Sudden Infant Death Associated with Rhinovirus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
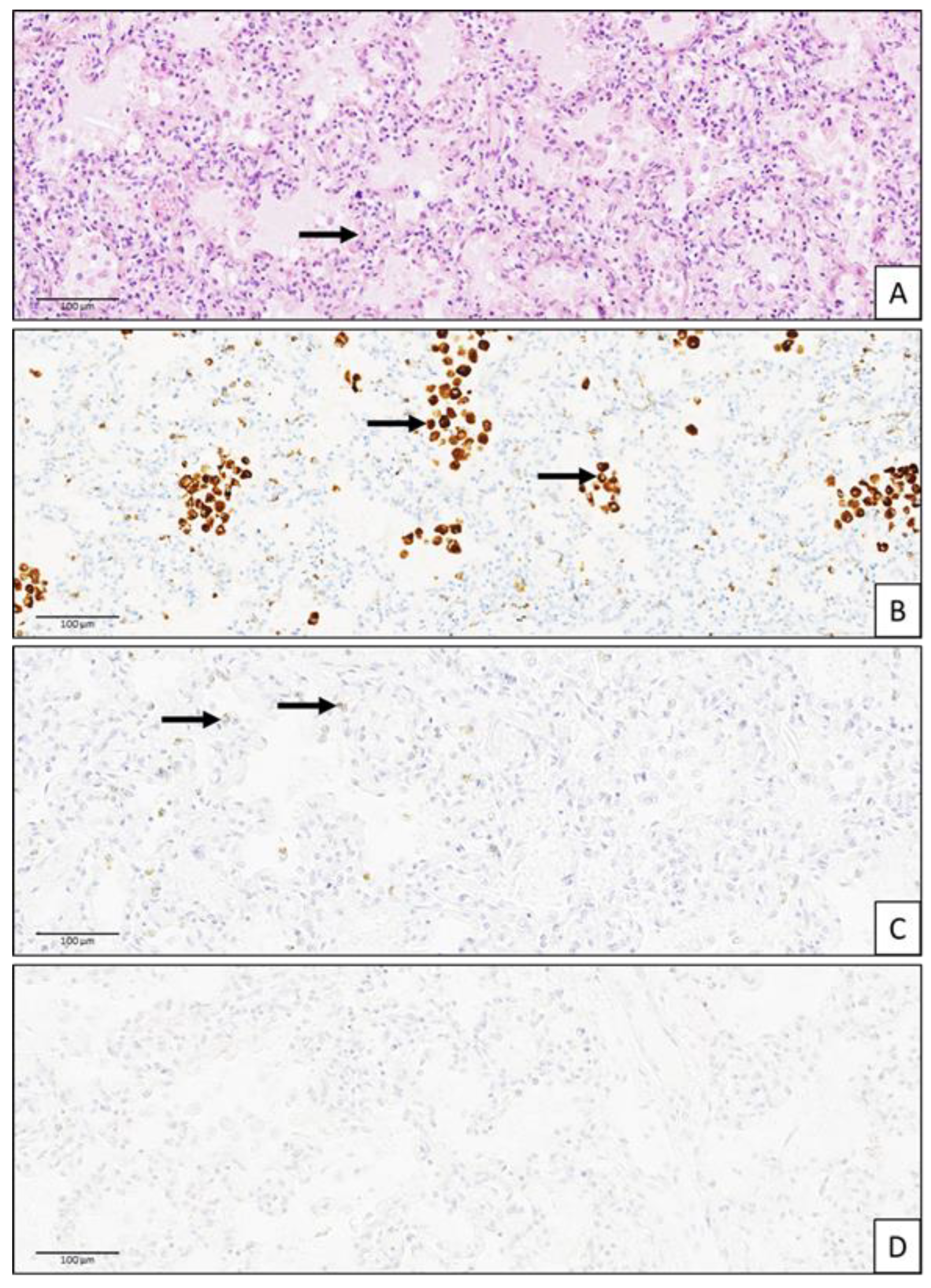
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, S.E.; Lamson, D.M.; St George, K.; Walsh, T.J. Human rhinoviruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Benten, I.; Koopman, L.; Niesters, B.; Hop, W.; van Middelkoop, B.; de Waal, L.; van Drunen, K.; Osterhaus, A.; Neijens, H.; Fokkens, W. Predominance of rhinovirus in the nose of symptomatic and asymptomatic infants. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 14, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieninger, E.; Fuchs, O.; Latzin, P.; Frey, U.; Regamey, N. Rhinovirus infections in infancy and early childhood. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.K.; Lu, X.; Erdman, D.D.; Poehling, K.A.; Zhu, Y.; Griffin, M.R.; Hartert, T.V.; Anderson, L.J.; Weinberg, G.A.; Hall, C.B.; et al. Rhinovirus-associated hospitalizations in young children. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.K.; Williams, J.V.; Gebretsadik, T.; Carroll, K.N.; Dupont, W.D.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Morin, L.L.; Heil, L.; Minton, P.A.; Woodward, K.; et al. Host and viral factors associated with severity of human rhinovirus-associated infant respiratory tract illness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, A.; Bour, J.B.; Darniot, M.; Pitoiset, C.; Aho-Glele, L.S.; Manoha, C. Epidemiological characteristics and clinical outcomes of human rhinovirus infections in a hospitalized population. Severity is independently linked to RSV coinfection and comorbidities. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 125, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, H.; Nickle, D.; Carter, L. Rhinovirus and asthma: Challenges and opportunities. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coriolani, G.; Ferranti, S.; Biasci, F.; Lotti, F.; Grosso, S. Acute flaccid myelitis temporally associated with rhinovirus infection: Just a coincidence? Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazama, K.; Shiihara, T.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Matsushige, T.; Dowa, Y.; Watanabe, M. Rhinovirus-associated acute encephalitis/encephalopathy and cerebellitis. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzel, A.; Smith, P.A.; Tobin, J.O. A New Type of Meningo-Encephalitis Associated with a Rhinovirus. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1965, 54, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soma, N.; Aizawa, Y.; Matsunaga, M.; Saitoh, A. Clinically Mild Encephalitis/Encephalopathy with a Reversible Splenial Lesion Associated with Rhinovirus. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e122–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savolainen, C.; Blomqvist, S.; Mulders, M.N.; Hovi, T. Genetic clustering of all 102 human rhinovirus prototype strains: Serotype 87 is close to human enterovirus 70. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83 Pt 2, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirand, A.; Henquell, C.; Archimbaud, C.; Chambon, M.; Charbonne, F.; Peigue-Lafeuille, H.; Bailly, J.L. Prospective identification of enteroviruses involved in meningitis in 2006 through direct genotyping in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nix, W.