A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Axis in Innate Immune Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
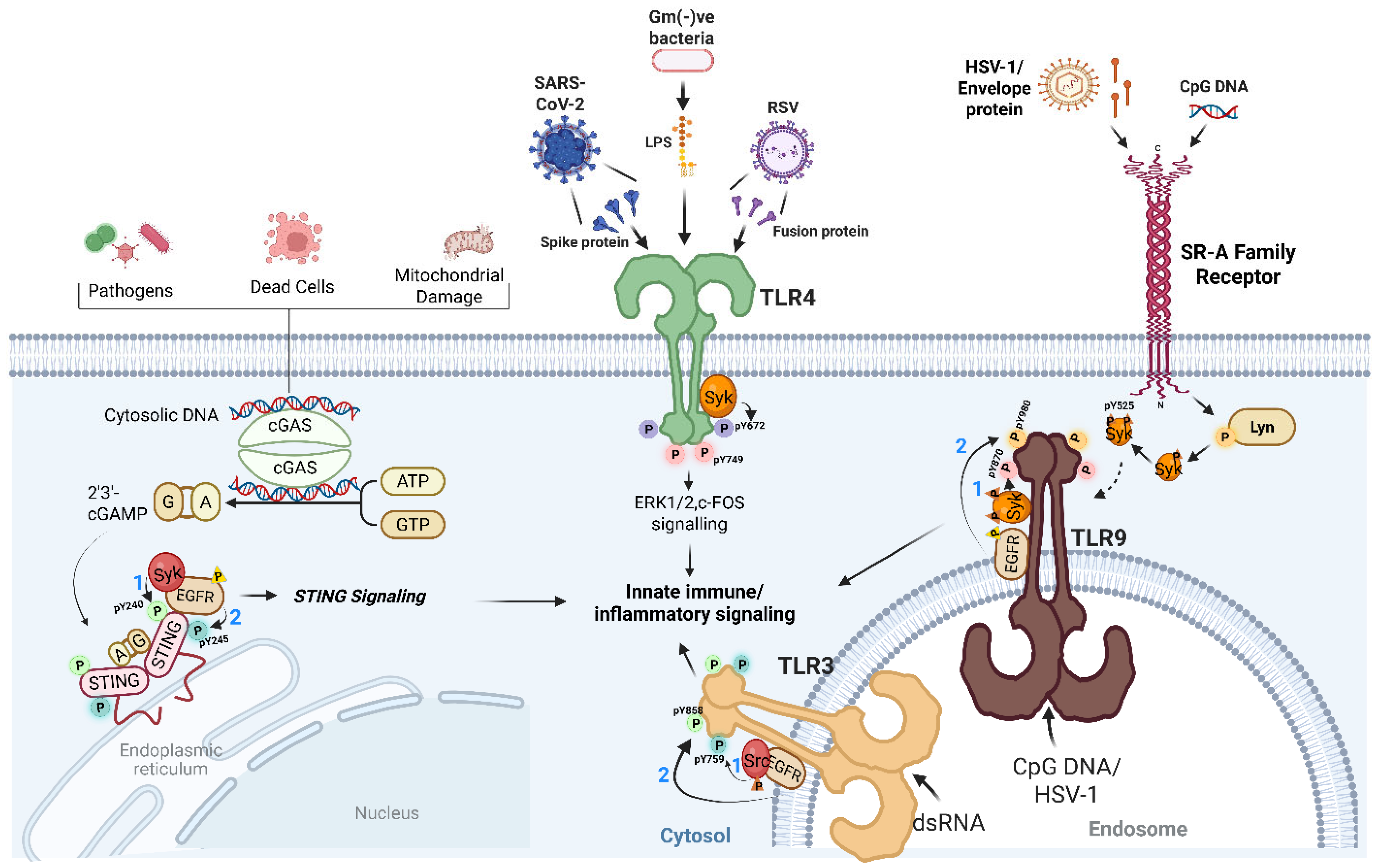
2. Tyrosine Kinases as Central Orchestrators of Antiviral TLR Signaling
3. Tyrosine Phosphorylation Extends to STING Signaling
4. Scavenger Receptors: Gatekeepers of the Tyrosine Kinase Axis
5. Conclusion: An Emerging ‘Tyrosine Kinase Axis’ Theme in Antiviral Innate Immunity
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Huizen, M.; Gack, M.U. The RIG-I-like receptor family of immune proteins. Mol. Cell 2025, 85, 3793–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, S.; Varghese, M.; Fan, S.; Taylor, R.T.; Chakravarti, R.; Chattopadhyay, S. IRF3 inhibits inflammatory signaling pathways in macrophages to prevent viral pathogenesis. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Chattopadhyay, S. Interferons in Viral Infections. Viruses 2024, 16, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salauddin, M.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Samanta, I.; Saha, S.; Xue, M.; Hossain, M.G.; Zheng, C. Role of TLRs as signaling cascades to combat infectious diseases: A review. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2025, 82, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Wu, K.H.; Wu, H.P. Unraveling the Complexities of Toll-like Receptors: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleeparambil, M.; Wang, C.; Kessler, P.M.; Sengupta, P.; Das, S.; Chakravarti, R.; Willard, B.; Sen, G.C.; Chattopadhyay, S. TLR9 signaling requires ligand-induced phosphorylation of two specific tyrosine residues by EGFR and Syk. mBio 2025, 16, e0027625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. Tyrosine phosphorylation in Toll-like receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2014, 25, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.N.; Peters, K.L.; Elco, C.P.; Sakamoto, S.; Pal, S.; Sen, G.C. Novel roles of TLR3 tyrosine phosphorylation and PI3 kinase in double-stranded RNA signaling. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Fensterl, V.; Saikia, P.; Wetzel, J.L.; Sen, G.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor is essential for Toll-like receptor 3 signaling. Sci. Signal 2012, 5, ra50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Veleeparambil, M.; Poddar, D.; Abdulkhalek, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Fensterl, V.; Sen, G.C. EGFR kinase activity is required for TLR4 signaling and the septic shock response. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Veleeparambil, M.; Kessler, P.M.; Willard, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. EGFR-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of STING determines its trafficking route and cellular innate immunity functions. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sharma, N.; Veleeparambil, M.; Kessler, P.M.; Willard, B.; Sen, G.C. STING-Mediated Interferon Induction by Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Requires the Protein Tyrosine Kinase Syk. mBio 2021, 12, e0322821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, C.A. Regulating IRFs in IFN Driven Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, K.-H.; Carsten, B.; Harrison, C. Scavenger receptor A1 is required for sensing HCMV by endosomal TLR-3/-9 in monocytic THP-1 cells. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansako, H.; Yamane, D.; Welsch, C.; McGivern, D.R.; Hu, F.; Kato, N.; Lemon, S.M. Class A scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1) restricts hepatitis C virus replication by mediating toll-like receptor 3 recognition of viral RNAs produced in neighboring cells. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanese, M.T.; Ansuini, H.; Graziani, R.; Huby, T.; Moreau, M.; Ball, J.K.; Paonessa, G.; Rice, C.M.; Cortese, R.; Vitelli, A.; et al. Role of scavenger receptor class B type I in hepatitis C virus entry: Kinetics and molecular determinants. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maler, M.D.; Nielsen, P.J.; Stichling, N.; Cohen, I.; Ruzsics, Z.; Wood, C.; Engelhard, P.; Suomalainen, M.; Gyory, I.; Huber, M.; et al. Key Role of the Scavenger Receptor MARCO in Mediating Adenovirus Infection and Subsequent Innate Responses of Macrophages. mBio 2017, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, J.; Neculai, D.; Grinstein, S. Scavenger receptors in homeostasis and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, C.R. Role of EGF Receptor Regulatory Networks in the Host Response to Viral Infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 820355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolinska, M.J.; Page, T.H.; Urbaniak, A.M.; Mutch, B.E.; Horwood, N.J. Hck tyrosine kinase regulates TLR4-induced TNF and IL-6 production via AP-1. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6043–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, P.; Dunne, A.; Brikos, C.; Jefferies, C.A.; Doyle, S.L.; O’Neill, L.A. MyD88 adapter-like (Mal) is phosphorylated by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase during TLR2 and TLR4 signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10489–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-G.; Xu, S.; Kang, Z.-H.; Huo, J.; Huang, M.; Liu, D.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Lam, K.-P. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase phosphorylates Toll-like receptor 3 to initiate antiviral response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5791–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curson, J.E.B.; Liu, L.; Luo, L.; Muusse, T.W.; Lucas, R.M.; Gunther, K.S.; Vajjhala, P.R.; Abrol, R.; Jones, A.; Kapetanovic, R.; et al. TLR4 phosphorylation at tyrosine 672 activates the ERK/c-FOS signaling module for LPS-induced cytokine responses in macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Piao, W.; Shoenfelt, J.; Rhee, S.H.; Chen, H.; Basu, S.; Wahl, L.M.; Fenton, M.J.; Vogel, S.N. Role of TLR4 tyrosine phosphorylation in signal transduction and endotoxin tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16042–16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veleeparambil, M.; Poddar, D.; Abdulkhalek, S.; Kessler, P.M.; Yamashita, M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. Constitutively Bound EGFR-Mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation of TLR9 Is Required for Its Ability To Signal. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2809–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumoto, N.; Saito, S.; Rifkin, I.R.; Bonegio, R.G.; Leal, D.N.; Sen, G.C.; Arditi, M.; Yamashita, M. EGF-Receptor-Dependent TLR7 Signaling in Macrophages Promotes Glomerular Injury in Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. Lab. Investig. 