Generation and Characterization of HDV-Specific Antisera with Respect to Their Application as Specific and Sensitive Research and Diagnostic Tools
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Protein Production and Purification
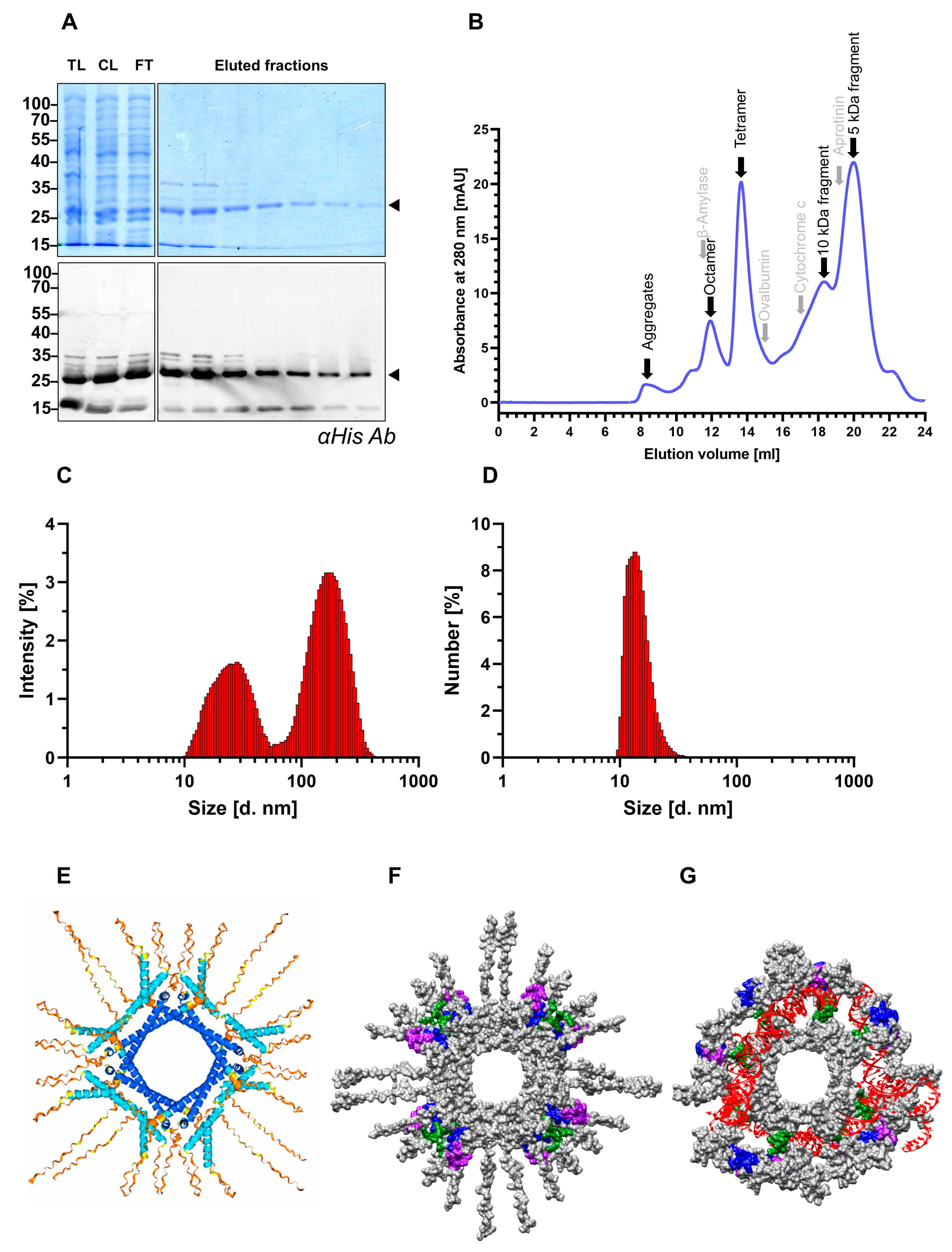
2.3. Analytical Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering Analysis
2.5. Structural Prediction
2.6. Immunization
2.7. Cell Cultivation and Transfection
2.8. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.9. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.10. Patient Sera and Ethics
2.11. Peptide Microarray
2.12. Surface Plasmon Resonance
2.13. Purification of Polyclonal HDAg-Specific Antibodies
2.14. RT-qPCR
2.15. ELISA Sample Preparation
2.16. ELISA Protocol
3. Results
3.1. Recombinant SHDAg Preserves Dynamic Multimeric Conformation Under Native Purification Conditions
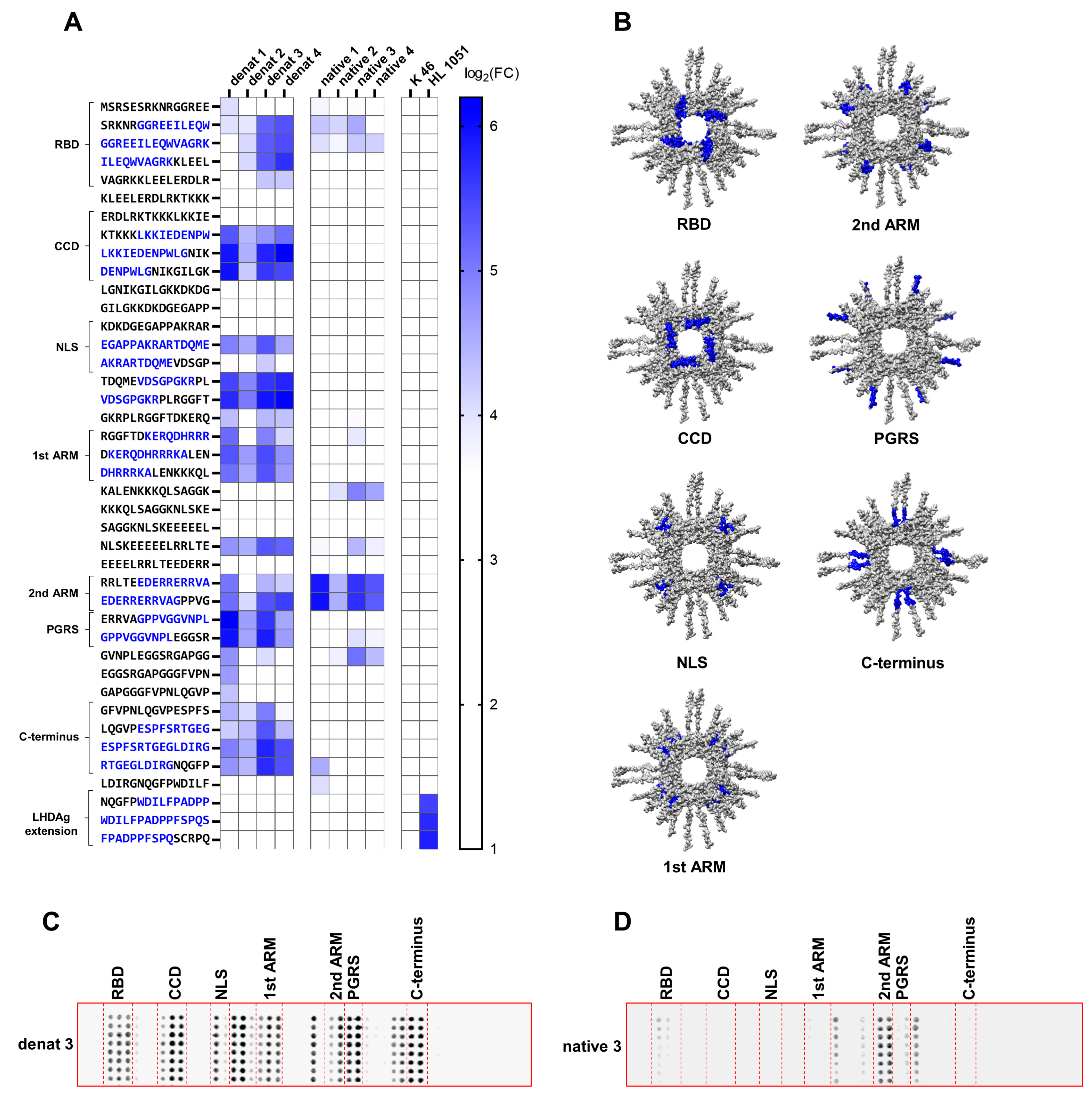
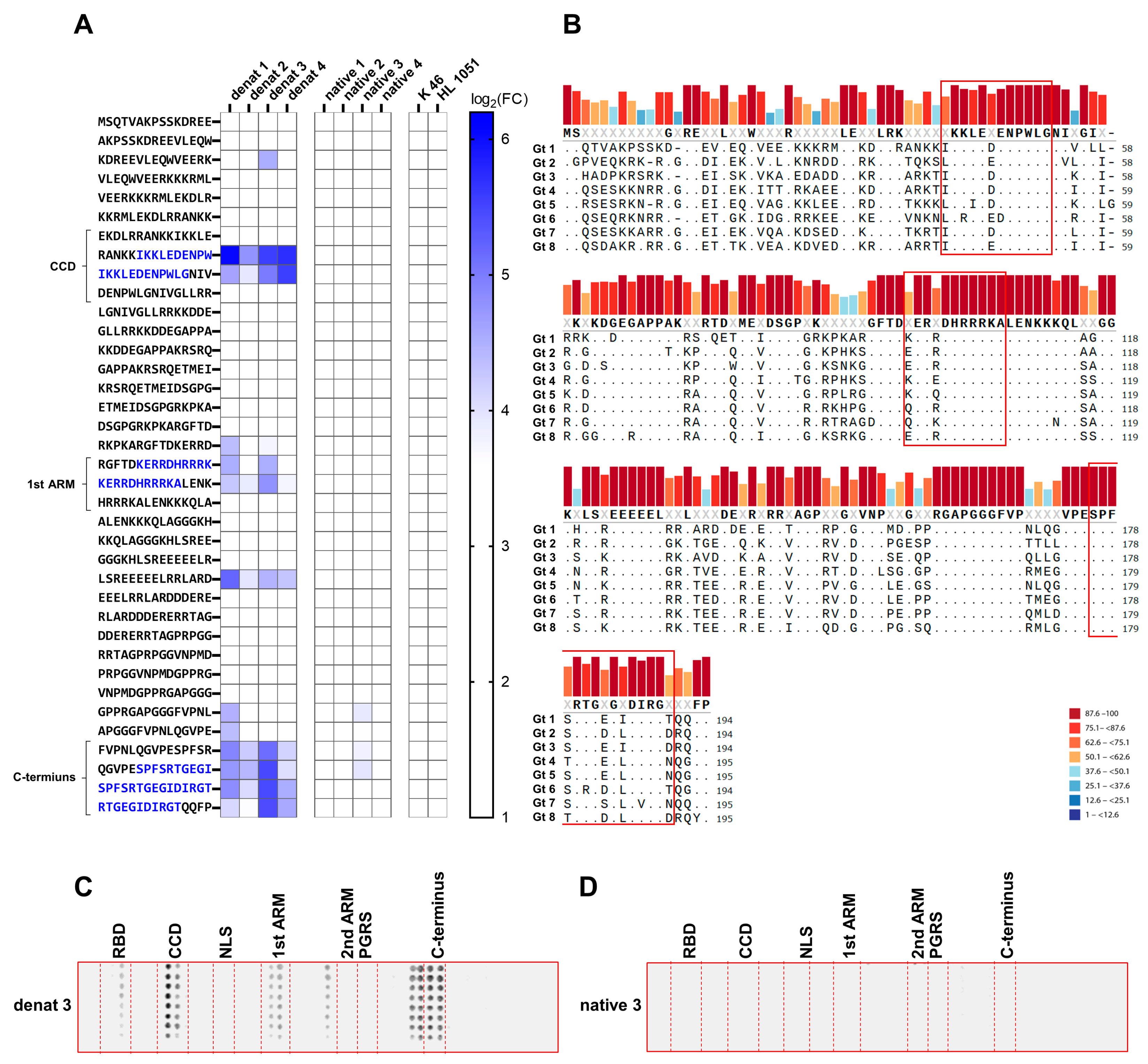
3.2. HDAg-Specific Antisera Show Major Differences in Their Binding Specificity
3.3. Distinct Immunogenic Epitopes Are Inaccessible During B-Cell Epitope Recognition in the Native Conformation of SHDAg
3.4. HDAg-Specific Antisera Show Pan-Genotypic Binding Capacity
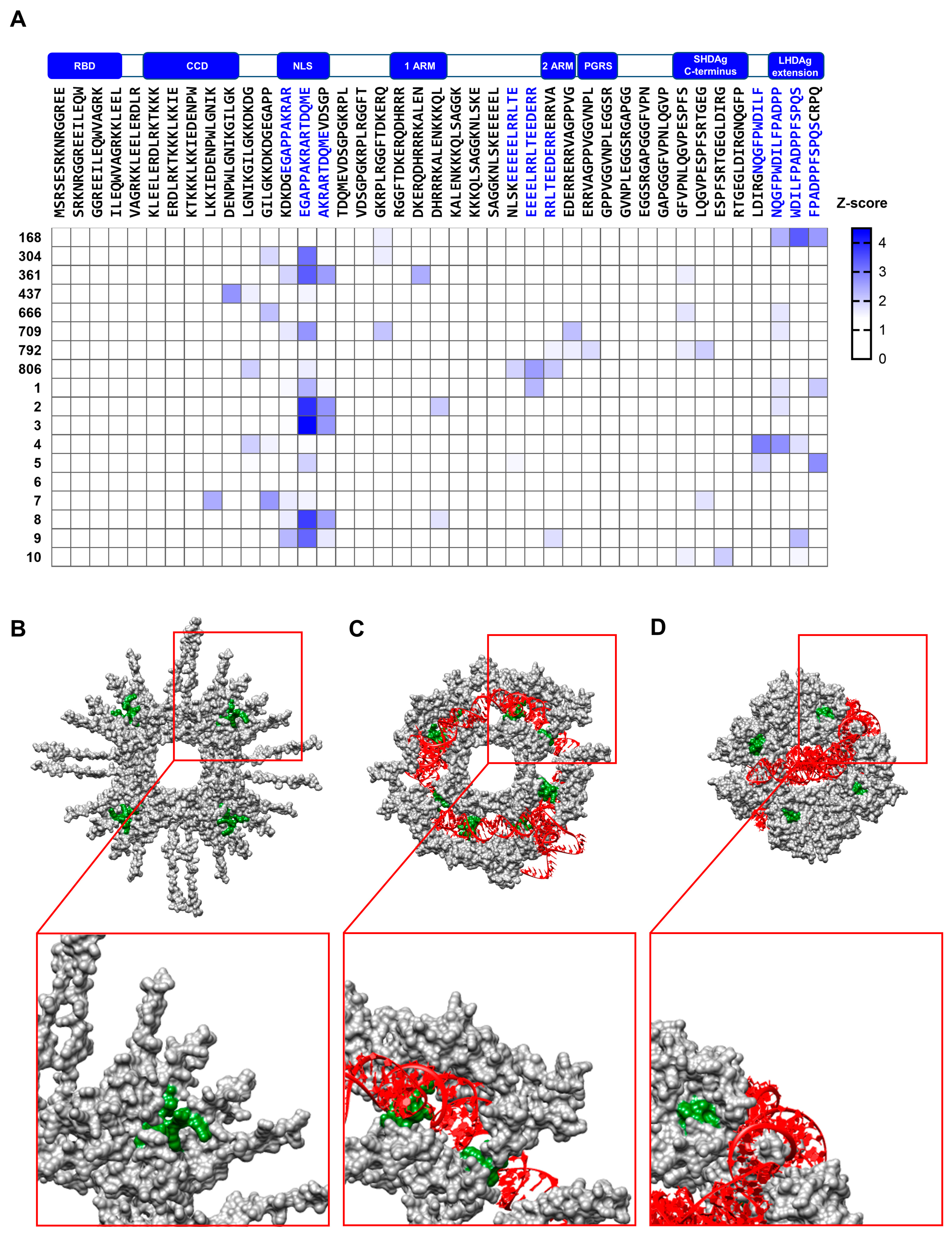
3.5. The NLS of HDAg Is a Prominent Target B-Cell Epitope in Chronically HDV-Infected Patients
3.6. HDAg-Specific Antisera Bind with High Affinity to the Target Antigen, Making Them Suitable for ELISA-Based HDV Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARM | Arginine-rich motif |
| CCD | Coiled-coil domain |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| FC | Fold change |
| FI | Fluorescence intensities |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HDAg | Hepatitis delta antigen |
| HDV | Hepatitis D virus |
| His6 | Polyhistidine-tag |
| LHDAg | Large hepatitis delta antigen |
| NLS | Nuclear localization signal |
| PGRS | Proline-glycine-rich sequence |
| pLDDT | Predicted local distance difference test |
| pt | Post-transfection |
| RBD | RNA binding domain |
