Applying Genomic and Bioinformatic Resources to Human Adenovirus Genomes for Use in Vaccine Development and for Applications in Vector Development for Gene Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Synopsis of HAdV biology
1.2. Early genomics of HAdV
1.3. Current genomics of HAdV
2. Tools and methodologies of bioinformatics for adenovirus genomes
2.1. Genomics: acquisition of data
2.2. Bioinformatics
2.2.1. Genome analysis
2.2.2. Proteome analysis
2.2.3. Informatics support
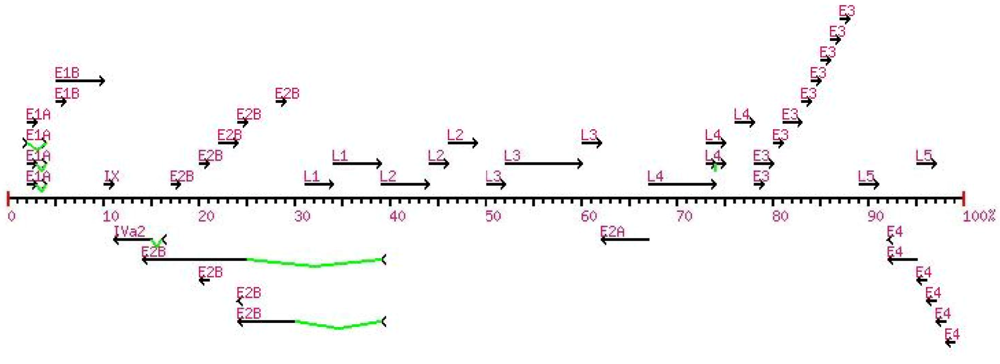
2.2.4. Bioinformatics Tools Summary
| Tool | Purpose | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Sequencher | sequence assembly | Commercial |
| PipMaker | genome sequence analysis | http://pipmaker.bx.psu.edu/cgi-bin/pipmaker?basic |
| zPicture | genome sequence analysis | http://zpicture.dcode.org |
| MAVID | whole genome alignment | http://baboon.math.berkeley.edu/mavid |
| MEGA4 | alignment viewer, phylogeny | http://www.megasoftware.net/ |
| Simplot | recombination analysis | http://sray.med.som.jhmi.edu/SCRoftware/simplot/ |
| pDRAW32 | in silico restriction enzyme digest | http://www.acaclone.com/ |
| Artemis | sequence viewer, annotation tool | http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Software/Artemis/ |
| EMBOSS | sequence analysis | http://emboss.sourceforge.net/ |
| Auto % Id beta | sequence % id | available upon request |
| Clustal | sequence alignment | http://www.clustal.org/ |
| Adenovirus Wiki | repository of adenovirus data | http://www.binf.gmu.edu/wiki/index.php/Main_Page |
| Mapping Tool beta | create gene maps | www.irgolf.com/genemapv2 |
| VGAT beta | automated virus genome annotation | http://binf.gmu.edu/zenith/tool/lghmms.php |
3. Considerations of HAdVs for vaccine development and for vectors development for gene transfer and delivery
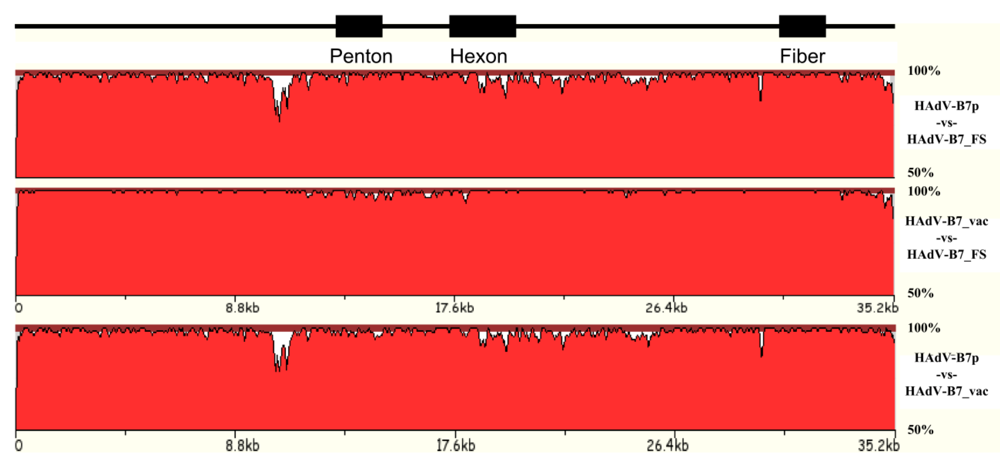
3.1. Natural variation of HAdV genomes
| HAdV-B7_FS | HAdV-B7_vac | HAdV-B7p |
|---|---|---|
| E1A 28 kDa protein | 98.9 | 99.6 |
| E1A 32 kDa protein | 98.3 | 99.6 |
| E1A 6 kDa protein | 98.3 | 100.0 |
| E1B 20 kDa protein | 100.0 | 98.3 |
| E1B 55 kDa protein | 100.0 | 99.0 |
| IX protein | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| IVa2 protein | 99.3 | 98.9 |
| DNA polymerase | 99.7 | 98.2 |
| Hypothetical | 99.1 | 98.1 |
| agnoprotein | 99.5 | 72.7 |
| Hypothetical | 100.0 | 68.4 |
| Terminal protein | 100.0 | 98.8 |
| Hypothetical | 99.2 | 95.5 |
| Hypothetical | 98.9 | 93.4 |
| 52 kDa protein | 99.2 | 97.4 |
| IIIa protein | 99.1 | 99.7 |
| penton base protein | 98.7 | 99.3 |
| VII protein | 98.4 | 99.5 |
| V protein | 98.3 | 98.3 |
| X protein | 98.3 | 98.3 |
| VI protein | 96.4 | 96.8 |
| hexon | 99.8 | 97.0 |
| protease | 100.0 | 97.6 |
| DBP | 99.8 | 97.7 |
| 100 kDa protein | 99.6 | 98.2 |
| 33 kDa protein | 98.3 | 83.9 |
| 22 kDa protein | 100.0 | 97.5 |
| VIII protein | 86.8 | 86.3 |
| E3 12.1 kDa | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| E3 CR1-α | 100.0 | 99.3 |
| E3 glycoprotein | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| E3 CR1-β | 95.5 | 93.3 |
| E3 CR1-γ | 99.5 | 98.4 |
| E3 7.7 kDa protein | 100.0 | 59.1 |
| E3 RID-α | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| E3 RID-β | 92.4 | 100.0 |
| E3 14.7 kDa protein | 100.0 | 99.3 |
| U protein | 100.0 | 98.1 |
| fiber | 99.7 | 98.8 |
| E4 ORF 6/7 protein | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| E4 32 kDa protein | 99.3 | 98.7 |
| E4 ORF 4 protein | 98.4 | 95.9 |
| agnoprotein | 99.4 | 97.0 |
| E4 ORF 3 protein | 99.1 | 99.1 |
| E4 ORF 2 protein | 96.9 | 98.4 |
| E4 ORF 1 protein | 98.4 | 96.0 |
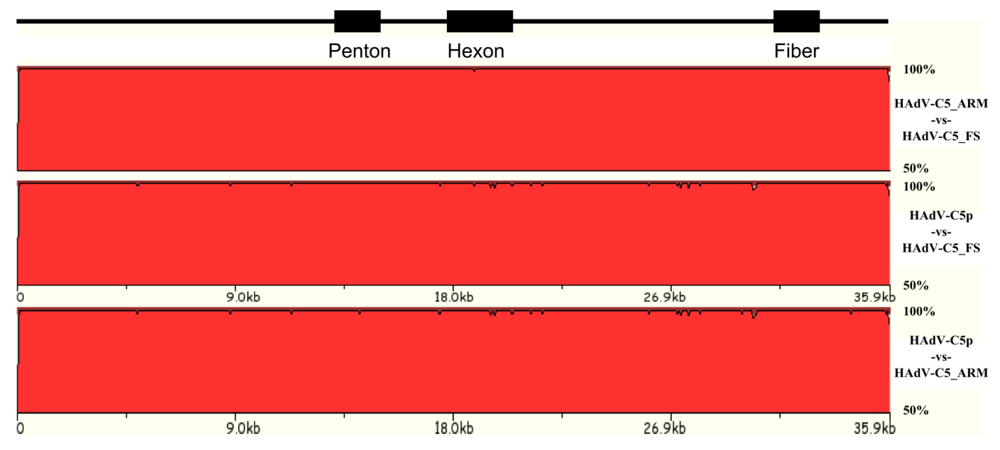
3.2. Natural variation of HAdV genomes: new types, new species, and vector candidate
| Adenovirus | Percent Identity, relative to HAdV-G52 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1A | E1B 55 kDa protein | IVa2 | DNA Pol | pTP | L1 55 kDa protein | L2 penton | L3 hexon | E2A DBP | CR1-alpha1 (RL1) | CR1-beta1 (RL2) | RL3* | L5 fiber1 | L5 fiber2 | E4 34 kDa | |
| SAdV-G1 | 92.3 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 98.6 | 99.5 | 100 | 99.2 | 92.3 | 94.6 | 97.7 | 97.0 | - | 82.6 | 98.6 | 100 |
