Development and Validation of a Genotypic Assay to Quantify CXCR4- and CCR5-Tropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1) Populations and a Comparison to Trofile®
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RNA Extraction, cDNA Generation and HIV Env V3 Amplification
2.2. MiSeq™ Data Analysis
2.3. HIV Tropism Determined by PSSM, Geno2pheno and Codon Analysis
2.4. Cost of Assay
3. Results
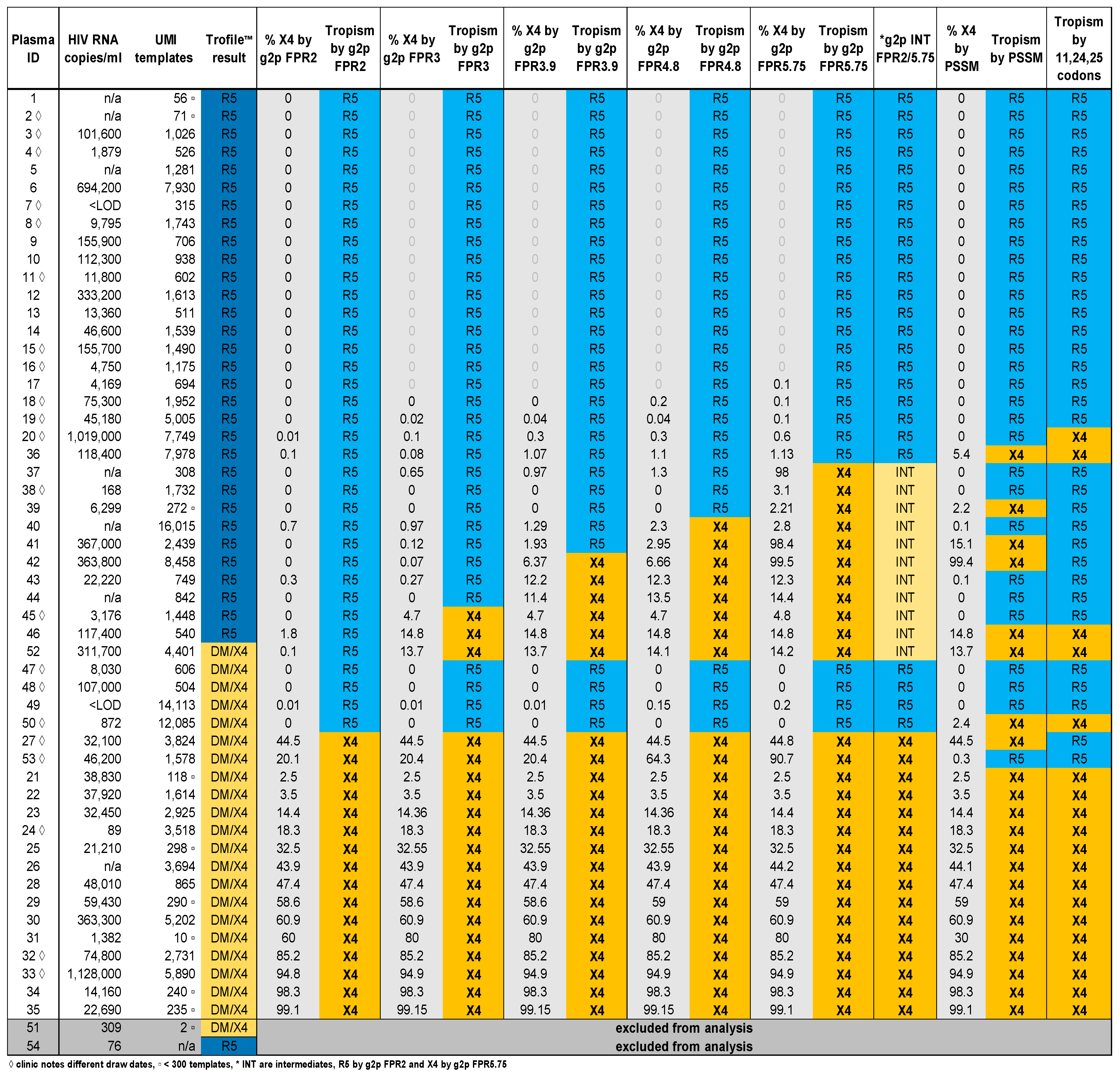
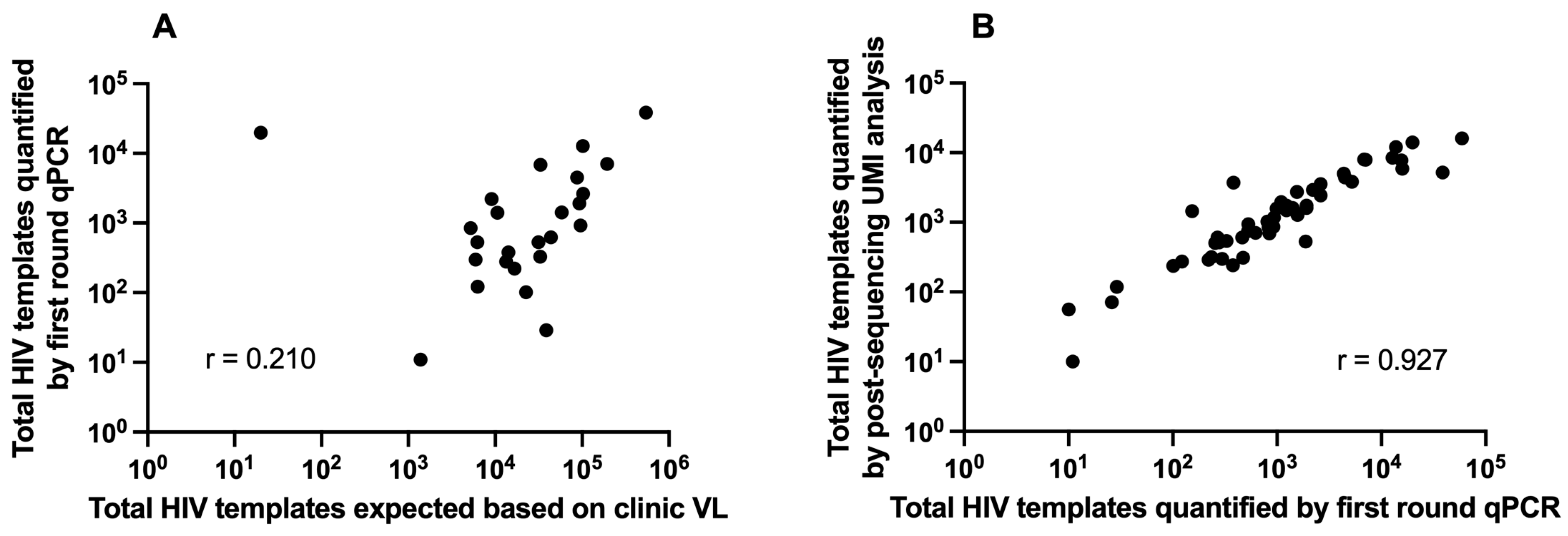
3.1. Clinical Plasma HIV RNA and HIV Template Recovery
3.2. Comparison of V3-UMI Sequences Interpreted by Genotypic Analysis to Trofile®
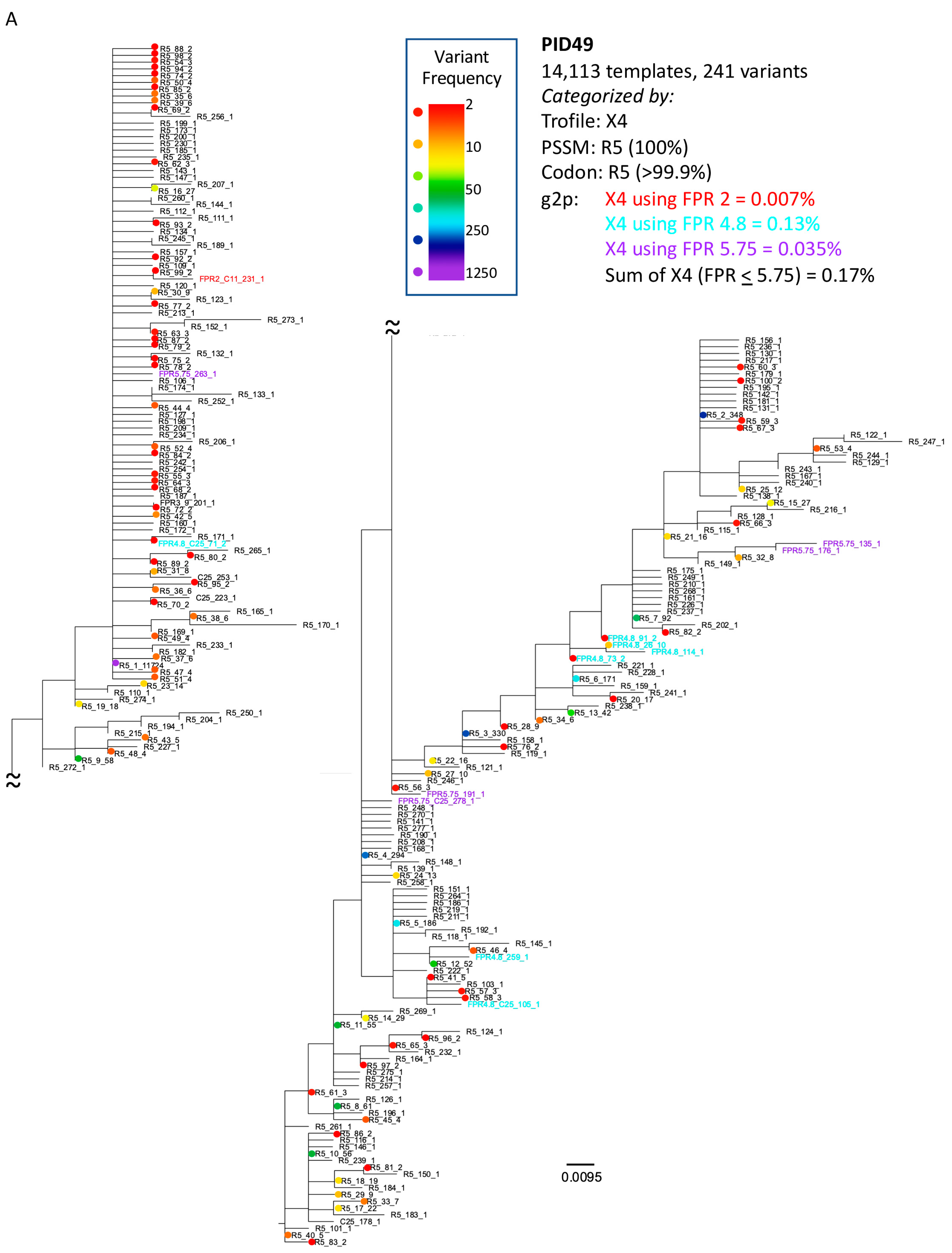
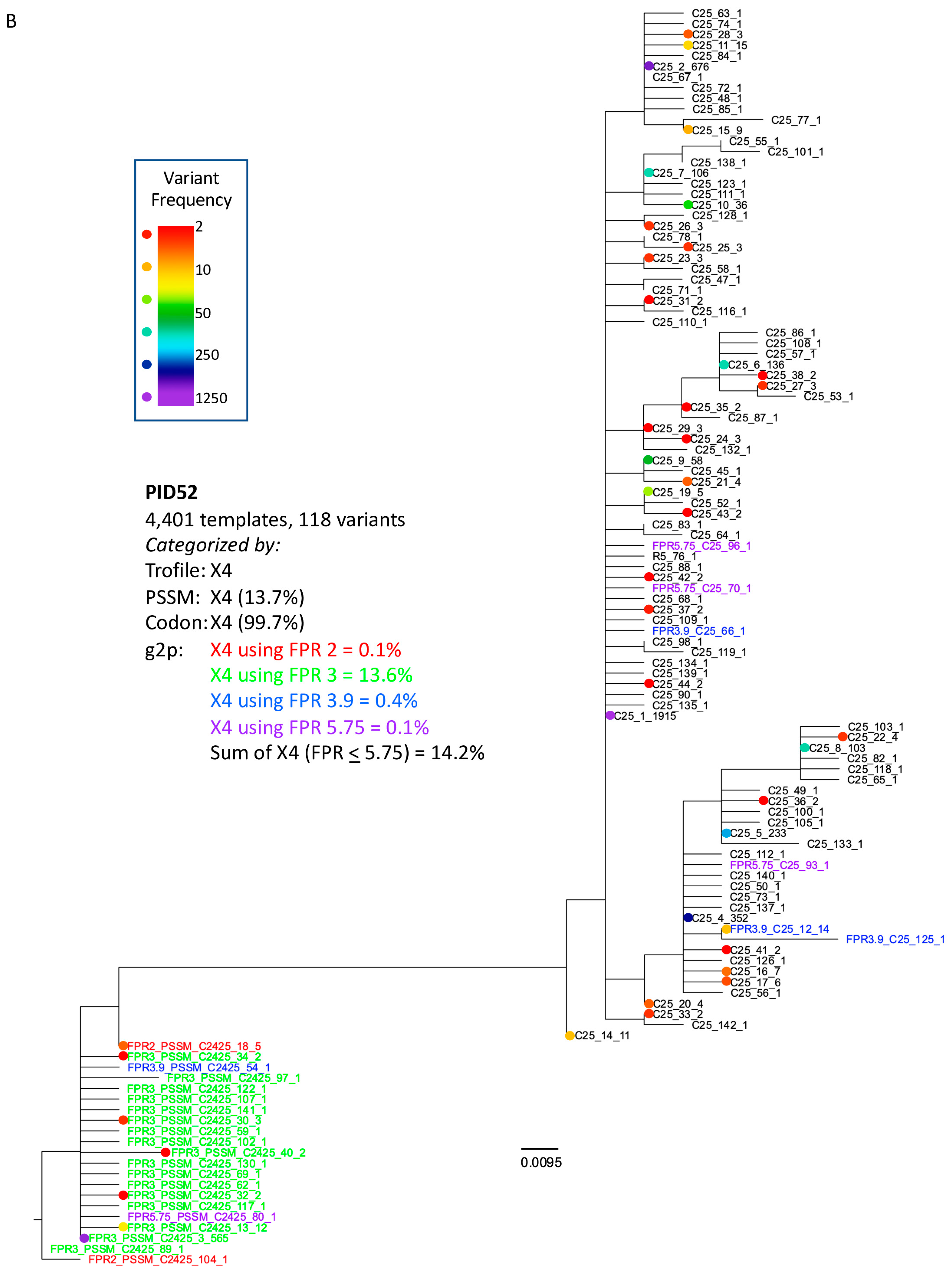
3.3. Analysis of Classifications Discordant by Trofile® vs. Genotypic Algorithms
3.4. Cost Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, T.; Mo, H.; Wang, N.; Nam, D.S.; Cao, Y.; Koup, R.A.; Ho, D.D. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of HIV-1 patients with primary infection. Science 1993, 261, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; MacKenzie, P.; Cleland, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Brown, A.J.; Simmonds, P. Selection for specific sequences in the external envelope protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 upon primary infection. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3345–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankarappa, R.; Margolick, J.B.; Gange, S.J.; Rodrigo, A.G.; Upchurch, D.; Farzadegan, H.; Gupta, P.; Rinaldo, C.R.; Learn, G.H.; He, X.; et al. Consistent viral evolutionary changes associated with the progression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 10489–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, J.C.; Jacobson, L.P.; Qiao, W.; Jamieson, B.D.; Phair, J.P.; Piazza, P.; Quinn, T.C.; Margolick, J.B. Emergence and persistence of CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 in a population of men from the multicenter AIDS cohort study. J Infect Dis. 2008, 198, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorr, P.; Westby, M.; Dobbs, S.; Griffin, P.; Irvine, B.; Macartney, M.; Mori, J.; Rickett, G.; Smith-Burchnell, C.; Napier, C.; et al. Maraviroc (UK-427,857), a potent, orally bioavailable, and selective small-molecule inhibitor of chemokine receptor CCR5 with broad-spectrum anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4721–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulick, R.M.; Lalezari, J.; Goodrich, J.; Clumeck, N.; DeJesus, E.; Horban, A.; Nadler, J.; Clotet, B.; Karlsson, A.; Wohlfeiler, M.; et al. Maraviroc for previously treated patients with R5 HIV-1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westby, M.; Lewis, M.; Whitcomb, J.; Youle, M.; Pozniak, A.L.; James, I.T.; Jenkins, T.M.; Perros, M.; van der Ryst, E. Emergence of CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) variants in a minority of HIV-1-infected patients following treatment with the CCR5 antagonist maraviroc is from a pretreatment CXCR4-using virus reservoir. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4909–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saag, M.; Goodrich, J.; Fatkenheuer, G.; Clotet, B.; Clumeck, N.; Sullivan, J.; Westby, M.; van der Ryst, E.; Mayer, H.; Group, A.S. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of maraviroc in treatment-experienced patients infected with non-R5 HIV-1. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, L.C.; Mo, T.; Dong, W.W.; Zhong, X.; Woods, C.K.; Thielen, A.; Jensen, M.A.; Knapp, D.J.; Chapman, D.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Deep V3 sequencing for HIV type 1 tropism in treatment-naive patients: A reanalysis of the MERIT trial of maraviroc. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcomb, J.M.; Huang, W.; Fransen, S.; Limoli, K.; Toma, J.; Wrin, T.; Chappey, C.; Kiss, L.D.; Paxinos, E.E.; Petropoulos, C.J. Development and characterization of a novel single-cycle recombinant-virus assay to determine human immunodeficiency virus type 1 coreceptor tropism. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkin, T.J.; Goetz, M.B.; Leduc, R.; Skowron, G.; Su, Z.; Chan, E.S.; Heera, J.; Chapman, D.; Spritzler, J.; Reeves, J.D.; et al. Reanalysis of coreceptor tropism in HIV-1-infected adults using a phenotypic assay with enhanced sensitivity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents with HIV; Department of Health and Human Services. Page C-31. Available online: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/adult-adolescent-arv/guidelines-adult-adolescent-arv.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Kagan, R.M.; Johnson, E.P.; Siaw, M.; Biswas, P.; Chapman, D.S.; Su, Z.; Platt, J.L.; Pesano, R.L. A genotypic test for HIV-1 tropism combining Sanger sequencing with ultradeep sequencing predicts virologic response in treatment-experienced patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, L.C.; Mo, T.; Dong, W.W.; Zhong, X.; Woods, C.K.; Jensen, M.A.; Thielen, A.; Chapman, D.; Lewis, M.; James, I.; et al. Deep sequencing to infer HIV-1 co-receptor usage: Application to three clinical trials of maraviroc in treatment-experienced patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daumer, M.; Kaiser, R.; Klein, R.; Lengauer, T.; Thiele, B.; Thielen, A. Genotypic tropism testing by massively parallel sequencing: Qualitative and quantitative analysis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2011, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, J.; Braverman, M.S.; Taillon, B.E.; Desany, B.; James, I.; Harrigan, P.R.; Lewis, M.; Robertson, D.L. Detection of low-frequency pretherapy chemokine (CXC motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4)-using HIV-1 with ultra-deep pyrosequencing. Aids 2009, 23, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Ijaz, U.Z.; D’Amore, R.; Hall, N.; Sloan, W.T.; Quince, C. Insight into biases and sequencing errors for amplicon sequencing with the Illumina MiSeq platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabara, C.B.; Jones, C.D.; Roach, J.; Anderson, J.A.; Swanstrom, R. Accurate sampling and deep sequencing