Abstract
Commercially produced cyanobacteria preparations sold under the name spirulina are widely consumed, due to their traditional use as a nutrient-rich foodstuff and subsequent marketing as a superfood. Despite their popularity, the microbial composition of ponds used to cultivate these bacteria is understudied. A total of 19 pond samples were obtained from small-scale spirulina farms and subjected to metagenome and/or virome sequencing, and the results were analysed. A remarkable level of prokaryotic and viral diversity was found to be present in the ponds, with Limnospira sp. and Arthrospira sp. sometimes being notably scarce. A detailed breakdown of prokaryotic and viral components of 15 samples is presented. Twenty putative Limnospira sp.-infecting bacteriophage contigs were identified, though no correlation between the performance of these cultures and the presence of phages was found. The high diversity of these samples prevented the identification of clear trends in sample performance over time, between ponds or when comparing successful and failed fermentations.
Keywords:
spirulina; virome; metagenome; cyanobacteria; blue-green algae; superfood; Arthrospira; Limnospira 1. Introduction
Spirulina, as we know it, has been consumed traditionally for hundreds if not thousands of years across the globe [1,2]. The first commercially produced food supplement produced under controlled conditions and using the name spirulina was the Linagreen range produced by the DIC corporation in 1978. Since that time, spirulina has been extensively marketed as a superfood, i.e., one that is nutrient rich and generally considered to be beneficial for good health and well-being [3,4,5]. Despite this, the actual content of these products has been a matter of confusion and some debate since their inception, at least in part due to the complexity in cultivating the relevant organisms in the lab environment [2,6]. Spirulina has at different times been referred to as ‘green algae’, ‘blue-green algae’, or as a ‘plant’, but is now known to be a member of the cyanobacteria group. Though it is sold as one product, the actual bacterial content of commercial products may be highly heterogenous, in some cases with over 100 bacterial operational taxonomic units (OTUs) identified [7].
The potential applications of spirulina are diverse, and include agriculture [3,8,9,10,11], aquaculture [12,13,14,15], and human nutrition [5,16], including for those who are immunocompromised (reviewed by [17,18]) and for individuals who live and work in highly pressurised habitats in which space is a major consideration [19]. As a result, spirulina is grown both traditionally (such as by lake surface harvesting and sun drying [20]) and commercially (such as large-scale US and Asian production [21,22]) in many areas worldwide. It is also an important cyanobacterium in numerous ecological niches, and culture breakdown has been implicated in the decline in certain bird populations that rely on it as a food source [23]. Despite this widespread use by humans and generally favourable reputation, concerns regarding its effectiveness [24,25], toxicity [26,27], and contamination with heavy metals persist [4].
A 2019 article [28] shed some much-needed light on the subject of the taxonomic classification of those cyanobacteria that are prepared and sold as spirulina. Among the authors’ findings were that (i) members of the true Spirulina genus are not closely related to those species sold under the name, (ii) the genus Arthrospira was most cultivated and sold as ‘spirulina’, and (iii) a further genus (Limnospira) should be created to encompass commercially grown and sold cyanobacteria. Since that time, additional Limnospira genomes have been sequenced and published [29,30], and comparative genomics findings involving members of this genus have been published [31], indicative of expanding interest in this organism. Recent taxonomic undertakings [32,33] provided further clarity on the appropriate nomenclature of this genus and, in line with these, cyanobacterial species grown and sold as spirulina will be referred to as Limnospira/Arthrospira or Limnospira platensis for the purposes of this study.
The biology of bacteriophages infecting Limnospira species is an emerging field with only a single lytic phage of the genus described [34] and no complete genome sequences published to our knowledge, though some research on prophages has been performed [35]. Despite this paucity of data, evidence that Limnospira defends itself against incoming alien DNA has recently emerged [36], some of which is presumed to be viral in nature, as deduced from the presence of CRISPR-Cas systems and associated CRISPR arrays. Although some of the described CRISPR systems target invading RNA, the majority are known to target double-stranded (ds) DNA. This, combined with the DNA-harbouring nature of the only lytic phage infecting this species described, indicates that Limnospira- and Arthrospira-infecting phages are likely DNA-harbouring viruses of the Caudoviricetes class. Considering the detrimental effect that phages have on the progression and end results of commercial dairy fermentations [37], it is highly likely that phage contamination in commercial spirulina fermentation would have a similar effect. Indeed, bacteriophages of the genus have been proposed as the cause of a breakdown in a major spirulina-driven food chain in a series of African lakes [23], highlighting the importance of this area of study.
The aim of the current study was to analyse the bacterial and viral components of French open ponds used for commercial spirulina cultivation to identify any compositional trends relating to cultivation failure and phage presence. Our work also aimed to elucidate the microbial composition of open spirulina ponds, and, as such, facilitate more detailed safety and effectiveness assessments of cultivations that generate this widely used product.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Processing
Spirulina cultivations from two French farms were carried out in ‘ponds’ approximately 25 m3 in volume over a period of one week in a proprietary defined medium consisting (in part) of bicarbonates, phosphates, and nitrates. Individual cultivations were deemed to have failed if growth was observed to have stalled approximately 2–3 days after inoculation (the inoculum consisting typically of a 5 m3 sample of a previously successful cultivation). A typical pond sample in the context of this study consisted of 1.5–2 L of liquid medium (containing visible biomass), which was bottled and transported in a cooled container to University College Cork, Ireland (UCC), whereupon it was kept refrigerated (4 °C) until processing. A total of 19 samples (Table 1) were processed individually, 3 of which (S2B1, S2B2, S2B3) had been collected upon cultivation failure.

