Epidemiologic Observations from Passive and Targeted Surveillance during the First Wave of the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic in Milwaukee, WI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Passive Surveillance

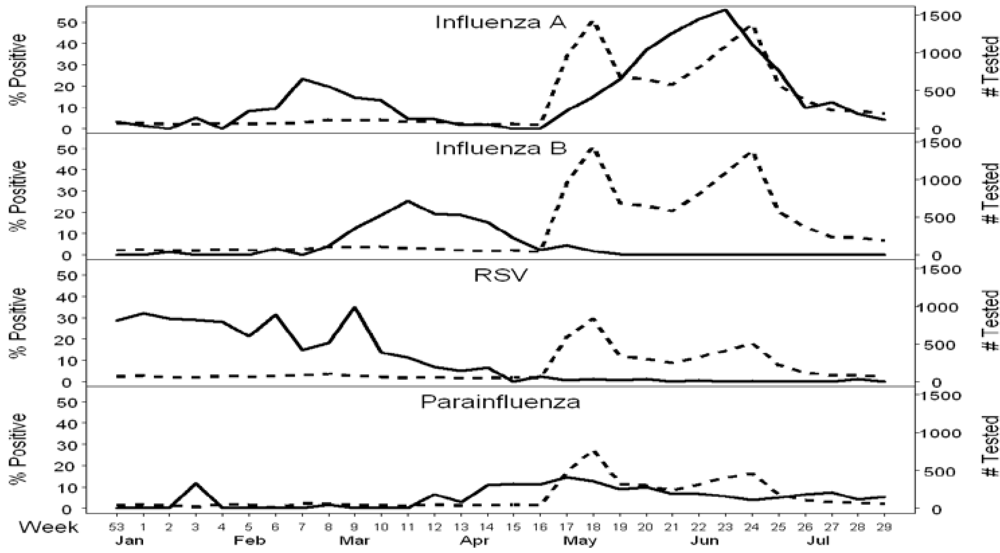
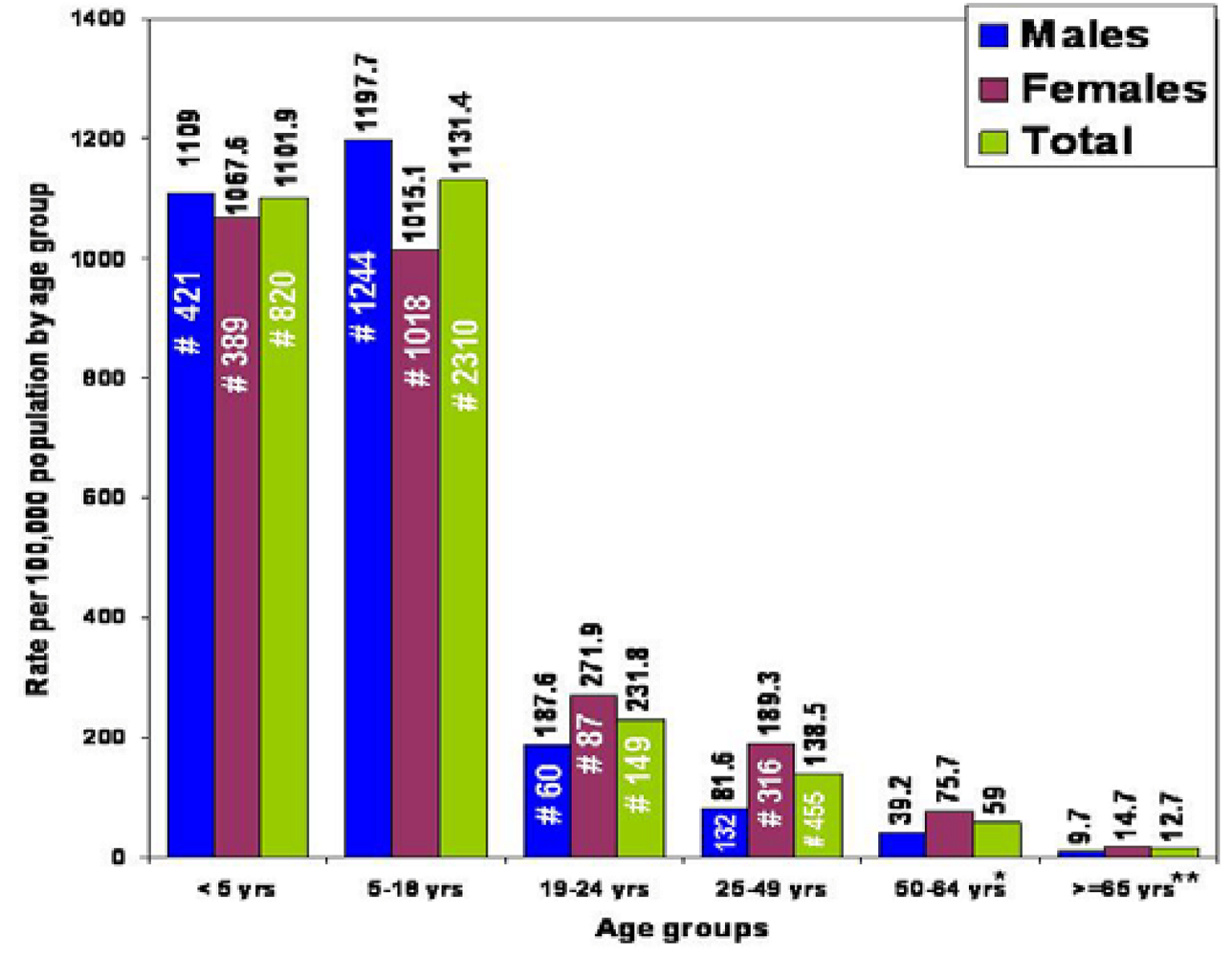
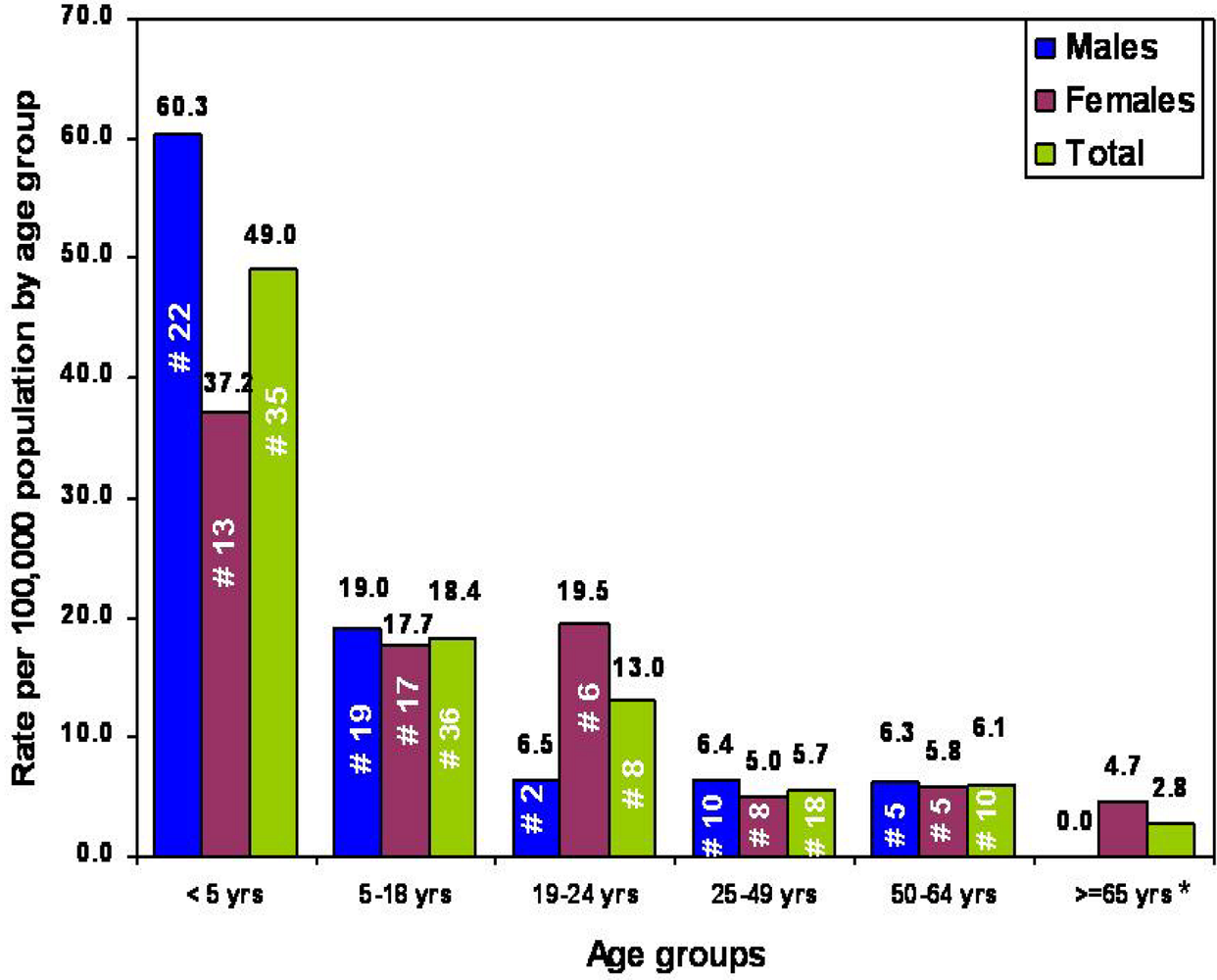
2.2. Targeted Surveillance
| Symptom/s | H1N1pdm Positive (%) N=50 | H1N1pdm Negative (%) N=564 | p-value | “Symptomatic” (%) N=251 | “Asymptomatic” (%) N=363 | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinorrhea | 82 | 31.2 | <0.001 | 75.3 | 7.7 | <0.001 |
| Cough | 80 | 32.8 | <0.001 | 82.1 | 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Fever | 78 | 19.3 | <0.001 | 59 | 0 | <0.001 |
| Sore throat | 38 | 16.8 | <0.001 | 40.2 | 3.6 | <0.001 |
| Headache | 34 | 15.6 | 0.018 | 28.3 | 9.4 | <0.001 |
| Diarrhea | 8 | 8.2 | 0.99 | 15.5 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Vomiting | 8 | 10.5 | 0.99 | 17.1 | 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Nausea | 8 | 10.3 | 0.99 | 28.3 | 9.4 | <0.001 |
| Myalgias | 6 | 2 | 0.58 | 4.8 | 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Seizure | 0 | 0.2 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.99 |
| Rash | 0 | 3.4 | 0.99 | 4.8 | 1.9 | 0.11 |
| Fever and cough (no sore throat) | 36 | 7.4 | - | 23.9 | 0 | - |
| Fever and sore throat (no cough) | 2 | 1.2 | - | 3.2 | 0 | - |
| ILI ** | 68 | 15.4 | <0.001 | 48.2 | 0 | <0.001 |
| No ILI | 32 | 84.6 | - | 51.8 | 100 | - |
| “Symptomatic” | 90 | 36.5 | <0.001 | - | - | - |
| “Asymptomatic” | 10 | 63.5 | - | - | - | - |
2.3. Predicting the Burden of Pandemic Influenza Infection in the Second Wave
3. Discussion
4. Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Tables and Figures
Acknowledgments
