Abstract
In recent years, numerous viruses have been identified from ticks, and some have been linked to clinical cases of emerging tick-borne diseases. Chinese northeast frontier is tick infested. However, there is a notable lack of systematic monitoring efforts to assess the viral composition in the area, leaving the ecological landscape of viruses carried by ticks not clear enough. Between April and June 2017, 7101 ticks were collected to perform virus surveillance on the China–North Korea border, specifically in Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian. A total of 2127 Ixodes persulcatus were identified. Further investigation revealed the diversity of tick-borne viruses by transcriptome sequencing of Ixodes persulcatus. All ticks tested negative for tick-borne encephalitis virus. Transcriptome sequencing expanded 121 genomic sequence data of 12 different virus species from Ixodes persulcatus. Notably, a new segmented flavivirus, named Baishan Forest Tick Virus, were identified, closely related to Alongshan virus and Harz mountain virus. Therefore, this new virus may pose a potential threat to humans. Furthermore, the study revealed the existence of seven emerging tick-borne viruses dating back to 2017. These previously identified viruses included Mudanjiang phlebovirus, Onega tick phlebovirus, Sara tick phlebovirus, Yichun mivirus, and three unnamed viruses (one belonging to the Peribunyaviridae family and the other two belonging to the Phenuiviridae family). The existence of these emerging tick-borne viruses in tick samples collected in 2017 suggests that their history may extend further than previously recognized. This study provides invaluable insights into the virome of Ixodes persulcatus in the China–North Korea border region, enhancing our ongoing efforts to manage the risks associated with tick-borne viruses.
1. Introduction
Ticks, blood-sucking arthropods, have the ability to parasitize a wide range of animals, such as humans, livestock, and poultry [1]. Notably, ticks play a significant role as carriers and transmitters of viruses, potentially causing diseases in humans and other mammals through their blood-feeding activities. Ixodes persulcatus is a common species of tick and is one of the primary vectors for tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) [2]. TBEV can lead to tick-borne encephalitis, a condition that poses a threat to the human central nervous system. Globally, there are around 10,000–12,000 reported cases of tick-borne encephalitis each year [3].
Furthermore, I. persulcatus has been identified as a carrier of viruses from at least seven different virus families, including Peribunyaviridae, Nairoviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, Phenuiviridae, Reoviridae, Flaviviridae, and Phenuiviridae [4,5]. Some of these viruses, such as TBEV and Powassan virus (POWV), are closely associated with human diseases. Although the transmission efficiency of tick-borne viruses is not as high as that of respiratory viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 or influenza virus, the diseases caused by tick-borne viruses still impose a significant burden on affected patients.
Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian, situated in northeastern China, border the neighboring region of North Korea. Located within the transnational area of Changbai Mountain, these border cities are characterized by a temperate monsoon climate and is abundant in forests and wildlife resources. These environmental characteristics provide favorable conditions for tick proliferation and the circulation of tick-borne viruses [6]. TBEV has been prevalent in this region for a considerable time [7,8]. Additionally, SFTSV, one of the main tick-borne viruses in central and east China, has also been found [9]. It can cause severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with a mortality rate of 10–15% [10]. Moreover, the discovery of novel tick-borne viruses, including Alongshan virus (ALSV) [11], Songling virus (SGLV) [12] and Antu virus (ATV) [13] that may pose risks for human health, was first reported in the nearby area. Prior investigations have already revealed a notable diversity of tick-borne viruses, highlighting the persistent threat posed by tick-borne diseases. Nevertheless, the continuous identification of new tick-borne viruses also suggests that routine surveillance efforts may not be adequately comprehensive. Therefore, it is crucial for additional research to obtain a deeper understanding of the ecological landscape of tick-borne viruses in this border region.
Metatranscriptomics is a powerful analytical approach that utilizes high-throughput sequencing to study the total RNA content of samples. This method offers significant advantages in terms of throughput and unbiased analysis, enabling the comprehensive analysis of pathogen information and enhancing our understanding of the virosphere. In recent years, the application of metatranscriptomics has greatly expanded our understanding of viruses, with the number of known viruses increasing from thousands to tens of thousands [14,15]. This advancement has encompassed diverse domains, including mammals [16], arthropods [17], and marine resources [18]. Furthermore, metatranscriptomics has played a crucial role in tracing the origins of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic [19].
Transcriptomics methods have been valuable in the study of tick-borne viruses, leading to the identification of numerous new viruses [5]. While many of these newly identified viruses have not been detected in human populations, they belong to viral families capable of infecting vertebrates [5,20]. These findings have significantly updated our understanding of the diversity of viruses carried by ticks and have contributed to clinical diagnosis. A compelling example is the identification of Beiji nairovirus in questing I. persulcatus before it caused clinical illness in patients [21]. Therefore, the continued utilization of metatranscriptomics to explore the virome of I. persulcatus is a highly worthwhile effort that holds great potential for further discoveries.
In this study, we utilized metatranscriptomics to investigate the virome of I. persulcatus on the China–North Korea border. The object of this study was to analyze the diversity of the virome carried by I. persulcatus and to identify and characterize RNA viruses that have the potential to infect humans or other mammals. Additionally, we aimed to gain insights into the early ecology of newly discovered tick-borne viruses. We expect that these data provide valuable information that can contribute to disease prevention and control efforts in the China–North Korea border region. Understanding the composition and characteristics of the tick virome can assist the identification and surveillance of potential viral threats, thus enhancing preparedness and response strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ticks Collection and Sample Processing
Between April and June 2017, comprehensive tick collection was carried out in Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian, located in Jilin Province, China (Figure 1A). The collection process involved gathering from various sources, including free-living ticks found in forests and grasslands, as well as ticks parasitizing on cattle and sheep. Free-living ticks were collected by dragging a flannel flag over vegetation. Parasitizing ticks were collected from animals by using tweezers. The collected ticks were then subjected to identification and classification by experienced entomologists. Approximately ten ticks of the same species were placed into a tube. The ticks were kept alive during transportation to the laboratory, then promptly stored at −80 °C for subsequent analysis and investigation.