Table 1.
Sample information and absolute filtered read numbers generated by metagenome and virome sequencing of pond samples. Reads taxonomically assigned to the Limnospira genus are given in absolute numbers and as a percentage of overall metagenomic reads, providing an indication of their abundance in each sample. ‘-’; not calculated. 1 = collected from Farm 1 (all other samples collected from Farm 2).
2.2. Metagenome DNA Extraction and Analysis
DNA extraction was performed using a modified version of a commercial kit protocol (Nucleobond AXG 100 with Buffer set III, Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany). Presumed cells were firstly pelleted (5000× g for 20 min) and pre-treated with lysozyme (final concentration of 0.8 mg/mL; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and mutanolysin (final conc. 50 units/mL; Merck) with incubation at 37 °C for one hour. Proteinase K (Macherey-Nagel) was then added to a final conc. of 100 µg/mL, and the samples were incubated at 50 °C for one hour. The remaining protocol was performed as per the manufacturer’s instructions, and DNA was resuspended in 10 mM Tris (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) buffer prior to shipment to the contract sequencing facility.
According to the manufacturer’s instructions, DNA library preparation was performed using the Nextera XT DNA sample preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). One ng of input DNA from each sample was used for library preparation. The isolated DNA underwent fragmentation, adapter ligation, and amplification. Sequencing was performed by GenProbio, s.r.l. (Parma, Italy) on a NextSeq 550 instrument (Illumina, CA, USA) using a paired-end 150 bp High Output sequencing kit and a deliberate spiking of 1% PhiX control library. Filtered reads were collected and taxonomically classified through the METAnnotatorX2 bioinformatic pipeline [38] using the up-to-date genome RefSeq database retrieved from NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). DNA sequences were subjected to whole-metagenome assembly using Spades v3.14 [39] with default parameters and the metagenomic flag option (--meta) together with k-mer sizes of 21, 33, 55, and 77. METAnnotatorX2 [38] classified, at the species level, those reads with a nucleotide identity of >94% to reference genomes, normalising species abundances based on the reference genome size.
2.3. Virome DNA Extraction and Analysis
Virome DNA extraction was performed using a method established by UCC (adapted from [40,41],) by firstly enriching for viral particles followed by DNA extraction. Firstly, 200 mL of each sample was centrifuged at 5000× g for one hour. The supernatant was then treated with NaCl (Merck, Germany; to 1 M) for one hour at 4 °C on a rotary shaker. Samples were then centrifuged at 28,000× g for 15 min or 10,000× g for 35 min, followed by double filtration (firstly using 0.45 µm pore size filters, followed by 0.2 µm). Viral particles were precipitated with PEG8000 (Merck) at a final concentration of 10% on a rotary shaker overnight at 4 °C. Following precipitation, the samples were centrifuged at 10,000× g for 25 min and the pellet was resuspended in 1 mL of SM buffer [42]. DNase treatment (20 units/mL) was performed at room temperature for 15 min to remove any remaining contaminating host DNA. The DNAse was then inactivated at 75 °C for 10 min. Viral DNA extraction was then performed using a Norgen phage DNA extraction kit (Norgen Biotek Corp., Thorold, ON, Canada), as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Library preparation and sequencing was performed according to the metagenome analysis protocol described above. Filtered reads were collected and taxonomically classified through the METAnnotatorX2 [38] pipeline using the up-to-date genome RefSeq and Virus RefSeq databases retrieved from NCBI and assembled as described above.
All assembled contigs were then submitted to the PhaBOX online server [43], an integrated web server which incorporates phage contig identification by PhaMer [43], taxonomy classification by PhaGCN [44], host prediction using Cherry [45], and lifestyle prediction by PhaTYP [46]. Standard PhaBOX parameters were used for all analyses. The relative abundance of individual viral sequences was determined by establishing the Reads Per Kilobase per Million mapped reads (RPKM) of each contig using CoverM version 0.4.0 (B. Woodcroft, unpublished, https://github.com/wwood/CoverM) contig RPKM method, with minimum read % identity, minimum read aligned %, and minimum covered fraction all set to 80%. The manual curation of PhaBOX and CoverM outputs enabled the assessment of overall phage diversity, individual phage contigs, and trends in viral presence/absence and abundance across multiple ponds and time points.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metagenome Sequencing
The metagenomic analysis of a total of 15 pond samples (all successful cultivations) resulted in between 5815 (sample S2B3-21-9) and 18,632 (sample S2B3-7-1-22) classified reads (Table 1). Those reads classified as bacteria were further subclassified (as per Section 2) into 90 distinct bacterial genera and sorted by % relative abundance per sample, corrected for genome size. As expected, no reads resulting from the metagenomic sequencing were classified as viral. A snapshot of the distribution of the bacterial component of these reads across all 15 samples is provided in Figure 1, with the number and proportion of those reads which were assigned to either the Limnospira genus or the Limnospira indica species given in Table 1. Interestingly, the number of reads assigned to the Limnospira genus were generally in the minority, comprising 7% of the total number of reads classified as bacteria (% per sample given in Table 1). This result was unexpected given that Limnospira is the bacterial genus intended to be cultivated. This may indicate (i) a limitation of the DNA extraction method employed and/or (ii) a higher level of diversity in these cultivations than might have been predicted prior to analysis.
