Persistent Type I Interferon Signaling Impairs Innate Lymphoid Cells During HIV-1 Infection Under Suppressive ART
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
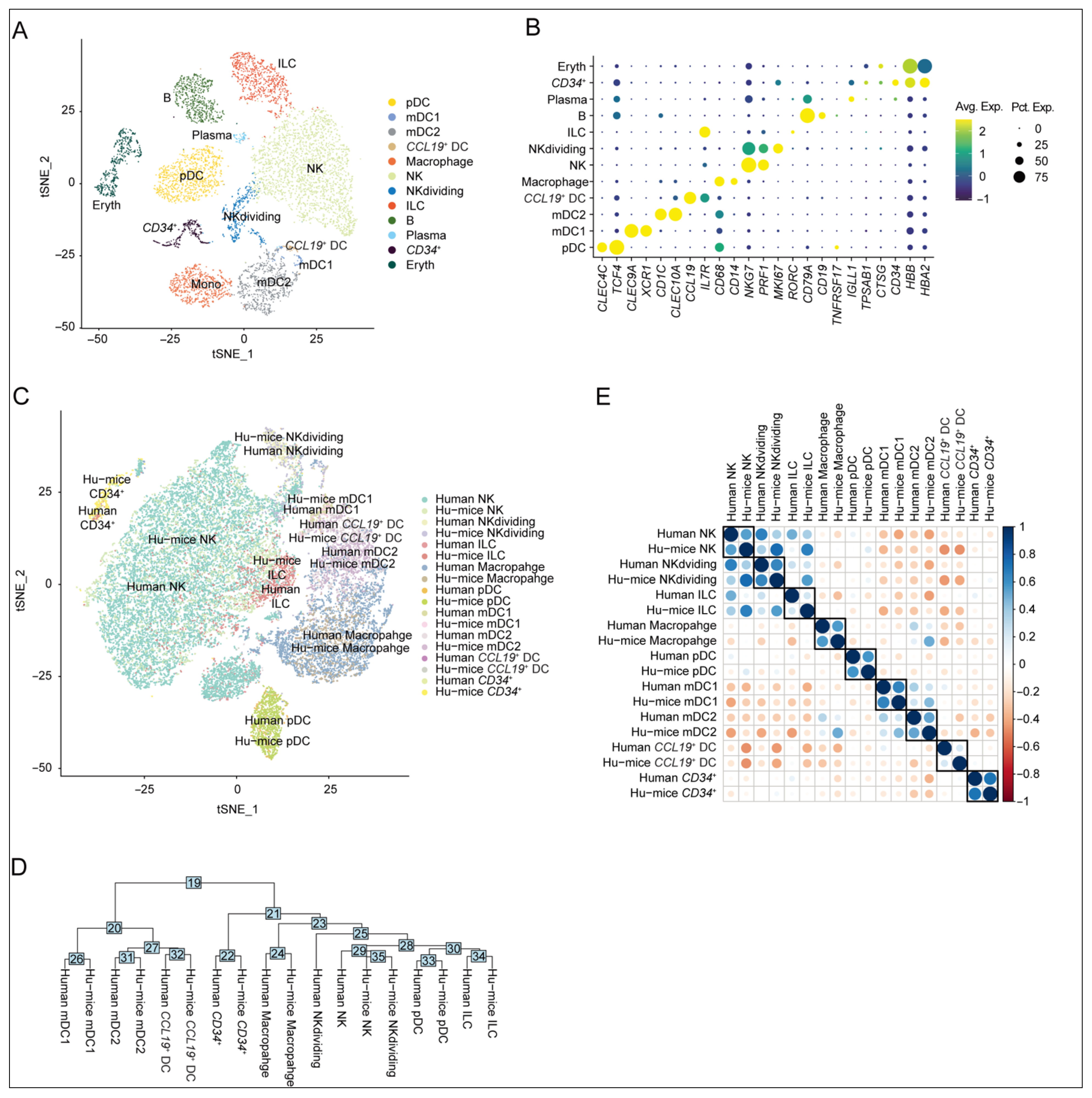
2.1. Similarity in Innate Immune Cell Subtypes Between Humanized Mouse Spleens and Human Spleen-Derived Counterparts
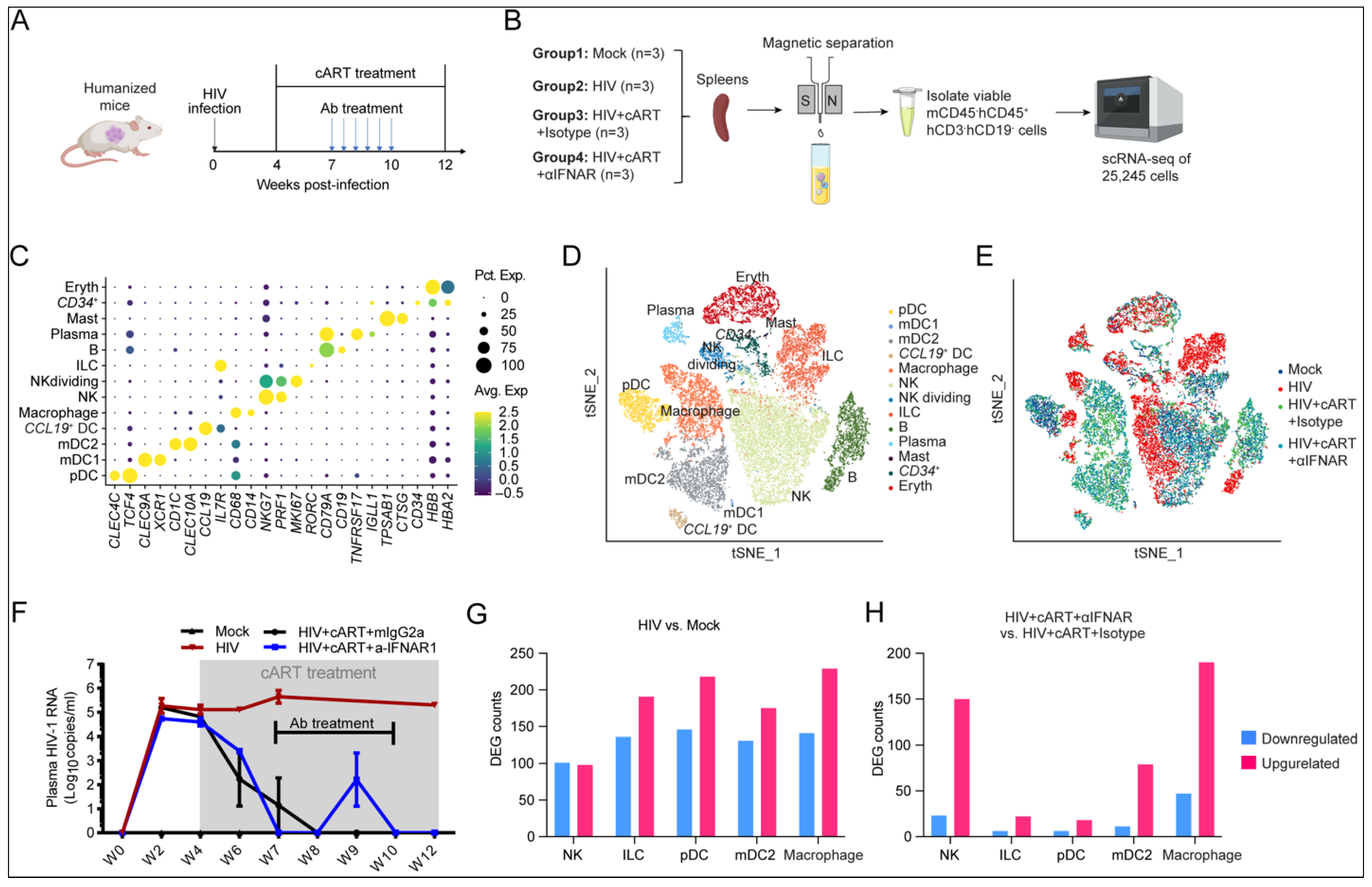
2.2. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Landscape Reveals HIV-1- and IFN-I-Driven Transcriptional Reprogramming of Innate Immune Cells
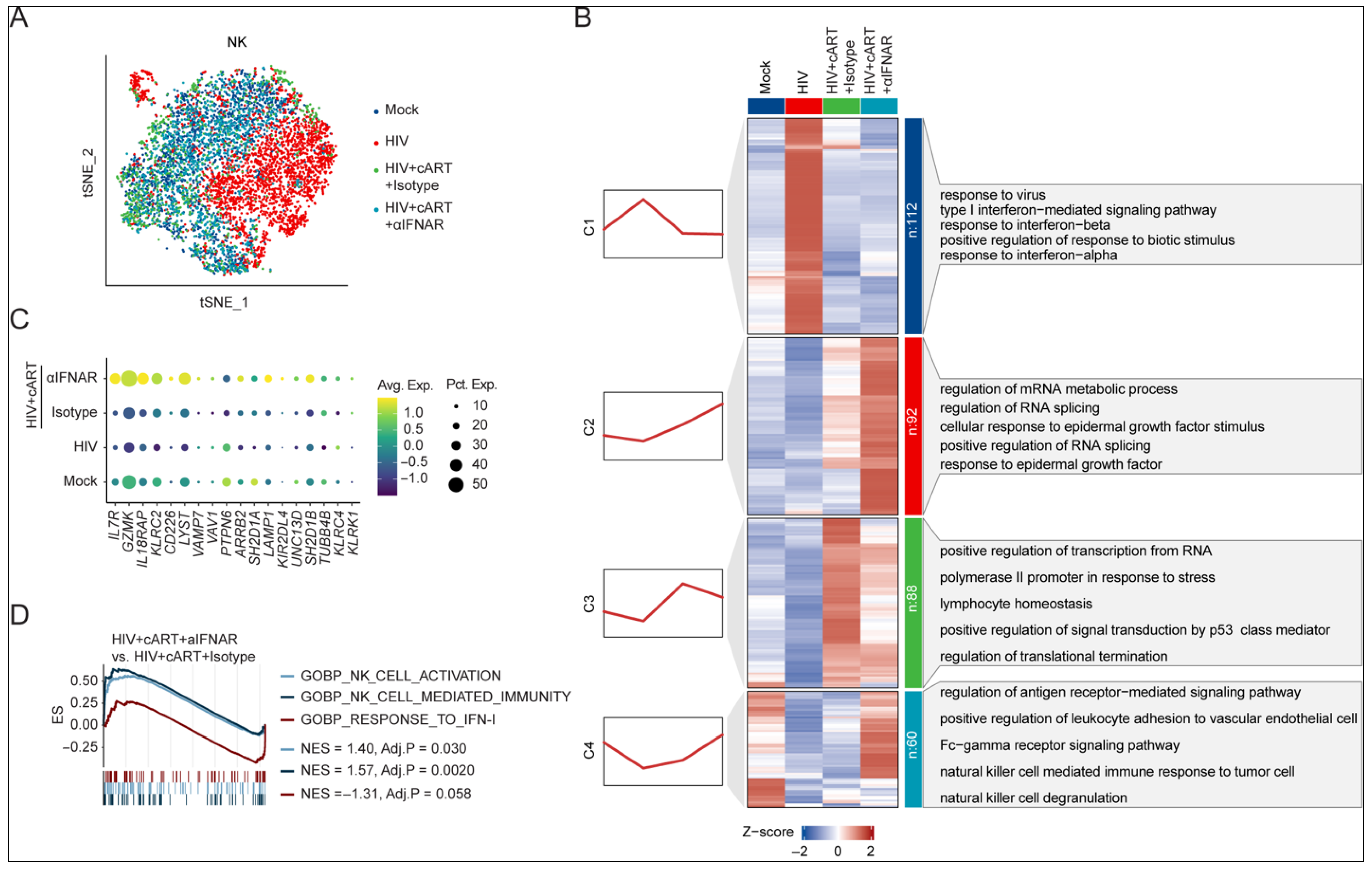
2.3. IFNAR Blockade Reverses Transcriptional Dysregulation of NK Cells in Chronic HIV-1 Infection Under cART
2.4. HIV-Induced CD9+ dNK-like Cells Persist via IFN-Dependent Mechanisms Under cART
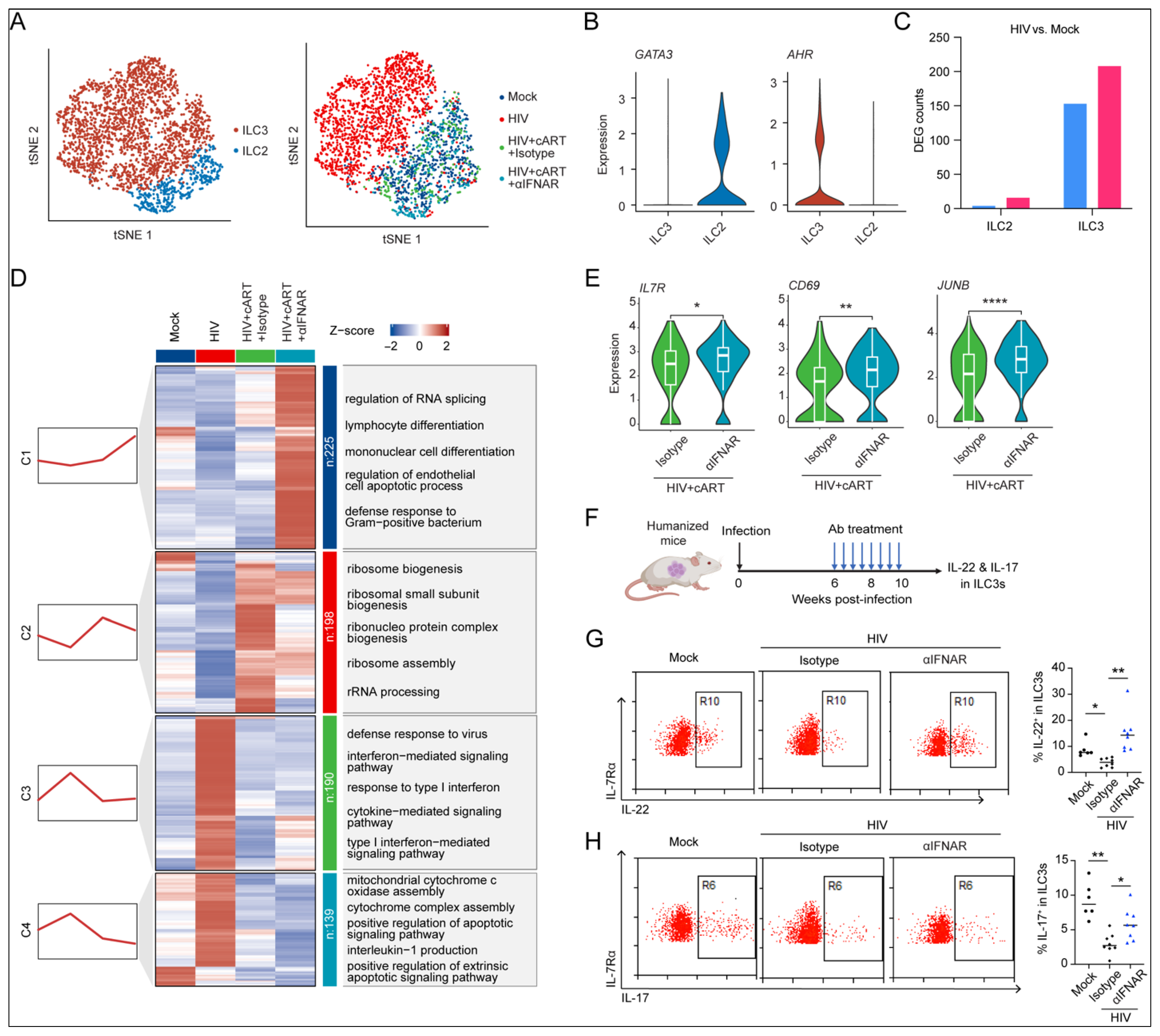
2.5. IFN-I Signaling Drives HIV-1-Induced Dysfunction of ILC3s
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Hu-Mice
4.2. HIV-1 Infection of Humanized Mice
4.3. Combination Antiretroviral Therapy
4.4. IFNAR Blocking Antibody Generation and Treatments
4.5. Isolation of mCD45–hCD3–hCD19–hCD45+ Splenocytes from Humanized Mice
4.6. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Library Preparation
4.7. Quality Control and Data Analysis of scRNA-Seq
4.8. Cell Clustering Analysis
4.9. Cell Type Correlation Analysis
4.10. Gene Clustering Analysis
4.11. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
4.12. Flow Cytometry
4.13. Statistics
4.14. Study Approval
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Archin, N.M.; Sung, J.M.; Garrido, C.; Soriano-Sarabia, N.; Margolis, D.M. Eradicating HIV-1 infection: Seeking to clear a persistent pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, J.; Taiwo, B.; Seedat, S.; Autran, B.; Katlama, C. HIV. Lancet 2018, 392, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, V.; Ho, D.D.; Abdool Karim, Q. HIV/AIDS epidemiology, pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment. Lancet 2006, 368, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells: 