Molecular Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus from Ticks Collected from Cattle in Kyrgyzstan, 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
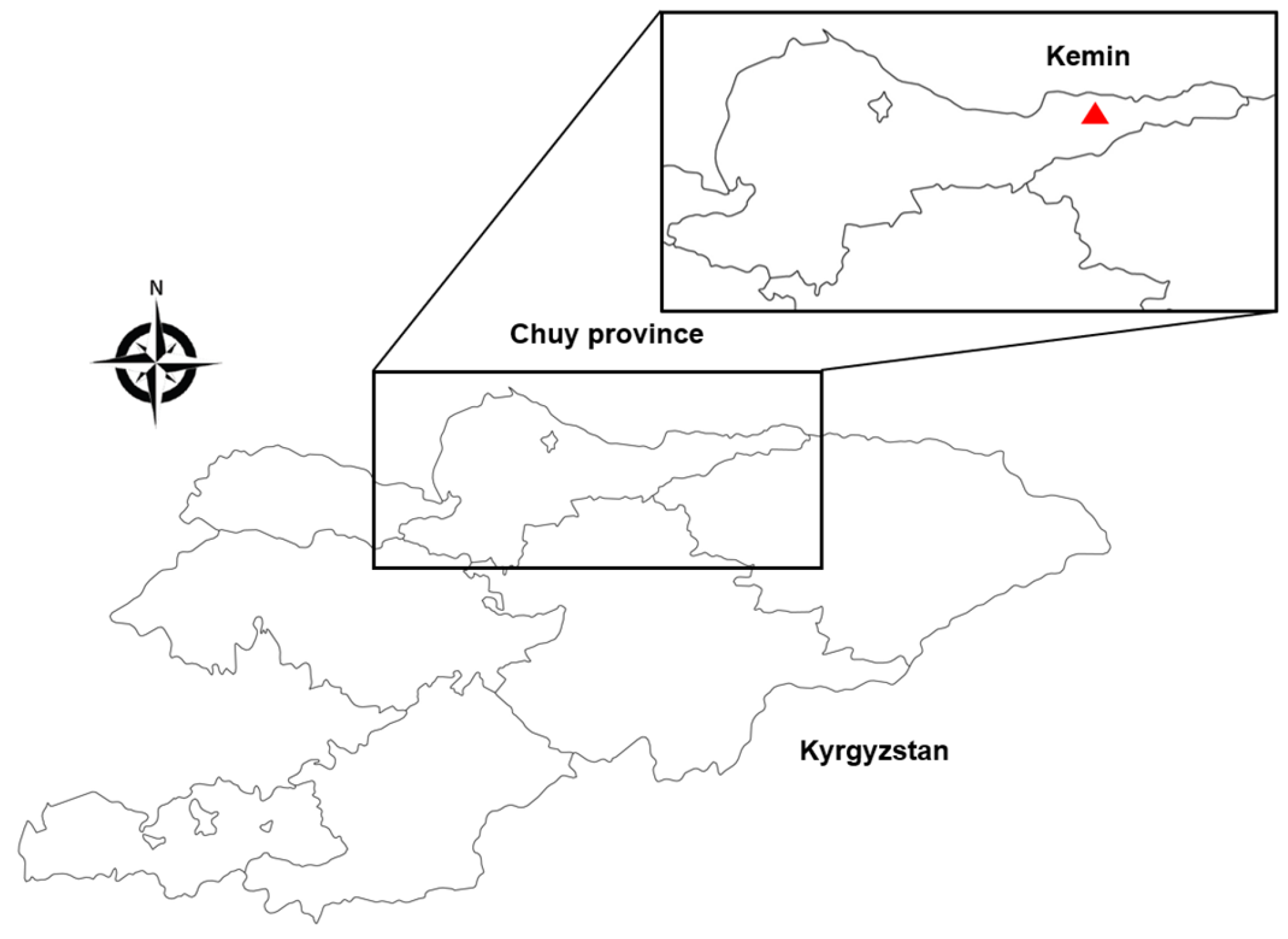
2.1. Tick Collection
2.2. Tick Sample Preparation