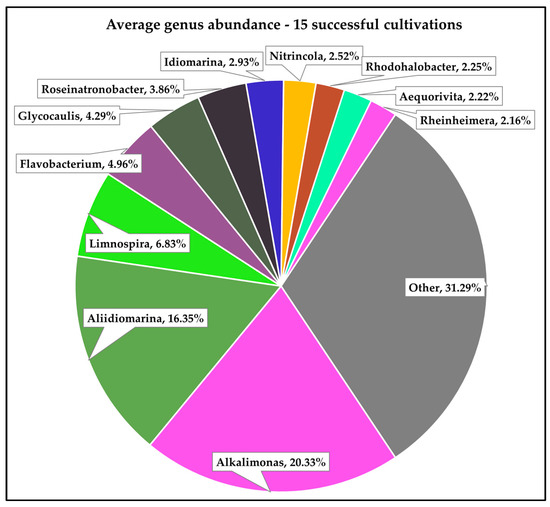
Figure 1.
% relative abundance (normalised) of bacterial genera across 15 distinct successful spirulina cultivations.
Aside from Limnospira, the most abundant bacterial genera detected were Alkalimonas (20% of total bacterial reads), Aliidiomarina (16%), and Flavobacterium (5%), with Glycocaulis and Roseinatronobacter comprising 4% of reads each (Figure 1). Alkalimonas and Aliidiomarina species are halophilic and alkaliphilic, though they may be found in a range of environments [47,48] such as alkaline soil [49,50], soda lakes [51,52], and the deep sea [53,54]. Flavobacteria are most widely known as fish pathogens [55] and have consequently been found to inhabit freshwater, saltwater, and ice [56]. Interestingly, species in the Glycocaulis genus have been described in samples originating from hydrothermal vents [57] and other extreme environments such as crude oil [58] and the Mariana Trench [59], while Roseinatronobacteria are commonly found in soda lakes [60,61] and reportedly in aquatic spring environments of up to pH 12 [62]. Considering that the ponds analysed in this study are not exposed to environments such as these, it is reasonable to assume that the presence of a wide variety of bacterial genera therein is attributable to co-inoculation with Limnospira spp., which are found to naturally inhabit similar environments [31,33,63]. The identification of this highly diverse cohort of Gram-negative bacteria, though not entirely expected, is reminiscent of previous metagenomic analyses of commercial spirulina products [7].
3.2. Virome Sequencing
The study of the virome of a particular environment has been employed in various studies as a method to ascertain its microbial composition, diversity, and population dynamics [64,65,66,67,68]. As such, a virome study was undertaken on the 19 pond samples (Table 1) in the present study to elucidate their viral and putative host composition. As dictated by the method employed, the scope of this analysis was limited to DNA-harbouring bacteriophages.
Virome reads were generated and assembled as per Section 2, producing a total of 6500 individual contigs. Following PhaBOX (and, in particular, PhaMer) analysis, these were further filtered into phage and non-phage contigs. Interestingly, the majority (65% or 4241) of contigs were designated as non-phage by PhaMer, despite efforts to remove as much host/bacterial DNA as possible from the preparation (see Section 2). Separate taxonomic profiling of the virome reads indicated that, similarly to the metagenomic analysis, sequences associated with Limnospira, Glycocaulis, Flavobacterium, and Idiomarina (amongst other genera) were detected; however, it is not known whether these reads corresponded to the ‘non-viral’ cohort or if these corresponded to integrated prophages. This finding was not necessarily surprising given the relative amounts of bacterial and viral DNA in a given environmental sample, and it is a known issue in virome studies [69]. In this sense, PhaMer proved to be an exceedingly useful tool which identified and segregated 2259 phage contigs rapidly as part of the PhaBOX toolset.
Following this assignment, we conducted an analysis on the spread of contig sizes in the above set, whereupon it was found that the majority of viral contigs identified were between 5000 and 10,000 bp in length (Figure 2). A small number (n = 3) of viral contigs were over 200,000 bp in length. Two of these were assigned to the newly created Kyanoviridae family and one to the newly created Straboviridae family [70], both of which incorporate T4-like phages which were previously classed as Myoviridae. The two Kyanoviridae phages were predicted (by CHERRY) to infect members of the Flavobacterium genus, though the majority of this phage family are known to infect Synechococcus, based on a manual search of the NCBI Virus database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/virus/vssi/#/, accessed on 1 March 2024). The third (Straboviridae) phage was predicted to infect Streptococcus cristatus, a human oral bacterium [71], for which no lytic phages have yet been described to our knowledge.
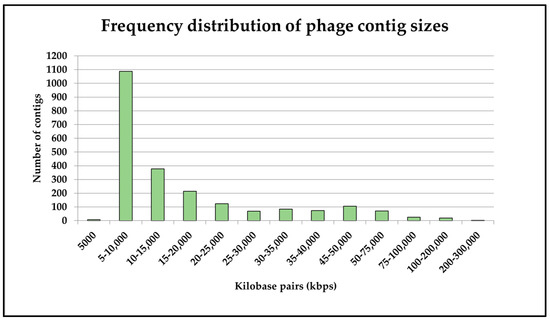
Figure 2.
Frequency distribution of viral contig sizes generated using the described sequencing and assembly methods.
