Assessing the Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations on Antibody Binding: A Comparative Assessment of the Wuhan and JN.1 Variants’ Full-Length Spikes in a Multiplex Luminex Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Sets and Ethical Considerations
2.2. Construct Design and Protein Expression
2.3. ELISA Assays
2.4. Luminex Assay
2.5. Data Analysis
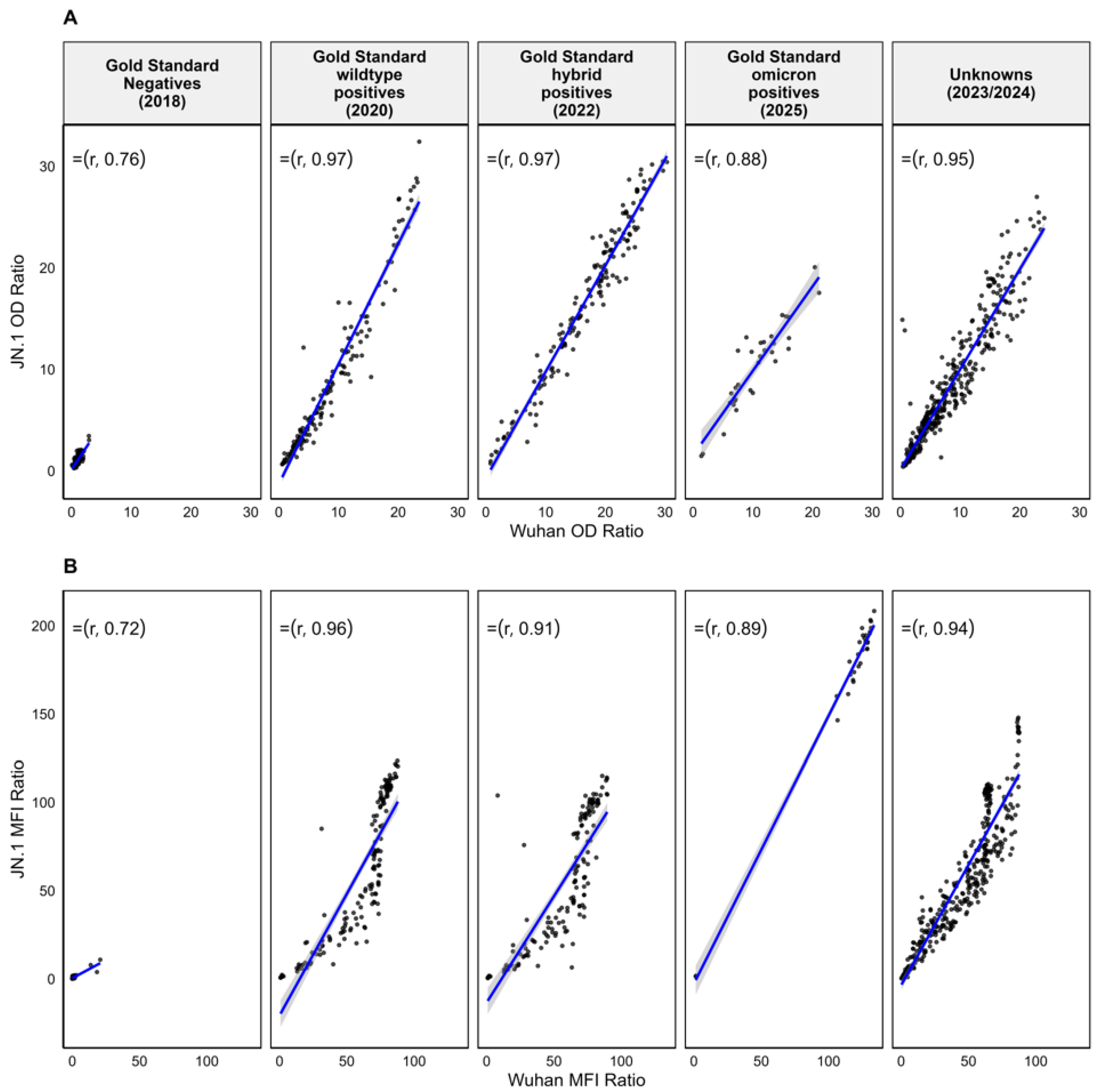
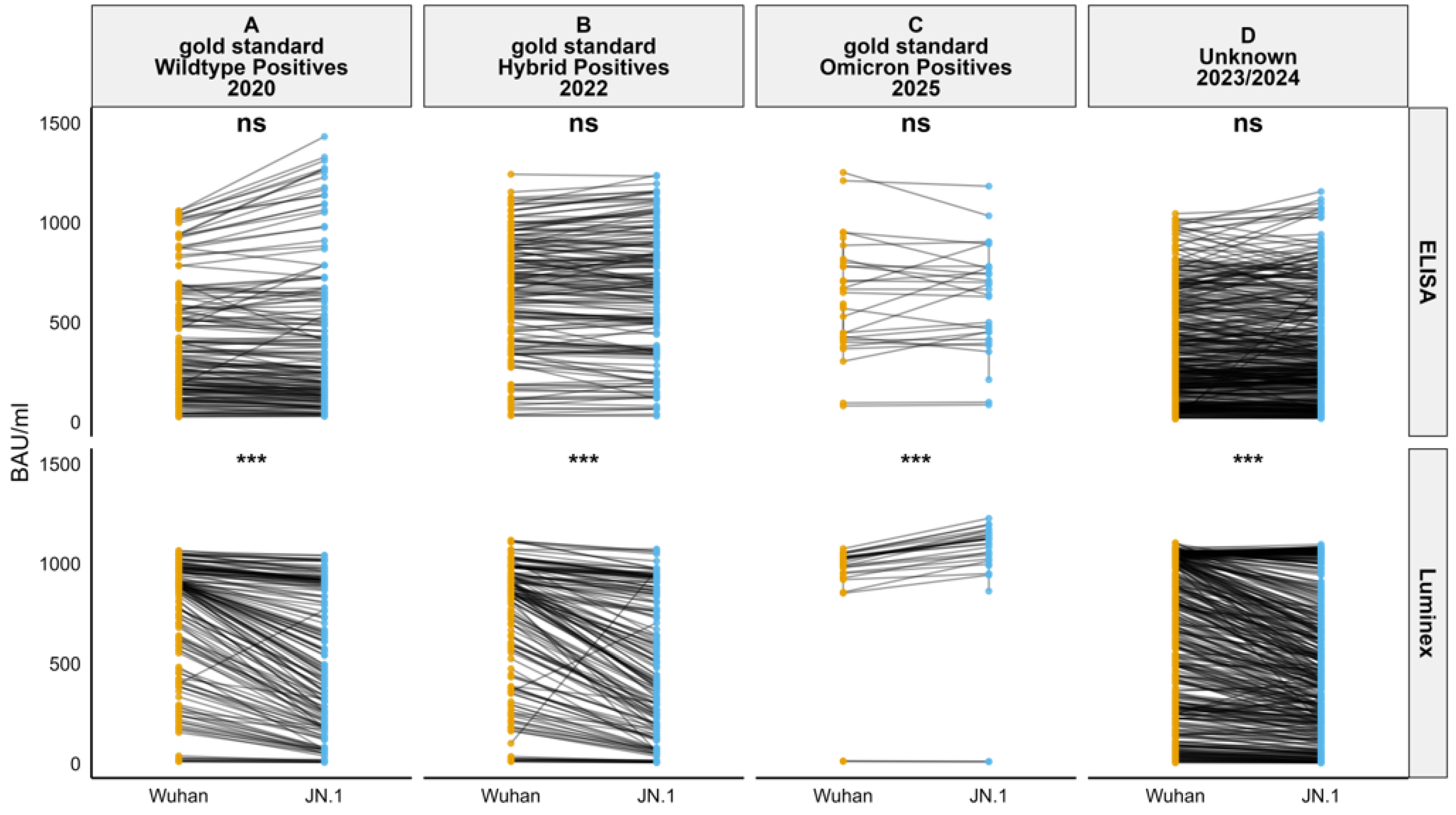
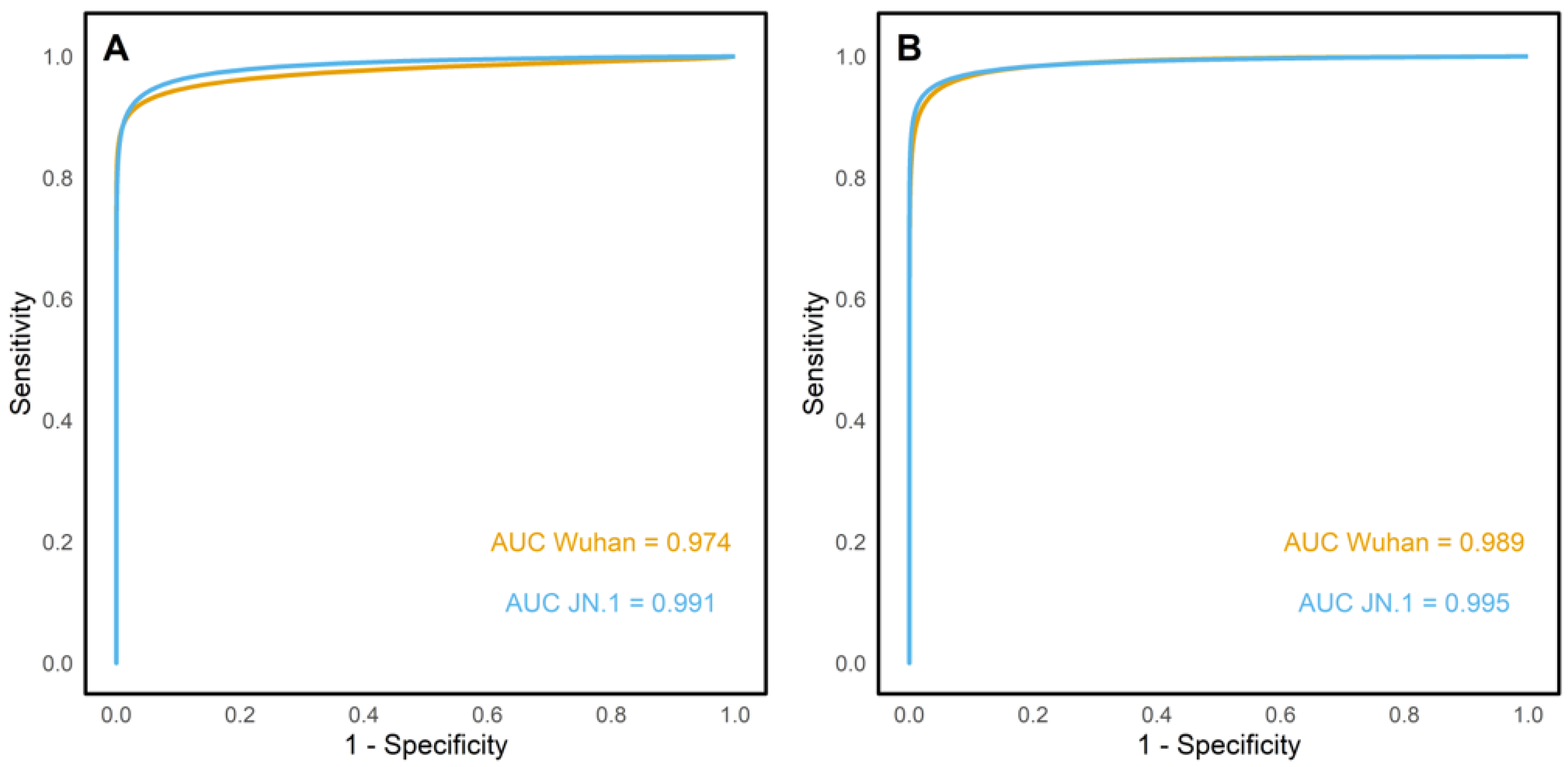
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MFI | Mean Fluorescence Intensity |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| OD | Optical Density |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| BAU | Binding Antibody Units |
References
- Li, Z.; Yi, Y.; Luo, X.; Xiong, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, W.; et al. Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1518–1524. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jmv.25727 (accessed on 6 February 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Zhu, F.; Guo, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, T. Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1735–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.; Lindsley, A.; Courter, J.; Assa’ad, A. Clinical testing for COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Peng, H.; Sterling, S.M.; Walsh, R.M., Jr.; Rawson, S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Chen, B. Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science 2020, 369, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Mohammed, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, K.; Cheng, S.; Binder, R.A.; Mantis, N.J.; Crawford, J.M.; Okoye, N.; Braun, J.G.; Joung, S.; Wang, M.; Lozanski, G.; et al. Clinical Utility of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Testing and Defining a Correlate of Protection. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.A.; Lee, J.-H.; Brescia, P.B.; Kumar, D.; Nong, T.B.; Shih, R.; Woodle, E.S.; Maltzman, J.S.; Gebel, H.M. Development and Validation of a Multiplex, Bead-based Assay to Detect Antibodies Directed Against SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Transplantation 2021, 105, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Srivastava, Y.