Screening of Single-Domain Antibodies to Adeno-Associated Viruses with Cross-Serotype Specificity and a Wide pH Tolerance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
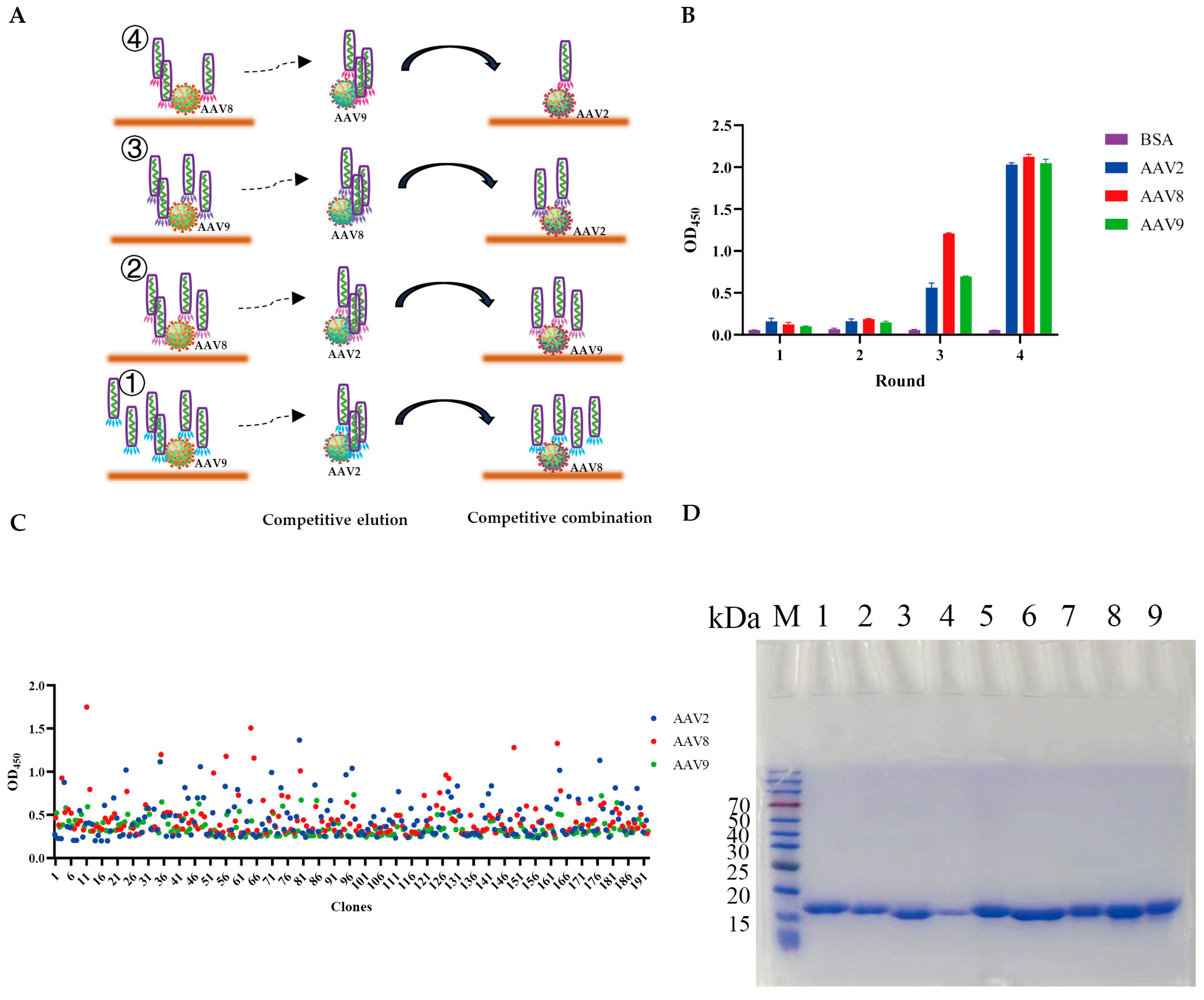
2.2. Competitive Biopanning Strategy
2.3. Phage ELISA
2.4. VHHs Expression and Purification
2.5. Affinity Measurements
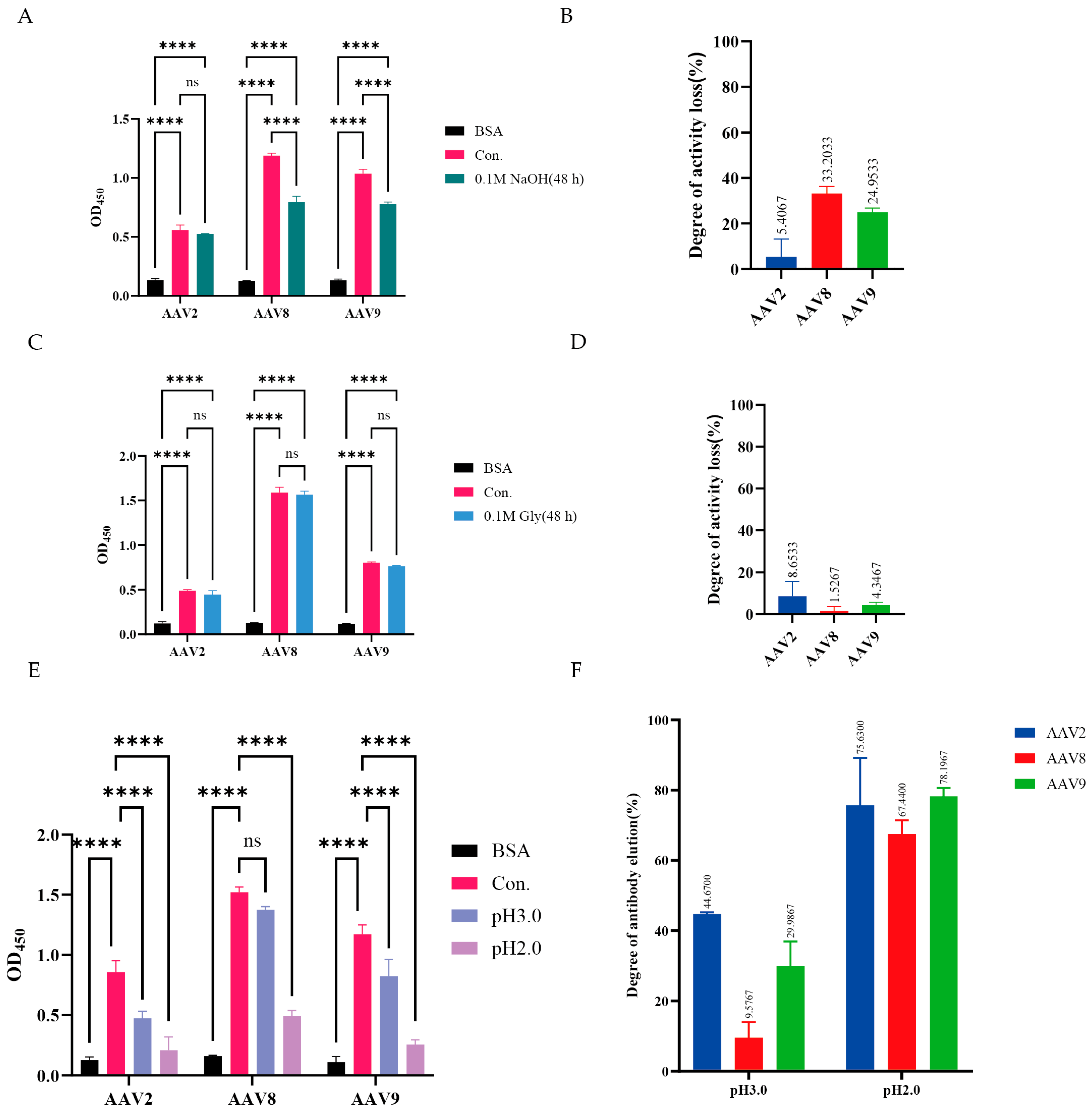
2.6. Acid and Alkali Stability Assessment
2.7. Acid Elution Simulation Verification
2.8. VHH Coupling to CNBr-Activated Agarose Beads
2.9. AAV Production and Purification
2.10. AAV Infection and Transduction Assays
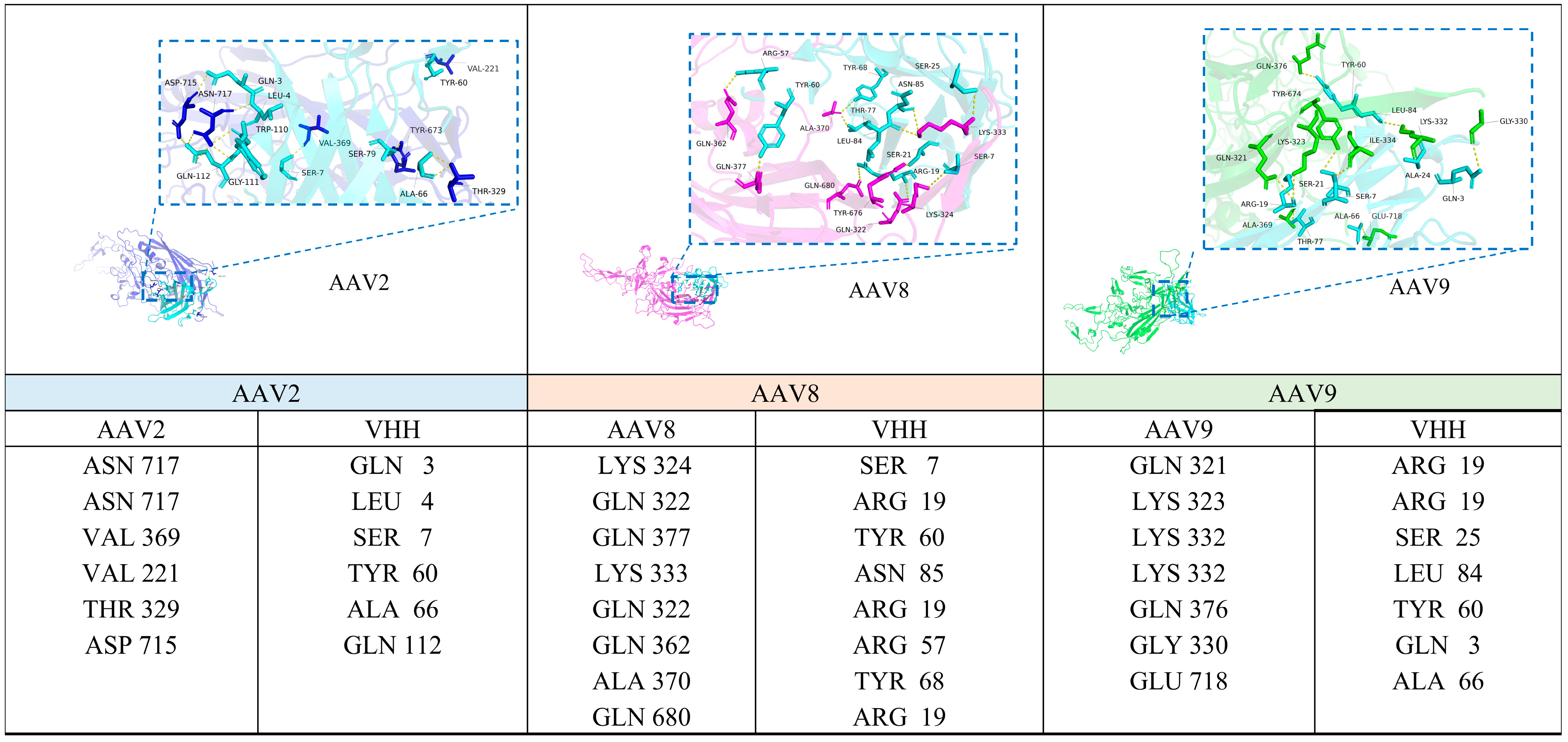
2.11. Prediction of Potential Binding Sites Between VHH and AAV2, AAV8, and AAV9
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection and Characterization of VHHs Targeting AAV2, AAV8, and AAV9
3.2. Expression and Purification of VHHs
3.3. Binding Specificity and Affinity of the VHHs
3.4. Stability Assessment of VHH8
3.5. Affinity Purification of AAV with VHH8-Based Chromatography Resin
3.6. Preservation of In Vitro Bioactivity of AAV Serotypes Following Purification
3.7. Prediction of the VHH8 Binding Epitope on the AAV Capsid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pupo, A.; Fernández, A.; Low, S.H.; François, A.; Suárez-Amarán, L.; Samulski, R.J. AAV Vectors: The Rubik’s Cube of Human Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naso, M.F.; Tomkowicz, B.; Perry, W.L., III; Strohl, W.R. Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) as a Vector for Gene Therapy. Biodrugs 2017, 31, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Amaran, L.; Song, L.; Tretiakova, A.P.; Mikhail, S.A.; Samulski, R.J. AAV Vector Development, Back to the Future. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2025, 33, 1903–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, L.H.; Wilson, J.M.; Gao, G. Tailoring the AAV Vector Capsid for Gene Therapy. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Voretigene Neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in Patients with RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Dystrophy: A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Al-Zaidy, S.; Shell, R.; Arnold, W.D.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Prior, T.W.; Lowes, L.; Alfano, L.; Berry, K.; Church, K.; et al. Single-Dose Gene-Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Gessler, D.J.; Zhan, W.; Gallagher, T.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-Associated Virus as a Delivery Vector for Gene Therapy of Human Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozelo, M.C.; Mahlangu, J.; Pasi, K.J.; Giermasz, A.; Leavitt, A.D.; Laffan, M.; Symington, E.; Quon, D.V.; Wang, J.-D.; Peerlinck, K.; et al. Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec Gene Therapy for Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Samulski, R.J. Engineering Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors for Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipe, S.W.; Leebeek, F.W.G.; Recht, M.; Key, N.S.; Castaman, G.; Miesbach, W.; Lattimore, S.; Peerlinck, K.; Van der Valk, P.; Coppens, M.; et al. Gene Therapy with Etranacogene Dezaparvovec for Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Lee, J.S.; Wang, L.; Desai, T.; Akache, B.; Storm, T.A.; Kay, M.A. In Vitro and In Vivo Gene Therapy Vector Evolution via Multispecies Interbreeding and Retargeting of Adeno-Associated Viruses. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5887–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.; Daugherty, A.L.; Khadir, F.; Duzenli, O.F.; Hoffman, A.; Tinklenberg, J.A.; Kang, P.B.; Aslanidi, G.; Pacak, C.A. AAV-DJ Is Superior to AAV9 for Targeting Brain and Spinal Cord, and de-Targeting Liver across Multiple Delivery Routes in Mice. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietersz, K.L.; Plessis, F.D.; Pouw, S.M.; Liefhebber, J.M.; van Deventer, S.J.; Martens, G.J.M.; Konstantinova, P.S.; Blits, B. PhP.B Enhanced Adeno-Associated Virus Mediated-Expression Following Systemic Delivery or Direct Brain Administration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 679483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Kurial, S.N.; Choksi, P.K.; Nunez, M.; Lunow-Luke, T.; Bartel, J.; Driscoll, J.; Her, C.L.; Dhillon, S.; Yue, W.; et al. AAV Capsid Prioritization in Normal and Steatotic Human Livers Maintained by Machine Perfusion. Nat. Biotechnol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanes-Creus, M.; Navarro, R.G.; Liao, S.H.Y.; Scott, S.; Carlessi, R.; Roca-Pinilla, R.; Knight, M.; Baltazar, G.; Zhu, E.; Jones, M.; et al. Characterization of the Humanized FRG Mouse Model and Development of an AAV-LK03 Variant with Improved Liver Lobular Biodistribution. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 28, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, B.; Shu, Y. Approaches and Vectors for Efficient Cochlear Gene Transfer in Adult Mouse Models. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.K.; Likhite, S.; Vetter, T.A.; Baird, M.C.; McGovern, V.; Sierra Delgado, A.; Mendel, T.; Burghes, A.; Meyer, K.C. In-Depth Comparison of Anc80L65 and AAV9 Retinal Targeting and Characterization of Cross-Reactivity to Multiple AAV Serotypes in Humans. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 30, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnyandu, N.Z.; Limani, S.W.; Ely, A.; Wadee, R.; Arbuthnot, P.; Maepa, M.B. Long-Term Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Gene Expression by a Primary Microrna Expressing Ancestral Adeno-Associated Viral Vector. Virol. J. 2025, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabou, H.; Desrosiers, M.; Winckler, C.; Fouquet, S.; Auregan, G.; Bemelmans, A.P.; Sahel, J.A.; Dalkara, D. Insight into the Mechanisms of Enhanced Retinal Transduction by the Engineered AAV2 Capsid Variant -7m8. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietzsch, M.; Smith, J.K.; Yu, J.C.; Banala, V.; Emmanuel, S.N.; Jose, A.; Chipman, P.; Bhattacharya, N.; McKenna, R.; Agbandje-McKenna, M. Characterization of AAV-Specific Affinity Ligands: Consequences for Vector Purification and Development Strategies. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 19, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, M.; Nicolaou, F.; Pacouret, S.; Zinn, E.M.; Sanmiguel, J.; Andres-Mateos, E.; Unzu, C.; Wagers, A.J.; Vandenberghe, L.H. High-Efficiency Purification of Divergent AAV Serotypes Using AAVX Affinity Chromatography. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 28, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lock, M.; Prongay, A.J.; Alvira, M.R.; Petkov, B.; Wilson, J.M. Identification of an Adeno-Associated Virus Binding Epitope for AVB Sepharose Affinity Resin. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2015, 2, 15040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Shastry, S.; Barbieri, E.; Prodromou, R.; Greback-Clarke, P.; Smith, W.; Moore, B.; Kilgore, R.; Cummings, C.; Pancorbo, J.; et al. Peptide Ligands for the Affinity Purification of Adeno-Associated Viruses from HEK 293 Cell Lysates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2023, 120, 2283–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, S.; Chu, W.; Barbieri, E.; Greback-Clarke, P.; Smith, W.K.; Cummings, C.; Minzoni, A.; Pancorbo, J.; Gilleskie, G.; Ritola, K.; et al. Rational Design and Experimental Evaluation of Peptide Ligands for the Purification of Adeno-Associated Viruses via Affinity Chromatography. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, e2300230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lieshout, L.P.; Stegelmeier, A.A.; Rindler, T.N.; Lawder, J.J.; Sorensen, D.L.; Frost, K.L.; Booth, S.A.; Bridges, J.P.; Wootton, S.K. Engineered AAV8 Capsid Acquires Heparin and AVB Sepharose Binding Capacity but Has Altered in Vivo Transduction Efficiency. Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Odongo, S.; Radwanska, M.; Magez, S. NANOBODIES®: A Review of Generation, Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klooster, R.; Maassen, B.T.H.; Stam, J.C.; Hermans, P.W.; Ten Haaft, M.R.; Detmers, F.J.M.; de Haard, H.J.; Post, J.A.; Theo Verrips, C. Improved Anti-IgG and HSA Affinity Ligands: Clinical Application of VHH Antibody Technology. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 324, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zang, B.; Huang, C.; Ren, J.; Jia, L. One-Step Preparation of a VHH-Based Immunoadsorbent for the Extracorporeal Removal of Β2-Microglobulin. Molecules 2019, 24, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, S.S.; Shaimardanova, A.A.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Rizvanov, A.A. Various AAV Serotypes and Their Applications in Gene Therapy: An Overview. Cells 2023, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, G.; Cao, L.; Sun, Z.; He, Y.; Cui, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Qin, L.; et al. Divergent Engagements between Adeno-Associated Viruses with Their Cellular Receptor AAVR. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönberg, A.; Eriksson, M.; Ersoy, M.; Johansson, H.J. A Tool for Increasing the Lifetime of Chromatography Resins. MAbs 2011, 3, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