These 2259 identified viral contigs were then classified into known viral families, the distribution of which is presented in Figure 3. A large proportion of the contigs (62%) were not classified, and a visual assessment of the distribution suggested that those ‘unknown’ family contigs fell largely in the 5000–10,000 kbp size group, likely limiting the ability of PhaGCN to assign families correctly [44].
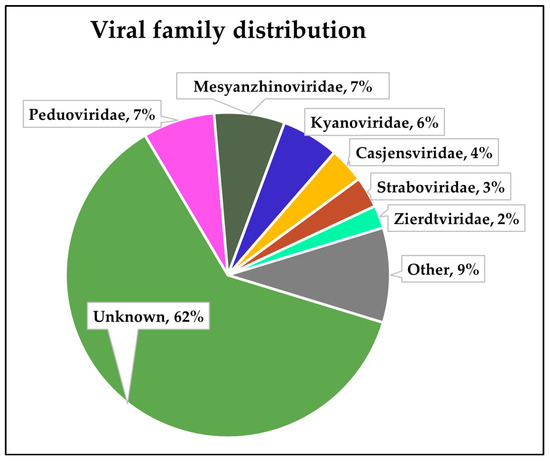
Figure 3.
Proportion of viral families amongst assembled phage contigs.
Phage host assignment has long been a challenge in the field of metagenomics, and a number of tools have emerged in the last decade to try and overcome this serious research bottleneck [72,73,74,75,76]. Of these, PhaBOX employs CHERRY [45], which claims to have an accuracy of 80% and also to outperform other currently available computational models. Figure 4 shows the proportion of host genera assigned to individual phage contigs in descending order by relative abundance (as based on a RPKM assessment), determined as per Section 2. Evident is the absence of conformity between those genera predicted by metagenomic analysis and those predicted by phage host assignment across the overall sample set. This disparity may have multiple explanations: (i) a potential bias towards Gram-negative bacteria in the metagenomic analysis, as discussed above; (ii) the large proportion (27%) of contigs for which CHERRY could not assign a host; or (iii) the enormous diversity in hosts assigned by CHERRY, i.e., the ‘other’ group (37%) in Figure 4, which represents a total of 468 distinct bacterial genera assigned as phage hosts. Despite these potential limitations, CHERRY analysis may be useful in developing an overall snapshot of the viral diversity in a given sample, when used in combination with PhaMer and PhaGCN.
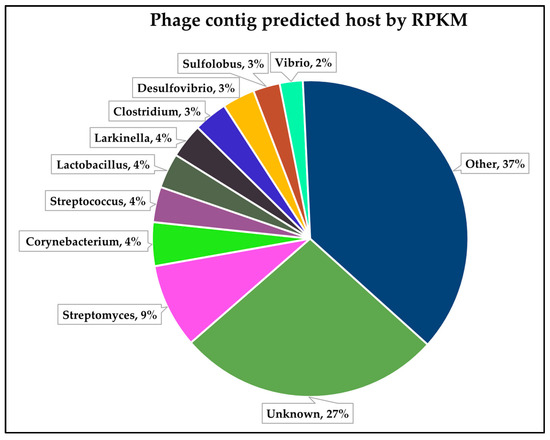
Figure 4.
Distribution of predicted phage hosts by relative abundance (RPKM).
3.3. Identification and Analysis of Putative Limnospira-Infecting Phages
To date, only a single Limnospira-infecting phage has been characterised [34] and neither the genome of this phage, nor of any other, has been sequenced. In total, across all samples, 20 contigs were assigned to either Limnospira indica, Limnospira maxima, or Arthrospira platensis as putative hosts by CHERRY, the characteristics of which are presented in Table 2. Manual searches using BLASTn (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 February 2024) allowed similar contigs to be identified, and those sharing 97% nucleotide identity over at least 50% of the contig have been colour-coded accordingly in Table 2 to give a broad indication of the diversity of these putative phages.

Table 2.
Contiguous sequence (contig) analysis of virome data. Contigs exhibiting amino acid identity to bacteriophage sequences are listed, along with the sizes of these contigs and the samples from which they were derived. Contigs exhibiting > 97% nucleotide identity to each other are coloured similarly and in adjacent rows for comparative purposes.
With the aforementioned limitations of phage host prediction tools in mind, each contig was subjected to a manual blastn [77] analysis in an attempt to verify the host prediction performed by CHERRY. In the majority of cases, the contigs were most similar at the nucleotide level to members of the Limnospira and (former) Arthrospira genus.
One contig which did not exhibit significant similarity to any sequence in the NCBI database was Node_28, a predicted virulent phage of Arthrospira platensis. This putative phage was subjected to further scrutiny due to its size, with 38.6 kb being of sufficient length to harbour the major functional modules usually found in phage genomes, such as those encoding the necessary proteins for DNA replication, DNA packaging, and virion assembly (a schematic diagram of this phage (termed Rory) genome is provided in Figure 5).
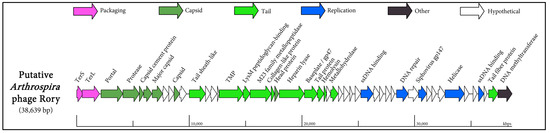
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the viral metagenome assembled genome (MAG) of putative Arthrospira platensis Rory phage.
Considering that no genome of a virulent phage of Arthrospira/Limnospira has been described thus far, we endeavoured to confirm the host specificity assigned by CHERRY. To this end, the entire nucleotide contig was supplied to three further and distinct web-based phage host prediction tools, the results of which are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Host assignment of Rory phage by four distinct web server prediction tools.