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Swine influenza A (H1N1) infection in two children---southern California, March-April 2009 . MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: Swine influenza A (H1N1) infections-California and Texas, April 2009 . MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Chusid, M.J.; Willoughby, R.E.; Havens, P.L.; Kehl, S.C.; Ledeboer, N.A.; Li, S.H.; Henrickson, K.J. Introduction of a Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus into Milwaukee, Wisconsin in 2009. Viruses 2009, 1, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Novel H1N1 Flu Situation Update. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/updates/072409.htm. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisconsin Human Cases of H1N1 Influenza Infection . Available online: http://pandemic.wisconsin.gov/category.asp?linkcatid=3191&linkid=1567&locid=106. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Guidance on Case Definitions to be Used For Investigations of Novel Influenza A (H1N1) Cases . Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/casedef.htm. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Guidance for Clinicians on Identifying and Caring for Patients with Swine-origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection . Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/identifyingpatients.htm. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrickson, K.J.; Hoover, S.; Kehl, K.S.; Hua, W. National disease burden of respiratory viruses detected in children by polymerase chain reaction. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004, 23, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, E.T.; Jurgens, L.A.; Kehl, S.C.; Bose, M.E.; Patitucci, T.; LaGue, E.; Darga, P.; Wilkinson, K.; Witt, L.M.; Fan, J.; He, J.; Kumar, S.; Henrickson, K.J. Development of a rapid automated influenza A, influenza B, and RSV A/B multiplex real-time