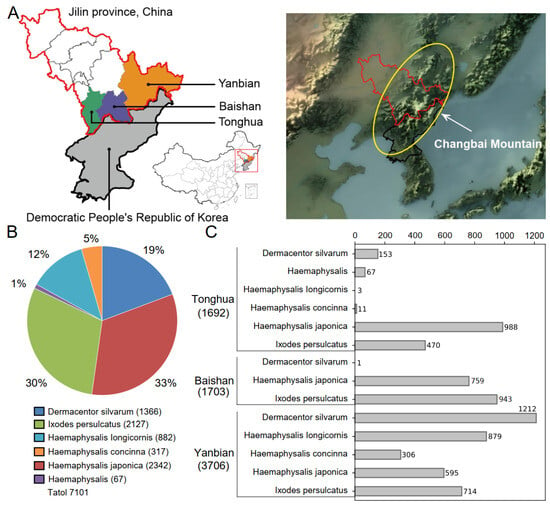
Figure 1.
Overview of tick sample collection. (A) Location of tick collection (the map resource is from http://datav.aliyun.com/portal/school/atlas/area_selector (accessed on 12 April 2023), map approval number is GS Jing(2022)1061). The yellow circle in the topographic map shows the Changbai Mountain. (B) The number and proportion of different tick species. (C) Statistics of tick species collection by regions.
2.2. RNA Extraction
To process the collected ticks, they were rinsed 3 times with PBS. Then, they were mixed with a solution of 5% penicillin and streptomycin in Minimum Essential Medium (Gibco, America). Next, the ticks were ground using a QIAGEN TissueLyserII (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) with 5 mm steel beads at a frequency of 25 Hz for 3 min. After grinding, the tick specimens were centrifuged at 4 °C and 20,000× g for 30 min. The supernatant was transferred to sterile EP tubes, ensuring that no particulate matter was transferred. Total RNA extraction and purification were carried out using a CqEx-DNA/RNA virus (CDC) kit (TIANLONG, Xi’an, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality of the extracted nucleic acid was evaluated using a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer (Thermo Fisher, Eugene, OR, USA).
2.3. Library Construction, and Sequencing
The construction of RNA sequencing libraries was carried out using the VAHTS Universal V8 RNA-seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). After library construction, paired-end sequencing with a read length of 150 bp was performed using the NovaSeq 6000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). All sequencing operations, including library loading, cluster generation, and sequencing, were conducted based on the protocols recommended by the manufacturer.
2.4. Virus Discovery and Viral Abundance Estimation
After sequencing, the quality of each library was evaluated using FastQC v0.11.9 [22]. To ensure high-quality data for downstream analyses, Trimmomatic 0.39 was used for quality control, including the elimination of adapters and low-quality sequences [23]. To eliminate host sequences, Bowtie2 was used in an “end-to-end” mode [24], utilizing the GenBank sequence (accession number: GCA_013358835.2). The remaining reads were de novo assembled into contigs using Megahit v1.2.9 [25]. The assembled contigs were then compared to the GenBank nr database using Diamond blastx with a threshold of 1E-5. The parameter setting of “more-sensitives” was employed to enhance sensitivity during the comparison [26]. Species annotation was performed using Megan [27]. Then, viral contigs were extracted from the assembly for further analysis. The quality of these contigs was evaluated by using Quast v5.2.0 [28]. To assess the abundance of viruses, Salmon v1.4.0 was used to quantify the transcripts per million (TPM) and read counts of the virus contigs [29]. A Python script was used to merge the abundance of the same family or species within the same library, generating viral operational taxonomic unit (vOTU) tables for further analysis and interpretation.
2.5. Genome Assembly
This study solely focuses on RNA viruses. The open reading frame (ORF) regions within the viral contigs were predicted by using Prokka v1.14.6 [30]. Next, the predicted ORF regions were compared to the RdRp-scan 0.90 database using Diamond blastx to gather information specifically related to RNA viruses [31]. To assemble the complete viral genomes, Bowtie2 was utilized using the corresponding reference sequence (Table S1).
To identify potential novel virus species, a threshold of <90% amino acid identity for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) was utilized. RdRp-scan 0.90 and the online blast tool (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) were used for double confirmation and validation. To ensure accurate assembly, the reads were mapped back to the assembled contigs using Bowtie2.
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
To examine the evolutionary characteristics of tick-borne viruses, we performed phylogenetic analysis. Sequences from external sources were obtained from the NCBI database, and their sequence information was recorded (Tables S2 and S3). Multiple sequence alignment was performed using Mafft v7.450 software [32]. Genetic distances were calculated using MEGA7 [33]. Maximum likelihood (ML) trees were constructed using IQ-TREE software version 1.6.12 [34]. The most appropriate substitution models were determined using ModelFinder in IQTREE [35]. The resulting phylogenetic tree was visualized using Chiplot (www.chiplot.online (accessed on 3 July 2023)) [36].
2.7. Statistical Analyses and Visualization
Kruskal–Wallis test was performed using the statannotations library in Python 3.7. Alpha diversity measures, including observed richness and Shannon index, were calculated using the vegan package in R. Beta diversity analysis, employing non-metric multi-dimensional scaling (NMDS), was also performed based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix using the vegan package in R [37]. Box plots, scatter plots, and bar charts were generated using the Seaborn library. The heatmap was created using the PyComplexHeatmap library. Stacked plots were created using the Pandas library and the venn diagram was created using the Venn library in Python 3.7.