| RNP | Ribonucleoprotein complex |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| SHDAg | Small hepatitis delta antigen |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| StII | Twin-Strep-tag II |
| v/v | Volume per volume |
| w/v | Weight per volume |
Appendix A
| Patient ID | Age | Gender | Therapy | HDV-RNA (Copies/mL) (qPCR) | HDAg (ng/mL) (ELISA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 168 | 35 | male | peg-IFNα-2a | 15,761 | N/A |
| 304 | 40 | male | peg-IFNα-2a | 350,561 | 0.42 |
| 361 | 55 | male | Entecavir | 21,202 | N/A |
| 437 | 62 | female | Lamivudine Tenofovir peg-IFNα-2a | 981,571 | N/A |
| 666 | 57 | male | peg-IFNα-2a Lamivudine | 3068 | N/A |
| 709 | 28 | male | peg-IFNα-2a Tenofovir | 357,292 | N/A |
| 792 | 33 | female | peg-IFNα-2a | 73,029 | N/A |
| 806 | 52 | female | Lamivudine peg-IFNα-2a | 22,941 | N/A |
| 1 | 27 | female | Tenofovir | 167,708 | N/A |
| 2 | 62 | male | Tenofovir | 138,542 | N/A |
| 3 | 68 | male | peg-IFNα-2a Entecavir | 5,569,712 | N/A |
| 4 | 58 | female | peg-IFNα-2a Entecavir | 118,966 | N/A |
| 5 | 50 | male | peg-IFNα-2a Entecavir | 6,713,942 | N/A |
| 6 | 31 | male | Tenofovir Bulevertide | 8,071,314 | N/A |
| 7 | 71 | female | Entecavir | 186,779 | 0.92 |
| 8 | 59 | male | Tenofovir | 384,215 | N/A |
| 9 | 32 | male | Entecavir | 3926 | N/A |
| 10 | 42 | male | peg-IFNα-2a | 98,550 | N/A |
References
- Puigvehí, M.; Moctezuma-Velázquez, C.; Villanueva, A.; Llovet, J.M. The oncogenic role of hepatitis delta virus in hepatocellular carcinoma. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattovich, G.; Giustina, G.; Christensen, E.; Pantalena, M.; Zagni, I.; Realdi, G.; Schalm, S.W. Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type B. The European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (Eurohep). Gut 2000, 46, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Lazinski, D.W. Replicating hepatitis delta virus RNA is edited in the nucleus by the small form of ADAR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15118–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccola, H.J.; Rozzelle, J.E.; Lemon, S.M.; Erickson, B.W.; Hogle, J.M. Structural