Neurocognitive Impairment in ART-Experienced People Living with HIV: An Analysis of Clinical Risk Factors, Injection Drug Use, and the sCD163
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Recruitment of PLHIV, and Data Collection
2.2. Blood Collection and HIV Recency Testing
2.3. IHDS-Based Neurocognitive Impairment (NCI) Screening
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for sCD163
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PLHIV Characteristics and Recency Testing
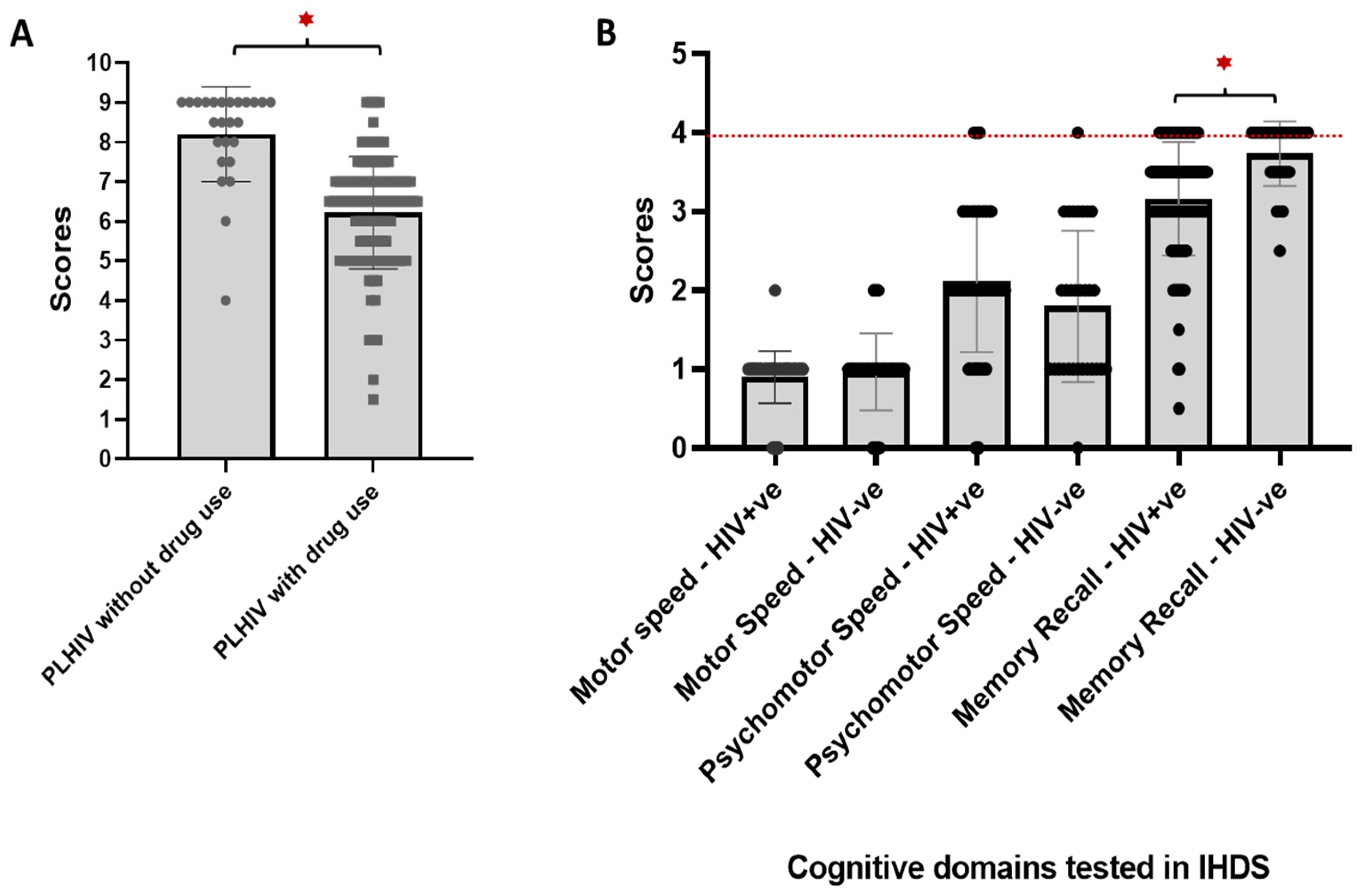
3.2. Prevalence of Neurocognitive Impairment Among Study Subjects
3.3. Comparison of Clinical and Sociodemographic Data Among PLHIV with and Without Neurocognitive Impairment
3.4. Correlates of Neurocognitive Impairment Among PLHIV
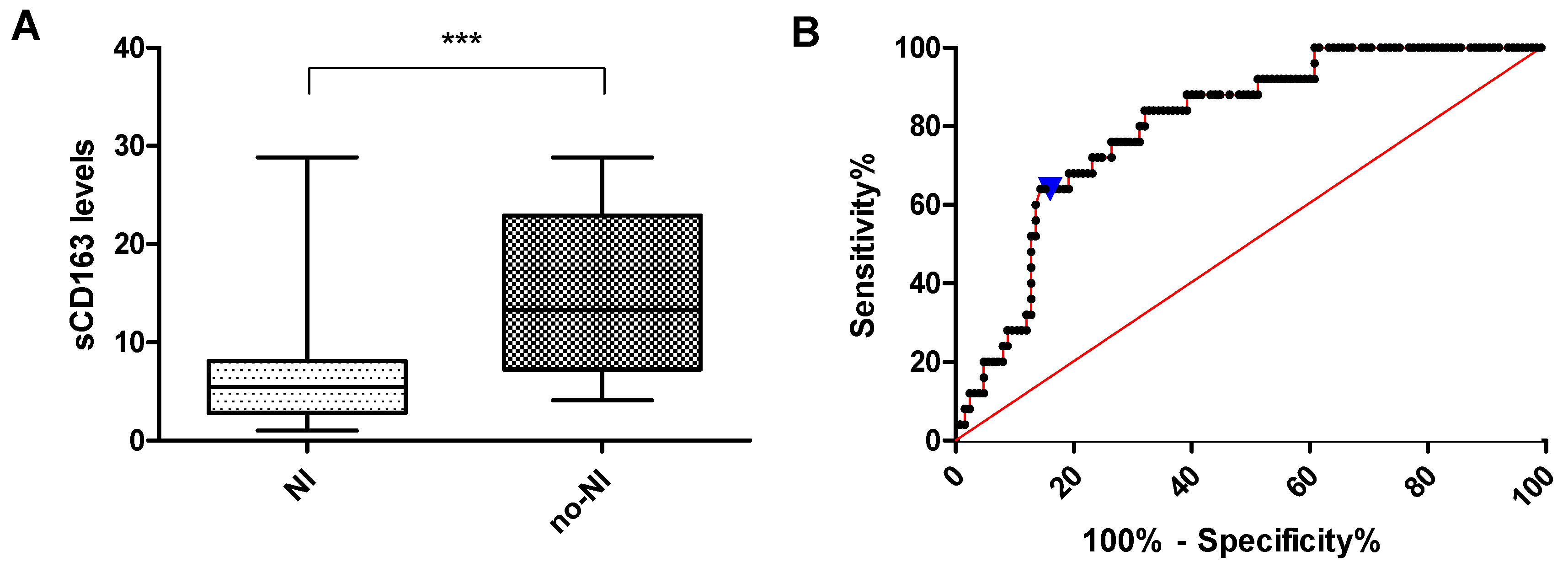
3.5. sCD163 Levels in PLHIV with and Without Neurocognitive Impairment
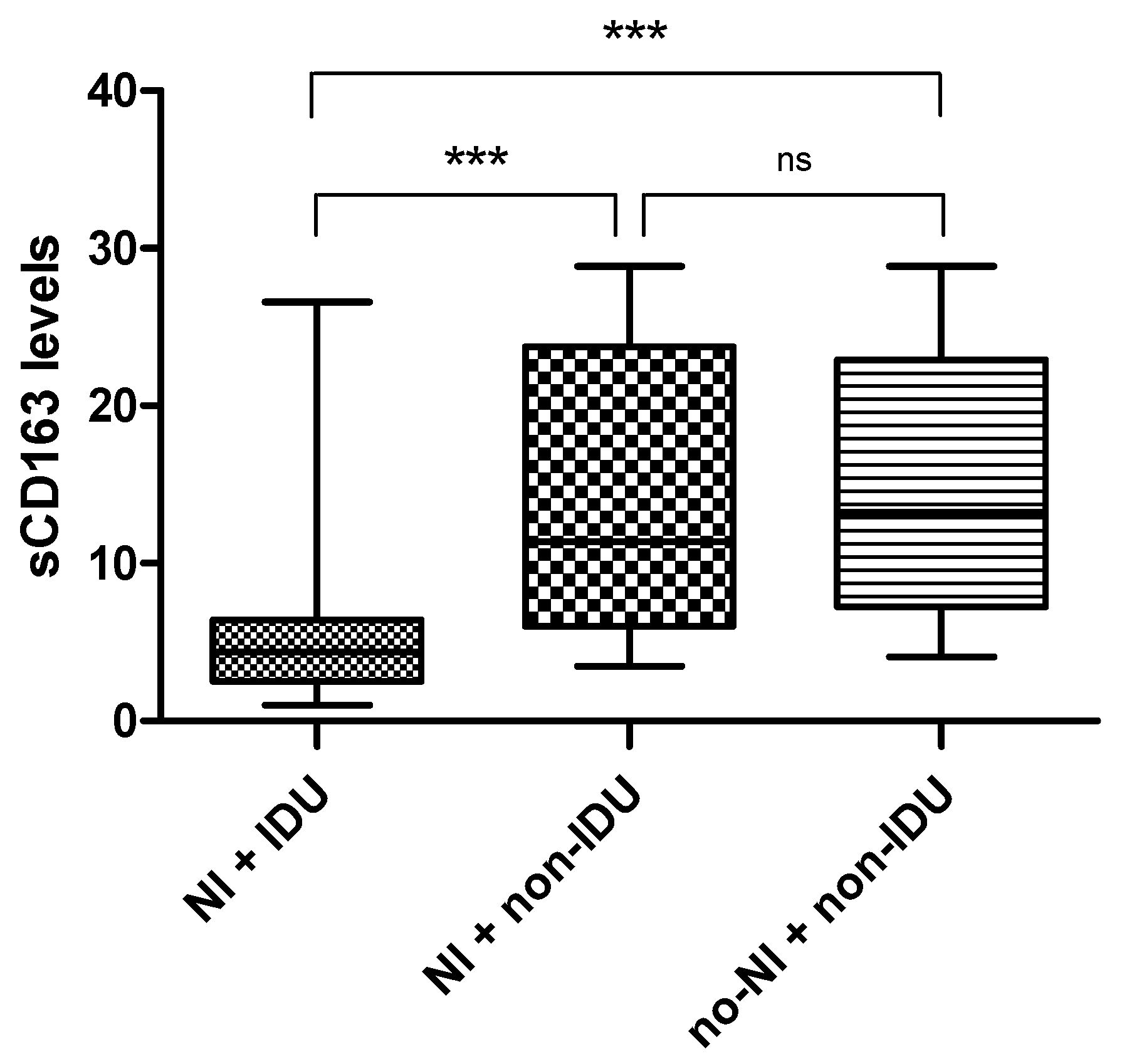
3.6. Association Between sCD163 Levels, IDU History, and Neurocognitive Impairment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buonaguro, L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype distribution in the worldwide epidemic: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10209–10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedema, F.; Hazenberg, M.D.; Tesselaar, K.; van Baarle, D.; de Boer, R.J.; Borghans, J.A.M. Immune activation and collateral damage in AIDS pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinori, A.; Arendt, G.; Becker, J.T.; Brew, B.J.; Byrd, D.A.; Cherner, M.; Clifford, D.B.; Cinque, P.; Epstein, L.G.; Goodkin, K.; et al. Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology 2007, 69, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassel, N.; Shaw, S.A.; Dasgupta, A.; Strathdee, S.A. Drug use as a driver of HIV risks: Re-emerging and emerging issues. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.R.; Ruiz, A.P.; Prasad, V.R. Viral and cellular factors underlying neuropathogenesis in HIV associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). AIDS Res. Ther. 2014, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenebe, Y.; Necho, M.; Yimam, W.; Akele, B. Worldwide Occurrence of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders and Its Associated Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 814362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debalkie Animut, M.; Sorrie, M.B.; Birhanu, Y.W.; Teshale, M.Y.; Cysique, L.A. High prevalence of neurocognitive disorders observed among adult people living with HIV/AIDS in Southern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0204636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yideg Yitbarek, G.; Mossie Ayana, A.; Bariso Gare, M.; Garedew Woldeamanuel, G. Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment and Its Predictors among HIV/AIDS Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in Jimma University Medical Center, Southwest Ethiopia. Psychiatry J. 2019, 2019, 8306823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilunda, V.; Calderon, T.M.; Martinez-Aguado, P.; Berman, J.W. The impact of substance abuse on HIV-mediated neuropathogenesis in the current ART era. Brain Res. 2019, 1724, 146426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayegi-Nik, S.; Honer, W.G.; Vila-Rodriguez, F.; Nanditha, N.G.A.; Patterson, T.L.; Guillemi, S.; Nathani, H.; Trigg, J.; Yin, W.; Fonseca, A.; et al. Incidence and contributing factors of dementia among people living with HIV in British Columbia, Canada, from 2002 to 2016: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Public Health 2024, 2, e000627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J.A.; Campa, A.; Martinez, S.S.; Li, T.; Sherman, K.E.; Zarini, G.; Meade, C.S.; Mandler, R.N.; Baum, M.K. Cognitive Impairment among People Who Use Heroin and Fentanyl: Findings from the Miami Adult Studies on HIV (MASH) Cohort. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2020, 53, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.-S.; Li, Y.-H.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, N.; Bechara, A.; Sui, N. Working memory and affective decision-making in addiction: A neurocognitive comparison between heroin addicts, pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 134, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.E.; Ipser, J.C.; Stein, D.J.; Joska, J.A.; Naudé, P.J.W. Peripheral immune dysregulation in the ART era of HIV-associated neurocognitive impairments: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 118, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdo, T.H.; Weiffenbach, A.; Woods, S.P.; Letendre, S.; Ellis, R.J.; Williams, K.C. Elevated sCD163 in plasma but not cerebrospinal fluid is a marker of neurocognitive impairment in HIV infection. AIDS 2013, 27, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imp, B.M.; Rubin, L.H.; Tien, P.C.; Plankey, M.W.; Golub, E.T.; French, A.L.; Valcour, V.G. Monocyte Activation Is Associated With Worse Cognitive Performance in HIV-Infected Women With Virologic Suppression. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, A.K.; Moore, D.J.; Burdo, T.H.; Lakritz, J.R.; Gouaux, B.; Soontornniyomkij, V.; Achim, C.L.; Masliah, E.; Grant, I.; Levine, A.J.; et al. Plasma soluble CD163 is associated with postmortem brain pathology in human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS 2017, 31, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.F.; Murrell, B.; Pérez-Santiago, J.; Vargas, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Letendre, S.; Grant, I.; Smith, D.M.; Woods, S.P.; Gianella, S. Circulating HIV DNA Correlates With Neurocognitive Impairment in Older HIV-infected Adults on Suppressive ART. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Long, J.; Feng, Q.; Wang, R.; Su, L.; Zhao, T.; Wei, B. Diagnostic accuracy of the International HIV Dementia Scale and HIV Dementia Scale: A meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 4, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, M.; Sacktor, N.; Nakigozi, G.; Anok, A.; Batte, J.; Kisakye, A.; Myanja, R.; Nakasujja, N.; Robertson, K.R.; Gray, R.H.; et al. Utility of the International HIV Dementia Scale for HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2020, 83, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Abidi, S.H.; Soomro, A.A.; Farooqui, N.; Ansari, T.; Khanani, R. Evaluation of the Training Program to Train HIV Treatment Center Staff in Pakistan. Cureus 2024, 16, e61972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidi, S.H.; Nduva, G.M.; Siddiqui, D.; Rafaqat, W.; Mahmood, S.F.; Siddiqui, A.R.; Nathwani, A.A.; Hotwani, A.; Shah, S.A.; Memon, S.; et al. Phylogenetic and Drug-Resistance Analysis of HIV-1 Sequences From an Extensive Paediatric HIV-1 Outbreak in Larkana, Pakistan. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 658186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, D.; Badar, U.; Javaid, M.; Farooqui, N.; Shah, S.A.; Iftikhar, A.; Sultan, F.; Mir, F.; Furqan, S.; Mahmood, S.F.; et al. Genetic and antiretroviral drug resistance mutations analysis of reverse transcriptase and protease gene from Pakistani people living with HIV-1. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, U.; Nazziwa, J.; Sasinovich, S.; Shah, S.A.; Naeem, S.; Abidi, S.H.; Esbjörnsson, J. Phylogenetic Characterization of HIV-1 Sub-Subtype A1 in Karachi, Pakistan. Viruses 2022, 14, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Kang, L.; Yi, F.; Chu, Q.; Shah, S.A.; Mahmood, S.F.; Getaneh, Y.; Wei, M.; Chang, S.; Abidi, S.H.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Genetic Diversity and Drugs Resistance Mutations among People Living with HIV in Karachi, Pakistan. Viruses 2024, 16, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Feaster, D.J.; Kizhner, A.; Forrest, D.W.; Nakamura, N.; Iyer, A.; Ghanta, P.P.; Jayaweera, D.T.; Rodriguez, A.E.; et al. Opioids exacerbate inflammation in people with well-controlled HIV. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1277491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hileman, C.O.; Bowman, E.R.; Gabriel, J.; Kettelhut, A.; Labbato, D.; Smith, C.; Avery, A.; Parran, T.; Funderburg, N.; McComsey, G.A. Impact of Heroin and HIV on Gut Integrity and Immune Activation. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2022, 89, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebe, E.; Facente, S.; Hampton, D.; Cheng, C.; Owen, R.; Keating, S. Asanté™ HIV-1 Rapid Recency® Assay Evaluation Report, Version 1.0; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Facente, S.N.; Grebe, E.; Maher, A.D.; Fox, D.; Scheer, S.; Mahy, M.; Dalal, S.; Lowrance, D.; Marsh, K. Use of HIV Recency Assays for HIV Incidence Estimation and Other Surveillance Use Cases: Systematic Review. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022, 8, e34410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yufenyuy, E.L.; Detorio, M.; Dobbs, T.; Patel, H.K.; Jackson, K.; Vedapuri, S.; Parekh, B.S.; Shin, S. Performance evaluation of the Asante Rapid Recency Assay for verification of HIV diagnosis and detection of recent HIV-1 infections: Implications for epidemic control. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2022, 2, e0000316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacktor, N.C.; Wong, M.; Nakasujja, N.; Skolasky, R.L.; Selnes, O.A.; Musisi, S.; Robertson, K.; McArthur, J.C.; Ronald, A.; Katabira, E. The International HIV Dementia Scale: A new rapid screening test for HIV dementia. AIDS Behav. 2005, 19, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Joska, J.A.; Witten, J.; Thomas, K.G.; Robertson, C.; Casson-Crook, M.; Roosa, H.; Creighton, J.; Lyons, J.; McArthur, J.; Sacktor, N.C. A Comparison of Five Brief Screening Tools for HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders in the USA and South Africa. AIDS Behav. 2016, 20, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, J.J.; Bosch, R.J.; Benson, C.A.; Collier, A.C.; Robbins, G.K.; Shafer, R.W.; Hughes, M.D. Long-term increase in CD4+ T-cell counts during combination antiretroviral therapy for HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2010, 24, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meintjes, W.; Van Wijk, C. International HIV Dementia Scale: Screening for HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders in Oc-cupational Settings. Occup. Health South. Afr. (Online) 2015, 21, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, C.C.; Treisman, G.J. Cognitive impairment in patients with AIDS–prevalence and severity. HIV AIDS 2015, 7, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Webb, V.; Jessen, H.; Kopp, U.; Jessen, A.B.; Hahn, K. Validation of the International HIV Dementia Scale as a Screening Tool for HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders in a German-Speaking HIV Outpatient Clinic. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y. Neurological manifestations of HIV/AIDS to tertiary care hospital in KP, Peshawar, Pakistan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, P.M.; Bilal, M.; Khan, Y. Frequency of Common Neurological Manifestations among Patients Presenting with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Positivity. J. Saidu Med. Coll. 2022, 12, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Springer, S.A.; Copenhaver, M.M.; Altice, F.L. Neurocognitive impairment and HIV risk factors: A reciprocal relationship. AIDS Behav. 2010, 14, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.A.; Zerbo, E. HIV-related neurocognitive disorders and drugs of abuse: Mired in confound, surrounded by risk. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2014, 1, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorder: Pathophysiology in relation to drug addiction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1187, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.; Haq, M.M.U.; Khan, A.; Naeem, S.; Hussain, I.; Shafiullah, M. Pattern of Drugs Misuse among Patients attending Iftikhar Psychiatric Hospital, Peshawar. J. Saidu Med. Coll. 2020, 10, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallhi, T.H.; Khan, Y.H.; Khan, A.; Alotaibi, N.H.; Alzarea, A.I.; Hashmi, F.K. The association of HIV and easy access to narcotics in Pakistan; calling drug policy makers. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.A.; Brown, G.G. HIV-associated executive dysfunction in the era of modern antiretroviral therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2018, 40, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.W.; Proskovec, A.L.; Heinrichs-Graham, E.; O’nEill, J.; Robertson, K.R.; Fox, H.S.; Swindells, S. Aberrant Neuronal Dynamics during Working Memory Operations in the Aging HIV-Infected Brain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, E.A.; Greenwald, M.K.; Chen, I.; Feng, D.; Cohn, J.A.; Lundahl, L.H. HIV chronicity as a predictor of hippocampal memory deficits in daily cannabis users living with HIV. Drug Alcohol Depend. Rep. 2023, 9, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Santerre, M.; Tempera, I.; Martin, K.; Mukerjee, R.; Sawaya, B.E. HIV-1 Vpr disrupts mitochondria axonal transport and accelerates neuronal aging. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, W.D.; Paris, J.J.; Barbour, A.J.; Moon, J.; Carpenter, V.J.; McLane, V.D.; Lark, A.R.S.; Nass, S.R.; Zhang, J.; Yarotskyy, V.; et al. HIV-1 Tat and Morphine Differentially Disrupt Pyramidal Cell Structure and Function and Spatial Learning in Hippocampal Area CA1: Continuous versus Interrupted Morphine Exposure. eNeuro 2021, 8, ENEURO.0547–20.2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elendu, C.; Aguocha, C.M.; Okeke, C.V.; Okoro, C.B.; Peterson, J.C. HIV-related neurocognitive disorders: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Mental Health Implications: A Review. Medicine 2023, 102, e35652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, H.L.; Alagaratnam, J.; Chan, P.; Chow, F.C.; Joska, J.; Falutz, J.; Letendre, S.L.; Lin, W.; Muñoz-Moreno, J.A.; Cinque, P.; et al. Cognitive Health in Persons With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: The Impact of Early Treatment, Comorbidities, and Aging. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227 (Suppl. S1), S38–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Lu, P.-L.; Yang, Y.-H.; Feng, M.-C. Prevalence and the associated factors of cognitive impairment among people living with HIV in Taiwan: A cross-sectional study. AIDS Care 2023, 35, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Fulcher, J.A.; Roach, M.E.; Dilworth, S.E.; Chahine, A.; Pallikkuth, S.; Fuchs, D.; Pahwa, S.; Carrico, A.W. Getting to the point: Methamphetamine injection is associated with biomarkers relevant to HIV pathogenesis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 213, 108133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, M.L.; Nguyen, T.; Uebelhoer, L.S.; Kunkel, L.E.; Korthuis, P.T.; Lancioni, C.L. Altered monocyte phenotype and dysregulated innate cytokine responses among people living with HIV and opioid-use disorder. AIDS 2020, 34, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, K.E.; Meeds, H.L.; Rouster, S.D.; Abdel-Hameed, E.A.; Hernandez, J.; Tamargo, J.; Chen, J.; Ehman, R.L.; Baum, M. Soluble CD163 Identifies Those at Risk for Increased Hepatic Inflammation & Fibrosis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, R.; Morsey, B.; Boyer, C.W.; Fox, H.S.; Sarvetnick, N.; Ho, W. Methamphetamine administration targets multiple immune subsets and induces phenotypic alterations suggestive of immunosuppression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallóczy, Z.; Martinez, J.; Joset, D.; Ray, Y.; Gácser, A.; Toussi, S.; Mizushima, N.; Nosanchuk, J.; Goldstein, H.; Loike, J.; et al. Methamphetamine inhibits antigen processing, presentation, and phagocytosis. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, G.-F.; Jia, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.-R.; Kong, D.; Lu, D.; Li, Y.; Peng, Q.-Y.; Yu, J.; et al. Dynamics and correlations in multiplex immune profiling reveal persistent immune inflammation in male drug users after withdrawal. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, D.J.; Boretti, F.S.; Schoedon, G.; Schaffner, A. Induction of the CD163-dependent haemoglobin uptake by macrophages as a novel anti-inflammatory action of glucocorticoids. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 119, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechler, C.; Ritter, M.; Orsó, E.; Langmann, T.; Klucken, J.; Schmitz, G. Regulation of scavenger receptor CD163 expression in human monocytes and macrophages by pro- and antiinflammatory stimuli. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleissner, C.A.; Shaked, I.; Erbel, C.; Böckler, D.; Katus, H.A.; Ley, K. CXCL4 downregulates the atheroprotective hemoglobin receptor cd163 in human macrophages. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiong, P.; Xie, Z.; Ding, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, K. Dynamic immune and exosome transcriptomic responses in patients undergoing psychostimulant methamphetamine withdrawal. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 961131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosein, M.; Saylor, D.; Nakigozi, G.; Nakasujja, N.; Kong, X.; Robertson, K.; Wawer, M.J.; Gray, R.H.; Sacktor, N. 453. Validation of the International HIV Dementia Scale Screening Tool for HAND in Uganda. In Proceedings of the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), Seattle, WA, USA, 23–26 February 2015; Available online: https://www.croiconference.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/posters/2015/453.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Atashili, J.; Gaynes, B.N.; Pence, B.W.; Tayong, G.; Kats, D.; O’donnell, J.K.; Ndumbe, P.M.; Njamnshi, A.K. Prevalence, characteristics and correlates of a positive-dementia screen in patients on antiretroviral therapy in Bamenda, Cameroon: A cross-sectional study. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, A.J.; Mburu, G.; Welton, N.J.; May, M.T.; Davies, C.F.; French, C.; Turner, K.M.; Looker, K.J.; Christensen, H.; McLean, S.; et al. Impact of Opioid Substitution Therapy on Antiretroviral Therapy Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Rivero, I.; Madoz-Gurpide, A.; Parro-Torres, C.; Hernandez-Huerta, D.; Ochoa Mangado, E. Influence of substance use and cognitive impairment on adherence to antiretroviral therapy in HIV+ patients. Adicciones. Adicciones 2018, 32, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, J.; Qureshi, S.U.H.; Zafar, M.; Busz, M.; Maher, L. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV positive men who inject drugs in Pakistan. Int. J. Drug Policy 2021, 96, 103281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergenova, G.; Davis, A.; Gilbert, L.; El-Bassel, N.; Terlikbayeva, A.; Primbetova, S.; Nugmanova, Z.; Pala, A.N.; Gustafson, D.; Rosenthal, S.L.; et al. Mental health and cognition in relation to adherence to antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV in Kazakhstan: A cross-sectional study. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2024, 27 (Suppl. S3), e26320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmbhatt, H.; Boivin, M.; Ssempijja, V.; Kagaayi, J.; Kigozi, G.; Serwadda, D.; Violari, A.; Gray, R.H. Impact of HIV and Atiretroviral Therapy on Neurocognitive Outcomes Among School-Aged Children. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable (PLHIV) | Median (IQR 25 to 75% Percentile) |
