HIV Genetic Diversity and Drug Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Genesis of HIV Types and Groups
| Type | Group | Origin | Isolates (%)1 | Epidemiology | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-1 | M | SIVcpz | 259,678 (98.2%) | All continents with exception of Antarctica | Major group responsible for the AIDS pandemic; more fit than HIV-1 group O and HIV-2. |
| O | SIVgor or SIVcpz | 1,095 (0.4%) | Majorly found in Central and West Africa | Naturally resistant to NNRTI; less fit than group HIV-1 M and HIV-2. | |
| N | Recombinant group M ancestor / SIVcpz | 22 (<0.001%) | Only found in Cameroon | Very rare epidemically; few studies on drug resistance published. | |
| P | SIVgor | Single case | Undetermined | Described in 2009 in a Cameroonian woman. The actual number of infections is unknown. | |
| HIV-2 | — | SIVsm | 3,593 (1.4%) | Mainly found in Western and Central Africa; some cases in Western Europe, India, United States, Brazil and Japan | Apparently slower progression to AIDS; less susceptible to some anti-HIV-1 drugs; naturally resistant to NNRTI. |
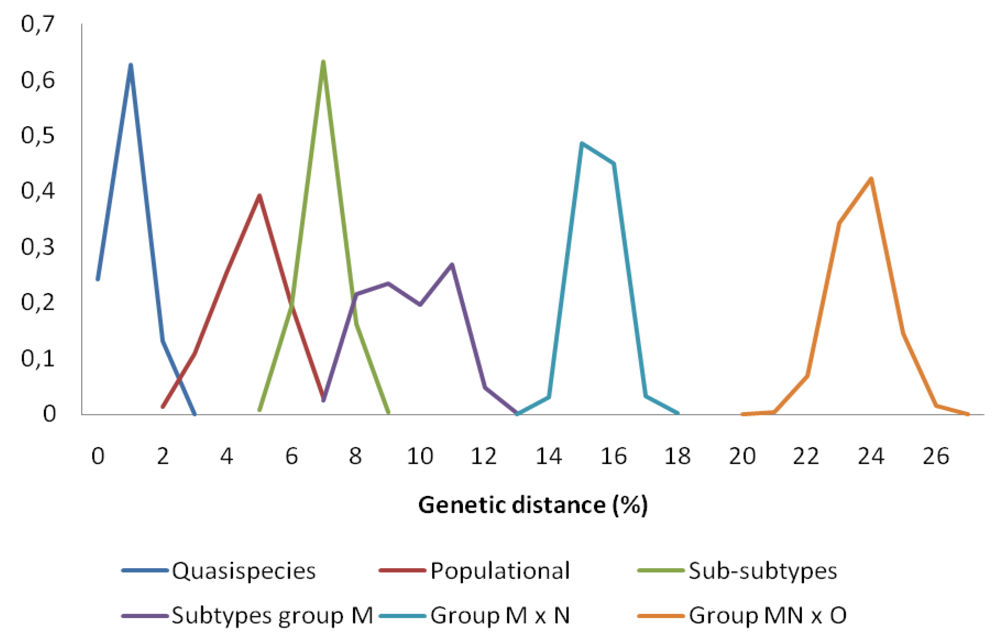
1.2. HIV-1 Group M Diversity
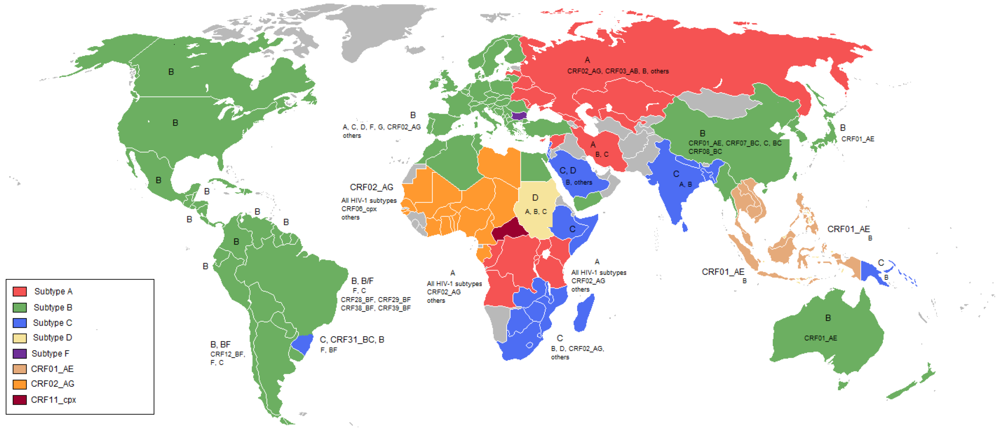
2. The challenge of HIV-1 non-B subtypes
| Drug-associated mutation | Drugs | % in Subtype B | Signatures | Polymorphisms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I13V | TPV | 13% | 90%–98% in subtypes A, G and CRF02 | 4%–78% in other subtypes non-B |
| K20I | ATV | 2% | 93%–98% in subtypes G and CRF02 | 1%–3.5% in subtypes A, F and CRF01 |
| M36I | ATV, IDV, NFV and TPV | 13% | 81%–99% in several non-B subtypes | — |
| H69K | TPV | 2% | 96%–97% in subtypes A, C and G, CRF01 and CRF02 | 2% in subtype F |
| V82I | ATV | 2% | 87% in subtype G | 1%–6% in several non-B subtypes |
| I93L | ATV | 33% | 94% in subtype C | 5%–40% in several non-B subtypes |
3. Drug Susceptibility in Treatment-Naive Patients Infected with HIV-1 non-B Subtypes
4. Selection of Major Drug Resistance Mutations in HIV-1 Non-B Subtypes
5. Drug Resistance Mutations and Fitness
6. Genetic Barriers in Different HIV-1 Subtypes
| Codon Position (pol genomic region) | Resistance mutation | Codon change | Genetic barrier in non-B subtypes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 82 (PR) | V82A V82T | GTC → GCC (1 ts); GTC → ACC (2 ts) | G: 14% GTC; Other subtypes: 87%–100% GTC |
| 82 (PR) | I82A I82T | ATC → GCC (2 ts); ATC → ACC (1 ts) | G: 84% ATC; Other subtypes: 0%–9% ATC |
| 118* (RT) | V118I | GTT / GTC / GTA → ATT / ATC / ATA (1 ts); GTG → ATA (2 ts) | G: 63% ATA; Other subtypes: 0%–6% ATA |
| 151 (RT) | Q151M | CAG → ATG (2 tv); CAA → ATG (1 ts, 2 tv) | D: 37% CAA; F: 83% CAA; Other subtypes: 2%–12% CAA |
| 210 (RT) | L210W | TTG → TGG (1 tv); TTA / CTG → TGG (1ts, 1 tv); CTA → TGG (2 ts, 1 tv) | C: 30% TTA / CTG; F: 50% TTA / CTG and 23% CTA; G: 82% TTA / CTG; CRF02_AG: 83% TTA / CTG; Other subtypes: 82%–87% TTG |
| 106 (RT) | V106M | GTG → ATG (1 ts); GTA → ATG (2 ts) | C: 83% GTG; Other subtypes: 0–7% GTG |
| 108* (RT) | V108I | GTA → ATA (1 ts); GTG → ATA (2 ts) | G: 62% GTG; Other subtypes: 88%–100% |
7. Kinetics of DRM Emergence
8. HIV Subtype-specific Mutations
10. Differential Resistance Conferred by the Same DRM
11. Impact of HIV-1 Subtype on Therapeutic and Clinical Response
12. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Gallo, R.C.; Sarin, P.S.; Gelmann, E.P.; Robert-Guroff, M.; Richardson, E.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Mann, D.; Sidhu, G.D.; Stahl, R.E.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Leibowitch, J.; Popovic, M. Isolation of human T-cell leukemia virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 1983, 220, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barré-Sinouss,. F.; Chermann, J.C.; Rey, F.; Nugeyre, M.T.; Chamaret, S.; Gruest, J.; Dauguet, C.; Axler-Blin, C.; Vézinet-Brun, F.; Rouzioux, C.; Rozenbaum, W.; Montagnier, L. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 1983, 220, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korber, B.; Muldoon, M.; Theiler, J.; Gao, F.; Gupta, R.; Lapedes, A.; Hahn, B.H.; Wolinsky, S.; Bhattacharya, T. Timing the ancestor of the HIV-1 pandemic strains. Science 2000, 288, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worobey, M.; Gemmel, M.; Teuwen, D.E.; Haselkorn, T.; Kunstman, K.; Bunce, M.; Muyembe, J.J.; Kabongo, J.M.; Kalengayi, R.M.; Van Marck, E.; Gilbert, M.T.; Wolinsky, S.M. Direct evidence of extensive diversity of HIV-1 in Kinshasa by 1960. Nature 2008, 455, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS. Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. Available online: http://www.unaids.org/en/KnowledgeCentre/HIVData/GlobalReport/2008/2008_Global_report.asp (accessed on 15 July 2009).
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Reid, A.H.; Janczewski, T.A.; Fanning, T.G. Integrating historical, clinical and molecular genetic data in order to explain the origin and virulence of the 1918 Spanish influenza virus. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liégeois, F.; Lafay, B.; Formenty, P.; Locatelli, S.; Courgnaud, V.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M. Full-length genome characterization of a novel simian immunodeficiency virus lineage (SIVolc) from olive Colobus (Procolobus verus) and new SIVwrcPbb strains from Western Red Colobus (Piliocolobus badius badius) from the Tai Forest in Ivory Coast. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, S.; Lafay, B.; Liegeois, F.; Ting, N.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M. Full molecular characterization of a simian immunodeficiency virus, SIVwrcpbt from Temminck's red colobus (Piliocolobus badius temminckii) from Abuko Nature Reserve, The Gambia. Virology 2008, 376, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalish, M.L.; Wolfe, N.D.; Ndongmo, C.B.; McNicholl, J.; Robbins, K.E.; Aidoo, M.; Fonjungo, P.N.; Alemnji, G.; Zeh, C.; Djoko, C.F.