| SAdV-G7 | 38.6 | 90.3 | 98.9 | 97.6 | 98.8 | 99.7 | 93.3 | 90.0 | 94.8 | - | - | - | 59.3 | 72.1 | 98.3 |
| HAdV-F40 | 47.1 | 68.2 | 87.7 | 78.5 | 82.4 | 82.6 | 86.1 | 84.7 | 62.3 | 44.3 | 35.7 | + | 37.8 | 52.7 | 62.3 |
| HAdV-F41 | 42.8 | 68.5 | 89.5 | 79.9 | 84.4 | 83.8 | 87.1 | 87.8 | 66.1 | 44.3 | 34.8 | + | 38.5 | 53.4 | 61.2 |
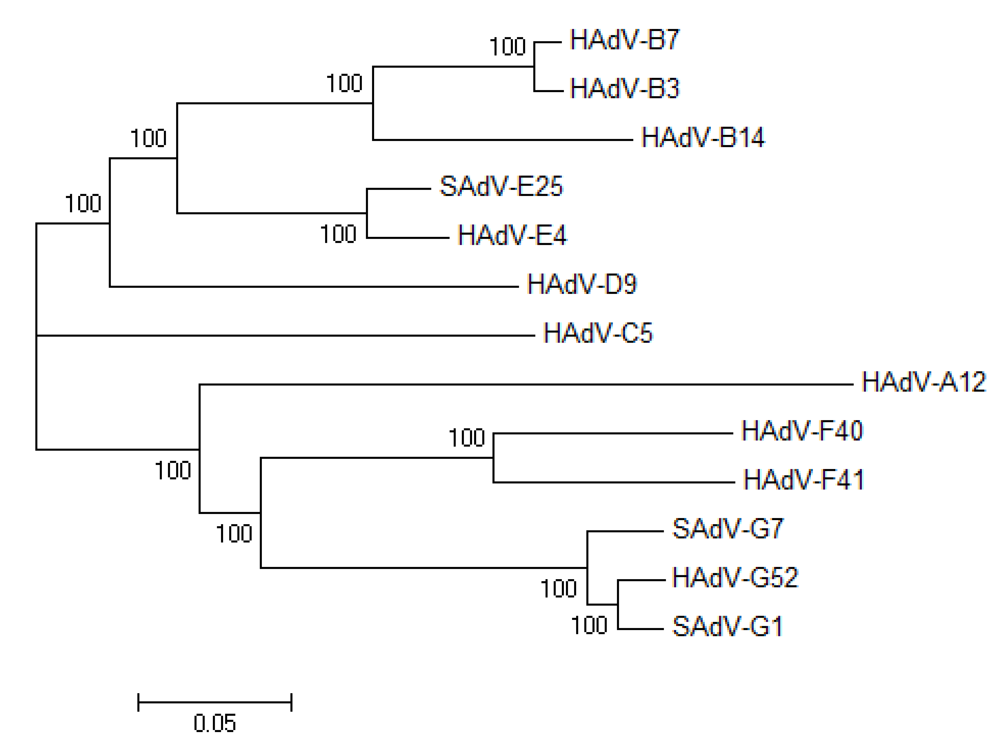
3.3. Natural variation of AdV genomes: non-human primate AdV genomics and vector candidates
4. Applications
4.1. Applications: development of HAdV-B3 vaccine
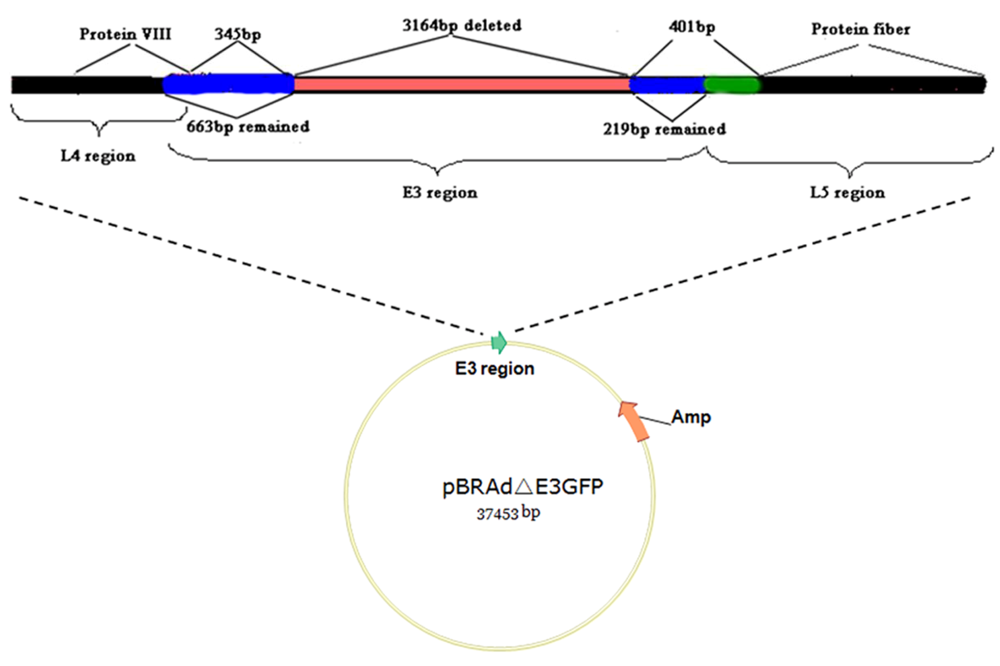
4.2. Applications: development of HAdV-B3 as a vector for gene delivery
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Berg, M.; Difatta, J.; Hoiczyk, E.; Schlegel, R.; Ketner, G. Viable Adenovirus Vaccine Prototypes: High-Level Production of a Papillomavirus Capsid Antigen from the Major Late Transcriptional Unit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005, 102, 4590–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radosevic, K.; Wieland, C.W.; Rodriguez, A.; Weverling, G.J.; Mintardjo, R.; Gillissen, G.; Vogels, R.; Skeiky, Y.A.; Hone, D. M.; Sadoff, J.C.; van der Poll, T.; Havenga, M.; Goudsmit, J. Protective Immune Responses to a Recombinant Adenovirus Type 35 Tuberculosis Vaccine in Two Mouse Strains: CD4 and CD8 T-Cell Epitope Mapping and Role of Gamma Interferon. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4105–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, F. L.; Prevec, L. Adenovirus-Based Expression Vectors and Recombinant Vaccines. Biotechnology 1992, 20, 363–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shott, J.P.; McGrath, S.M.; Pau, M.G.; Custers, J.H.; Ophorst, O.; Demoitie, M.A.; Dubois, M.C.; Komisar, J.; Cobb, M.; Kester, K.E.; Dubois, P.; Cohen, J.; Goudsmit, J.; Heppner, D.G.; Stewart, V.A. Adenovirus 5 and 35 Vectors Expressing Plasmodium Falciparum Circumsporozoite Surface Protein Elicit Potent Antigen-Specific Cellular IFN-Gamma and Antibody Responses in Mice. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenstein, P.R.; Mandel, R.J.; Xiong, W.D.; Kroeger, K.; Castro, M.G. Immune Responses to Adenovirus and Adeno-Associated Vectors Used for Gene Therapy of Brain Diseases: The Role of Immunological Synapses in Understanding the Cell Biology of Neuroimmune Interactions. Curr. Gene. Ther. 2007, 7, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, E.E.; Timares, L.; Matthews, Q.L. Strategies to Overcome Host Immunity to Adenovirus Vectors in Vaccine Development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, R.; Zuijdgeest, D.; van Rijnsoever, R.; Hartkoorn, E.; Damen, I.; de Bethune, M.P.; Kostense, S.; Penders, G.; Helmus, N.; Koudstaal, W.; Cecchini, M.; Wetterwald, A.; Sprangers, M.; Lemckert, A.; Ophorst, O.; Koel, B.; van Meerendonk, M.; Quax, P.; Panitti, L.; Grimbergen, J.; Bout, A.; Goudsmit, J.; Havenga, M. Replication-Deficient Human Adenovirus Type 35 Vectors for Gene Transfer and Vaccination: Efficient Human Cell Infection and Bypass of Preexisting Adenovirus Immunity. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8263–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, R.B.; Chanock, R.M.; Cate, T.R.; Lang, D.J.; Knight, V.; Huebner, R.J. Immunization with Types 4 and 7 Adenovirus by Selective Infection of the Intestinal Tract. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1963, 88, SUPPL394–SUPPL403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gray, G.C.; Goswami, P.R.; Malasig, M.D.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Trump, D.H.; Ryan, M.A.; Schnurr, D.P. Adult Adenovirus Infections: Loss of Orphaned Vaccines Precipitates Military Respiratory Disease Epidemics. For the Adenovirus Surveillance Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilleman, M.R.; Stallones, R.A.; Gauld, R.L.; Warfield, M.S.; Anderson, S.A. Vaccination Against Acute Respiratory Illness of Adenovirus (RI-APC-ARD) Etiology. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1957, 47, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Binn, L.N.; Sanchez, J.L.; Gaydos, J.C. Emergence of Adenovirus Type 14 in US Military Recruits--a New Challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1436–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasiole, D.A.; Metzgar, D.; Daum, L.T.; Ryan, M.A.; Wu, J.; Wills, C.; Le, C.T.; Freed, N.E.; Hansen, C.J.; Gray, G.C.; Russell, K.L. Molecular Analysis of Adenovirus Isolates from Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Young Adults. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarria, M. Adenovirus, 6thZuckerman, A.J., Banatvala, J.E., Pattison, J.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, 2009; pp. 463–488. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiko, H.; Aoki, K. Spread of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis Due to a Novel Serotype of Human Adenovirus in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2678–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, J.K.; Kajon, A.E.; Holodniy, M.; Guardia-LaBar, L.; Lee, B.; Petru, A.M.; Hacker, J.K.; Schnurr, D.P. Severe Pneumonia Due to Adenovirus Serotype 14: A New Respiratory Threat? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzgar, D.; Osuna, M.; Kajon, A.E.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Irvine, M.; Russell, K.L. Abrupt Emergence of Diverse Species B Adenoviruses at US Military Recruit Training Centers. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yu, P.; Tian, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, L.; Mao, N.; Ji, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, W. Outbreak of Acute Respiratory Disease in China Caused by B2 Species of Adenovirus Type 11. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, A.; Longfield, J.; Kuschner, R.; Straight, T.; Binn, L.; Seriwatana, J.; Reitstetter, R.; Froh, I.B.; Craft, D.; McNabb, K.; Russell, K.; Metzgar, D.; Liss, A.; Sun, X.; Towle, A.; Sun, W. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Safety and Immunogenicity of Live, Oral Type 4 and Type 7 Adenovirus Vaccines in Adults. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarria, M. Adenoviruses in Immunocompromised Hosts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnett, C.T.; Talekar, G.; Mahr, J.A.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ornelles, D.A.; Gooding, L.R. Latent Species C Adenoviruses in Human Tonsil Tissues. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.P.; Chintakuntlawar, A.; Robinson, C.M.; Madisch, I.; Harrach, B.; Hudson, N.R.; Schnurr, D.; Heim, A.; Chodosh, J.; Seto, D.; Jones, M.S. Evidence of Molecular Evolution Driven by Recombination Events Influencing Tropism in a Novel Human Adenovirus That Causes Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Tan, X.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, W. Genomic Analyses of Recombinant Adenovirus Type 11a in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, J.C.; Wermenbol, A.G.; Verweij-Uijterwaal, M.W.; Slaterus, K.W.; Wertheim-Van Dillen, P.; Van Doornum, G.J.; Khoo, S.H.; Hierholzer, J.C. Adenoviruses from Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Individuals, Including Two Strains That Represent New Candidate Serotypes Ad50 and Ad51 of Species B1 and D, Respectively. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3940–3945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Echavarria, M.; Maldonado, D.; Elbert, G.; Videla, C.; Rappaport, R.; Carballal, G. Use of PCR to Demonstrate Presence of Adenovirus Species B, C, or F as Well as Coinfection with Two Adenovirus Species in Children with Flu-Like Symptoms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Wang, Z.; Vora, G.J.; Thornton, J.A.; Schnur, J.M.; Thach, D.C.; Blaney, K.M.; Ligler, A.G.; Malanoski, A.P.; Santiago, J.; Walter, E.A.; Agan, B.K.; Metzgar, D.; Seto, D.; Daum, L. T.; Kruzelock, R.; Rowley, R.K.; Hanson, E.H.; Tibbetts, C.; Stenger, D.A. Broad-Spectrum Respiratory Tract Pathogen Identification Using Resequencing DNA Microarrays. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzgar, D.; Osuna, M.; Yingst, S.; Rakha, M.; Earhart, K.; Elyan, D.; Esmat, H.; Saad, M.D.; Kajon, A.; Wu, J.; Gray, G.C.; Ryan, M.A.; Russell, K.L. PCR Analysis of Egyptian Respiratory Adenovirus Isolates, Including Identification of Species, Serotypes, and Coinfections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5743–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, G.J.; Lin, B.; Gratwick, K.; Meador, C.; Hansen, C.; Tibbetts, C.; Stenger, D.A.; Irvine, M.; Seto, D.; Purkayastha, A.; Freed, N.E.; Gibson, M.G.; Russell, K.; Metzgar, D. Co-Infections of Adenovirus Species in Previously Vaccinated Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer, J.C.; Wigand, R.; Anderson, L.J.; Adrian, T.; Gold, J.W. Adenoviruses from Patients with AIDS: A Plethora of Serotypes and a Description of Five New Serotypes of Subgenus D (types 43-47). J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 158, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crawford-Miksza, L.K.; Schnurr, D.P. Adenovirus Serotype Evolution Is Driven by Illegitimate Recombination in the Hypervariable Regions of the Hexon Protein. Virology 1996, 224, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursnell, M.; Mautner, V. In Vitro Construction of a Recombinant Adenovirus Ad2:Ad5. Gene 1981, 13, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursnell, M.E.; Mautner, V. Recombination in Adenovirus: Crossover Sites in Intertypic Recombinants Are Located in Regions of Homology. Virology 1981, 112, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mautner, V.; Mackay, N. Recombination in Adenovirus: Analysis of Crossover Sites in Intertypic Overlap Recombinants. Virology 1984, 139, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Grodzicker, T.; Sharp, P.; Sambrook, J. Adenovirus Recombination: Physical Mapping of Crossover Events. Cell 1975, 4, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, K.; Liang, M.; Ye, X.; Ni, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Ye, S.L.; Hu, F.; Lieber, A. A New Type of Adenovirus Vector That Utilizes Homologous Recombination to Achieve Tumor-Specific Replication. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10994–11002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.E.; Manos, M.M.; Gluzman, Y. Sequence of the Junction in Adenovirus 2-SV40 Hybrids: Examples of Illegitimate Recombination. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1982, 10, 8099–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, T.; Bastian, B.; Benoist, W.; Hierholzer, J.C.; Wigand, R. Characterization of Adenovirus 15/H9 Intermediate Strains. Intervirology 1985, 23, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewicz, B.; Benzler, J.; Pauli, G.; Krause, G.; Bergmann, F.; Schweiger, B. Respiratory Disease Caused by a Species B2 Adenovirus in a Military Camp in Turkey. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 77, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, I.; Madisch, I.; Pommer, H.; Heim, A. An Outbreak of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis Caused by a New Intermediate Adenovirus 22/H8 Identified by Molecular Typing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, e64–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer, J.C.; Adrian, T.; Anderson, L.J.; Wigand, R.; Gold, J.W. Analysis of Antigenically Intermediate Strains of Subgenus B and D Adenoviruses from AIDS Patients. Arch. Virol. 1988, 103, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer, J.C.; Pumarola, A. Antigenic Characterization of Intermediate Adenovirus 14-11 Strains Associated with Upper Respiratory Illness in a Military Camp. Infect. Immun. 1976, 13, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishiko, H.; Shimada, Y.; Konno, T.; Hayashi, A.; Ohguchi, T.; Tagawa, Y.; Aoki, K.; Ohno, S.; Yamazaki, S. Novel Human Adenovirus Causing Nosocomial Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkö, M.H.B.; Both, G.W.; Russell, W.C.; Adair, B.M.; Ádám, É.; de Jong, J.C.; Hess, M.; Johnson, M.; Kajon, A.; Kidd, A.H.; Lehmkuhl, H.D.; Li, Q.; Mautner, V.; Pring-Akerblom, P.; Wadell, G. Family Adenoviridae. Fauquet C.M. Mayo, M.A., Maniloff J. Desselberger, U., Ball, L.A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A. J.; Benko, M.; Harrach, B. Genetic Content and Evolution of Adenoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2895–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.C. Adenoviruses: Update on Structure and Function. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.S.; Harrach, B.; Ganac, R.D.; Gozum, M.M.; Dela Cruz, W.P.; Riedel, B.; Pan, C.; Delwart, E.L.; Schnurr, D.P. New Adenovirus Species Found in a Patient Presenting with Gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5978–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, J.C.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Jones, M.S.; Harrach, B. Human Adenovirus Type 52: A Type 41 in Disguise? J. Virol. 2008, 82 author reply 3809-3810, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.J.; Akusjarvi, G.; Alestrom, P.; Gelinas, R.E.; Gingeras, T.R.; Sciaky, D.; Pettersson, U. A Consensus Sequence for the Adenovirus-2 Genome. Doerfler, W., Ed.; Martinus Nijhoff: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chroboczek, J.; Bieber, F.; Jacrot, B. The Sequence of the Genome of Adenovirus Type 5 and Its Comparison with the Genome of Adenovirus Type 2. Virology 1992, 186, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprengel, J.; Schmitz, B.; Heuss-Neitzel, D.; Doerfler, W. The Complete Nucleotide Sequence of the DNA of Human Adenovirus Type 12. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 199, 189–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davison, A.J.; Telford, E.A.; Watson, M.S.; McBride, K.; Mautner, V. The DNA Sequence of Adenovirus Type 40. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.M.; Rajaiya, J.; Walsh, M.P.; Seto, D.; Dyer, D.W.; Jones, M.S.; Chodosh, J. Computational Analysis of Human Adenovirus Type 22 Provides Evidence for Recombination Between Human Adenoviruses Species D in the Penton Base Gene. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8980–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugarman, B.J.; Hutchins, B.; McAllister, D.L.; Lu, F.; Thomas, B.K. The Complete Nucleotide Acid Sequence of the Adenovirus Type 5 Reference Material (ARM) Genome. Bioprocessing J. 2003, September/October, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Robbins, P.D.; Gambotto, A. Human Adenovirus Type 35: Nucleotide Sequence and Vector Development. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.F.; Skog, J.; Lindman, K.; Wadell, G. Comparative Analysis of the Genome Organization of Human Adenovirus 11, a Member of the Human Adenovirus Species B, and the Commonly Used Human Adenovirus 5 Vector, a Member of Species C. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, D.; Furthmann, A.; Sandig, V.; Lieber, A. The Complete Nucleotide Sequence, Genome Organization, and Origin of Human Adenovirus Type 11. Virology 2003, 309, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, K.P.; Llorente, I.; Blair, E.; Seto, J.; Krasnov, V.; Purkayastha, A.; Ditty, S.E.; Hadfield, T.L.; Buck, C.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Natural Variation Among Human Adenoviruses: Genome Sequence and Annotation of Human Adenovirus Serotype 1. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2615–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, A.; Ditty, S.E.; Su, J.; McGraw, J.; Hadfield, T.L.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Genomic and Bioinformatics Analysis of HAdV-4, a Human Adenovirus Causing Acute Respiratory Disease: Implications for Gene Therapy and Vaccine Vector Development. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, A.; Su, J.; Carlisle, S.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Genomic and Bioinformatics Analysis of HAdV-7, a Human Adenovirus of Species B1 That Causes Acute Respiratory Disease: Implications for Vector Development in Human Gene Therapy. Virology 2005, 332, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, A.; Su, J.; McGraw, J.; Ditty, S.E.; Hadfield, T.L.; Seto, J.; Russell, K.L.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Genomic and Bioinformatics Analyses of HAdV-4vac and HAdV-7vac, Two Human Adenovirus (HAdV) Strains That Constituted Original Prophylaxis Against HAdV-Related Acute Respiratory Disease, a Reemerging Epidemic Disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, J.; Walsh, M.P.; Mahadevan, P.; Purkayastha, A.; Clark, J.M.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Genomic and Bioinformatics Analyses of HAdV-14p, Reference Strain of a Re-Emerging Respiratory Pathogen and Analysis of B1/B2. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Gao, G.; Clawson, D.S.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Farina, S.F.; Wilson, J.M. Complete Nucleotide Sequences and Genome Organization of Four Chimpanzee Adenoviruses. Virology 2004, 324, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Gao, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lock, M.; Calcedo, R.; Wilson, J.M. Characterization of a Family of Chimpanzee Adenoviruses and Development of Molecular Clones for Gene Transfer Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henquell, C.; Boeuf, B.; Mirand, A.; Bacher, C.; Traore, O.; Dechelotte, P.; Labbe, A.; Bailly, J.L.; Peigue-Lafeuille, H. Fatal Adenovirus Infection in a Neonate and Transmission to Health-Care Workers. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 45, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, H.; Haack, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Eizema, K.; Pauschinger, M.; Schoemaker, R.; Veghel, R.; Houtsmuller, A.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Lamers, J.; Poller, W. Expression of Coxsackie Adenovirus Receptor and Alphav-Integrin Does Not Correlate with Adenovector Targeting in Vivo Indicating Anatomical Vector Barriers. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggar, A.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Lieber, A. CD46 Is a Cellular Receptor for Group B Adenoviruses. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomko, R.P.; Xu, R.; Philipson, L. HCAR and MCAR: The Human and Mouse Cellular Receptors for Subgroup C Adenoviruses and Group B Coxsackieviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1997, 94, 3352–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornberg, A. Ten Commandments of Enzymology, Amended. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.; Zhang, Z.; Frazer, K. A.; Smit, A.; Riemer, C.; Bouck, J.; Gibbs, R.; Hardison, R.; Miller, W. PipMaker--a Web Server for Aligning Two Genomic DNA Sequences. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.; Pachter, L. MAVID: Constrained Ancestral Alignment of Multiple Sequences. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-Length Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Genomes from Subtype C-Infected Seroconverters in India, with Evidence of Intersubtype Recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Etherington, G.J.; Dicks, J.; Roberts, I.N. Recombination Analysis Tool (RAT): A Program for the High-Throughput Detection of Recombination. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berriman, M.; Rutherford, K. Viewing and Annotating Sequence Data with Artemis. Brief. Bioinform. 2003, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X Windows Interface: Flexible Strategies for Multiple Sequence Alignment Aided by Quality Analysis Tools. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, R.C.; Down, T.A.; Pocock, M.; Prlic, A.; Huen, D.; James, K.; Foisy, S.; Drager, A.; Yates, A.; Heuer, M.; Schreiber, M.J. BioJava: An Open-Source Framework for Bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2096–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darr, S.; Madisch, I.; Hofmayer, S.; Rehren, F.; Heim, A. Phylogeny and Primary Structure Analysis of Fiber Shafts of All Human Adenovirus Types for Rational Design of Adenoviral Gene Therapy Vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2849–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madisch, I.; Harste, G.; Pommer, H.; Heim, A. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Main Neutralization and Hemagglutination Determinants of All Human Adenovirus Prototypes as a Basis for Molecular Classification and Taxonomy. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15265–15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madisch, I.; Hofmayer, S.; Moritz, C.; Grintzalis, A.; Hainmueller, J.; Pring-Akerblom, P.; Heim, A. Phylogenetic Analysis and Structural Predictions of Human Adenovirus Penton Proteins as a Basis for Tissue-Specific Adenovirus Vector Design. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8270–8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, D.; di Paolo, N.C.; Lieber, A. Development of Group B Adenoviruses as Gene Transfer Vectors. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2006, 22, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peruzzi, D.; Dharmapuri, S.; Cirillo, A.; Bruni, B.E.; Nicosia, A.; Cortese, R.; Colloca, S.; Ciliberto, G.; La Monica, N.; Aurisicchio, L. A Novel Chimpanzee Serotype-Based Adenoviral Vector as Delivery Tool for Cancer Vaccines. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, S.F.; Gao, G.; Xiang, Z.Q.; Rux, J.J.; Burnett, R.M.; Alvira, M.R.; Marsh, J.; Ertl, H.C.J.; Wilson, J.M. Replication-Defective Vector Based on a Chimpanzee Adenovirus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11603–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Zhi, Y.; Kobinger, G.P.; Figueredo, J.; Calcedo, R.; Miller, J.R.; Feldmann, H.; Wilson, J.M. Generation of an Adenoviral Vaccine Vector Based on Simian Adenovirus 21. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, X.; Seto, D.; Zheng, B.J.; Tian, X.; Sheng, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R. Construction and Characterization of a Replication-Competent Human Adenovirus Type 3-Based Vector as a Live-Vaccine Candidate and a Viral Delivery Vector. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, R.; Chen, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Gong, S. A Recombinant Replication-Defective Human Adenovirus Type 3: A Vaccine Candidate. Vaccine 2009, 27, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, D.; Ni, S.; Li, Z.Y.; Gaggar, A.; DiPaolo, N.; Feng, Q.; Sandig, V.; Lieber, A. Development and Assessment of Human Adenovirus Type 11 as a Gene Transfer Vector. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5090–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirena, D.; Ruzsics, Z.; Schaffner, W.; Greber, U.F.; Hemmi, S. The Nucleotide Sequence and a First Generation Gene Transfer Vector of Species B Human Adenovirus Serotype 3. Virology 2005, 343, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, X.; Peng, B.; Hahn, T.W.; Richardson, E.; Lizonova, A.; Kovesdi, I.; Robert-Guroff, M. Development of an Ad7 Cosmid System and Generation of an Ad7deltaE1deltaE3HIV(MN) Env/Rev Recombinant Virus. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajon, A.E.; Xu, W.; Erdman, D.D. Sequence Polymorphism in the E3 7.7K ORF of Subspecies B1 Human Adenoviruses. Virus Res. 2005, 107, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, P.; Seto, J.; Tibbetts, C.; Seto, D. Natural Variants of Human Adenovirus Type 3 Provide Evidence for Relative Genome Stability Across Time and Geographic Space . Virology 2009, E-pub 23 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, H.Y.; Pieniazek, N.; Pieniazek, D.; Luftig, R.B. Genetic Organization, Size, and Complete Sequence of Early Region 3 Genes of Human Adenovirus Type 41. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2658–2663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Kryazhimskiy, S.; Grant, R.; Calcedo, R.; Yuan, X.; Keough, M.; Sandhu, A.; Wang, Q.; Medina-Jaszek, C.A.; Plotkin, J.B.; Wilson, J.M. Isolation and Characterization of Adenoviruses Persistently Shed from the Gastrointestinal Tract of Non-Human Primates. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, W.C.; Russell, D.J.; Tibbetts, C. Fiber Gene and Genomic Origin of Human Adenovirus Type 4. Virology 1993, 196, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.G.; Wadell, G. The Degree of Genetic Variability Among Adenovirus Type 4 Strains Isolated from Man and Chimpanzee. Arch. Virol. 1988, 101, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, X.; Gong, S.; Zeng, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wu, Z.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, R. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Strains of Human Adenovirus Type 3 Isolated from Children with Acute Respiratory Infection in Southern China. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, T.; Hamamoto, I.; Taniguchi, K.; Chikahira, M.; Okabe, N. Molecular Epidemiology of Adenovirus Type 3 Detected from 1994 to 2006 in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.A.; Gray, G.C.; Smith, B.; McKeehan, J.A.