The Impact of COVID-19 and Related Public Health Measures on Hepatitis C Testing in Ontario, Canada
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Population
2.2. Variable Definitions and Data Sources
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Cohort
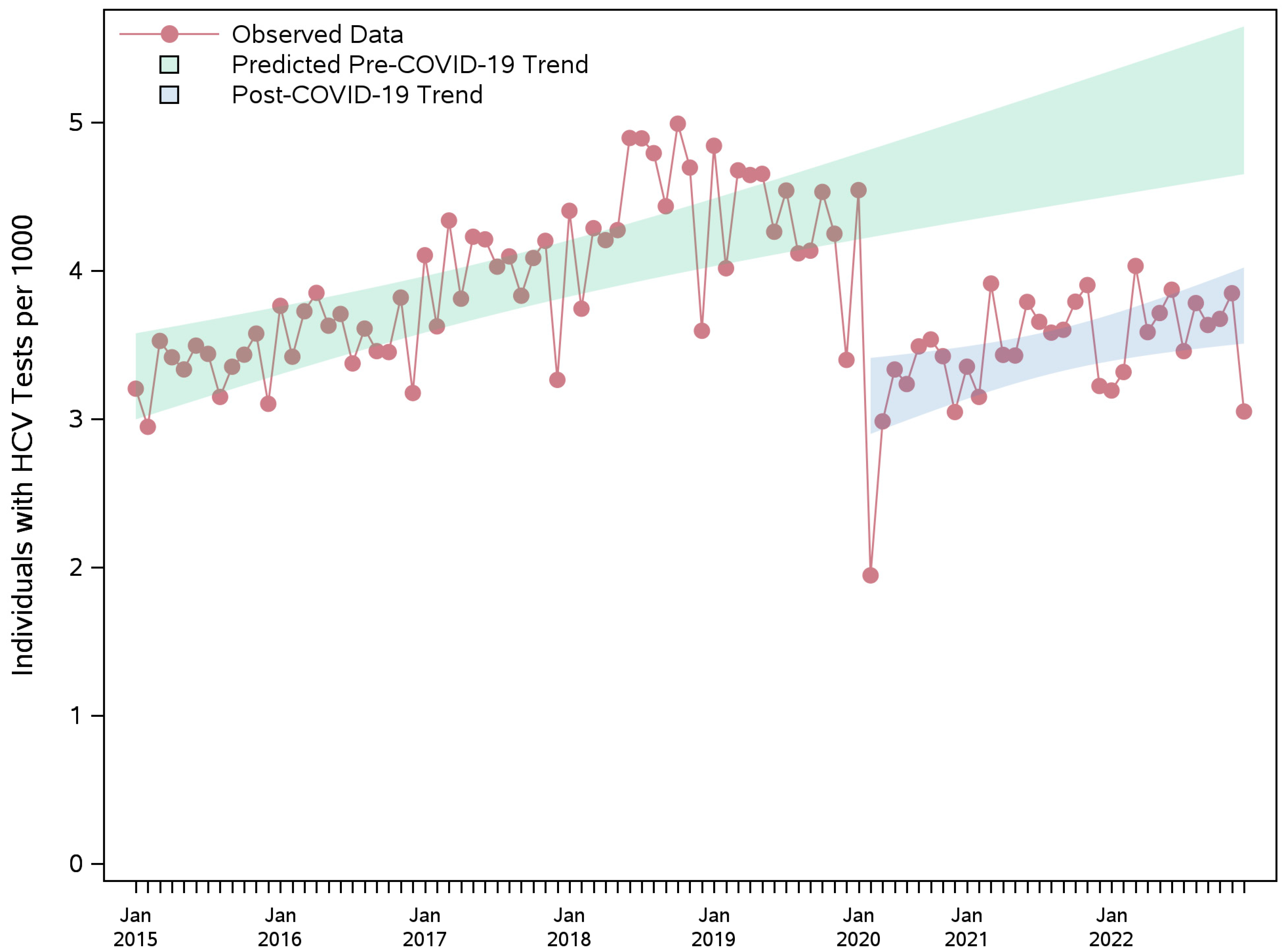
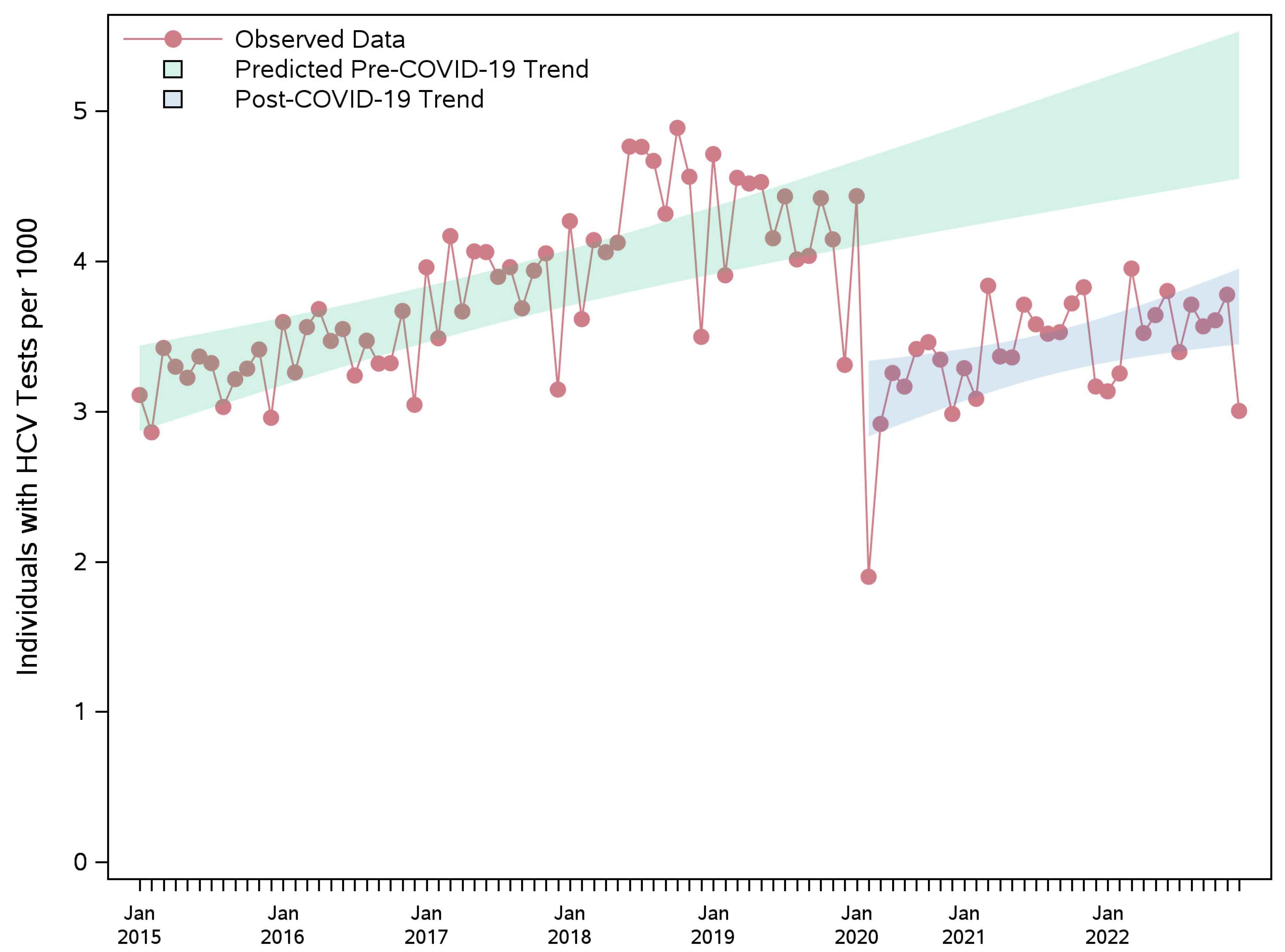
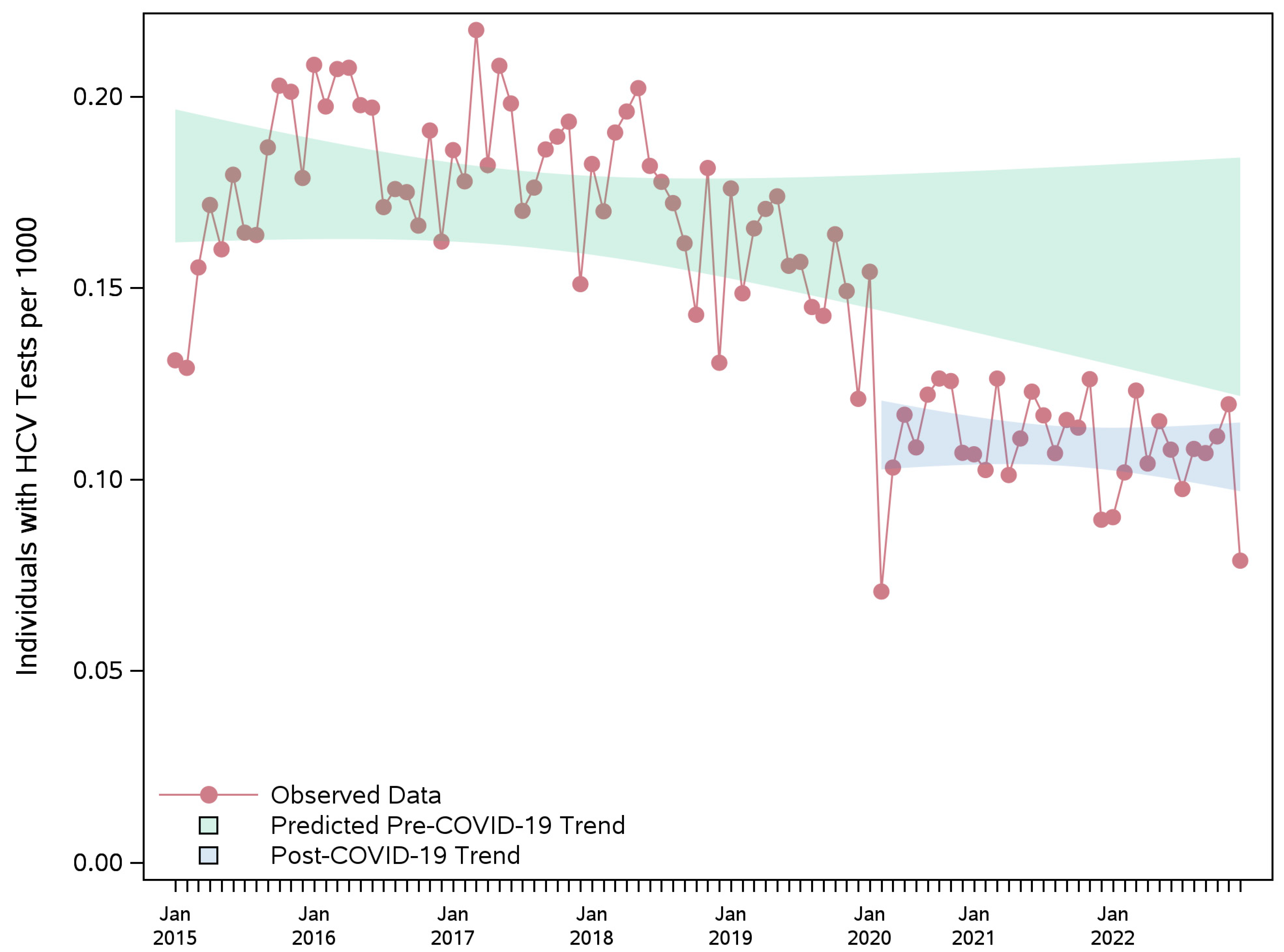
3.2. HCV Testing Rate
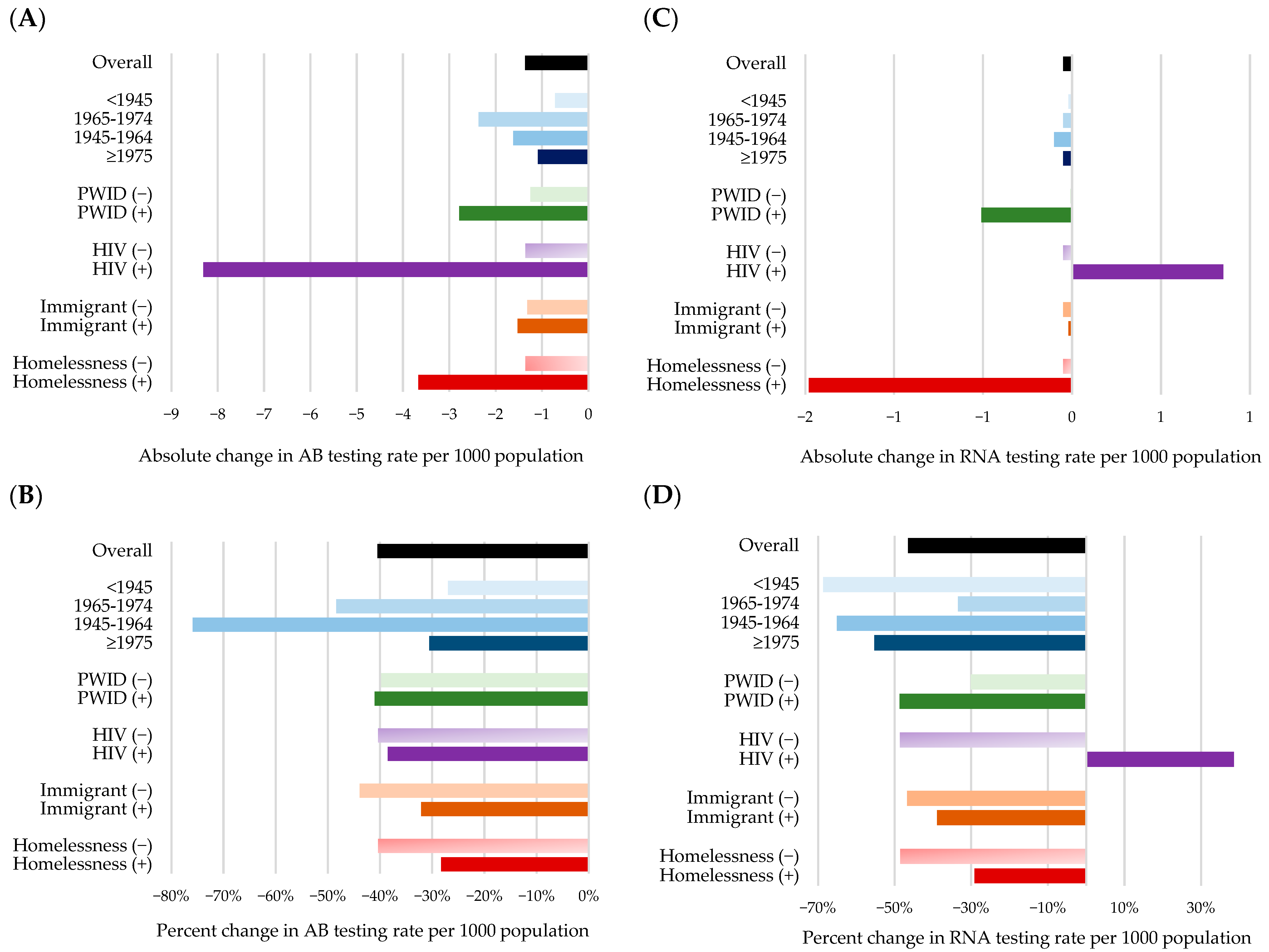
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canadian Institute for Health Information. Canadian COVID-19 Intervention Timeline. Available online: https://www.cihi.ca/en/canadian-covid-19-intervention-timeline (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Government of Ontario Office of the Premier. Ontario Declares Second Provincial Emergency to Address COVID-19 Crisis and Save Lives. Province Issues Stay-at-Home Order and Introduces Enhanced Enforcement Measures to Reduce Mobility. 12 January 2021. Available online: https://news.ontario.ca/en/release/59922/ontario-declares-second-provincial-emergency-to-address-covid-19-crisis-and-save-lives (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Government of Ontario Office of the Premier. Ontario Enacts Provincial Emergency and Stay-at-Home Order. Additional Measures Needed to Protect Health System Capacity and Save Lives During Third Wave of COVID-19. 7 April 2021. Available online: https://news.ontario.ca/en/release/61029/ontario-enacts-provincial-emergency-and-stay-at-home-order (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Lee, M.H.; Xu, G.; Cheng, F.; Khalid, A.F. Testing surge capacity-A Canadian COVID-19 experience, Ontario’s surge capacity for the first wave. Health Policy 2021, 125, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolla, G.; Bowles, J.M.; Upham, K.; Ali, H.; Pinch, S.; Majid, H.; Bellony, L.; Werb, D.; Mitra, S. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to harm reduction and treatment services among people who inject drugs in Toronto, Canada: A qualitative investigation. SSM-Qual. Res. Health 2025, 8, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Canada. Survey on Access to Health Care and Pharmaceuticals During the Pandemic, March 2020 to May 2021. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/daily-quotidien/211123/dq211123b-eng.htm (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Moynihan, R.; Sanders, S.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Scott, A.M.; Clark, J.; To, E.J.; Jones, M.; Kitchener, E.; Fox, M.; Johansson, M.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on utilisation of healthcare services: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barocas, J.A.; Savinkina, A.; Lodi, S.; Epstein, R.L.; Bouton, T.C.; Sperring, H.; Hsu, H.E.; Jacobson, K.R.; Schechter-Perkins, E.M.; Linas, B.P.; et al. Projected Long-Term Impact of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic on Hepatitis C Outcomes in the United States: A Modeling Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e1112–e1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada’s Source for HIV and Hepatitis C Information. CATIE FACT SHEET: The Epidemiology of Hepatitis C in Canada. Available online: https://www.catie.ca/the-epidemiology-of-hepatitis-c-in-canada-0#:~:text=How%20many%20people%20have%20ever%20had%20hepatitis%20C%20in%20Canada,had%20ever%20had%20hepatitis%20C (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Tadrous, M.; Mason, K.; Dodd, Z.; Guyton, M.; Powis, J.; McCormack, D.; Gomes, T. Prescribing trends in direct-acting antivirals for the treatment of hepatitis C in Ontario, Canada. Can. Liver J. 2021, 4, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada’s Source for HIV and Hepatitis C Information. Hepatitis C: An In-Depth Guide. Available online: https://www.catie.ca/hepatitis-c-an-in-depth-guide/approaches-to-hepatitis-c-testing-in-canada (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- The Canadian Network on Hepatitis C; Blueprint Writing Committee and Working Groups. Blueprint to Inform Hepatitis C Elimination Efforts in Canada. Montreal, QC, Canda. Available online: https://cdn.ca.yapla.com/company/CPYfgPV3CnIUJxhGEwBsuytvM/asset/files/blueprint/blueprint_hcv_2019_05.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Mandel, E.; Underwood, K.; Masterman, C.; Kozak, R.A.; Dale, C.H.; Hassall, M.; Capraru, C.; Shah, H.; Janssen, H.; Feld, J.J.; et al. Province-to-province variability in hepatitis C testing, care, and treatment across Canada. Can. Liver J. 2023, 6, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, R.L.; Binka, M.; Li, J.; Irvine, M.; Bartlett, S.R.; Wong, S.; Jeong, D.; Makuza, J.D.; Wong, J.; Yu, A.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Hepatitis C Treatment Initiation in British Columbia, Canada: An Interrupted Time Series Study. Viruses 2024, 16, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binka, M.; Bartlett, S.; Velasquez Garcia, H.A.; Darvishian, M.; Jeong, D.; Adu, P.; Alvarez, M.; Wong, S.; Yu, A.; Samji, H.; et al. Impact of COVID-19-related public health measures on HCV testing in British Columbia, Canada: An interrupted time series analysis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronfli, N.; Leone, F.; Dussault, C.; Miliani, G.; Gallant, E.; Potter, M.; Cox, J. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on hepatitis C virus screening in provincial prisons in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Front. Public. Health 2024, 12, 1380126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, E.; Peci, A.; Cronin, K.; Capraru, C.I.; Shah, H.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Tran, V.; Biondi, M.J.; Feld, J.J. The impact of the first, second and third waves of covid-19 on hepatitis B and C testing in Ontario, Canada. J. Viral Hepat. 2022, 29, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantelos, N.; Shakeri, A.; McCormack, D.; Feld, J.J.; Gomes, T.; Tadrous, M. Impact of COVID-19 on Prescribing Trends of Direct-Acting Antivirals for the Treatment of Hepatitis C in Ontario, Canada. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1738–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binka, M.; Butt, Z.A.; McKee, G.; Darvishian, M.; Cook, D.; Wong, S.; Yu, A.; Alvarez, M.; Samji, H.; Wong, J.; et al. Differences in risk factors for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and human immunodeficiency virus infection by ethnicity: A large population-based cohort study in British Columbia, Canada. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 106, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K. Difficulties accessing health care in Canada during the COVID-19 pandemic: Comparing individuals with and without chronic conditions. Health Rep. 2022, 33, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, B.; Larney, S.; Degenhardt, L.; Janjua, N.; Hoj, S.; Krajden, M.; Grebely, J.; Bruneau, J. Prevalence of Injecting Drug Use and Coverage of Interventions to Prevent HIV and Hepatitis C Virus Infection Among People Who Inject Drugs in Canada. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.; Bilodeau, M.; Burak, K.W.; Cooper, C.; Klein, M.; Ramji, A.; Smyth, D.; Feld, J.J.; Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver. The management of chronic hepatitis C: 2018 guideline update from the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2018, 190, E677–E687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchimol, E.I.; Smeeth, L.; Guttmann, A.; Harron, K.; Moher, D.; Petersen, I.; Sorensen, H.T.; von Elm, E.; Langan, S.M.; Committee, R.W. The REporting of studies Conducted using Observational Routinely-collected health Data (RECORD) statement. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eHealth Ontario. Ontario Laboratories Information System. Available online: https://www.ehealthontario.on.ca/en/for-healthcare-professionals/ontario-laboratories-information-system-olis (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- eHealth Ontario. Ontario Laboratory Information System: OLIS-Data Contributors: Q2 Fiscal Year 2020/2021. Available online: https://ehealthontario.on.ca/en/health-care-professionals/lab-results (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Arum, C.; Fraser, H.; Artenie, A.A.; Bivegete, S.; Trickey, A.; Alary, M.; Astemborski, J.; Iversen, J.; Lim, A.G.; MacGregor, L.; et al. Homelessness, unstable housing, and risk of HIV and hepatitis C virus acquisition among people who inject drugs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e309–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, L.; Easterbrook, P.; Gower, E.; McDonald, B.; Sabin, K.; McGowan, C.; Yanny, I.; Razavi, H.; Vickerman, P. Prevalence and burden of HCV co-infection in people living with HIV: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, L.; Booth, R.; Rayner, J.; Clemens, K.K.; Forchuk, C.; Shariff, S.Z. Testing, infection and complication rates of COVID-19 among people with a recent history of homelessness in Ontario, Canada: A retrospective cohort study. CMAJ Open 2021, 9, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, L.; Carter, B.; Nisenbaum, R.; Liu, M.; Hwang, S.W. Identification of homelessness using health administrative data in Ontario, Canada following a national coding mandate: A validation study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2024, 172, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, T.; Zagorski, B.; Loutfy, M.R.; Strike, C.; Glazier, R.H. Validation of case-finding algorithms derived from administrative data for identifying adults living with human immunodeficiency virus infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwald, Z.R.; Werb, D.; Feld, J.J.; Austin, P.C.; Fridman, D.; Bayoumi, A.M.; Gomes, T.; Kendall, C.E.; Lapointe-Shaw, L.; Scheim, A.I.; et al. Validation of case-ascertainment algorithms using health administrative data to identify people who inject drugs in Ontario, Canada. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2024, 170, 111332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe-Shaw, L.; Georgie, F.; Carlone, D.; Cerocchi, O.; Chung, H.; Dewit, Y.; Feld, J.J.; Holder, L.; Kwong, J.C.; Sander, B.; et al. Identifying cirrhosis, decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in health administrative data: A validation study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Johns Hopkins ACG® System, version 13.0; Johns Hopkins Medicine: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.hopkinsacg.org/ (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Paisi, M.; Crombag, N.; Burns, L.; Bogaerts, A.; Withers, L.; Bates, L.; Crowley, D.; Witton, R.; Shawe, J. Barriers and facilitators to hepatitis C screening and treatment for people with lived experience of homelessness: A mixed-methods systematic review. Health Expect. 2022, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiessing, L.; Sypsa, V.; Abagiu, A.O.; Arble, A.; Berndt, N.; Bosch, A.; Buskin, S.; Chemtob, D.; Combs, B.; Conyngham, C.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 & Response Measures on HIV-HCV Prevention Services and Social Determinants in People Who Inject Drugs in 13 Sites with Recent HIV Outbreaks in Europe, North America and Israel. AIDS Behav. 2023, 27, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Bouck, Z.; Larney, S.; Zolopa, C.; Hoj, S.; Minoyan, N.; Upham, K.; Rammohan, I.; Mok, W.Y.; Hayashi, K.; et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people who use drugs in three Canadian cities: A cross-sectional analysis. Harm Reduct. J. 2024, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guss, D.; Sherigar, J.; Rosen, P.; Mohanty, S.R. Diagnosis and Management of Hepatitis C Infection in Primary Care Settings. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Combating Hepatitis B and C to Reach Elimination by 2030. World Health Organization. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/combating-hepatitis-b-and-c-to-reach-elimination-by-2030 (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Forouzannia, F.; Hamadeh, A.; Passos-Castilho, A.M.; Erman, A.; Yu, A.; Feng, Z.; Janjua, N.Z.; Sander, B.; Greenaway, C.; Wong, W.W.L. Impact of new direct-acting antiviral therapy on the prevalence and undiagnosed proportion of chronic hepatitis C infection. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, R.H.; Green, M.E.; Wu, F.C.; Frymire, E.; Kopp, A.; Kiran, T. Shifts in office and virtual primary care during the early COVID-19 pandemic in Ontario, Canada. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2021, 193, E200–E210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettner, B.; Mason, K.; Greenwald, Z.R.; Broad, J.; Mandel, E.; Feld, J.J.; Powis, J. Rapid hepatitis C virus point-of-care RNA testing and treatment at an integrated supervised consumption service in Toronto, Canada: A prospective, observational cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2023, 22, 100490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebely, J.; Applegate, T.L.; Cunningham, P.; Feld, J.J. Hepatitis C point-of-care diagnostics: In search of a single visit diagnosis. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokuo, J.K.; Masson, C.L.; Anderson, A.; Powell, J.; Bush, D.; Ricco, M.; Zevin, B.; Ayala, C.; Khalili, M. Recommendations for Implementing Hepatitis C Virus Care in Homeless Shelters: The Stakeholder Perspective. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broad, J.; Mason, K.; Guyton, M.; Lettner, B.; Matelski, J.; Powis, J. Peer outreach point-of-care testing as a bridge to hepatitis C care for people who inject drugs in Toronto, Canada. Int. J. Drug Policy 2020, 80, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, P.; Valencia, J.; Cuevas, G.; Torres-Macho, J.; Troya, J.; Pueyo, A.; Jose Munoz-Gomez, M.; Munoz-Rivas, N.; Vazquez-Moron, S.; Martinez, I.; et al. Detection of active hepatitis C in a single visit and linkage to care among marginalized people using a mobile unit in Madrid, Spain. Int. J. Drug Policy 2021, 96, 103424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.A.; Plitt, S.S.; Zhuo, R.; Charlton, C.L. The effect of first-wave COVID-19 restrictions on HCV testing in Alberta, Canada: A trend analysis from 2019 to 2022. Can. Liver J. 2024, 7, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.W.; Bull-Otterson, L.; Meyer, W.A., III; Huang, X.; Doshani, M.; Thompson, W.W.; Osinubi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Harris, A.M.; Gupta, N.; et al. Decreases in Hepatitis C Testing and Treatment During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2021, 61, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Prevention, Testing, Diagnosis and Care for Sexually Transmitted Infections, HIV and Viral Hepatitis in England. Provisional Data: January to September 2020. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/943657/Impact_of_COVID-19_Report_2020.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Brouard, C.; Schwager, M.; Expert, A.; Drewniak, N.; Laporal, S.; de Lagasnerie, G.; Lot, F. Impact of Public Policy and COVID-19 Pandemic on Hepatitis C Testing and Treatment in France, 2014-2021. Viruses 2024, 16, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Canada. Measuring the Correlation Between COVID-19 Restrictions and Economic Activity. Analytical Studies: Methods and References (2022). Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/en/pub/11-633-x/11-633-x2022003-eng.pdf?st=QhRnEZpx (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- MHASEF Research Team. Mental Health and Addictions System Performance in Ontario: A Baseline Scorecard; ICES: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018; Available online: https://www.ices.on.ca/Publications/Atlases-and-Reports/2018/MHASEF (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Public Health Ontario. Surveillance Report. Hepatitis C in Ontario: Focus on 2023. Available online: https://www.publichealthontario.ca/-/media/Documents/H/25/hepatitis-c-ontario-focus-2023.pdf?rev=a1bd2a5910e74ab8a0a1e7561453cd4a&sc_lang=en&hash=13868AC0F8C282C33E36FB08880C4923 (accessed on 31 March 2025).
