Incidence of HBV Reactivation in Psoriasis Patients Undergoing Cytokine Inhibitor Therapy: A Single-Center Study and Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
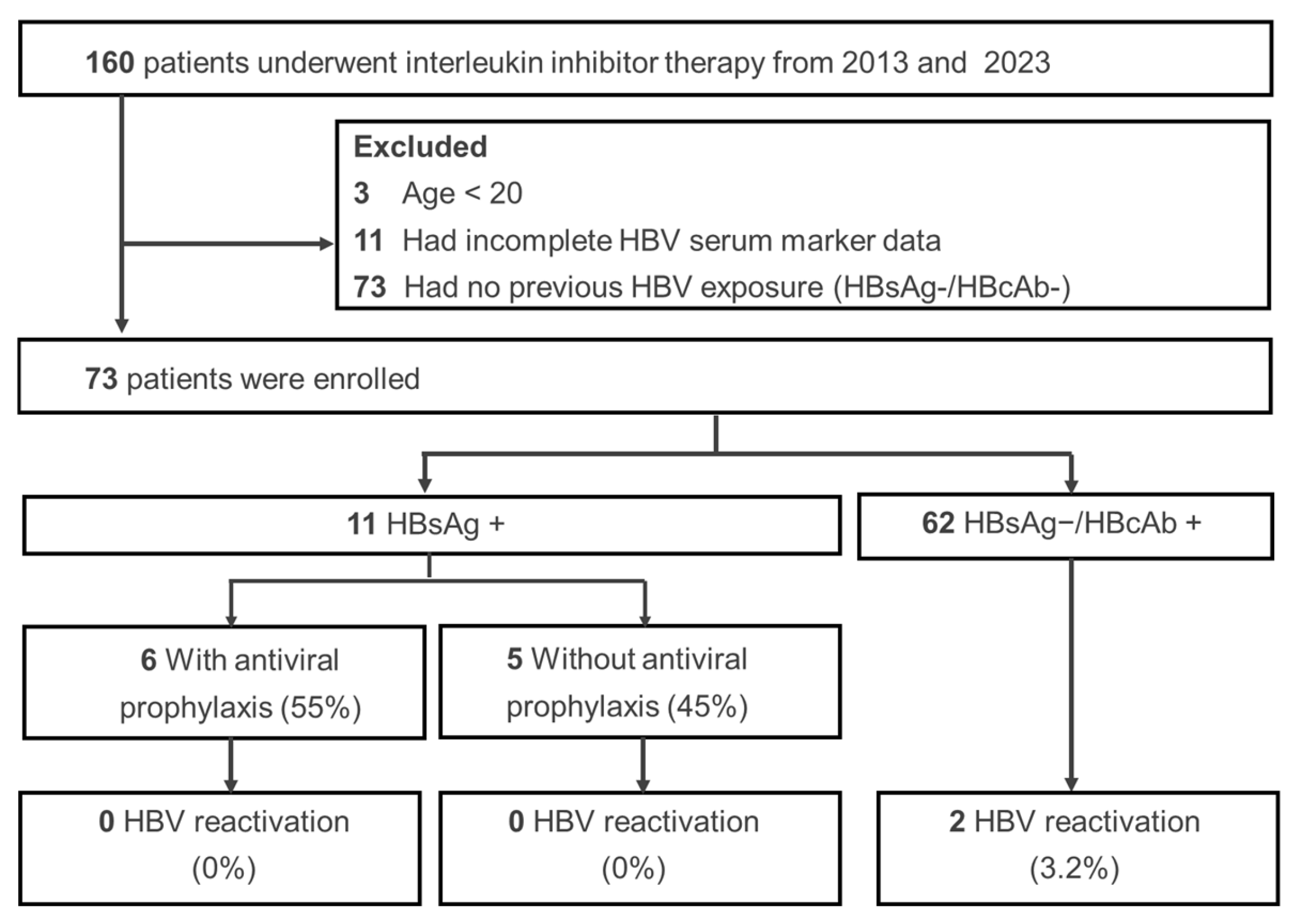
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
3.2. Clinical Features in Patients with HBV
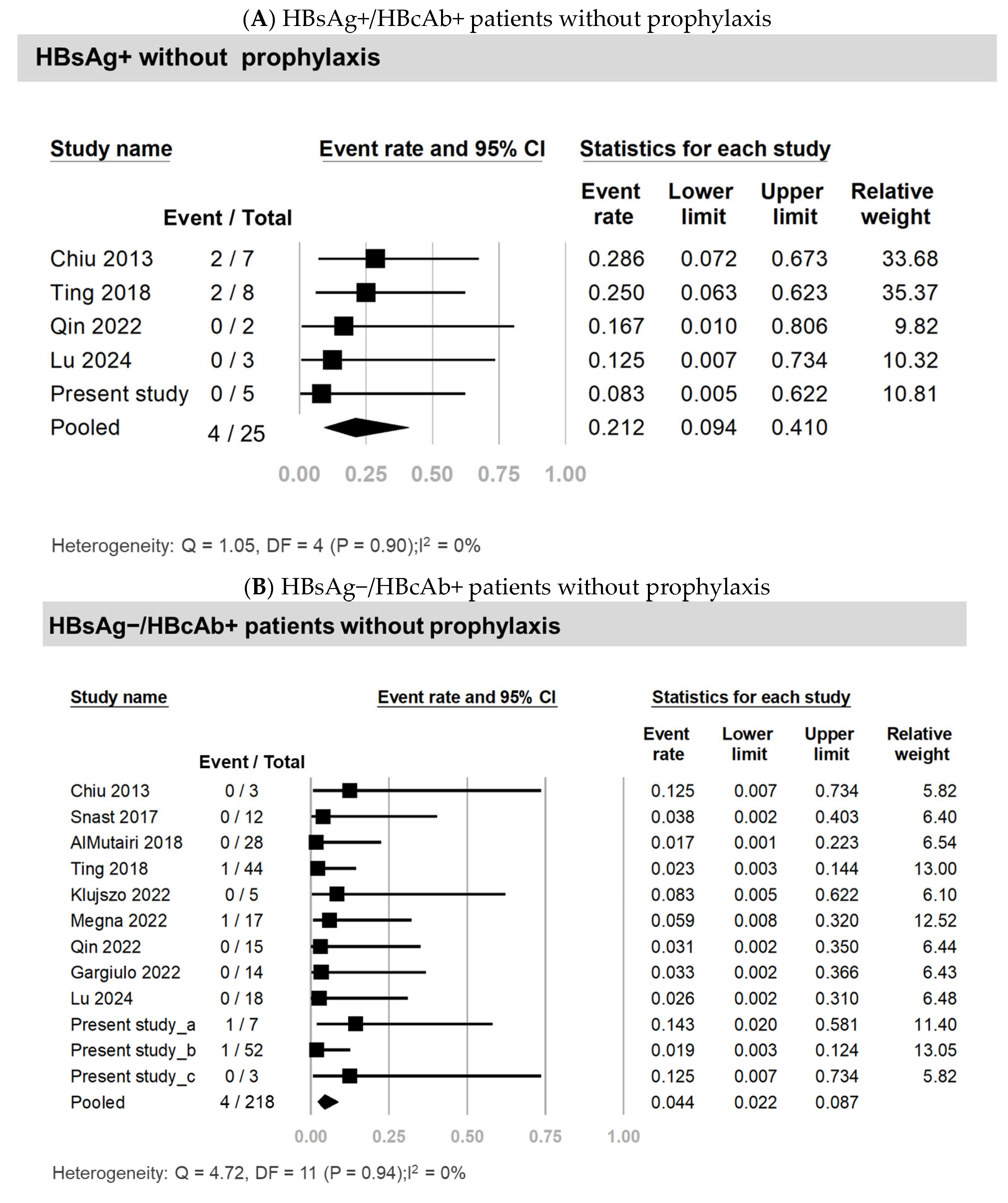
3.3. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brownstone, N.D.; Hong, J.; Mosca, M.; Hadeler, E.; Liao, W.; Bhutani, T.; Koo, J. Biologic treatments of psoriasis: An update for the clinician. Biol. Targets Ther. 2021, 15, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, M. Challenges and Future Trends in the Treatment of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Noe, M.H. The best psoriasis medications emerge. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, R.; Zhao, J. Reactivation Risk of Latent Tuberculosis or Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Effectiveness of Ustekinumab in Chinese Plaque Psoriasis Patients: A 28-Week Retrospective, Observational Study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, A.; Mostafa, A. Association of hepatitis B virus infection and psoriasis: A meta-analysis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2020, 61, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.-Y.; Yoon, Y.-B.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Park, M.-Y.; Youn, J.-I. Association of Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Psoriasis. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 822–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Chang, M.-H.; Chen, H.-L.; Cheng, F.-W.; Wu, J.-F.; Su, W.-J.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Ni, Y.-H. Survey of hepatitis B virus infection status after 35 years of universal vaccination implementation in Taiwan. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, G.; Yu, M.L.; Wong, G.; Thompson, A.; Ghazinian, H.; Hou, J.L.; Piratvisuth, T.; Jia, J.D.; Mizokami, M.; Cheng, G.; et al. APASL clinical practice guideline on hepatitis B reactivation related to the use of immunosuppressive therapy. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.-M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S.J.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Lekakis, V.; Voulgaris, T.; Lampertico, P.; Berg, T.; Chan, H.L.; Kao, J.-H.; Terrault, N.; Lok, A.S.; Reddy, K.R. Hepatitis B virus reactivation associated with new classes of immunosuppressants and immunomodulators: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and expert opinion. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1670–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, M.S.; Cheng, Y.P.; Tsai, T.F. The safety profile of ustekinumab in the treatment of patients with psoriasis and concurrent hepatitis B or C. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, S.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-H. Risk of Hepatitis B Reactivation in Patients with Psoriasis on Ustekinumab. Clin. Drug Investig. 2018, 38, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Liu, N.; Hu, Y.; Yu, N.; Yi, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, F.; Gu, J.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y. Safety and efficacy of secukinumab in psoriasis patients infected with hepatitis B virus: A retrospective study. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2022, 32, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- AlMutairi, N.; Abouzaid, H.A. Safety of biologic agents for psoriasis in patients with viral hepatitis. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2018, 29, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megna, M.; Patruno, C.; Bongiorno, M.R.; Gambardella, A.; Guarneri, C.; Romita, P.; Raimondo, A.; Loconsole, F.; Fabbrocini, G. Hepatitis Virus Reactivation in Patients with Psoriasis Treated with Secukinumab in a Real-World Setting of Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Infection. Clin. Drug Investig. 2022, 42, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snast, I.; Atzmony, L.; Braun, M.; Hodak, E.; Pavlovsky, L. Risk for hepatitis B and C virus reactivation in patients with psoriasis on biologic therapies: A retrospective cohort study and systematic review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 88–97.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.M.; Chang Liao, N.F.; Chi, C.C.; Tsai, T.F.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Lai, K.L.; Chiu, T.M.; Wu, N.L.; et al. Predictors of hepatitis B and C virus reactivation in patients with psoriasis treated with biologic agents: A 9-year multicenter cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłujszo, E.H.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Kręcisz, B.; Witkowska, A. Safety of therapies using ustekinumab in patients with psoriasis who have had hepatitis B virus infection. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Tseng, C.W.; Shao, S.C. Letter: Incidence of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with psoriasis treated with cytokine inhibitors. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 58, 850–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jamaly, H.; Eslick, G.D.; Weltman, M. Meta-analysis: Hepatitis B reactivation in patients receiving biological therapy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Tang, C.H.; Goh, C.H.; Chang, C.L.; Qiu, H.; Yang, Y.W.; Saadoun, C.; Chang, C.L.; Liu, Y. Persistence and Adherence to Biologics in Patients with Psoriasis in Taiwan: A New Biologics User Cohort Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 880985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J. Elimination of Hepatitis B in Highly Endemic Settings: Lessons Learned in Taiwan and Challenges Ahead. Viruses 2020, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.H.; Tseng, C.W.; Lee, C.H.; Tung, C.H.; Tseng, K.C.; Lai, N.S. Moderate Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in HBsAg(-)/HBcAb(+) Carriers Receiving Rituximab for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, W.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Yang, S.S.; Lan, J.L.; Chen, D.Y. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection following rituximab treatment in HBsAg-negative, HBcAb-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients: A long-term, real-world observation. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Tseng, C.W.; Ko, P.H.; Wang, S.T.; Lu, M.C.; Tung, C.H.; Tseng, K.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lai, N.S. HBV reactivation in HBsAg-/HBcAb+ rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving biologic/targeted synthetic DMARDs. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables # | All (N = 72) | HBsAg+ (N = 11) | HBsAg−/HBcAb+ (N = 62) | p-Value & |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 51 (28–87) | 50 (28–80) | 54 (34–87) | 0.16 |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 45 (63%) | 8 (73%) | 37 (60%) | 0.52 |
| Baseline HBsAb+ (>10 mIU/mL) ʃ | 42 (58%) | 0 (0%) | 42 (68%) | <0.001 |
| Baseline ALT, IU/mL | 24 (8–87) | 22 (8–65) | 24 (8–87) | 0.93 |
| HCV positive, n (%) | 5 (7%) | 1 (9%) | 4 (6%) | 0.57 |
| HBV prophylaxis | 6 (8%) | 6 (55%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 |
| Disease follow-up time (year) | 8.1 (0.3–23.6) | 7.0 (2.3–23.3) | 8.1 (0.3–23.6) | 0.67 |
| Time from cytokine inhibitor initiated (year) | 2.7 (0.3–8.3) | 2.8 (1.5–8.2) | 2.6 (0.3–8.3) | 0.15 |
| Time from bDMARDs initiated (year) | 5.0 (0.1–22.3) | 5.3 (2.3–20.2) | 5.0 (0.1–22.3) | 0.69 |
| Cytokine at the end of follow up | ||||
| IL-17 inhibitor | 61 (84%) | 9 (82%) | 52 (84%) | 1.00 |
| IL-12/23 inhibitor | 9 (13%) | 2 (18%) | 7 (11%) | 0.62 |