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Pallansch, M.A. Sensitive, seminested PCR amplification of VP1 sequences for direct identification of all enterovirus serotypes from original clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, S.; Lawn, J.E.; Hogan, D.R.; Mathers, C.; Cousens, S.N. Neonatal cause-of-death estimates for the early and late neonatal periods for 194 countries: 2000–2013. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 93, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Heras, J.; Swanson, V.L. Sudden death of an infant with rhinovirus infection complicating bronchial asthma: Case report. Pediatr. Pathol. 1983, 1, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, G.E.; Grist, N.R. Virological studies of sudden, unexplained infant deaths in Glasgow 1967-70. J. Clin. Pathol. 1972, 25, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierres-Surer, N.; Beby-Defaux, A.; Bourgoin, A.; Venot, C.; Berthier, M.; Grollier, G.; Oriot, D.; Agius, G. Rhinovirus infections in hospitalized children: A 3-year study. Arch. Pediatr. 1998, 5, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Martin Perceval, L.; Scherdel, P.; Jarry, B.; de Visme, S.; Levieux, K.; Gras-Le Guen, C. Sudden Unexpected Death in Infancy: Current Practices in Virological Investigations and Documentation in the French Registry. J. Pediatr. 2023, 257, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.Y.; Lu, X.D.; Lin, G.Y.; Cai, Z.W.; Lin, C.X.; Chen, P.Z.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhou, X.H.; Feng, X.Y.; Xiao, Z.X. Monitoring of viral pathogens in pediatric intensive care unit and analysis of clinical significance. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2013, 51, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen, T.; Roine, I.; Anjos, E.; Kaijalainen, S.; Roivainen, M.; Peltola, H.; Pitkaranta, A. Picornaviruses in cerebrospinal fluid of children with meningitis in Luanda, Angola. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel-Ambrocio, A.H.; Bautista-Carbajal, P.; Garcia-Leon, M.L.; Gomora-Herrera, M.J.; Pedernera-Astegiano, E.A.; Wong-Chew, R.M. Microglia HMC3 cells are highly susceptible to Rhinovirus infection. Virus Res. 2020, 288, 198110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Burrell, R.; Dale, R.C.; Kesson, A.; Blyth, C.C.; Clark, J.E.; Crawford, N.; Jones, C.A.; Britton, P.N.; Holmes, E.C. Diagnosis and analysis of unexplained cases of childhood encephalitis in Australia using metatranscriptomic sequencing. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Qian, S.; Xu, L.; Gao, H.; Xie, Z. A severe case of human rhinovirus A45 with central nervous system involvement and viral sepsis. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvala, H.; McIntyre, C.L.; McLeish, N.J.; Kondracka, J.; Palmer, J.; Molyneaux, P.; Gunson, R.; Bennett, S.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. High detection frequency and viral loads of human rhinovirus species A to C in fecal samples; diagnostic and clinical implications. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.M.; Tan, B.H.; Wu, S.; Gui, Y.; Suo, J.L.; Li, Y.C. Evidence of central nervous system infection and neuroinvasive routes, as well as neurological involvement, in the lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Riel, D.; Verdijk, R.; Kuiken, T. The olfactory nerve: A shortcut for influenza and other viral diseases into the central nervous system. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, J.; Schuffenecker, I.; Morel-Baccard, C.; Bardet, J.; Payen, V.; Kaiser, L.; Constant, S.; Lobrinus, J.A.; Lin-Marq, N.; Lina, B.; et al. Disseminated rhinovirus C8 infection with infectious virus in blood and fatal outcome in a child with repeated episodes of bronchiolitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, V.A.; Sebire, N.J. Natural Diseases Causing Sudden Death in Infancy and Early Childhood. In SIDS Sudden Infant and Early Childhood Death: The Past, the Present and the Future; Duncan, J.R., Byard, R.W., Eds.; University of Adelaide Press: Adelaide, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goldwater, P.N. Current SIDS research: Time to resolve conflicting research hypotheses and collaborate. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Engelmann, T.A.; Preuss, V.; Hagemeier, L.; Radomsky, L.; Beushausen, K.; Keil, J.; Vennemann, B.; Falk, C.S.; Klintschar, M. Pulmonary immune profiling of SIDS: Impaired immune maturation and age-related cytokine imbalance. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morichi, S.; Urabe, T.; Morishita, N.; Takeshita, M.; Ishida, Y.; Oana, S.; Yamanaka, G.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Kawashima, H. Pathological analysis of children with childhood central nervous system infection based on changes in chemokines and interleukin-17 family cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerar, S.; Kucan, R.; Paro-Panjan, D.; Nosan, G. The burden of viral lower respiratory tract infections during the neonatal period: Six-year experience at a tertiary referral hospital. Croat. Med. J. 2022, 63, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mage, D.T.; Donner, E.M. Is excess male infant mortality from sudden infant death syndrome and other respiratory diseases X-linked? Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Yang, Y.N.; Wu, C.Y.; Wu, P.L.; Tey, S.L.; Yang, S.N.; Liu, H.K. Maternal Age, the Disparity across Regions and Their Correlation to Sudden Infant Death Syndrome in Taiwan: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Children 2021, 8, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarczuk, N.; Milner, A.; Greenough, A. The Role of Maternal Smoking in Sudden Fetal and Infant Death Pathogenesis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 586068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chen, Q.; Xie, M. Smoking increases the risk of infectious diseases: A narrative review. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2020, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Blood Parameters (Day of Sudden Death) | Normal Range | |
|---|---|---|
| WBC (×103/μL) | 8.6 | 5.0–20.0 |
