Dendritic Cells and HIV-1 Trans-Infection
Abstract
:1. Dendritic cells and immune control
3. HIV-1 trans-infection at the infectious synapse
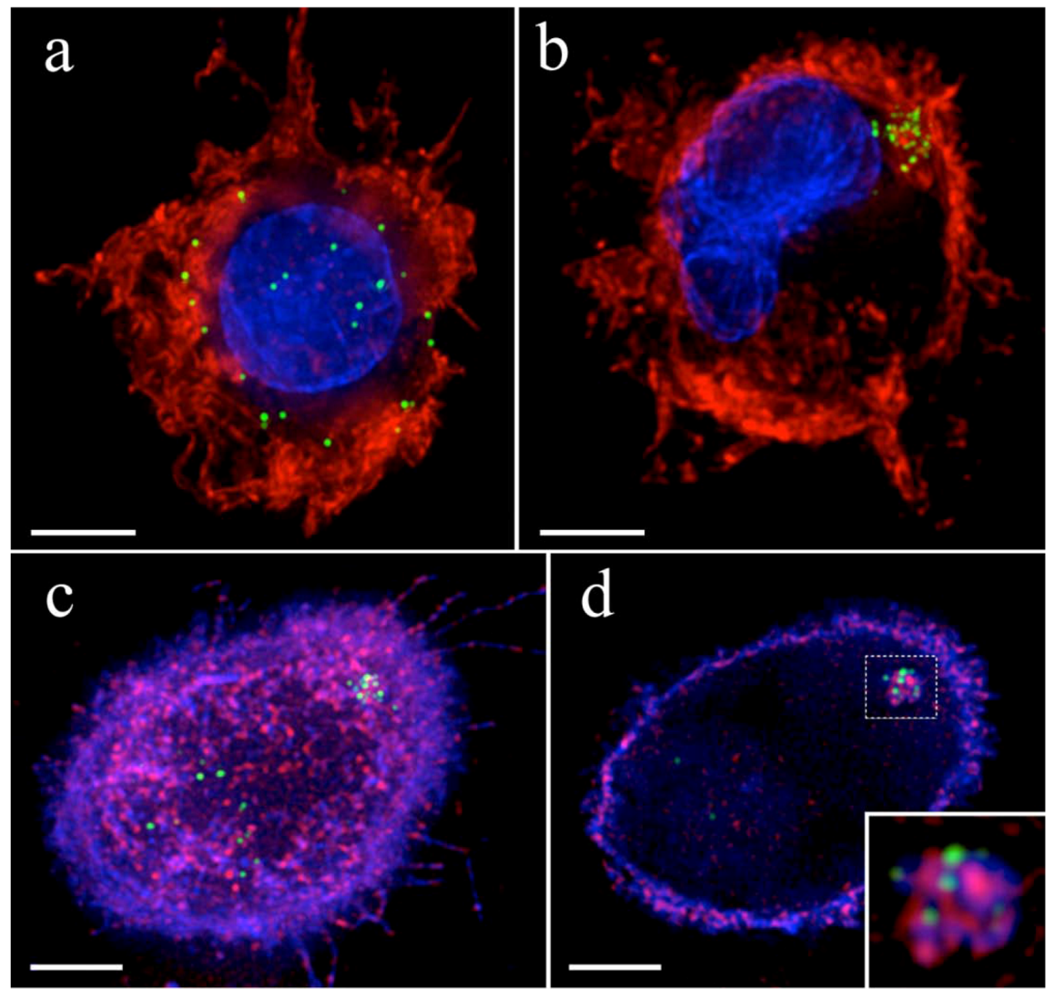
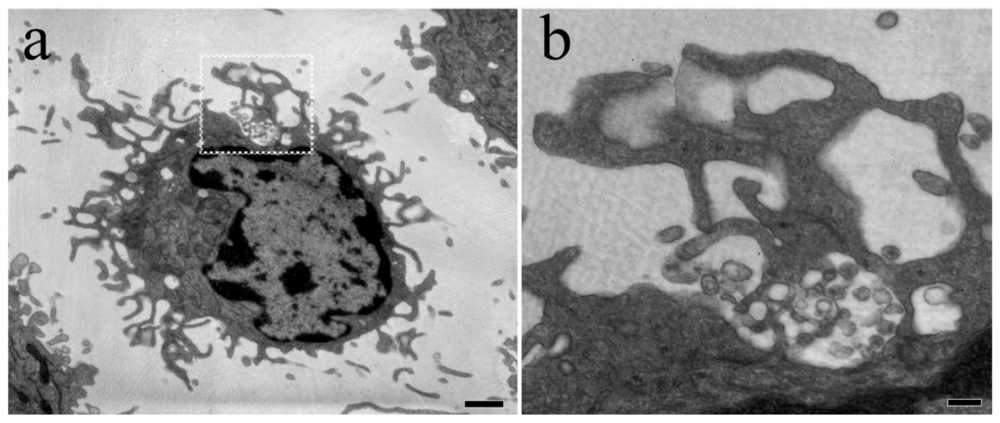
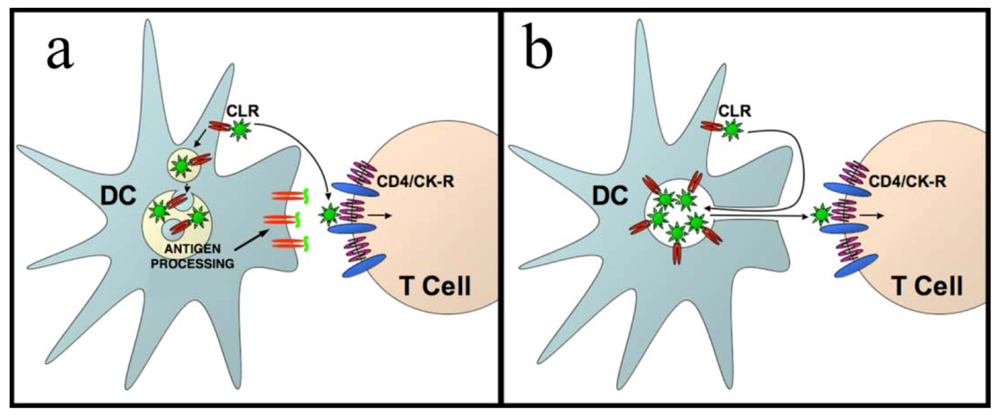
4. HIV-1 dissemination in lymphoid tissues
5. Conclusions
References
- Banchereau, J.; Briere, F.; Caux, C.; Davoust, J.; Lebecque, S.; Liu, Y.J.; Pulendran, B.; Palucka, K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 767–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, R.M.; Idoyaga, J. Features of the dendritic cell lineage. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 234, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, W.S.; Chen, L.M.; Kroschewski, R.; Ebersold, M.; Turley, S.; Trombetta, S.; Galan, J. E.; Mellman, I. Developmental control of endocytosis in dendritic cells by Cdc42. Cell 2000, 102, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cella, M.; Engering, A.; Pinet, V.; Pieters, J.; Lanzavecchia, A. Inflammatory stimuli induce accumulation of MHC class II complexes on dendritic cells. Nature 1997, 388, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askew, D.; Chu, R.S.; Krieg, A.M.; Harding, C.V. CpG DNA induces maturation of dendritic cells with distinct effects on nascent and recycling MHC-II antigen-processing mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6889–6895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pai, R.K.; Askew, D.; Boom, W.H.; Harding, C.V. Regulation of class II MHC expression in APCs: roles of types I, III, and IV class II transactivator. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monks, C.R.; Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Sciaky, N.; Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 1998, 395, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grakoui, A.; Bromley, S.K.; Sumen, C.; Davis, M.M.; Shaw, A.S.; Allen, P.M.; Dustin, M.L. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 1999, 285, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumen, C.; Mempel, T.R.; Mazo, I. B.; von Andrian, U.H. Intravital Microscopy: Visualizing Immunity in Context. Immunity 2004, 21, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Revy, P.; Sospedra, M.; Barbour, B.; Trautmann, A. Functional antigen-independent synapses formed between T cells and dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzer, K.; van Eijk, M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Jakobson, E.; de Groot, C.; Geuze, H.J. Follicular dendritic cells carry MHC class II-expressing microvesicles at their surface. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Egen, J.G.; Huang, A.Y.; Germain, R.N. Extrafollicular activation of lymph node B cells by antigen-bearing dendritic cells. Science 2006, 312, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzer, K.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Heijnen, H.F.; Stoorvogel, W.; Geuze, H. J. Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device . J. Cell. Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 19, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Courreges, M.C.; Burzyn, D.; Nepomnaschy, I.; Piazzon, I.; Ross, S.R. Critical role of dendritic cells in mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3769–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.R. MMTV Infectious Cycle and the Contribution of Virus-encoded Proteins to Transformation of Mammary Tissue. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2008, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golde, W.T.; Nfon, C.K.; Toka, F.N. Immune evasion during foot-and-mouth disease virus infection of swine. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 225, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Glushakova, S.; Margolis, L.B. HIV-infected human Langerhans cells transmit infection to human lymphoid tissue ex vivo. Aids 2000, 14, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugaya, M.; Lore, K.; Koup, R.A.; Douek, D.C.; Blauvelt, A. HIV-infected Langerhans cells preferentially transmit virus to proliferating autologous CD4+ memory T cells located within Langerhans cell-T cell clusters. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Witte, L.; Nabatov, A.; Pion, M.; Fluitsma, D.; de Jong, M.A.; de Gruijl, T.; Piguet, V.; van Kooyk, Y.; Geijtenbeek, T.B. Langerin is a natural barrier to HIV-1 transmission by Langerhans cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Estes, J.D.; Schlievert, P.M.; Duan, L.; Brosnahan, A.J.; Southern, P.J.; Reilly, C.S.; Peterson, M.L.; Schultz-Darken, N.; Brunner, K.G.; Nephew, K.R.; Pambuccian, S.; Lifson, J. D.; Carlis, J.V.; Haase, A.T. Glycerol monolaurate prevents mucosal SIV transmission. Nature 2009, 458, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, J.N.; Barry, A.P.; Vanderford, T.H.; Kozyr, N.; Chavan, R.; Klucking, S.; Barrat, F.J.; Coffman, R.L.; Staprans, S.I.; Feinberg, M.B. Divergent TLR7 and TLR9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and nonpathogenic AIDS virus infections. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pion, M.; Granelli-Piperno, A.; Mangeat, B.; Stalder, R.; Correa, R.; Steinman, R.M.; Piguet, V. APOBEC3G/3F mediates intrinsic resistance of monocyte-derived dendritic cells to HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goujon, C.; Arfi, V.; Pertel, T.; Luban, J.; Lienard, J.; Rigal, D.; Darlix, J.L.; Cimarelli, A. Characterization of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVSM/human immunodeficiency virus type 2 Vpx function in human myeloid cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12335–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goujon, C.; Riviere, L.; Jarrosson-Wuilleme, L.; Bernaud, J.; Rigal, D.; Darlix, J.L.; Cimarelli, A. SIVSM/HIV-2 Vpx proteins promote retroviral escape from a proteasome-dependent restriction pathway present in human dendritic cells. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, P.U.; Freudenthal, P.S.; Barker, J.M.; Gezelter, S.; Inaba, K.; Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cells exposed to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 transmit a vigorous cytopathic infection to CD4+ T cells. Science 1992, 257, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pope, M.; Betjes, M.G.; Romani, N.; Hirmand, H.; Cameron, P.U.; Hoffman, L.; Gezelter, S.; Schuler, G.; Steinman, R.M. Conjugates of dendritic cells and memory T lymphocytes from skin facilitate productive infection with HIV-1. Cell 1994, 78, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Kwon, D.S.; Torensma, R.; van Vliet, S.J.; van Duijnhoven, G.C.; Middel, J.; Cornelissen, I.L.; Nottet, H.S.