basis of the oligomerization of hepatitis delta antigen. Structure 1998, 6, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisson, F.; Roingeard, P.; Baillou, A.; Dubois, F.; Bonelli, F.; Calogero, R.A.; Goudeau, A. Characterization of RNA-binding domains of hepatitis delta antigen. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Z.; Lin, J.H.; Chao, M.; McKnight, K.; Lai, M.M. RNA-binding activity of hepatitis delta antigen involves two arginine-rich motifs and is required for hepatitis delta virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Freitas, N.; Cunha, C. Characterization of the nuclear localization signal of the hepatitis delta virus antigen. Virology 2008, 370, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, M.F. A novel chromosome region maintenance 1-independent nuclear export signal of the large form of hepatitis delta antigen that is required for the viral assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8142–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.S.; Watson, J.A.; Havel, C.M.; White, J.M. Identification of a prenylation site in delta virus large antigen. Science 1992, 256, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonino, F.; Heermann, K.H.; Rizzetto, M.; Gerlich, W.H. Hepatitis delta virus: Protein composition of delta antigen and its hepatitis B virus-derived envelope. J. Virol. 1986, 58, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajah, K.; Basic, M.; Hildt, E. Cellular Factors Involved in the Hepatitis D Virus Life Cycle. Viruses 2023, 15, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ou, X.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Liu, J.; Pan, Q. Estimating the Global Prevalence, Disease Progression, and Clinical Outcome of Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockdale, A.J.; Kreuels, B.; Henrion, M.Y.R.; Giorgi, E.; Kyomuhangi, I.; Martel, C.d.; Hutin, Y.; Geretti, A.M. The global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodoridi, M.; Papatheodoridis, G.V. Is hepatitis delta underestimated? Liver Int. 2021, 41 (Suppl. 