IL-2 and IL-7 Contribution to Immune Response: Effects of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Adults
Abstract
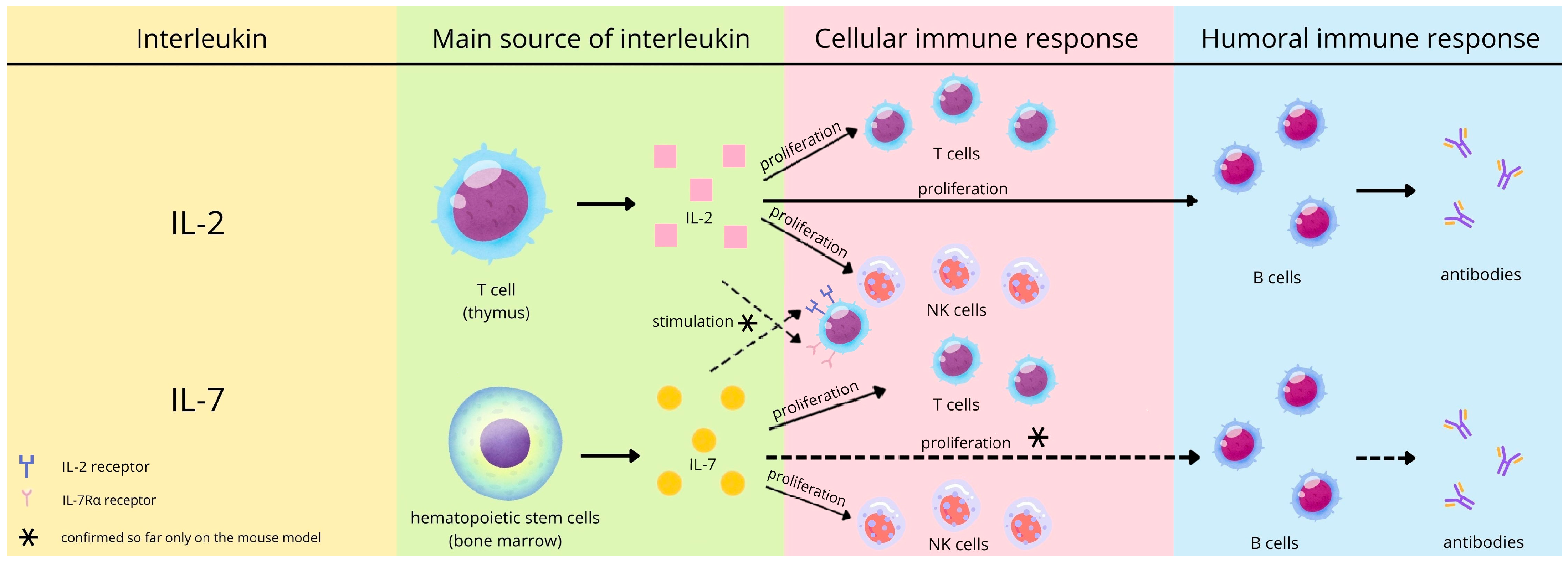
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurements and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| IGRA | Interferon Gamma Release Assay |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL-2 | Interleukin 2 |
| IL-7 | Interleukin 7 |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| RBD | Receptor-Binding Domain |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| S1 | Subunit 1 of the Viral Spike Protein |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Shereen, M.A.; Khan, S.; Kazmi, A.; Bashir, N.; Siddique, R. COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosińska, M.; Czarkowski, M.P.; Sadkowska-Todys, M. Infectious diseases in Poland in 2020. Przegl Epidemiol. 2022, 76, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, T. Konturek Fizjologia Człowieka, 3rd ed.; Edra Urban & Partner: Wroclaw, Poland, 2019; pp. 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, E. Szczepienia—Wspaniałe osiągnięcie nauki i medycyny. Wszechświat 2011, 112, 2571–2573. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, Comirnaty: EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/comirnaty (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, Spikevax (Previously COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna): EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/spikevax (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, Vaxzevria (Previously COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca): EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/vaxzevria (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, Jcovden (Previously COVID-19 Vaccine Janssen): EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/jcovden-previously-covid-19-vaccine-janssen (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, Nuvaxovid: EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/nuvaxovid (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, VidPrevtyn Beta: EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/vidprevtyn-beta (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, Bimervax: EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/bimervax (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Science Medicines Health, COVID-19 Vaccine (Inactivated, Adjuvanted) Valneva: EPAR—Product Information. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/covid-19-vaccine-inactivated-adjuvanted-valneva (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Our World in Data. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccinations. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Mansourabadi, A.H.; Aghamajidi, A.; Dorfaki, M.; Keshavarz, F.; Shafeghat, Z.; Moazzeni, A.; Arab, F.L.; Rajabian, A.; Roozbehani, M.; Falak, R.; et al. B lymphocytes in COVID-19: A tale of harmony and discordance. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Tabarsi, P.; Varahram, M.; Folkerts, G.; Adcock, I.M. The Immune Response and Immunopathology of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primorac, D.; Vrdoljak, K.; Brlek, P.; Pavelić, E.; Molnar, V.; Matišić, V.; Erceg Ivkošić, I.; Parčina, M. Adaptive Immune Responses and Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 848582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanshylla, K.; Di Cristanziano, V.; Kleipass, F.; Dewald, F.; Schommers, P.; Gieselmann, L.; Gruell, H.; Schlotz, M.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Stumpf, R.; et al. Kinetics and correlates of the neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans. Cell Host Microbe. 2021, 29, 917–929.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenborn, J.R.; Wilson, C.B. Regulation of interferon-gamma during innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv. Immunol. 2007, 96, 41–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz-Deptuła, B.; Miller, T.; Deptuła, W. The interleukin-1 family of cytokines. Post. Mikrobiol. 2011, 50, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Mizel, S.B. The interleukins. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendickova, K.; Fric, J. Roles of IL-2 in bridging adaptive and innate immunity, and as a tool for cellular immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzman, S.D.; Hoyer, K.K.; Dooms, H.; Gratz, I.K.; Rosenblum, M.D.; Paw, J.S.; Isakson, S.H.; Abbas, A.K. Opposing functions of IL-2 and IL-7 in the regulation of immune responses. Cytokine 2011, 56, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Wakefield, M.R.; Ding, V.A.; Bai, Q.; Fang, Y. The role of IL-7 in Immunity and Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tang, T.X.; Deng, H.; Yang, X.P.; Tang, Z.H. Interleukin-7 Biology and Its Effects on Immune Cells: Mediator of Generation, Differentiation, Survival, and Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooms, H.; Wolslegel, K.; Lin, P.; Abbas, A.K. Interleukin-2 enhances CD4+ T cell memory by promoting the generation of IL-7R alpha-expressing cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Huo, S.; Cao, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhong, F. Mutual enhancement of IL-2 and IL-7 on DNA vaccine immunogenicity mainly involves regulations on their receptor expression and receptor-expressing lymphocyte generation. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, C.; Hopkins, B.; Huhn, S.; Du, Z.; Huang, Z.; Kelly, W.J. Investigation of the Impact from IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 on the Growth and Signaling of Activated CD4+ T Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, D.; Ludziejewska, A.; Bielawska, L.; Baszczuk, A.; Gawron, M.; Danielewicz, M.; Wysocka, E. Humoral response against COVID-19 in the population of western region of Poland. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1648937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhana, S.A.; Wolchok, J.D. The many faces of the anti-COVID immune response. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, K.; Chi, H.; Xia, Z.; Li, X. IL-7: A promising adjuvant ensuring effective T cell responses and memory in combination with cancer vaccines? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1022808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, L.A.; Mac Donald, A.; Kandlur, A.; Bose, D.; Xiao, P.; Gagnon, J.; Villinger, F.; Chebloune, Y. Cytokine Adjuvants IL-7 and IL-15 Improve Humoral Responses of a SHIV LentiDNA Vaccine in Animal Models. Vaccines 2022, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Camara, C.; Lopez-Granados, E.; Nozal, P.; Del Pino-Molina, L.; Bravo-Gallego, L.Y.; Paz-Artal, E.; Pion, M.; Correa-Rocha, R.; Ortiz, A.; et al. Differential effects of the second SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine dose on T cell immunity in naive and COVID-19 recovered individuals. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gebo, K.A.; Abraham, A.G.; Habtehyimer, F.; Patel, E.U.; Laeyendecker, O.; Gniadek, T.J.; Fernandez, R.E.; Baker, O.R.; Ram, M.; et al. Dynamics of inflammatory responses after SARS-CoV-2 infection by vaccination status in the USA: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Microbe. 2023, 4, e692–e703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damås, J.K.; Waehre, T.; Yndestad, A.; Otterdal, K.; Hognestad, A.; Solum, N.O.; Gullestad, L.; Frøland, S.S.; Aukrust, P. Interleukin-7-mediated inflammation in unstable angina: Possible role of chemokines and platelets. Circulation 2003, 107, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikker, A.; Hack, C.E.; Lafeber, F.P.; van Roon, J.A. Interleukin-7: A key mediator in T cell-driven autoimmunity, inflammation, and tissue destruction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfarth, J.; Sivagurunathan, S.; Ricken, S.; Weinreich, G.; Olbrich, L.; Taube, C.; Mayatepek, E.; Schramm, D.; Jacobsen, M. Higher Interleukin-7 serum concentrations in patients with cystic fibrosis correlate with impaired lung function. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavani, M.A.; Richardson, A. The effect of age on the expression of interleukin-2. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1996, 89, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, I.M.; Stewart, M.; Campbell, P.; Alexander, H.D.; Crockard, A.D.; Morris, T.C. Changes in lymphocyte subsets, interleukin 2, and soluble interleukin 2 receptor in old and very old age. Gerontology 1996, 42, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Guo, C.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Q.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X. Immunosenescence: Molecular mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Yehuda, A.; Weksler, M.E. Immune senescence: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Cancer Investig. 1992, 10, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borger, P.; Kauffman, H.F.; Postma, D.S.; Vellenga, E. IL-7 differentially modulates the expression of IFN-gamma and IL-4 in activated human T lymphocytes by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, H.; Ito, M.; Sudo, T.; Hattori, M.; Kano, S.; Katsura, Y.; Minato, N. IL-7 promotes thymocyte proliferation and maintains immunocompetent thymocytes bearing alpha beta or gamma delta T-cell receptors in vitro: Synergism with IL-2. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 2917–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | All n = 76 | |
| Age [years] | Me (Q1–Q3) | 46.50 (34.00–57.00) |
| mean ± SD | 44.5 ± 13.5 | |
| min–max | 19.0–69.0 | |
| Gender [F/M] | 66/10 | |
| BMI [kg/m2] | Me (Q1–Q3) | 24.57 (22.25–27.63) |
| mean ± SD | 25.41 ± 4.60 | |
| min–max | 17.58–42.52 | |
| Categoryof chronic disease | Number of study participants [n] | |
| Cardiovascular | 11 | |
| Endocrine | 9 | |
| Autoimmune | 9 | |
| Respiratory | 8 | |
| Metabolic | 5 | |
| Oncological | 2 | |
| Connective tissue | 1 | |
| Liver | 1 | |
| Set of chronic disease | Number of study participants [n] | |
| 1 disease | 25 | |
| 2 diseases | 8 | |
| 3 diseases | 1 | |
| 4 diseases | 1 | |
| Parameter | All n = 76 | ChrD-Neg n = 41 | ChrD-Pos n = 35 | p Mann–Whitney Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 46.50 (34.00–57.00) | 45.00 (31.00–52.00) | 47.00 (36.00–58.00) | 0.18 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 24.57 (22.25–27.63) | 25.03 (22.31–27.55) | 24.24 (22.10–27.68) | 0.95 |