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Littman, D.R.; Figdor, C.G.; van Kooyk, Y. DC-SIGN, a dendritic cell-specific HIV-1-binding protein that enhances trans-infection of T cells. Cell 2000, 100, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Engering, A.; Van Kooyk, Y. DC-SIGN, a C-type lectin on dendritic cells that unveils many aspects of dendritic cell biology. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Torensma, R.; van Vliet, S.J.; van Duijnhoven, G.C.; Adema, G.J.; van Kooyk, Y.; Figdor, C.G. Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell 2000, 100, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turville, S.G.; Arthos, J.; Donald, K.M.; Lynch, G.; Naif, H.; Clark, G.; Hart, D.; Cunningham, A.L. HIV gp120 receptors on human dendritic cells. Blood 2001, 98, 2482–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, A.A.; Gilbert, C.; Richard, M.; Beaulieu, A.D.; Tremblay, M.J. The C-type lectin surface receptor DCIR acts as a new attachment factor for HIV-1 in dendritic cells and contributes to trans- and cis-infection pathways. Blood 2008, 112, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Witte, L.; Bobardt, M.; Chatterji, U.; Degeest, G.; David, G.; Geijtenbeek, T. B.; Gallay, P. Syndecan-3 is a dendritic cell-specific attachment receptor for HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 19464–19469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, S.C.; Archer, J.; Gummuluru, S. Glycosphingolipid composition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) particles is a crucial determinant for dendritic cell-mediated HIV-1 trans-infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3496–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.S.; Gregorio, G.; Bitton, N.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Littman, D.R. DC-SIGN-mediated internalization of HIV is required for trans- enhancement of T cell infection. Immunity 2002, 16, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Wu, L.; Bohks, S.M.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Unutmaz, D.; Hope, T.J. Recruitment of HIV and its receptors to dendritic cell-T cell junctions. Science 2003, 300, 1295–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, C.; Kashefi, K.; Hollinshead, M.; Sattentau, Q.J. HIV-1 cell to cell transfer across an Env-induced, actin-dependent synapse. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigdomenech, I.; Massanella, M.; Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Ruiz-Hernandez, R.; Curriu, M.; Bofill, M.; Martinez-Picado, J.; Juan, M.; Clotet, B.; Blanco, J. HIV transfer between CD4 T cells does not require LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 and is governed by the interaction of HIV envelope glycoprotein with CD4. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Kwas, C.; Wu, L. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), but not ICAM-2 and -3, is important for dendritic cell-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4195–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turville, S.G.; Santos, J.J.; Frank, I.; Cameron, P.U.; Wilkinson, J.; Miranda-Saksena, M.; Dable, J.; Stossel, H.; Romani, N.; Piatak Jr., M.; Lifson, J.D.; Pope, M.; Cunningham, A.L. Immunodeficiency virus uptake, turnover, and 2-phase transfer in human dendritic cells. Blood 2004, 103, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobile, C.; Petit, C.; Moris, A.; Skrabal, K.; Abastado, J.P.; Mammano, F.; Schwartz, O. Covert human immunodeficiency virus replication in dendritic cells and in DC-SIGN-expressing cells promotes long-term transmission to lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5386–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, E.; Nikolic, D.S.; Piguet, V. HIV-1 replication in dendritic cells occurs through a tetraspanin-containing compartment enriched in AP-3. Traffic 2008, 9, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turville, S.G.; Aravantinou, M.; Stossel, H.; Romani, N.; Robbiani, M. Resolution of de novo HIV production and trafficking in immature dendritic cells. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, R.W.; De Jong, E.C.; Baldwin, C.E.; Schuitemaker, J.H.; Kapsenberg, M.L.; Berkhout, B. Differential transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by distinct subsets of effector dendritic cells. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 7812–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moris, A.; Nobile, C.; Buseyne, F.; Porrot, F.; Abastado, J.P.; Schwartz, O. DC-SIGN promotes exogenous MHC-I-restricted HIV-1 antigen presentation. Blood 2004, 103, 2648–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.; McDonald, D.; Canaday, D.H. Rapid MHC-II antigen presentation of HIV type 1 by human dendritic cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 2007, 23, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, E.; Pion, M.; Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Collinson, L.; Arrighi, J.F.; Blot, G.; Leuba, F.; Escola, J.M.; Demaurex, N.; Marsh, M.; Piguet, V. HIV-1 trafficking to the dendritic cell-T-cell infectious synapse uses a pathway of tetraspanin sorting to the immunological synapse. Traffic 2005, 6, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, R.D.; Gummuluru, S. Immature dendritic cell-derived exosomes can mediate HIV-1 trans infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Blanco, J.; Erkizia, I.; Fernandez-Figueras, M.T.; Borras, F.E.; Naranjo-Gomez, M.; Bofill, M.; Ruiz, L.; Clotet, B.; Martinez-Picado, J. Maturation of blood-derived dendritic cells enhances human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capture and transmission. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7559–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Naranjo-Gomez, M.; Archer, J.; Hatch, S.C.; Erkizia, I.; Blanco, J.; Borras, F.E.; Puertas, M.C.; Connor, J.H.; Fernandez-Figueras, M.T.; Moore, L.; Clotet, B.; Gummuluru, S.; Martinez-Picado, J. Capture and transfer of HIV-1 particles by mature dendritic cells converges with the exosome-dissemination pathway. Blood 2009, 113, 2732–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Janas, A.M.; Olson, W.J.