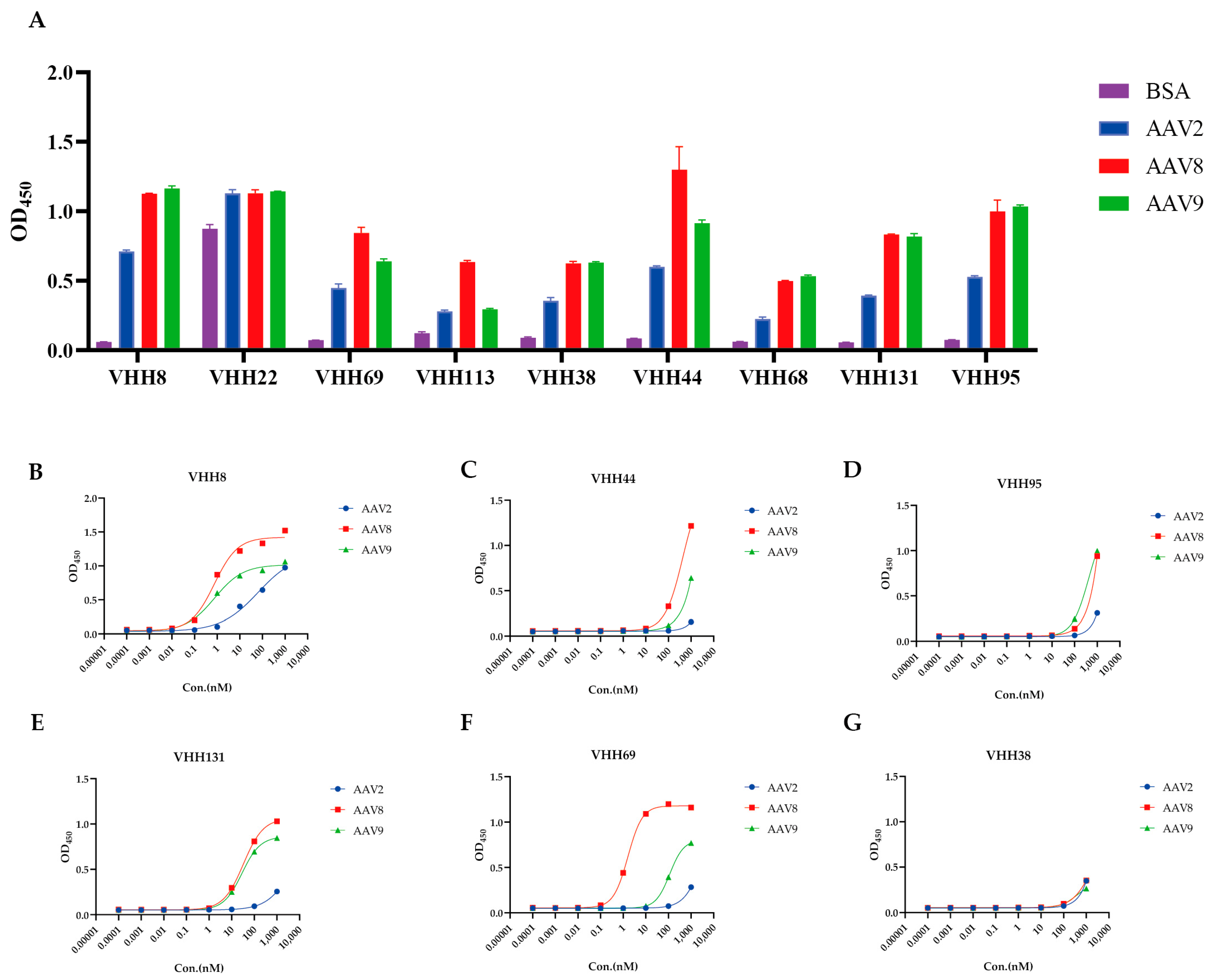


| Name | EC50 (nM) | R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAV2 | AAV8 | AAV9 | AAV2 | AAV8 | AAV9 | |
| VHH8 | 64.78 | 0.7559 | 0.7733 | 0.9919 | 0.9910 | 0.9941 |
| VHH69 | >1000 | 1.615 | 114.1 | 1.000 | 0.9996 | 1.000 |
| VHH38 | >1000 | >1000 | 378.4 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| VHH44 | >1000 | 433.5 | >1000 | 0.9920 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| VHH131 | >1000 | 32.96 | 28.55 | 0.9999 | 0.9998 | 0.9999 |
| VHH95 | >1000 | >1000 | 421.6 | 0.9996 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Feng, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Ma, N. Screening of Single-Domain Antibodies to Adeno-Associated Viruses with Cross-Serotype Specificity and a Wide pH Tolerance. Viruses 2025, 17, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101289
Guo H, Wang S, Feng L, Xu W, Zhang J, Zhou X, Ma N. Screening of Single-Domain Antibodies to Adeno-Associated Viruses with Cross-Serotype Specificity and a Wide pH Tolerance. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101289
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hailing, Shuo Wang, Lujin Feng, Weiwei Xu, Jiandong Zhang, Xiaoju Zhou, and Ningning Ma. 2025. "Screening of Single-Domain Antibodies to Adeno-Associated Viruses with Cross-Serotype Specificity and a Wide pH Tolerance" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101289
APA StyleGuo, H., Wang, S., Feng, L., Xu, W., Zhang, J., Zhou, X., & Ma, N. (2025). Screening of Single-Domain Antibodies to Adeno-Associated Viruses with Cross-Serotype Specificity and a Wide pH Tolerance. Viruses, 17(10), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101289