| IL-23 inhibitor | 3 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (5%) | 1.00 |
| Therapies before cytokine therapy | ||||
| Methotrexate, n (%) | 65 (90%) | 9 (82%) | 56 (90%) | 0.59 |
| Cyclosporine, n (%) | 28 (39%) | 6 (55%) | 22 (35%) | 0.33 |
| TNF-alfa | ||||
| Adalimumab, n (%) | 16 (22%) | 3 (27%) | 13 (21%) | 0.69 |
| Etanercept, n (%) | 9 (13%) | 3 (27%) | 6 (10%) | 0.13 |
| Golimumab, n (%) | 11 (15%) | 2 (18%) | 9 (15%) | 0.67 |
| HBVr, n (%) | 2 (2.7%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (3.2%) | 1.00 |
| Patient Group | No. of Records | No. of Patients | Incidence Rate (%) | 95% CI | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg+ without antiviral prophylaxis | 5 | 25 | 21.2 | 9.4–41.0 | 0 |
| HBsAg+ with antiviral prophylaxis | 6 | 31 | 0 | 0 | - |
| HBsAg−/HBcAb+ without prophylaxis | 12 | 218 | 4.4 | 2.2–8.7 | 0 |
| Subgroup of HBsAg−/HBcAb+ without prophylaxis | |||||
| Drug catalog | |||||
| Interleukin 12/23 inhibitor | 7 | 117 | 4.9 | 1.9–11.8 | 0 |
| Interleukin 17 inhibitor | 3 | 84 | 3.3 | 1.0–10.8 | 0 |
| Interleukin 23 inhibitor | 2 | 17 | 6.3 | 0.9–34.3 | 0 |
| Study region | |||||
| Asian | 7 | 142 | 4.5 | 1.9–10.6 | 0 |
| Non-Asian | 5 | 76 | 4.3 | 1.4–12.5 | 0 |
| HBsAb status | |||||
| HBsAb+ | 10 | 118 | 6.0 | 2.6–13.4 | 0 |
| HBsAb− | 7 | 31 | 14.0 | 5.5–31.4 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, M.H.; Ko, P.-H.; Wang, S.-T.; Tseng, C.-W. Incidence of HBV Reactivation in Psoriasis Patients Undergoing Cytokine Inhibitor Therapy: A Single-Center Study and Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2025, 17, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010042
Kuo MH, Ko P-H, Wang S-T, Tseng C-W. Incidence of HBV Reactivation in Psoriasis Patients Undergoing Cytokine Inhibitor Therapy: A Single-Center Study and Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis. Viruses. 2025; 17(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Meng Hsuan, Ping-Hung Ko, Sz-Tsan Wang, and Chih-Wei Tseng. 2025. "Incidence of HBV Reactivation in Psoriasis Patients Undergoing Cytokine Inhibitor Therapy: A Single-Center Study and Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis" Viruses 17, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010042
APA StyleKuo, M. H., Ko, P.-H., Wang, S.-T., & Tseng, C.-W. (2025). Incidence of HBV Reactivation in Psoriasis Patients Undergoing Cytokine Inhibitor Therapy: A Single-Center Study and Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis. Viruses, 17(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010042






