB retains its immortalizing potential for primary T-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 271, 6698–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, Y.; Tsukahara, T.; Ohashi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Arai, M.; Nakamura, M.; Ohtani, K.; Koya, Y.; Kannagi, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Fujii, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax protein abrogates interleukin-2 dependence in a mouse T-cell line. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Ono, H.; Nyunoya, H.; Shimotohno, K. Characterization of peripheral blood T-lymphocytes transduced with HTLV-I Tax mutants with different trans-activating phenotypes. Oncogene 1997, 14, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robek, M.D.; Ratner, L. Immortalization of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax mutants expressed in a functional molecular clone. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4856–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.M.; Narayan, M.; Fang, Z.Y.; Minella, A.C.; Green, P.L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 2 tax mutants that selectively abrogate NFkappaB or CREB/ATF activation fail to transform primary human T cells. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, I.; Shinohara, T.; Bilakovics, J.; Brown, D.A.; Xu, X.; Nerenberg, M. Ablation of transplanted HTLV-I Tax-transformed tumors in mice by antisense inhibition of NF-kappa B. Science 1992, 258, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Yamada, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Tsukasaki, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Fujii, M. Bay 11–7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 2002, 100, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, R.; El-Sabban, M.E.; Karam, J.A.; Dbaibo, G.; Kfoury, Y.; Arnulf, B.; Lepelletier, Y.; Bex, F.; de Thé, H.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A. Efficacy and mechanism of action of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in T-cell lymphomas and HTLV-I associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Oncogene 2005, 24, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Nosaka, K.; Koya, Y.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Toyokuni, S.; Matsuoka, M. Proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, potently inhibits the growth of adult T-cell leukemia cells both in vivo and in vitro. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanda, T.; Asamitsu, K.; Ogura, H.; Iida, S.; Utsunomiya, A.; Ueda, R.; Okamoto, T. Induction of cell death in adult T-cell leukemia cells by a novel IkappaB kinase inhibitor. Leukemia 2006, 20, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra-Kaushik, S.; Harding, J.C.; Hess, J.L.; Ratner, L. Effects of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 on tumor growth in HTLV-1 Tax transgenic mice and Tax tumor transplants. Blood 2004, 104, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Ogle, L.; Benitez, B.; Bohuslav, J.; Montano, M.; Felsher, D.W.; Greene, W.C. Lethal cutaneous disease in transgenic mice conditionally expressing type I human T cell leukemia virus Tax. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35713–35722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, R.; Ozono, E.; Fujisawa, J.; Ikeda, M.A.; Okamura, N.; Huang, Y.; Ohtani, K. Activation of the cyclin D2 and cdk6 genes through NF-kappaB is critical for cell-cycle progression induced by HTLV-I Tax. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5635–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Tsubata, C.; Kondo, R.; Yoshida, S.; Takahashi, M.; Oie, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Mahieux, R.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujii, M. Cooperation of NF-kappaB2/p100 activation and the PDZ domain binding motif signal in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax1 but not HTLV-2 Tax2 is crucial for interleukin-2-independent growth transformation of a T-cell line. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11900–11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Petrus, M.; Bryant, B.R.; Phuc Nguyen, V.; Stamer, M.; Goldman, C.K.; Bamford, R.; Morris, J.C.; Janik, J.E.; Waldmann, T.A. Induction of the IL-9 gene by HTLV-I Tax stimulates the spontaneous proliferation of primary adult T-cell leukemia cells by a paracrine mechanism. Blood 2008, 111, 5163–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Nagakubo, D.; Shirakawa, A.K.; Nakayama, T.; Shigeta, A.; Hieshima, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yoshie, O. CXCR7 is inducible by HTLV-1 Tax and promotes growth and survival of HTLV-1-infected T cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larousserie, F.; Bardel, E.; Pflanz, S.; Arnulf, B.; Lome-Maldonado, C.; Hermine, O.; Brégeaud, L.; Perennec, M.; Brousse, N.; Kastelein, R.; Devergne, O. Analysis of interleukin-27 (EBI3/p28) expression in Epstein-Barr virus- and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated lymphomas: heterogeneous expression of EBI3 subunit by tumoral cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Weber, M.; Giaisi, M.; Chlichlia, K.; Khazaie, K.; Krammer, P.H. Human T cell leukemia virus type I Tax enhances IL-4 gene expression in T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, M.; Asao, H.; Hara, T.; Higuchi, M.; Fujii, M.; Nakamura, M. Transcriptional activation of the interleukin-21 gene and its receptor gene by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax in human T-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25501–25511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Fujii, M.; Cheng, G.; Ikeda, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Yamamoto, N. