Immune and Safety Analysis of ultraIPVTM, a Novel UVC-Inactivated Polio Vaccine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Production and Purification
2.2. UVC Inactivation of Polio Viruses
2.3. Rat Immunization
2.4. Analysis of Immune Responses: Total Binding Antibodies to Polioviruses, Neutralization Titers, and Responses to the Decapeptide
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistical Analyses
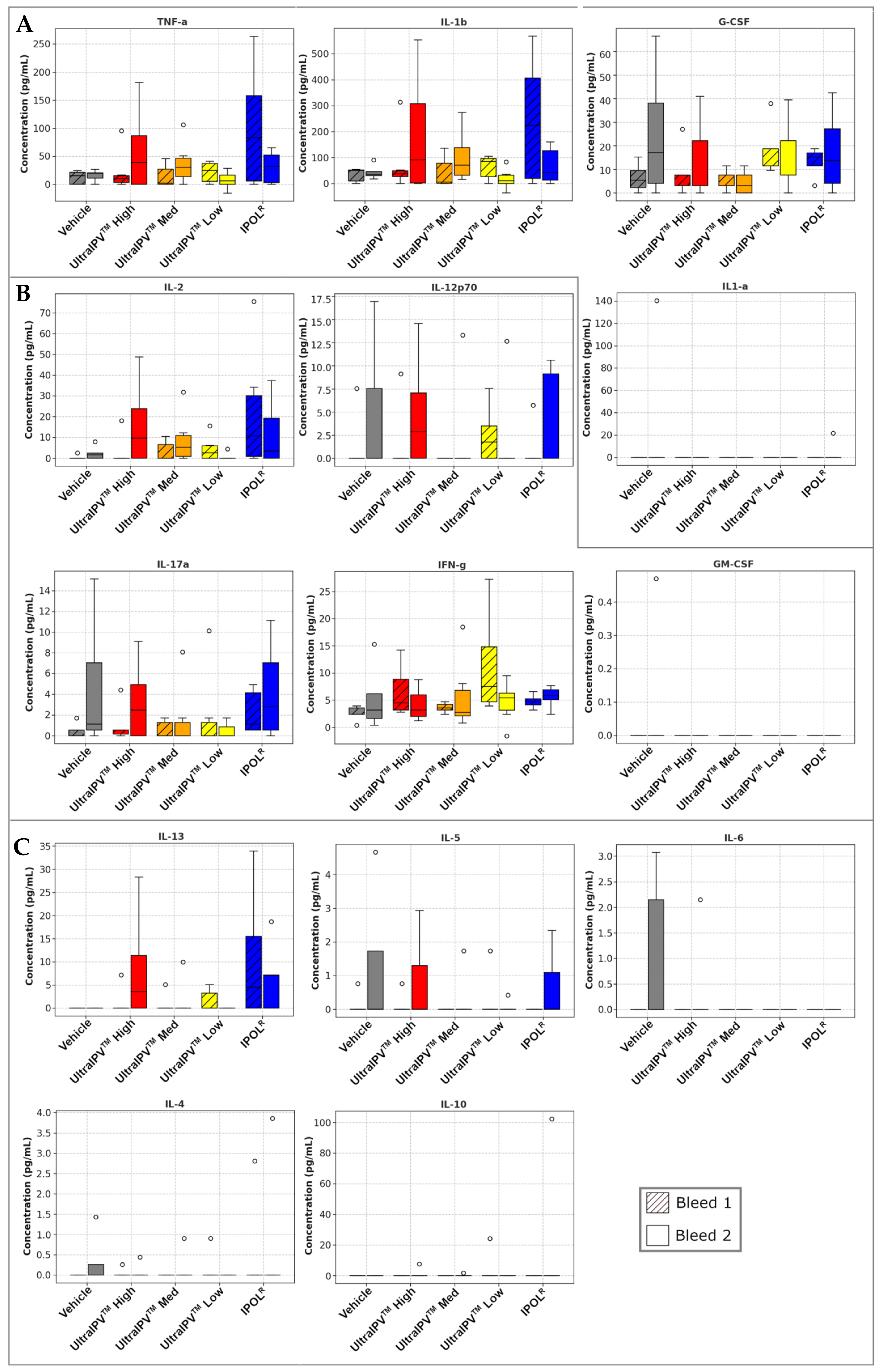
3. Results
4. Discussion
Future Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| °C | Degrees in Celsius |
| g | gravitational force used in centrifugation |
| IPV | Inactivated polio vaccine |
| MDP | Manganese-decapeptide-phosphate antioxidant complex |
| MES | 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid buffer |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| OPV | Oral polio vaccine |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PV1 | Poliovirus serotype 1 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| sIPV | Sabin-based IPV |
| SMEM | Spinner modification of minimum essential Eagle’s medium |
| UVC | Ultraviolet light in the C band (254 nm) |
| VAPP | Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis |
| VDPV | Vaccine-derived poliovirus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WPV1 | Wild-type poliovirus serotype 1 |
References
- Chard, A.N.; Datta, S.D.; Tallis, G.; Burns, C.C.; Wassilak, S.G.F.; Vertefeuille, J.F.; Zaffran, M. Progress Toward Polio Eradication—Worldwide, January 2018–March 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Requirements for Poliomyelitis Vaccine (Inactivated) WHO Annex 2. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2002, 910. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.; Cochi, S. Addressing the Challenges and Opportunities of the Polio Endgame: Lessons for the Future. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPEI. OPV—Oral Polio Vaccine. Global Polio Eradication Initiative (April 2025). Available online: https://polioeradication.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Platt, L.R.; Estívariz, C.F.; Sutter, R.W. Vaccine-Associated Paralytic Poliomyelitis: A Review of the Epidemiology and Estimation of the Global Burden. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210 (Suppl. S1), S380–S389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopalco, P.L. Wild and Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus Circulation, and Implications for Polio Eradication. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka-Anstadt, J.L.; Campagnoli, R.; Vincent, A.; Shaw, J.; Wei, L.; Wynn, N.T.; Smithee, S.E.; Bujaki, E.; Te Yeh, M.; Laassri, M.; et al. Development of a New Oral Poliovirus Vaccine for the Eradication End Game Using Codon Deoptimization. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcet, M.R.; Modrof, J.; Rabel, P.O.; Schirmer, A.; Macadam, A.J.; Fox, H.; Minor, P.D.; Kreil, T.R. Continued Use of Poliovirus after Eradication: Hyper-attenuated Strains as a Safe Alternative for Release Testing of Human Immunoglobulins. Transfusion 2018, 58, 3084–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, B.P.; De Los Rios Oakes, I.; Van Hoek, V.; Bockstal, V.; Kamphuis, T.; Uil, T.G.; Song, Y.; Cooper, G.; Crawt, L.E.; Martín, J.; et al. Cold-Adapted Viral Attenuation (CAVA): Highly Temperature Sensitive Polioviruses as Novel Vaccine Strains for a Next Generation Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, B.P.; Oakes, I.D.L.R.; Van Hoek, V.; Liu, Y.; Marissen, W.; Minor, P.D.; Wimmer, E.; Schuitemaker, H.; Custers, J.H.H.V.; Macadam, A.; et al. Production of High Titer Attenuated Poliovirus Strains on the Serum-Free PER.C6® Cell Culture Platform for the Generation of Safe and Affordable next Generation IPV. Vaccine 2015, 33, 6611–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.T.; Bujaki, E.; Dolan, P.T.; Smith, M.; Wahid, R.; Konz, J.; Weiner, A.J.; Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Van Damme, P.; De Coster, I.; et al. Engineering the Live-Attenuated Polio Vaccine to Prevent Reversion to Virulence. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 736–751.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, P.; De Coster, I.; Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Revets, H.; Withanage, K.; De Smedt, P.; Suykens, L.; Oberste, M.S.; Weldon, W.C.; Costa-Clemens, S.A.; et al. The Safety and Immunogenicity of Two Novel Live Attenuated Monovalent (Serotype 2) Oral Poliovirus Vaccines in Healthy Adults: A Double-Blind, Single-Centre Phase 1 Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoge, M.; Futa, A.C.; Umesi, A.; Affleck, L.; Kotei, L.; Daffeh, B.; Saidy-Jah, E.; Njie, A.; Oyadiran, O.; Edem, B.; et al. Safety of the Novel Oral Poliovirus Vaccine Type 2 (nOPV2) in Infants and Young Children Aged 1 to <5 Years and Lot-to-Lot Consistency of the Immune Response to nOPV2 in Infants in The Gambia: A Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickley, E.B.; Strauch, C.B.; Wieland-Alter, W.F.; Connor, R.I.; Lin, S.; Weiner, J.A.; Ackerman, M.E.; Arita, M.; Oberste, M.S.; Weldon, W.C.; et al. Intestinal Immune Responses to Type 2 Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) Challenge in Infants Previously Immunized With Bivalent OPV and Either High-Dose or Standard Inactivated Polio Vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Medina, E.; Melgar, M.; Gaensbauer, J.T.; Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Borate, B.R.; Weldon, W.C.; Rüttimann, R.; Ward, J.; Clemens, R.; Asturias, E.J. Inactivated Polio Vaccines from Three Different Manufacturers Have Equivalent Safety and Immunogenicity When given as 1 or 2 Additional Doses after Bivalent OPV: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial in Latin America. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3591–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilton, T. Methods for the Quality Control of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccines. In Poliovirus; Martín, J., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1387, pp. 279–297. ISBN 978-1-4939-3291-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.J.; Heath, A.B.; Sawyer, L.A. A WHO Collaborative Study on Assays of the Antigenic Content of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccines. Biologicals 1995, 23, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/diseases/poliomyelitis-(polio) (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Famulare, M.; Selinger, C.; McCarthy, K.A.; Eckhoff, P.A.; Chabot-Couture, G. Assessing the Stability of Polio Eradication after the Withdrawal of Oral Polio Vaccine. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2002468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duizer, E.; Rutjes, S.; Husman, A.M.D.R.; Schijven, J. Risk Assessment, Risk Management and Risk-Based Monitoring Following a Reported Accidental Release of Poliovirus in Belgium, September to November 2014. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdle, W.R.; Wolff, C.; Sanders, R.; Lambert, S.; Best, M. Will Containment of Wild Poliovirus in Laboratories and Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Production Sites Be Effective for Global Certification? Bull. World Health Organ. 