2023, 103, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Li, L.; Puliyappadamba, V.T.; Guo, G.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Mickey, B.; Souza, R.F.; Vo, P.; Herz, J.; Chen, M.R.; et al. Constitutive and ligand-induced EGFR signalling triggers distinct and mutually exclusive downstream signalling networks. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sharma, N.; Kessler, P.M.; Sen, G.C. Interferon induction by STING requires its translocation to the late endosomes. Traffic 2023, 24, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Yi, X.M.; Wu, X.; Shang, J.; Shu, H.B. PTPN1/2-mediated dephosphorylation of MITA/STING promotes its 20S proteasomal degradation and attenuates innate antiviral response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20063–20069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Li, L.; Tan, W.; Chen, D.; et al. PTK2B promotes TBK1 and STING oligomerization and enhances the STING-TBK1 signaling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruah, V.; O’Connor, C.M. The BTK-DDX41 axis of the STING pathway is activated during cytomegalovirus lytic infection. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e01048-01025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubiana, J.; Rossi, A.L.; Belaidouni, N.; Grimaldi, D.; Pene, F.; Chafey, P.; Comba, B.; Camoin, L.; Bismuth, G.; Claessens, Y.E.; et al. Src-family-tyrosine kinase Lyn is critical for TLR2-mediated NF-κB activation through the PI 3-kinase signaling pathway. Innate Immune 2015, 21, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, N.; Saminathan, H.; Jin, H.; Neal, M.; Harischandra, D.S.; Gordon, R.; Kanthasamy, K.; Lawana, V.; Sarkar, S.; Luo, J.; et al. Fyn Kinase Regulates Microglial Neuroinflammatory Responses in Cell Culture and Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10058–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Préhaud, C.; Mégret, F.; Lafage, M.; Lafon, M. Virus infection switches TLR-3-positive human neurons to become strong producers of beta interferon. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12893–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Y.I.; Choi, S.H.; Wiesner, P.; Bae, Y.S. The SYK side of TLR4: Signalling mechanisms in response to LPS and minimally oxidized LDL. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Pan, H.; Shively, J.E. CEACAM1 negatively regulates IL-1β production in LPS activated neutrophils by recruiting SHP-1 to a SYK-TLR4-CEACAM1 complex. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, S.; Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Strazzabosco, G.; Fernandez, M.; Caccuri, F.; Caruso, A.; Rizzo, R. TLR3 and TLR7 RNA Sensor Activation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, A.; Zheng, M.; Atherton, S.S.; Yu, F.S. Herpes simplex virus 1 infection induces the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, interferons and TLR7 in human corneal epithelial cells. Immunology 2006, 117, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, I.A.; Stephen, S.L.; Mughal, N.A.; Russell, D.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Wheatcroft, S.B.; Ponnambalam, S. Scavenger receptor structure and function in health and disease. Cells 2015, 4, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PrabhuDas, M.R.; Baldwin, C.L.; Bollyky, P.L.