Oncogenic Viruses in Organ Transplantation: Implications of Virus-Host Interactions for Cancer Development
Abstract
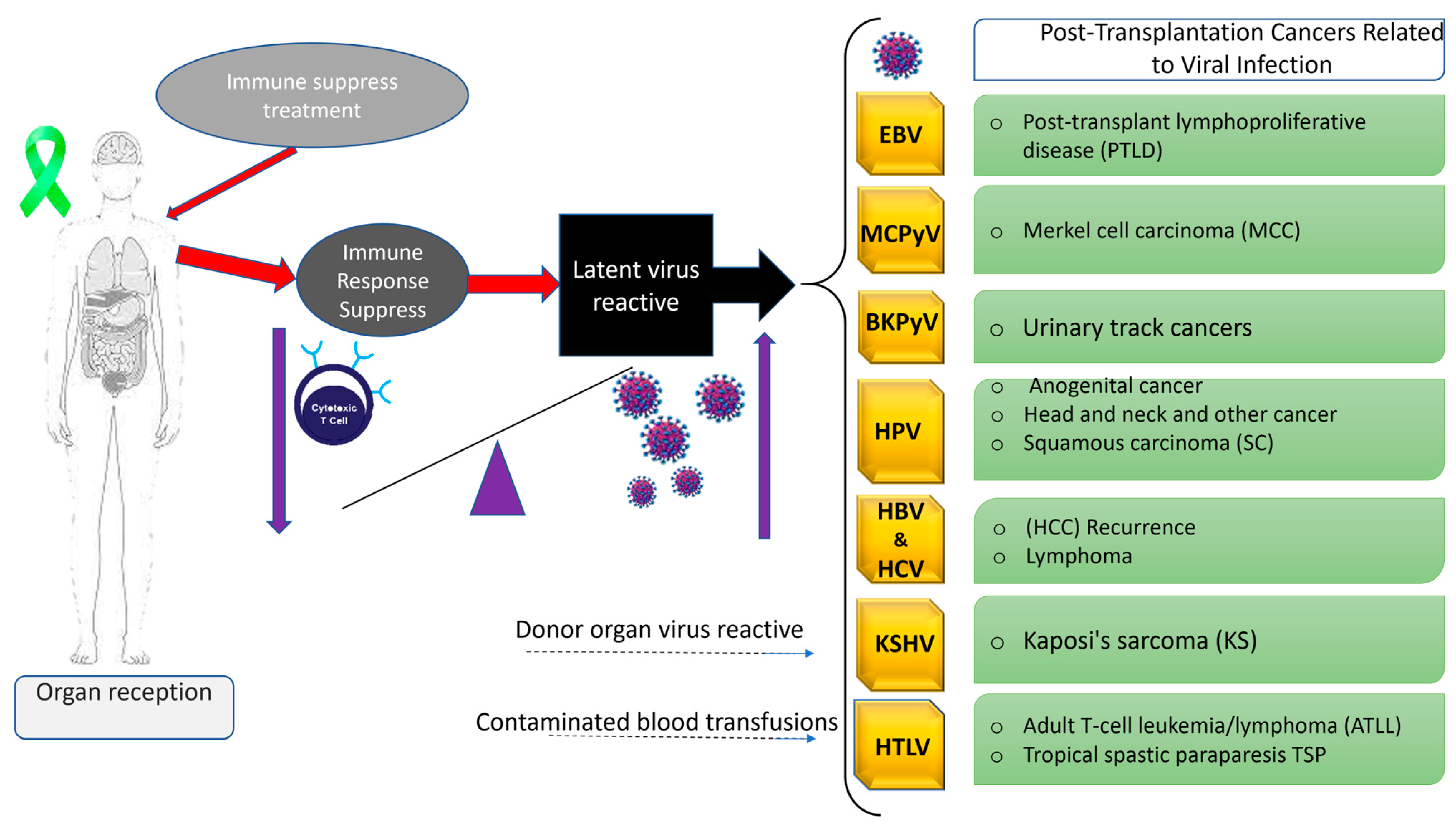
1. Introduction
2. Oncogenic Viruses
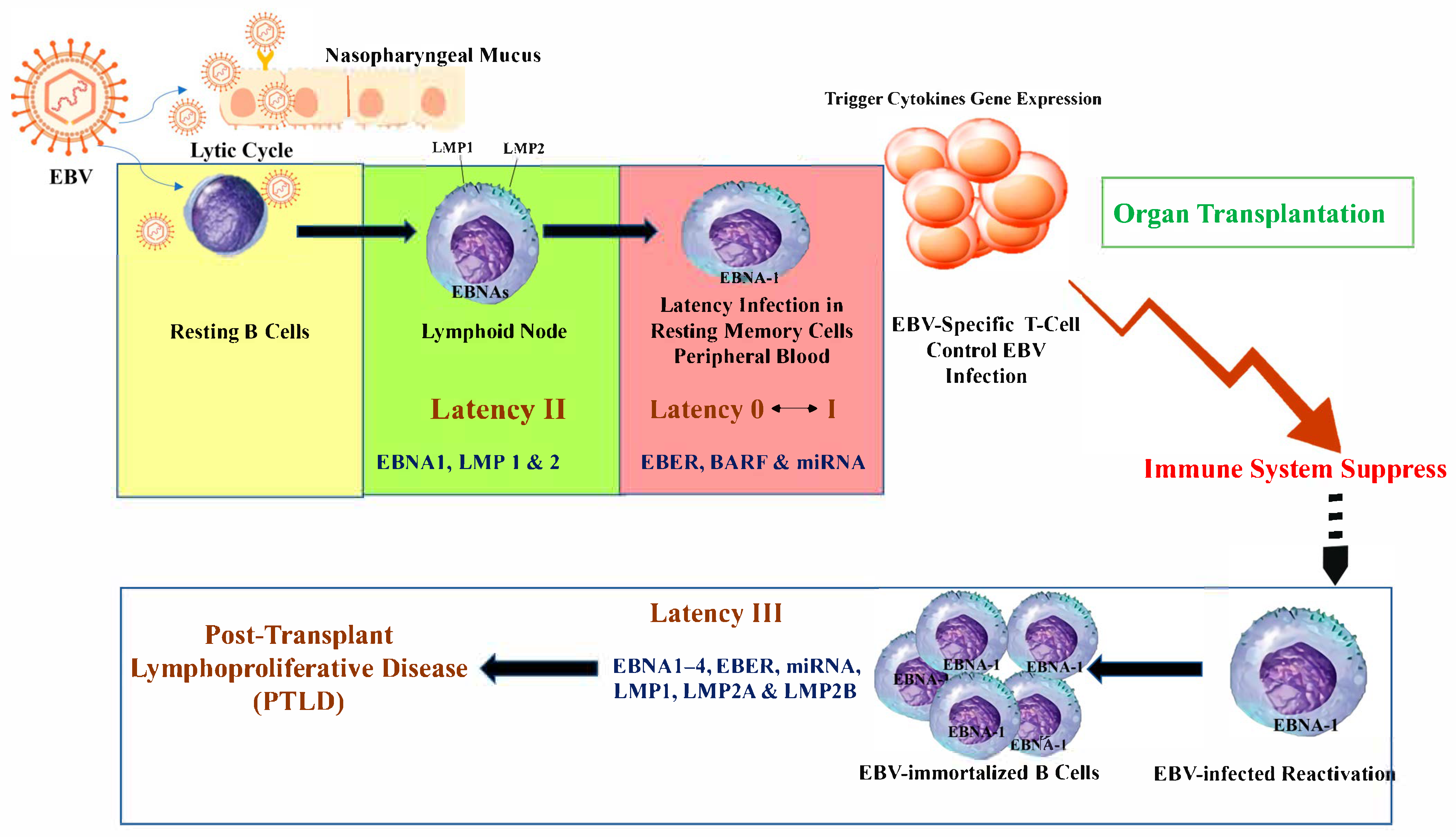
2.1. EBV in Transplantation
2.1.1. EBV Infection and Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease
2.1.2. EBV-Associated PTLD: Incidence and Risk Factors
2.1.3. EBV-Associated PTLD: Diagnosis
2.1.4. EBV-Associated PTLD: Treatment and Preemptive Intervention Strategy
2.1.5. EBV-Associated PTLD: Prognosis
2.2. KSHV in Transplantation
2.2.1. KSHV-Related Cancers: Incidence and Risk Factors
2.2.2. KSHV-Related Cancers: Diagnosis
2.2.3. KSHV-Related Cancers: Prevention and Treatment
2.2.4. KSHV-Related Cancers: Prognosis
2.3. HPV in Transplantation
2.3.1. HPV-Related Cancers: Incidence and Risk Factors
2.3.2. HPV-Related Cancers: Diagnosis
2.3.3. HPV-Related Cancers: Prevention and Treatment
2.3.4. HPV-Related Cancers: Prognosis
2.4. Hepatitis Viruses in Transplantation
2.4.1. HBV-Related Cancers in Transplantation
HBV-Related Cancers: Prevention and Treatment
HBV-Related Cancers: Prognosis
2.4.2. HCV-Related Cancers in Transplantation
HCV-Related Cancers: Prevention and Treatment
HCV-Related Cancers: Prognosis
2.5. Polyomaviridae Family (PyVs)
2.5.1. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV)-Related Cancers in Transplantation
MCPyV-Related Cancers: Prognosis
2.5.2. BK Polyomavirus (BKPyV) and Kidney Transplantation
BK-Related Cancer: Diagnosis
BK-Related Cancer: Prognosis
2.5.3. John Cunningham Polyomavirus (JCPyV)
JC-Related Cancer: Prognosis
2.5.4. Trichodysplasia Spinulosa Polyomavirus (TSPyV)
TSPyV Diagnosis
2.6. Human T-Lymphotropic Virus-1 (HTLV-1): Cancer and Incidence
2.6.1. HTLV-Related Cancers in Transplantation
2.6.2. HTLV-Related Cancers: Diagnosis
2.6.3. HTLV-Related Cancers: Prognosis
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GVHD | Graft-versus-host disease |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| HHV-8 | Human herpesvirus 8 |
| HPV | Human papillomavirus |
| IM | Infectious mononucleosis |
| PTLD | Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease |
| KSHV | Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus |
| KICS | KSHV inflammatory cytokine syndrome |
| LANA | Latency-associated nuclear antigen |
| ART | Antiretroviral therapy |
| KS | Kaposi’s sarcoma |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| MCPyV | Merkel cell polyomavirus |
| HpyV | Human polyomavirus |
| HTLV-1 | Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 |
| PT-KS | Post-transplant Kaposi’s sarcoma |
| PEL | Primary effusion lymphoma |
| CIM | Cell-mediated immunity |
| VLP | Virus-like particles |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| DAAs | Direct-acting antivirals |
| HBeAg | HBV extracellular antigen |
| PyVs | Polyomaviridae family |
| NAT | Nucleic acid testing |
| BKPyV | BK polyomavirus |
| JCPyV | John Cunningham polyomavirus |
| TSPyV | Trichodysplasia spinulosa polyomavirus |
| MCC | Merkel cell carcinomas |
| TS | Trichodysplasia spinulosa |
| ATLL | Acute adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma |
| TSP | Subacute myelopathy referred to as tropical spastic paraparesis |
| LMP-1 | Latent Membrane Protein-1 |
| HBZ | HTLV-1 bZIP factor |
| CREB | cAMP-response element binding protein |
| CSC | Cancer Stem Cell |
| CTLs | Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes |
| NK | Natural Killer |
References
- Gutierrez-Dalmau, A.; Campistol, J.M. Immunosuppressive therapy and malignancy in organ transplant recipients: A systematic review. Drugs 2007, 67, 1167–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, I.; Grinyó, J.M. Malignancy after renal transplantation: The role of immunosuppression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transplantation Market: Industry Analysis and Forecast (2024–2030). 2024. Available online: https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/transplantation-market/187076/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Dangi, A.; Yu, S.; Luo, X. Emerging approaches and technologies in transplantation: The potential game changers. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.A.; Rubin, R.H. Infection in organ-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Limaye, A.P. Infections in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 3440–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, J.; Gäbel, H.; Lindelöf, B.; Ekström, K.; Rydh, B.; Glimelius, B.; Ekbom, A.; Adami, H.-O.; Granath, F. Cancer risk following organ transplantation: A nationwide cohort study in Sweden. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turra, V.; Manzi, J.; Rombach, S.; Zaragoza, S.; Ferreira, R.; Guerra, G.; Conzen, K.; Nydam, T.; Livingstone, A.; Vianna, R.; et al. Donors with Previous Malignancy: When Is It Safe to Proceed with Organ Transplantation? Transpl. Int. 2025, 38, 13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.C.; Lanier, L.L. NK cells in host responses to viral infections. Curr. Opin Immunol. 2017, 44, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nath, A.; Berger, J.R. Complications of immunosuppressive/immunomodulatory therapy in neurological diseases. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2012, 14, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierickx, D.; Tousseyn, T.; Gheysens, O. How I treat posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2015, 126, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.A. Infection in Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 856–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Shah, S.S.; Johnson, C.D.; De Witt, A.S.; Thomassen, A.S.; Daniel, C.P.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; Tirumala, S.; Bembenick, K.N.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Tacrolimus- and Mycophenolate-Mediated Toxicity: Clinical Considerations and Options in Management of Post-Transplant Patients. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmudden, M.; Gustafsson, J.; Bertrand, Y.J.K.; Schliep, A.; Norberg, P. Evolution shapes and conserves genomic signatures in viruses. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, O.M.; de Gruijl, F.R. Molecular and immunologic mechanisms of cancer pathogenesis in solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakite, M.; Shaw-Saliba, K.; Lau, C.-Y. Malignancy and viral infections in Sub-Saharan Africa: A review. Front. Virol. 2023, 3, 1103737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed-Khorrami, S.M.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Łos, M.J.; Zandi, K.; Emameh, R.Z. Oncolytic viruses as emerging therapy against cancers including Oncovirus-induced cancers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 939, 175393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugl, A.; Andersen, C.L. Epstein-Barr virus and its association with disease—A review of relevance to general practice. BMC Fam. Pract. 2019, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damania, B.; Kenney, S.C.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus: Biology and clinical disease. Cell 2022, 185, 3652–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, B.N.; Lynch, D.T. Kaposi Sarcoma; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brianti, P.; De Flammineis, E.; Mercuri, S.R. Review of HPV-related diseases and cancers. New Microbiol. 