Epidemiological Characteristics of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Longyou County, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
- (1)
- Patients with a history of epidemiology and clinical manifestations, defined as suspected cases, are those who seek medical attention for fever or gastrointestinal symptoms;
- (2)
- Cases suspected to be diagnosed with hypotension, renal function impairment, elevated peripheral blood cell counts, thrombocytopenia, and positive urine protein are defined as clinically diagnosed cases;
- (3)
- Cases that meet one or more of the following clinical diagnostic criteria are defined as confirmed cases: positive serum-specific IgM antibodies; specific IgG antibodies that are four times higher than in the acute phase.
2.3. Rodent Surveillance
2.4. Statistical Methods
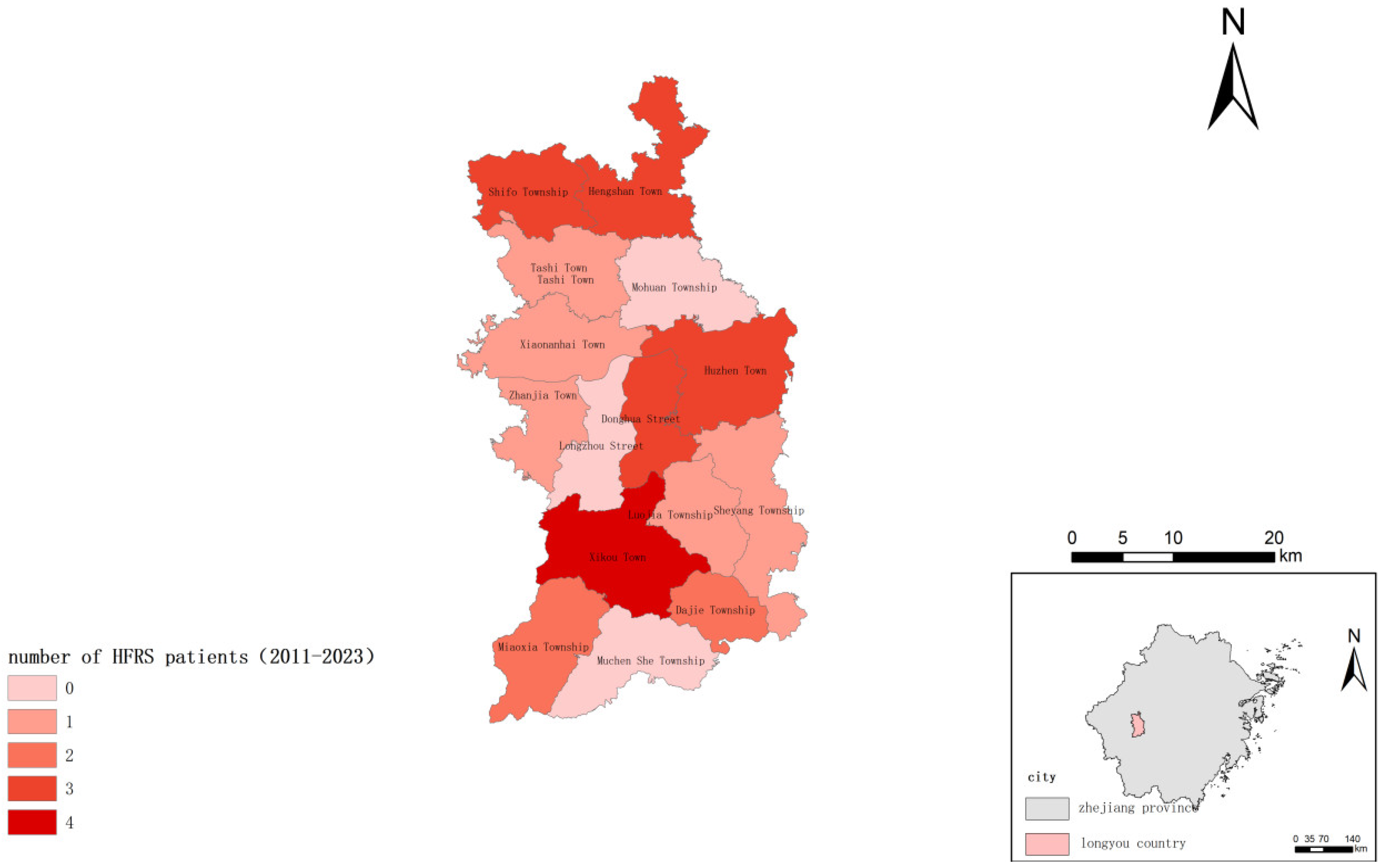
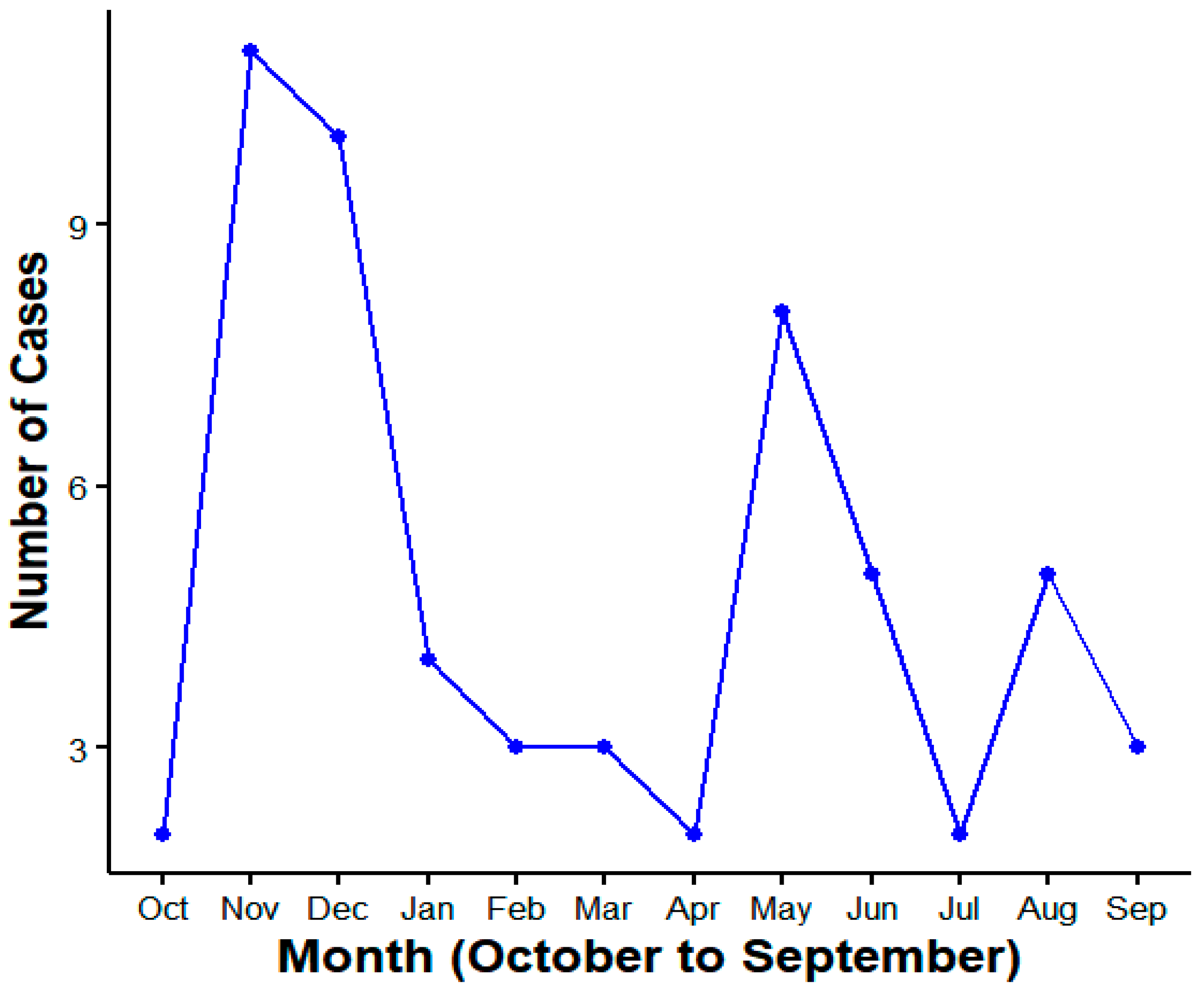
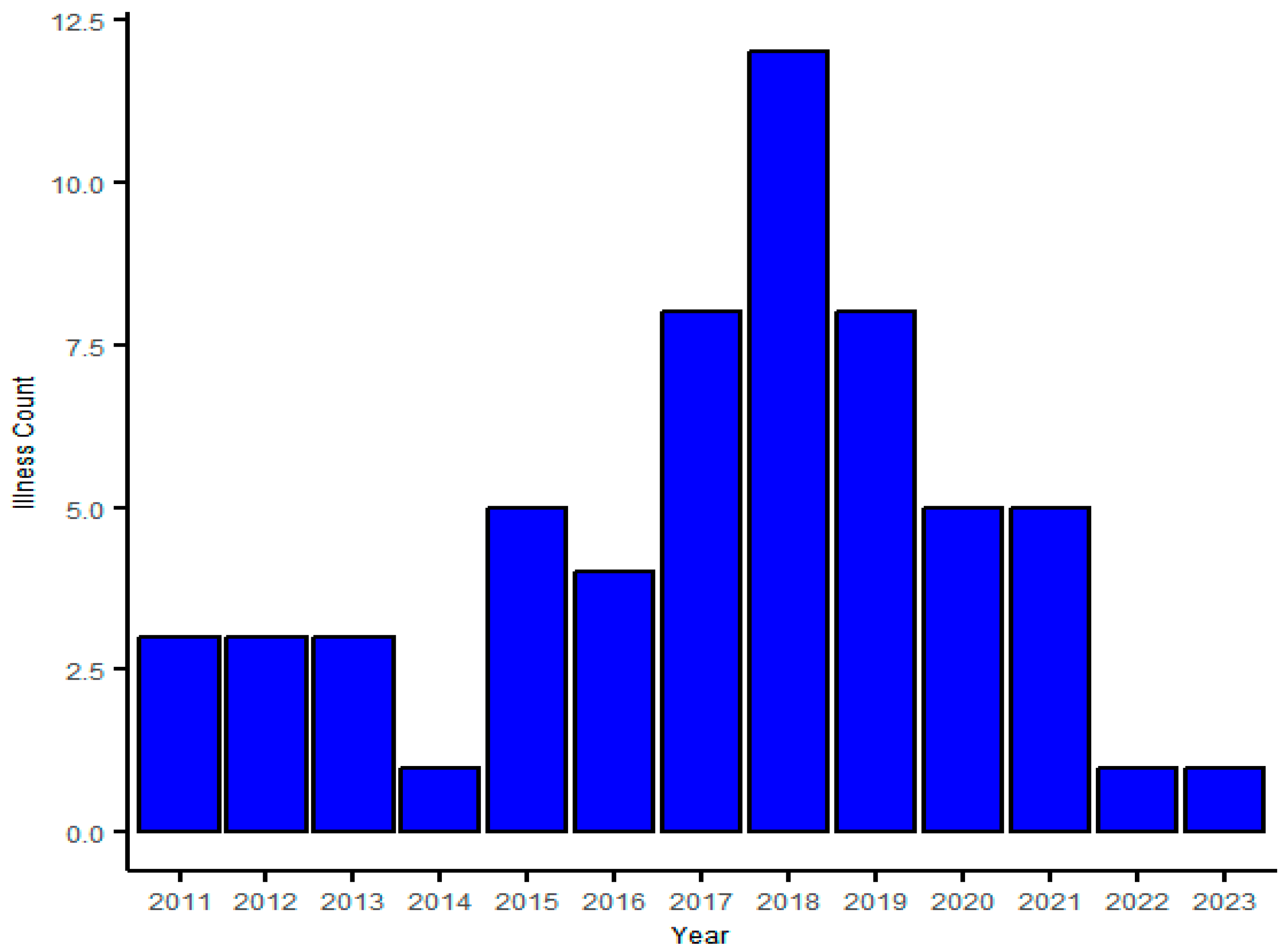
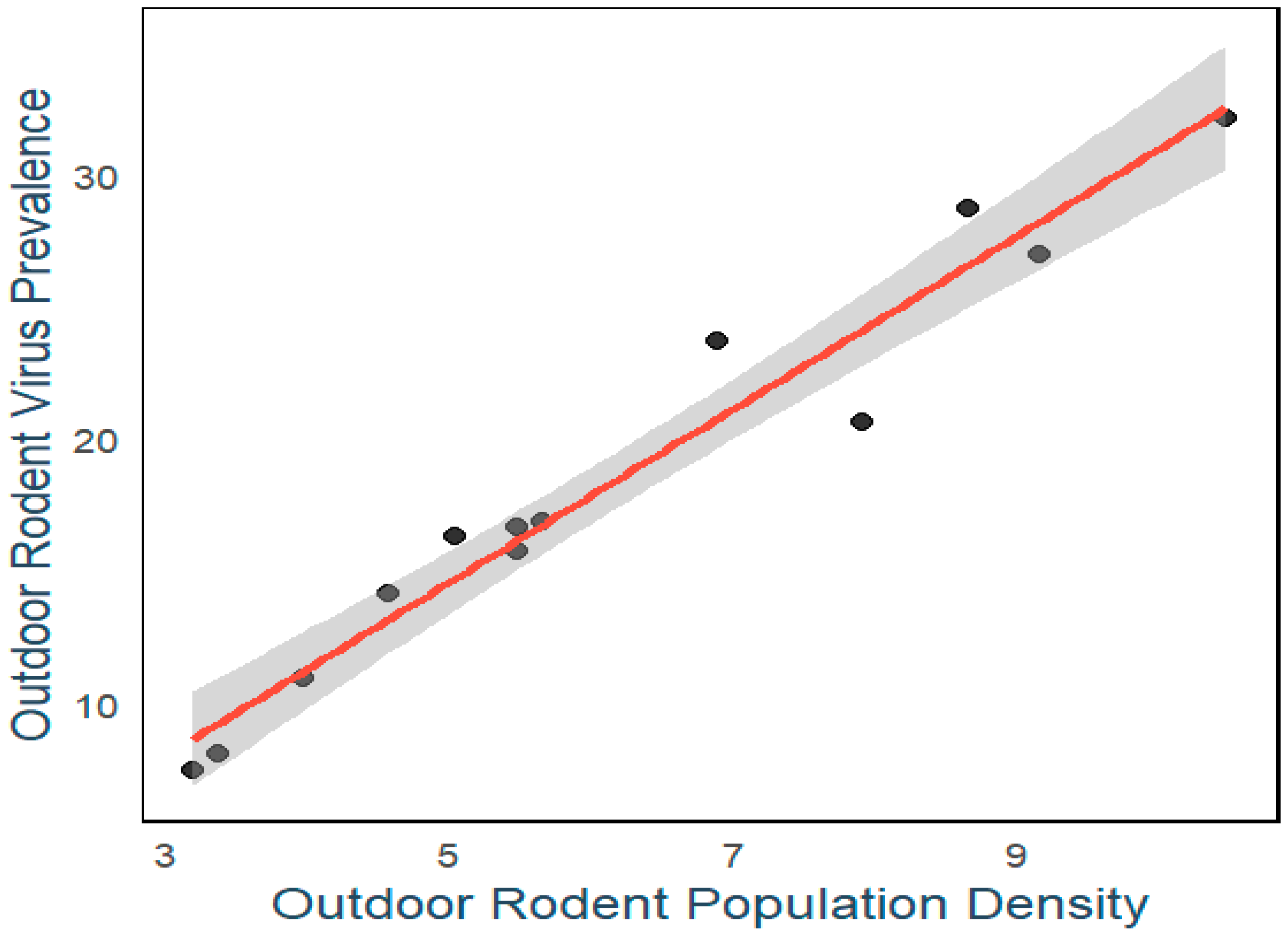
3. Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sehgal, A.; Mehta, S.; Sahay, K.; Martynova, E.; Rizvanov, A.; Baranwal, M.; Chandy, S.; Khaiboullina, S.; Kabwe, E.; Davidyuk, Y. Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Asia: History, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. Viruses 2023, 18, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Qing, S.; Xi, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, F. Asymmetric impact of climatic parameters on hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Shandong using a nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Du, H.; Wang, L.M.; Wang, P.Z.; Bai, X.F. Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome: Pathogenesis and Clinical Picture. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korva, M.; Rus, K.R.; Pavletič, M.; Saksida, A.; Knap, N.; Jelovšek, M.; Smrdel, K.S.; Jakupi, X.; Humolli, I.; Dedushaj, J.; et al. Characterization of Biomarker Levels in Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever and Hantavirus Fever with Renal Syndrome. Viruses 2019, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreychev, A.; Boyarova, E.; Brandler, O.; Tukhbatullin, A.; Kapustina, S. Terrestrial and Subterranean Mammals as Reservoirs of Zoonotic Diseases in the Central Part of European Russia. Diversity 2022, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Tian, H.Y.; Gao, L.D.; Liu, H.N.; Duan, L.S.; Basta, N.; Cazelles, B.; Li, X.J.; Lin, X.L.; Wu, H.W.; et al. Animal reservoir, natural and socioeconomic variations and the transmission of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Chenzhou, China, 2006–2010. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, B.T.; Sehrawat, S. Immunity and immunopathology to viruses: What decides the outcome? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Chang, N.; Tao, Y.; et al. Spatiotemporal trends of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in China under climate variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2312556121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Xiao, X.; Yin, W.; He, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; Tong, S.; Guo, Y.; et al. Climate and socio-economic factors drive the spatio-temporal dynamics of HFRS in Northeastern China. One Health 2022, 15, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.