UBL5 and Its Role in Viral Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Expression and Structure of the UBL5 Protein
3. UBL5 in Pre-mRNA Splicing
4. UBL5 in the Fanconi Anemia (FA) Pathway
5. UBL5 in mtUPR
6. UBL5 in ER Stress Response
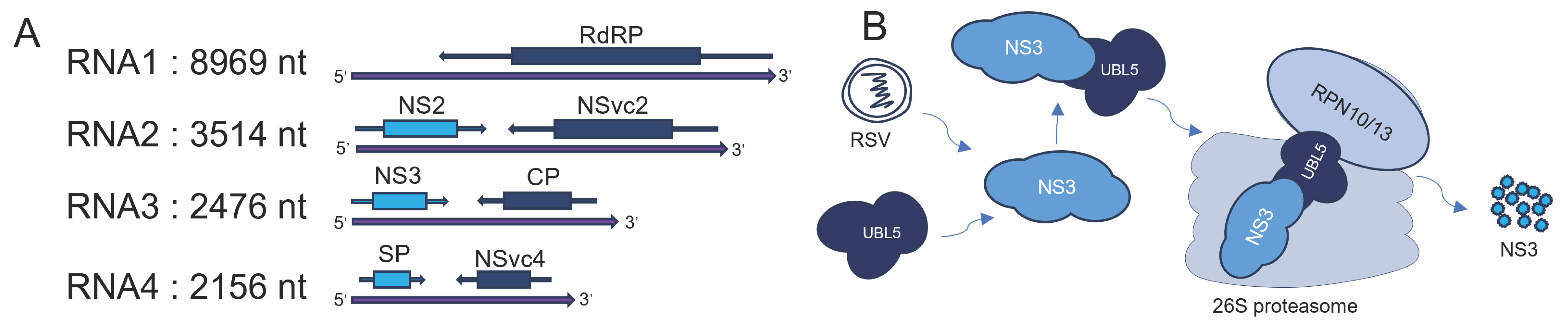
7. UBL5 in Viral Infections
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swatek, K.N.; Komander, D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolathur, K.K.; Mallya, S.; Barve, S.; Bojja, S.L.; Wagle, M.M. Moonlighting functions of the ubiquitin-like protein, Hub1/UBL-5. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2023, 162, 106445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappadocia, L.; Lima, C.D. Ubiquitin-like Protein Conjugation: Structures, Chemistry, and Mechanism. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanarat, S. UBL5/Hub1: An Atypical Ubiquitin-Like Protein with a Typical Role as a Stress-Responsive Regulator. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentsch, S.; Pyrowolakis, G. Ubiquitin and its kin: How close are the family ties? Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhachoo, J.S.; Garvin, A.J. SUMO and the DNA damage response. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.T.; Lee, A.; Kho, C. Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Proteins in Cancer, Neurodegenerative Disorders, and Heart Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, E.; Falqui, M.; Sin, L.; McGrail, J.P.; Perdiguero, B.; Coloma, R.; Marcos-Villar, L.; Tárrega, C.; Esteban, M.; Gómez, C.E.; et al. Unveiling the Multifaceted Roles of ISG15: From Immunomodulation to Therapeutic Frontiers. Vaccines 2024, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramelot, T.A.; Cort, J.R.; Yee, A.A.; Semesi, A.; Edwards, A.M.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Kennedy, M.A. Solution structure of the yeast ubiquitin-like modifier protein Hub1. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2003, 4, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.S.; Koop, B.F.; Raymond, V.; Walter, M.A. Isolation of a Ubiquitin-like (UBL5) Gene from a Screen Identifying Highly Expressed and Conserved Iris Genes. Genomics 2001, 71, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.K.; Ammon, T.; Popowicz, G.M.; Krajewski, M.; Nagel, R.J.; Ares, M.; Holak, T.A.; Jentsch, S. Role of the ubiquitin-like protein Hub1 in splice-site usage and alternative splicing. Nature 2011, 474, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, T.; Huang, Q.; Janis, R.S.; Liu, Z.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Reilly, R.M. Structural analysis of UBL5, a novel ubiquitin-like modifier. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Nie, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, A. 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene causes mitochondrial toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans by affecting electron transport. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svagusa, T.; Sikiric, S.; Milavic, M.; Sepac, A.; Seiwerth, S.; Milicic, D.; Gasparovic, H.; Biocina, B.; Rudez, I.; Sutlic, Z.; et al. Heart failure in patients is associated with downregulation of mitochondrial quality control genes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 53, e14054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozaoglu, K.; Curran, J.E.; Elliott, K.S.; Walder, K.R.; Dyer, T.D.; Rainwater, D.L.; VandeBerg, J.L.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Collier, G.R.; Zimmet, P. Association of genetic variation within UBL5 with phenotypes of metabolic syndrome. Hum. Biol. 2006, 78, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jowett, J.B.; Elliott, K.S.; Curran, J.E.; Hunt, N.; Walder, K.R.; Collier, G.R.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Blangero, J. Genetic variation in BEACON influences quantitative variation in metabolic syndrome-related phenotypes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sentinelli, F.; Romeo, S.; Cambuli, V.; Cossu, E.; Cavallo, M.; Zavarella, S.; Spoletini, M.; Buzzetti, R.; Baroni, M. Identification of sequence variants in the UBL5 (ubiquitin-like 5 or BEACON) gene in obese children by PCR-SSCP: No evidence for association with obesity. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 21, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüders, J.; Pyrowolakis, G.; Jentsch, S. The ubiquitin-like protein HUB1 forms SDS-resistant complexes with cellular proteins in the absence of ATP. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammon, T.; Mishra, S.K.; Kowalska, K.; Popowicz, G.M.; Holak, T.A.; Jentsch, S. The conserved ubiquitin-like protein Hub1 plays a critical role in splicing in human cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Kumar, V.; Dybkov, O.; Will, C.L.; Urlaub, H.; Stark, H.; Lührmann, R. Cryo-EM analyses of dimerized spliceosomes provide new insights into the functions of B complex proteins. EMBO J. 2024, 43, 1065–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varikkapulakkal, A.; Ghosh, A.; Mishra, S.K. Broader roles of the ubiquitin-like protein Hub1 indicated by its yeast two-hybrid interactors. MicroPubl. Biol. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. Spliceosome Structure and Function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 3, a003707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M.C.; Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. The Spliceosome: Design Principles of a Dynamic RNP Machine. Cell 2009, 136, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordin, O.; Beggs, J.D. RNA helicases in splicing. RNA Biol. 2014, 10, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordin, O.; Hahn, D.; Beggs, J.D. Structure, function and regulation of spliceosomal RNA helicases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustino, N.A.; Cooper, T.A. Pre-mRNA splicing and human disease. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes, M.; Sanford, B.L.; Comiskey, D.F.; Chandler, D.S. RNA Splicing and Disease: Animal Models to Therapies. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaduman, R.; Chanarat, S.; Pfander, B.; Jentsch, S. Error-Prone Splicing Controlled by the Ubiquitin Relative Hub1. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 423–432.e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-Z.; Newnham, C.M.; Kameoka, S.; Huang, T.; Konarska, M.M.; Query, C.C. Prp5 bridges U1 and U2 snRNPs and enables stable U2 snRNP association with intron RNA. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantham, L.; Kerr-Bayles, L.; Godde, N.; Quick, M.; Webb, R.; Sunderland, T.; Bond, J.; Walder, K.; Augert, G.; Collier, G. Beacon interacts with cdc2/cdc28-like kinases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, Y.; Letwin, K.; Tannock, L.; Bernstein, A.; Pawson, T. A mammalian protein kinase with potential for serine/threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation is related to cell cycle regulators. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Fu, X.-D. Regulation of splicing by SR proteins and SR protein-specific kinases. Chromosoma 2013, 122, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z. Serine/arginine-rich splicing factors: The bridge linking alternative splicing and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Gapsys, V.; Kim, H.-Y.; Bessonov, S.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Möhlmann, S.; Klaukien, V.; Ficner, R.; Becker, S.; Urlaub, H.; et al. Phosphorylation Drives a Dynamic Switch in Serine/Arginine-Rich Proteins. Structure 2013, 21, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermoud, J.E.; Cohen, P.T.; Lamond, A.I. Regulation of mammalian spliceosome assembly by a protein phosphorylation mechanism. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 5679–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.; Miotto, B.; Saint-Ruf, C.; Said, M.; Barra, V.; Nähse, V.; Ravera, S.; Cappelli, E.; Naim, V. FANCD2 modulates the mitochondrial stress response to prevent common fragile site instability. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; Mailand, N. Ubiquitin-like proteinUBL 5 promotes the functional integrity of the Fanconi anemia pathway. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.; Varmark, H.; Vitting-Seerup, K.; Beli, P.; Waage, J.; Hakobyan, A.; Mistrik, M.; Choudhary, C.; Rohde, M.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; et al. UBL5 is essential for pre-mRNA splicing and sister chromatid cohesion in human cells. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaldi, R.; Sarangi, P.; D’Andrea, A.D. The Fanconi anaemia pathway: New players and new functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, A.D.; Grompe, M. The Fanconi anaemia/BRCA pathway. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zong, R.; Tan, K. The mitochondrial unfolded protein response: A multitasking giant in the fight against human diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 81, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, C.; Haynes, C.M.; Yang, Y.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Ubiquitin-Like Protein 5 Positively Regulates Chaperone Gene Expression in the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response. Genetics 2006, 174, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, C.M.; Petrova, K.; Benedetti, C.; Yang, Y.; Ron, D. ClpP Mediates Activation of a Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response in C. elegans. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, D. Intestinal mitochondrial unfolded protein response induced by nanoplastic particles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hawkridge, A.M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Mangrum, J.B.; Hassan, Z.H.; He, T.; Blat, S.; Guo, C.; Zhou, H.; et al. Ubiquitin-like protein 5 is a novel player in the UPR–PERK arm and ER stress–induced cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, B.W.; Tsai, J.H. Biology and molecular biology of viruses in the genus Tenuivirus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1998, 36, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Characterization and subcellular localization of an RNA silencing suppressor encoded by Rice stripe tenuivirus. Virology 2009, 387, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Shi, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Sun, F.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Qin, Q.; et al. Rice stripe virus NS3 protein regulates primary miRNA processing through association with the miRNA biogenesis factor OsDRB1 and facilitates virus infection in rice. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lin, L.; Lu, Y.; Peng, J.; Zheng, H.; Yang, Q.; Rao, S.; Wu, G.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Ubiquitin-Like protein 5 interacts with the silencing suppressor p3 of rice stripe virus and mediates its degradation through the 26S proteasome pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.-X.; Wang, X.-Q.; Liu, X.-F. NS1: A Key Protein in the “Game” Between Influenza A Virus and Host in Innate Immunity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 670177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Nemeroff, M.; Krug, R.M. The influenza virus NS1 protein binds to a specific region in human U6 snRNA and inhibits U6-U2 and U6-U4 snRNA interactions during splicing. RNA 1995, 1, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kjems, J.; Sharp, P.A. The basic domain of Rev from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 specifically blocks the entry of U4/U6.U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in spliceosome assembly. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4769–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Fan, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Wen, M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. MVIP: Multi-omics portal of viral infection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D817–D827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, L.; He, Y.; Sui, Y.; Feng, X.; Qian, X.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Z. UBL5 and Its Role in Viral Infections. Viruses 2024, 16, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121922
Xia L, He Y, Sui Y, Feng X, Qian X, Liu Y, Qi Z. UBL5 and Its Role in Viral Infections. Viruses. 2024; 16(12):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121922
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Liancheng, Yanhua He, Yifan Sui, Xijia Feng, Xijing Qian, Yangang Liu, and Zhongtian Qi. 2024. "UBL5 and Its Role in Viral Infections" Viruses 16, no. 12: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121922
APA StyleXia, L., He, Y., Sui, Y., Feng, X., Qian, X., Liu, Y., & Qi, Z. (2024). UBL5 and Its Role in Viral Infections. Viruses, 16(12), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121922