It is evident from the results presented in Table 3 that we were unable to conclusively assign a bacterial host to this phage, given that the four different tools tested not only assigned different bacterial species as the potential host, but different genera, families, orders, classes, and phyla. These results align with the enormous effort that has been placed into developing bioinformatic tools to solve this problem. Further studies in this area should aim to reconcile the variety of bioinformatic methods used to assign bacterial hosts to unknown phages, but in the case of Limnospira phages, this will likely also require traditional microbiological techniques to establish a definitive infection profile.
4. Conclusions
Artisanal foods are coming under increasing scrutiny with regard to microbiological diversity as well as from a safety perspective [82,83,84,85,86,87]. In the present study, we investigated the metagenomes and viromes of a number of open ponds which are used to grow spirulina on a relatively small scale. As such, virome sequencing of 19 pond samples and metagenomic sequencing of 15 pond samples was performed and the results analysed. A large amount of diversity across the prokaryotic and viral content of the ponds was exhibited by most of the samples provided, with Limnospira/Arthrospira genera apparently in the minority. Several distinct genera were found to be present that were postulated to have originated from those environments in which Limnospira spp. can also be found, i.e., in the initial pond inocula (the source of which is currently unknown). Further studies around spirulina cultivation will be useful in establishing if this bacterial profile is maintained in other spirulina farms, which in turn may shed further light on the relationships, if any, between these genera.
Twenty putative Arthrospira- or Limnospira-infecting phage contigs were identified and analysed, with a single contig being subjected to detailed analysis including gene prediction and annotation because of its large size. The area of host assignment to unknown putative phages continues to pose difficulties. Host assignment of this putative phage was attempted using various online tools as well as manual curation but could not be resolved unambiguously. Further studies in this area will likely require the isolation of Limnospira-infecting phages in the laboratory environment to conclusively verify their infectivity profiles, prior to phenotypic and genotypic analyses, greatly expanding the current knowledge base. The requirement for scientifically informed strategies for the mitigation of phage-induced spoilage will undoubtedly increase concomitantly with the popularity of spirulina and other culture-based foodstuffs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.M., J.M., T.S., F.M. and D.v.S.; methodology, B.M., E.P., E.V. and G.A.L.; software, F.B., G.A.L., K.C. and L.P.K.; validation, F.B., G.A.L., K.C. and L.P.K.; formal analysis, B.M. and G.A.L.; investigation, B.M., G.A.L., K.C. and L.P.K.; resources, F.M.; data curation, B.M., G.A.L., F.B., K.C. and L.P.K.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M.; writing—review and editing, F.M., J.M. and D.v.S.; supervision, F.B., M.V., J.M. and D.v.S.; project administration, F.M., M.V., J.M. and D.v.S.; funding acquisition, F.M., J.M. and D.v.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the (Micro-Ecological Life Support System Alternative) project, https://www.melissafoundation.org/, funding the POMP (pool of MELiSSA PhDs) programme through which Tom Sassen received sponsorship. This publication began from research conducted with the financial support of Science Foundation Ireland under Grant numbers 15/SIRG/3430, SFI/12/RC/2273-P1 and SFI/12/RC/2273-P2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw virome and metagenome reads, as well as assembled virome contigs, have been uploaded to the Sequencing Reads Archive (SRA) at NCBI and are available under BioProject number PRJNA1114024.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the French spirulina farmers and the “Fédération des Spiruliniers de France” (FSF) for generously supplying the pond samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ciferri, O. Spirulina, the Edible Microorganism. Microbiol. Rev. 1983, 47, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, R.A.; Sudhakar, K.; Rana, R.S. Spirulina—From Growth to Nutritional Product: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeva, R.; Jordanova, G.; Kistanova, E.; Shumkov, K.; Georgiev, B.; Abadgieva, D.; Kacheva, D.; Shimkus, A.; Shimkine, A. Effect of the Addition of Spirulina Platensis on the Productivity and Some Blood Parameters on Growing Pigs. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 680–684. [Google Scholar]
- Grosshagauer, S.; Kraemer, K.; Somoza, V. The True Value of Spirulina. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4109–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Bhadouria, P.; Bisen, P.S. Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential of Spirulina. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2005, 6, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFadhly, N.K.Z.; Alhelfi, N.; Altemimi, A.B.; Verma, D.K.; Cacciola, F. Tendencies Affecting the Growth and Cultivation of Genus Spirulina: An Investigative Review on Current Trends. Plants 2022, 11, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardaka, E.; Kormas, K.A.; Katsiapi, M.; Genitsaris, S.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. Molecular Diversity of Bacteria in Commercially Available “Spirulina” Food Supplements. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyomizu, M.; Sato, K.; Taroda, H.; Kato, T.; Akiba, Y. Effects of Dietary Spirulina on Meat Colour in Muscle of Broiler Chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2001, 42, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, E.; Dominy, W. The Nutritional Value of Dehydrated, Blue-Green Algae (Spirulina plantensis) for Poultry. Poult. Sci. 1990, 69, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiretti, P.G.; Meineri, G. Effects of Diets with Increasing Levels of Spirulina platensis on the Performance and Apparent Digestibility in Growing Rabbits. Livest. Sci. 2008, 118, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Malau-Aduli, A.E.O. Spirulina as a Livestock Supplement and Animal Feed. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 97, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, C.B.; Pantastico, J.B.; Baldia, S.F.; Reyes, O.S. Milkfish (Chanos chanos) Fingerling Production in Freshwater Ponds with the Use of Natural and Artificial Feeds. Aquaculture 1989, 77, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayag, C.M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Li, C.-C.; Liou, C.-H.; Chen, J.-C. Administration of the Hot-Water Extract of Spirulina Platensis Enhanced the Immune Response of White Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei and Its Resistance against Vibrio Alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2010, 28, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.G.; Umino, T.; Nakagawa, H. The Effect of Spirulina Feeding on Muscle Protein Deposition in Red Sea Bream, Pagrus major. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 1994, 10, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaza, J.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Meiler, K.A.; Velasquez, S.F.; Kumar, V. A Review on Spirulina: Alternative Media for Cultivation and Nutritive Value as an Aquafeed. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2371–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Bhat, A.G.; OKeefe, J. Effects of Spirulina on Weight Loss and Blood Lipids: A Review. Open Heart 2020, 7, e001003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHenry, M.S.; Dixit, A.; Vreeman, R.C. A Systematic Review of Nutritional Supplementation in HIV-Infected Children in Resource-Limited Settings. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care (JIAPAC) 2014, 14, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobler, L.; Siegfried, N.; Visser, M.E.; Mahlungulu, S.S.N.; Volmink, J. Nutritional Interventions for Reducing Morbidity and Mortality in People with HIV. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, CD004536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallec, J.; Vandermies, M.; Coene, C.; Lamaze-Lefebvre, B.; Demey, D.; Frappart, M.; Couallier, E. Implementation of an Automated Process for Limnospira Indica Harvesting and Culture Medium Recycling for Space Applications. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2023, 10, 1229043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcea, M.; Sorto, M.; Batello, C.; Narducci, V.; Aguzzi, A.; Azzini, E.; Fantauzzi, P.; Finotti, E.; Gabrielli, P.; Galli, V.; et al. Nutritional Characterization of Traditional and Improved Dihé, Alimentary Blue-Green Algae from the Lake Chad Region in Africa. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-M.; Xiang, W.-Z.; Wen, Y.-H. Spirulina (Arthrospira) Industry in Inner Mongolia of China: Current Status and Prospects. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamatsu, H. Mass Production of Spirulina, an Edible Microalga. Hydrobiologia 2004, 512, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduzzi, P.; Gruber, M.; Gruber, M.; Schagerl, M. The Virus’s Tooth: Cyanophages Affect an African Flamingo Population in a Bottom-up Cascade. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Katsura, H.; Takenaka, S.; Fujita, T.; Abe, K.; Tamura, Y.; Nakatsuka, T.; Nakano, Y. Pseudovitamin B12 Is the Predominant Cobamide of an Algal Health Food, Spirulina Tablets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4736–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muys, M.; Sui, Y.; Schwaiger, B.; Lesueur, C.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Vermeir, P.; Vlaeminck, S.E. High Variability in Nutritional Value and Safety of Commercially Available Chlorella and Spirulina Biomass Indicates the Need for Smart Production Strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, D.J.; Kauffman, K.W.; Hall, R.A.; Huang, X.; Chu, F.S. Assessing Potential Health Risks from Microcystin Toxins in Blue-Green Algae Dietary Supplements. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussner, A.H.; Mazija, L.; Fastner, J.; Dietrich, D.R. Toxin Content and Cytotoxicity of Algal Dietary Supplements. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 265, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Mühlsteinová, R.; Hauer, T. Detailed Characterization of the Arthrospira Type Species Separating Commercially Grown Taxa into the New Genus Limnospira (Cyanobacteria). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghembe, R.; Michael, A.; Harish, A.; Nyandoro, S.S.; Lyantagaye, S.L.; Hati-Kaul, R. Draft Genome Sequence of Limnospira sp. Strain BM01, Isolated from a Hypersaline Lake of the Momela Ecosystem in Tanzania. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00132-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, M.; Tran-Dao, T.-K.; Mulroney, L.; Bernick, D.L. De-Novo Assembly of Limnospira Fusiformis Using Ultra-Long Reads. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 657995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misztak, A.E.; Waleron, M.; Furmaniak, M.; Waleron, M.M.; Bazhenova, O.; Daroch, M.; Waleron, K.F. Comparative Genomics and Physiological Investigation of a New Arthrospira/Limnospira Strain O9.13F Isolated from an Alkaline, Winter Freezing, Siberian Lake. Cells 2021, 10, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, T.; Halary, S.; Duval, C.; Piquet, B.; Cadoret, J.-P.; Vernès, L.; Bernard, C.; Marie, B. Monospecific Renaming within the Cyanobacterial Genus Limnospira (Spirulina) and Consequences for Food Authorization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de S. Santos, K.R.; Hentschke, G.S.; Ferrari, G.; Andreote, A.P.D.; de F. Fiore, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sant’Anna, C.L. Molecular, Morphological and Ecological Studies of Limnospira Platensis (Cyanobacteria), from Saline and Alkaline Lakes, Pantanal Biome, Braz. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1204787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, S.; Zhong, X.; Parvathi, A.; Ram, A.S.P. First Description of a Cyanophage Infecting the Cyanobacterium Arthrospira Platensis (Spirulina). J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekri, M.A.; Schagerl, M.; Schweichhart, J.; Lang, I. Confocal Microscopy Reveals Alterations of Thylakoids in Limnospira Fusiformis during Prophage Induction. Protoplasma 2021, 258, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, M.; Guevara, G.; Baldanta, S.; Rodríguez, P.S.; Agudo, L.; Nogales, J.; Carrasco, A.D.; Arribas-Aguilar, F.; Pérez-Pérez, J.; García, J.L.; et al. Characterization of Limnospira Platensis PCC 9108 R-M and CRISPR-Cas Systems. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 279, 127572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturino, J.M.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Engineered Bacteriophage-Defence Systems in Bioprocessing. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Lugli, G.A.; Fontana, F.; Mancabelli, L.; Alessandri, G.; Longhi, G.; Anzalone, R.; Viappiani, A.; Turroni, F.; van Sinderen, D. METAnnotatorX2: A Comprehensive Tool for Deep and Shallow Metagenomic Data Set Analyses. Msystems 2021, 6, e00583-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, M.; Hooper, L.V.; Duerkop, B.A. Evaluation of Methods to Purify Virus-like Particles for Metagenomic Sequencing of Intestinal Viromes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Casey, E.; Lugli, G.A.; Moore, R.; Kaczorowska, J.; Feehily, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Mancabelli, L.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; et al. Tracing Mother-Infant Transmission of Bacteriophages by Means of a Novel Analytical Tool for Shotgun Metagenomic Datasets: METAnnotatorX. Microbiome 2018, 6, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Long Island, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 0-87969-309-6. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, J.; Peng, C.; Liao, H.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y. PhaBOX: A Web Server for Identifying and Characterizing Phage Contigs in Metagenomic Data. Bioinform. Adv. 2023, 3, vbad101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y. Bacteriophage Classification for Assembled Contigs Using Graph Convolutional Network. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, i25–i33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Sun, Y. CHERRY: A Computational metHod for accuratE pRediction of Virus–pRokarYotic Interactions Using a Graph Encoder–Decoder Model. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y. PhaTYP: Predicting the Lifestyle for Bacteriophages Using BERT. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-P.; Chang, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-S.; Jean, W.D.; Shieh, W.Y. Aliidiomarina taiwanensis gen. nov., sp. nov., Isolated from Shallow Coastal Water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xue, Y.; Grant, W.D.; Collins, N.C.; Duckworth, A.W.; van Steenbergen, R.P.; Jones, B.E. Alkalimonas amylolytica gen. nov., sp. nov., and Aliidiomarina taiwanensis gen. nov., sp. nov., Novel Alkaliphilic Bacteria from Soda Lakes in China and East Africa. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Takano, T.; Liu, S. Isolation and Characterization of Novel Bacterial Taxa from Extreme Alkali-Saline Soil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sun, J.-Q.; Wang, L.-J.; Liu, X.-Z.; Ji, Y.-Y.; Shao, Z.-Q.; Wu, X.-L. Aliidiomarina soli sp. nov., Isolated from Saline–Alkaline Soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsodi, A.K.; Knáb, M.; Czeibert, K.; Márialigeti, K.; Vörös, L.; Somogyi, B. Planktonic Bacterial Community Composition of an Extremely Shallow Soda Pond during a Phytoplankton Bloom Revealed by Cultivation and Molecular Cloning. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xue, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, M.; Kumar, S.; Li, W.; et al. Aliidiomarina halalkaliphila sp. nov., a Haloalkaliphilic Bacterium Isolated from a Soda Lake in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, A.; Uchimura, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Horikoshi, K. Collagenolytic Subtilisin-like Protease from the Deep-Sea Bacterium Alkalimonas Collagenimarina AC40T. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Dai, X.; Zhou, Y. Aliidiomarina indica sp. nov., Isolated from Deep Seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchaud, E.; Boussaha, M.; Loux, V.; Bernardet, J.-F.; Michel, C.; Kerouault, B.; Mondot, S.; Nicolas, P.; Bossy, R.; Caron, C.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of the Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium Psychrophilum. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardet, J.-F.; Bowman, J.P. The Genus Flavobacterium. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 481–531. ISBN 978-0-387-25497-5. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, W.-R.; Lünsdorf, H.; Vancanneyt, M.; Smit, J. Cauliform Bacteria Lacking Phospholipids from an Abyssal Hydrothermal Vent: Proposal of Glycocaulis abyssi gen. nov., sp. nov., Belonging to the Family Hyphomonadaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.; Pan, X.-C.; Mei, R.; Wang, Y.-N.; Liu, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-B.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Wu, X.-L. Glycocaulisalkaliphilus sp. nov., a Dimorphic Prosthecate Bacterium Isolated from Crude Oil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.-H. Glycocaulis profundi sp. nov., a Marine Bacterium Isolated from Seawater of the Mariana Trench. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, D.I.; Turova, T.; Kuznetsov, B.; Briantseva, I.; Gorlenko, V. Roseinatronobacter thiooxidans gen. nov., sp. nov., a New Alkaliphilic Aerobic Bacteriochlorophyll-Alpha-Containing Bacteria from a Soda Lake. Mikrobiologiia 2000, 69, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boldareva, E.; Bryantseva, I.; Tsapin, A.; Nelson, K.; Sorokin, D.Y.; Tourova, T.; Boichenko, V.; Stadnichuk, I.; Gorlenko, V. The New Alkaliphilic Bacteriochlorophyll A-Containing Bacterium Roseinatronobacter monicus sp. nov. from the Hypersaline Soda Mono Lake (California, United States). Microbiology 2007, 76, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trutschel, L.R.; Rowe, A.R.; Sackett, J.D. Complete Genome Sequence of Roseinatronobacter sp. Strain S2, a Chemolithoheterotroph Isolated from a pH 12 Serpentinizing System. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e00288-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálmai, T.; Szabó, B.; Lengyel, E.; Kotut, K.; Krienitz, L.; Padisák, J. Growth Response of the Picoplanktic Picocystis salinarum and the Microplanktic Limnospira (Arthrospira) fusiformis Strains from Lake Nakuru (Kenya) to Rapidly Changing Environmental Conditions. Hydrobiologia 2023, 851, 1873–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkoporov, A.N.; Clooney, A.G.; Sutton, T.D.; Ryan, F.J.; Daly, K.M.; Nolan, J.A.; McDonnell, S.A.; Khokhlova, E.V.; Draper, L.A.; Forde, A. The Human Gut Virome Is Highly Diverse, Stable, and Individual Specific. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, A.C.; Zablocki, O.; Zayed, A.A.; Howell, A.; Bolduc, B.; Sullivan, M.B. The Gut Virome Database Reveals Age-Dependent Patterns of Virome Diversity in the Human Gut. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szafrański, S.P.; Slots, J.; Stiesch, M. The Human Oral Phageome. Periodontology 2000 2021, 86, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z. Metagenomics of Wastewater Phageome Identifies an Extensively Cored Antibiotic Resistome in a Swine Feedlot Water Treatment Environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanic, S.; Deacon, J.M.; Chen, I.A. The Chronic Wound Phageome: Phage Diversity and Associations with Wounds and Healing Outcomes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02777-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurasz, H.; Pawłowski, T.; Perlejewski, K. Contamination Issue in Viral Metagenomics: Problems, Solutions, and Clinical Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 745076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Shkoporov, A.N.; Lood, C.; Millard, A.D.; Dutilh, B.E.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; van Zyl, L.J.; Aziz, R.K.; Oksanen, H.M.; Poranen, M.M.; et al. Abolishment of Morphology-Based Taxa and Change to Binomial Species Names: 2022 Taxonomy Update of the ICTV Bacterial Viruses Subcommittee. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, P.; Coykendall, A.; Beighton, D.; Hardie, J.M.; Whiley, R.A. Streptococcus Crista Sp. Nov., a Viridans Streptococcus with Tufted Fibrils, Isolated from the Human Oral Cavity and Throat. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1991, 41, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel, J.; Kleinheinz, K.A.; Jurtz, V.I.; Zschach, H.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M.; Larsen, M.V. HostPhinder: A Phage Host Prediction Tool. Viruses 2016, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.C. DeepHost: Phage Host Prediction with Convolutional Neural Network. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab385. [Google Scholar]
- Zielezinski, A.; Barylski, J.; Karlowski, W.M. Taxonomy-Aware, Sequence Similarity Ranking Reliably Predicts Phage–Host Relationships. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Hou, S.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Sun, F. Phage–Bacterial Contig Association Prediction with a Convolutional Neural Network. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, i45–i52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Sun, Y. Predicting the Hosts of Prokaryotic Viruses Using GCN-Based Semi-Supervised Learning. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.H.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, S.C. PhageScope: A Well-Annotated Bacteriophage Database with Automatic Analyses and Visualizations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D756–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, M.; Bin, Y.; Xia, J. PhaGAA: An Integrated Web Server Platform for Phage Genome Annotation and Analysis. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amgarten, D.; Iha, B.K.V.; Piroupo, C.M.; da Silva, A.M.; Setubal, J.C. vHULK, a New Tool for Bacteriophage Host Prediction Based on Annotated Genomic Features and Neural Networks. PHAGE 2022, 3, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Dhall, A.; Patiyal, S.; Choudhury, S.; Arora, A.; Raghava, G.P.S. An Ensemble Method for Prediction of Phage-Based Therapy against Bacterial Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1148579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, T.V.; Grabarnik, I.P.; Klyukina, A.A.; Zayulina, K.S.; Elizarov, I.M.; Shestakova, O.O.; Gavirova, L.A.; Malysheva, A.D.; Shcherbakova, P.A.; Barkhutova, D.D.; et al. Microbial Communities of Artisanal Fermented Milk Products from Russia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, C.; Câmara, S.; Enes Dapkevicius, M.d.L.N.; Vinuesa, P.; da Silva, C.C.G.; Malcata, F.X.; Rego, O.A. Characterization of the Bacterial Biodiversity in Pico Cheese (an Artisanal Azorean Food). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 192, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwaiwu, O.; Aduba, C.C.; Igbokwe, V.C.; Sam, C.E.; Ukwuru, M.U. Traditional and Artisanal Beverages in Nigeria: Microbial Diversity and Safety Issues. Beverages 2020, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, F.; Maury-Sintjago, E.; Leal, F.C.; Acuña, S.; Aguirre, J.; Troncoso, M.; Figueroa, G.; Parra-Flores, J. Presence of Listeria Monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat Artisanal Chilean Foods. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, A.C.; de Araújo, J.P.A.; Fusieger, A.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Nero, L.A. Microbiological Quality and Safety of Brazilian Artisanal Cheeses. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, S.; Murray, M.; Kampff, Z.; McDonnell, B.; Lugli, G.A.; Ventura, M.; Todaro, M.; Settanni, L.; van Sinderen, D.; Mahony, J. Microbial Ecology of Pecorino Siciliano PDO Cheese Production Systems. Fermentation 2023, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).