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Sample Collection
From April to June 2017, a total of 7101 ticks were collected in Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian of Jilin Province, China (Table S4). These ticks belonged to five different identified species, with their proportions listed in descending order: Haemaphysalis japonica (ticks = 2342, 33%), I. persulcatus (ticks = 2127, 30%), Dermacentor silvarum (ticks = 1366, 19%), Haemaphysalis iongicornis (ticks = 882, 12%), and Haemaphysalis concinna (ticks = 317, 5%). There were also a small number of unidentified Haemaphysalis ticks (ticks = 67, 1%) (Figure 1B). Among the three regions studied, both Tonghua and Yanbian were found to have all five species of ticks, while Baishan only had three species, namely D. silvarum, H. japonica, and I. persulcatus (Figure 1C).
3.2. Overview of RNA Sequencing of I. persulcatus
In subsequent investigations, we specifically focused on I. persulcatus, given its potential to harbor novel viruses capable of infecting humans. To facilitate library preparation and sequencing, whole ticks of I. persulcatus were grouped into pools consisting of 20–75 individuals per tube. A total of 53 libraries were generated, with 13 pools from Tonghua, 19 from Baishan, and 21 from Yanbian. Each library yielded a range of 3,709,032–37,987,814 clean reads, and within these reads, there were 3213–3,380,664 viral reads (Table S5). The proportion of viral reads in the clean reads varied from 0.03% to 13.90%. Following assembly, a total of 157,766 viral contigs (>500 bp) were obtained, with an average N50 length of 1349 bp (Table S5).
3.3. Diversity of I. persulcatus Virome in Tonghua, Baishan and Yanbian
To examine the viral load and diversity of ticks from the three regions, a comparative analysis was conducted on the viral reads. The proportion of viral reads in Baishan was slightly higher (5.2%) than in the other two areas, but the difference was not statistically significant (Kruskal–Wallis test, p > 0.05). The number and proportion of viral reads did not show a significant difference among the three regions (Figure 2A and Table S6).
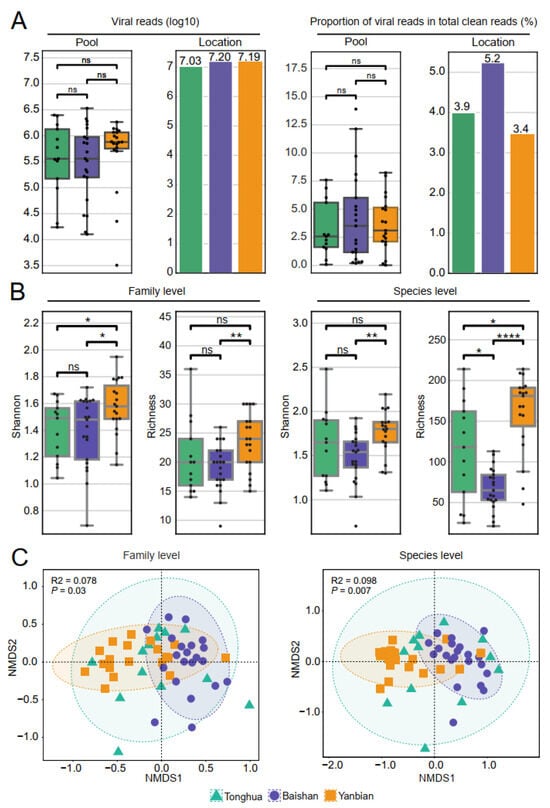
Figure 2.
Diversity and composition of the tick virome. (A) Counts and proportions of virus reads in each library or region, with each dot representing one library. Alpha diversity and beta diversity analyses at family and species level based on vOTUs. (B) Alpha diversity analysis of virus reads from I. persulcatus in Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian. Kruskal–Wallis test: p < 1 (ns), p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.0001 (****). (C) NMDS analysis based on Bray–Curtis distance, reflecting the viral composition characteristics among the three regions. Green, purple, and orange represent Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian respectively.
To further examine the characteristics of virus diversity in ticks from the three regions, we performed alpha and beta diversity analysis at the family and species levels based on viral operational taxonomic units (vOTUs). The Shannon index and observed richness analysis indicated the degree of diversity within each group. Ticks from Yanbian showed significantly higher viral diversity compared to those from Baishan (Kruskal–Wallis test, p-values ranging from 5.695 × 10−6 to 3.130 × 10−2) at the family and species levels. The viral diversity in ticks from Yanbian was slightly higher than in ticks from Tonghua (Kruskal–Wallis test, p-values ranged from 2.868 × 10−2 to 1.987 × 10−1) (Figure 2B and Table S6). However, there was no significant difference in viral diversity between ticks from Baishan and Tonghua (all three indices showed p > 0.05). Beta diversity analysis, specifically NMDS, based on the Bray–Curtis distance was performed to visualize the differences in species composition. Ticks from Baishan and Yanbian showed distinct clustering patterns (Figure 2C). The Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) test confirmed significant differences in viral diversity between Baishan and Yanbian at both the family level (p < 0.05 and R2 = 0.09) and the species level (p < 0.05 and R2 = 0.10) (Table S6).
3.4. Vertebrate-Associated RNA Virus Families
In this study, 7 RNA virus families that may infect humans or other mammals (Figure 3A) were identified among the vOTUs, including Chuviridae, Flaviviridae, Nairoviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, Peribunyaviridae, Phenuiviridae, and Phenuiviridae. Among these families, Nairoviridae showed a high abundance in all three regions (Figure 3A,B).
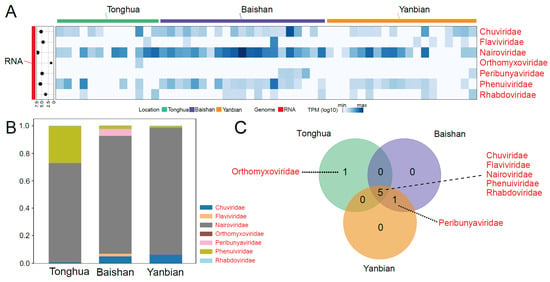
Figure 3.
