N-Glycan Profiles of Neuraminidase from Avian Influenza Viruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
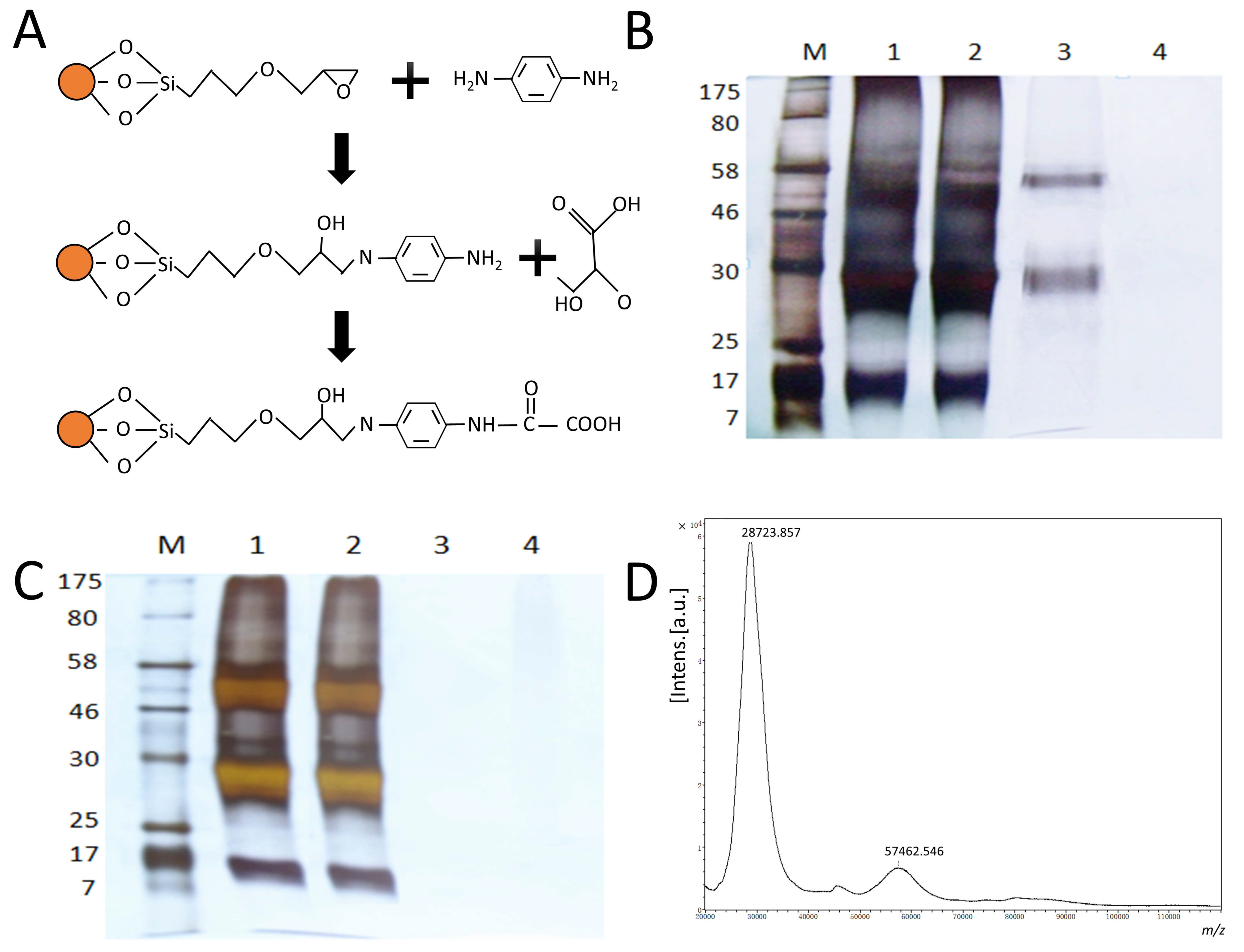
2.1. Preparation of the AAMPs
2.2. Viral Whole Protein Preparation
2.3. NA Isolation
2.4. NA Identification by MALDI-TOF-MS
2.5. Glycopattern Analysis of NA Using Lectin Microarray
2.6. Characterization of N-Glycan Profiles of NAs by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS
2.7. Docking Analysis for NA and p-Aminophenyloxamic Acid Interaction
3. Results
3.1. NA Isolation by the AAMPs
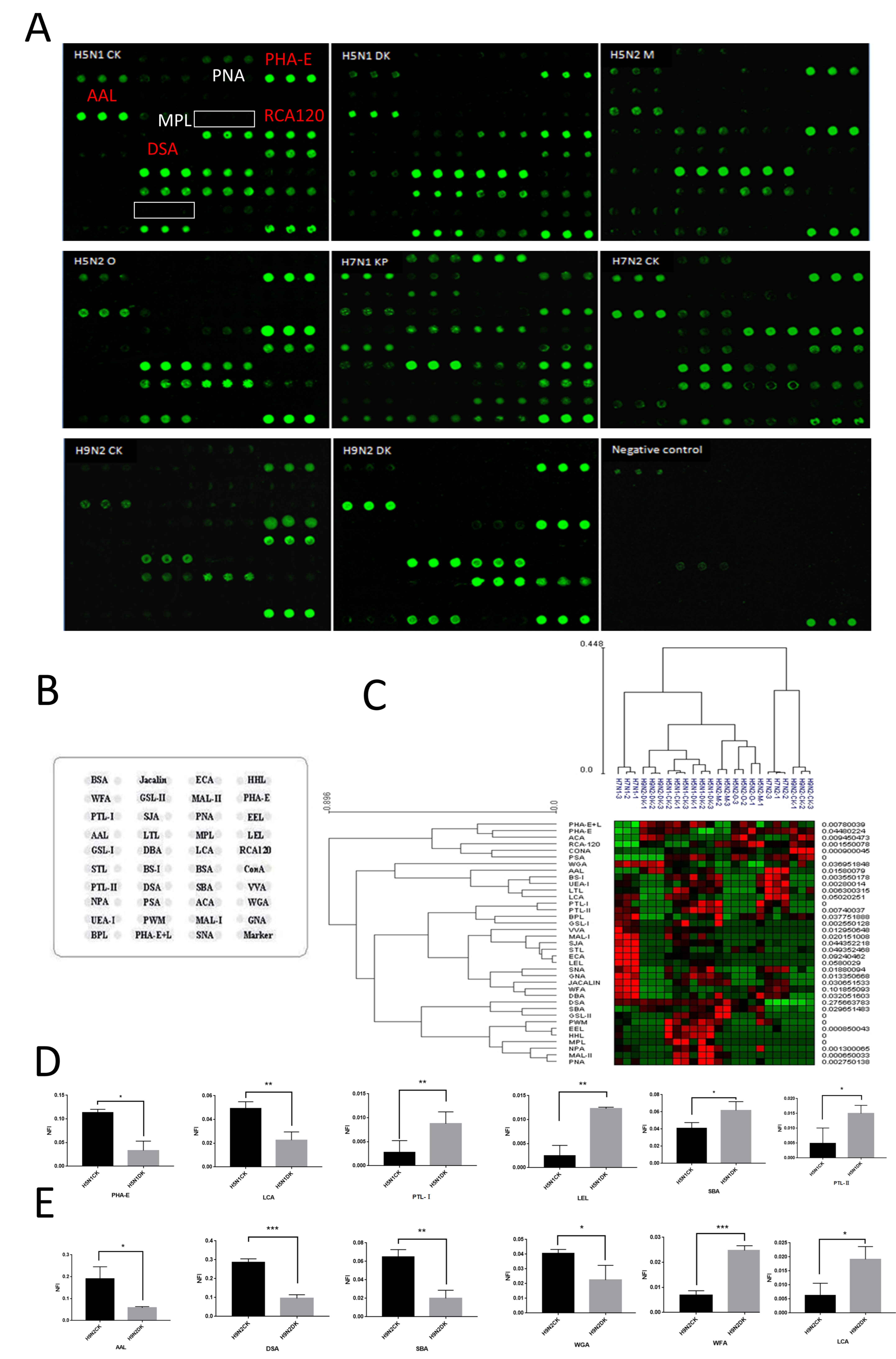
3.2. Glycopatterns Analysis of NAs by Lectin Microarray
3.3. N-Glycan Profiles of NAs by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS Analysis
3.4. Docking Analysis of NA and p-Aminophenyloxamic Acid
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, H.; Shu, J.; Ma, T.; Li, Z. Genetic variation and co-evolutionary relationship of RNA polymerase complex segments in influenza A viruses. Virology 2017, 511, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, J.; Liang, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Coinfection with influenza A virus enhances SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Sun, S.; Li, Z. Two glycosylation sites in H5N1 influenza virus hemagglutinin that affect binding preference by computer-based analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, Y.; Qin, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, Z. The evolutionary pattern of glycosylation sites in influenza virus (H5N1) hemagglutinin and neu-raminidase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49224. [Google Scholar]
- Shtyrya, Y.A.; Mochalova, L.V.; Bovin, N.V. Influenza virus neuraminidase: Structure and function. Acta Naturae 2009, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrasinovic, P.M. On the structure-based design of novel inhibitors of H5N1 influenza A virus neuraminidase (NA). Biophys. Chem. 2009, 140, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Cheng, L.P.; Pang, W.; Zhong, Z.J.; Guo, L.L. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Acylhydrazone Derivatives as Potent Neuraminidase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavricka, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Kiyota, H.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Qi, J.; Tanaka, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; et al. Influenza neuraminidase operates via a nucleophilic mechanism and can be targeted by covalent inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Influenza neuraminidase inhibitors: Antiviral action and mechanisms of resistance. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7 (Suppl. S1), 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.M.; Attwood, R.M.; Mohr, P.G.; Barrett, S.A.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. A generic system for the expression and purification of soluble and stable influenza neuraminidase. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, M.; Paskel, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Zengel, J.R.; Cheng, X.; Treanor, J.J.; Jin, H.; Subbarao, K. A Single Dose of an Avian H3N8 Influenza Virus Vaccine Is Highly Immunogenic and Efficacious against a Recently Emerged Seal Influenza Virus in Mice and Ferrets. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6907–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilei, E.M.; Johansson, A.; Schlatter, Y.; Redhead, K.; Frey, J. Genetic and functional characterization of the NanA sialidase from Clostridium chauvoei. Vet.-Res. 2011, 42, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cui, T.; Chen, Q.; Ma, T.; Li, Z. Isolation and identification of native membrane glycoproteins from living cell by concanavalin A–magnetic particle conjugates. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, G.; Ma, T.; Jia, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Z. Profiling of concanavalin A-binding glycoproteins in human hepatic stellate cells activated with transforming growth factor-beta1. Molecules 2014, 19, 19845–19867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.X.; Chen, W.; Bian, H.; Li, Z. Characterization and sub-cellular localization of GalNAc-binding proteins isolated from human hepatic stellate cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Sun, X.X.; Zhang, P.; Qin, X.; Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Jia, Z.; Bian, H.; Li, Z. Identification and localization of xylose-binding proteins as potential biomarkers for liver fibro-sis/cirrhosis. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, M.; Dang, L.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Age- and sex-associated differences in the glycopatterns of human salivary glycoproteins and their roles against influenza A virus. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2742–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Guo, Y.; et al. Avian influenza virus infection risk in humans with chronic diseases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, Y.; Su, R.; Qi, H.; Deng, W.; Sun, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; et al. N-glycan profiles in H9N2 avian influenza viruses from chicken eggs and human embryonic lung fibroblast cells. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, J.; Shu, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Yan, W.; Zhao, B.