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; Burke, D.S.; Folks, T.M. Central African hunters exposed to simian immunodeficiency virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1928–1930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, N.D.; Switzer, W.M.; Carr, J.K.; Bhullar, V.B.; Shanmugam, V.; Tamoufe, U.; Prosser, A.T.; Torimiro, J.N.; Wright, A.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; McCutchan, F.E.; Birx, D.L.; Folks, T.M.; Burke, D.S.; Heneine, W. Naturally acquired simian retrovirus infections in central African hunters. Lancet 2004, 363, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Bailes, E.; Robertson, D.L.; Chen, Y.; Rodenburg, C.M.; Michael, S.F.; Cummins, L.B.; Arthur, L.O.; Peeters, M.; Shaw, G.M.; Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. Origin of HIV-1 in the chimpanzee Pan troglodytes troglodytes. Nature 1999, 397, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Yue, L.; White, A.T.; Pappas, P.G.; Barchue, J.; Hanson, A.P.; Greene, B.M.; Sharp, P.M.; Shaw, G.M.; Hahn, B.H. Human infection by genetically diverse SIVSM-related HIV-2 in west Africa. Nature 1992, 358, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heuverswyn, F.; Li, Y.; Neel, C.; Bailes, E.; Keele, B.F.; Liu, W.; Loul, S.; Butel, C.; Liegeois, F.; Bienvenue, Y.; Ngolle, E.M.; Sharp, P.M.; Shaw, G.M.; Delaporte, E.; Hahn, B.H.; Peeters, M. Human immunodeficiency viruses: SIV infection in wild gorillas. Nature 2006, 444, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takehisa, J.; Kraus, M.H.; Ayouba, A.; Bailes, E.; Van Heuverswyn, F.; Decker, J.M.; Li, Y.; Rudicell, R.S.; Learn, G.H.; Neel, C.; Ngole, E.M.; Shaw, G.M.; Peeters, M.; Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. Origin and biology of simian immunodeficiency virus in wild-living western gorillas. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayouba, A.; Mauclère, P.; Martin, P.M.; Cunin, P.; Mfoupouendoun, J.; Njinku, B.; Souquières, S.; Simon, F. HIV-1 group O infection in Cameroon, 1986 to 1998. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.A.; Bodelle, P.; Coffey, R.; Devare, S.G.; Golden, A.; Hackett Jr., J.; Harris, B.; Holzmayer, V.; Luk, K.C.; Schochetman, G.; Swanson, P.; Yamaguchi, J.; Vallari, A.; Ndembi, N.; Ngansop, C.; Makamche, F.; Mbanya, D.; Gürtler, L.G.; Zekeng, L.; Kaptué, L. The prevalence of diverse HIV-1 strains was stable in Cameroonian blood donors from 1996 to 2004. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2008, 49, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, F.; Mauclère, P.; Roques, P.; Loussert-Ajaka, I.; Müller-Trutwin, M.C.; Saragosti, S.; Georges-Courbot, M.C.; Barré-Sinoussi, F.; Brun-Vénizet, F. Identification of a new human immunodeficiency virus type 1 distinct from group M and group O. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, P.; Robertson, D.L.; Souquière, S.; Apetrei, C.; Nerrienet, E.; Barré-Sinoussi, F.; Müller-Trutwin, M.; Simon, F. Phylogenetic characteristics of three new HIV-1 N strains and implications for the origin of group N. AIDS 2004, 18, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayouba, A.; Souquières, S.; Njinku, B.; Martin, P.M.; Müller-Trutwin, M.C.; Roques, P.; Barré-Sinoussi, F.; Mauclère, P.; Simon, F.; Nerrienet, E. HIV-1 group N among HIV-1-seropositive individuals in Cameroon. AIDS 2000, 14, 2623–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodelle, P.; Vallari, A.; Coffey, R.; McArthur, C.P.; Beyeme, M.; Devare, S.G.; Schochetman, G.; Brennan, C.A. Identification and genomic sequence of an HIV type 1 group N isolate from Cameroon. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2004, 20, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plantier, J.C.; Leoz, M.; Dickerson, J.E.; De Oliveira, F.; Cordonnier, F.; Lemée, V.; Damond, F.; Robertson, D.L.; Simon, F. A new human immunodeficiency virus derived from gorillas. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HIV sequence database. The Human Retroviruses and AIDS 1994 Compendium, III23-III33. Available online: http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/sequence/HIV/COMPENDIUM/94compendium.html (accessed on 18 July 2009).
- Janssens, W.; Heyndrickx, L.; Fransen, K.; Motte, J.; Peeters, M.; Nkengasong, J.N.; Ndumbe, P.M.; Delaporte, E.; Perret, J.L.; Atender, C.; Piot, P.; van der Groen, G. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of env subtypes G and H in central Africa. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1994, 10, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kostrikis, L.G.; Bagdades, E.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dimitriou, D.; Ho, D.D. Genetic analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains from patients in Cyprus: identification of a new subtype designated subtype I. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6122–6130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laukkanen, T.; Albert, J.; Liitsola, K.; Green, S.D.; Carr, J.K.; Leitner, T.; McCutchan, F.E.; Salminen, M.O. Virtually full-length sequences of HIV type 1 subtype J reference strains. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1999, 15, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Triques, K.; Bourgeois, A.; Vidal, N.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; Mulanga-Kabeya, C.; Nzilambi, N.; Torimiro, N.; Saman, E.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M. Near-full-length genome sequencing of divergent African HIV type 1 subtype F viruses leads to the identification of a new HIV type 1 subtype designated K. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2000, 16, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Robertson, D.L.; Morrison, S.G.; Hui, H.; Craig, S.; Decker, J.; Fultz, P.N.; Girard, M.; Shaw, G.M.; Hahn, B.H.; Sharp, P.M. The heterosexual human immunodeficiency virus type 1 epidemic in Thailand is caused by an intersubtype (A/E) recombinant of African origin. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7013–7029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carr, J.K.; Salminen, M.O.; Albert, J.; Sanders-Buell, E.; Gotte, D.; Birx, D.L.; McCutchan, F.E. Full genome sequences of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes G and A/G intersubtype recombinants. Virology 1998, 247, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutchan, F.E.; Carr, J.K.; Bajani, M.; Sanders-Buell, E.; Harry, T.O.; Stoeckli, T.C.; Robbins, K.E.; Gashau, W.; Nasidi, A.; Janssens, W.; Kalish, M.L. Subtype G and multiple forms of A/G intersubtype recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in Nigeria. Virology 1999, 254, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Robertson, D.L.; Carruthers, C.D.; Li, Y.; Bailes, E.; Kostrikis, L.G.; Salminen, M.O.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Peeters, M.; Ho, D.D.; Shaw, G.M.; Sharp, P.M.; Hahn, B.H. An isolate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 originally classified as subtype I represents a complex mosaic comprising three different group M subtypes (A, G, and I). J. Virol. 1998, 72, 10234–10241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasioulas, G.; Paraskevis, D.; Magiorkinis, E.; Theodoridou, M.; Hatzakis, A. Molecular analysis of the full-length genome of HIV type 1 subtype I: evidence of A/G/I recombination. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1999, 15, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, D.L.; Anderson, J.P.; Bradac, J.A.; Carr, J.K.; Foley, B.; Funkhouser, R.K.; Gao, F.; Hahn, B.H.; Kalish, M.L.; Kuiken, C.; Learn, G.H.; Leitner, T.; McCutchan, F.; Osmanov, S.; Peeters, M.; Pieniazek, D.; Salminen, M.; Sharp, P.M.; Wolinsky, S.; Korber, B. HIV-1 nomenclature proposal. Science 2000, 288, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Vidal, N.; Li, Y.; Trask, S.A.; Chen, Y.; Kostrikis, L.G.; Ho, D.D.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.D.; Choe, K.; Salminen, M.; Robertson, D.L.; Shaw, G.M.; Hahn, B.H.; Peeters, M. Evidence of two distinct subsubtypes within the HIV-1 subtype A radiation. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2001, 17, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meloni, S.T.; Kim, B.; Sankalé, J.L.; Hamel, D.J.; Tovanabutra, S.; Mboup, S.; McCutchan, F.E.; Kanki, P.J. Distinct human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype A virus circulating in West Africa: sub-subtype A3. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12438–12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triques, K.; Bourgeois, A.; Saragosti, S.; Vidal, N.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; Nzilambi, N.; Apetrei, C.; Ekwalanga, M.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M. High diversity of HIV-1 subtype F strains in Central Africa. Virology 1999, 259, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemelaar, J.; Gouws, E.; Ghys, P.D.; Osmanov, S. Global and regional distribution of HIV-1 genetic subtypes and recombinants in 2004. AIDS 2006, 20, W13–W23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; Schrago, C.G.; Martinez, A.M.; Mendoza-Sassi, R.; Silveira, J.; Sousa, T.M.; Lengruber, R.B.; Soares, E.A.; Sprinz, E.; Soares, M.A. Epidemiologic and evolutionary trends of HIV-1 CRF31_BC-related strains in southern Brazil. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 45, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; de Oliveira, T.; Soares, M.A.; Pybus, O.; Dumans, A.T.; Vandamme, A.M.; Tanuri, A.; Cassol, S.; Fitch, W.M. Different epidemic potentials of the HIV-1B and C subtypes. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, G.; Passaes, C.P.; Guimarães, M.L.; Lorete, R.S.; Matos Almeida, S.E.; Medeiros, R.M.; Alencastro, P.R.; Morgado, M.G. Origin and evolutionary history of HIV-1 subtype C in Brazil. AIDS 2008, 22, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, E.A.; Martínez, A.M.; Souza, T.M.; Santos, A.F.; Da Hora, V.; Silveira, J.; Bastos, F.I.; Tanuri, A.; Soare,s M.A. HIV-1 subtype C dissemination in southern Brazil. AIDS 2005, 19, S81–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brígido, L.F.; Nunes, C.C.; Oliveira, C.M.; Knoll, R.K.; Ferreira, J.L.; Freitas, C.A.; Alves, M.A.; Dias, C.; Rodrigues, R.; Research Capacity Program. HIV type 1 subtype C and CB Pol recombinants prevail at the cities with the highest AIDS prevalence rate in Brazil. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2007, 23, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locateli, D.; Stoco, P.H.; de Queiroz, A.T.; Alcântara, L.C.; Ferreira, L.G.; Zanetti, C.R.; Rodrigues, R.; Grisard, E.C.; Pinto, A.R. Molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 in Santa Catarina State confirms increases of subtype C in Southern Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, E.A.; Santos, R.P.; Pellegrini, J.A.; Sprinz, E.; Tanuri, A.; Soares, M.A. Epidemiologic and molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in southern Brazil. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2003, 34, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, C.; Engelbrecht, S.; Lambrick, M.; van Rensburg, E.J.; Wood, R.; Bredell, W.; Williamson, A.L. HIV-1 subtypes in different risk groups in South Africa. Lancet 1995, 346, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Harmelen, J.; Wood, R.; Lambrick, M.; Rybicki, E.P.; Williamson, A.L.; Williamson, C. An association between HIV-1 subtypes and mode of transmission in Cape Town, South Africa. AIDS 1997, 11, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantz, R.J.; Horn, D.L. Twenty years of therapy for HIV-1 infection. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulick, R.M.; Meibohm, A.; Havlir, D.; Eron, J.J.; Mosley, A.; Chodakewitz, J.A.; Isaacs, R.; Gonzalez, C.; McMahon, D.; Richman, D.D.; Robertson, M.; Mellors, J.W. Six-year follow-up of HIV-1-infected adults in a clinical trial of antiretroviral therapy with indinavir, zidovudine, and lamivudine. AIDS 2003, 17, 2345–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussmann, H.; Wester, C.W.; Ndwapi, N.; Grundmann, N.; Gaolathe, T.; Puvimanasinghe, J.; Avalos, A.; Mine, M.; Seipone, K.; Essex, M.; Degruttola, V.; Marlink, R.G. Five-year outcomes of initial patients treated in Botswana's National Antiretroviral Treatment Program. AIDS 2008, 22, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larder, B.A.; Darby, G.; Richman, D.D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science 1989, 243, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volberding, P.A.; Lagakos, S.W.; Grimes, J.M.; Stein, D.S.; Rooney, J.; Meng, T.C.; Fischl, M.A.; Collier, A.C.; Phair, J.P.; Hirsch, M.S.; Hardy, W.D.; Balfour, H.H.; Reichman, R.C; For the AIDS Clinical Trials Group. A comparison of immediate with deferred zidovudine therapy for asymptomatic HIV-infected adults with CD4 cell counts of 500 or more per cubic millimeter. AIDS Clinical Trials Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, J.E.; Farnham, A.E.; Sperber, S.J.; Kim, H.; Dubin, D.T. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pol gene mutations in an AIDS patient treated with multiple antiretroviral drugs. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7271–7275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Preston, B.D.; Poiesz, B.J.; Loeb, L.A. Fidelity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science 1988, 242, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perelson, A.S.; Neumann, A.U.; Markowitz, M.; Leonard, J.M.; Ho, D.D. HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science 1996, 271, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A.; Holmes, E.C. The causes and consequences of HIV evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, V.A.; Brun-Vezinet, F.; Clotet, B.; Gunthard, H.F.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Pillay, D.; Schapiro, J.M.; Richman, D.D. Update of the Drug Resistance Mutations in HIV-1. Top. HIV Med. 2008, 16, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Picado, J.; Savara, A.V.; Shi, L.; Sutton, L.; D'Aquila, R.T. Fitness of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease inhibitor-selected single mutants. Virology 2000, 275, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Ussel, M.D.; Casado, C.; Yuste, E.; Olivares, I.; López-Galíndez, C. In vitro analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to nevirapine and fitness determination of resistant variants. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.D.; Lamy, P.D.; Fuller, M.D.; Mulato, A.S.; Margot, N.A.; Cihlar, T.; Cherrington, J.M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase expressing the K70E mutation exhibits a decrease in specific activity and processivity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, K.L.; Margot, N.A.; Wrin, T.; Petropoulos, C.J.; Miller, M.D.; Naeger, L.K. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with reverse transcriptase mutations K65R and K65R+M184V and their effects on enzyme function and viral replication capacity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3437–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Picado, J.; Savara, A.V.; Sutton, L.; D'Aquila, R.T. Replicative fitness of protease inhibitor-resistant mutants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3744–3752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nijhuis, M.; Schuurman, R.; de Jong, D.; Erickson, J.; Gustchina, E.; Albert, J.; Schipper, P.; Gulnik, S.; Boucher, C.A. Increased fitness of drug resistant HIV-1 protease as a result of acquisition of compensatory mutations during suboptimal therapy. AIDS 1999, 13, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammano, F.; Trouplin, V.; Zennou, V.; Clavel, F. Retracing the evolutionary pathways of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to protease inhibitors: virus fitness in the absence and in the presence of drug. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8524–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, K.; Wakasa-Morimoto, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Miki, S.; Noshi, T.; Seki, T.; Kanamori-Koyama, M.; Kawauchi, S.; Suyama, A.; Fujishita, T.; Yoshinaga, T.; Garvey, E.P.; Johns, B.A.; Foster, S.A.; Underwood, M.R.; Sato, A.; Fujiwara, T. Secondary mutations in viruses resistant to HIV-1 integrase inhibitors that restore viral infectivity and replication kinetics. Antiviral Res. 2009, 81, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, A.C.; Araújo, F.; Duque, V.; Borges, F.; Paixão, M.T.; Camacho, R.; Portuguese SPREAD Network. Molecular epidemiology and prevalence of drug resistance-associated mutations in newly diagnosed HIV-1 patients in Portugal. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2007, 7, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatt, I.D.; Barlow, K.L.; Clewley, J.P.; Gill, O.N.; Parry, J.V. Surveillance of HIV-1 subtypes among heterosexuals in England and Wales, 1997-2000. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2004, 36, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps, D.; Chaix, M.L.; André, P.; Brodard, V.; Cottalorda, J.; Deveau, C.; Harzic, M.; Ingrand, D.; Izopet, J.; Kohli, E.; Masquelier, B.; Mouajjah, S.; Palmer, P.; Pellegrin, I.; Plantier, J.C.; Poggi, C.; Rogez, S.; Ruffaut, A.; Schneider, V.; Signori-Schück, A.; Tamalet, C.; Wirden, M.; Rouzioux, C.; Brun-Venizet, F.; Meyer, L.; Costagliola, D. French national sentinel survey of antiretroviral drug resistance in patients with HIV-1 primary infection and in antiretroviral-naive chronically infected patients in 2001-2002. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2005, 38, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevis, D.; Magiorkinis, E.; Magiorkinis, G.; Sypsa, V.; Paparizos, V.; Lazanas, M.; Gargalianos, P.; Antoniadou, A.; Panos, G.; Chrysos, G.; et al. Multicentre Study on HIV Heterogeneity. Increasing prevalence of HIV-1 subtype A in Greece: estimating epidemic history and origin. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntemgwa, M.L.; Toni, T.D.; Brenner, B.G.; Camacho, R.J.; Wainberg, M.A. Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2 (HIV-2). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3611–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witvrouw, M.; Pannecouque, C.; Switzer, W.M.; Folks, T.M.; De Clercq, E.; Heneine, W. Susceptibility of HIV-2, SIV and SHIV to various anti-HIV-1 compounds: implications for treatment and postexposure prophylaxis. Antivir. Ther. 2004, 9, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reid, P.; MacInnes, H.; Cong, M.E.; Heneine, W.; García-Lerma, J.G. Natural resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 to zidovudine. Virology 2005, 336, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hizi, A.; Tal, R.; Shaharabany, M.; Currens, M.J.; Boyd, M.R.; Hughes, S.H.; McMahon, J.B. Specific inhibition of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and the chimeric enzymes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and type 2 by nonnucleoside inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Descamps, D.; Collin, G.; Letourneur, F.; Apetrei, C.; Damond, F.; Loussert-Ajaka, I.; Simon, F.; Saragosti, S.; Brun-Vézinet, F. Susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group O isolates to antiretroviral agents: in vitro phenotypic and genotypic analyses. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8893–8898. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieniazek, D.; Rayfield, M.; Hu, D.J.; Nkengasong, J.; Wiktor, S.Z.; Downing, R.; Biryahwaho, B.; Mastro, T.; Tanuri, A.; Soriano, V.; Lal, R.; Dondero, T. Protease sequences from HIV-1 group M subtypes A-H reveal distinct amino acid mutation patterns associated with protease resistance in protease inhibitor-naive individuals worldwide. HIV Variant Working Group. AIDS 2000, 14, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergne, L.; Peeters, M.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; Bourgeois, A.; Liegeois, F.; Toure-Kane, C.; Mboup, S.; Mulanga-Kabeya, C.; Saman, E.; Jourdan, J.; Reynes, J.; Delaporte, E. Genetic diversity of protease and reverse transcriptase sequences in non-subtype-B human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains: evidence of many minor drug resistance mutations in treatment-naive patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fonjungo, P.N.; Mpoudi, E.N.; Torimiro, J.N.; Alemnji, G.A.; Eno, L.T.; Lyonga, E.J.; Nkengasong, J.N.; Lal, R.B.; Rayfield, M.; Kalish, Folks; Pieniazek, D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group m protease in cameroon: genetic diversity and protease inhibitor mutational features. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holguín, A.; Alvarez, A.; Soriano, V. High prevalence of HIV-1 subtype G and natural polymorphisms at the protease gene among HIV-infected immigrants in Madrid. AIDS 2002, 16, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantor, R.; Katzenstein, D. Polymorphism in HIV-1 non-subtype B protease and reverse transcriptase and its potential impact on drug susceptibility and drug resistance evolution. AIDS Rev. 2003, 5, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.; Margot, N.; Gilbert, H.; Shaw, N.; Buckheit Jr., R.; Miller, M. Tenofovir, adefovir, and zidovudine susceptibilities of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates with non-B subtypes or nucleoside resistance. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2001, 17, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vergne, L.; Stuyver, L.; Van Houtte, M.; Butel, C.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M. Natural polymorphism in protease and reverse transcriptase genes and in vitro antiretroviral drug susceptibilities of non-B HIV-1 strains from treatment-naive patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2006, 36, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holguín, A.; Paxinos, E.; Hertogs, K.; Womac, C.; Soriano, V. Impact of frequent natural polymorphisms at the protease gene on the in vitro susceptibility to protease inhibitors in HIV-1 non-B subtypes. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 31, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, Z.; Paxinos, E.E.; Averbuch, D.; Maayan, S.; Parkin, N.T.; Engelhard, D.; Lorber, M.; Istomin, V.; Shaked, Y.; Mendelson, E.; Ram, D.; Petropoulos, C.J.; Schapiro, J.M. Mutation D30N is not preferentially selected by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C in the development of resistance to nelfinavir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda, E.; de Mendoza, C.; Parkin, N.; Choe, S.; García-Gasco, P.; Corral, A.; Soriano, V. Evidence for different susceptibility to tipranavir and darunavir in patients infected with distinct HIV-1 subtypes. AIDS 2008, 22, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abecasis, A.B.; Deforche, K.; Bacheler, L.T.; McKenna, P.; Carvalho, A.P.; Gomes, P.; Vandamme, A.M.; Camacho, R.J. Investigation of baseline susceptibility to protease inhibitors in HIV-1 subtypes C, F, G and CRF02_AG. Antivir. Ther. 2006, 11, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agwale, S.M.; Zeh, C.; Paxinos, E.; Odama, L.; Pienazek, D.; Wambebe, C.; Kalish, M.L.; Ziermann, R. Genotypic and phenotypic analyses of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in antiretroviral drug-naive Nigerian patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2006, 22, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cane, P.A.; de Ruiter, A.; Rice, P.; Wiselka, M.; Fox, R.; Pillay, D. Resistance-associated mutations in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype c protease gene from treated and untreated patients in the United Kingdom. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2652–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirivichayakul, S.