of the HIV-1 protease gene using a Primer ID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20166–20171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, J.R.; Zhou, S.; Anderson, J.A.; Eron, J.J., Jr.; Rackoff, L.A.; Jabara, C.; Swanstrom, R. Primer ID Informs Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms and Reveals Preexisting Drug Resistance Mutations in the HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Coding Domain. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2015, 31, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Jones, C.; Mieczkowski, P.; Swanstrom, R. Primer ID Validates Template Sampling Depth and Greatly Reduces the Error Rate of Next-Generation Sequencing of HIV-1 Genomic RNA Populations. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8540–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Bednar, M.M.; Sturdevant, C.B.; Hauser, B.M.; Swanstrom, R. Deep Sequencing of the HIV-1 env Gene Reveals Discrete X4 Lineages and Linkage Disequilibrium between X4 and R5 Viruses in the V1/V2 and V3 Variable Regions. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7142–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, S.; Swenson, L.C.; Hu, S.; Hughes, P.; Harrigan, P.R.; Coombs, R.W.; Frenkel, L.M. Development of a novel codon-specific polymerase chain reaction for the detection of CXCR4-utilizing HIV type 1 subtype B. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2013, 29, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, N.A.; Fass, J.N. Sickle: A Sliding-Window, Adaptive, Quality-Based Trimming Tool for FastQ Files. Available online: https://github.com/najoshi/sickle (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Maust, B.S.; Nickle, D.C.; Learn, G.H.; Liu, Y.; Heath, L.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Mullins, J.I. DIVEIN: A web server to analyze phylogenies, sequence divergence, diversity, and informative sites. Biotechniques 2010, 48, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.; Fleharty, M.; Abreu, J.; Farjoun, Y.; Ferriera, S.; Holmes, L.; Granger, B.; Green, L.; Howd, T.; Mason, T.; et al. Characterization and remediation of sample index swaps by non-redundant dual indexing on massively parallel sequencing platforms. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.A.; Li, F.S.; van‘t Wout, A.B.; Nickle, D.C.; Shriner, D.; He, H.X.; McLaughlin, S.; Shankarappa, R.; Margolick, J.B.; Mullins, J.I. Improved coreceptor usage prediction and genotypic monitoring of R5-to-X4 transition by motif analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env V3 loop sequences. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13376–13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengauer, T.; Sander, O.; Sierra, S.; Thielen, A.; Kaiser, R. Bioinformatics prediction of HIV coreceptor usage. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.A.; Coetzer, M.; van‘t Wout, A.B.; Morris, L.; Mullins, J.I. A reliable phenotype predictor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C based on envelope V3 sequences. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4698–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, L.M.; Mullins, J.I.; Learn, G.H.; Manns-Arcuino, L.; Herring, B.L.; Kalish, M.L.; Steketee, R.W.; Thea, D.M.; Nichols, J.E.; Liu, S.L.; et al. Genetic evaluation of suspected cases of transient HIV-1 infection of infants. Science 1998, 280, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, W.D.; Gulick, R.M.; Mayer, H.; Fatkenheuer, G.; Nelson, M.; Heera, J.; Rajicic, N.; Goodrich, J. Two-year safety and virologic efficacy of maraviroc in treatment-experienced patients with CCR5-tropic HIV-1 infection: 96-week combined analysis of MOTIVATE 1 and 2. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2010, 55, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Madero, J.; Di Perri, G.; Wood, R.; Saag, M.; Frank, I.; Craig, C.; Burnside, R.; McCracken, J.; Pontani, D.; Goodrich, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of maraviroc versus efavirenz, both with zidovudine/lamivudine: 96-week results from the MERIT study. HIV Clin. Trials 2010, 11, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Purpose | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| cDNA | cDNA synthesis | 5′-CCCGCGTGGCCTCCTGAATTAT[ill.1]-CCGCTCCGTCCGACGACTCACTATA[ill.2]-SSMVSBYNNNNN[UMI]-CAGTAGAAAAATTCCCCTCCACAATT[HIV7377-7353] -3′ |
