HACD3 Prevents PB1 from Autophagic Degradation to Facilitate the Replication of Influenza A Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Antibodies
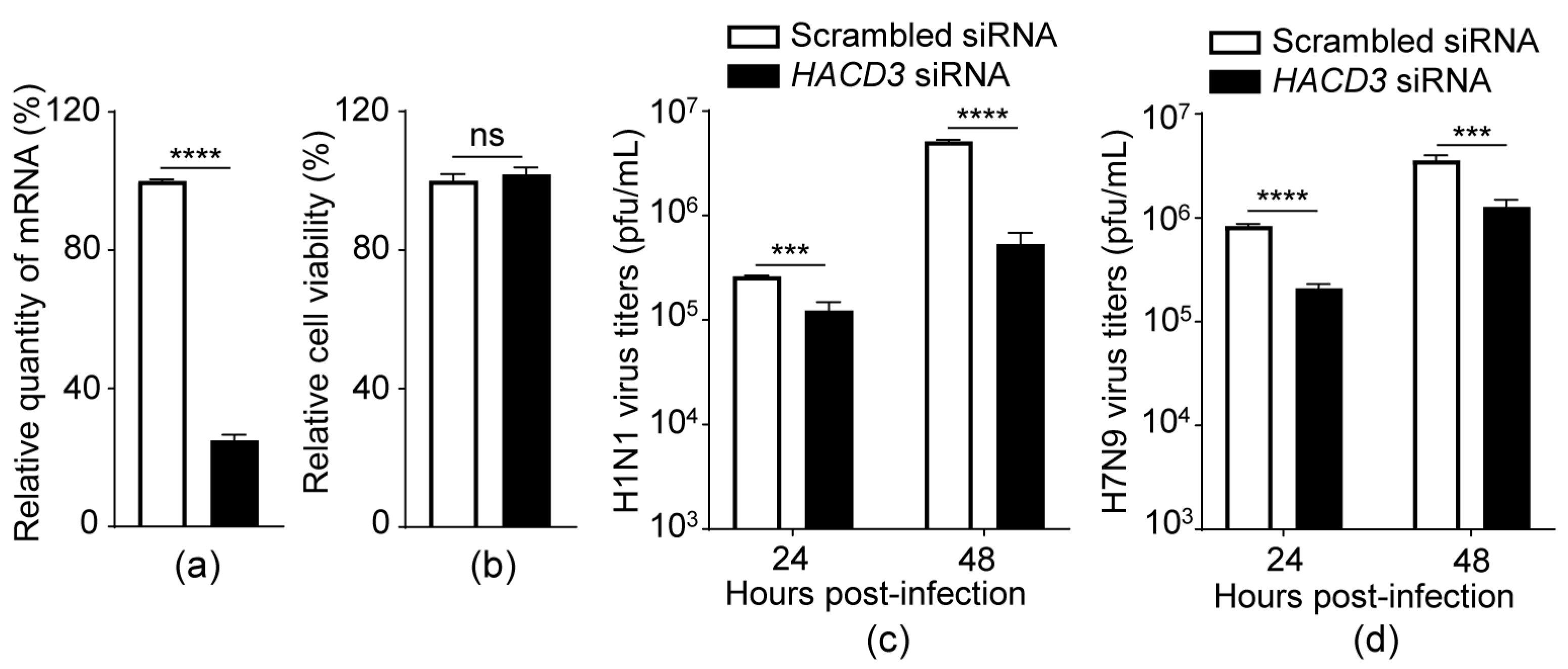
2.4. siRNA Transfection and Virus Infection
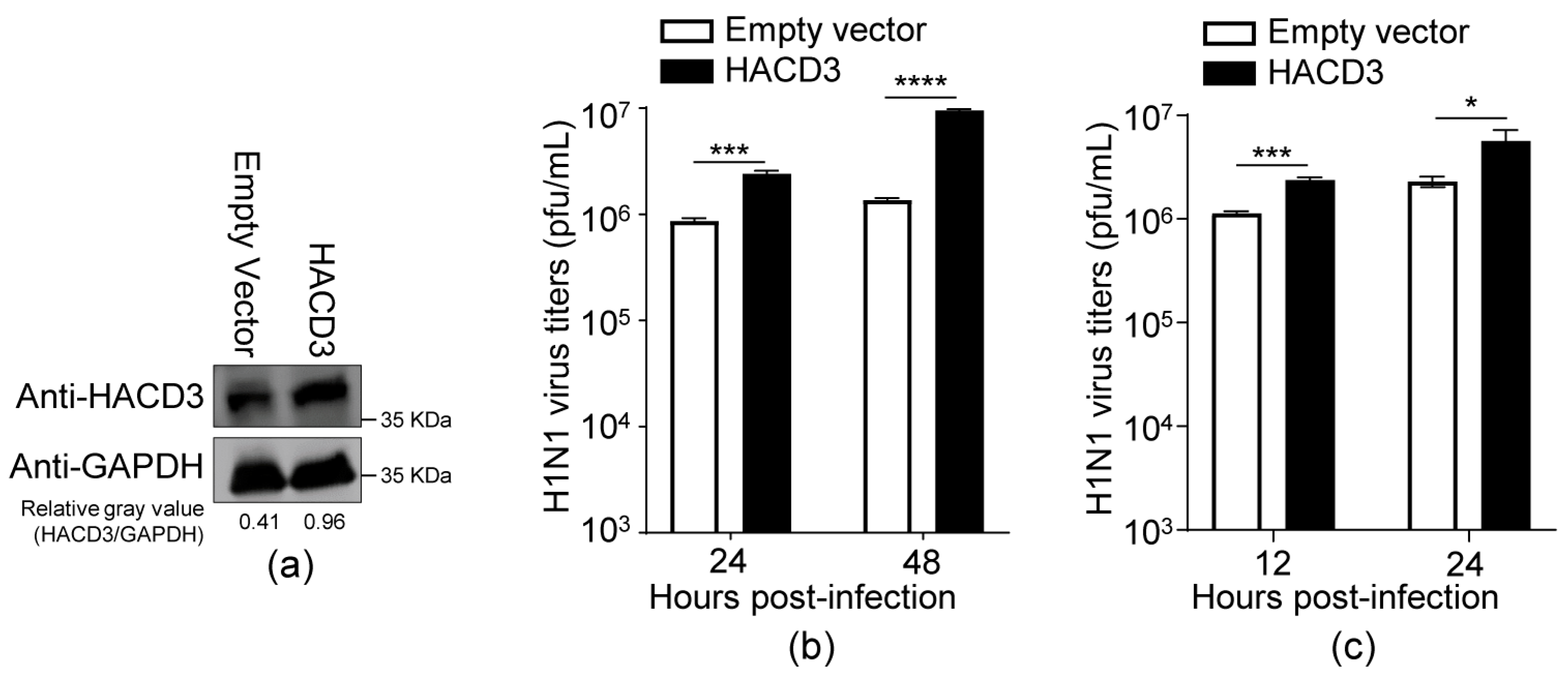
2.5. Plasmid Transfection and Virus Infection
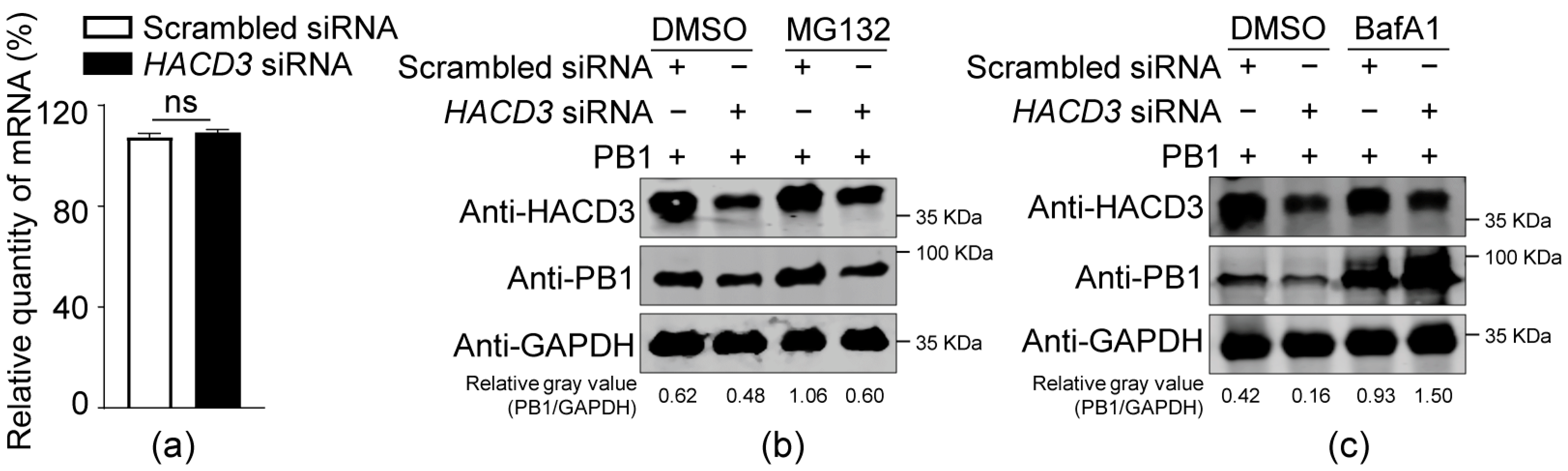
2.6. RT-qPCR Assay
2.7. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Assay
2.8. Confocal Assay
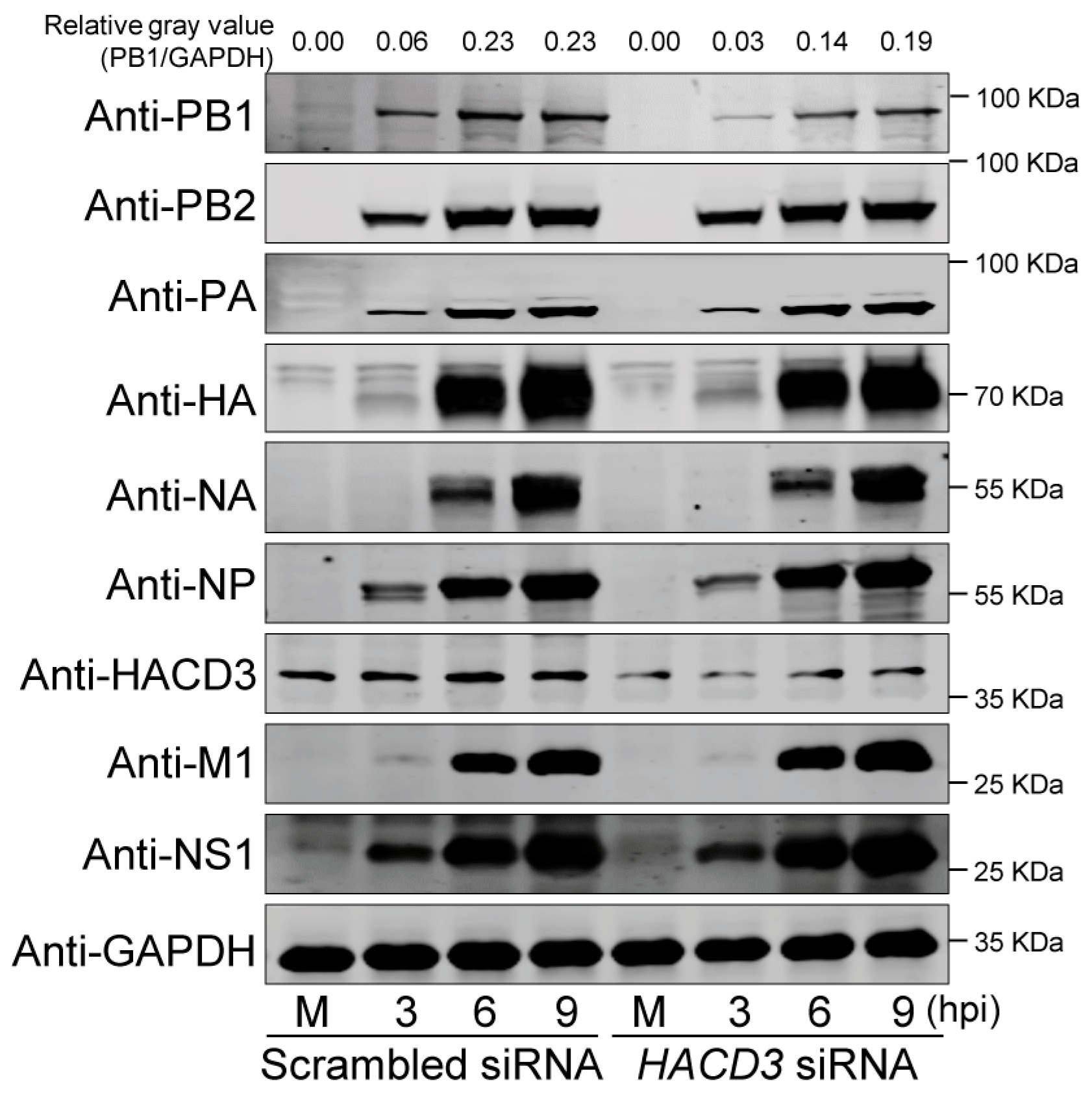
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.11. Cell Viability Assay
2.12. Plaque Assay
3. Results
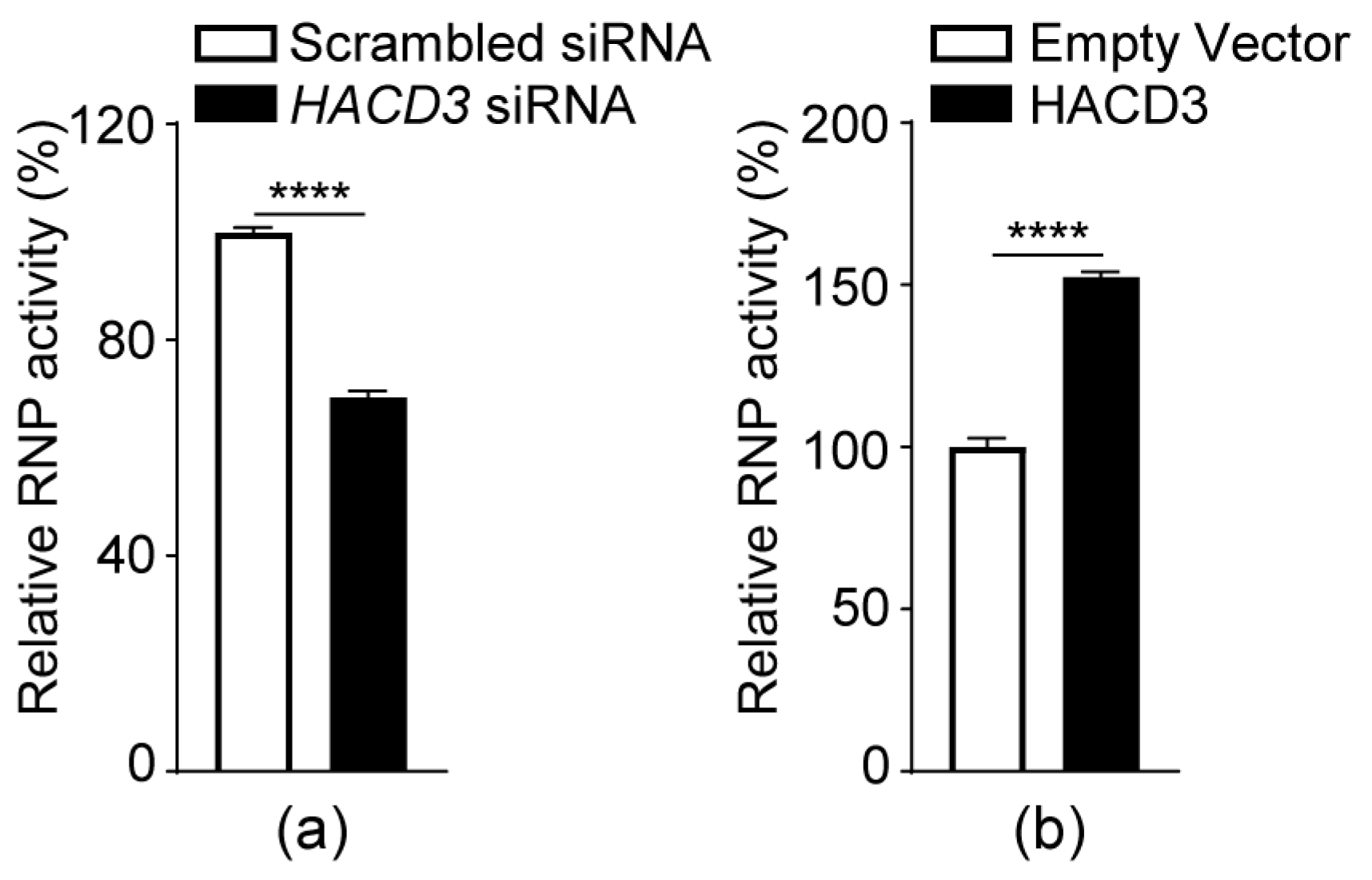
3.1. siRNA Knockdown of HACD3 Suppresses the Replication of IAV
3.2. Overexpression of HACD3 Promotes the Replication of IAV
3.3. HACD3 Downregulation Suppresses the Expression of the IAV PB1 Protein
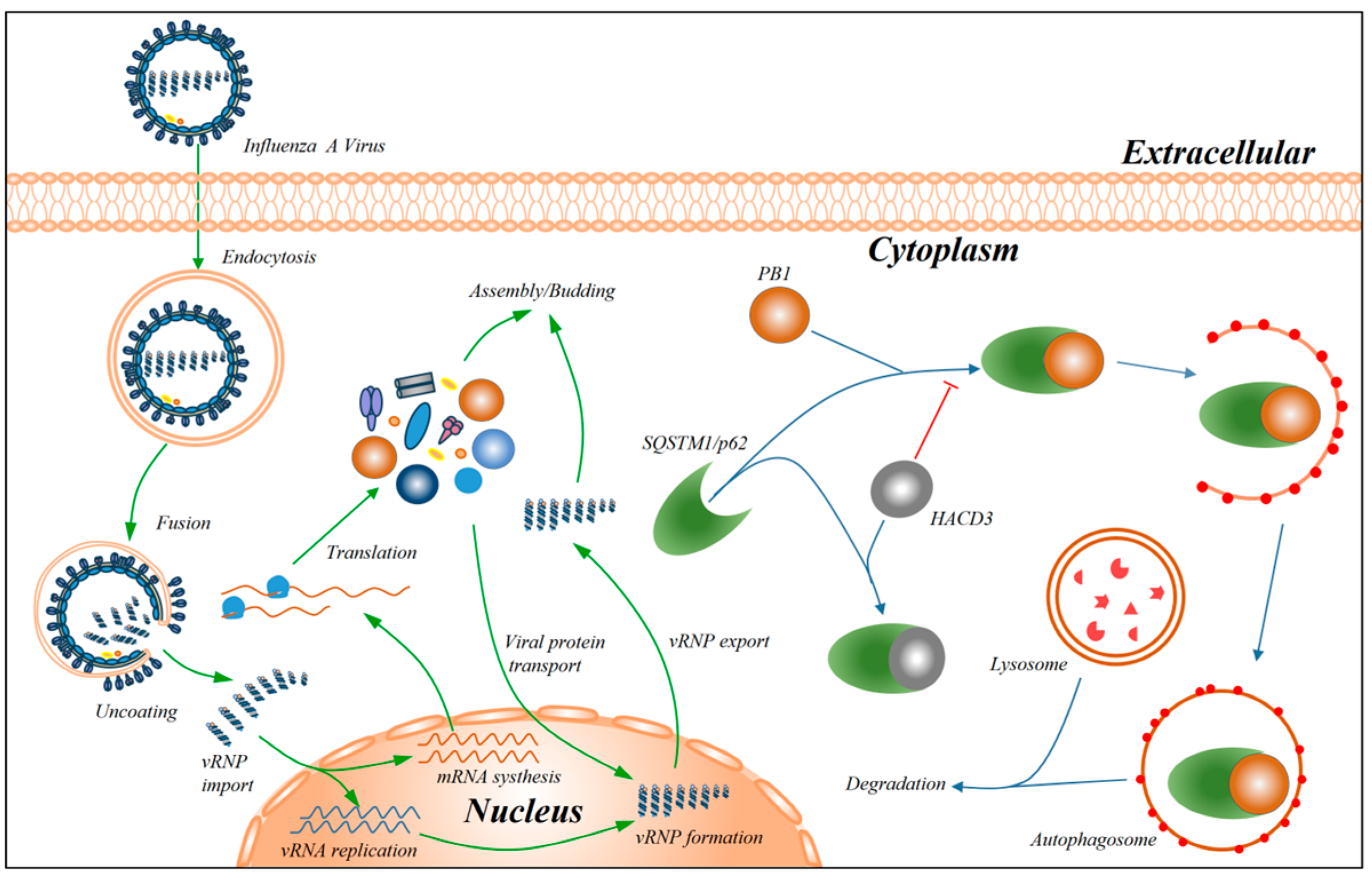
3.4. HACD3 Silencing Promotes PB1 Degradation through the Lysosome Pathway
3.5. HACD3 Overexpression Enhances the Expression of PB1 Protein
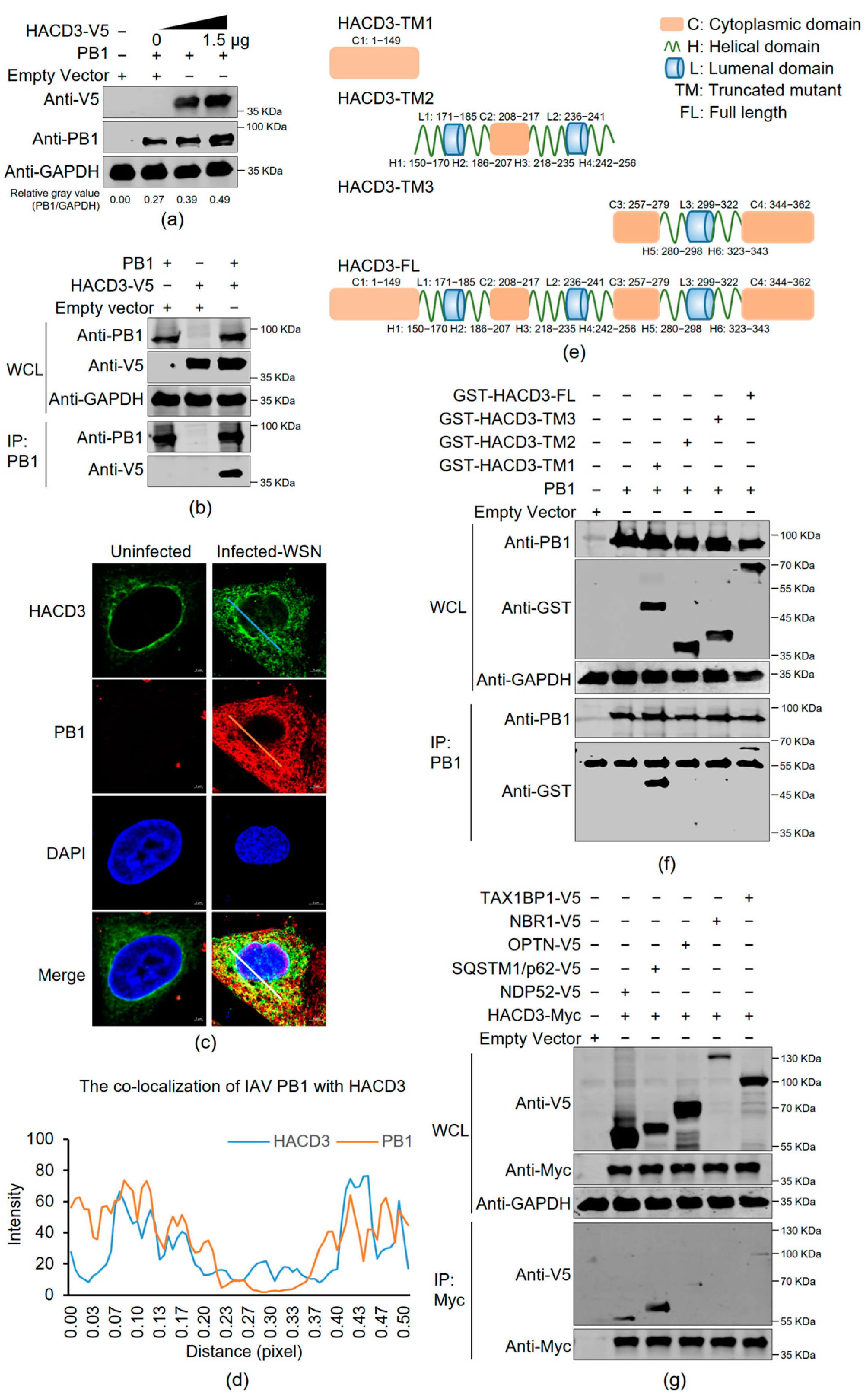
3.6. HACD3 Interacts with IAV PB1 and SQSTM1/p62
3.7. HACD3 Competes with SQSTM1/p62 in the Interaction with PB1
3.8. HACD3 Positively Regulates the vRNP Complex Activity of IAV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hause, B.M.; Collin, E.A.; Liu, R.; Huang, B.; Sheng, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, D.; Nelson, E.A.; Li, F. Characterization