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; et al. The glycopatterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a potential biomarker for its carbapenem resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Shu, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, L.; Yu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, J.; et al. Machine learning reveals salivary glycopatterns as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, T.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, B.; Chen, W.; Sun, S.; Li, Z. Purification of sialoglycoproteins from bovine milk using serotonin-functionalized magnetic particles and their application against influenza A virus. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6911–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Yu, H.; Du, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Li, Z. Identification of N- and O-linked glycans recognized by AAL in saliva of patients with atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Ren, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, S.; Yue, L.; Li, X.; Yin, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Hui, Z.; et al. Beneficial or detrimental: Recruiting more types of benign cases for cancer diagnosis based on salivary glycopatterns. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yu, H.; Ma, T.; Yang, F.; Jia, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Niu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Analysis of Glycosphingolipid Glycans by Lectin Microarrays. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10663–10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Ma, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yu, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Z. The Abnormal Glycopatterns of Salivary Glycoproteins in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 637730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.J.; Haire, L.F.; Stevens, D.J.; Collins, P.J.; Lin, Y.P.; Blackburn, G.M.; Hay, A.J.; Gamblin, S.J.; Skehel, J.J. The structure of H5N1 avian influenza neuraminidase suggests new opportunities for drug design. Nature 2006, 443, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.M.; Shakil, S.; Haneef, M. A simple click by click protocol to perform docking: AutoDock 4.2 made easy for non-bioinformaticians. EXCLI J. 2013, 12, 831–857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohne, A.; Lang, E.; von der Lieth, C.W. SWEET—WWW-based rapid 3D construction of oligo- and polysaccharides. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Seiler, J.P.; Rehg, J.E.; Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. Effect of neuraminidase inhibitor-resistant mutations on pathogenicity of clade 2.2 A/Turkey/15/06 (H5N1) influenza virus in ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Du, H.; Shu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Jia, Z.; Niu, L.; et al. Identification of abnormal fucosylated-glycans recognized by LTL in saliva of HBV-induced chron-ic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Y.-M.; Farnsworth, A.; Li, X.; Cyr, T.D. Topological N-glycosylation and site-specific N-glycan sulfation of influenza proteins in the highly expressed H1N1 candidate vaccines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.L.; Lipman, D.J.; Nikolskaya, A.; Wolf, Y.I. Evolutionary dynamics of N-glycosylation sites of influenza virus hemagglutinin. PLoS Curr. 2009, 1, RRN1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, A.; Nagae, M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Analysis of protein landscapes around N-glycosylation sites from the PDB repository for under-standing the structural basis of N-glycoprotein processing and maturation. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Lin, J. The Mechanism by which 146-N-Glycan Affects the Active Site of Neuraminidase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lambert, J. Clade-specific genes and the evolutionary origin of novelty; new tools in the toolkit. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 145, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youk, S.; Lee, D.H.; Ferreira, H.L.; Afonso, C.L.; Absalon, A.E.; Swayne, D.E.; Suarez, D.L.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J. Rapid evolution of Mexican H7N3 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in poultry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, H.; Shu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. N-Glycan Profiles of Neuraminidase from Avian Influenza Viruses. Viruses 2024, 16, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020190
Chen W, Ma T, Liu S, Zhong Y, Yu H, Shu J, Wang X, Li Z. N-Glycan Profiles of Neuraminidase from Avian Influenza Viruses. Viruses. 2024; 16(2):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020190
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wentian, Tianran Ma, Sinuo Liu, Yaogang Zhong, Hanjie Yu, Jian Shu, Xiurong Wang, and Zheng Li. 2024. "N-Glycan Profiles of Neuraminidase from Avian Influenza Viruses" Viruses 16, no. 2: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020190
APA StyleChen, W., Ma, T., Liu, S., Zhong, Y., Yu, H., Shu, J., Wang, X., & Li, Z. (2024). N-Glycan Profiles of Neuraminidase from Avian Influenza Viruses. Viruses, 16(2), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16020190