2017, 40, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, M.P.; Buti, M.; Gane, E.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Razavi, H.; Terrault, N.; Younossi, Z. Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, M.E.; Lambert, P.F. Merkel cell polyomavirus: A newly discovered human virus with oncogenic potential. Virology 2013, 435, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawinski, D.; Goral, S. BK virus infection: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczy, M.W.; Marshall, L.J.; Nelson, C.D.; Atwood, W.J.; Nath, A.; Khalili, K.; Major, E.O. Molecular biology, epidemiology, and pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, the JC virus-induced demyelinating disease of the human brain. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezioso, C.; Van Ghelue, M.; Moens, U.; Pietropaolo, V. HPyV6 and HPyV7 in urine from immunocompromised patients. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagasi, A.A.; Khandaker, T.; Clark, G.; Akagha, T.; Ball, J.K.; Irving, W.L.; McClure, C.P. Trichodysplasia Spinulosa Polyomavirus in Respiratory Tract of Immunocompromised Child. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1744–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Jeang, K.-T. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijland, M.L.; Kersten, M.J.; Pals, S.T.; Bemelman, F.J.; Ten Berge, I.J. Epstein-Barr Virus–Positive Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disease After Solid Organ Transplantation: Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Management. Transplant. Direct 2016, 2, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremers, W.; Devarbhavi, H.; Wiesner, R.; Krom, R.; Macon, W.; Habermann, T. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders following liver transplantation: Incidence, risk factors and survival. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, H.; Omer, Z.; Wima, K.; Magge, T.; Shah, S.A.; Latif, T. Outcomes and Prognostic Assessment of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: 20-Year Experience. Lymphatics 2025, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.; Qu, L.; Reyes, J.; Jabbour, N.; Yunis, E.; Putnam, P.; Todo, S.; Green, M. Use of quantitative competitive PCR to measure Epstein-Barr virus genome load in the peripheral blood of pediatric transplant patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, P.; Crawford, D.H. The role of EBV in post-transplant malignancies: A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 53, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanova, J.; Caillard, S.; Rousseau, A.; Marquet, P. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD): Pharmacological, virological and other determinants. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, T.; Thomas, J.A.; Parratt, R.; Hunt, B.J.; Yacoub, M.H.; Crawford, D.H. A Prospective Study in Heart and Lung Transplant Recipients Correlating Persistent Epstein-Barr Virus Infection with Clinical Events1. Transplantation 1997, 64, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, A.L.; Martinez, O.M. Epstein-Barr virus: Evasive maneuvers in the development of PTLD. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.S.; Cho, Y.W.; Shah, T.; Bunnapradist, S.; Hutchinson, I.V. Impact of Epstein–Barr virus donor and recipient serostatus on the incidence of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in kidney transplant recipients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hamed, R.; Bazarbachi, A.H.; Mohty, M. Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (EBV-PTLD) in the setting of allogeneic stem cell transplantation: A comprehensive review from pathogenesis to forthcoming treatment modalities. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020, 55, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Habermann, T.M.; Maurer, M.J.; Geyer, S.M.; Ristow, K.M.; Larson, T.S.; Walker, R.C.; Ansell, S.M.; Macon, W.R.; Gores, G.G.; et al. Prognostic analysis for survival in adult solid organ transplant recipients with post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7574–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M. Management of Epstein–Barr Virus-induced Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease in Recipients of Solid Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2001, 1, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, U.; Preiksaitis, J. Epstein-Barr virus and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiksaitis, J.; Pang, X.; Fox, J.; Fenton, J.; Caliendo, A.; Miller, G.; American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Interlaboratory comparison of Epstein-Barr virus viral load assays. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.J.; Verschuuren, E.A.; Verkuijlen, S.A.; Van Den Brule, A.J.; Meijer, C.J.; Middeldorp, J.M. Role of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load monitoring in prevention and early detection of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Leuk. Lymphoma 2002, 43, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.; Douglas, L.; Andreadis, C.; Vogl, D.; Arnoldi, S.; Kotloff, R.; Svoboda, J.; Bloom, R.D.; Olthoff, K.M.; Brozena, S.C.; et al. EBV PCR in the diagnosis and monitoring of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: Results of a two-arm prospective trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, F.; Latinne, D.; Bazin, H.; Reding, R.; Otte, J.-B.; Buts, J.-P.; Sokal, E.M. Ratio between Epstein-Barr viral load and anti-Epstein-Barr virus specific T-cell response as a predictive marker of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease1. Transplantation 2002, 73, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.-J.; Cheng, Y.C.; Huls, M.H.; Gee, A.P.; Kuehnle, I.; Krance, R.A.; Brenner, M.K.; Rooney, C.M.; Heslop, H.E. Prompt versus preemptive intervention for EBV lymphoproliferative disease. Blood 2004, 103, 3979–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Juan, R.; Comoli, P.; Caillard, S.; Moulin, B.; Hirsch, H.H.; Meylan, P. Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Bowles, K.; Bradley, J.A.; Emery, V.; Featherstone, C.; Gupte, G.; Marcus, R.; Parameshwar, J.; Ramsay, A.; Newstead, C.; et al. Management of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in adult solid organ transplant recipients–BCSH and BTS Guidelines. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funch, D.P.; Walker, A.M.; Schneider, G.; Ziyadeh, N.J.; Pescovitz, M.D. Ganciclovir and acyclovir reduce the risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in renal transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2894–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barozzi, P.; Bosco, R.; Vallerini, D.; Potenza, L.; Torelli, G.; Luppi, M.; Facchetti, F.; Guaraldi, G.; Schulz, T.F. KSHV/HHV-8 infection of tubular epithelial cells in transplantation kidney. Transplantation 2006, 82, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattani, P.; Capuano, M.; Graffeo, R.; Ricci, R.; Cerimele, F.; Cerimele, D.; Nanni, G.; Fadda, G. Kaposi’s sarcoma associated with previous human herpesvirus 8 infection in kidney transplant recipients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uldrick, T.S.; Wang, V.; O’Mahony, D.; Aleman, K.; Wyvill, K.M.; Marshall, V.; Steinberg, S.M.; Pittaluga, S.; Maric, I.; Whitby, D.; et al. An interleukin-6-related systemic inflammatory syndrome in patients co-infected with Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and HIV but without Multicentric Castleman disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, V.; Wood, C. Epidemiology and transmission of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Viruses 2014, 6, 4178–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantina, H.; Kankasa, C.; Klaskala, W.; Brayfield, B.; Campbell, J.; Du, Q.; Bhat, G.; Kasolo, F.; Mitchell, C.; Wood, C. Vertical transmission of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 94, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothaman, P.; Dabral, P.; Gupta, N.; Sarkar, R.; Verma, S.C. KSHV Genome Replication and Maintenance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablashi, D.V.; Chatlynne, L.G.; Whitman, J.E., Jr.; Cesarman, E. Spectrum of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, or human herpesvirus 8, diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Velasco, P.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; Flores, R.; Gómez-Román, J.J.; Lozano, M.-J.; Leyva-Cobián, F. Simultaneous Multiorgan Presence of Human Herpesvirus 8 and Restricted Lymphotropism of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Sequences in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus—Negative Immunodeficient Infant. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fatahzadeh, M. Kaposi sarcoma: Review and medical management update. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 113, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temelkova, I.; Tronnier, M.; Terziev, I.; Wollina, U.; Lozev, I.; Goldust, M.; Tchernev, G. A series of patients with kaposi sarcoma (mediterranean/classical type): Case presentations and short update on pathogenesis and treatment. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, L.D. Human herpesvirus-8: Kaposi sarcoma, multicentric Castleman disease, and primary effusion lymphoma. In Hematology 2013, the American Society of Hematology Education Program Book; The American Society of Hematology: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 2013, pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Mariggiò, G.; Koch, S.; Schulz, T.F. Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus pathogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesri, E.A.; Cesarman, E.; Boshoff, C. Kaposi’s sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, A.-G.; Calvez, V.; Dussaix, E. KSHV after an organ transplant: Should we screen? In Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus: New Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Regamey, N.; Tamm, M.; Wernli, M.; Witschi, A.; Thiel, G.; Cathomas, G.; Erb, P. Transmission of human herpesvirus 8 infection from renal-transplant donors to recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz Akçay, E.; Tepeoğlu, M.; Özdemir, B.H.; Deniz, E.; Börcek, P.; Haberal, M. De Novo Malignant Neoplasms in Renal Transplant Patients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 14 (Suppl. 3), 100–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luppi, M.; Barozzi, P.; Santagostino, G.; Trovato, R.; Schulz, T.F.; Marasca, R.; Bottalico, D.; Bignardi, L.; Torelli, G. Molecular evidence of organ-related transmission of Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus or human herpesvirus-8 in transplant patients. Blood 2000, 96, 3279–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frances, C.; Marcelin, A.; Legendre, C.; Chevret, S.; Dussaix, E.; Lejeune, J.; Euvrard, S.; Bigorie, A.; Schulz, T.; Agbalika, F.; et al. The impact of preexisting or acquired Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus infection in kidney transplant recipients on morbidity and survival. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 2580–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parravicini, C.; Olsen, S.J.; Capra, M.; Poli, F.; Sirchia, G.; Gao, S.-J.; Berti, E.; Nocera, A.; Rossi, E.; Bestetti, G.; et al. Risk of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus transmission from donor allografts among Italian posttransplant Kaposi’s sarcoma patients. Blood 1997, 90, 2826–2829. [Google Scholar]
- Serraino, D.; Piselli, P.; Scuderi, M.; Gabbrielli, F.; Venettoni, S.; Grossi, P.; Costa, A.N.; Ippolito, G.; e Infezioni, S.I.T. Screening for human herpesvirus 8 antibodies in Italian organ transplantation centers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cesarman, E.; Damania, B.; Krown, S.E.; Martin, J.; Bower, M.; Whitby, D. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollard, S.C.; Douglas, D.; Basavaraju, S.V.; Schmid, D.S.; Kuehnert, M.; Aqel, B. Donor-derived Kaposi’s sarcoma in a liver-kidney transplant recipient. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellett Madan, R.; Hand, J. Human herpesvirus 6, 7, and 8 in solid organ transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Zizzo, M.; Palicelli, A.; Bassi, M.C.; Santandrea, G.; Martino, G.; Soriano, A.; Caprera, C.; Corsi, M.; et al. Primary effusion lymphoma occurring in the setting of transplanted patients: A systematic review of a rare, life-threatening post-transplantation occurrence. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamna, A.; Yahav, D.; Hirzel, C. Prevention of Oncogenic Gammaherpesvirinae (EBV and HHV8) Associated Disease in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haręża, D.A.; Wilczyński, J.R.; Paradowska, E. Human papillomaviruses as infectious agents in gynecological cancers. Oncogenic properties of viral proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGraw, S.L.; Ferrante, J.M. Update on prevention and screening of cervical cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, E.M. Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2003, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farahmand, Z.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Garshasbi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Zafari, E. Distribution of the most common types of HPV in Iranian women with and without cervical cancer. Women’s Health 2021, 61, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghian, Z.; Bannazadeh Baghi, H.; Poortahmasebi, V.; Sadeghi, J.; Hasani, A.; Azadi, A.; Ahangar Oskouee, M. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Infection in Gastric Cancer in Ardebil Province, Northwest of Iran. Iran. J. Virol. 2022, 16, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Moscicki, A.B. Cell-mediated immune response to human papillomavirus infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewavisenti, R.V.; Arena, J.; Ahlenstiel, C.L.; Sasson, S.C. Human papillomavirus in the setting of immunodeficiency: Pathogenesis and the emergence of next-generation therapies to reduce the high associated cancer risk. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: From basic studies to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kundu, R. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7: The Cervical Cancer Hallmarks and Targets for Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, T.; Mokos, A.; Prasianakis, N.I.; Leyer, S. first_page settings Order Article Reprints Open AccessArticle Pore-Level Multiphase Simulations of Realistic Distillation Membranes for Water Desalination. Membranes 2022, 12, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, T.A.; Schiller, J.T. Human papillomavirus in cervical cancer and oropharyngeal cancer: One cause, two diseases. Cancer 2017, 123, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin-Hong, P.V. Human Papillomavirus in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeuwis, K.A.; Melchers, W.J.; Bouten, H.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.; Hinten, F.; Quint, W.G.; Massuger, L.F.; Hoitsma, A.J.; van Rossum, M.M.; de Hullu, J.A. Anogenital malignancies in women after renal transplantation over 40 years in a single center. Transplantation 2012, 93, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, L.; Asfour, L.; Stephany, M.; Lear, J.; Stasko, T. Management of non-melanoma skin cancer in transplant recipients. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeleine, M.M.; Finch, J.L.; Lynch, C.F.; Goodman, M.T.; Engels, E.A. HPV-related cancers after solid organ transplantation in the United States. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 3202–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.D.; Otoa, R.O.; Youssef, A.H.; Fontan, C.T.; Sannigrahi, M.K.; Windle, B.; Basu, D.; Morgan, I.M. HPV16 genome structure analysis in oropharyngeal cancer PDXs identifies tumors with integrated and episomal genomes. Tumour Virus Res. 2024, 18, 200285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, G.M.; Vieira, É.C.; Garcia, L.C.; De Carvalho-Leite, M.L.R.; Guedes, A.C.M.; Araújo, M.G. Update on human papilloma virus—Part I: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical spectrum. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2021, 96, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillman, F.H.; Sentovich, S.; Shaffer, D. Ano-genital neoplasia in renal transplant patients. Ann. Transplant. 1997, 2, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Aboulafia, D.M. Cancer screening in women living with HIV infection. Women’s Health 2017, 13, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin-Hong, P.V.; Kwak, E.J. Human papillomavirus in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13 (Suppl. S4), 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Zhai, L.; Tumban, E. Virus-like Particle-Based L2 Vaccines against HPVs: Where Are We Today? Viruses 2019, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhatova, A.; Azizan, A.; Atageldiyeva, K.; Ashimkhanova, A.; Marat, A.; Iztleuov, Y.; Suleimenova, A.; Shamkeeva, S.; Aimagambetova, G. Prophylactic Human Papillomavirus Vaccination: From the Origin to the Current State. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin-Hong, P.V.; Palefsky, J.M. Natural history and clinical management of anal human papillomavirus disease in men and women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisseling, K.C.; Bekkers, R.L.; Rome, R.M.; Quinn, M.A. Treatment of microinvasive adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: A retrospective study and review of the literature. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 107, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenau, J.; Hooman, N.; Hadem, J.; Rifai, K.; Bahr, M.J.; Philipp, G.; Tillmann, H.L.; Klempnauer, J.; Strassburg, C.P.; Manns, M.P. Failure of hepatitis B vaccination with conventional HBsAg vaccine in patients with continuous HBIG prophylaxis after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2007, 13, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Czyz, M. WNT/β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: The aberrant activation, pathogenic roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinzari, V.; Barnaba, V.; Piconese, S. Chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections and cancer: Synergy between viral and host factors. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmore, T.N.; Shah, N.L.; Loomba, R.; Borg, B.B.; Lopatin, U.; Feld, J.J.; Khokhar, F.; Lutchman, G.; Kleiner, D.E.; Young, N.S.; et al. Reactivation of hepatitis B with reappearance of hepatitis B surface antigen after chemotherapy and immunosuppression. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiangte, B.; Kothakota, S.R.; Sasidharan, M.; Kareem, H.; Nair, A.K.; Kumar, V.V.; Kanala, J.R.; Kumar, P.C. Hepatitis B Reactivation in Liver Transplant Recipients With Hepatitis B Virus Core Antibody Positive Grafts: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, W.S.; Martin, P.; Bhamidimarri, K.R. Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Organ Transplantation. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Omata, M. Significance of extrahepatic replication of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 1990, 12, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerut, J.P.; Donataccio, M.; Ciccarelli, O.; Roggen, F.; Jamart, J.; Laterre, P.F.; Cornu, C.; Mazza, D.; Hanique, G.; Rahier, J.; et al. Liver transplantation and HBsAg-positive postnecrotic cirrhosis: Adequate immunoprophylaxis and delta virus co-infection as the significant determinants of long-term prognosis. J. Hepatol. 1999, 30, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, J.S.; Martin, P.; Conrad, A.J.; Markmann, J.F.; Seu, P.; Yersiz, H.; Goss, J.A.; Schmidt, P.; Pakrasi, A.; Artinian, L.; et al. Prophylaxis against hepatitis B recurrence following liver transplantation using combination lamivudine and hepatitis B immune globulin. Hepatology 1998, 28, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, H.E.; Dodson, F.S.; Rakela, J. A concise update on the status of liver transplantation for hepatitis B virus: The challenges in 2002. Liver Transplant. 2002, 8, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.G.; McGory, R.W.; Gaffey, M.J.; McCullough, C.C.; Shephard, B.L.; Houlgrave, C.W.; Ryan, T.S.; Kuhns, M.; McNamara, A.; Caldwell, S.H.; et al. Improved clinical outcomes with liver transplantation for hepatitis B-induced chronic liver failure using passive immunization. Ann. Surg. 1998, 227, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venook, A.P.; Papandreou, C.; Furuse, J.; Ladrón de Guevara, L. The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist 2010, 15 (Suppl. S4), 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCain, J.D.; Dickson, R.C.; Cai, J.; Zhang, N.; Pungpapong, S.; Aqel, B.A.; Chascsa, D.M. Hepatitis B reactivation after solid organ transplantation: A single-center experience. J. Liver Transplant. 2024, 15, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, J.H. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36 (Suppl. S1), S21–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoofnagle, J.H. Hepatitis C: The clinical spectrum of disease. Hepatology 1997, 26 (Suppl. S1), 15s–20s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiffman, M.L.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Lindsay, K.L.; Morishima, C.; Wright, E.C.; Everson, G.T.; Lok, A.S.; Morgan, T.R.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Lee, W.M.; et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C who have failed prior treatment. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1015–1023; discussion 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, N.; Garcia-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sanchez-Campos, S.; Majano, P.L.; Benedicto, I.; Rosado, J.A.; Salido, G.M.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J. Hepatitis C virus NS5A and core proteins induce oxidative stress-mediated calcium signalling alterations in hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Ocampo, W.A.; Navas, M.-C.; Buist-Homan, M.; Faber, K.N.; Daemen, T.; Moshage, H. Hepatitis C Virus Proteins Core and NS5A Are Highly Sensitive to Oxidative Stress-Induced Degradation after eIF2α/ATF4 Pathway Activation. Viruses 2020, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoulfas, G.; Goulis, I.; Giakoustidis, D.; Akriviadis, E.; Agorastou, P.; Imvrios, G.; Papanikolaou, V. Hepatitis C and liver transplantation. Hippokratia 2009, 13, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Sreekumar, R.; Gonzalez-Koch, A.; Maor-Kendler, Y.; Batts, K.; Moreno-Luna, L.; Poterucha, J.; Burgart, L.; Wiesner, R.; Kremers, W.; Rosen, C.; et al. Early identification of recipients with progressive histologic recurrence of hepatitis C after liver transplantation. Hepatology 2000, 32, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, D.; Forns, X.; Berenguer, M.; Trautwein, C.; Burroughs, A.; Rizzetto, M.; Trepo, C. Report of the monothematic EASL conference on liver transplantation for viral hepatitis (Paris, France, 12–14 January 2006). J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, R.H.; Sorrell, M.; Villamil, F. Report of the first International Liver Transplantation Society expert panel consensus conference on liver transplantation and hepatitis C. Liver Transplant. 2003, 9, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalambokis, G.; Manousou, P.; Samonakis, D.; Grillo, F.; Dhillon, A.P.; Patch, D.; O’bEirne, J.; Rolles, K.; Burroughs, A.K. Clinical outcome of HCV-related graft cirrhosis and prognostic value of hepatic venous pressure gradient. Transpl. Int. 2009, 22, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, M.; Wright, T.L. Liver transplantation in the management of chronic viral hepatitis. Profr. Howard Thomas 2005, 345. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, E.P.; Bellido, C.B.; Matín, M.S.; Franco, C.C.; Martínez, J.Á.; Artacho, G.S.; Gómez, L.M.; Ruiz, J.P.; Bravo, M.G. (Eds.) Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation: Analysis of risk factors. In Transplantation Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012, 379, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bina Possatto, M.; de Ataíde, E.C.; Fazzio Escanhoela, C.A.; Sevá-Pereira, T.; de Cassia Martins Alves da Silva, R.; Felicio, H.; Amado, L.d.N.; da Silva, R.F.; Lima, A.S.; Boin, I. Factors Related to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Liver Transplantation-A Brazilian Multicenter Study. Transplant. Proc. 2017, 49, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea Del Pozo, E.; Bernal Bellido, C.; Sendín Matín, M.; Cepeda Franco, C.; Álamo Martínez, J.M.; Suarez Artacho, G.; Gómez, L.M.; Ruiz, J.P.; Bravo, M.G. Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation: Analysis of Risk Factors. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 2990–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halazun, K.J.; Najjar, M.; Abdelmessih, R.M.; Samstein, B.; Griesemer, A.D.; Guarrera, J.V.; Kato, T.; Verna, E.C.; Emond, J.C.; Brown, R.S., Jr. Recurrence After Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New MORAL to the Story. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrink, J.M.; Byrns, J.; Berg, C.; Kappus, M.; King, L.; Ellis, M.J.; Sanoff, S.; Agarwal, R.; DeVore, A.D.M.; Reynolds, J.M.; et al. Real-world Experiences in the Transplantation of Hepatitis C-NAAT-positive Organs. Transplant. Direct 2023, 9, e1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyomaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Feltkamp, M.C.; Daugherty, M.D.; Moens, U.; Ramqvist, T.; Johne, R.; Ehlers, B. A taxonomy update for the family Polyomaviridae. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Langhoff, E. Polyomavirus in human cancer development. In Polyomaviruses and Human Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Kazem, S.; Van Der Meijden, E.; Wang, R.C.; Rosenberg, A.S.; Pope, E.; Benoit, T.; Fleckman, P.; Feltkamp, M.C.W.; Deb, S. Polyomavirus-associated Trichodysplasia spinulosa involves hyperproliferation, pRB phosphorylation and upregulation of p16 and p21. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yang, J.F.; Senay, T.E.; Liu, W.; You, J. Characterization of the impact of merkel cell polyomavirus-induced interferon signaling on viral infection. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e01907–e01922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, B.D.; Storer, B.E.; Iyer, J.G.; Phillips, J.L.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Fang, L.C.; Johnson, T.M.; Liegeois-Kwon, N.J.; Otley, C.C.; Paulson, K.G.; et al. Pathologic nodal evaluation improves prognostic accuracy in Merkel cell carcinoma: Analysis of 5823 cases as the basis of the first consensus staging system. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.W.; Rabkin, C.S. Merkel cell carcinoma and melanoma: Etiological similarities and differences. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Krynitz, B.; Edgren, G.; Lindelöf, B.; Baecklund, E.; Brattström, C.; Wilczek, H.; Smedby, K.E. Risk of skin cancer and other malignancies in kidney, liver, heart and lung transplant recipients 1970 to 2008—A Swedish population-based study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.; Jaimes, N.; Lemos, B.; Mostaghimi, A.; Wang, L.C.; Peñas, P.F.; Nghiem, P. Clinical characteristics of Merkel cell carcinoma at diagnosis in 195 patients: The AEIOU features. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, K.G.; Iyer, J.G.; Blom, A.; Warton, E.M.; Sokil, M.; Yelistratova, L.; Schuman, L.; Nagase, K.; Bhatia, S.; Asgari, M.M. Systemic immune suppression predicts diminished merkel cell carcinoma–specific survival independent of stage. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.; Pye, I.; Chinnadurai, R. Merkel Cell Carcinoma in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Dermato 2023, 3, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.; Baker, K.; Redman, M.; Lachance, K.; Nguyen, M.H.; Parvathaneni, U.; Bhatia, S.; Nghiem, P.; Tseng, Y.D. Differential outcomes among immunosuppressed patients with Merkel cell carcinoma: Impact of immunosuppression type on cancer-specific and overall survival. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, G.L.; Zargham, H.; Schulman, J.M.; Jafarian, F.; Yu, S.S.; Arron, S.T. Merkel cell carcinoma in organ transplant recipients: Case reports and review of the literature. JAAD Case Rep. 2015, 1, S29–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrándiz-Pulido, C.; Gómez-Tomás, A.; Llombart, B.; Mendoza, D.; Marcoval, J.; Piaserico, S.; Baykal, C.; Bouwes-Bavinck, J.; Rácz, E.; Kanitakis, J.; et al. Clinicopathological features, MCPyV status and outcomes of Merkel cell carcinoma in solid-organ transplant recipients: A retrospective, multicentre cohort study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Kwun, H.J.; Liu, X.; Gjoerup, O.; Stolz, D.B.