RT-PCR assay and its use during the 2009 H1N1 swine-origin influenza virus (S-OIV) epidemic in Milwaukee, Wisconsin . J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, M.E.; Beck, E.T.; Ledeboer, N.; Kehl, S.C.; Jurgens, L.A.; Patitucci, T. Rapid semi-automated Subtyping of influenza during the 2009 swine-origin influenza A H1N1 virus epidemic in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Bose, M.E.; Beck, E.T.; Fan, J.; Tiwari, S.; Metallo, J.; Jurgens, L.; Kehl, S.C.; Ledeboer, N.; Kumar, S.; Weisburg, W.; Henrikson, K.J. Rapid multiplex RT-PCR typing of influenza A and B and subtyping of influenza A into H1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, N1 (human), N1 (animal), N2 and N7 including typing of novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus during the current 2009 outbreak in Milwaukee, WI. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2772–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.; Spiro, D.J.; Wentworth, D.E.; Beck, E.T.; Fan, J.; Elodie, G.; Halpin, R.; Bera, J.; Hine, E.; Proudfoot, K.; Stockwell, T.; Lin, X.; Griesemer, S.; Kumar, S.; Bose, M.; Viboud, C.; Holmes, E.; Henrickson, K.J. The early diversification of influenza A/H1N1pdm. PLoS Currents 2009 . Article No. RRN1126. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Health Services. Weekly Surveillance Report . . Available online: http://pandemic.wisconsin.gov/docview.asp?docid=16834&locid=106. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2008 Census Estimates. U.S Census Bureau . Available online: http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTSubjectShowTablesServlet?_ts=269732443505. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novel influenza A (H1N1) virus infections, Wisconsin (Surveillance summary) . Bureau of Communicable Diseases, Wisconsin Division of Public Health, 2009 6 16; provisional data.