10 Years On. Cell 2018, 174, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Alvarez, L.; Hernandez, J.C.; Zapata, W. NK Cells in HIV-1 Infection: From Basic Science to Vaccine Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, E.; Zhang, C.X.; Kiani, Z.; Lisovsky, I.; Tallon, B.; Del Corpo, A.; Gilbert, L.; Bruneau, J.; Thomas, R.; Cote, P.; et al. HIV exposed seronegative (HESN) compared to HIV infected individuals have higher frequencies of telomeric Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptor (KIR) B motifs; Contribution of KIR B motif encoded genes to NK cell responsiveness. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, F.; Nicco, E.; Bozzano, F.; Di Biagio, A.; Dentone, C.; Pontali, E.; Boni, S.; Setti, M.; Orofino, G.; Mantia, E. Natural killer cells in HIV controller patients express an activated effector phenotype and do not up-regulate NKp44 on IL-2 stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11970–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.E.; Pohlmeyer, C.W.; Kwaa, A.K.; Mankowski, M.C.; Bailey, J.R.; Blankson, J.N. Combined effects of HLA-B* 57/5801 elite suppressor CD8+ T cells and NK cells on HIV-1 replication. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, S.; Reeves, R.K.; Jost, S. Learning to Be Elite: Lessons From HIV-1 Controllers and Animal Models on Trained Innate Immunity and Virus Suppression. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 858383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderko, R.R.; DePuyt, A.E.; Bronson, R.; Bullotta, A.C.; Aga, E.; Bosch, R.J.; Jones, R.B.; Eron, J.J.; Mellors, J.W.; Gandhi, R.T.; et al. Persistence of a Skewed Repertoire of NK Cells in People with HIV-1 on Long-Term Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Immunol. 2024, 212, 1564–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavilio, D.; Benjamin, J.; Daucher, M.; Lombardo, G.; Kottilil, S.; Planta, M.A.; Marcenaro, E.; Bottino, C.