of a novel influenza virus in cattle and Swine: Proposal for a new genus in the Orthomyxoviridae family. mBio 2014, 5, e00031-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamayoshi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Goto, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Identification of a Novel Viral Protein Expressed from the PB2 Segment of Influenza A Virus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chu, J.T.S.; Wang, Y.; Chin, A.W.H.; Chong, T.H.; Dai, Z.; Poon, L.L.M.; Cheung, P.P.-H.; Huang, X. A novel mechanism of enhanced transcription activity and fidelity for influenza A viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 8796–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Watanabe, T.; Ito, H.; Watanabe, S.; Goto, H.; Gao, P.; Hughes, M.; Perez, D.R.; Donis, R.; Hoffmann, E.; et al. Generation of influenza A viruses entirely from cloned cDNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9345–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, E.; Devenish, L.; Engelhardt, O.G.; Palese, P.; Brownlee, G.G.; García-Sastre, A. Rescue of Influenza A Virus from Recombinant DNA. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9679–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, Y.; Honda, Y.; Sakata, Y.; Kato, H.; Toyoda, T. Fine Mapping of the Subunit Binding Sites of Influenza Virus RNA Polymerase. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 46, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.; Ortín, J. Characterization of influenza virus PB1 protein binding to viral RNA: Two separate regions of the protein contribute to the interaction domain. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; et al. Viral RNA-binding ability conferred by SUMOylation at PB1 K612 of influenza A virus is essential for viral pathogenesis and transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse-Post, D.J.; Franks, J.; Boyd, K.; Salomon, R.; Hoffmann, E.; Yen, H.L.; Webby, R.J.; Walker, D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Webster, R.G. Molecular Changes in the Polymerase Genes (PA and PB1) Associated with High Pathogenicity of H5N1 Influenza Virus in Mallard Ducks. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8515–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Deng, G.; Kong, H.; Tao, S.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Guan, Y.; Chen, H. Glycine at Position 622 in PB1 Contributes to the Virulence of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus in Mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, F.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; et al. PB1 S524G mutation of wild bird-origin H3N8 influenza A virus enhances virulence and fitness for transmission in mammals. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Bowman, J.W.; Jung, J.U. Autophagy during viral infection—A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Tu, S.; Ding, L.; Jin, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H. The role of autophagy in viral infections. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Zhang, W.; Dong, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Tang, B. The battle for autophagy between host and influenza A virus. Virulence 2022, 13, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ren, C.; Li, P.; Chen, H.; Jin, M.; Zhou, H. Autophagy Promotes Replication of Influenza A Virus In Vitro. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01984-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, D.; Fan, Z.; Hu, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, M.; Gao, G.F. Autophagy is involved in influenza A virus replication. Autophagy 2009, 5, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.; Yan, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, J.; Hu, B. Influenza A Virus Induces Autophagy by Its Hemagglutinin Binding to Cell Surface Heat Shock Protein 90AA1. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, C.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Xia, H.; et al. A/(H1N1) pdm09 NS1 promotes viral replication by enhancing autophagy through hijacking the IAV negative regulatory factor LRPPRC. Autophagy 2023, 19, 1533–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, S.; Liu, M.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shen, W.; Lei, C.-Q.; Zhu, Q. The nucleoprotein of influenza A virus inhibits the innate immune response by inducing mitophagy. Autophagy 2023, 19, 1916–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wang, W.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The PB1 protein of influenza A virus inhibits the innate immune response by targeting MAVS for NBR1-mediated selective autophagic degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courilleau, D.; Chastre, E.; Sabbah, M.; Redeuilh, G.; Atfi, A.; Mester, J. B-ind1, a novel mediator of Rac1 signaling cloned from sodium butyrate-treated fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17344–17348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, M.; Uchida, Y.; Ohno, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Nishioka, C.; Itohara, S.; Sassa, T.; Kihara, A. The 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratases HACD1 and HACD2 exhibit functional redundancy and are active in a wide range of fatty acid elongation pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15538–15551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Kanao, Y.; Yamanaka, M.; Sakuraba, H.; Mizutani, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Kihara, A. Characterization of four mammalian 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratases involved in very long-chain fatty acid synthesis. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, M.; Saucier, C.; Redeuilh, G. Human B-ind1 gene promoter: Cloning and regulation by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Gene 2006, 374, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutchueng-Djidjou, M.; Collard-Simard, G.; Fortier, S.; Hébert, S.S.; Kelly, I.; Landry, C.R.; Faure, R.L. The last enzyme of the de novo purine synthesis pathway 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase (ATIC) plays a central role in insulin signaling and the Golgi/endosomes protein network. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguwa, S.; Okamoto, T.; Abe, T.; Mori, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Moriishi, K.; Matsuura, Y. Human butyrate-induced transcript 1 interacts with hepatitis C virus NS5A and regulates viral replication. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G.; Shi, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zeng, X.; Tian, G.; Deng, G.; Shi, J.; et al. Influenza A virus use of BinCARD1 to facilitate the binding of viral NP to importin α7 is counteracted by TBK1-p62 axis-mediated autophagy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1168–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Liang, L.; Shao, X.; Luo, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Host Cellular Protein TRAPPC6A Interacts with Influenza A Virus M2 Protein and Regulates Viral Propagation by Modulating M2 Trafficking. J. Virol. 2016, 91, e01757-16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-H.; Wen, X.; Li, Q.-B.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G.-W.; Liang, L.-B.; Wang, X.-R.; Chen, H.-L.; Li, C.-J. Generation and application of two monoclonal antibodies targeting conserved linear epitopes in the NP protein of influenza A virus. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; et al. Phospholipid scramblase 1 interacts with influenza A virus NP, impairing its nuclear import and thereby suppressing virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Kash, J.C. Influenza Virus Evolution, Host Adaptation, and Pandemic Formation. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Abdelwhab, E.M.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Pleschka, S. Zoonotic Potential of Influenza A Viruses: A Comprehensive Overview. Viruses 2018, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Hsu, P.W.-C.; Tung, K.-F.; Jeng, K.-S.; Lai, M.M.C. Pooled RNAi screen identifies ubiquitin ligase Itch as crucial for influenza A virus release from the endosome during virus entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17516–17521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.L.; Stertz, S. Role of Host Genes in Influenza Virus Replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 419, 151–189. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, C. Advances in deciphering the interactions between viral proteins of influenza A virus and host cellular proteins. Cell Insight 2023, 2, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Shan, Z.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, C. HACD3 Prevents PB1 from Autophagic Degradation to Facilitate the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Viruses 2024, 16, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050702
Li Q, Jiang L, Wang Y, Liu X, Wang B, Shan Z, Wang Y-H, Wang Y, Chen H, Li C. HACD3 Prevents PB1 from Autophagic Degradation to Facilitate the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050702
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qibing, Li Jiang, Yihan Wang, Xuwei Liu, Bo Wang, Zhibo Shan, Yi-Han Wang, Yuqin Wang, Hualan Chen, and Chengjun Li. 2024. "HACD3 Prevents PB1 from Autophagic Degradation to Facilitate the Replication of Influenza A Virus" Viruses 16, no. 5: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050702
APA StyleLi, Q., Jiang, L., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Wang, B., Shan, Z., Wang, Y.-H., Wang, Y., Chen, H., & Li, C. (2024). HACD3 Prevents PB1 from Autophagic Degradation to Facilitate the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Viruses, 16(5), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050702