1), 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Leus, M.; Battersby, T.R.; Glenn, J.; Gordien, E.; Kamili, S.; Kapoor, H.; Kessler, H.H.; Lenz, O.; Lütgehetmann, M.; et al. HDV RNA assays: Performance characteristics, clinical utility, and challenges. Hepatology 2025, 81, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, F.; Brichler, S.; Sahli, R.; Chevret, S.; Gordien, E. First international external quality assessment for hepatitis delta virus RNA quantification in plasma. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzetto, M.; Shih, J.W.; Gocke, D.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Verme, G.; Gerin, J.L. Incidence and significance of antibodies to delta antigen in hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 1979, 2, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeywickrama-Samarakoon, N.; Cortay, J.-C.; Sureau, C.; Müller, S.; Alfaiate, D.; Guerrieri, F.; Chaikuad, A.; Schröder, M.; Merle, P.; Levrero, M.; et al. Hepatitis Delta Virus histone mimicry drives the recruitment of chromatin remodelers for viral RNA replication. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.L.; Chasovskikh, S.; Dritschilo, A.; Casey, J.L. Hepatitis delta antigen requires a flexible quasi-double-stranded RNA structure to bind and condense hepatitis delta virus RNA in a ribonucleoprotein complex. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7402–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Delcourte, L.; van Belleghem, C.; Fonte, S.; Gerard, K.; Baconnais, S.; Callon, M.; Le Cam, E.; Fogeron, M.-L.; Levrero, M.; et al. Structure and nucleic acid interactions of the SΔ60 domain of the hepatitis delta virus small antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2411890122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Cheng, H.; Roder, H.; Taylor, J. Intrinsic disorder and oligomerization of the hepatitis delta virus antigen. Virology 2010, 407, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiyagarajah, K.; Glitscher, M.; Peiffer, K.-H.; Hildt, E. Differential impact of hepatitis delta virus replication and expression of viral antigens on the cellular kinome profile. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Chao, M.; Taylor, J. Initiation of replication of the human hepatitis delta virus genome from cloned DNA: Role of delta antigen. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, H.; Taketa, K.; Miyano, K.; Yamane, T.; Sato, J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield, R.B. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. I. The Synthesis of a Tetrapeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, Z.; Velkov, S.; Protzer, U.; Roggendorf, M.; Frishman, D.; Karimzadeh, H. HDVdb: A Comprehensive Hepatitis D Virus Database. Viruses 2020, 12, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggendorf, M.; Pahlke, C.; Bohm, B.; Rasshofer, R. Characterization of Proteins Associated with Hepatitis Delta Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 2953–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Cullen, J.; Lemon, S.M. Immunoblot analysis demonstrates that the large and small forms of hepatitis delta virus antigen have different C-terminal amino acid sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73 Pt 1, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsar, M.; Landahl, J.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; zur Schulze Wiesch, J. Human hepatitis D virus-specific T cell epitopes. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichko, V.V.; Lemon, S.M.; Wang, J.G.; Hwang, S.; Lai, M.M.; Taylor, J.M. Epitopes exposed on hepatitis delta virus ribonucleoproteins. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5807–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, M.-B.; Cortay, J.-C.; Cortès, S.; Bloquel, B.; Brichler, S.; Brakha, C.; Kay, A.; Falah, N.; Zoulim, F.; Marquette, C.; et al. Protein-peptide arrays for detection of specific anti-hepatitis D virus (HDV) genotype 1, 6, and 8 antibodies among HDV-infected patients by surface plasmon resonance imaging. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Jansen, R.W.; Brown, E.A.; Lemon, S.M. Immunogenic domains of hepatitis delta virus antigen: Peptide mapping of epitopes recognized by human and woodchuck antibodies. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lempp, F.A.; Schlund, F.; Walter, L.; Decker, C.C.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Urban, S. Assembly and infection efficacy of hepatitis B virus surface protein exchanges in 8 hepatitis D virus genotype isolates. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpini, R.; Piermatteo, L.; Caviglia, G.P.; Bertoli, A.; Brunetto, M.R.; Bruzzone, B.; Callegaro, A.; Caudai, C.; Cavallone, D.; Chessa, L.; et al. Comparison of diagnostic performances of HDV-RNA quantification assays used in clinical practice: Results from a national quality control multicenter study. J. Clin. Virol. 2025, 180, 105850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sequence | |
|---|---|
| Primer 1 | AAACATATGAGCCGGTCCGAGTCGAGGAAGAAC |
| Primer 2 | AAAGCGGCCGCTGGAAATCCCTGGTTTCCCCTGATGTCCA |
| Primer 3 | AAAGCGGCCGCTCATCACTTCTCGAACTGCGGGTGGCTCCACGCGCTGCCACCAGAGCCACCACCACCGGAGCCGCCACCTTTTTCAAATTGG |
| Epitope Sequence | Region/Domain | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|
| GGREEILEQWAGRK | RBD | accessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| LKKIEDENPWLG | CCD | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| IKKLEDENPWLG * | CCD | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| EGAPPAKRARTDQME | NLS | accessible in HDV in vivo inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| VDSGPGKR | downstream NLS | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| KERQDHRRRKAL | 1st ARM | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| KERRDHRRK * | 1st ARM | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| EDERRERRVA | 2nd ARM | accessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| EEEEELRRLTEEDERR | upstream 2nd ARM | accessible in HDV in vivo |
| GPPVGGVNPL | PGRS | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| ESPFSRTGEGLDIRG | C-terminus of SHDAg | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| SPFSRTGEGIDIRGT * | C-terminus of SHDAg | inaccessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| LDIRGNQGFP | C-terminus of SHDAg | accessible in purified HDAg oligomer |
