Simultaneous Detection of Three Subgroups of Avian Leukosis Virus Using the Nanoparticle-Assisted PCR Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Sample Collection
2.2. Primer Design
2.3. Standard DNA Template Construction
2.4. Establishment of the Conventional Multiple PCR Assay
2.5. Establishment of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
2.5.1. Optimization of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
2.5.2. Sensitivity Analysis of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
2.5.3. Specificity of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
2.6. Evaluation of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay with Clinical Specimens
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
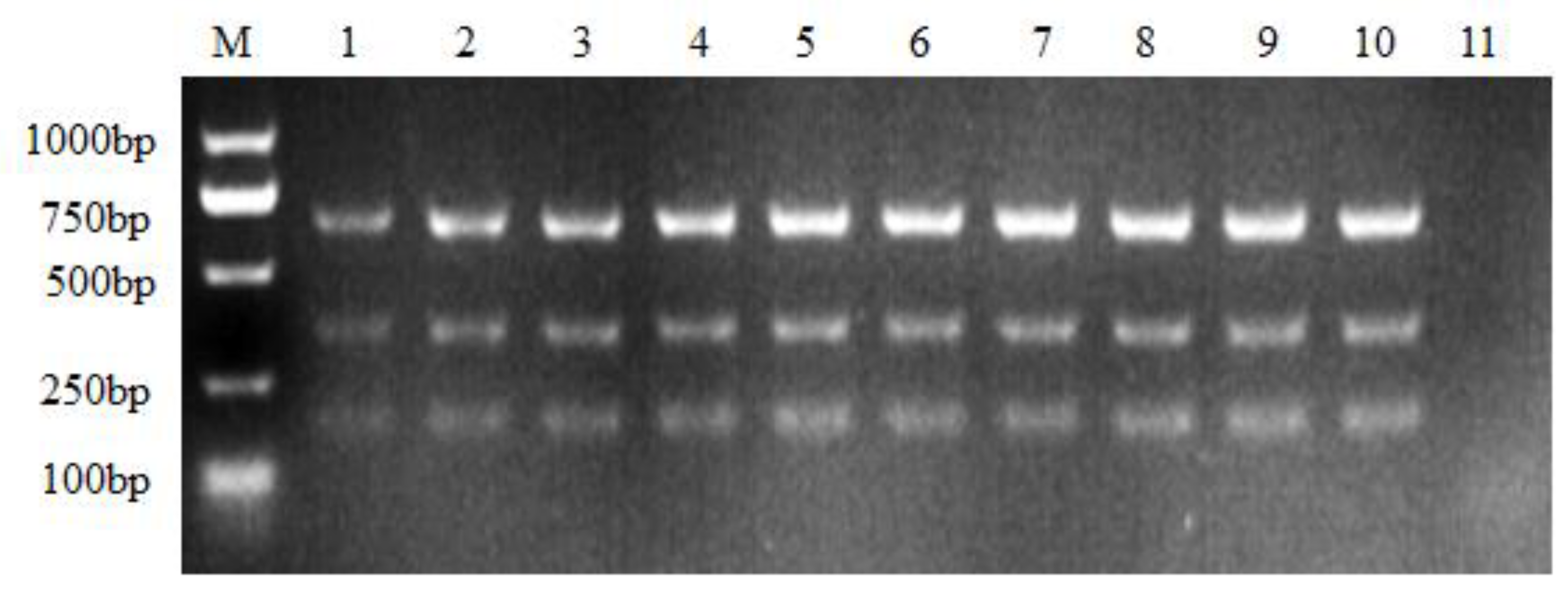
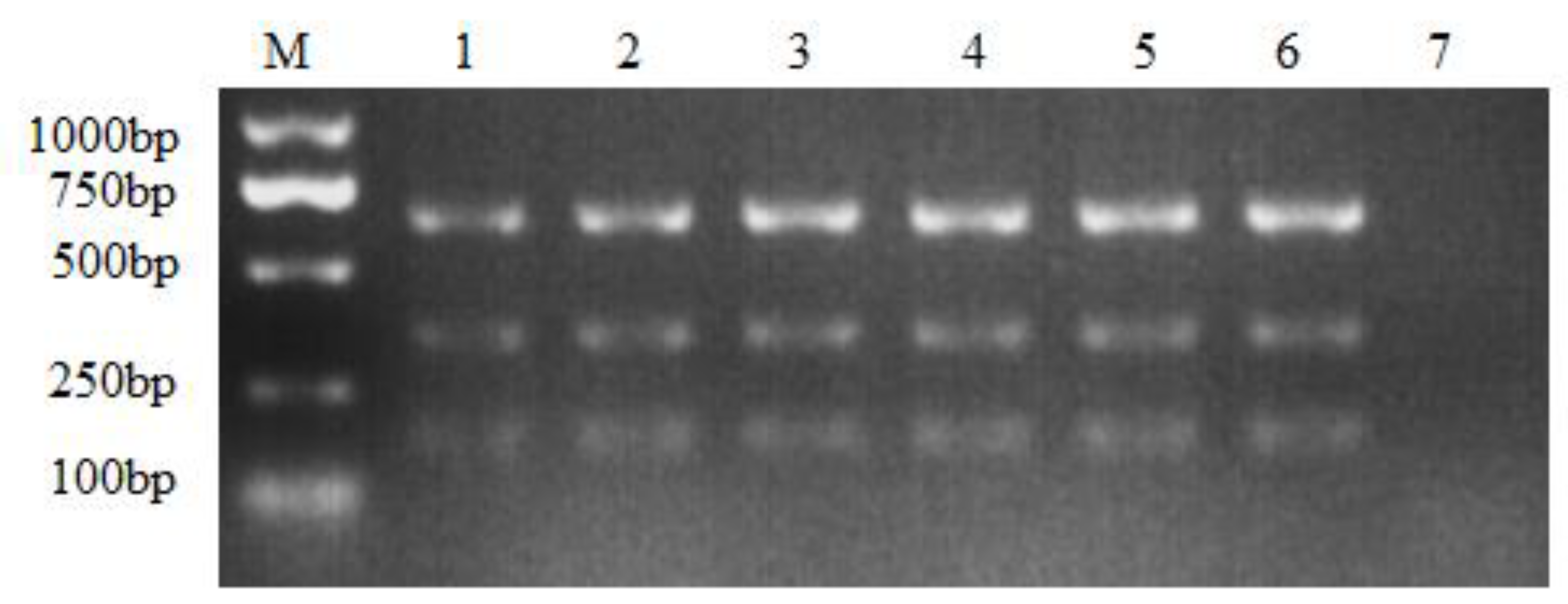
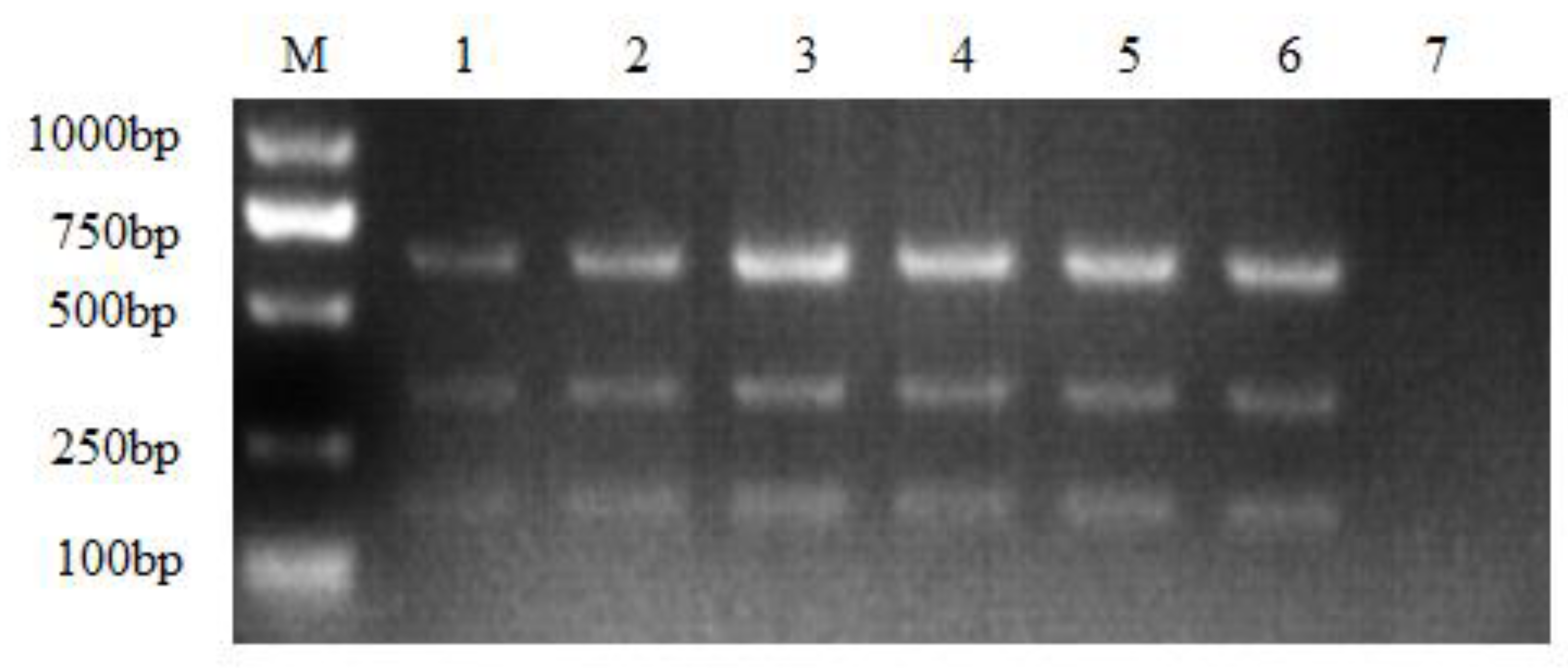
3.2. Sensitivity of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
3.3. Specificity of the Multiple NanoPCR Assay
3.4. Evaluation of the NanoPCR Assay Using Clinical Specimens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Lin, L.; Shi, M.; Gu, Z.; Huang, T.; Mo, M.L.; Wei, T.; Zhang, H.; Wei, P. The emergence of the infection of subgroup J avian leucosis virus escalated the tumour incidence in commercial Yellow chickens in Southern China in recent years. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, L.N.; Nair, V. The long view: 40 years of avian leukosis research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.P.; Reddy, M.R.; Bagust, T.J. Single and concurrent avian leukosis virus infections with avian leukosis virus-J and avian leukosis virus-A in Australian meat-type chickens. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Fan, W.; Ji, P.; Wang, K.; Zhou, E.M.; Zhao, Q. Co-infection with avian hepatitis E virus and avian leukosis virus subgroup J as the cause of an outbreak of hepatitis and liver hemorrhagic syndromes in a brown layer chicken flock in China. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Tan, M.; Zhang, F.; Ji, H.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tan, J.; Huang, J.; Su, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Diversity of Avian leukosis virus subgroup J in local chickens, Jiangxi, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Bi, Y.; Lin, L.; Shi, M.; Huang, T.; Mo, M.; Wei, T.; Wei, P. ALV-J-contaminated commercial live vaccines induced pathogenicity in Three-Yellow chickens: One of the transmission routes of ALV-J to commercial chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, S. Simultaneous endemic infections with subgroup J avian leukosis virus and reticuloendotheliosis virus in commercial and local breeds of chickens. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodin, A.M.; Emanuilova, Z.V.; Smolov, S.V.; Ogneva, O.A.; Konovalova, N.V.; Terentyeva, E.V.; Serova, N.Y.; Efimov, D.N.; Fisinin, V.I.; Greenberg, A.J.; et al. Eradication of avian leukosis virus subgroups J and K in broiler cross chickens by selection against infected birds using multilocus PCR. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, A.; Ochiai, K.; Nakamura, S.; Kobara, A.; Sunden, Y.; Umemura, T. Molecular Characteristics and Pathogenicity of an Avian Leukosis Virus Isolated from Avian Neurofibrosarcoma. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federspiel, M.J. Reverse Engineering Provides Insights on the Evolution of Subgroups A to E Avian Sarcoma and Leukosis Virus Receptor Specificity. Viruses 2019, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.F.; Fadly, A.M.; Taylor, S.P. Development of a polymerase chain reaction to differentiate avian leukosis virus (ALV) subgroups: Detection of an ALV contaminant in commercial Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, M.; Jiao, P.; Luo, K.; Zhang, H.; Ren, T.; Zhang, G.; Xu, C.; Xin, C.; Cao, W. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of subgroup J avian leukosis virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2116–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatai, H.; Ochiai, K.; Tomioka, Y.; Toyoda, T.; Hayashi, K.; Anada, M.; Kato, M.; Toda, A.; Ohashi, K.; Ono, E.; et al. Nested polymerase chain reaction for detection of the avian leukosis virus causing so-called fowl glioma. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, S.; Manoharan, P.; Kathaperumal, K.; Chidambaram, B.; Divya, K.C. Differential detection of avian oncogenic viruses in poultry layer farms and Turkeys by use of multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Q.; Russell, M.; Birch, D.E.; Raymond, J.; Bloch, W. Prevention of pre-PCR mis-priming and primer dimerization improves low-copy-number amplifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Rothberg, L. Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14036–14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhuang, H. An ultrasensitive gold nanoparticles improved real-time immuno-PCR assay for detecting diethyl phthalate in foodstuff samples. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 480, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yang, W.; Ji, Q.; Maki, H.; Dong, A.; Zhang, Z. NanoPCR observation: Different levels of DNA replication fidelity in nanoparticle-enhanced polymerase chain reactions. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 455103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseini, D.M.; Helmy, N.M.; Tammam, R.H. Application of gold nanoparticle-assisted PCR for equine herpesvirus 1 diagnosis in field samples. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2297–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Rothberg, L.J. DNA sequence detection using selective fluorescence quenching of tagged oligonucleotide probes by gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5414–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Wang, J.; Cui, S.J. Development of a nanoparticle-assisted PCR assay to distinguish canine coronaviruses I and II. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; et al. Simultaneous Detection of Bovine Rotavirus, Bovine Parvovirus, and Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Using a Gold Nanoparticle-Assisted PCR Assay With a Dual-Priming Oligonucleotide System. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzhe, Y.; Jianuan, L.; Peng, L.; Jiguo, S.; Ligong, C.; Juxiang, L. Development of a nano-particle-assisted PCR assay for detection of duck tembusu virus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Lin, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, T.; Wei, P. Diversity and evolution analysis of glycoprotein GP85 from avian leukosis virus subgroup J isolates from chickens of different genetic backgrounds during 1989–2016: Coexistence of five extremely different clusters. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Tian, X.; Shao, H.; Ye, J.; Yao, Y.; Nair, V.; Qin, A. Identification of novel B-cell epitope in gp85 of subgroup J avian leukosis virus and its application in diagnosis of disease. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.W.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wang, W.; Tian, J.; Xiao, Z.G. Enhanced inhibition of Avian leukosis virus subgroup J replication by multi-target miRNAs. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Gao, Y.; Ni, W.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Yin, C.; Qi, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, X. Development and application of real-time PCR for detection of subgroup J avian leukosis virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, C.; Xie, X.; Lin, Y. The biological applications of DNA nanomaterials: Current challenges and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Yuno, M.; Kitaura, F.; Fujii, H. A refined two-step oligoribonucleotide interference-PCR method for precise discrimination of nucleotide differences. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.V.; Paul, N.; Yee, J.; Timoshchuk, V.A.; Shum, J.; Miyagi, K.; Kellum, J.; Hogrefe, R.I.; Zon, G. Hot start PCR with heat-activatable primers: A novel approach for improved PCR performance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehia, N.; El-Sayed, H.S.; Omar, S.E.; Amer, F. Genetic variability of the Avian leukosis virus subgroup J gp85 gene in layer flocks in Lower Egypt. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Sequence | Target | Sequence ID | Site | Amplicon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP1 | ACTGGCGGCCCTGACAACAG | ALV-A | HM775328.1 | 219–555 | 336 bp |
| AP2 | CGCACCGCAATACTCACTCCC | ||||
| BP1 | CTACAACTGTTGGGTTCCCAGT | ALV-B | JF826241.1 | 482–1107 | 625 bp |
| BP2 | GACCCCCTACCGGACGACTGG | ||||
| JP1 | ACAAGCAAGAAAGACCCGG | ALV-J | DQ115805.1 | 82–248 | 167 bp |
| JP2 | GTCATATTCGCCCAGGTGA | ||||
| AP1 | ACTGGCGGCCCTGACAACAGCA | ALV-A | HM775328.1 | 219–555 | 336 bp |
| AP2 | CGCACCGCAATACTCACTCCC | ||||
| BP1 | CTACAACTGTTGGGTTCCCAGTCTCT | ALV-B | JF826241.1 | 482–1107 | 625 bp |
| BP2 | GACCCCCTACCGGACGACTGGG | ||||
| JP1 | ACAAGCAAGAAAGACCCGG | ALV-J | DQ115805.1 | 82–248 | 167 bp |
| JP2 | GTCATATTCGCCCAGGTGA |
| Virus | Nano-PCR Positive Specimens | Sequencing Positive Specimens | Coincidence Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALV-A | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| ALV-B | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| ALV-J | 11 | 11 | 100 |
| ALV-A + B | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| ALV-A + J | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| ALV-B + J | 2 | 2 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Hu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cong, F.; Liu, S. Simultaneous Detection of Three Subgroups of Avian Leukosis Virus Using the Nanoparticle-Assisted PCR Assay. Viruses 2024, 16, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010015
Wu M, Hu S, Zhu Y, Cong F, Liu S. Simultaneous Detection of Three Subgroups of Avian Leukosis Virus Using the Nanoparticle-Assisted PCR Assay. Viruses. 2024; 16(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Miaoli, Shuaiqi Hu, Yujun Zhu, Feng Cong, and Shengwang Liu. 2024. "Simultaneous Detection of Three Subgroups of Avian Leukosis Virus Using the Nanoparticle-Assisted PCR Assay" Viruses 16, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010015
APA StyleWu, M., Hu, S., Zhu, Y., Cong, F., & Liu, S. (2024). Simultaneous Detection of Three Subgroups of Avian Leukosis Virus Using the Nanoparticle-Assisted PCR Assay. Viruses, 16(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010015