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A.; et al. Natural killer cells in HIV-1 infection: Dichotomous effects of viremia on inhibitory and activating receptors and their functional correlates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15011–15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtfuss, G.F.; Cheng, W.J.; Farsakoglu, Y.; Paukovics, G.; Rajasuriar, R.; Velayudham, P.; Kramski, M.; Hearps, A.C.; Cameron, P.U.; Lewin, S.R.; et al. Virologically suppressed HIV patients show activation of NK cells and persistent innate immune activation. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabatanzi, R.; Bayigga, L.; Cose, S.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Canderan, G.; Joloba, M.; Nakanjako, D. Aberrant natural killer (NK) cell activation and dysfunction among ART-treated HIV-infected adults in an African cohort. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 201, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloverpris, H.N.; Kazer, S.W.; Mjosberg, J.; Mabuka, J.M.; Wellmann, A.; Ndhlovu, Z.; Yadon, M.C.; Nhamoyebonde, S.; Muenchhoff, M.; Simoni, Y.; et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells Are Depleted Irreversibly during Acute HIV-1 Infection in the Absence of Viral Suppression. Immunity 2016, 44, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, B.; Goeser, F.; Lutz, P.; Glassner, A.; Boesecke, C.; Schwarze-Zander, C.; Kaczmarek, D.; Nischalke, H.D.; Branchi, V.; Manekeller, S.; et al. Compartment-specific distribution of human intestinal innate lymphoid cells is altered in HIV patients under effective therapy. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yasui, F.; Ye, C.; et al. Blocking type I interferon signaling enhances T cell recovery and reduces HIV-1 reservoirs. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Chi, L.; Zhang, L.; Su, L. Type I interferons suppress viral replication but contribute to T cell depletion and dysfunction during chronic HIV-1 infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 2, e94366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cheng, M.; Nunoya, J.; Cheng, L.; Guo, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.J.; Su, L.; Zhang, L. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells suppress HIV-1 replication but contribute to HIV-1 induced immunopathogenesis in humanized mice. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, A.; Rezek, V.; Youn, C.; Lam, B.; Chang, N.; Rick, J.; Carrillo, M.; Martin, H.; Kasparian, S.; Syed, P.; et al. Targeting type I interferon-mediated activation restores immune function in chronic HIV infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, H.; Wrobel, J.A.; Li, G.; Liu, P.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.N.; Su, L. Identification of pathogenic TRAIL-expressing innate immune cells during HIV-1 infection in humanized mice by scRNA-Seq. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5, e135344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madissoon, E.; Wilbrey-Clark, A.; Miragaia, R.J.; Saeb-Parsy, K.; Mahbubani, K.T.; Georgakopoulos, N.; Harding, P.; Polanski, K.; Huang, N.; Nowicki-Osuch, K.; et al. scRNA-seq assessment of the human lung, spleen, and esophagus tissue stability after cold preservation. Genome Biol. 2019, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, S.; Tanaskovic, S.; Helbig, K.; Rajasuriar, R.; Kramski, M.; Murray, J.M.; Beard, M.; Purcell, D.; Lewin, S.R.; Price, P.; et al. CD4+ T-cell deficiency in HIV patients responding to antiretroviral therapy is associated with increased expression of interferon-stimulated genes in CD4+ T cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, R.M.; Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Yukl, S.A.; Broadhurst, M.J.; Loke, P.; Albright, R.G.; Wong, J.K.; Lederman, M.M.; Somsouk, M.; Hunt, P.W.; et al. Discordance between peripheral and colonic markers of inflammation during suppressive ART. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2014, 65, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkar, S.A.; Yin, L.; Venturi, G.M.; Shen, J.; Chang, K.-F.; Fischer, B.M.; Nepal, U.; Raplee, I.D.; Sleasman, J.W.; Goodenow, M.M. Youth Who Control HIV on Antiretroviral Therapy Display Unique Plasma Biomarkers and Cellular Transcriptome Profiles Including DNA Repair and RNA Processing. Cells 2025, 14, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, L.A.; Kopcow, H.D.; Rybalov, B.; Boyson, J.E.; Orange, J.S.; Schatz, F.; Masch, R.; Lockwood, C.J.; Schachter, A.D.; Park, P.J.; et al. Human decidual natural killer cells are a unique NK cell subset with immunomodulatory potential. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrantia, A.; Vazquez-De Luis, E.; Astarloa-Pando, G.; Terren, I.; Amarilla-Irusta, A.; Polanco-Alonso, D.; Gonzalez, C.; Uranga, A.; Carrascosa, T.; Mateos-Mazon, J.J.; et al. In vivo expansion of a CD9(+) decidual-like NK cell subset following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. iScience 2022, 25, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umotoy, J.C.; Kroon, P.Z.; Man, S.; van Dort, K.A.; Atabey, T.; Schriek, A.I.; Dekkers, G.; Herrera-Carrillo, E.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.H.; Heukers, R.; et al. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by nanobodies targeting tetraspanin CD9. iScience 2024, 27, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinet, L.; Smyth, M.J. Balancing natural killer cell activation through paired receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houchins, J.P.; Lanier, L.L.; Niemi, E.C.; Phillips, J.H.; Ryan, J.C. Natural killer cell cytolytic activity is inhibited by NKG2-A and activated by NKG2-C. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3603–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Maenaka, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamamoto, K. The inhibitory NK cell receptor CD94/NKG2A and the activating receptor CD94/NKG2C bind the top of HLA-E through mostly shared but partly distinct sets of HLA-E residues. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Nie, W.; Reszka-Blanco, N.J.; Wang, F.S.; Su, L. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote HIV-1-induced group 3 innate lymphoid cell depletion. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3692–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Tu, B.; Fu, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Infection and depletion of CD4+ group-1 innate lymphoid cells by HIV-1 via type-I interferon pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarade, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Serafini, N. Group 3 innate lymphoid cells mediate host defense against attaching and effacing pathogens. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 63, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, N.; Di Santo, J.P. Group 3 innate lymphoid cells: A trained Gutkeeper. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 323, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, H.; Clark, K.M.; Mugisha, C.S.; Davis, K.; Tang, J.P.; Harlan, G.H.; DeSelm, C.J.; Presti, R.M.; Kutluay, S.B. CARD8 is an inflammasome sensor for HIV-1 protease activity. Science 2021, 371, eabe1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Liu, C.; Gu, Z.; Yang, X.; Lan, X.; Guo, X. Dysregulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling contributes to intestinal inflammation through regulation of group 3 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkstrom, N.K.; Strunz, B.; Ljunggren, H.G. Natural killer cells in antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabrane-Ferrat, N. Features of Human Decidual NK Cells in Healthy Pregnancy and During Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulich, A.E.; van Leeuwen, M.T.; Falster, M.O.; Vajdic, C.M. Incidence of cancers in people with HIV/AIDS compared with immunosuppressed transplant recipients: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2007, 370, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.T.; Kaplan, J.E.; Holmes, K.K.; Benson, C.; Pau, A.; Masur, H. HIV-associated opportunistic infections--going, going, but not gone: The continued need for prevention and treatment guidelines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Shores, E.W.; Hu-Li, J.; Anver, M.R.; Kelsall, B.L.; Russell, S.M.; Drago, J.; Noguchi, M.; Grinberg, A.; Bloom, E.T.; et al. Defective lymphoid development in mice lacking expression of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain. Immunity 1995, 2, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochi, T.; Denton, P.W.; Wahl, A.; Garcia, J.V. Cryptopatches are essential for the development of human GALT. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A.N.J.; Spits, H.; Eberl, G. Innate lymphoid cells in inflammation and immunity. Immunity 2014, 41, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587 e3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, R.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Su, L.; Cheng, L. Persistent Type I Interferon Signaling Impairs Innate Lymphoid Cells During HIV-1 Infection Under Suppressive ART. Viruses 2025, 17, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081099
Han R, Yu H, Li G, Su L, Cheng L. Persistent Type I Interferon Signaling Impairs Innate Lymphoid Cells During HIV-1 Infection Under Suppressive ART. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081099
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Runpeng, Haisheng Yu, Guangming Li, Lishan Su, and Liang Cheng. 2025. "Persistent Type I Interferon Signaling Impairs Innate Lymphoid Cells During HIV-1 Infection Under Suppressive ART" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081099
APA StyleHan, R., Yu, H., Li, G., Su, L., & Cheng, L. (2025). Persistent Type I Interferon Signaling Impairs Innate Lymphoid Cells During HIV-1 Infection Under Suppressive ART. Viruses, 17(8), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081099