- Monto, A. Epidemiology of influenza. Vaccine 2008, 26, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Novel H1N1 Flu: Facts and Figures . Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/surveillanceqa.htm. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infections, Chicago, Illinois, April-July 2009 . MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 913–940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloom, B.; Cohen, R.A. Vital Health Stat 10 2009, 239 National Center for Health Statistics.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2007-08 U.S. Influenza Season Summary . Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/weeklyarchives2007-2008/07-08summary.htm.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: Influenza Activity --- United States, September 28, 2008--April 4, 2009, and Composition of the 2009--10 Influenza Vaccine . MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patrozou, E.; Mermel, L.A. Does influenza transmission occur from asymptomatic infection or prior to symptom onset? Public Health Rep. 2009, 124, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Couch, R.B.; Douglas, R.G.; Fedson, D.S.; Kasel, J.A. J. Infect Dis. 1971, 124, 473–480. [PubMed]
- Carrat, F.; Vergu, E.; Ferguson, N.M.; Lamaitre, M.; Cauchemez, S.; Leach, S.; Valleron, A.J. Time lines of infection and disease in human influenza: A review of volunteer challenge studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheat, K. An investigation into an explosive outbreak of influenza—New Plymouth. Commun. Dis. N. Z. 1992, 92, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, K.; Veguilla, V.; Lu, X.; Zhong, W.; Butler, E.N.; Sun, H.; Liu, F.; Dong, L.; DeVos, J.R.; Gargiullo, P.M.; Brammer, T.L; Tumpeym, T.M.; Katz, J.M. Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses to the 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus . N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Chusid, M.J.; Willoughby, R.E.; Havens, P.L.; Kehl, S.C.; Ledeboer, N.A.; Simpson, P.; VanDyke, M.; Davis, E.; Gaffney, K.; et al. Epidemiologic Observations from Passive and Targeted Surveillance during the First Wave of the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic in Milwaukee, WI. Viruses 2010, 2, 782-795. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2040782
Kumar S, Chusid MJ, Willoughby RE, Havens PL, Kehl SC, Ledeboer NA, Simpson P, VanDyke M, Davis E, Gaffney K, et al. Epidemiologic Observations from Passive and Targeted Surveillance during the First Wave of the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic in Milwaukee, WI. Viruses. 2010; 2(4):782-795. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2040782
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Swati, Michael J. Chusid, Rodney E. Willoughby, Peter L. Havens, Sue C. Kehl, Nathan A. Ledeboer, Pippa Simpson, Meredith VanDyke, Elizabeth Davis, Kate Gaffney, and et al. 2010. "Epidemiologic Observations from Passive and Targeted Surveillance during the First Wave of the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic in Milwaukee, WI" Viruses 2, no. 4: 782-795. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2040782
APA StyleKumar, S., Chusid, M. J., Willoughby, R. E., Havens, P. L., Kehl, S. C., Ledeboer, N. A., Simpson, P., VanDyke, M., Davis, E., Gaffney, K., Li, S.-H., Bose, M. E., & Henrickson, K. J. (2010). Epidemiologic Observations from Passive and Targeted Surveillance during the First Wave of the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic in Milwaukee, WI. Viruses, 2(4), 782-795. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2040782