| WDILFPADPPFSPQS | LHDAg extension | accessible in HDV in vivo |
| ka (1/Ms) | kd (1/s) | KD (nM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| denat 1 | 1958 ± 198 | 2.26 × 10−4 ± 7.63 × 10−5 | 121 ± 51 |
| denat 4 | 2182 ± 266 | 1.05 × 10−4 ± 3.08 × 10−5 | 51 ± 20 |
| native 1 | 1540 ± 248 | 2.52 × 10−4 ± 5.19 × 10−5 | 173 ± 62 |
| native 4 | 2492 ± 278 | 6.47 × 10−5 ± 3.00 × 10−7 | 26 ± 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thiyagarajah, K.; Hein, S.; Raupach, J.; Adeel, N.; Miller, J.; Knapp, M.; Welsch, C.; Glitscher, M.; Görgülü, E.; Stoffers, P.; et al. Generation and Characterization of HDV-Specific Antisera with Respect to Their Application as Specific and Sensitive Research and Diagnostic Tools. Viruses 2025, 17, 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091220
Thiyagarajah K, Hein S, Raupach J, Adeel N, Miller J, Knapp M, Welsch C, Glitscher M, Görgülü E, Stoffers P, et al. Generation and Characterization of HDV-Specific Antisera with Respect to Their Application as Specific and Sensitive Research and Diagnostic Tools. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091220
Chicago/Turabian StyleThiyagarajah, Keerthihan, Sascha Hein, Jan Raupach, Nirmal Adeel, Johannes Miller, Maximilian Knapp, Christoph Welsch, Mirco Glitscher, Esra Görgülü, Philipp Stoffers, and et al. 2025. "Generation and Characterization of HDV-Specific Antisera with Respect to Their Application as Specific and Sensitive Research and Diagnostic Tools" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091220
APA StyleThiyagarajah, K., Hein, S., Raupach, J., Adeel, N., Miller, J., Knapp, M., Welsch, C., Glitscher, M., Görgülü, E., Stoffers, P., Lembeck, P., Trebicka, J., Ciesek, S., Peiffer, K.-H., & Hildt, E. (2025). Generation and Characterization of HDV-Specific Antisera with Respect to Their Application as Specific and Sensitive Research and Diagnostic Tools. Viruses, 17(9), 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091220