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein induces the expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-xL in human T-cells through nuclear factor-kappaB and c-AMP responsive element binding protein pathways. Virus Genes 2001, 22, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, K.; Schneider, G.; Grassmann, R. MicroRNA miR-146a and further oncogenesis-related cellular microRNAs are dysregulated in HTLV-1-transformed T lymphocytes. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Mori, N. MicroRNA miR-146a is induced by HTLV-1 tax and increases the growth of HTLV-1-infected T-cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, T.; Kannagi, M.; Ohashi, T.; Kato, H.; Arai, M.; Nunez, G.; Iwanaga, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohtani, K.; Nakamura, M.; Fujii, M. Induction of Bcl-x(L) expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax through NF-kappaB in apoptosis-resistant T-cell transfectants with Tax. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7981–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, K.; Kawata, S.; Shimotohno, K. p21WAF1 modulates NF-kappaB signaling and induces anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 in Tax-expressing rat fibroblast. Virology 2005, 332, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbermann, K.; Schneider, G.; Grassmann, R. Stimulation of interleukin-13 expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 oncoprotein Tax via a dually active promoter element responsive to NF-kappaB and NFAT. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2788–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariner, J.M.; Lantz, V.; Waldmann, T.A.; Azimi, N. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I Tax activates IL-15R alpha gene expression through an NF-kappa B site. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Mukaida, N.; Ballard, D.W.; Matsushima, K.; Yamamoto, N. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax transactivates human interleukin 8 gene through acting concurrently on AP-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB-like sites. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3993–4000. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, N.; Ueda, A.; Ikeda, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Morikawa, S.; Geleziunas, R.; Yoshimura, T. Yamamoto N., Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax activates transcription of the human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene through two nuclear factor-kappaB sites. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4939–4945. [Google Scholar]
- Pichler, K.; Kattan, T.; Gentzsch, J.; Kress, A.K.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R.; Grassmann, R. Strong induction of 4–1BB, a growth and survival promoting costimulatory receptor, in HTLV-1-infected cultured and patients’ T cells by the viral Tax oncoprotein. Blood 2008, 111, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankow, R.; Dürkop, H.; Latza, U.; Krause, H.; Kunzendorf, U.; Pohl, T.; Bulfone-Paus, S. The HTLV-I tax protein transcriptionally modulates OX40 antigen expression. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, K.; Tsujimoto, A.; Tsukahara, T.; Numata, N.; Miura, S.; Sugamura, K.; Nakamura, M. Molecular mechanisms of promoter regulation of the gp34 gene that is trans-activated by an oncoprotein Tax of human T cell leukemia virus type I. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14119–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Fujii, M.; Hinz, M.; Nakayama, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kashanchi, F.; Tanaka, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Yamamoto, N. Activation of cyclin D1 and D2 promoters by human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein is associated with IL-2-independent growth of T cells. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wäldele, K.; Silbermann, K.; Schneider, G.; Ruckes, T.; Cullen, B.R.; Grassmann, R. Requirement of the human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-1) tax-stimulated HIAP-1 gene for the survival of transformed lymphocytes. Blood 2006, 107, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Shirakawa, F.; Shimizu, H.; Murakami, S.; Oda, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Eto, S. Transcriptional regulation of the human interleukin-6 gene promoter in human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected T-cell lines: evidence for the involvement of NF-kappa B. Blood 1994, 84, 2904–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Pang, J.; Yu, J.; Lehmann, E.; Huynh, L.; Vukosavljevic, T.; Takeki, M.; Klisovic, R.B.; et al. Bortezomib induces DNA hypomethylation and silenced gene transcription by interfering with Sp1/NF-kappaB-dependent DNA methyltransferase activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, C.; Mahieux, R.; Pise-Masison, C.; Brady, J.; Gessain, A.; Yamaoka, S.; Franchini, G. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax represses c-Myb-dependent transcription through activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and modulation of coactivator usage. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 7391–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uittenbogaard, M.N.; Armstron, A.P.; Chiaramello, A.; Nyborg, J.K. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein represses gene expression through the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22466–22469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uittenbogaard, M.N.; Giebler, H.A.; Reisman, D.; Nyborg, J.K. Transcriptional repression of p53 by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28503–28506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, R.; Mookerjee, B.; van Hensbergen, Y.; Bedi, G.C.; Giordano, A.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Fuchs, E.J.; Bedi, A. p53-mediated repression of nuclear factor-kappaB RelA via the transcriptional integrator p300. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4531–4536. [Google Scholar]