| CoV2-IgG [U/mL] | 9.15 (5.00–19.75) | 9.40 (5.10–19.60) | 8.50 (4.80–20.50) | 0.62 |
| IFN-γ [mIU/mL] | 553.53 (257.77–1287.52) | 619.56 (323.14–1293.61) | 494.96 (176.14–1017.70) | 0.29 |
| IL-2 [pg/mL] | 15.60 (15.60–95.91) | 15.60 (15.60–104.79) | 15.60 (15.60–64.11) | 0.93 |
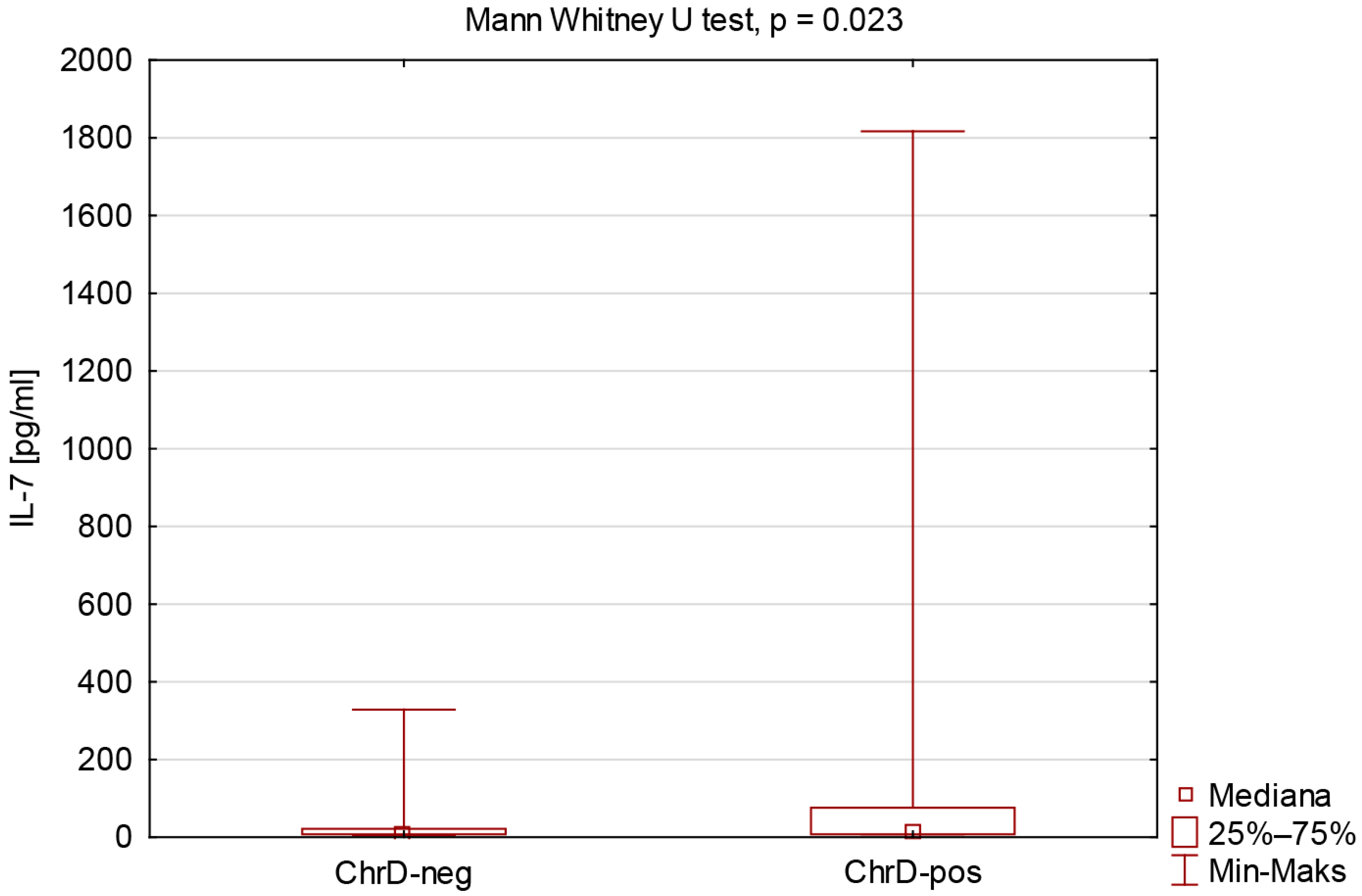
| IL-7 [pg/mL] | 7.80 (7.80–47.67) | 7.80 (7.80–21.84) | 11.53 (7.80–76.07) | 0.023 * |
| Parameters | All n = 76 | ChrD-Neg n = 41 | ChrD-Pos n = 35 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-2 and age | R = −0.252, p = 0.028 * | R = −0.259, p = 0.10 | R = −0.264, p = 0.13 |
| IL-2 and BMI | R = 0.036, p = 0.76 | R = 0.180, p = 0.26 | R = −0.145, p = 0.41 |
| IL-2 and CoV2-IgG | R = 0.128, p = 0.27 | R = 0.252, p = 0.11 | R = −0.005, p = 0.98 |
| IL-2 and IFN-γ | R = −0.075, p = 0.52 | R = −0.137, p = 0.39 | R = 0.025, p = 0.89 |
| IL-7 and age | R = −0.101, p = 0.38 | R = −0.059, p = 0.72 | R = −0.240, p = 0.16 |
| IL-7 and BMI | R = 0.062, p = 0.60 | R = 0.218, p = 0.17 | R = −0.056, p = 0.75 |
| IL-7 and CoV2-IgG | R = −0.065, p = 0.58 | R = −0.143, p = 0.37 | R = 0.043, p = 0.81 |
| IL-7 and IFN-γ | R = −0.295, p = 0.010 * | R = −0.213, p = 0.18 | R = −0.297, p = 0.08 |
| IL-2 and IL-7 | R = 0.305, p = 0.007 * | R = 0.273, p = 0.08 | R = 0.358, p = 0.035 * |
| Parameter | IGRA-Negative n = 8 | IGRA-Borderline n = 7 | IGRA-Positive n = 61 | p Kruskal–Wallis Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 55.00 (40.50–61.00) | 50.00 (38.00–59.00) | 45.00 (31.00–55.00) | a, c 1.00 b 0.34 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 25.73 (22.21–28.92) | 24.61 (22.60–27.34) | 24.52 (22.23–27.68) | a, b, c 1.00 |
| CoV2-IgG [U/mL] | 11.60 (6.75–16.10) | 6.20 (1.30–13.90) | 9.30 (5.00–23.50) | a 0.56 b 1.00 c 0.20 |
| IL-2 [pg/mL] | 75.09 (15.60–359.39) | 15.60 (15.60–34.80) | 15.60 (15.60–80.35) | a 0.76 b 0.87 c 1.00 |
| IL-7 [pg/mL] | 11.72 (9.23–24.24) | 30.00 (7.80–228.43) | 7.80 (7.80–47.89) | a, b 1.00 c 0.43 |
| Parameters | IGRA-Negative n = 8 | IGRA-Borderline n = 7 | IGRA-Positive n = 61 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-2 and age | R = −0.868, p = 0.005 * | R = −0.022, p = 0.96 | R = −0.208, p = 0.11 |
| IL-2 and BMI | R = 0.241, p = 0.57 | R = 0.445, p = 0.32 | R = −0.022, p = 0.86 |
| IL-2 and CoV2-IgG | R = 0.355, p = 0.39 | R = −0.668, p = 0.10 | R = 0.119, p = 0.36 |
| IL-7 and age | R = −0.024, p = 0.95 | R = 0.736, p = 0.06 | R = −0.218, p = 0.09 |