| env6880F | 1st round, forward | 5′-CCCCGGCTGGTTTTGCGATTCTAAAGTGTA[HIV6880-6909] -3′ |
| ill.1 | 1st round, reverse | 5′-CCCGCGTGGCCTCCTGAATTAT -3′ |
| envC2F6 | 2nd round, forward | 5′-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG[MiSeq adapter]-GCACAGTACAATGTACACATGGAATTA[HIV6952-6978] -3′ |
| ill.2 | 2nd round, reverse | 5′-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG[MiSeq adapter]-CCGCTCCGTCCGACGACTCACTATA[ill.2] -3′ |
| cDNA oligo, 5′-3′ (HXB2 7353-7377) | ||||||||||||||
| 99% | 99% | 90% | 95% | 99% | 95% | 99% | 99% | 90% | 99% | 99% | 90% | 99% | ||
| 5′-C | A | G | T | A | G | A | A | A | A | A | T | T- | ||
| 99% | 90% | 99% | 99% | 95% | 95% | 90% | 95% | 99% | 99% | 95% | 95% | 99% | ||
| -C | C | C | C | T | C | C | A | C | A | A | T | T-3′ | ||
| env6880, 5′-3′ (HXB2 6880-6909) | ||||||||||||||
| 99% | 99% | 99% | 90% | 75% | 99% | 99% | 99% | 99% | 99% | 95% | 99% | 95% | 99% | 99% |
| 5′-C | C | C | C | G | G | C | T | G | G | T | T | T | T | G- |
| 99% | 90% | 90% | 99% | 95% | 90% | 99% | 95% | 95% | 95% | 70% | 99% | 99% | 95% | 99% |
| -C | G | A | T | T | C | T | A | A | A | G | T | G | T | A-3′ |
| Model. (n = 52) | Sensitivity (%) | False Positives | Specificity (%) | False Negatives | Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | Negative Predictive Value (NPV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g2p FPR 2 | 76% | 0 | 100% | 5 | 100% | 86% |
| g2p FPR 3 | 81% | 2 | 93.5% | 4 | 89.5% | 88% |
| g2p FPR 3.9 | 81% | 5 | 84% | 4 | 77% | 87% |
| g2p FPR 4.8 | 81% | 7 | 77% | 4 | 71% | 86% |
| g2p FPR 5.75 | 81% | 10 | 68% | 4 | 63% | 84% |
| PSSM | 81% | 5 | 84% | 4 | 77% | 87% |
| codon analysis | 76% | 3 | 90% | 5 | 84% | 85% |