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Singh, S.K.; Verma, G.; Tiwari, S.; Tandel, N.; Beura, S.K.; Panigrahi, A.R.; Maji, S.; et al. Understanding Mutations in Human SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein: A Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2023, 15, 856. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, P.V.; Ghafari, M.; Beer, M.; Lythgoe, K.; Simmonds, P.; Stilianakis, N.I.; Katzourakis, A. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Xia, N.; Yuan, Q. Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants: Genetic Impact on Viral Fitness. Viruses 2024, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Consortium, C.-G.U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; De Marco, A.; Lempp, F.A.; Tortorici, M.A.; Pinto, D.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Chen, A.; Liu, Z.; Zatta, F.; et al. N-terminal domain antigenic mapping reveals a site of vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2021, 184, 2332–2347.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayou, L.; Prakash, S.; Vahed, H.; Dhanushkodi, N.R.; Quadiri, A.; Belmouden, A.; Lemkhente, Z.; Chentoufi, A.; Gil, D.; Ulmer, J.B.; et al. Dynamics of spike-specific neutralizing antibodies across five-year emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern reveal conserved epitopes that protect against severe COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1503954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wei, D.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Qu, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, E. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant to antibody neutralization elicited by booster vaccination. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hong, W.; Lei, H.; He, C.; Lei, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, T.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; et al. Low levels of neutralizing antibodies against XBB Omicron subvariants after BA.5 infection. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 252. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-023-01495-4 (accessed on 19 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Lugano, D.; Kutima, B.; Kimani, M.; Sigilai, A.; Gitonga, J.; Karani, A.; Akech, D.; Karia, B.; Ziraba, A.K.; Maina, A.; et al. Evaluation of population immunity against SARS-CoV-2 variants, EG.5.1, FY.4, BA.2.86, JN.1, JN.1.4, and KP.3.1.1 using samples from two health demographic surveillance systems in Kenya. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheward, D.J.; Kim, C.; Ehling, R.A.; Pankow, A.; Dopico, X.C.; Dyrdak, R.; Martin, D.P.; Reddy, S.T.; Dillner, J.; Hedestam, G.B.K.; et al. Neutralisation sensitivity of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) variant: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Woo, H.G. Omicron: A Heavily Mutated SARS-CoV-2 Variant Exhibits Stronger Binding to ACE2 and Potently Escapes Approved COVID-19 Therapeutic Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 830527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, D.N.; Perkmann, T.; Jani, C.M.; Mucher, P.; Prüger, K.; Marculescu, R.; Reuberger, E.; Camp, J.V.; Graninger, M.; Borsodi, C.; et al. Reduced Sensitivity of Commercial Spike-Specific Antibody Assays after Primary Infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Microbiol. Spectrum. 2022, 10, e02129-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statement on the Antigen Composition of COVID-19 Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/23-12-2024-statement-on-the-antigen-composition-of-covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Uyoga, S.; Adetifa, I.M.O.; Karanja, H.K.; Nyagwange, J.; Tuju, J.; Wanjiku, P.; Aman, R.; Mwangangi, M.; Amoth, P.; Kasera, K.; et al. Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in Kenyan blood donors. Science 2021, 371, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyagwange, J.; Kutima, B.; Mwai, K.; Karanja, H.K.; Gitonga, J.N.; Mugo, D.; Uyoga, S.; Tuju, J.; Ochola-Oyier, L.I.; Ndungu, F.; et al. Comparative performance of WANTAI ELISA for total immunoglobulin to receptor binding protein and an ELISA for IgG to spike protein in detecting SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Kenyan populations. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 146, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagucia, E.W.; Ziraba, A.K.; Nyagwange, J.; Kutima, B.; Kimani, M.; Akech, D.; Ng’ODa, M.; Sigilai, A.; Mugo, D.; Karanja, H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and implications for population immunity: Evidence from two Health and Demographic Surveillance System sites in Kenya, February–December 2022. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössler, A.; Knabl, L.; Raschbichler, L.-M.; Peer, E.; von Laer, D.; Borena, W.; Kimpel, J. Reduced sensitivity of antibody tests after omicron infection. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e10–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.P.; Huang, Y.; Nguyen, A.W.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Olaluwoye, O.S.; Kaoud, T.S.; Wilen, E.R.; Qerqez, A.N.; Park, J.-G.; Khalil, A.M.; et al. Identification of a conserved S2 epitope present on spike proteins from all highly pathogenic coronaviruses. eLife 2023, 12, e83710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Su, S.-C.; Lin, H.-T.; Ke, F.-Y.; Liang, K.-H.; Hsu, F.-F.; Kumari, M.; Fu, C.-Y.; Wu, H.-C. Monoclonal antibodies against S2 subunit of spike protein exhibit broad reactivity toward SARS-CoV-2 variants. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Ratnasri, K.; Valloly, P.; Sharma, R.; Maurya, S.; Gaigore, A.; Ardhya, C.; Biligi, D.S.; Desiraju, B.K.; Natchu, U.C.M.; et al. Evaluation of spike protein antigens for SARS-CoV-2 serology. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 296, 114222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, G.; Zhang, D.; Lu, D.; Changxin, W. Evaluation of IgG binding capability to SARS-CoV-2 variants in early COVID-19 convalescent sera using an indirect ELISA. Virus Res. 2025, 352, 199520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthning, D.; Raafat, D.; Holtfreter, S.; Gramenz, J.; Wittmann, N.; Bröker, B.M.; Meyer-Bahlburg, A. Variant-specific antibody profiling for tracking SARS-CoV-2 variant infections in children and adolescents. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1434291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Population | N | Date | Location | Participant Group | Timeline | Designation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult blood donors | 160 | 2018 | Coastal Kenya | Adults investigated for blood transfusion safety | No previous SARS-CoV-2 infection | Gold standard negatives |
| SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive cohort | 160 | 2020 | Nairobi | Adults with wildtype confirmed sequences | Collected ≥7 days and <120 days after PCR positive diagnosis | Gold standard wildtype positives |
| Nairobi HDSS vaccinated | 160 | 2022 | Nairobi | Adults and children investigated for SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence | Median 271 days post vaccination; previous exposure possible but timing unknown | Gold standard hybrid positives |
| Kilifi HDSS | 32 | 2025 | Kilifi | Adults with omicron-confirmed sequences | Collected ≤3 months post infection | Gold standard omicron positives |
| Kilifi household samples | 400 | 2023/24 | Kilifi | Adults and children investigated for respiratory viruses’ reinfection | No records for infection or vaccination | Unknowns |
| Wuhan Luminex/ELISA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Total | ||
| JN.1 Luminex/ELISA | Negative | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Positive | 0 | 30 | 30 | |
| Total | 2 | 30 | 32 | |
| Negatives | Positives | Total | Cohen’s Kappa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JN.1 ELISA | |||||
| Wuhan ELISA | Negatives | 178 (35%) | 4 (0.8%) | 182 (35.8%) | 0.94 |
| Positives | 9 (1.8%) | 321 (62.7%) | 330 (64.2%) | ||
| Total | 187 (36.8%) | 325 (63.5%) | 512 (100%) | ||
| JN.1 Luminex | |||||
| Wuhan Luminex | Negatives | 174 (34%) | 1 (0.2%) | 175 (34.2%) | 0.98 |
| Positives | 3 (0.6%) | 334 (65.2%) | 337 (65.8%) | ||
| Total | 177 (34.6%) | 335 (65.4%) | 512 (100%) | ||
| Wuhan Luminex | |||||
| Wuhan ELISA | Negatives | 168 (32.8%) | 14 (2.7%) | 182 (35.5%) | 0.91 |