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Ungsedhapand, C.; Techasathit, W.; Ubolyam, S.; Chuenyam, T.; Emery, S.; Cooper, D.; Lange, J.; Phanuphak, P. Nucleoside analogue mutations and Q151M in HIV-1 subtype A/E infection treated with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. AIDS 2003, 17, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, C.; Descamps, D.; Collin, G.; Robertson, D.L.; Pandrea, I.; Groza, P.; Prisecariu, L.; Teodorescu, I.; Luca, V.; Brun-Vézinet, F. HIV type 1 diversity in northeastern Romania in 200-2001 based on phylogenic analysis of pol sequences from patient failing antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2003, 19, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.Y.; Subramaniam, R.; Bacheler, L.; Paton, N.I. Characterization of mutations in CRF01_AE virus isolates from antiretroviral treatment-naive and -experienced patients in Singapore. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2005, 38, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantor, R.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Efron, B.; Carvalho, A.P.; Wynhoven, B.; Cane, P.; Clarke, J.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Soares, M.A.; Snoeck, J.; Pillay, C.; Rudich, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Holguin, A.; Ariyoshi, K.; Bouzas, M.B.; Cahn, P.; Sugiura, W.; Soriano, V.; Brigido, L.F.; Grossman, Z.; Morris, L.; Vandamme, A.M.; Tanuri, A.; Phanuphak, P.; Weber, J.N.; Pillay, D.; Harrigan, P.R.; Camacho, R.; Schapiro, J.M.; Shafer, R.W. Impact of HIV-1 subtype and antiretroviral therapy on protease and reverse transcriptase genotype: results of a global collaboration. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doualla-Bell, F.; Avalos, A.; Gaolathe, T.; Mine, M.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Ndwapi, N.; Novitsky, V.A.; Brenner, B.; Oliveira, M.; Moisi, D.; Moffat, H.; Thior, I.; Essex, M.; Wainberg, M.A. Impact of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C on drug resistance mutations in patients from Botswana failing a nelfinavir-containing regimen. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2210–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyoshi, K.; Matsuda, M.; Miura, H.; Tateishi, S.; Yamada, K.; Sugiura, W. Patterns of point mutations associated with antiretroviral drug treatment failure in CRF01_AE (subtype E) infection differ from subtype B infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2003, 33, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dumans, A.T.; Barreto, C.C.; Santos, A.F.; Arruda, M.; Sousa, T.M.; Machado, E.S.; Sabino, E.C.; Brindeiro, R.M.; Tanuri, A.; Duarte, A.J.; Soares, M.A. Distinct resistance mutation and polymorphism acquisition in HIV-1 protease of subtypes B and F1 from children and adult patients under virological failure. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novitsky, V.; Wester, C.W.; DeGruttola, V.; Bussmann, H.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Thomas, A.; Moyo, S.; Musonda, R.; Van Widenfelt, E.; Marlink, R.G.; Essex, M. The reverse transcriptase 67N 70R 215Y genotype is the predominant TAM pathway associated with virologic failure among HIV type 1C-infected adults treated with ZDV/ddI-containing HAART in southern Africa. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2007, 23, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebit, D.M.; Sangaré, L.; Makamtse, A.; Yameogo, S.; Somlare, H.; Bado, G.; Kouldiaty, B.G.; Sathiandee, K.; Tiba, F.; Sanou, I.; Ouédraogo-Traoré, R.; Zoungrana, L.; Diallo, I.; Drabo, J.Y.; Kraüsslich, H.G. HIV drug resistance pattern among HAART-exposed patients with suboptimal virological response in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2008, 49, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Chrystie, I.L.; O'Shea, S.; Mullen, J.E.; Kulasegaram, R.; Tong, C.Y. K65R and Y181C are less prevalent in HAART-experienced HIV-1 subtype A patients. AIDS 2005, 19, 1916–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Shahar, E.; Katchman, E.; Kedem, E.; Matus, N.; Katzir, M.; Hassoun, G.; Pollack, S.; Kessner, R.; Wainberg, M.A.; Avidor, B. Prevalence of the K65R resistance reverse transcriptase mutation in different HIV-1 subtypes in Israel. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshleman, S.H.; Hoover, D.R.; Chen, S.; Hudelson, S.E.; Guay, L.A.; Mwatha, A.; Fiscus, S.A.; Mmiro, F.; Musoke, P.; Jackson, J.B.; Kumwenda, N.; Taha, T. Nevirapine (NVP) resistance in women with HIV-1 subtype C, compared with subtypes A and D, after the administration of single-dose NVP. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshleman, S.H.; Hoover, D.R.; Chen, S.; Hudelson, S.E.; Guay, L.A.; Mwatha, A. Resistance after single-dose nevirapine prophylaxis emerges in a high proportion of Malawian newborns. AIDS 2005, 19, 2167–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flys, T.S.; Chen, S.; Jones, D.C.; Hoover, D.R.; Church, J.D.; Fiscus, S.A.; Mwatha, A.; Guay, L.A.; Mmiro, F.; Musoke, P.; et al. Quantitative analysis of HIV-1 variants with the K103N resistance mutation after single-dose nevirapine in women with HIV-1 subtypes A, C, and D. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 42, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conway, B.; Wainberg, M.A.; Hall, D.; Harris, M.; Reiss, P.; Cooper, D.; Vella, S.; Curry, R.; Robinson, P.; Lange, J.M.; Montaner, J.S. Development of drug resistance in patients receiving combinations of zidovudine, didanosine and nevirapine. AIDS 2001, 15, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.A.; Thompson, M.G.; Paintsil, E.; Ricketts, M.; Gedzior, J.; Alexander, L. Competitive fitness of nevirapine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantor, R.; Fessel, W.J.; Zolopa, A.R.; Israelski, D.; Shulman, N.; Montoya, J.G.; Harbour, M.; Schapiro, J.M.; Shafer, R.W. Evolution of primary protease inhibitor resistance mutations during protease inhibitor salvage therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammano, F.; Trouplin, V.; Zennou, V.; Clavel, F. Retracing the evolutionary pathways of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to protease inhibitors: virus fitness in the absence and in the presence of drug. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8524–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Picado, J.; Savara, A.V.; Sutton, L.; D'Aquila, R.T. Replicative fitness of protease inhibitor-resistant mutants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3744–3752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.M.; Brindeiro, R.M.; Aguiar, R.S.; Pereira, H.S.; Abreu, C.M.; Soares, M.A.; Tanuri, A. Impact of nelfinavir resistance mutations on in vitro phenotype, fitness, and replication capacity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with subtype B and C proteases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3552–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, K.L. Replicative capacity differences of thymidine analog resistance mutations in subtype B and C human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Vijver, D.A.; Wensing, A.M.; Angarano, G.; Asjö, B.; Balotta, C.; Boeri, E.; Camacho, R.; Chaix, M.L.; Costagliola, D.; De Luca, A. The calculated genetic barrier for antiretroviral drug resistance substitutions is largely similar for different HIV-1 subtypes. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 41, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waléria-Aleixo, A.; Martins, A.N.; Arruda, M.B.; Brindeiro, R.M.; Da-Silva, R.M.; Nobre, F.F.; Greco, D.B.; Tanuri, A. Drug resistance mutation profile and accumulation kinetics in human immunodeficiency virus-positive individuals infected with subtypes B and F failing highly active antiretroviral therapy are influenced by different viral codon usage patterns. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumans, A.T.; Soares, M.A.; Machado, E.S.; Hué, S.; Brindeiro, R.M.; Pillay, D.; Tanuri, A. Synonymous genetic polymorphisms within Brazilian human immunodeficiency virus Type 1 subtypes may influence mutational routes to drug resistance. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, B.; Turner, D.; Oliveira, M.; Moisi, D.; Detorio, M.; Carobene, M.; Marlink, R.G,.; Schapiro, J.; Roger, M.; Wainberg, M.A. A V106M mutation in HIV-1 clade C viruses exposed to efavirenz confers cross-resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. AIDS 2003, 17, F1–F5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, Z.; Istomin, V.; Averbuch, D.; Lorber, M.; Risenberg, K.; Levi, I.; Chowers, M.; Burke, M.; Bar Yaacov, N.; Schapiro, J.M.; Israel AIDS Multi-Center Study Group. Genetic variation at NNRTI resistance-associated positions in patients infected with HIV-1 subtype C. AIDS 2004, 18, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrell, C.; Walensky, R.P.; Losina, E.; Pitt, J.; Freedberg, K.A.; Wood, R. HIV type-1 clade C resistance genotypes in treatment-naive patients and after first virological failure in a large community antiretroviral therapy programme. Antivir. Ther. 2009, 14, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallis, C.; Sanne, I.; Venter, F.; Mellors, J.; Stevens, W. Varied Patterns of HIV-1 Drug Resistance on Failing First-Line Antiretroviral Therapy in South Africa. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2009, (1 October 2009 Epub ahead of print). [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, B.G.; Oliveira, M.; Doualla-Bell, F.; Moisi, D.D.; Ntemgwa, M.; Frankel, F.; Essex, M.; Wainberg, M.A. HIV-1 subtype C viruses rapidly develop K65R resistance to tenofovir in cell culture . AIDS 2006, 20, F9–F13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntemgwa, M.L.; Toni, T.; Brenner, B.G.; Oliveira, M.; Asahchop, E.L.; Moisi, D.; Wainberg, M.A. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs select in culture for different patterns of drug resistance in human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutsinos, D.; Invernizzi, C.F.; Xu, H.; Moisi, D.; Oliveira, M.; Brenner, B.G.; Wainberg, M.A. Template usage is responsible for the preferential acquisition of the K65R reverse transcriptase mutation in subtype C variants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Shahar, E.; Katchman, E.; Kedem, E.; Matus, N.; Katzir, M.; Hassoun, G.; Pollack, S.; Kessner, R.; Wainberg, M.A.; Avidor, B. Prevalence of the K65R resistance reverse transcriptase mutation in different HIV-1 subtypes in Israel. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, V.; Pillay, C.; Kantor, R.; Venter, F.; Levin, L.; Morris, L. HIV type 1 subtype C drug resistance among pediatric and adult South African patients failing antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2008, 24, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doualla-Bell, F.; Avalos, A.; Brenner, B.; Gaolathe, T.; Mine, M.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Oliveira, M.; Moisi, D.; Ndwapi, N.; Moffat, H. High prevalence of the K65R mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C isolates from infected patients in Botswana treated with didanosine-based regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 4182–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, E.A.; Santos, A.F.; Sousa, T.M.; Sprinz, E.; Martinez, A.M.; Silveira, J.; Tanuri, A.; Soares, M.A. Differential drug resistance acquisition in HIV-1 of subtypes B and C . PLoS One 2007, 2, e730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.F.; Abecasis, A.B.; Vandamme, A.M.; Camacho, R.J.; Soares, M.A. Discordant genotypic interpretation and phenotypic role of protease mutations in HIV-1 subtypes B and G. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abecasis, A.B.; Deforche, K.; Snoeck, J.; Bacheler, L.T.; McKenna, P.; Carvalho, A.P.; Gomes, P.; Camacho, R.J.; Vandamme, A.M. Protease mutation M89I/V is linked to therapy failure in patients infected with the HIV-1 non-B subtypes C, F or G. AIDS 2005, 19, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.M.; Santos, A.F.; Abecasis, A.B.; Van Laethem, K.; Soares, E.A.; Deforche, K.; Tanuri, A.; Camacho, R.; Vandamme, A.M.; Soares, M.A. Impact of HIV-1 protease mutations A71V/T and T74S on M89I/V-mediated protease inhibitor resistance in subtype G isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, A.C.; Abecasis, A.B.; Vercauteren, J.; Carvalho, A.P.; Cabanas, J.; Vandamme, A.M.; Camacho, R.J. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease inhibitor therapy and subtype on development of resistance in subtypes B and G . Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, (2 July 2009, Epub ahead of print). [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya, Y.; Winters, M.A.; Fessel, W.J.; Rhee, S.Y.; Hurley, L.; Horberg, M.; Schiffer, C.A.; Zolopa, A.R.; Shafer, R.W. N88D facilitates the co-occurrence of D30N and L90M and the development of multidrug resistance in HIV type 1 protease following nelfinavir treatment failure. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2006, 22, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziermann, R.; Limoli, K.; Das, K.; Arnold, E.; Petropoulos, C.J.; Parkin, N.T. A mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease, N88S, that causes in vitro hypersensitivity to amprenavir. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4414–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ode, H.; Matsuyama, S.; Hata, M.; Hoshino, T.; Kakizawa, J.; Sugiura, W. Mechanism of drug resistance due to N88S in CRF01_AE HIV-1 protease, analyzed by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ode, H.; Matsuyama, S.; Hata, M.; Neya, S.; Kakizawa, J.; Sugiura, W.; Hoshino, T. Computational characterization of structural role of the non-active site mutation M36I of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, E.A.; Santos, A.F.; Gonzalez, L.M.; Lalonde, M.S.; Tebit, D.M.; Tanuri, A.; Arts, E.J.; Soares, M.A. Mutation T74S in HIV-1 subtype B and C proteases resensitizes them to ritonavir and indinavir and confers fitness advantage. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delviks-Frankenberry, K.A.; Nikolenko, G.N.; Maldarelli, F.; Hase, S.; Takebe, Y.; Pathak, V.K. Subtype-specific differences in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase connection subdomain of CRF01_AE are associated with higher levels of resistance to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8502–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frater, A.J.; Dunn, D.T.; Beardall, A.J.; Ariyoshi, K.; Clarke, J.R.; McClure, M.O.; Weber, J.N. Comparative response of African HIV-1-infected individuals to highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2002, 16, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocket, L.; Cheret, A.; Deuffic-Burban, S.; Choisy, P.; Gerard, Y.; de la Tribonnière, X.; Viget, N.; Ajana, F.; Goffard, A.; Barin, F.; Mouton, Y.; Yazdanpanah, Y. Impact of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype on first-line antiretroviral therapy effectiveness. Antivir. Ther. 2005, 10, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.S.; Montessori, V.; Wynhoven, B.; Dong, W.; Chan, K.; O'Shaughnessy, M.V.; Mo, T.; Piaseczny, M.; Montaner, J.S.; Harrigan, P.R. Prevalence and response to antiretroviral therapy of non-B subtypes of HIV in antiretroviral-naive individuals in British Columbia. Antivir. Ther. 2002, 7, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Wit, S.; Boulmé, R.; Poll, B.; Schmit, J.C.; Clumeck, N. Viral load and CD4 cell response to protease inhibitor-containing regimens in subtype B vs. non-B treatment-naive HIV-1 patients. AIDS 2004, 18, 2330–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, W.P.; Ruiz, L.; Loveday, C.; Vella, S.; Zilmer, K.; Kjaer, J.; Knysz, B.; Phillips, A.N.; Mocroft, A.; EuroSIDA Study Group. HIV-1 subtypes and response to combination antiretroviral therapy in Europe . Antivir. Ther. 2006, 11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garrido, C.; Zahonero, N.; Fernándes, D.; Serrano, D.; Silva, A.R.; Ferraria, N.; Antúnes, F.; González-Lahoz, J.; Soriano, V.; de Mendoza, C. Subtype variability, virological response and drug resistance assessed on dried blood spots collected from HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy in Angola. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geretti, A.M.; Harrison, L.; Green, H.; Sabin, C.; Hill, T.; Fearnhill, E.; Pillay, D.; Dunn, D.; UK Collaborative Group on HIV Drug Resistance. Effect of HIV-1 subtype on virologic and immunologic response to starting highly active antiretroviral therapy . Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, A.; Granath, F.; Lindstrom, A.; Lidman, K.; Lindbacl, S.; Alaeus, A. Impact of HIV type 1 genetic subtype on the outcome of antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2005, 21, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruelle, J; Roman, F.; Vandenbroucke, A.T.; Lambert. C.; Fransen, K.; Echahidi, F.; Piérard, D.; Verhofstede, C.; Van Laethem, K.; Delforge, M.L.; Vaira, D.; Schmit, J.C.; Goubau, P. Transmitted drug resistance, selection of resistance mutations and moderate antiretroviral efficacy in HIV-2: analysis of the HIV-2 Belgium and Luxembourg database . BMC Infec. Dis. 2008, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
Santos, A.F.; Soares, M.A. HIV Genetic Diversity and Drug Resistance. Viruses 2010, 2, 503-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020503
Santos AF, Soares MA. HIV Genetic Diversity and Drug Resistance. Viruses. 2010; 2(2):503-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020503
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, André F., and Marcelo A. Soares. 2010. "HIV Genetic Diversity and Drug Resistance" Viruses 2, no. 2: 503-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020503
APA StyleSantos, A. F., & Soares, M. A. (2010). HIV Genetic Diversity and Drug Resistance. Viruses, 2(2), 503-531. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020503