| Model (n = 31) | Sensitivity (%) | False Positives | Specificity (%) | False Negatives | Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | Negative Predictive Value (NPV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g2p FPR 2 | 85% | 0 | 100% | 2 | 100% | 90% |
| g2p FPR 3 | 92% | 1 | 94% | 1 | 92% | 94% |
| g2p FPR 3.9 | 92% | 4 | 78% | 1 | 75% | 93% |
| g2p FPR 4.8 | 92% | 6 | 67% | 1 | 67% | 92% |
| g2p FPR 5.75 | 92% | 8 | 56% | 1 | 60% | 91% |
| PSSM | 92% | 5 | 72% | 1 | 71% | 93% |
| codon analysis | 92% | 2 | 89% | 1 | 86% | 94% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, D.; McLaughlin, S.; Deng, W.; Mullins, J.I.; Dragavon, J.; Harb, S.; Coombs, R.W.; Frenkel, L.M. Development and Validation of a Genotypic Assay to Quantify CXCR4- and CCR5-Tropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1) Populations and a Comparison to Trofile®. Viruses 2024, 16, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040510
Ko D, McLaughlin S, Deng W, Mullins JI, Dragavon J, Harb S, Coombs RW, Frenkel LM. Development and Validation of a Genotypic Assay to Quantify CXCR4- and CCR5-Tropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1) Populations and a Comparison to Trofile®. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040510
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Daisy, Sherry McLaughlin, Wenjie Deng, James I. Mullins, Joan Dragavon, Socorro Harb, Robert W. Coombs, and Lisa M. Frenkel. 2024. "Development and Validation of a Genotypic Assay to Quantify CXCR4- and CCR5-Tropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1) Populations and a Comparison to Trofile®" Viruses 16, no. 4: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040510
APA StyleKo, D., McLaughlin, S., Deng, W., Mullins, J. I., Dragavon, J., Harb, S., Coombs, R. W., & Frenkel, L. M. (2024). Development and Validation of a Genotypic Assay to Quantify CXCR4- and CCR5-Tropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1) Populations and a Comparison to Trofile®. Viruses, 16(4), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040510