| Positives | 7 (1.4%) | 323 (63.1%) | 330 (64.5%) | ||
| Total | 175 (34.2%) | 337 (65.8%) | 512 (100%) | ||
| JN.1 Luminex | |||||
| JN.1 ELISA | Negatives | 168 (32.8%) | 19 (3.7%) | 187 (36.5%) | 0.88 |
| Positives | 9 (1.8%) | 316 (61.7%) | 325 (63.5%) | ||
| Total | 177 (38.5%) | 335 (61.5%) | 512 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waweru, G.; Nyakundi, R.; Kutima, B.; Owuor, S.; Konyino, G.; Gitonga, J.; Lugano, D.; Maina, A.; Musyoki, J.; Ochola, L.; et al. Assessing the Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations on Antibody Binding: A Comparative Assessment of the Wuhan and JN.1 Variants’ Full-Length Spikes in a Multiplex Luminex Assay. Viruses 2025, 17, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091248
Waweru G, Nyakundi R, Kutima B, Owuor S, Konyino G, Gitonga J, Lugano D, Maina A, Musyoki J, Ochola L, et al. Assessing the Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations on Antibody Binding: A Comparative Assessment of the Wuhan and JN.1 Variants’ Full-Length Spikes in a Multiplex Luminex Assay. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091248
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaweru, Gerald, Ruth Nyakundi, Bernadette Kutima, Sharon Owuor, Gloria Konyino, John Gitonga, Doreen Lugano, Angela Maina, Jennifer Musyoki, Lucy Ochola, and et al. 2025. "Assessing the Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations on Antibody Binding: A Comparative Assessment of the Wuhan and JN.1 Variants’ Full-Length Spikes in a Multiplex Luminex Assay" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091248
APA StyleWaweru, G., Nyakundi, R., Kutima, B., Owuor, S., Konyino, G., Gitonga, J., Lugano, D., Maina, A., Musyoki, J., Ochola, L., Omondi, M., Kariuki, C. K., Ogongo, P., Mwachari, C., Shee, F., Agoti, C., Sande, C., Uyoga, S., Kagucia, E., ... Nyagwange, J. (2025). Assessing the Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations on Antibody Binding: A Comparative Assessment of the Wuhan and JN.1 Variants’ Full-Length Spikes in a Multiplex Luminex Assay. Viruses, 17(9), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091248