2004, 82, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Singh, H.; Fournier-Caruana, J.; Modlin, J.F.; Wenger, J.; Partridge, J.; Sutter, R.W.; Zaffran, M.J. Facility-Associated Release of Polioviruses into Communities-Risks for the Posteradication Era. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Gast, C.; Brickley, E.B.; Rüttimann, R.; Clemens, R.; Oberste, M.S.; Weldon, W.C.; Ackerman, M.E.; Connor, R.I.; Wieland-Alter, W.F.; et al. A Randomized Phase 4 Study of Immunogenicity and Safety After Monovalent Oral Type 2 Sabin Poliovirus Vaccine Challenge in Children Vaccinated with Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine in Lithuania. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.; Klapsa, D.; Wilton, T.; Stone, L.; Minor, P.D.; Martin, J. Twenty-Eight Years of Poliovirus Replication in an Immunodeficient Individual: Impact on the Global Polio Eradication Initiative. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkasova, E.A.; Yakovenko, M.L.; Rezapkin, G.V.; Korotkova, E.A.; Ivanova, O.E.; Eremeeva, T.P.; Krasnoproshina, L.I.; Romanenkova, N.I.; Rozaeva, N.R.; Sirota, L.; et al. Spread of Vaccine-Derived Poliovirus from a Paralytic Case in an Immunodeficient Child: An Insight into the Natural Evolution of Oral Polio Vaccine. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.J.; Sutter, R.W.; Dowdle, W.R. Stopping Poliovirus Vaccination after Eradication: Issues and Challenges. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Minor, P.D.; Lane, B.; Mimms, S.; Bar, P. Scientific Consultation on the Safety and Containment of New Poliovirus Strains for Vaccine Production, Clinical/Regulatory Testing and Research. Report of a Meeting Held at NIBSC, Potters Bar, Hertfordshire, UK, 6/7th July 2016. Biologicals 2017, 48, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elghaffar, A.A.; Rashed, M.E.; Ali, A.E.; Amin, M.A. In-Vitro Inactivation of Sabin-Polioviruses for Development of Safe and Effective Polio Vaccine. Vaccines 2020, 8, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, K.; Ehrenfeld, E. Vaccines: New Generation of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccines for Universal Immunization after Eradication of Poliomyelitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayasu, H.; Sein, C.; Hamidi, A.; Bakker, W.A.M.; Sutter, R.W. Development of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine from Sabin Strains: A Progress Report. Biologicals 2016, 44, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.P.; Jimeno, J.; Han, H.H.; Lin, S.; Hartmann, K.; Borkowski, A.; Sáez-Llorens, X. Safety and Immunogenicity of Experimental Stand-Alone Trivalent, Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine Formulations in Healthy Infants: A Randomized, Observer-Blind, Controlled Phase 1/2 Trial. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5313–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, G. Antigenic and Immunogenic Properties of Inactivated Polio Vaccine Made from Sabin Strains. Vaccine 1999, 17, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tano, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Martin, J.; Nishimura, Y.; Simizu, B.; Miyamura, T. Antigenic Characterization of a Formalin-Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Derived from Live-Attenuated Sabin Strains. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7041–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Crossland, G.; Wood, D.J.; Minor, P.D. Characterization of Formaldehyde-Inactivated Poliovirus Preparations Made from Live-Attenuated Strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawt, L.; Atkinson, E.; Tedcastle, A.; Pegg, E.; sIPV Study Group; Dobly, A.; Wei, C.; Lei, S.; Ling, P.; Li, C.; et al. Differences in Antigenic Structure of Inactivated Polio Vaccines Made From Sabin Live-Attenuated and Wild-Type Poliovirus Strains: Impact on Vaccine Potency Assays. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 221, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong-Lim, A.L.; Shukarev, G.; Trinidad-Aseron, M.; Caparas-Yu, D.; Greijer, A.; Duchene, M.; Scheper, G.; Van Paassen, V.; Le Gars, M.; Cahill, C.P.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of 3 Formulations of a Sabin Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Produced on the PER.C6® Cell Line: A Phase 2, Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Study in Infants Vaccinated at 6, 10 and 14 Weeks of Age. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2044255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, K.; Dragunsky, E.; Ivshina, A.; Enterline, J.; Wells, V.; Nomura, T.; Gromeier, M.; Wimmer, E. Inactivated Vaccines Based on Alternatives to Wild-Type Seed Virus. Dev. Biol. 2001, 105, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bockstal, V.; Tiemessen, M.M.; Achterberg, R.; Van Wordragen, C.; Knaapen, A.M.; Serroyen, J.; Marissen, W.E.; Schuitemaker, H.; Zahn, R. An Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Using Sabin Strains Produced on the Serum-Free PER.C6® Cell Culture Platform Is Immunogenic and Safe in a Non-Human Primate Model. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6979–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, G.; Chu, K.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, F.; Ying, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Sabin Strain–Based Inactivated Polio Vaccine: A Phase 3 Clinical Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Different Sequential Schedules of Sabin Strain-Based Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccination: A Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase IV Clinical Trial in China. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6274–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H. Development and Introduction of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccines Derived from Sabin Strains in Japan. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.-J.; Hara, D.; Gbormittah, F.; Chang, H.; Chang, B.S.; Jung, J.U. Development of Thermostable Lyophilized Sabin Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine. mBio 2018, 9, e02287-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, E.P. Plant Molecular Farming of Virus-like Nanoparticles as Vaccines and Reagents. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, M.W.; Porta, C.; Fox, H.; Macadam, A.J.; Fry, E.E.; Stuart, D.I. Mammalian Expression of Virus-like Particles as a Proof of Principle for next Generation Polio Vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsian, J.; Fox, H.; Bahar, M.W.; Kotecha, A.; Fry, E.E.; Stuart, D.I.; Macadam, A.J.; Rowlands, D.J.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Plant-Made Polio Type 3 Stabilized VLPs—A Candidate Synthetic Polio Vaccine. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, L.; Bahar, M.W.; Porta, C.; Fox, H.; Grehan, K.; Nasta, V.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; De Colibus, L.; Marsian, J.; Murdoch, I.; et al. Recombinant Expression Systems for Production of Stabilised Virus-like Particles as next-Generation Polio Vaccines. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.J.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Vasilenko, A.; Zhai, M.; Venkateswaran, A.; Hess, M.; Omelchenko, M.V.; Kostandarithes, H.M.; Makarova, K.S.; et al. Accumulation of Mn(II) in Deinococcus radiodurans Facilitates Gamma-Radiation Resistance. Science 2004, 306, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.J.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Vasilenko, A.; Zhai, M.; Leapman, R.D.; Lai, B.; Ravel, B.; Li, S.-M.W.; Kemner, K.M.; et al. Protein Oxidation Implicated as the Primary Determinant of Bacterial Radioresistance. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.J.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Kiang, J.G.; Fukumoto, R.; Lee, D.-Y.; Wehr, N.B.; Viteri, G.A.; Berlett, B.S.; Levine, R.L. Small-Molecule Antioxidant Proteome-Shields in Deinococcus radiodurans. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidamakova, E.K.; Myles, I.A.; McDaniel, D.P.; Fowler, C.J.; Valdez, P.A.; Naik, S.; Gayen, M.; Gupta, P.; Sharma, A.; Glass, P.J.; et al. Preserving Immunogenicity of Lethally Irradiated Viral and Bacterial Vaccine Epitopes Using a Radio- Protective Mn2+-Peptide Complex from Deinococcus. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, M.; Gupta, P.; Morazzani, E.M.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Knollmann-Ritschel, B.; Daly, M.J.; Glass, P.J.; Maheshwari, R.K. Deinococcus Mn2+-Peptide Complex: A Novel Approach to Alphavirus Vaccine Development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3672–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollery, S.J.; Harro, J.M.; Wiggins, T.J.; Wille, B.P.; Kim, P.C.; Tobin, J.K.; Bushnell, R.V.; Tasker, N.J.P.E.R.; MacLeod, D.A.; Tobin, G.J. Select Whole-Cell Biofilm-Based Immunogens Protect against a Virulent Staphylococcus Isolate in a Stringent Implant Model of Infection. Vaccines 2022, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollery, S.J.; Zurawski, D.V.; Bushnell, R.V.; Tobin, J.K.; Wiggins, T.J.; MacLeod, D.A.; Tasker, N.J.P.E.R.; Alamneh, Y.A.; Abu-Taleb, R.; Czintos, C.M.; et al. Whole-Cell Vaccine Candidates Induce a Protective Response against Virulent Acinetobacter Baumannii. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollery, S.J.; Zurawski, D.V.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Tobin, J.K.; Wiggins, T.J.; Bushnell, R.V.; MacLeod, D.A.; Alamneh, Y.A.; Abu-Taleb, R.; et al. Radiation-Inactivated Acinetobacter Baumannii Vaccine Candidates. Vaccines 2021, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, G.J.; Tobin, J.K.; Gaidamakova, E.K.; Wiggins, T.J.; Bushnell, R.V.; Lee, W.-M.; Matrosova, V.Y.; Dollery, S.J.; Meeks, H.N.; Kouiavskaia, D.; et al. A Novel Gamma Radiation-Inactivated Sabin-Based Polio Vaccine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, G.J.; Tobin, J.K.; Wiggins, T.J.; Bushnell, R.V.; Kozar, A.V.; Maale, M.F.; MacLeod, D.A.; Meeks, H.N.; Daly, M.J.; Dollery, S.J. A Highly Immunogenic UVC Inactivated Sabin Based Polio Vaccine. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouiavskaia, D.; Puligedda, R.D.; Dessain, S.K.; Chumakov, K. Universal ELISA for Quantification of D-Antigen in Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccines. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 276, 113785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Expert Committee on Biological Standardization; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9 789241 210256. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, J.S.; Ward, P.A.; Johnson, K.J. Tumor Necrosis Factor: A Plurifunctional Mediator of Acute Inflammation. Mod. Pathol. 1988, 1, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, T.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Kawashima, H. Long-Term Regulation of Local Cytokine Production Following Immunization in Mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Hansen, M.K.; Nguyen, K.T.; Lee, J.E.; Maier, S.F. Dynamic Regulation of the Proinflammatory Cytokine, Interleukin-1beta: Molecular Biology for Non-Molecular Biologists. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 449–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoglio, J.H. B-Cell-Derived Human Interleukin 1. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 1988, 8, 299–313. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, K.R.; Wong, H.L.; Witko-Sarsat, V.; Wicks, I.P. G-CSF—A Double Edge Sword in Neutrophil Mediated Immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 54, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Sawada, A.; Ito, T. Increased Production of Inflammatory Cytokines after Inoculation with Recombinant Zoster Vaccine in Mice. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Ramirez, N.; Woytschak, J.; Boyman, O. Interleukin-2: Biology, Design and Application. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait Wojno, E.D.; Hunter, C.A.; Stumhofer, J.S. The Immunobiology of the Interleukin-12 Family: Room for Discovery. Immunity 2019, 50, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNγ: Signalling, Epigenetics and Roles in Immunity, Metabolism, Disease and Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, B.A.; Reif, D.M.; Rock, M.T.; Edwards, K.M.; Kingsmore, S.F.; Moore, J.H.; Crowe, J.E. Cytokine Expression Patterns Associated with Systemic Adverse Events Following Smallpox Immunization. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Homer, R.J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Geba, G.P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Elias, J.A. Pulmonary Expression of Interleukin-13 Causes Inflammation, Mucus Hypersecretion, Subepithelial Fibrosis, Physiologic Abnormalities, and Eotaxin Production. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
MacLeod, D.A.; Tobin, J.K.; Bushnell, R.V.; Wiggins, T.J.; TS, S.; Nadipelly, R.; Lawson, S.; Pillai, V.V.; Tobin, G.J.; Dollery, S.J. Immune and Safety Analysis of ultraIPVTM, a Novel UVC-Inactivated Polio Vaccine. Viruses 2025, 17, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070915
MacLeod DA, Tobin JK, Bushnell RV, Wiggins TJ, TS S, Nadipelly R, Lawson S, Pillai VV, Tobin GJ, Dollery SJ. Immune and Safety Analysis of ultraIPVTM, a Novel UVC-Inactivated Polio Vaccine. Viruses. 2025; 17(7):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070915
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacLeod, David A., John K. Tobin, Ruth V. Bushnell, Taralyn J. Wiggins, Shyamkumar TS, Ramchander Nadipelly, Steven Lawson, Viju V. Pillai, Gregory J. Tobin, and Stephen J. Dollery. 2025. "Immune and Safety Analysis of ultraIPVTM, a Novel UVC-Inactivated Polio Vaccine" Viruses 17, no. 7: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070915
APA StyleMacLeod, D. A., Tobin, J. K., Bushnell, R. V., Wiggins, T. J., TS, S., Nadipelly, R., Lawson, S., Pillai, V. V., Tobin, G. J., & Dollery, S. J. (2025). Immune and Safety Analysis of ultraIPVTM, a Novel UVC-Inactivated Polio Vaccine. Viruses, 17(7), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17070915