| Characteristics | Pre-Pandemic 01/01/2015–29/02/2020 N = 2,353,170 | Pandemic 01/03/2020–31/12/2022 N = 1,312,942 |
|---|---|---|
| Age at index, years, mean (sd) | 44.29 (17.75) | 42.97 (17.96) |
| Birth year, n (%) | ||
| <1945 | 156,430 (6.6) | 69,307 (5.3) |
| 1945–1965 | 656,973 (27.9) | 293,734 (22.4) |
| 1965–1974 | 380,416 (16.2) | 179,677 (13.7) |
| >1974 | 1,159,351 (49.3) | 770,224 (58.7) |
| Male sex, n (%) | 1,092,990 (46.4) | 595,357 (45.3) |
| Immigrant status, n (%) | 684,444 (29.1) | 385,980 (29.4) |
| Rural, n (%) | 158,652 (6.7) | 94,754 (7.2) |
| Neighborhood income quintile, n (%) | ||
| 1st quintile (lowest) | 532,432 (22.6) | 297,002 (22.6) |
| 2nd quintile | 482,521 (20.5) | 270,962 (20.6) |
| 3rd quintile | 459,315 (19.5) | 258,428 (19.7) |
| 4th quintile | 438,110 (18.6) | 244,367 (18.6) |
| 5th quintile | 432,644 (18.4) | 237,654 (18.1) |
| Household and dwellings quintile, n (%) | ||
| 1st quintile (lowest) | 507,983 (21.6) | 275,249 (21.0) |
| 2nd quintile | 391,983 (16.7) | 214,853 (16.4) |
| 3rd quintile | 375,219 (15.9) | 209,582 (16.0) |
| 4th quintile | 403,462 (17.1) | 231,401 (17.6) |
| 5th quintile | 652,137 (27.7) | 367,470 (28.0) |
| Material resources quintile, n (%) | ||
| 1st quintile (lowest) | 501,587 (21.3) | 267,262 (20.4) |
| 2nd quintile | 466,205 (19.8) | 264,116 (20.1) |
| 3rd quintile | 441,675 (18.8) | 253,586 (19.3) |
| 4th quintile | 435,641 (18.5) | 241,679 (18.4) |
| 5th quintile | 485,676 (20.6) | 271,912 (20.7) |
| Racialized and newcomer populations quintile, n (%) | ||
| 1st quintile (lowest) | 259,613 (11.0) | 147,808 (11.3) |
| 2nd quintile | 304,978 (13.0) | 175,871 (13.4) |
| 3rd quintile | 381,040 (16.2) | 214,499 (16.3) |
| 4th quintile | 525,753 (22.3) | 294,579 (22.4) |
| 5th quintile | 859,400 (36.5) | 465,798 (35.5) |
| Homelessness, n (%) | 7028 (0.3) | 6789 (0.5) |
| PWID, n (%) (ever) | 313,189 (13.3) | 173,612 (13.2) |
| HIV positivity, n (%) | 10,959 (0.5) | 7028 (0.5) |
| ADG, mean (sd) | 6.12 (3.81) | 6.11 (3.84) |
| ADG categories, n (%) | ||
| 0–3 | 655,147 (27.8) | 373,897 (28.5) |
| 4–8 | 1,110,250 (47.2) | 608,403 (46.3) |
| 9–10 | 270,672 (11.5) | 150,390 (11.5) |
| >10 | 317,101 (13.5) | 180,252 (13.7) |
| Advanced liver disease, n (%) | ||
| Any advanced liver disease | 38,140 (1.6) | 21,438 (1.6) |
| Cirrhosis | 36,524 (1.6) | 20,440 (1.6) |
| Decompensated cirrhosis | 8715 (0.4) | 4559 (0.3) |
| HCC | 2422 (0.1) | 1170 (0.1) |
| Liver transplant recipients | 1280 (0.1) | 621 (<0.1) |
| Population | Absolute Difference (95% CI) | Percent Difference (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–Dec 2020 | Jan–Dec 2021 | Jan–Dec 2022 | May–Dec 2020 | Jan–Dec 2021 | Jan–Dec 2022 | |
| Overall | −1.41 (−1.64; −1.18) | −1.17 (−1.36; −0.99) | −1.41 (−1.59; −1.22) | −46.5 (−53.99; −39.01) | −34.24 (−39.66; −28.82) | −40.76 (−46.13; −35.39) |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | −1.37 (−1.61; −1.12) | −1.13 (−1.33; −0.93) | −1.44 (−1.64; −1.24) | −41.98 (−49.51; −34.46) | −30.84 (−36.31; −25.37) | −39.69 (−45.21; −34.17) |
| Male | −1.46 (−1.67; −1.25) | −1.22 (−1.39; −1.04) | −1.37 (−1.55; −1.20) | −51.91 (−59.44; −44.37) | −38.23 (−43.65; −32.80) | −41.98 (−47.25; −36.71) |
| Birth cohort | ||||||
| <1945 | −0.59 (−0.78; −0.41) | −0.53 (−0.68; −0.39) | −0.74 (−0.89; −0.59) | −23.72 (−30.95; −16.49) | −19.62 (−25.03; −14.20) | −27.47 (−32.95; −21.99) |
| 1945–1964 | −1.89 (−2.12; −1.67) | −2.02 (−2.21; −1.84) | −2.42 (−2.60; −2.23) | −64.28 (−71.96; −56.61) | −62.47 (−68.17; −56.77) | −75.11 (−80.85; −69.37) |
| 1965–1974 | −1.83 (−2.09; −1.58) | −1.49 (−1.69; −1.28) | −1.70 (−1.91; −1.50) | −60.74 (−69.05; −52.43) | −42.99 (−48.89; −37.09) | −49.44 (−55.36; −43.52) |
| ≥1975 | −1.25 (−1.50; −0.99) | −0.94 (−1.15; −0.73) | −1.13 (−1.34; −0.92) | −39.69 (−47.79; −31.60) | −26.36 (−32.18; −20.53) | −31.10 (−36.84; −25.35) |
| IDU status (ever) | ||||||
| PWID | −2.81 (−3.38; −2.24) | −2.56 (−3.03; −2.09) | −3.21 (−3.68; −2.73) | −38.07 (−45.84; −30.31) | −32.67 (−38.68; −26.65) | −42.53 (−48.78; −36.29) |