- Wadgaonkar, R.; Phelps, K.M.; Haque, Z.; Williams, A.J.; Silverman, E.S.; Collins, T. CREB-binding protein is a nuclear integrator of nuclear factor-kappaB and p53 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.A.; Perkins, N.D. Transcriptional cross talk between NF-kappaB and p53. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 3485–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Radonovich, M.F.; Brady, J.N.; Pise-Masison, C.A. HTLV-I Tax induces a novel interaction between p65/RelA and p53 that results in inhibition of p53 transcriptional activity. Blood 2004, 104, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pise-Masison, C.A.; Mahieux, R.; Jiang, H.; Ashcroft, M.; Radonovich, M.F.; Duvall, J.; Guillerm, C.; Brady, J.N. Inactivation of p53 by human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax requires activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and is dependent on p53 phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 3377–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Radonovich, M.F.; Park, H.U.; Brady, J.N. A novel NF-kappaB pathway involving IKKbeta and p65/RelA Ser-536 phosphorylation results in p53 Inhibition in the absence of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10326–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Padre, R.C.; De Mendoza, T.H.; Bottero, V,; Tergaonkar, V. B.; Verma, I.M. Phosphorylation of p53 by IkappaB kinase 2 promotes its degradation by beta-TrCP. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tergaonkar, V.; Pando, M.; Vafa, O.; Wahl, G.; Verma, I. p53 stabilization is decreased upon NFkappaB activation: a role for NFkappaB in acquisition of resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busuttil, V.; Droin, N.; McCormick, L.; Bernassola, F.; Candi, E.; Melino, G.; Green, D.R. NF-kappaB inhibits T-cell activation-induced, p73-dependent cell death by induction of MDM2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 18061–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon, M.; Nicot, C. Central role of PI3K in transcriptional activation of hTERT in HTLV-I-infected cells. Blood 2008, 112, 2946–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Datta, U.; Horikawa, I.; Michishita, E.; Datta, A.; Sigler-Nicot, J.C.; Brown, M.; Kazanji, M.; Barrett, J.C.; Nicot, C. Transcriptional activation of hTERT through the NF-kappaB pathway in HTLV-I-transformed cells. Blood 2004, 104, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Sato, H.; Hayashibara, T.; Senba, M.; Hayashi, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kamihira, S.; Ikeda, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Morikawa, S.; et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax transactivates the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene: potential role in mediating adult T-cell leukemia invasiveness. Blood 2002, 99, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okayama, A.; Chen, Y.M.; Tachibana, N.; Shioiri, S.; Lee, T.H.; Tsuda, K.; Essex, M. High incidence of antibodies to HTLV-I tax in blood relatives of adult T cell leukemia patients. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochikura, T.; Iwahashi, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Hinuma, Y; Yamamoto, N. Effect of human serum anti-HTLV antibodies on viral antigen induction in vitro cultured peripheral lymphocytes from adult T-cell leukemia patients and healthy virus carriers. Int. J. Cancer 1985, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanon, E.; Hall, S.; Taylor, G.P.; Saito, M.; Davis, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Usuku, K.; Osame, M.; Weber, J.N.; Bangham, C.R. Abundant tax protein expression in CD4+ T cells infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) is prevented by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood 2000, 95, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.; Seiki, M.; Yoshida, M. The second pX product p27 chi-III of HTLV-1 is required for gag gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1986, 209, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, M.; Inoue, J.; Yoshida, M.; Seiki, M. Post-transcriptional regulator (rex) of HTLV-1 initiates expression of viral structural proteins but suppresses expression of regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröne, M.; Koch, C.; Grassmann, R. The HTLV-1 Rex protein induces nuclear accumulation of unspliced viral RNA by avoiding intron excision and degradation. Virology 1996, 218, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, C.; Dundr, M.; Johnson, J.M.; Fullen, J.R.; Alonzo, N.; Fukumoto, R.; Princler, G.L.; Derse, D.; Misteli, T.; Franchini, G. HTLV-1-encoded p30II is a post-transcriptional negative regulator of viral replication. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Nisbet. J.W.; Albrecht, B.; Ding, W.; Kashanchi, F.; Bartoe, J.T.; Lairmore, M.D. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 p30(II) regulates gene transcription by binding CREB binding protein/p300. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9885–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Yoshida, M.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudray, G.; Gachon, F.; Basbous, J.; Biard-Piechaczyk, M.; Devaux, C.; Mesnard, J.M. The Complementary Strand of the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 RNA Genome Encodes a bZIP Transcription Factor That Down-Regulates Viral Transcription. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12813–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Zimmerman, B.; Li, M.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 antisense-encoded gene, Hbz, promotes T-lymphocyte proliferation. Blood 2008, 112, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, G.; Ratner, L. The HTLV-1 hbz antisense gene indirectly promotes tax expression via down-regulation of p30(II) mRNA. Virology 2011, 410, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Zhao, T.; Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, P.