| RBC (×1012/L) | 3.5 | 3.5–6.1 |
| Hemoglobin (g/100 mL) | 12 | 12.0–20.5 |
| Platelets (×103/μL) | 210 | 150–450 |
| NEU (×103/μL); % | 1.3; 15.2% | [1.0–9.0] |
| LYM (×103/μL); % | 6.51; 75.8% | [2.2–16.8] |
| MONO (×103/μL); % | 0.65; 7.6% | [0.05–1.1] |
| EOS (×103/μL); % | 0.06; 0.8% | [0.0–0.85] |
| CRP (mg/mL) | <4 | < 4 |
| Pre-Autopsy Samples | At-Autopsy Samples | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Throat | BAL | NS | NP Swab | Rectal Swab | Muscle | Heart | Blood | Serum | CSF | Liver | Heart | Lung | Kidney | |
| Film array meningitis/encephalitis panel * (Biofire, bioMérieux) | EV | |||||||||||||
| EV (RIDA®gene, R- Biopharm) | ||||||||||||||
| Bocavirus, Rotavirus A, Aichivirus | ||||||||||||||
| Norovirus, Sapovirus, Astrovirus | ||||||||||||||
| Parechovirus (R-gene, bioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| CMV (R-gene, BioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| HSV-1, HSV-2 (R-gene, bioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| EBV (R-gene, BioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| Parvovirus B19 (R-gene, BioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| HHV-6 (R-gene, BioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| Influenza A and B (Panther, Hologic) | ||||||||||||||
| RSV, hMPV (Panther, Hologic) | ||||||||||||||
| Parainfluenza 1, 2 3, and 4 (Panther, Hologic) | ||||||||||||||
| RV/EV (Panther, Hologic) | RV | |||||||||||||
| SARS-CoV2 (Panther, Hologic) | ||||||||||||||
| AdV (R-gene, BioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| Rubella IgM (VIDAS® BioMérieux) | ||||||||||||||
| M. pneumoniae IgM (Virclia) | ||||||||||||||
| Film array respiratory panel RP2 plus ** (Biofire, bioMérieux) | RV | |||||||||||||
| RV/EV Typing and sequencing | RV | RV | RV | |||||||||||
| RV&EV/Ctrl cell (R-gene, BioMérieux) | RV | RV | RV-neg | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Auvray, C.; Perez-Martin, S.; Schuffenecker, I.; Pitoiset, C.; Tarris, G.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Martin, L.; Dullier-Taillefumier, N.; Bour, J.-B.; Manoha, C. Sudden Infant Death Associated with Rhinovirus Infection. Viruses 2024, 16, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040518
Auvray C, Perez-Martin S, Schuffenecker I, Pitoiset C, Tarris G, Ambert-Balay K, Martin L, Dullier-Taillefumier N, Bour J-B, Manoha C. Sudden Infant Death Associated with Rhinovirus Infection. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAuvray, Christelle, Stéphanie Perez-Martin, Isabelle Schuffenecker, Cécile Pitoiset, Georges Tarris, Katia Ambert-Balay, Laurent Martin, Nathalie Dullier-Taillefumier, Jean-Baptiste Bour, and Catherine Manoha. 2024. "Sudden Infant Death Associated with Rhinovirus Infection" Viruses 16, no. 4: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040518
APA StyleAuvray, C., Perez-Martin, S., Schuffenecker, I., Pitoiset, C., Tarris, G., Ambert-Balay, K., Martin, L., Dullier-Taillefumier, N., Bour, J.-B., & Manoha, C. (2024). Sudden Infant Death Associated with Rhinovirus Infection. Viruses, 16(4), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040518






