Surface Gene Mutations of Hepatitis B Virus and Related Pathogenic Mechanisms: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Function of HBV S Gene
2.1. S Gene Encoding Domain
2.2. HBsAg Plays a Key Role in the Virus Life Cycle
3. Epidemiological Characteristics of Mutations in Region S
3.1. Pre-S/S Gene
3.2. Mutation Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen S Gene
4. Common Mutation Types
4.1. S Gene Mutation
4.2. Pre-S1/S2 Deletion Mutation
4.3. Truncation Mutations
5. Hepatitis B Virus S Gene Mutation and Pathogenesis
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen S Gene Mutation Leads to Virus Replication and Genome Integration
6. Occult Hepatitis and Chronic Inflammation
7. ER Stress and HCC
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Amino acid |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ATF4 | Activating transcription factor 4 |
| ATF6 | Activating transcription factor 6 |
| ASK-1 | Apoptosis signal transduction kinase-1 |
| BiP | Binding immunoglobulin protein |
| cccDNA | Covalently closed circular DNA |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| eIF2α | Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| GGH | Ground-glass hepatocytes |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| IKK | IκB kinase |
| IRE1α | Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| L-HBsAg | Large hepatitis B surface antigen |
| LEF | Lymphoid enhancer factor |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MHBst | Truncated middle hepatitis B surface protein |
| M-HBsAg | Middle hepatitis B surface antigen |
| MHR | Major hydrophilic region |
| NA | Nucleos(t)ide analogue |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NTCP | Sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide |
| OBI | Occult HBV infection |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| PERK | Protein kinase R-like ER kinase |
| RT | Reverse transcriptase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| S-HBsAg | Small hepatitis B surface antigen |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TCF | T-cell factor |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| VLP | Virus-like particle |
| XBP1 | X-Box binding protein 1 |
References
- Hsu, Y.C.; Huang, D.Q.; Nguyen, M.H. Global burden of hepatitis B virus: Current status, missed opportunities and a call for action. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, A.; Papac, L.; Barquera, R.; Key, F.M.; Spyrou, M.A.; Hübler, R.; Rohrlach, A.B.; Aron, F.; Stahl, R.; Wissgott, A.; et al. Ten millennia of hepatitis B virus evolution. Science 2021, 374, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locarnini, S.A.; Yuen, L. Molecular genesis of drug-resistant and vaccine-escape HBV mutants. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15 Pt B, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Yang, H.I.; Iloeje, U.H.; You, S.L.; Lu, S.N.; Wang, L.Y.; Su, J.; Sun, C.A.; Liaw, Y.F.; Chen, C.J. Carriers of inactive hepatitis B virus are still at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related death. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiollais, P.; Pourcel, C.; Dejean, A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature 1985, 317, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.H.; Laub, O.; Rutter, W.J. Hepatitis B virus gene function: The precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, V. Hepatitis B virus morphogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirk, H.J.; Thornton, J.M.; Howard, C.R. A topological model for hepatitis B surface antigen. Intervirology 1992, 33, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.J.; Shah, P.A.; Rehman, K.U.; Kaur, S.; Holzmayer, V.; Cloherty, G.A.; Kuhns, M.C.; Lau, D.T.Y. Immune-Escape Mutations Are Prevalent among Patients with a Coexistence of HBsAg and Anti-HBs in a Tertiary Liver Center in the United States. Viruses 2024, 16, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, C.; Xu, X.; Mei, C.; Cheng, J. Analysis of S gene characteristic sequences and changes in properties of protein expression in HBV ASCs with low-level HBsAg. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 948842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selzer, L.; Zlotnick, A. Assembly and Release of Hepatitis B Virus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Cacciola, I.; Saffioti, F.; Raimondo, G. Hepatitis B virus PreS/S gene variants: Pathobiology and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.F. Hepatitis B virus pre-S/S variants in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Huo, Z.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Syn, W.K. Characteristics of amino acid substitutions within the “a” determinant region of hepatitis B virus in chronically infected patients with coexisting HBsAg and anti-HBs. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xie, S.; He, Y.; Lu, L. High prevalence of tryptophan-truncated S quasispecies in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotiyaputta, W.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis B virus variants. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2024; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti, A.R.; Tanzi, E.; Manzillo, G.; Maio, G.; Sbreglia, C.; Caporaso, N.; Thomas, H.; Zuckerman, A.J. Hepatitis B variant in Europe. Lancet 1988, 2, 1132–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.; Zoulim, F. Hepatitis B virus genetic variability and evolution. Virus Res. 2007, 127, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villet, S.; Billioud, G.; Pichoud, C.; Lucifora, J.; Hantz, O.; Sureau, C.; Dény, P.; Zoulim, F. In vitro characterization of viral fitness of therapy-resistant hepatitis B variants. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 168–176.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencay, M.; Hübner, K.; Gohl, P.; Seffner, A.; Weizenegger, M.; Neofytos, D.; Batrla, R.; Woeste, A.; Kim, H.S.; Westergaard, G.; et al. Ultra-deep sequencing reveals high prevalence and broad structural diversity of hepatitis B surface antigen mutations in a global population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieshout-Krikke, R.W.; Molenaar-de Backer, M.W.; van Swieten, P.; Zaaijer, H.L. Surface antigen-negative hepatitis B virus infection in Dutch blood donors. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Harrison, T.J.; He, X.; Chen, Q.Y.; Li, G.J.; Liu, M.H.; Li, H.; Yang, J.Y.; Fang, Z.L. The prevalence of mutations in the major hydrophilic region of the surface antigen of hepatitis B virus varies with subgenotype. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 3572–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jeng, L.B.; Chan, W.L.; Teng, C.F. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets of Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S Mutant-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis. Cancer Control 2025, 32, 10732748251320492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callea, F.; de Vos, R.; Togni, R.; Tardanico, R.; Vanstapel, M.J.; Desmet, V.J. Fibrinogen inclusions in liver cells: A new type of ground-glass hepatocyte. Immune light and electron microscopic characterization. Histopathology 1986, 10, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Lu, C.C.; Chen, W.C.; Yao, W.J.; Wang, H.C.; Chang, T.T.; Lei, H.Y.; Shiau, A.L.; Su, I.J. Prevalence and significance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) pre-S mutants in serum and liver at different replicative stages of chronic HBV infection. Hepatology 2001, 33, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Wu, H.C.; Chen, C.F.; Fausto, N.; Lei, H.Y.; Su, I.J. Different types of ground glass hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection contain specific pre-S mutants that may induce endoplasmic reticulum stress. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yen, T.S. Intracellular retention of surface protein by a hepatitis B virus mutant that releases virion particles. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.T. Development of HBV S gene mutants in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleotide/nucleoside analogue therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15 Pt B, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann-Fraune, M.; Beggel, B.; Pfister, H.; Kaiser, R.; Verheyen, J. High frequency of complex mutational patterns in lamivudine resistant hepatitis B virus isolates. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Tang, H. Nucleos(t)ide analogues causes HBV S gene mutations and carcinogenesis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2016, 15, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Ryu, C.J.; Hong, H.J. Hepatitis B virus preS1 functions as a transcriptional activation domain. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78 Pt 5, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildt, E.; Saher, G.; Bruss, V.; Hofschneider, P.H. The hepatitis B virus large surface protein (LHBs) is a transcriptional activator. Virology 1996, 225, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildt, E.; Urban, S.; Hofschneider, P.H. Characterization of essential domains for the functionality of the MHBst transcriptional activator and identification of a minimal MHBst activator. Oncogene 1995, 11, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar]
- Hildt, E.; Munz, B.; Saher, G.; Reifenberg, K.; Hofschneider, P.H. The PreS2 activator MHBs(t) of hepatitis B virus activates c-raf-1/Erk2 signaling in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupberger, J.; Hildt, E. Hepatitis B virus-induced oncogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubonja-Šonje, M.; Peruč, D.; Abram, M.; Mohar-Vitezić, B. Prevalence of occult hepatitis B virus infection and characterisation of hepatitis B surface antigen mutants among adults in western Croatia. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farazi, P.A.; DePinho, R.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbenson, M.; Thomas, D.L. Occult hepatitis B. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, R.; Si, L.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; et al. Characterization of Novel Hepatitis B Virus PreS/S-Gene Mutations in a Patient with Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.L.