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Cellular and viral factors regulating Merkel cell polyomavirus replication. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatizadeh Malekshahi, S.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Dorostkar, F.; Salimi, V.; Farahmand, M. Survey of BK Virus in Renal Transplant Recipients in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intervirology 2020, 64, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.E.; Hewlett, T.J.; Geldenhuys, L.; Kiberd, B.A.; Acott, P.D.; Hatchette, T.F. BK virus nephropathy in a heart transplant recipient: Case report and review of the literature. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2006, 8, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambalathingal, G.R.; Francis, R.S.; Smyth, M.J.; Smith, C.; Khanna, R. BK Polyomavirus: Clinical Aspects, Immune Regulation, and Emerging Therapies. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.A.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Straif, K.; WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. Carcinogenicity of malaria and of some polyomaviruses. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.K.; Khalili, K. Polyomaviruses and human cancer: Molecular mechanisms underlying patterns of tumorigenesis. Virology 2004, 324, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCaprio, J.A.; Garcea, R.L. A cornucopia of human polyomaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Sun, J.; Bao, J.; Zhu, T. BK polyomavirus infection promotes growth and aggressiveness in bladder cancer. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, J.C.; Randhawa, P.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Alexiev, B.; Hirsch, H.H. BK Polyomavirus Infection and Renourinary Tumorigenesis. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Singh, H.K.; Kenan, D.J.; Mieczkowski, P.A. The two-faced nature of BK polyomavirus: Lytic infection or non-lytic large-T-positive carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favi, E.; Puliatti, C.; Sivaprakasam, R.; Ferraresso, M.; Ambrogi, F.; Delbue, S.; Gervasi, F.; Salzillo, I.; Raison, N.; Cacciola, R. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of BK polyomavirus infection after kidney transplantation. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewski, W.; Kamińska, D.; Poterek, A.; Małkiewicz, B.; Kłak, J.; Zdrojowy, R.; Janczak, D. Pathogenicity of BK virus on the urinary system. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2020, 73, 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Starrett, G.J.; Buck, C.B. The case for BK polyomavirus as a cause of bladder cancer. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 39, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chaudhry, M.R.; Berrebi, A.A.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Haririan, A.; Alexiev, B.A. Polyomavirus Replication and Smoking Are Independent Risk Factors for Bladder Cancer After Renal Transplantation. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Yu, K.; Golubeva, Y.; Lenz, P.; Piaskowski, M.L.; Petersen, D.; Dean, M.; Israni, A.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Tucker, T.C.; et al. Evidence for virus-mediated oncogenesis in bladder cancers arising in solid organ transplant recipients. eLife 2023, 12, e82690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Kuppachi, S.; Kalil, R.S.; Buck, C.B.; Lynch, C.F.; Engels, E.A. Treatment for presumed BK polyomavirus nephropathy and risk of urinary tract cancers among kidney transplant recipients in the United States. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbarin, M.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Bakhshi, B.; Nasiri, Z.; Fakhredini, K. Detection of JC and BK polyomaviruses in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) by PCR. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2024, 45, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Bucay, A.; Ramirez-Andrade, S.E.; Gordon, C.E.; Francis, J.M.; Chitalia, V.C. Advances in BK Virus Complications in Organ Transplantation and Beyond. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanek, J.; Croul, S.; Ho, T.; Wang, J.Y.; Darbinyan, A.; Nowicki, M.; Del Valle, L.; Skorski, T.; Khalili, K.; Reiss, K. T-antigen of the human polyomavirus JC attenuates faithful DNA repair by forcing nuclear interaction between IRS-1 and Rad51. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 206, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, F.; Villani, S.; Ambrogi, F.; Signorini, L.; Dallari, S.; Binda, S.; Primache, V.; Pellegrinelli, L.; Ferrante, P.; Delbue, S. JC virus infection is acquired very early in life: Evidence from a longitudinal serological study. J. NeuroVirology 2017, 23, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Gulati, N.; Bihari, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Bansal, K.; Sasturkar, S.; Thapar, S.; Pamecha, V. JC Virus-Related Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy After Living-Donor Liver Transplant: A Rare Case. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 17, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Dunn, C.D.; Campbell, L.J.; Strand, D.W.; Vezina, C.M.; Bjorling, D.E.; Penniston, K.L.; Li, L.; Ricke, W.A.; Goldberg, T.L.; et al. A multi-omic investigation of male lower urinary tract symptoms: Potential role for JC virus. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskin, D.P.; Koralnik, I.J. Novel syndromes associated with JC virus infection of neurons and meningeal cells: No longer a gray area. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.C.; Yan, L.; Cui, L.; Guan, Y.F.; Takano, Y. Mapping the history and current situation of research on John Cunningham virus—A bibliometric analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kotton, C.N.; Fishman, J.A. Viral Infection in the Renal Transplant Recipient. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1758–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pjanic, M.; Aleckovic-Halilovic, M.; Basic-Jukic, N. JC Virus in Kidney Transplant Population: Are We Cautious Enough? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meijden, E.; Kazem, S.; Burgers, M.M.; Janssens, R.; Bouwes Bavinck, J.N.; de Melker, H.; Feltkamp, M.C.W. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossai, A.; Waterboer, T.; Nelson, H.H.; Michel, A.; Willhauck-Fleckenstein, M.; Farzan, S.F.; Hoen, A.G.; Christensen, B.C.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J.; et al. Seroepidemiology of Human Polyomaviruses in a US Population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curman, P.; Näsman, A.; Brauner, H. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: A comprehensive review of the disease and its treatment. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Aaltonen, L.-M.; Hedman, L.; Chen, T.; Söderlund-Venermo, M.; Hedman, K. Detection of TS polyomavirus DNA in tonsillar tissues of children and adults: Evidence for site of viral latency. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 59, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedergnana, V.; Martel-Jantin, C.; Nicol, J.T.; Leblond, V.; Tortevoye, P.; Coursaget, P.; Touzé, A.; Abel, L.; Gessain, A. Trichodysplasia spinulosa polyomavirus infection occurs during early childhood with intrafamilial transmission, especially from mother to child. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1181–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological aspects and world distribution of HTLV-1 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Seiki, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2534–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irigoyen, O.L.; Gordillo, B.L.; Palomino, S.B.; Perez, M.R.; Durán, B.M.; Augusto, D.E. Human T lymphotropic virus (HTLV I and II) antibodies seroprevalence among organ donors. Med. Intensiv. 2020, 44, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Vernant, J.; Maurs, L.; Barin, F.; Gout, O.; Calender, A.d.; De Thé, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 326, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roc, L.; de Mendoza, C.; Fernández-Alonso, M.; Reina, G.; Soriano, V. Rapid subacute myelopathy following kidney transplantation from HTLV-1 donors: Role of immunosuppresors and failure of antiretrovirals. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, 2049936119868028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemasson, I.; Lewis, M.R.; Polakowski, N.; Hivin, P.; Cavanagh, M.H.; Thébault, S.; Barbeau, B.; Nyborg, J.K.; Mesnard, J.-M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) bZIP protein interacts with the cellular transcription factor CREB to inhibit HTLV-1 transcription. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Corbett, C.; Rowe, I.A.; Taylor, G.P.; Neuberger, J.M. HTLV-1 in solid-organ transplantation: Current challenges and future management strategies. Transplantation 2012, 94, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.P. Editorial commentary: Lessons on transplant-acquired human T-cell lymphotropic virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1425–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, G.P. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection and solid organ transplantation. Rev Med Virol. 2018, 28, e1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, R.; Gil, J.; Sahagún, J.; Soriano, V. Clinical Outcome in Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 2 Carriers Following Organ Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.P. Editorial Commentary: Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-1–Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, R.C.; Willems, L.; Hasegawa, H.; HTLV-1 GVNsTFo. Screening transplant donors for HTLV-1 and-2. Blood 2016, 128, 3029–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tedla, F.; Brar, A.; John, D.; Sumrani, N. Risk of transmission of human T-lymphotropic virus through transplant. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Smid, J.; Haziot, M.E.; Assone, T.; Pinheiro, S.; Fonseca, L.A.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Casseb, J. High risk of heterosexual transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection in Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D.R.; Sharma, T.S.; AST ID Community of Practice. Human T-cell lymphotrophic virus in solid-organ transplant recipients: Guidelines from the American society of transplantation infectious diseases community of practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.J.M.; Diaz, E.P.C.; Buestán, M.E. HTLV-1-associated myelopathy in a solid organ transplant recipient. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016215243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Andersson, K.L.; Kotton, C.N.; Hertl, M.; Markmann, J.F.; Cosimi, A.B.; Chung, R.T. Prophylaxis of hepatitis B infection in solid organ transplant recipients. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L.M.; Gibson, T.M.; Clarke, C.A.; Lynch, C.F.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Engels, E.A. Hepatitis B or C virus infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among solid organ transplant recipients. Haematologica 2014, 99, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prado, J.C.M.; Monezi, T.A.; Amorim, A.T.; Lino, V.; Paladino, A.; Boccardo, E. Human polyomaviruses and cancer: An overview. Clinics 2018, 73, e558s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, C. Polyomavirinae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology, 3rd ed.; Lippincott-Raven Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 1997–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Manole, B.; Damian, C.; Giusca, S.E.; Caruntu, I.D.; Porumb-Andrese, E.; Lunca, C.; Dorneanu, O.S.; Iancu, L.S.; Ursu, R.G. The Influence of Oncogenic Viruses in Renal Carcinogenesis: Pros and Cons. Pathogens 2022, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arcy, M.E.; Castenson, D.; Lynch, C.F.; Kahn, A.R.; Morton, L.M.; Shiels, M.S.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; A Engels, E. Risk of Rare Cancers Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, A. Bioethics of organ transplantation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a015685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, J.-F.; Sonneville, R.; Kalil, A.C.; Bassetti, M.; Ferrer, R.; Jaber, S.; Lanternier, F.; Luyt, C.-E.; Machado, F.; Mikulska, M.; et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic approach to infectious diseases in solid organ transplant recipients. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ietto, G.; Gritti, M.; Pettinato, G.; Carcano, G.; Gasperina, D.D. Tumors after kidney transplantation: A population study. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, E.S.; Zaffiri, L. Infection prophylaxis and management of viral infection. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franquet, T.; Franks, T.J.; Lee, K.S.; Marchiori, E.; Mazzini, S.; Giménez, A.; Johkoh, T.; Cho, J.; Galvin, J.R. Human Oncoviruses and Thoracic Tumors: Understanding the Imaging Findings. RadioGraphics 2022, 42, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Avery, R. Screening of donor and recipient prior to solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, S7–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.I.; Fischer, S.A.; Ison, M.G. Infections transmitted by transplantation. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2010, 24, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinten, F.; Hilbrands, L.B.; Meeuwis, K.A.; IntHout, J.; Quint, W.G.; Hoitsma, A.J.; Massuger, L.F.A.G.; Melchers, W.J.G.; de Hullu, J. Reactivation of latent HPV infections after renal transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khansarinejad, B.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Mirab Samiee, S.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Paryan, M.; Sanahmadi, Y.; Karami, M.; Mondanizadeh, M. Monitoring human cytomegalovirus infection in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: Using an affordable in-house qPCR assay for management of HCMV infection under limited resources. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowalk, A.; Green, M. Epstein-Barr Virus. Microbiol Spectr. 2016, 4, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, D.; Habermann, T.M. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, M.; Taheri, S. Hepatitis B virus infection has no significant role on lymphoproliferative disorders post liver transplantation: PTLD. int survey. Ann. Hepatol. 2011, 10, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, L.M.; Landgren, O.; Chatterjee, N.; Castenson, D.; Parsons, R.; Hoover, R.N.; Engels, E.A. Hepatitis C virus infection and risk of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder among solid organ transplant recipients. Blood 2007, 110, 4599–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khedmat, H.; Taheri, S. Hepatitis C virus infection can affect lymphoproliferative disorders only as a cofactor for Epstein-Barr virus in liver transplant recipients: PTLD. Int survey. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 10, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begré, L.; Rohner, E.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Egger, M.; Bohlius, J. Is human herpesvirus 8 infection more common in men than in women? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharnidharka, V.R. Peripheral blood Epstein–Barr viral nucleic acid surveillance as a marker for posttransplant cancer risk. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, M.; Luo, Y. Hepatitis Virus and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recent Advances. Cancers 2023, 15, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.C.; Stang, A.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Cerroni, L.; Lebbé, C.; Veness, M.; Nghiem, P. Merkel cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.M.L.; Lee, T.K.W. Cancer Stem Cells: Emerging Key Players in Immune Evasion of Cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 692940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiaur, G.; Gerber, J.M.; Matsui, W.; Jones, R.J. Cancer stem cells: Relevance to clinical transplantation. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, M.S.; Ward, C.M.; Davies, C.C. DNA Repair and Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Xie, L.; Shi, F.; Tang, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Yu, X.; Luo, X.; et al. Targeting the signaling in Epstein–Barr virus-associated diseases: Mechanism, regulation, and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organista-Nava, J.; Gómez-Gómez, Y.; Garibay-Cerdenares, O.L.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A.; Illades-Aguiar, B. Cervical cancer stem cell-associated genes: Prognostic implications in cervical cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obanya, D.I.; Wootton, L.M.; Morgan, E.L. Advances in understanding the mechanisms of the human papillomavirus oncoproteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2025, 53, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, T.; Carroll, P.A.; Punjabi, A.S.; Margineantu, D.; Hockenbery, D.M.; Lagunoff, M. Induction of the Warburg effect by Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus is required for the maintenance of latently infected endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10696–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krump, N.A.; You, J. Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in humans. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.G.; Hsu, E.K.; Mack, C.L. The importance of prioritizing pre and posttransplant immunizations in an era of vaccine refusal and epidemic outbreaks. Transplantation 2020, 104, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Virus | Family | Genome | Genome Size (Approximately) | Transmission | Incidence | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV | Herpesviridae | ds-DNA | 172 kb | Saliva, close contact | Common/High, in solid organ | [19,20] |
| KSHV | Herpesviridae | ds-DNA | 165–170 kb | Saliva, sexual contact, organ transplantation | Increased risk in transplant recipients | [21] |
| HPV | Papillomaviridae | Circular ds-DNA | 8 kb | Sexual & skin-to-skin contact | Common/Increased risk in transplant recipients | [22] |
| HBV | Hepadnaviridae | Partially ds-DNA | 3.2 kb | Blood, sexual contact, vertical transmission | Varies by region/especially in liver transplant recipients | [23] |
| HCV | Flaviviridae | ss-RNA | 9.6 kb | Blood, sexual contact, vertical transmission | Varies by region/especially in liver transplant recipients | [24] |
| Merkel cell polyomavirus | Polyomaviridae | Circular ds-DNA | 5.4 kb | Likely through respiratory secretions | Relatively rare/ | [25] |
| BK virus | Polyomaviridae | Circular ds-DNA | 5.2 kb | Primarily through respiratory secretions and urine | Common, individuals with evidence of past infection/1–10% of kidney transplant recipients | [26] |
| JC virus | Polyomaviridae | Circular ds-DNA | 5.13 kb | respiratory secretions and urine | Reactivation occurs in immunocompromised patients | [27] |
| HPyV6, HPyV7, TSPyV | Polyomaviridae | Circular ds-DNA | 5.4 kb | Likely respiratory secretions or direct contact with infected individuals | Rare/specific rates are not provided | [28,29] |
| HTLV-1 | Retroviridae | Two copies of ss-RNA | 9 kb | breastfeeding, sexual contact, and blood transfusion | Endemic in certain regions, Japan, Caribbean, and parts of Africa and South America/Rare | [30] |
| Oncogene Virus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBV/HCV | HTLV-I | PyVs | KSHV | HPV | EBV | |
| Yes | Yes | No * | No * | No * | Yes | Screen before Transplantation |
| Serological | Serological | Serological | Serological | Cytology | Serological | Screen Method |
| HBsAg, HBsAb, HBcAb IgM HBcAb IgG HCV Antibody | Antibodies/NAT | Viremia | Latent Ag/Antibodies | CIN AIN | VCA IgG VCA IgM EA IgG EBNA-1 IgG | Diagnostic Test |
| NAT | Not done | Not done | Not done | Skin Examination 1 | Quantification PCR (DNA in PBMC) 2 | Monitoring after Transplant |
| Yes/No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Control via Vaccine |
| Antiviral | No cure; antiretroviral can manage symptoms | No specific antiviral | Antiviral | No cure | Antiviral | Treatment |
| [193,194] | [188,189] | [195,196] | [66,73] | [22,89] | [34,36] | References |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seyed-Khorami, S.-M.; Azadi, A.; Habibian, A.; Hosseini, M.; Fan, X.; Soleimanjahi, H.; Pourkarim, M.R. Oncogenic Viruses in Organ Transplantation: Implications of Virus-Host Interactions for Cancer Development. Viruses 2025, 17, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101299
Seyed-Khorami S-M, Azadi A, Habibian A, Hosseini M, Fan X, Soleimanjahi H, Pourkarim MR. Oncogenic Viruses in Organ Transplantation: Implications of Virus-Host Interactions for Cancer Development. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101299
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeyed-Khorami, Seyed-Mahmood, Arezou Azadi, Ala Habibian, Monireh Hosseini, Xiaofeng Fan, Hoorieh Soleimanjahi, and Mahmoud Reza Pourkarim. 2025. "Oncogenic Viruses in Organ Transplantation: Implications of Virus-Host Interactions for Cancer Development" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101299
APA StyleSeyed-Khorami, S.-M., Azadi, A., Habibian, A., Hosseini, M., Fan, X., Soleimanjahi, H., & Pourkarim, M. R. (2025). Oncogenic Viruses in Organ Transplantation: Implications of Virus-Host Interactions for Cancer Development. Viruses, 17(10), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101299