| Non-PWID | −1.31 (−1.51; −1.10) | −1.07 (−1.24; −0.90) | −1.26 (−1.43; −1.10) | −48.03 (−55.59; −40.46) | −34.39 (−39.79; −28.98) | −39.89 (−45.19; −34.59) |
| Immigration status | ||||||
| Yes | −2.08 (−2.40; −1.75) | −1.47 (−1.74; −1.21) | −1.55 (−1.81; −1.29) | −50.98 (−58.97; −42.99) | −31.34 (−36.96; −25.71) | −32.27 (−37.78; −26.77) |
| No | −1.24 (−1.44; −1.04) | −1.10 (−1.26; −0.93) | −1.37 (−1.53; −1.20) | −45.00 (−52.33; −37.67) | −35.74 (−41.11; −30.36) | −44.32 (−49.68; −38.96) |
| HIV status | ||||||
| HIV (+) | −9.64 (−12.49; −6.78) | −10.32 (−12.61; −8.03) | −8.00 (−10.29; −5.70) | −41.00 (−53.16; −28.83) | −47.02 (−57.45; −36.58) | −34.49 (−44.38; −24.59) |
| HIV (−) | −1.40 (−1.63; −1.17) | −1.16 (−1.35; −0.98) | −1.40 (−1.58; −1.21) | −46.56 (−54.07; −39.05) | −34.21 (−39.64; −28.78) | −40.82 (−46.2; −35.44) |
| Homelessness status | ||||||
| Yes | −4.83 (−7.13; −2.53) | −3.98 (−5.83; −2.13) | −4.77 (−6.62; −2.91) | −29.82 (−44.02; −15.63) | −23.26 (−34.06; −12.45) | −28.6 (−39.71; −17.49) |
| No | −1.41 (−1.64; −1.18) | −1.17 (−1.35; −0.98) | −1.40 (−1.59; −1.22) | −46.65 (−54.15; −39.14) | −34.33 (−39.76; −28.90) | −40.83 (−46.21; −35.45) |
| Population | Absolute Difference (95% CI) | Percent Difference (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–Dec 2020 | Jan–Dec 2021 | Jan–Dec 2022 | May–Dec 2020 | Jan–Dec 2021 | Jan–Dec 2022 | |
| Overall | −1.37 (−1.59; −1.15) | −1.13 (−1.31; −0.95) | −1.37 (−1.55; −1.18) | −46.16 (−53.68; −38.65) | −33.78 (−39.20; −28.36) | −40.35 (−45.72; −34.98) |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | −1.33 (−1.58; −1.09) | −1.10 (−1.29; −0.90) | −1.40 (−1.60; −1.21) | −41.61 (−49.14; −34.08) | −30.43 (−35.90; −24.96) | −39.25 (−44.75; −33.74) |
| Male | −1.41 (−1.61; −1.20) | −1.17 (−1.34; −1.00) | −1.33 (−1.50; −1.16) | −51.73 (−59.31; −44.15) | −37.78 (−43.22; −32.35) | −41.66 (−46.93; −36.39) |
| Birth cohort | ||||||
| <1945 | −0.58 (−0.76; −0.40) | −0.52 (−0.66; −0.37) | −0.72 (−0.87; −0.57) | −23.21 (−30.51; −15.92) | −19.04 (−24.49; −13.59) | −26.99 (−32.50; −21.47) |
| 1945–1964 | −1.82 (−2.04; −1.60) | −1.97 (−2.15; −1.79) | −2.37 (−2.55; −2.19) | −64.05 (−71.83; −56.26) | −62.69 (−68.45; −56.93) | −75.89 (−81.67; −70.10) |
| 1965–1974 | −1.76 (−2.01; −1.52) | −1.42 (−1.62; −1.22) | −1.62 (−1.82; −1.42) | −60.45 (−68.82; −52.08) | −42.30 (−48.21; −36.38) | −48.38 (−54.31; −42.45) |
| ≥1975 | −1.22 (−1.48; −0.97) | −0.91 (−1.12; −0.71) | −1.09 (−1.30; −0.89) | −39.54 (−47.63; −31.45) | −25.96 (−31.77; −20.14) | −30.58 (−36.31; −24.85) |
| IDU status (ever) | ||||||
| PWID | −2.44 (−2.95; −1.93) | −2.18 (−2.60; −1.76) | −2.79 (−3.21; −2.37) | −36.53 (−44.20; −28.86) | −30.81 (−36.74; −24.88) | −41.03 (−47.21; −34.84) |
| Non-PWID | −1.29 (−1.50; −1.09) | −1.06 (−1.22; −0.89) | −1.25 (−1.42; −1.09) | −47.81 (−55.41; −40.22) | −34.18 (−39.60; −28.76) | −39.79 (−45.10; −34.48) |
| Immigration status | ||||||
| Yes | −2.05 (−2.37; −1.73) | −1.45 (−1.71; −1.19) | −1.53 (−1.79; −1.27) | −50.80 (−58.81; −42.79) | −31.13 (−36.76; −25.50) | −32.13 (−37.64; −26.63) |
| No | −1.20 (−1.39; −1.00) | −1.06 (−1.22; −0.90) | −1.32 (−1.48; −1.16) | −44.60 (−51.94; −37.26) | −35.24 (−40.61; −29.86) | −43.90 (−49.25; −38.55) |
| HIV status | ||||||
| HIV (+) | −9.35 (−12.02; −6.68) | −10.31 (−12.44; −8.17) | −8.31 (−10.46; −6.17) | −43.12 (−55.43; −30.82) | −51.01 (−61.59; −40.43) | −38.51 (−48.43; −28.59) |
| HIV (−) | −1.36 (−1.58; −1.14) | −1.12 (−1.30; −0.94) | −1.36 (−1.54; −1.18) | −46.19 (−53.73; −38.66) | −33.72 (−39.15; −28.29) | −40.37 (−45.75; −35.00) |
| Homelessness status | ||||||
| Yes | −3.82 (−5.65; −1.98) | −3.20 (−4.68; −1.72) | −3.67 (−5.15; −2.19) | −29.49 (−43.65; −15.32) | −23.83 (−34.81; −12.84) | −28.28 (−39.67; −16.90) |
| No | −1.37 (−1.59; −1.15) | −1.13 (−1.31; −0.95) | −1.36 (−1.54; −1.18) | −46.28 (−53.80; −38.76) | −33.83 (−39.26; −28.40) | −40.39 (−45.77; −35.01) |