|---|---|
| Age | 34.5 (30–41) |
| ART duration (months) | 35 (17–54) |
| Viral load (copies/mL) | 124 (26.5–686.5) |
| CD4 count (cells/µL) | 326.5 (116–545.5) |
| Variable (PLHIV) | N (%) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 142 (94.7%) |
| Female | 8 (5.3%) |
| Recency testing | |
| Recent infection | 25 (16.7%) |
| Long-Term Infection | 125 (83.3%) |
| Risk factors or underlying conditions | |
| TB | 5 (3.33%) |
| Chronic Diarrhea | 2 (1.33%) |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 1 (0.67%) |
| Pneumocystis Pneumonia | 2 (1.33%) |
| Syphilis | 1 (0.67%) |
| Injection Drug Use | 100 (66.67%) |
| None | 39 (26.00%) |
| Variable (Controls) | |
| Age | Median (IQR): 36.5 (33.75–40.75) |
| Gender (male) | N(%): 30 (100%) |
| HIV status (negative) | N(%): 30 (100%) |
| Risk factors or underlying conditions | |
| Injection Drug Use | N(%): 30 (100%) |
| Variable | OR | 95%CI (Lower-Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.87 | 0.53–1.43 | 0.59 |
| ART Duration (months) | 0.92 | 0.32–2.71 | 0.89 |
| Infection duration (long-term) | 2.99 | 1.12–7.99 | 0.03 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.Z.; Amin, F.; Farooqui, N.; Omarova, Z.; Mahmood, S.F.; Khan, Q.u.a.; Naqvi, H.A.; Mumtaz, A.; Baig, S.; Khan, M.R.; et al. Neurocognitive Impairment in ART-Experienced People Living with HIV: An Analysis of Clinical Risk Factors, Injection Drug Use, and the sCD163. Viruses 2025, 17, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091232
Ahmed SZ, Amin F, Farooqui N, Omarova Z, Mahmood SF, Khan Qua, Naqvi HA, Mumtaz A, Baig S, Khan MR, et al. Neurocognitive Impairment in ART-Experienced People Living with HIV: An Analysis of Clinical Risk Factors, Injection Drug Use, and the sCD163. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091232
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Syed Zaryab, Faiq Amin, Nida Farooqui, Zhannur Omarova, Syed Faisal Mahmood, Qurat ul ain Khan, Haider A. Naqvi, Aida Mumtaz, Saeeda Baig, Muhammad Rehan Khan, and et al. 2025. "Neurocognitive Impairment in ART-Experienced People Living with HIV: An Analysis of Clinical Risk Factors, Injection Drug Use, and the sCD163" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091232
APA StyleAhmed, S. Z., Amin, F., Farooqui, N., Omarova, Z., Mahmood, S. F., Khan, Q. u. a., Naqvi, H. A., Mumtaz, A., Baig, S., Khan, M. R., Shah, S. A., Hassan, A., Bolla, S., Mushtaq, S., & Abidi, S. H. (2025). Neurocognitive Impairment in ART-Experienced People Living with HIV: An Analysis of Clinical Risk Factors, Injection Drug Use, and the sCD163. Viruses, 17(9), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091232