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Malasig, M.D. Large Epidemic of Respiratory Illness Due to Adenovirus Types 7 and 3 in Healthy Young Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudding, B.A.; Wagner, S.C.; Zeller, J.A.; Gmelich, J.T.; French, G.R.; Top, F.H. Fatal Pneumonia Associated with Adenovirus Type 7 in Three Military Trainees. N. Eng. J. Med. 1972, 286, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, W.P.; Purcell, R.H.; Gundelfinger, B.F.; Love, J.W.; Ludwig, W.; Chanock, R.M. Immunization by Selective Infection with Type 4 Adenovirus Grown in Human Diploid Tissue Culture II. Specific Protective Effect Against Epidemic Disease. JAMA 1966, 195, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, X.B.; Ma, X.; Hong, Z.Y.; Wu, H.B.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, L. [Epidemiological Study of Human Type 5 Adenovirus in Guangzhou Using Chemiluminescence for Neutralizing Antibody Assay]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao (J. Southern Med. Univ.) 2007, 27, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischli, C.; Sirena, D.; Lesage, G.; Havenga, M.J.; Cattaneo, R.; Greber, U.F.; Hemmi, S. Species B Adenovirus Serotypes 3, 7, 11 and 35 Share Similar Binding Sites on the Membrane Cofactor Protein CD46 Receptor. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, J.J.; Pereboev, A.V.; Kawakami, Y.; Vasu, C.; Holterman, M.J.; Curiel, D.T. Adenovirus Serotype 3 Utilizes CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) as Cellular Attachment Receptors. Virology 2004, 322, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, J.J.; Vasu, C.; Holterman, M.J.; Curiel, D.T.; Pereboev, A. Members of Adenovirus Species B Utilize CD80 and CD86 as Cellular Attachment Receptors. Virus Res. 2006, 122, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirena, D.; Lilienfeld, B.; Eisenhut, M.; Kalin, S.; Boucke, K.; Beerli, R.R.; Vogt, L.; Ruedl, C.; Bachmann, M.F.; Greber, U.F.; Hemmi, S. The Human Membrane Cofactor CD46 Is a Receptor for Species B Adenovirus Serotype 3. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4454–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuve, S.; Wang, H.; Ware, C.; Liu, Y.; Gaggar, A.; Bernt, K.; Shayakhmetov, D.; Li, Z.; Strauss, R.; Stone, D.; Lieber, A. A New Group B Adenovirus Receptor Is Expressed at High Levels on Human Stem and Tumor Cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12109–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holterman, L.; Vogels, R.; van der Vlugt, R.; Sieuwerts, M.; Grimbergen, J.; Kaspers, J.; Geelen, E.; van der Helm, E.; Lemckert, A.; Gillissen, G.; Verhaagh, S.; Custers, J.; Zuijdgeest, D.; Berkhout, B.; Bakker, M.; Quax, P.; Goudsmit, J.; Havenga, M. Novel Replication-Incompetent Vector Derived from Adenovirus Type 11 (Ad11) for Vaccination and Gene Therapy: Low Seroprevalence and Non-Cross-Reactivity with Ad5. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13207–13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
Seto, J.; Walsh, M.P.; Mahadevan, P.; Zhang, Q.; Seto, D. Applying Genomic and Bioinformatic Resources to Human Adenovirus Genomes for Use in Vaccine Development and for Applications in Vector Development for Gene Delivery. Viruses 2010, 2, 1-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010001
Seto J, Walsh MP, Mahadevan P, Zhang Q, Seto D. Applying Genomic and Bioinformatic Resources to Human Adenovirus Genomes for Use in Vaccine Development and for Applications in Vector Development for Gene Delivery. Viruses. 2010; 2(1):1-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeto, Jason, Michael P. Walsh, Padmanabhan Mahadevan, Qiwei Zhang, and Donald Seto. 2010. "Applying Genomic and Bioinformatic Resources to Human Adenovirus Genomes for Use in Vaccine Development and for Applications in Vector Development for Gene Delivery" Viruses 2, no. 1: 1-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010001
APA StyleSeto, J., Walsh, M. P., Mahadevan, P., Zhang, Q., & Seto, D. (2010). Applying Genomic and Bioinformatic Resources to Human Adenovirus Genomes for Use in Vaccine Development and for Applications in Vector Development for Gene Delivery. Viruses, 2(1), 1-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010001





