Lentiviral Vectors and Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Gene therapy of CF lung disease
| Vector | Packaging Capacity | Integration | Persistence of Expression | Pro-inflammatory/ Immunogenicity | Biosafety and efficiency studies on animal models | Efficacy studies on animal models (with CFTR transgene) | Clinical Trials for CF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenovirus | 8 kb | No | No | High | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Adeno-associated virus | 5 kb | Both episomal and integrated gene expression | Yes | Low | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lentivirus | 8 kb | Yes | Yes | Low | Yes | Yes | No |
5. Gene tranfer to the airway epithelium mediated by LV vectors
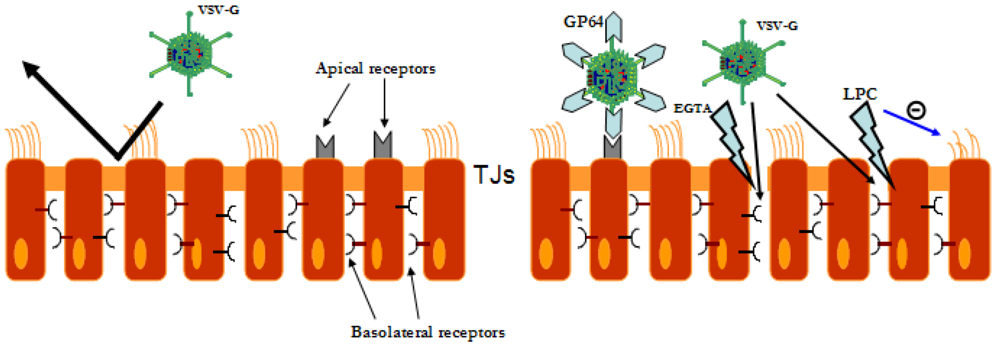
6. Safety of LV vectors in the lung
7. LV-mediated gene transfer into fetal airway epithelium
8. Conclusions and perspectives
Acknowledgments
References
- Farrell, P.M.; Rosenstein, B.J.; White, T.B.; Accurso, F.J.; Castellani, C.; Cutting, G.R.; Durie, P.R.; Legrys, V.A.; Massie, J.; Parad, R.B.; Rock, M.J.; Campbell, P.W. Guidelines for diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in newborns through older adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus report. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riordan, J.R.; Rommens, J.M.; Kerem, B.; Alon, N.; Rozmahel, R.; Grzelczak, Z.; Zielenski, J.; Lok, S.; Plavsic, N.; Chou, J.L.; Drumm, M.L.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Collins, F.S.; Tsui, L.-C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA (Erratum, Science 1989, 1245, 1437 ). Science 1989, 245, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kerem, B.; Rommens, J.M.; Buchanan, J.A.; Markiewicz, D.; Cox, T.K.; Chakravarti, A.; Buchwald, M.; Tsui, L.C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science 1989, 245, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drumm, M.L.; Pope, H.A.; Cliff, W.H.; Rommens, J.M.; Marvin, S.A.; Tsui, L.-C.; Collins, F.S.; Frizzel, R.A.; Wilson, J.M. Correction of the cystic fibrosis defect in vitro by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Cell 1990, 62, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, C.E.; Li, C.; Kartner, N.; Bridges, R.D.; Jensen, T.J.; Ramjeesingh, M.; Riordan, J.R. Purification and functional reconstitution of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Cell 1992, 68, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmiel, J.F.; Berger, M.; Konstan, M.W. The role of inflammation in the pathophysiology of CF lung disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 23, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, F.; Doring, G. Cystic fibrosis. The Lancet 2003, 361, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, R.C. New concepts of the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, S.M.; Miller, S.; Sorscher, E.J. Cystic Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, H.; Grubb, B.R.; Tarran, R.; Randell, S.H.; Gatzy, J.T.; Davis, C.W.; Boucher, R.C. Evidence for periciliary liquid layer depletion, not abnormal ion composition, in the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis airway disease. Cell 1998, 95, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, M.; Hipper, A.; Greger, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Wild type but not deltaF508 CFTR inhibits Na+ conductance when coexpressed in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1996, 381, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, M.; Grubb, B.R.; Harkema, J.R.; O'Neal, W.K.; Boucher, R.C. Increased airway epithelial Na+ absorption produces cystic fibrosis-like lung disease in mice. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.; Olsen, J.; Sarkadi, B.; Moore, K.; Swanstrom, R.; Boucher, R. Efficiency of gene transfer for restoration of normal airway epithelial function in cystic fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 1992, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorin, J.R.; Farley, R.; Webb, S.; Smith, S.N.; Farini, E.; Delaney, S.J.; Wainwright, B.J.; Alton, E.W.; Porteous, D.J. A demonstration using mouse models that successful gene therapy for cystic fibrosis requires only partial gene correction. Gene Ther. 1996, 3, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farmen, S.L.; Karp, P.H.; Ng, P.; Palmer, D.J.; Koehler, D.R.; Hu, J.; Beaudet, A.L.; Zabner, J.; Welsh, M.J. Gene transfer of CFTR to airway epithelia: low levels of expression are sufficient to correct Cl- transport and overexpression can generate basolateral CFTR. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L1123–L1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.G.; Boyles, S.E.; Wilson, J.; Boucher, R.C. Normalization of raised sodium absorption and raised calcium-mediated chloride secretion by adenovirus-mediated expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in primary human cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 95, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Wilson, J.M. Gene therapy in a xenograft model of cystic fibrosis lung corrects chloride transport more effectively than the sodium defect. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flotte, T.R.; Laube, B.L. Gene therapy in cystic fibrosis. Chest 2001, 120, 124S–131S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driskell, R.A.; Engelhardt, J.F. Current status of gene therapy for inherited lung diseases. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 585–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.W.; Matthews, D.A.; Blair, G.E. Novel molecular approaches to cystic fibrosis gene therapy. Biochem. J. 2005, 387, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flotte, T.R. Adeno-associated virus-based gene therapy for inherited disorders. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flotte, T.R.; Ng, P.; Dylla, D.E.; McCray Jr., P.B.; Wang, G.; Kolls, J.K.; Hu, J. Viral vector-mediated and cell-based therapies for treatment of cystic fibrosis. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copreni, E.; Penzo, M.; Carrabino, S.; Conese, M. Lentiviral-mediated gene transfer to the respiratory epithelium: a promising approach to gene therapy of Cystic Fibrosis. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, S67–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaiss, A.K.; Son, S.; Chang, L.J. RNA 3' readthrough of oncoretrovirus and lentivirus: implications for vector safety and efficacy. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 7209–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldini, L.; Blomer, U.; Gage, F.H.; Trono, D.; Verma, I.M. Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11382–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldini, L.; Blomer, U.; Gallay, P.; Ory, D.; Mulligan, R.; Gage, F.H.; Verma, I.M.; Trono, D. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science 1996, 272, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delenda, C. Lentiviral vectors: optimization of packaging, transduction and gene expression. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, S125–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follenzi, A.; Ailles, L.E.; Bakovic, S.; Geuna, M.; Naldini, L. Gene transfer by lentiviral vectors is limited by nuclear translocation and rescued by HIV-1 pol sequences. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zennou, V.; Petit, C.; Guetard, D.; Nerhbass, U.; Montagnier, L.; Charneau, P. HIV-1 genome nuclear import is mediated by a central DNA flap. Cell 2000, 101, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zufferey, R.; Donello, J.E.; Trono, D.; Hope, T.J. Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element enhances expression of transgenes delivered by retroviral vectors. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zufferey, R.; Dull, T.; Mandel, R.J.; Bukovsky, A.; Quiroz, D.; Naldini, L.; Trono, D. Self-inactivating lentivirus vector for safe and efficient in vivo gene delivery. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9873–9880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conese, M.; Castellani, S.; Palmieri, L.; Copreni, E. Lentivirus expression vectors. Research Signpost Transworld Research Network, 2007; pp. 81–122. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, B.L.; Humeau, L.M.; Boyer, J.; MacGregor, R.R.; Rebello, T.; Lu, X.; Binder, G.K.; Slepushkin, V.; Lemiale, F.; Mascola, J.R.; Bushman, F.D.; Dropulic, B.; June, C.H. Gene transfer in humans using a conditionally replicating lentiviral vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17372–17377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenbach, U.; Ferrari, S.; Geddes, D.M.; Alton, E.W. Gene therapy progress and prospects: cystic fibrosis. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conese, M.; Copreni, E.; Piro, D.; Rejman, J. Gene and Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. Adv. Gene Mol. Cell Ther. 2007, 1, 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, S.; Griesenbach, U.; Geddes, D.M.; Alton, E. Immunological hurdles to lung gene therapy. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.; Yue, Y.; Yan, Z.; McCray, P.B.; Engelhardt, J.F. Polarity influences the efficiency of recombinant adenoassociate virus infection in differentiated airway epithelia. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 2761–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Davidson, B.L.; Melchert, P.; Sleupushkin, V.A.; van Hes, H.H.G.; Bodner, M.; Jolly, D.J.; McCray Jr, P.B. Influence of cell polarity on retrovirus-mediated gene transfer to differentiated human airway epithelia. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9818–9826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walters, R.W.; Grunst, T.; Bergelson, J.M.; Finberg, R.W.; Welsh, M.J.; Zabner, J. Basolateral localization of fiber receptor limits adenovirus infection from the apical surface of airway epithelia. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10219–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragonzi, A.; Worlitzsch, D.; Pier, G.B.; Timpert, P.; Ulrich, M.; Hentzer, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Givskov, M.; Conese, M.; Doring, G. Nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa expresses alginate in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis and in a mouse model. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heeckeren, A.; Ferkol, T.; Tosi, M. Effects of bronchopulmonary inflammation induced by pseudomonas aeruginosa on adenovirus-mediated gene transfer to airway epithelial cells in mice. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tosi, M.F.; van Heeckeren, A.; Ferkol, T.W.; Askew, D.; Harding, C.V.; Kaplan, J.M. Effect of Pseudomonas-induced chronic lung inflammation on specific cytotoxic T-cell responses to adenoviral vectors in mice. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejman, J.; De Fino, I.; Paroni, M.; Bragonzi, A.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.; Conese, M. The impact of chronic pulmonary infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa on transfection mediated by viral and non-viral vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, M.J.; Lee, P.S.; Yang, J.S.; Wilson, J.M. Lentiviral vectors for Gene Therapy of cystic fibrosis. Hum. Gene Ther. 1997, 8, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillon, N.; Avril-Delplanque, A.; Coraux, C.; Delenda, C.; Peault, B.; Danos, O.; Puchelle, E. Regeneration of a well-differentiated human airway surface epithelium by spheroid and lentivirus vector-transduced airway cells. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, F.Y.; Kobinger, G.P.; Weiner, D.J.; Radu, A.; Wilson, J.M.; Crombleholme, T.M. Human fetal trachea-scid mouse xenografts: Efficacy of vesicular stomatitis virus-G pseudotyped lentiviral-mediated gene transfer. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003, 38, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Slepushkin, V.; Zabner, J.; Keshavjee, S.; Johnston, J.C.; Sauter, S.L.; Jolly, D.J.; Dubensky Jr, T.W.; Davidson, B.L.; McCray Jr., P.B. Feline immunodeficiency virus vectors persistently transduce nondividing airway epithelia and correct the cystic fibrosis defect. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 104, R55–R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.G.; Olsen, J.C.; Naldini, L.; Boucher, R. Pseudotyped human lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer to airway epithelia in vivo. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberis, M.; Anson, D.S.; Fuller, M.; Parsons, D.W. Recovery of airway cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function in mice with cystic fibrosis after single-dose lentivirus-mediated gene transfer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rejman, J.; Di Gioia, S.; Bragonzi, A.; Conese, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection destroys the barrier function of lung epithelium and enhances polyplex-mediated transfection. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007, 18, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copreni, E.; Castellani, S.; Palmieri, L.; Penzo, M.; Conese, M. Involvement of glycosaminoglycans in vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer into airway epithelial cells. J. Gene Med. 2008, 10, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, K.L.; Dunning, K.R.; Parsons, D.W.; Anson, D.S. Gene delivery to airway epithelial cells in vivo: a direct comparison of apical and basolateral transduction strategies using pseudotyped lentivirus vectors. J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, A.G.; Kremer, K.L.; Koldej, R.; Miller, D.S.; Anson, D.S.; Parsons, D.W. Single-dose lentiviral gene transfer for lifetime airway gene expression. J. Gene Med. 2009, 11, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borthwick, D.W.; Shahbazian, M.; Krantz, Q.T.; Dorin, J.R.; Randell, S.H. Evidence for stem-cell niches in the tracheal epithelium. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 24, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawlins, E.L.; Hogan, B.L. Ciliated epithelial cell lifespan in the mouse trachea and lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L231–L234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobinger, G.P.; Weiner, D.J.; Yu, Q.C.; Wilson, J.M. Filovirus-pseudotyped lentiviral vector can efficiently and stably transduce airway epithelia in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.F.; Kobinger, G.P.; Rux, J.; Gasmi, M.; Looney, D.J.; Bates, P.; Wilson, J.M. Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with minimal filovirus envelopes increased gene transfer in murine lung. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, P.L.; Burnight, E.R.; Hickey, M.A.; Blissard, G.W.; McCray Jr., P.B. Persistent gene expression in mouse nasal epithelia following feline immunodeficiency virus-based vector gene transfer. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12818–12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, T.; Patel, M.; Pickles, R.J.; Johnson, L.G.; Olsen, J.C. Influenza M2 envelope protein augments avian influenza hemagglutinin pseudotyping of lentiviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Stein, C.S.; Heth, J.A.; Sinn, P.L.; Penisten, A.K.; Staber, P.D.; Ratcliff, K.L.; Shen, S.; Barker, C.K.; Martins, I.; Sharkey, C.M.; Sanders, D.A.; McCray Jr., P.B.; Davidson, B.L. In vivo gene transfer using a nonprimate lentiviral vector pseudotyped with Ross River virus glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9378–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinn, P.L.; Penisten, A.K.; Burnight, E.R.; Hickey, M.A.; Williams, G.; McCoy, D.M.; Mallampalli, R.K.; McCray Jr., P.B. Gene transfer to respiratory epithelia with lentivirus pseudotyped with Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus envelope glycoprotein. Hum. Gene Ther. 2005, 16, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Innate immune recognition of viruses and viral vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Su, Q.; Wilson, J.M. Role of viral antigens in destructive cellular immune responses to adenovirus vector-trasduced cells in mouse lungs. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7209–7212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- VandenDriessche, T.; Thorrez, L.; Naldini, L.; Follenzi, A.; Moons, L.; Berneman, Z.; Collen, D.; Chuah, M.K.L. Lentiviral vectors containing the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 central polypurine tract can efficiently transduce nondividing hepatocytes and antigen-presenting cells in vivo. Blood 2002, 100, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follenzi, A.; Battaglia, M.; Lombardo, A.; Annoni, A.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Naldini, L. Targeting lentiviral vector expression to hepatocytes limits transgene-specific immune response and establishes long-term expression of human antihemophilic factor IX in mice. Blood 2004, 103, 3700–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auricchio, A.; Kobinger, G.; Anand, V.; Hildinger, M.; O'Connor, E.; Maguire, A.M.; Wilson, J.M.; Bennett, J. Exchange of surface proteins impacts on viral vector cellular specificity and transduction characteristics: the retina as a model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 3075–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafri, T.; Blomer, U.; Peterson, D.A.; Gage, F.H.; Verma, I.M. Sustained expression of genes delivered directly into liver and muscle by lentiviral vectors. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baekelandt, V.; Eggermont, K.; Michiels, M.; Nuttin, B.; Debyser, Z. Optimized lentiviral vector production and purification procedure prevents immune response after transduction of mouse brain. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinn, P.L.; Arias, A.C.; Brogden, K.A.; McCray Jr., P.B. Lentivirus vector can be readministered to nasal epithelia without blocking immune responses. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10684–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberis, M.P.; Bell, C.L.; Heath, J.; Wilson, J.M. Activation of Transgene-specific T Cells Following Lentivirus-mediated Gene Delivery to Mouse Lung. Mol. Ther. 2009, 15, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, J.; Limberis, M.P.; Wilson, J.M. Prediction of cellular immune responses against CFTR in patients with cystic fibrosis after gene therapy. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberis, M.P.; Figueredo, J.; Calcedo, R.; Wilson, J.M. Activation of CFTR-specific T Cells in cystic fibrosis mice following gene transfer. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challita, P.M.; Kohn, D.B. Lack of expression from a retroviral vector after transduction of murine hematopoietic stem cells is associated with methylation in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2567–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowtell, D.D.; Johnson, G.R.; Kelso, A.; Cory, S. Expression of genes transferred to haemopoietic stem cells by recombinant retroviruses. Mol. Biol. Med. 1987, 4, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; McCormack, M.P.; Wulffraat, N.; Leboulch, P.; Lim, A.; Osborne, C.S.; Pawliuk, R.; Morillon, E.; Sorensen, R.; Forster, A.; Fraser, P.; Cohen, J.I.; de Saint Basile, G.; Alexander, I.; Wintergerst, U.; Frebourg, T.; Aurias, A.; Stoppa-Lyonnet, D.; Romana, S.; Radford-Weiss, I.; Gross, F.; Valensi, F.; Delabesse, E.; Macintyre, E.; Sigaux, F.; Soulier, J.; Leiva, L.E.; Wissler, M.; Prinz, C.; Rabbitts, T.H.; Le Deist, F.; Fischer, A.; Cavazzana-Calvo, M. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science 2003, 302, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, B.; Senadheera, D.; Mishra, S.; Bui, K.C.; Wang, X.; Chan, B.; Petersen, D.; Pepper, K.; Lutzko, C. Development of lentiviral vectors with regulated respiratory epithelial expression in vivo. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, G.; Legarda, D.; Ryan, L.K. The innate immune response of the respiratory epithelium. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 173, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bals, R.; Hiemstra, P.S. Innate immunity in the lung: how epithelial cells fight against respiratory pathogens. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Schleimer, R.P. Beyond inflammation: airway epithelial cells are at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Message, S.D.; Johnston, S.L. Host defense function of the airway epithelium in health and disease: clinical background. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.P.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Innate immunity to respiratory viruses. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copreni, E.; Nicolis, E.; Tamanini, A.; Bezzerri, V.; Castellani, S.; Palmieri, L.; Giri, M.G.; Vella, A.; Colombatti, M.; Rizzotti, P.; Conese, M.; Cabrini, G. Late generation lentiviral vectors: Evaluation of inflammatory potential in human airway epithelial cells. Virus Res. 2009, 144, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarsgard, E.D.; Huang, L.; Reebye, S.C.; Yeung, A.Y.; Jia, W.W. Lentiviral vector-mediated, in vivo gene transfer to the tracheobronchial tree in fetal rabbits. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantal, A.F.; McDonald, R.J.; Jimenez, D.F.; Lee, C.C.; O'Shea, C.E.; Leapley, A.C.; Won, R.H.; Plopper, C.G.; Lutzko, C.; Kohn, D.B. Intrapulmonary and intramyocardial gene transfer in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta): safety and efficiency of HIV-1-derived lentiviral vectors for fetal gene delivery. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, S.M.; Howe, S.J.; Sheard, V.; Ward, N.J.; Coutelle, C.; Thrasher, A.J.; Waddington, S.N.; McKay, T.R. Lentiviral transduction of the murine lung provides efficient pseudotype and developmental stage-dependent cell-specific transgene expression. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.; Galea-Lauri, J.; Farzaneh, F.; Darling, D. Streptavidin paramagnetic particles provide a choice of three affinity-based capture and magnetic concentration strategies for retroviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, M.-F.; Chi, K.-M.; Lau, K.-H. W.; Baylink, D.J.; Chen, S.-T. Generation of magnetic retroviral vectors with magnetic nanoparticles. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2003, 5, 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Grubb, B.R.; Boucher, R.C. Pathophysiology of gene-targeted mouse models for cystic fibrosis. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, S193–S214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yan, Z.; Yi, Y.; Li, Z.; Lei, D.; Rogers, C.S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Welsh, M.J.; Leno, G.H.; Engelhardt, J.F. Adeno-associated virus-targeted disruption of the CFTR gene in cloned ferrets. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.S.; Hao, Y.; Rokhlina, T.; Samuel, M.; Stoltz, D.A.; Li, Y.; Petroff, E.; Vermeer, D.W.; Kabel, A.C.; Yan, Z.; Spate, L.; Wax, D.; Murphy, C.N.; Rieke, A.; Whitworth, K.; Linville, M.L.; Korte, S.W.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Welsh, M.J.; Prather, R.S. Production of CFTR-null and CFTR-DeltaF508 heterozygous pigs by adeno-associated virus-mediated gene targeting and somatic cell nuclear transfer. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
Castellani, S.; Conese, M. Lentiviral Vectors and Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy. Viruses 2010, 2, 395-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020395
Castellani S, Conese M. Lentiviral Vectors and Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy. Viruses. 2010; 2(2):395-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020395
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellani, Stefano, and Massimo Conese. 2010. "Lentiviral Vectors and Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy" Viruses 2, no. 2: 395-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020395
APA StyleCastellani, S., & Conese, M. (2010). Lentiviral Vectors and Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy. Viruses, 2(2), 395-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2020395