| IL-7 and BMI | R = 0.491, p = 0.22 | R = 0.126, p = 0.79 | R = 0.011, p = 0.93 |
| IL-7 and CoV2-IgG | R = 0.132, p = 0.76 | R = 0.090, p = 0.85 | R = −0.038, p = 0.77 |
| IL-2 and IL-7 | R = −0.274, p = 0.51 | R = 0.360, p = 0.43 | R = 0.359, p = 0.005 * |
| Parameter | IGRA-Positive n = 61 | p Mann–Whitney Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChrD-Neg n = 35 | ChrD-Pos n = 26 | ||
| Age [years] | 43.00 (26.00–54.00) | 45.50 (36.00–57.00) | 0.37 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 25.03 (22.23–27.34) | 24.13 (21.37–27.77) | 0.95 |
| CoV2-IgG [U/mL] | 9.30 (4.70–21.40) | 8.95 (5.20–25.50) | 0.76 |
| IL-2 [pg/mL] | 15.60 (15.60–97.99) | 15.60 (15.60–64.11) | 0.71 |
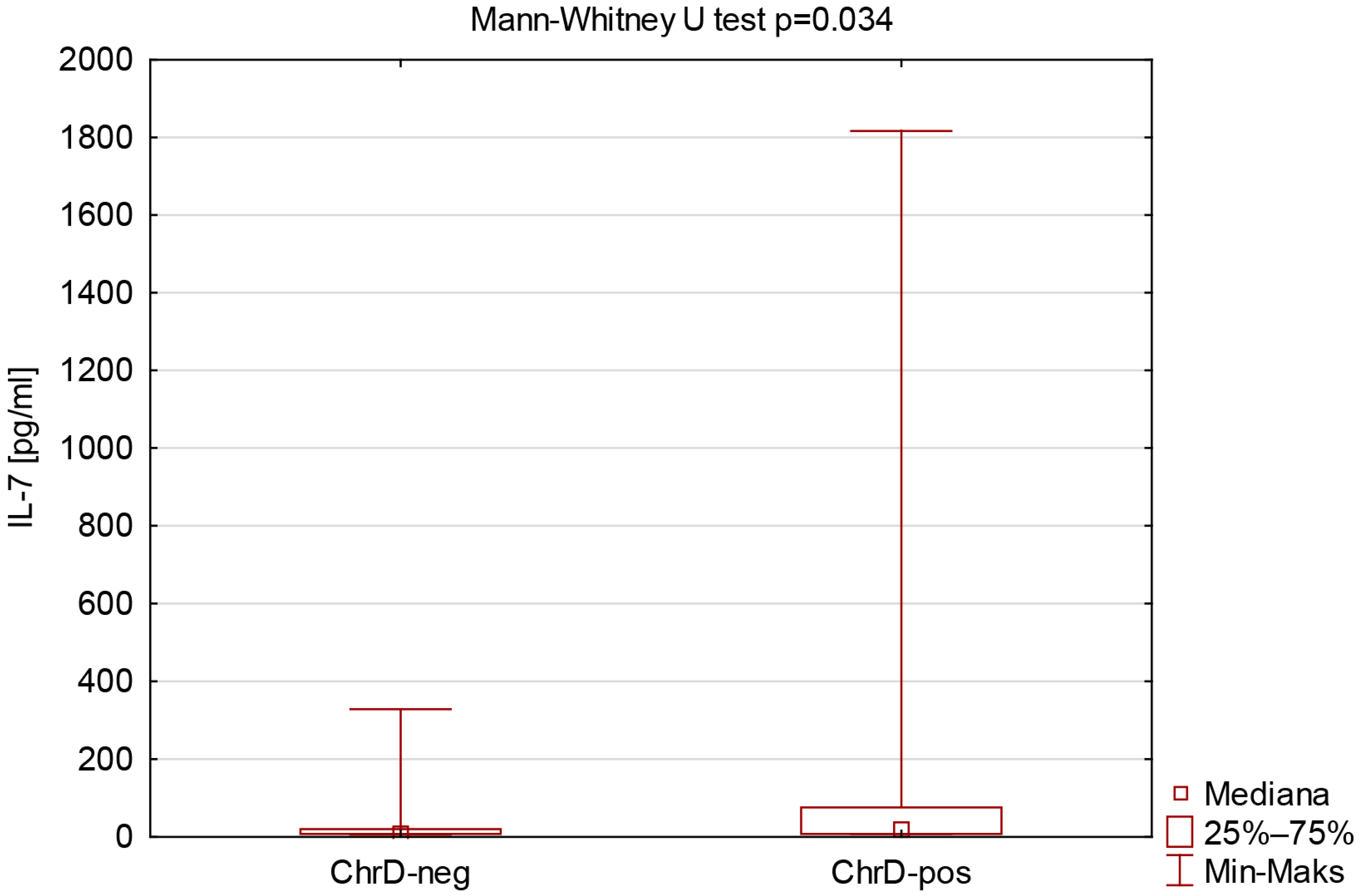
| IL-7 [pg/mL] | 7.80 (7.80–20.15) | 16.84 (7.80–76.07) | 0.034 * |
| Parameters | IGRA-Positive n = 61 | |
|---|---|---|
| ChrD-Neg n = 35 | ChrD-Pos n = 26 | |
| IL-2 and age | R = −0.261, p = 0.13 | R = −0.139, p = 0.50 |
| IL-2 and BMI | R = 0.151, p = 0.39 | R = −0.233, p = 0.25 |
| IL-2 and CoV2-IgG | R = 0.217, p = 0.21 | R = −0.007, p = 0.97 |
| IL-7 and age | R = −0.119, p = 0.50 | R = −0.444, p = 0.023 * |
| IL-7 and BMI | R = 0.190, p = 0.27 | R = −0.124, p = 0.54 |
| IL-7 and CoV2-IgG | R = −0.177, p = 0.31 | R = 0.084, p = 0.68 |
| IL-2 and IL-7 | R = 0.315, p = 0.07 | R = 0.398, p = 0.044 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siedlecka, D.; Bielawska, L.; Ludziejewska, A.; Baszczuk, A.; Wysocka, E. IL-2 and IL-7 Contribution to Immune Response: Effects of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Adults. Viruses 2025, 17, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111416
Siedlecka D, Bielawska L, Ludziejewska A, Baszczuk A, Wysocka E. IL-2 and IL-7 Contribution to Immune Response: Effects of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Adults. Viruses. 2025; 17(11):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111416
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiedlecka, Dominika, Lena Bielawska, Aleksandra Ludziejewska, Aleksandra Baszczuk, and Ewa Wysocka. 2025. "IL-2 and IL-7 Contribution to Immune Response: Effects of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Adults" Viruses 17, no. 11: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111416
APA StyleSiedlecka, D., Bielawska, L., Ludziejewska, A., Baszczuk, A., & Wysocka, E. (2025). IL-2 and IL-7 Contribution to Immune Response: Effects of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Adults. Viruses, 17(11), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111416