| Population | Absolute Difference (95% CI) | Percent Difference (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–Dec 2020 | Jan–Dec 2021 | Jan–Dec 2022 | May–Dec 2020 | Jan–Dec 2021 | Jan–Dec 2022 | |
| Overall | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −41.12 (−48.96; −33.28) | −39.85 (−46.33; −33.38) | −46.50 (−53.23; −39.77) |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | −0.04 (−0.04; −0.03) | −0.04 (−0.04; −0.03) | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −40.89 (−49.13; −32.64) | −41.12 (−47.98; −34.27) | −53.91 (−61.00; −46.83) |
| Male | −0.06 (−0.07; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −41.51 (−49.67; −33.36) | −39.09 (−45.60; −32.59) | −41.71 (−48.56; −34.86) |
| Birth cohort | ||||||
| <1945 | −0.01 (−0.01; 0.00) | −0.02 (−0.03; −0.02) | −0.02 (−0.03; −0.02) | −9.37 (−20.50; 1.76) | −59.92 (−73.93; −45.90) | −68.67 (−83.26; −54.08) |
| 1945–1964 | −0.08 (−0.09; −0.07) | −0.07 (−0.08; −0.06) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −49.53 (−57.63; −41.42) | −44.65 (−51.52; −37.78) | −33.50 (−40.77; −26.22) |
| 1965–1974 | −0.08 (−0.09; −0.06) | −0.08 (−0.09; −0.07) | −0.10 (−0.11; −0.09) | −51.03 (−58.99; −43.08) | −50.31 (−56.41; −44.21) | −65.09 (−71.66; −58.52) |
| ≥1975 | −0.03 (−0.04; −0.02) | −0.03 (−0.04; −0.03) | −0.05 (−0.05; −0.04) | −35.97 (−45.02; −26.93) | −37.19 (−44.05; −30.33) | −55.34 (−62.33; −48.36) |
| IDU status (ever) | ||||||
| PWID | −0.43 (−0.53; −0.34) | −0.42 (−0.50; −0.34) | −0.51 (−0.59; −0.43) | −42.27 (−51.72; −32.82) | −38.54 (−45.75; −31.32) | −48.71 (−56.22; −41.21) |
| Non-PWID | −0.02 (−0.02; −0.01) | −0.02 (−0.02; −0.01) | −0.01 (−0.01; −0.01) | −39.64 (−47.97; −31.31) | −40.83 (−48.25; −33.41) | −30.13 (−37.94; −22.31) |
| Immigration status | ||||||
| Yes | −0.04 (−0.04; −0.03) | −0.03 (−0.04; −0.03) | −0.02 (−0.03; −0.02) | −58.84 (−68.31; −49.37) | −47.65 (−55.17; −40.14) | −38.90 (−46.84; −30.97) |
| No | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.05) | −38.55 (−46.55; −30.55) | −38.44 (−44.84; −32.05) | −46.72 (−53.51; −39.93) |
| HIV status | ||||||
| HIV (+) | −0.15 (−0.54; 0.24) | 0.26 (−0.05; 0.58) | 0.85 (0.54; 1.17) | −6.12 (−22.11; 9.87) | 11.38 (−2.15; 24.91) | 38.53 (24.32; 52.74) |
| HIV (-) | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.06; −0.04) | −41.85 (−49.82; −33.88) | −41.19 (−47.55; −34.83) | −48.61 (−55.67; −41.55) |
| Homelessness status | ||||||
| Yes | −1.31 (−1.97; −0.65) | −1.08 (−1.61; −0.56) | −1.48 (−2.00; −0.95) | −28.68 (−43.03; −14.32) | −21.42 (−31.81; −11.03) | −29.14 (−39.54; −18.75) |
| No | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −0.04 (−0.05; −0.04) | −0.05 (−0.05; −0.04) | −42.45 (−50.33; −34.56) | −41.90 (−48.19; −35.61) | −48.57 (−55.55; −41.59) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahakyan, Y.; Drover, S.S.M.; Greenwald, Z.R.; Wong, W.W.L.; Kopp, A.; Morrow, R.L.; Janjua, N.Z.; Sander, B. The Impact of COVID-19 and Related Public Health Measures on Hepatitis C Testing in Ontario, Canada. Viruses 2025, 17, 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091163
Sahakyan Y, Drover SSM, Greenwald ZR, Wong WWL, Kopp A, Morrow RL, Janjua NZ, Sander B. The Impact of COVID-19 and Related Public Health Measures on Hepatitis C Testing in Ontario, Canada. Viruses. 2025; 17(9):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091163
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahakyan, Yeva, Samantha S. M. Drover, Zoë R. Greenwald, William W. L. Wong, Alexander Kopp, Richard L. Morrow, Naveed Z. Janjua, and Beate Sander. 2025. "The Impact of COVID-19 and Related Public Health Measures on Hepatitis C Testing in Ontario, Canada" Viruses 17, no. 9: 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091163
APA StyleSahakyan, Y., Drover, S. S. M., Greenwald, Z. R., Wong, W. W. L., Kopp, A., Morrow, R. L., Janjua, N. Z., & Sander, B. (2025). The Impact of COVID-19 and Related Public Health Measures on Hepatitis C Testing in Ontario, Canada. Viruses, 17(9), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17091163