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Ge, X.M.; Harrison, T.J. Hepatitis B virus genotypes, phylogeny and occult infection in a region with a high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 3264–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Shuai, L.; Wang, A.; Zeng, J.; Candotti, D.; Allain, J.P.; Li, C. Characterization of occult hepatitis B virus infection from blood donors in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, S.; Nirei, K.; Tamura, A.; Nakamura, H.; Matsumura, H.; Oshiro, S.; Arakawa, Y.; Yamagami, H.; Tanaka, N.; Moriyama, M. Influence of occult hepatitis B virus coinfection on the incidence of fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C. Intervirology 2008, 51, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, M. Hepatitis B virus persistence and reactivation. BMJ 2020, 370, m2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Kamata, H.; Luo, J.L.; Leffert, H.; Karin, M. IKKbeta couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 2005, 121, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucur, M.; Reisinger, F.; Gautheron, J.; Janssen, J.; Roderburg, C.; Cardenas, D.V.; Kreggenwinkel, K.; Koppe, C.; Hammerich, L.; Hakem, R.; et al. RIP3 inhibits inflammatory hepatocarcinogenesis but promotes cholestasis by controlling caspase-8- and JNK-dependent compensatory cell proliferation. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedtke, C.; Bangen, J.M.; Freimuth, J.; Beraza, N.; Lambertz, D.; Cubero, F.J.; Hatting, M.; Karlmark, K.R.; Streetz, K.L.; Krombach, G.A.; et al. Loss of caspase-8 protects mice against inflammation-related hepatocarcinogenesis but induces non-apoptotic liver injury. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 2176–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, E.; Arlier, S.; Guzeloglu-Kayisli, O.; Tabak, M.S.; Ekiz, T.; Semerci, N.; Larsen, K.; Schatz, F.; Lockwood, C.J.; Kayisli, U.A. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Homeostasis in Reproductive Physiology and Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.S.; Blower, M.D. The endoplasmic reticulum: Structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Navarro, N.; Miller, E. Protein sorting at the ER-Golgi interface. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, P.A.; Ploegh, H.L. Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, F.V.; Klopchin, K.; Moriyama, T.; Pasquinelli, C.; Dunsford, H.A.; Sell, S.; Pinkert, C.A.; Brinster, R.L.; Palmiter, R.D. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell 1989, 59, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar-Kimber, K.L.; Jarocki-Witek, V.; Dheer, S.K.; Vernon, S.K.; Conley, A.J.; Davis, A.R.; Hung, P.P. Distinctive properties of the hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.M.; Yang, W.L.; Wang, P. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Sepsis. Shock 2015, 44, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeri, M.; Knox, B.E. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response Pathways: Potential for Treating Age-related Retinal Degeneration. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2012, 7, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Lee, A.S. Role of the unfolded protein response, GRP78 and GRP94 in organ homeostasis. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettigole, S.E.; Glimcher, L.H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Li, Z. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatic steatosis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnop, M.; Foufelle, F.; Velloso, L.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B.J. Naturally Occurring Hepatitis B Virus Mutations Leading to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Their Contribution to the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, B.M.; Pincus, D.; Gotthardt, K.; Gallagher, C.M.; Walter, P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing in the unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a013169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, N.; Guan, G.; Wang, J. Protein kinase R-like ER kinase and its role in endoplasmic reticulum stress-decided cell fate. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimata, Y.; Oikawa, D.; Shimizu, Y.; Ishiwata-Kimata, Y.; Kohno, K. A role for BiP as an adjustor for the endoplasmic reticulum stress-sensing protein Ire1. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley, E.C.; Osborn, A.R.; Scott, J.E.; Scholl, A.G.; Mercado, V.; McMahan, Y.T.; Coffman, Z.G.; Brewster, J.L. Moderate endoplasmic reticulum stress activates a PERK and p38-dependent apoptosis. Cell Stress. Chaperones 2017, 22, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Tirasophon, W.; Shen, X.; Michalak, M.; Prywes, R.; Okada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Mori, K.; Kaufman, R.J. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes. Dev. 2002, 16, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wong, H.N.; Schauerte, J.A.; Kaufman, R.J. The protein kinase/endoribonuclease IRE1alpha that signals the unfolded protein response has a luminal N-terminal ligand-independent dimerization domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18346–18356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 2001, 107, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, F.; Wang, X.; Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, P.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 2000, 287, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Cui, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Ji, Q.Y.; He, J.T.; Yao, M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shao, Y.K.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of Activin A on endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptotic and autophagic PC12 cell death. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimoto, S.; Ninagawa, S.; Okada, T.; Koba, H.; Sugimoto, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Kato, K.; Takeda, S.; Mori, K. The unfolded protein response transducer ATF6 represents a novel transmembrane-type endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation substrate requiring both mannose trimming and SEL1L protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31517–31527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haze, K.; Okada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Yanagi, H.; Yura, T.; Negishi, M.; Mori, K. Identification of the G13 (cAMP-response-element-binding protein-related protein) gene product related to activating transcription factor 6 as a transcriptional activator of the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biochem. J. 2001, 355 Pt 1, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadanaka, S.; Yoshida, H.; Kano, F.; Murata, M.; Mori, K. Activation of mammalian unfolded protein response is compatible with the quality control system operating in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck, S.; Prinz, W.A.; Thorn, K.S.; Voss, C.; Walter, P. Membrane expansion alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress independently of the unfolded protein response. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-kappaB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikarsky, E.; Porat, R.M.; Stein, I.; Abramovitch, R.; Amit, S.; Kasem, S.; Gutkovich-Pyest, E.; Urieli-Shoval, S.; Galun, E.; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, J.H.; Su, I.J.; Lei, H.Y.; Wang, H.C.; Lin, W.C.; Chang, W.T.; Huang, W.; Chang, W.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 through activation of NF-kappaB and pp38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 46384–46392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugorria, M.J.; Olaizola, P.; Labiano, I.; Esparza-Baquer, A.; Marzioni, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. Wnt-β-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pez, F.; Lopez, A.; Kim, M.; Wands, J.R.; Caron de Fromentel, C.; Merle, P. Wnt signaling and hepatocarcinogenesis: Molecular targets for the development of innovative anticancer drugs. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reya, T.; Clevers, H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 2005, 434, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, P.; Pillot, J. At least three epitopes are recognized by the human repertoire in the hepatitis B virus group a antigen inducing protection; possible consequences for seroprevention and serodiagnosis. Res. Virol. 1998, 149, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Peng, X.M.; Huang, Y.S.; Gu, L.; Xie, Q.F.; Gao, Z.L. Yeast expression and DNA immunization of hepatitis B virus S gene with second-loop deletion of alpha determinant region. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
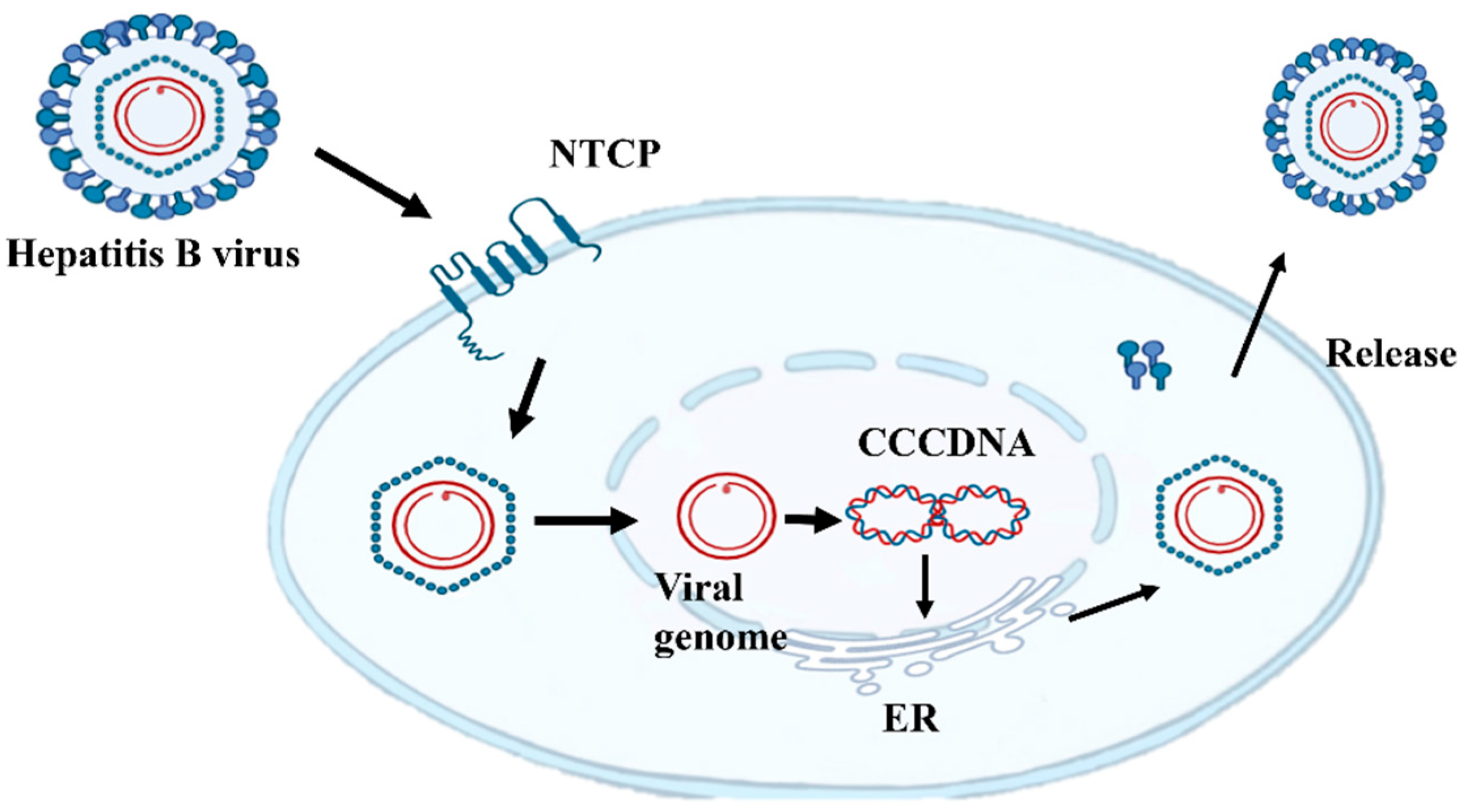
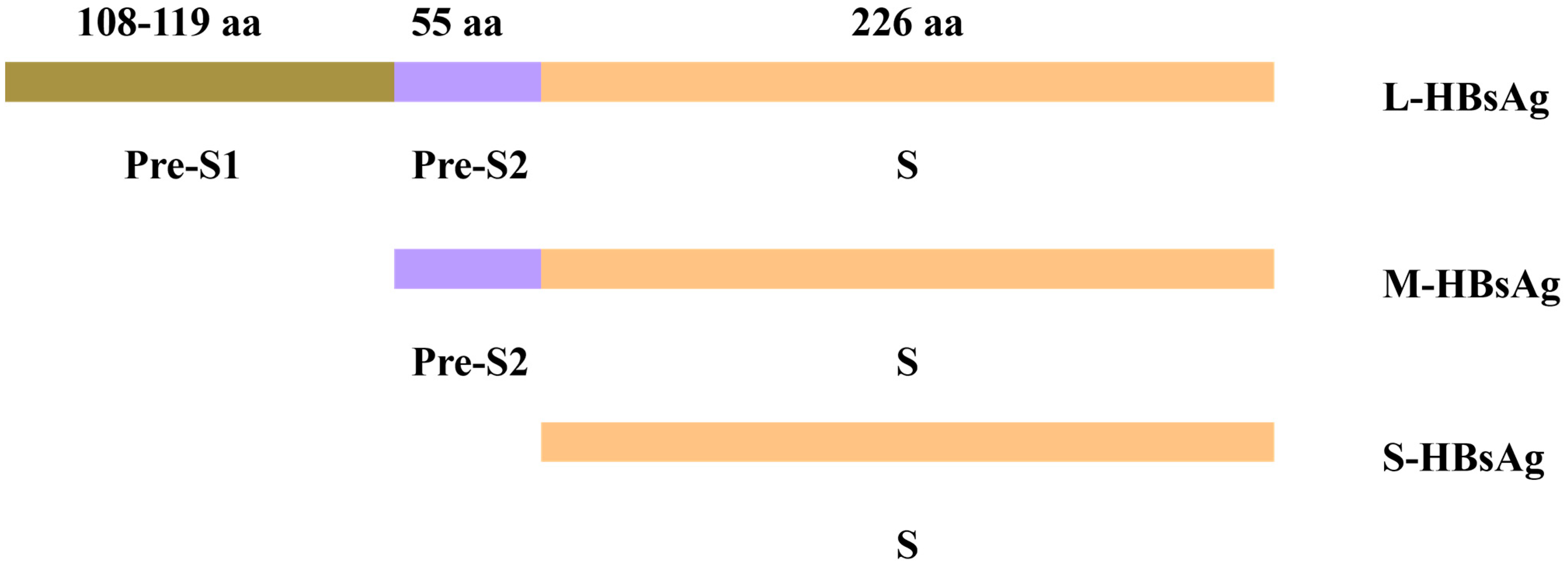

| Mutation Type | Representative Mutations | Molecular Mechanism | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point Mutations | G145R (“a” determinant) 345+ MHR variants |
|
|
| Pre-S1 Deletions | nt2854-3210 deletion |
|
|
| Pre-S2 Deletions | nt3211-3221/1-154 deletion |
|
|
| Truncation Mutations | rtA181T/sW172 rtM204I/sW196 rtV191I/sW182 |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, N.; Wang, X.; Yan, W.; Yin, J. Surface Gene Mutations of Hepatitis B Virus and Related Pathogenic Mechanisms: A Narrative Review. Viruses 2025, 17, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070974
Yan T, Zhang Y, Zhou H, Jiang N, Wang X, Yan W, Yin J. Surface Gene Mutations of Hepatitis B Virus and Related Pathogenic Mechanisms: A Narrative Review. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070974
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Tingxi, Yusheng Zhang, Huifang Zhou, Ning Jiang, Xiaotong Wang, Wei Yan, and Jianhua Yin. 2025. "Surface Gene Mutations of Hepatitis B Virus and Related Pathogenic Mechanisms: A Narrative Review" Viruses 17, no. 7: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070974
APA StyleYan, T., Zhang, Y., Zhou, H., Jiang, N., Wang, X., Yan, W., & Yin, J. (2025). Surface Gene Mutations of Hepatitis B Virus and Related Pathogenic Mechanisms: A Narrative Review. Viruses, 17(7), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070974