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Wu, L. CD4 coexpression regulates DC-SIGN-mediated transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavrois, M.; Neidleman, J.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Greene, W.C. In vitro derived dendritic cells trans-infect CD4 T cells primarily with surface-bound HIV-1 virions. PloS Pathog. 2007, 3, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.J.; Reuter, M.A.; McDonald, D. HIV traffics through a specialized, surface-accessible intracellular compartment during trans-infection of T cells by mature dendritic cells. PloS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrbach, K.M.; Barry, S.M.; Ayehunie, S.; Lamore, S.; Klausner, M.; Hope, T.J. Activated CD34-derived Langerhans cells mediate transinfection with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6858–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Kramer, B.; Marsh, M. Infectious HIV-1 assembles in late endosomes in primary macrophages. J. Cell. Biol. 2003, 162, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneka, M.; Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Byland, R.; Ruiz-Mateos, E.; Marsh, M. In macrophages, HIV-1 assembles into an intracellular plasma membrane domain containing the tetraspanins CD81, CD9, and CD53. J. Cell. Biol. 2007, 177, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, S.; Keppler, O.T.; Habermann, A.; Allespach, I.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Krausslich, H.G. HIV-1 Buds Predominantly at the Plasma Membrane of Primary Human Macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.E.; Narayan, K.; Shi, D.; Hartnell, L.M.; Gousset, K.; He, H.; Lowekamp, B.C.; Yoo, T.S.; Bliss, D.; Freed, E.O.; Subramaniam, S. Ion-abrasion scanning electron microscopy reveals surface-connected tubular conduits in HIV-infected macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gousset, K.; Ablan, S.D.; Coren, L.V.; Ono, A.; Soheilian, F.; Nagashima, K.; Ott, D.E.; Freed, E.O. Real-time visualization of HIV-1 GAG trafficking in infected macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, I.; Stossel, H.; Gettie, A.; Turville, S.G.; Bess Jr., J.W.; Lifson, J.D.; Sivin, I.; Romani, N.; Robbiani, M. A fusion inhibitor prevents spread of immunodeficiency viruses, but not activation of virus-specific T cells, by dendritic cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5329–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, N.M.; Lehmann, M.J.; Jimenez-Soto, L.F.; Horensavitz, C.; Pypaert, M.; Mothes, W. Retroviruses can establish filopodial bridges for efficient cell-to-cell transmission. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowinski, S.; Jolly, C.; Berninghausen, O.; Purbhoo, M.A.; Chauveau, A.; Kohler, K.; Oddos, S.; Eissmann, P.; Brodsky, F.M.; Hopkins, C.; Onfelt, B.; Sattentau, Q.; Davis, D.M. Membrane nanotubes physically connect T cells over long distances presenting a novel route for HIV-1 transmission. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Duan, L.; Estes, J.D.; Ma, Z.M.; Rourke, T.; Wang, Y.; Reilly, C.; Carlis, J.; Miller, C.J.; Haase, A.T. Peak SIV replication in resting memory CD4+ T cells depletes gut lamina propria CD4+ T cells. Nature 2005, 434, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattapallil, J.J.; Douek, D.C.; Hill, B.; Nishimura, Y.; Martin, M.; Roederer, M. Massive infection and loss of memory CD4+ T cells in multiple tissues during acute SIV infection. Nature 2005, 434, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veazey, R.S.; DeMaria, M.; Chalifoux, L.V.; Shvetz, D.E.; Pauley, D.R.; Knight, H.L.; Rosenzweig, M.; Johnson, R.P.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Lackner, A.A. Gastrointestinal tract as a major site of CD4+ T cell depletion and viral replication in SIV infection. Science 1998, 280, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Schacker, T.W.; Ruff, L.E.; Price, D.A.; Taylor, J.H.; Beilman, G.J.; Nguyen, P.L.; Khoruts, A.; Larson, M.; Haase, A.T.; Douek, D.C. CD4+ T cell depletion during all stages of HIV disease occurs predominantly in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, S.M.; Robertson, K.B.; Pan, S.C.; Mawhinney, S.; Meditz, A.L.; Folkvord, J.M.; Connick, E.; McCarter, M.D.; Wilson, C.C. Plasmacytoid and myeloid dendritic cells with a partial activation phenotype accumulate in lymphoid tissue during asymptomatic chronic HIV-1 infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2008, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douek, D.C.; Brenchley, J.M.; Betts, M.R.; Ambrozak, D.R.; Hill, B.J.; Okamoto, Y.; Casazza, J.P.; Kuruppu, J.; Kunstman, K.; Wolinsky, S.; Grossman, Z.; Dybul, M.; Oxenius, A.; Price, D. A.; Connors, M.; Koup, R.A. HIV preferentially infects HIV-specific CD4+ T cells. Nature 2002, 417, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Ruff, L.E.; Casazza, J.P.; Koup, R.A.; Price, D.A.; Douek, D.C. Preferential infection shortens the life span of human immunodeficiency virus-specific CD4+ T cells in vivo. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6801–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 64. Brenchley, J.M.; Ruff, L.E.; Casazza, J.P.; Koup, R.A.; Price, D.A.; Douek, D.C. Preferential infection shortens the life span of human immunodeficiency virus-specific CD4+ T cells in vivo. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6801–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
McDonald, D. Dendritic Cells and HIV-1 Trans-Infection. Viruses 2010, 2, 1704-1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2081704
McDonald D. Dendritic Cells and HIV-1 Trans-Infection. Viruses. 2010; 2(8):1704-1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2081704
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcDonald, David. 2010. "Dendritic Cells and HIV-1 Trans-Infection" Viruses 2, no. 8: 1704-1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2081704
APA StyleMcDonald, D. (2010). Dendritic Cells and HIV-1 Trans-Infection. Viruses, 2(8), 1704-1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2081704