The abundance and diversity of the vertebrate-associated RNA virome. (A) A heatmap represents the abundance of viral families in TPM levels, while the scatter plot on the left represents the total number of reads (log10) for each viral family. The color bar indicates the region or genome type. (B) A stacked bar chart displays the relative abundance of viral families in three different locations. (C) A Venn diagram illustrates the viral families shared or unique among three different locations. The red font represents RNA viruses.
The Venn diagram illustrates the overlap of virus families among the three regions. Five virus families (Chuviridae, Flaviviridae, Nairoviridae, Phenuiviridae, and Phenuiviridae) were shared among the three regions (Figure 3C). Peribunyaviridae and Orthomyxoviridae were sporadically identified (Figure 3C). Overall, the RNA virus families with the potential to infect humans or other mammals showed consistency across the three locations along the China–North Korea border.
3.5. Characteristics of New Tick-Borne Viral Genome Phylogeny
The analysis based on vOTUs tends to reflect the viral environment encountered by ticks, but it may mistakenly attribute viral presence in the host’s blood to tick-borne transmission, when in reality, it may only be transient. To gain better insights into actively replicating viruses within tick hosts at the time of sampling and to identify novel viruses, we attempted whole-genome assembly for RNA viruses. A total of 121 complete or near-complete genomes of 12 viruses from 6 families were identified. For segmented viruses, we obtained at least the sequence of the gene containing RdRp.
Among the identified viruses, we found 2 species belonging to the Jingmenvirus of Flaviviridae (Figure 4A). One of them was identified as the Yanggou tick virus (YGTV). The nucleotide similarities between the new Yanggou tick virus and the previously identified strain were to be 94.9–96.5% for Segment 1, 94.7–97.2% for Segment 2, 93.3–96.7% for Segment 3, and 94.5–95.9% for Segment 4 (Table S7). The other virus was considered a novel virus and tentatively named the Baishan forest tick virus (BSFTV) (Figure 4B,C). We identified four gene segments belonging to BSFTV in the sequencing data. Blast analysis revealed that these gene sequences share close phylogenetic relationships with Alongshan virus and Harz mountain virus. At the nucleotide level, the highest similarity was observed between Segment 1 of BSFTV and Segment 1 of Harz mountain virus (strain NLGAP7), with a similarity of 76.6% (Query cover 92%). For Segment 2, Segment 3, and Segment 4, BSFTV showed the closest relationship with ALSV. The similarities between BSFTV and ALSV (strain H3) were 74.7% (query cover 80%), 76.1% (query cover 89%) and 76.8% (query cover 91%).
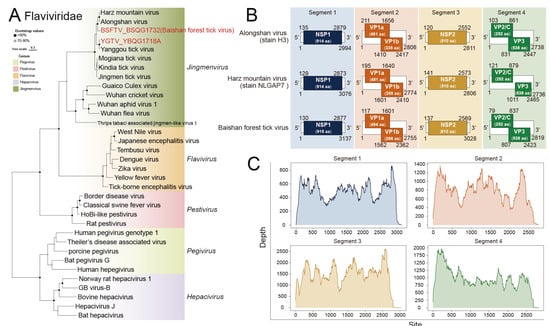
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of the novel strains of Flaviviridae. (A) ML tree of representative viruses of Flaviviridae based on the RdRp region. (B) The genomic structure and protein sizes (sequence length in given number of amino acids (aa) per protein) of Baishan forest tick virus, Alongshan virus (strain H3), and Harz mountain virus (strain NLGAP7). (C) Sequencing depth plot of Baishan forest tick virus.
Two viruses belonging to the Nairoviridae family were identified (Figure 5). One of them is the Yezo virus (YEZV), which falls under the genus Orthonairovirus. The nucleotide similarities of the S, M, and L genes of three new YEZV strains and previously identified strains ranged from 92.4 to 99.9%, 96.1 to 99.1%, and 95.1 to 99.0%, respectively (Table S7). The ML tree revealed that the three new strains belonged to different sub-lineages in the M and L genes, indicating a certain level of diversity of YEZV in the region (Figure S1). The other identified virus was Beiji nairovirus, which accounted for nearly half of the libraries with a total of 25 strains. The nucleotide similarities of the S gene and L gene between the new strain and previously identified strains were 94.9% to 99.3% and 99.16% to 99.9%, respectively (Table S7). In the ML tree, these newly discovered viruses and previous Beiji nairoviruses formed two distinct branches in the S segment, but were intermixed in the L segment (Figure S1).
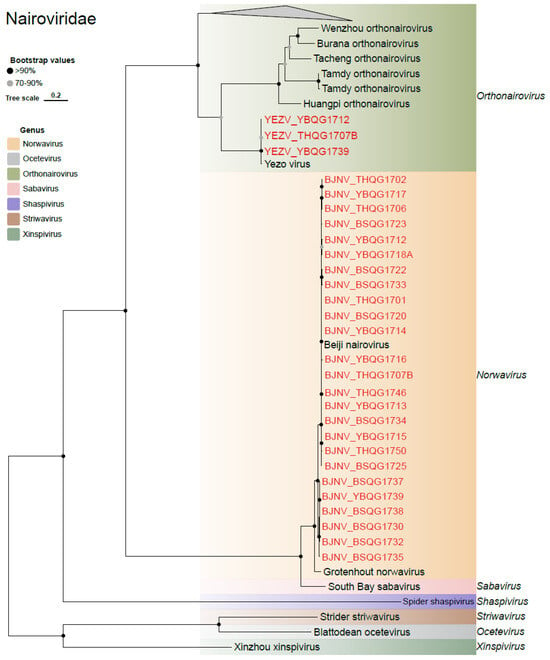
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of the novel strains of Nairoviridae. ML tree of representative viruses of Nairoviridae based on the RdRp region.