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Drickamer, K.; Febbraio, M.; Herz, J.; Kobzik, L.; Krieger, M.; Loike, J.; et al. A Consensus Definitive Classification of Scavenger Receptors and Their Roles in Health and Disease. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3775–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Alcántara, E.; Mendlovic, F. Scavenger Receptor A1 Signaling Pathways Affecting Macrophage Functions in Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 1725–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, Q.; Mumtaz, P.T.; Masoodi, K.Z.; Haq, E.; Ahmad, S.M. Scavenger receptors in host defense: From functional aspects to mode of action. Cell Commun. Signal 2022, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, D.T.; Nakatsuji, T.; Wang, Z.; di Nardo, A.; Gallo, R.L. Vaccinia virus binds to the scavenger receptor MARCO on the surface of keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Gregory, D.; Smith, A.; Kobzik, L. MARCO regulates early inflammatory responses against influenza: A useful macrophage function with adverse outcome. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Wan, L.; Yan, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, D.; Deng, Y.; et al. HDL-scavenger receptor B type 1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kakinami, C.; Li, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, H. Human Apolipoprotein A-I Is Associated with Dengue Virus and Enhances Virus Infection through SR-BI. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauvillain, C.; Meloni, F.; Sirard, J.C.; Blanchard, S.; Jarry, U.; Scotet, M.; Magistrelli, G.; Delneste, Y.; Barnaba, V.; Jeannin, P. The scavenger receptors SRA-1 and SREC-I cooperate with TLR2 in the recognition of the hepatitis C virus non-structural protein 3 by dendritic cells. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Innate Immune Sensors | Ligands and Stimuli | Tyrosine Kinases Involved | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 | Lipoproteins, Peptidoglycans, Pam3CSK4 | Fyn, Btk, Lyn | [21,32,33] |
| TLR3 | dsRNA, Rabies, HSV-1 | Src, EGFR, Btk | [9,22,34] |
| TLR4 | LPS, SARS-CoV-2, RSV | EGFR, Syk, Lyn, Hck | [10,20,23,35,36] |
| TLR7 | R848, SARS-CoV-2, HSV-1 | EGFR | [26,37,38] |
| TLR9 | CpG DNA, HSV-1 | Syk, EGFR, Lyn | [6,7,25] |
| cGAS–STING | Cytosolic DNA, HSV-1, cytomegalovirus | Syk, EGFR | [11,12,31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Das, S.; Sengupta, P.; Veleeparambil, M.; Chattopadhyay, S. A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Axis in Innate Immune Signaling. Viruses 2026, 18, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/v18010010
Das S, Sengupta P, Veleeparambil M, Chattopadhyay S. A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Axis in Innate Immune Signaling. Viruses. 2026; 18(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/v18010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Santanu, Pracheta Sengupta, Manoj Veleeparambil, and Saurabh Chattopadhyay. 2026. "A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Axis in Innate Immune Signaling" Viruses 18, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/v18010010
APA StyleDas, S., Sengupta, P., Veleeparambil, M., & Chattopadhyay, S. (2026). A Novel Tyrosine Kinase Axis in Innate Immune Signaling. Viruses, 18(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/v18010010