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohshima, K.; Green, P.L.; Ohkura, N.; et al. HTLV-1 bZIP Factor Induces T-Cell Lymphoma and Systemic Inflammation In vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rende, F.; Cavallari, I.; Corradin, A.; Silic-Benussi, M.; Toulza, F.; Toffolo, G.M.; Tanaka, Y.; Jacobson, S.; Taylor, G.P.; D’Agostino, D.M.; et al. Kinetics and intracellular compartmentalization of HTLV-1 gene expression: Nuclear retention of HBZ mRNA. Blood 2011, 117, 4855–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Saito, K.; Arimura, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Ohara, Y. In vivo expression of the HBZ gene of HTLV-1 correlates with proviral load, inflammatory markers and disease severity in HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Retrovirology 2009, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilburn, S.; Rowan, A.; Demontis, M.A.; MacNamara, A.; Asquith, B.; Bangham, C.R.; Taylor, G.P. In vivo expression of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 basic leucine-zipper protein generates specific CD8+ and CD4+ T-lymphocyte responses that correlate with clinical outcome. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Yamamoto, B.; Li, M.; Phipps, A.J.; Younis, I.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Enhancement of infectivity and persistence in vivo by HBZ, a natural antisense coded protein of HTLV-1. Blood 1996, 107, 3976–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ego, T.; Ariumi, Y.; Shimotohno, K. The interaction of HTLV-1 Tax with HDAC1 negatively regulates the viral gene expression. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7241–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Linton, R.; Park, H.U.; Schiltz, R.L.; Sartorelli, V.; Brady, J.N. Tax relieves transcriptional repression by promoting histone deacetylase 1 release from the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6735–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Qu, Z.; Ishikawa, C.; Mori, N.; Xiao, G. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I-mediated repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 involves DNA methylation but independent of the viral oncoprotein tax. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Fu, J.; Yan, P.; Hu, J.; Cheng, S.Y.; Xiao, G. Epigenetic repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2: implications for the biology and treatment of breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 11786–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Yan, P.; Fu, J.; Jiang, J.; Grusby, M.J.; Smithgall, T.E.; Xiao, G. DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Yan, P.; Qu, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiao, G. Hsp90 regulates processing of NF-kappa B2 p100 involving protection of NF-kappa B-inducing kinase (NIK) from autophagy-mediated degradation. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, G.; Yan, P.; Xiao, G. Hsp90 inhibition results in autophagy-mediated proteasome-independent degradation of IkappaB kinase (IKK). Cell Res. 2006, 16, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G. Autophagy and NF-kappaB: fight for fate. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Walsh, I.; Waterfiled, M.; Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling pathway governs TRAIL gene expression and human T-cell leukemia virus-I Tax-induced T-cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40385–40388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaims, A.Y.; Khani, F.; Zhang, Y.; Roberts, A.I.; Devadas, S.; Shi, Y.; Rabson, A.B. Immune activation induces immortalization of HTLV-1 LTR-Tax transgenic CD4+ T cells. Blood 2010, 116, 2994–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, G.; Mulloy, J.C.; Koralnik, I.J.; Lo Monico, A.; Sparkowski, J.J.; Andresson, T.; Goldstein, D.J.; Schlegel, R. The human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I p12I protein cooperates with the E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus in cell transformation and binds the 16-kilodalton subunit of the vacuolar H+ ATPase. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7701–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derse, D.; Mikovits, J.; Ruscetti, F. X-I and X-II open reading frames of HTLV-I are not required for virus replication or for immortalization of primary T-cells in vitro. Virology 1997, 237, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robek, M.D.; Wong, F.H.; Ratner, L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 pX-I and pX-II open reading frames are dispensable for the immortalization of primary lymphocytes. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4458–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Silverman, L.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. HTLV-1 Rex is required for viral spread and persistence in vivo but is dispensable for cellular immortalization in vitro. Blood 2003, 102, 3963–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2011 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, Z.; Xiao, G. Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus: A Model of NF-κB-Associated Tumorigenesis. Viruses 2011, 3, 714-749. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3060714
Qu Z, Xiao G. Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus: A Model of NF-κB-Associated Tumorigenesis. Viruses. 2011; 3(6):714-749. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3060714
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Zhaoxia, and Gutian Xiao. 2011. "Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus: A Model of NF-κB-Associated Tumorigenesis" Viruses 3, no. 6: 714-749. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3060714
APA StyleQu, Z., & Xiao, G. (2011). Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus: A Model of NF-κB-Associated Tumorigenesis. Viruses, 3(6), 714-749. https://doi.org/10.3390/v3060714