Four viruses belonging to the Phenuiviridae family were identified, namely Sara tick phlebovirus (STPV), Onega tick phlebovirus (OTPV), Mukawa virus (MKWV), and Mudanjiang phlebovirus (MDJV) (Figure 6). STPV was first detected in I. persulcatus ticks collected in 2018 (Table 1). This study identified 20 new strains of STPV, accounting for 37.7% (20/53) of the total libraries. The nucleotide similarity of the S gene between these viruses and previously identified strains was greater than 99.0%, while the nucleotide similarity of the L gene ranged from 92.9% to 99.9% (Table S7). Moreover, these new strains clustered together with the previous strains without forming new lineages, indicating a close relationship between the strains from 2017 and the previously discovered ones. Nine new MKWV strains were detected, bridging the gap between previously distant strains and suggesting the crucial role of MKWV in viral evolution in this region. The nucleotide similarities of the S, M, and L genes between the new and previous strains of MKWV were 93.2–97.3%, 94.5–99.9%, and 91.8–96.8%, respectively (Table S7). OTPV and MDJV were newly discovered viruses detected in I. persulcatus samples in 2018 and 2021, respectively (Table 1). In this study, three new strains of OTPV and three new strains of MDJV were identified in I. persulcatus samples from 2017, indicating the early presence of these two viruses. The nucleotide similarities between the new OTPVs and the previous strains in the S gene and the L gene were 98.3–99.8% and 98.3–99.9%, respectively (Table S7). The nucleotide similarities between the new MDJVs and the previous strains in the S gene, M gene, and L gene were 95.4–99.2%, 99.6%, and 94.9–99.0%, respectively (Table S7).
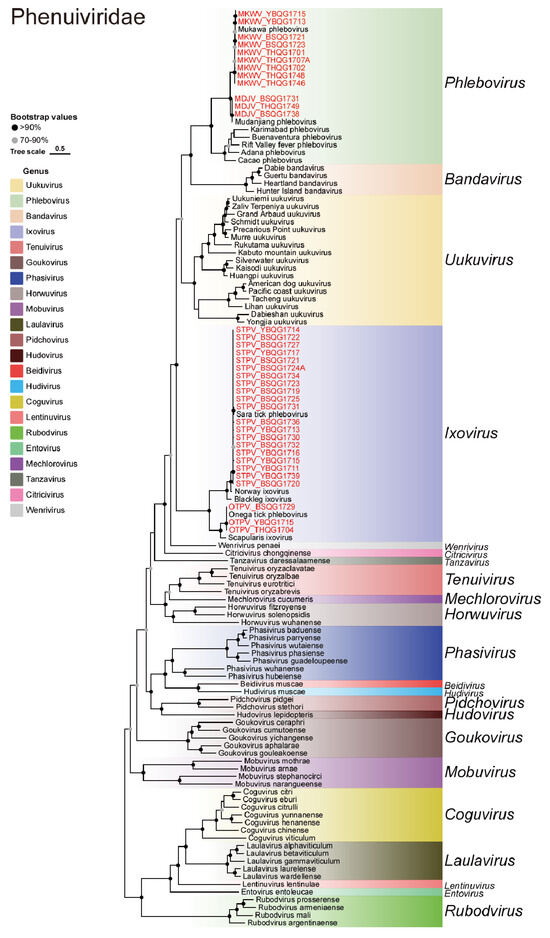
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic analysis of the novel strains of Phenuiviridae. ML tree of representative viruses of Phenuiviridae based on the RdRp region.

Table 1.
Records of virus reporting and host history before this study *.
Yichun mivirus (YCMV), a virus belonging to the Nigecruvirus genus of Chuviridae, was detected in the sequencing data (Figure 7A). YCMV was initially discovered in I. persulcatus ticks in Northeast China in 2020 (Table 1). In this study, eight new strains of YCMV were identified in the I. persulcatus samples from 2017, indicating the presence of this virus in the region even earlier (Figure S2A). The nucleotide similarity between these new strains and the previously identified strains ranged from 98.9% to 99.9% at the whole-genome level (Figure S2A).
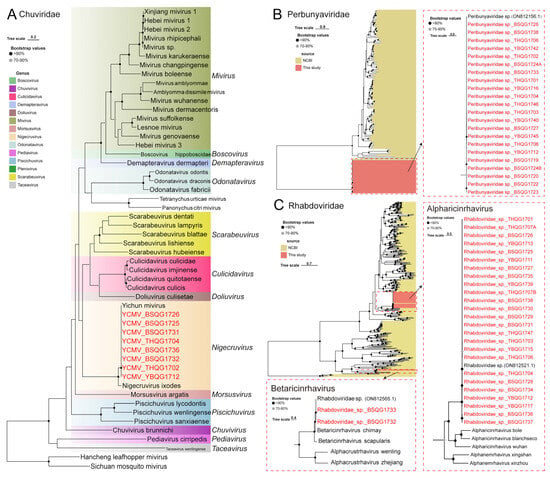
Figure 7.
Phylogenetic analysis of the novel strains of Chuviridae, Perbunyaviridae and Rhabdoviridae. (A) ML tree of representative viruses of Chuviridae based on the RdRp region, (B) ML tree of representative viruses of Perbunyaviridae based on the RdRp region, (C) ML tree of representative viruses of Rhabdoviridae based on the RdRp region.
A large number of Peribunyaviridae-like viruses were also found, with complete L gene sequences of 21 strains. These viruses exhibited high similarity with Peribunyaviridae sp. (ON812156.1) previously detected in ticks in 2019 (Figure 7B). The nucleotide identity of the L genes among this group of viruses was greater than 99.0% (Figure S2B). Although we adopted the previous classification, the phylogenetic tree suggests that these new viruses are more like an outgroup of Peribunyaviridae (Figure S2B).