-X.; Sun, L. Analysis of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome Using Wavelet Tools in Mainland China, 2004–2019. Front. Public Health 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Liu, Y.; Ling, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J. Epidemiology of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome and Host Surveillance in Zhejiang Province, China, 1990–2021. Viruses 2024, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Hou, J.; Fu, G.M.; Chen, R.F.; Lei, J.B.; Chen, Z.P.; Yang, T.C.; Lu, L.; Ren, Z.Y.; et al. Study on the integrated monitoring program regarding mouse and main mouse-borne disease in Zhejiang province. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2011, 32, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.Y.; Hou, J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Lei, J.B.; Chen, Z.B.; Fang, C.F.; Zhu, H.P.; Ling, F.; Sun, J.M. Study on comprehensive monitoring of mouse and effect of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome vaccine in high prevalence areas of natural focus infectious disease of Zhejiang province in 1994–2010. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 46, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenseth, N.C.; Chan, K.S.; Tong, H.; Boonstra, R.; Boutin, S.; Krebs, C.J.; Post, E.; O’Donoghue, M.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Forchhammer, M.C.; et al. Common dynamic structure of canada lynx populations within three climatic regions. Science 1999, 285, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, M.R.T.; Souza-Junior, J.B.F.; Castelo, T.S.; Lago, A.E.A.; Silva, A.R. Understanding how environmental factors influence reproductive aspects of wild myomorphic and hystricomorphic rodents. Anim. Reprod. 2021, 18, e20200213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.H.; Chen, L.B.; Hambly, C.; Speakman, J.R.; Zhao, Z.J. Exposure to hot temperatures during lactation in Swiss mice stunts offspring growth and decreases future reproductive performance of female offspring. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, W.S.D.; Tildesley, M.J.; Spencer, S.E.F.; Keeling, M.J. Climate drivers of plague epidemiology in British India, 1898–1949. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20200538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.F.; Fernandes, D.; Rocha, I.V.; Pitta, J.; Freitas, N.D.A.; Oliveira, A.L.S.; Guimarães, R.; Gomes, E.C.S.; de Andreazzi, C.S.; Sobreira, M.; et al. Ecologic, Geoclimatic, and Genomic Factors Modulating Plague Epidemics in Primary Natural Focus, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1850–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, B.; Xue, R.; Yi, C. Investigating the impact of climatic and environmental factors on HFRS prevalence in Anhui Province, China, using satellite and reanalysis data. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1447501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Mao, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Qin, S.; Tian, H.; Guo, S.; Ren, J.; Shi, X.; et al. The changing epidemiology of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Southeastern China during 1963-2020: A retrospective analysis of surveillance data. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Yang, Z.; Ren, S.; Fu, T.; Li, R.; Lu, M.; Qin, X.; Li, A.; Kou, Z.; Shao, Z.; et al. Spatial-temporal patterns and influencing factors for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A 16-year national surveillance analysis in China. One Health 2024, 18, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.L.; Tian, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.J.; Jiang, B.G.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, L.P.; Hay, S.I.; Liu, W.; et al. Dual seasonal pattern for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and its potential determinants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Zuo, S.; Li, X. The characteristics of current natural foci of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Shandong Province, China, 2012–2015. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Xia, Z.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Cheng, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Du, Z. Investigation on risk factors of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Xuancheng City in Anhui Province, Mainland China. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, M.; Pang, B.; Tian, X.; Ma, W.; Kou, Z.; et al. Spatial-temporal drivers and incidence heterogeneity of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome transmission in Shandong Province, China, 2016–2022. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Ren, H.; Lu, L. Urbanization-Related Environmental Factors and Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome: A Review Based on Studies Taken in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Li, Y.P.; Lu, L.; Li, S.J.; Ren, H.Y. Spatial Heterogeneity and Influencing Factors of HFRS Epidemics in Rural and Urban Areas: A Study in Guanzhong Plain of Shaanxi Province, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Ding, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Hu, X. Bayesian spatiotemporal modelling analysis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome outbreaks in China using R-INLA. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Z. Comparison of simulation and predictive efficacy for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome incidence in mainland China based on five time series models. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1365942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huo, X.; Xiang, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Jia, C.; Liu, Q. Interactions and marginal effects of meteorological factors on haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in different climate zones: Evidence from 254 cities of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Kuai, Q.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Q.; et al. Epidemic Characteristics and Meteorological Risk Factors of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in 151 Cities in China from 2015 to 2021: Retrospective Analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2024, 10, e52221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Ali, L.; Batool, A.; Afzal, M.; Kanwal, N.; Hassan, M.; Safdar, M.; Ahmad, A.; Yang, J. Hantavirus: An overview and advancements in therapeutic approaches for infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1233433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Shin, O.S.; Na, J.; Kim, J.K.; Seong, R.K.; Park, M.S.; Noh, J.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Cheong, H.J.; Park, Y.H.; et al. A Systems Vaccinology Approach Reveals the Mechanisms of Immunogenic Responses to Hantavax Vaccination in Humans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


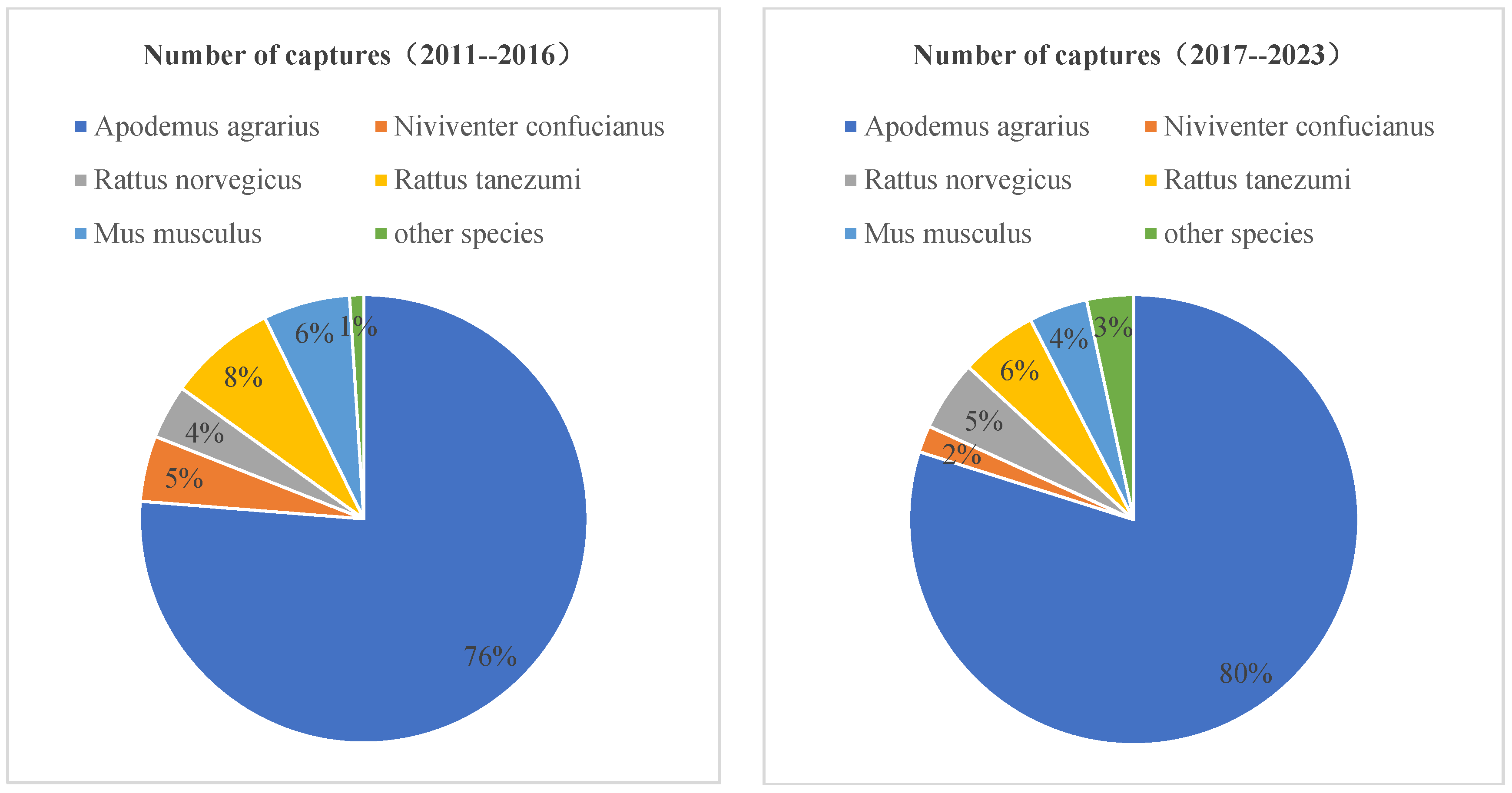
| Year | Rodent | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apodemus agrarius | Niviventer confucianus | Rattus norvegicus | Rattus tanezumi | Mus musculus | Maxomys surifer | Micromys minutus | Rattus nitidus | Suncus murinus | Microtus fortis | Total | |
| 2011 | 100 | 4 | 3 | 20 | - | 4 | - | - | 3 | - | 135 |
| 2012 | 88 | 7 | 2 | 1 | - | 7 | - | 2 | - | - | 107 |
| 2013 | 106 | 8 | 1 | 1 | - | 5 | - | 1 | - | - | 122 |
| 2014 | 94 | 1 | 5 | 2 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 103 |