The sequencing data revealed the presence of two unnamed viruses belonging to Rhabdoviridae family, specifically 25 strains of Alpharicinrhavirus and 2 strains of Betaricinrhavirus (Figure 7C). These two viruses were already detected in samples from 2019 (Table 1). In Alpharicinrhavirus, the nucleotide similarity between the new strains identified in this study and the previously discovered Rhabdoviridae sp. virus from 2019 ranged from 95.8% to 99.9% at the whole-genome level (Figure S8C). As for Betaricinrhavirus, the new strains identified in this study exhibited nucleotide similarity greater than 99.0% with the newly discovered Rhabdoviridae sp. virus in 2019 at the whole-genome level (Figure S8D).
4. Discussion
From April to June 2017, an extensive tick collection was carried out in the border regions between China and North Korea, with a specific focus on Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian. Employing transcriptome sequencing, we thoroughly characterized the viral composition of I. persulcatus. The study encompassed 2127 samples of I. persulcatus ticks, revealing a high abundance and diversity of viruses carried by ticks. Interestingly, we observed differences in the tick-borne virus spectrum among ticks from Tonghua, Baishan, and Yanbian, despite their geographic proximity. Furthermore, our findings suggest that the presence of some emerging tick-borne viruses in northeast China is not isolated but rather commonly found within the tick ecological circle. Through phylogenetic analysis, we discovered that certain viruses in the region play a crucial role in viral evolution and transmission. Importantly, this study extends the earliest known presence of seven emerging tick-borne viruses back to 2017, including MDJV, OTPV, STPV, YCMV and three unnamed viruses from the Peribunyaviridae and Phenuiviridae families.
While differences were identified in the I. persulcatus virome among different regions, no apparent distinction was found for viruses with the potential to infect humans. Although previous metagenomic studies have explored the tick-borne pathogen spectrum in the region [5,6], we provided a more comprehensive understanding of tick-borne virus diversity across the three regions. Alpha and beta diversity analyses revealed that Yanbian shows significantly greater diversity at the viral family and species levels compared to Baishan, and the viral spectrum composition of I. persulcatus also differs between these two regions. Conversely, the geographical characteristics of the tick-borne virus spectrum in Tonghua were less evident. Geographical variations in virus abundance and diversity have also been observed in studies on tick-borne virus diversity in Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia [38]. As ticks themselves lack the ability for long-distance transmission, the viruses they carry are likely acquired from local organisms that they come into contact with. The observed geographical differences in viral spectra encompass viral pathogens in animals, plants, bacteria, and fungi. Notably, the three locations shared most of the known viral families capable of infecting humans, which is expected given the smaller evolutionary divergence between mammals and arthropods compared to other organisms. Overall, administrative regional divisions have not overridden the shaping influence of natural geography when it comes to natural human threats.
In this study, we detected two emerging tick-borne viruses associated with human febrile illnesses [21,39], namely the Yezo virus and the Beiji nairovirus. Fever cases related to Yezo virus have been reported in Japan and China, with YEZV antibodies also detected in wild deer and raccoons in Hokkaido, Japan [39,40]. Currently, YEZV nucleic acid has only been detected in I. persulcatus in China, with a positivity rate of approximately 0.5% [39]. In Japan, YEZV nucleic acid has only been detected in H. megaspinosa, I. ovatus, and I. persulcatus, with an overall positivity rate of 2.1% [40]. Although our study only identified three new YEZV strains with a low positive rate, it is important to note that our pooled sequencing cannot determine the individual tick-level positivity rate. Beiji nairovirus has exclusively been found in northeastern China, with the earliest detection dating back to 2015 in I. persulcatus [6,21,41]. In our study, Beiji nairovirus was detected in 25 out of 53 libraries, indicating a relatively high positivity rate. Our findings demonstrate the presence of the Yezo virus and Beiji nairovirus in the China–North Korea border area in 2017, and these viruses from 2017 share a close phylogenetic relationship with the recently discovered Yezo virus (Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia) and Beiji nairovirus in northeastern China. This suggests that these viruses have likely established stable circulation cycles and may continue to spread in the future. Consequently, it is important for regional managers to be attentive to the diseases that may be caused by these two viruses.
An important finding of our study is the discovery of the novel Baishan forest tick virus, which belongs to Flaviviridae family, and Jingmenviruses genus. BSFTV shows a close genetic relationship with the Alongshan virus and the Harz mountain virus. Typically, Jingmenviruse is known to have four- or five-segment genes. For instance, the Alongshan virus and Harz mountain virus are four-segment viruses [42,43], while the Guaico Culex virus has five segments [44]. In our sequencing libraries, we recovered four segments of the Baishan forest tick virus. It is important to note that virus isolation experiments are the gold standard for confirming the existence of a real virus. However, as of the publication of this article, such experiments have not been successful. Nevertheless, this does not diminish the significance of highlighting the importance of this virus, because Alongshan virus is considered to be associated with febrile illnesses [9], and serological investigations have found ALSV-specific antibodies in sheep and cattle [45]. Therefore, it is possible that BSFTV, which is closely related to ALSV, may also be associated with mammalian diseases. While there is currently insufficient evidence to directly link these viruses to human diseases, it is worth noting that RNA viruses, particularly segmented RNA viruses, can quickly acquire new viral features through mutation or reassortment [46]. As a result, we should remain vigilant regarding the potential evolution of these viruses within the tick population and the future threats they may pose.
There are additional noteworthy phenomena that deserve attention in this study. Consistent with previous studies, we observed that newly tick-borne viruses in China were closely related to strains found in Japan [47]. We also identified some viruses, such as YGTV, that were closely related to Russian strains. The phenomenon of long-distance virus transmission has already been observed, as exemplified by TBEV. TBEV is known to comprise three primary subtypes, each associated with distinct geographical regions: European, Siberian, and Far East. These subtypes have the capacity to induce varying clinical presentations in humans, each with varying morbidity and mortality rates [48]. Furthermore, recent research has unveiled two additional subtypes: the Baikalian subtype, comprising 13 distinct strains identified in eastern Siberia and northern Mongolia, and the Himalayan subtype, isolated in rodents from the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region of China [49,50]. This raises the possibility of similar scenarios occurring in other tick-borne viruses.
Migratory birds are considered one of the pathways for the long-distance transmission of vector-borne viruses [51,52]. The migration route of birds from Japan to Northeast China passes through South Korea and North Korea, while the path from Russia to Northeast China passes through Mongolia [53]. As a consequence, it is conceivable that these viruses may have already expanded their range to intermediary countries, potentially establishing viral reservoirs within these regions. However, definitive evidence would require the detection of the virus within bird samples.
There are certain limitations in this study. We were not able to identify some well-known tick-borne viruses, such as TEBV, SFTSV, and Nairobi sheep disease virus. Moreover, there are other species of tick present in the region, such as D. silvarum, H. concinna, H. japonica, and H. iongicornis. Although we collected tick samples from these species, we did not perform metatranscriptomic sequencing or qRT-PCR testing on them. Undoubtedly, conducting transcriptomic analysis on a wider range of tick samples would provide insights into the spectrum of tick-borne viruses and help us understand the cycling of viruses among ticks, as well as uncover tick species-specific tick-borne viruses. Furthermore, our study did not explore the viral differences between unfed and feeding ticks. This will be the focus of our future work.
Furthermore, the results of metatranscriptomic studies require further experimental validation to accurately reflect the existence and practical threat of the viruses. Additionally, natural environmental changes are influencing tick habitats, which in turn affects the ecology of tick-borne viruses [54]. Therefore, further studies should record the environmental factors in tick activity areas, enabling the use of advanced methods such as mathematical models or machine learning to enhance our understanding of virus transmission [55,56].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study examined the viral spectrum characteristics of I. persulcatus at the China–North Korea border, shedding light on the evolutionary history and potential risks associated with certain viruses. The findings provide valuable reference data for the prevention and control of tick-borne diseases in this region. It is important to note that the emergence of some viruses may have occurred earlier than what was identified in this study. Therefore, it is critical to enhance the monitoring of tick-borne viruses and conduct high-throughput sequencing on tick samples from previous years to better understand the historical ecology of tick-borne viruses. These efforts will support a more comprehensive understanding of the threats posed by tick-borne viruses and aid the development of effective management strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v16010062/s1, Table S1: Reference sequences used for virus genome assembly. Table S2: GenBank accession numbers of RdRp sequences of reconstructing ML trees. Table S3: GenBank accession numbers of sequences used for reconstructing ML trees, similarity analysis, and collecting report time, location, and hosts information for each virus. Table S4: Sample information. Table S5: Details of sequencing data. Table S6: Raw results of statistical analysis. Table S7: The results of genetic distance analysis for each virus. Figure S1: ML trees for each virus found in this study. Figure S2: Similarity matrix of the Yichun mivirus, the Peribunyaviridae sp. and the Rhabdoviridae sp. of Alpharicinrhavirus and Betaricinrhavirus sorted by viral isolation time.
Author Contributions
L.D., Q.W. and H.W. conceived and designed the experiments and were involved in the interpretation of the results and critically read the manuscript. H.S., X.W. and L.D. collected tick samples. R.W., S.L., H.S., Q.Y., C.X. and Y.W. performed the experiments. R.W., X.W., W.Z., K.N., F.L., S.F., Y.H., S.X. and G.L. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. R.W. analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (grant no. 2022YFC2302700).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data generated during the current study are included in the manuscript and/or the Supplementary Data. All sequencing reads have been deposited in the CNCB databases (www.cncb.ac.cn, access on 1 September 2023) under the GSA accession CRA011751. Relevant virus genome sequences have been deposited in the GenBase databases (accession: C_AA030968.1-C_AA031172.1). Additional data related to this article may be requested from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Hongliang Sun and Yanhan Wen come from Changchun Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd. There are no potential commercial interests among authors. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mansfield, K.L.; Jizhou, L.; Phipps, L.P.; Johnson, N. Emerging tick-borne viruses in the twenty-first century. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Vector Control Response 2017–2030; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Shi, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H.; Sun, Y. Diversity of RNA viruses of three dominant tick species in North China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1057977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.B.; Cui, X.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Ye, R.Z.; Wu, Y.Q.; Jiang, J.F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shum, M.H.; Chang, Q.C.; et al. Metavirome of 31 tick species provides a compendium of 1801 RNA virus genomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Sui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.; et al. Extensive diversity of RNA viruses in ticks revealed by metagenomics in northeastern China. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0011017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, F.; Yin, Q.; Liu, W.; Fu, S.; He, Y.; Lei, W.; Xu, S.; Liang, G.; Wang, S.; et al. Epidemiology of tick-borne encephalitis in China, 2007–2018. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.X.; Lai, S.J.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.L.; Liu, K.; Yao, H.W.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.P.; Mu, D.; et al. Mapping the distribution of tick-borne encephalitis in mainland China. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Liang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Jia, L.; et al. Survey of tick species and molecular detection of selected tick-borne pathogens in Yanbian, China. Parasite 2022, 29, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chai, C.; Wang, C.; Amer, S.; Lv, H.; He, H.; Sun, J.; Lin, J. Systematic review of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: Virology, epidemiology, and clinical characteristics. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wang, B.; Wei, F.; Han, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.T.; Yan, Y.; Lv, X.L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.C.; et al. A new segmented virus associated with human febrile illness in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lv, X.L.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.Z.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, L.; Sun, H.T.; Ma, L.X.; Cheng, Z.L.; Shao, J.W.; et al. Identification of a new orthonairovirus associated with human febrile illness in China. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, J.; Song, J.; Yin, Q.; Nie, K.; Xu, S.; He, Y.; Fu, S.; Liang, G.; Wei, Q.; et al. Novel orthonairovirus isolated from ticks near China–North Korea border. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Sadiq, S.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.D.; Shen, J.J.; Chen, H.; Hao, Z.Y.; Wille, M.; Zhou, Z.C.; et al. RNA viromes from terrestrial sites across China expand environmental viral diversity. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Qin, X.C.; Holmes, E.C. Expanding the RNA virosphere by unbiased metagenomics. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.T.; Hou, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Si, W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Xing, G.; et al. Virome characterization of game animals in China reveals a spectrum of emerging pathogens. Cell 2022, 185, 1117–1129.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, N.; Wang, S.; Shi, C.; Yu, p.; Zhao, L.; Huang, D.; Ma, H.; Xiao, S.; Wang, F.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Dynamic surveillance of mosquitoes and their viromes in Wuhan during 2020. Zoonoses 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.A.; Wainaina, J.M.; Dominguez-Huerta, G.; Pelletier, E.; Guo, J.; Mohssen, M.; Tian, F.; Pratama, A.A.; Bolduc, B.; Zablocki, O.; et al. Cryptic and abundant marine viruses at the evolutionary origins of Earth’s RNA virome. Science 2022, 376, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; du Plessis, L.; Liu, Z.; Hill, V.; Kang, M.; Lin, H.; Sun, J.; François, S.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Faria, N.R.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Guangdong Province, China. Cell 2020, 181, 997–1003.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, L.; Shi, W. The human-infection potential of emerging tick-borne viruses is a global public health concern. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wei, Z.; Lv, X.; Han, S.; Wang, Z.; Fan, C.; Zhang, X.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Sui, L.; et al. A new nairo-like virus associated with human febrile illness in China. Emerg. Microbes Infec. 2021, 10, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B.J.B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Reuter, K.; Drost, H.-G. Sensitive protein alignments at tree-of-life scale using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charon, J.; Buchmann, J.P.; Sadiq, S.; Holmes, E.C. RdRp-scan: A bioinformatic resource to identify and annotate divergent RNA viruses in metagenomic sequence data. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y. Metatranscriptomics reveals the diversity of the tick virome in northwest China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0111522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Sui, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Yezo virus infection in tick-bitten patient and ticks, northeastern China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Park, E.; Tatemoto, K.; Sashika, M.; Nakao, R.; Terauchi, Y.; Mizuma, K.; Orba, Y.; Kariwa, H.; et al. A novel nairovirus associated with acute febrile illness in Hokkaido, Japan. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Cai, X.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Fu, L.; Men, X.; Zhu, Y. Virome analysis of ticks and tick-borne viruses in Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, China. Virus Res. 2022, 323, 199006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmant, A.M.G.; Charrel, R.N.; Coutard, B. Jingmenviruses: Ubiquitous, understudied, segmented flavi-like viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 997058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. The discovery of segmented flaviviruses: Implications for viral emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 40, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, J.T.; Wiley, M.R.; Beitzel, B.; Auguste, A.J.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Lindquist, M.E.; Sibley, S.D.; Kota, K.P.; Fetterer, D.; Eastwood, G.; et al. A Multicomponent animal virus isolated from mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wang, W.; Wang, N.N.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, X.; Tana, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Prevalence of the emerging novel Alongshan virus infection in sheep and cattle in Inner Mongolia, northeastern China. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, C.R.; Holmes, E.C.; Morens, D.M.; Park, E.C.; Burke, D.S.; Calisher, C.H.; Laughlin, C.A.; Saif, L.J.; Daszak, P. Cross-species virus transmission and the emergence of new epidemic diseases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 72, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Jiang, F.; Luo, Q.; Zong, K.; Dong, L.; Mei, G.; Du, H.; Dong, H.; Song, Q.; Song, J.; et al. Diversity analysis of tick-borne viruses from Hedgehogs and Hares in Qingdao, China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0534022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajkowska, J.; Czupryna, P.; Pancewicz, S.; Adamczyk-Przychodzeń, A.; Kondrusik, M.; Grygorczuk, S.; Moniuszko, A. Fatal outcome of tick-borne encephalitis–a case series. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2011, 45, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhorukov, G.A.; Paramonov, A.I.; Lisak, O.V.; Kozlova, I.V.; Bazykin, G.A.; Neverov, A.D.; Karan, L.S. The Baikal subtype of tick-borne encephalitis virus is evident of recombination between Siberian and Far-Eastern subtypes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Shang, G.; Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. A new subtype of eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus discovered in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, E.; Cecere, J.G.; Iapaolo, F.; Di Gennaro, A.; Sacchi, M.; Savini, G.; Spina, F.; Monaco, F. West Nile and Usutu virus introduction via migratory Birds: A retrospective analysis in Italy. Viruses 2022, 14, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, H.J.; Liefting, Y.; Ibáñez-Justicia, A.; van der Jeugd, H.; van Turnhout, C.A.M.; Stroo, A.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; de Boer, W.F. Spatial risk analysis for the introduction and circulation of six arboviruses in the Netherlands. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, D.L.; Heim, W.; Chowdhury, S.U.; Choi, C.Y.; Ktitorov, P.; Kulikova, O.; Kondratyev, A.; Round, P.D.; Allen, D.; Trainor, C.R.; et al. The state of migratory landbirds in the East Asian Flyway: Distributions, threats, and conservation needs. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 613172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.P.; Wang, Y.X.; Fan, Z.W.; Ji, Y.; Liu, M.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, S.X.; Li, H.; Liang, S.; et al. Mapping ticks and tick-borne pathogens in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Dai, K.; Zhao, G.P.; Li, X.L.; Shi, W.Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Fang, L.Q. Mapping the global potential transmission hotspots for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome by machine learning methods. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulyok, M.; Richter, H.; Sulyok, Z.; Kapitány-Fövény, M.; Walker, M.D. Predicting tick-borne encephalitis using Google Trends. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).