| 2015 | 93 | 9 | 2 | 3 | - | 7 | - | - | 1 | - | 115 |
| 2016 | 66 | 5 | 4 | 15 | - | 11 | - | - | 1 | - | 102 |
| 2017 | 86 | 1 | 3 | 6 | - | 5 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 103 |
| 2018 | 92 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | - | 100 |
| 2019 | 97 | - | 3 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 101 |
| 2020 | 35 | 3 | 18 | 32 | 1 | 5 | - | - | 6 | - | 100 |
| 2021 | 114 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 1 | - | - | 2 | - | - | 131 |
| 2022 | 55 | 8 | 6 | 5 | - | 2 | 1 | 14 | 14 | 3 | 108 |
| 2023 | 86 | - | 3 | 10 | - | - | - | 15 | 8 | - | 122 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, J.; Kong, D.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, W.; Zhan, B.; Gong, Z. Epidemiological Characteristics of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Longyou County, China. Viruses 2025, 17, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030313
Ni J, Kong D, Chen Z, Zeng W, Zhan B, Gong Z. Epidemiological Characteristics of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Longyou County, China. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030313
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Jing, Dejun Kong, Zhongbing Chen, Weiming Zeng, Bingdong Zhan, and Zhenyu Gong. 2025. "Epidemiological Characteristics of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Longyou County, China" Viruses 17, no. 3: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030313
APA StyleNi, J., Kong, D., Chen, Z., Zeng, W., Zhan, B., & Gong, Z. (2025). Epidemiological Characteristics of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Longyou County, China. Viruses, 17(3), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030313