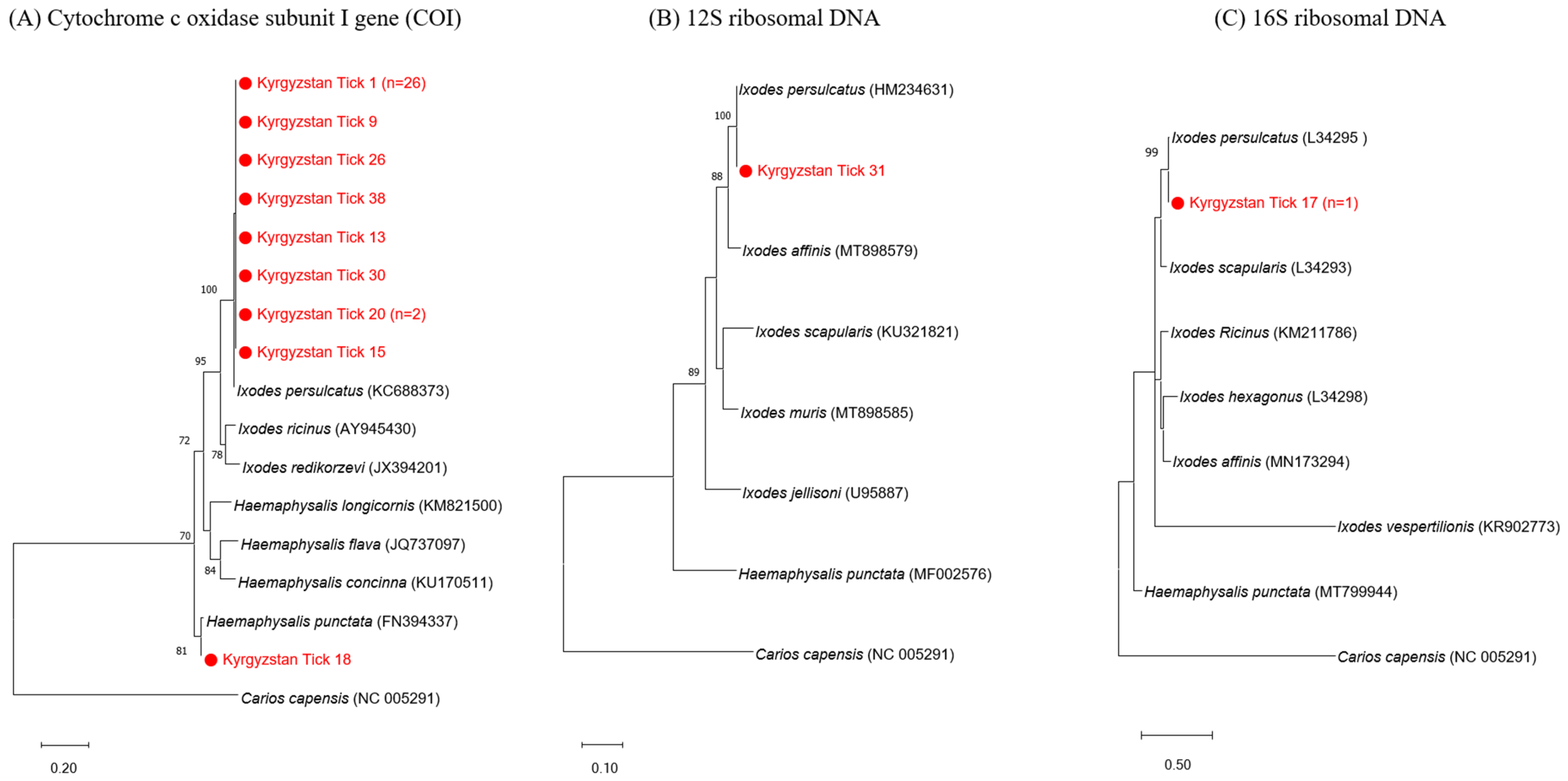
2.3. Molecular Identification of Tick Species
2.4. Molecular Detection of TBEV and CCHFV
2.5. Nucleotide Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. NGS Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tick Identification
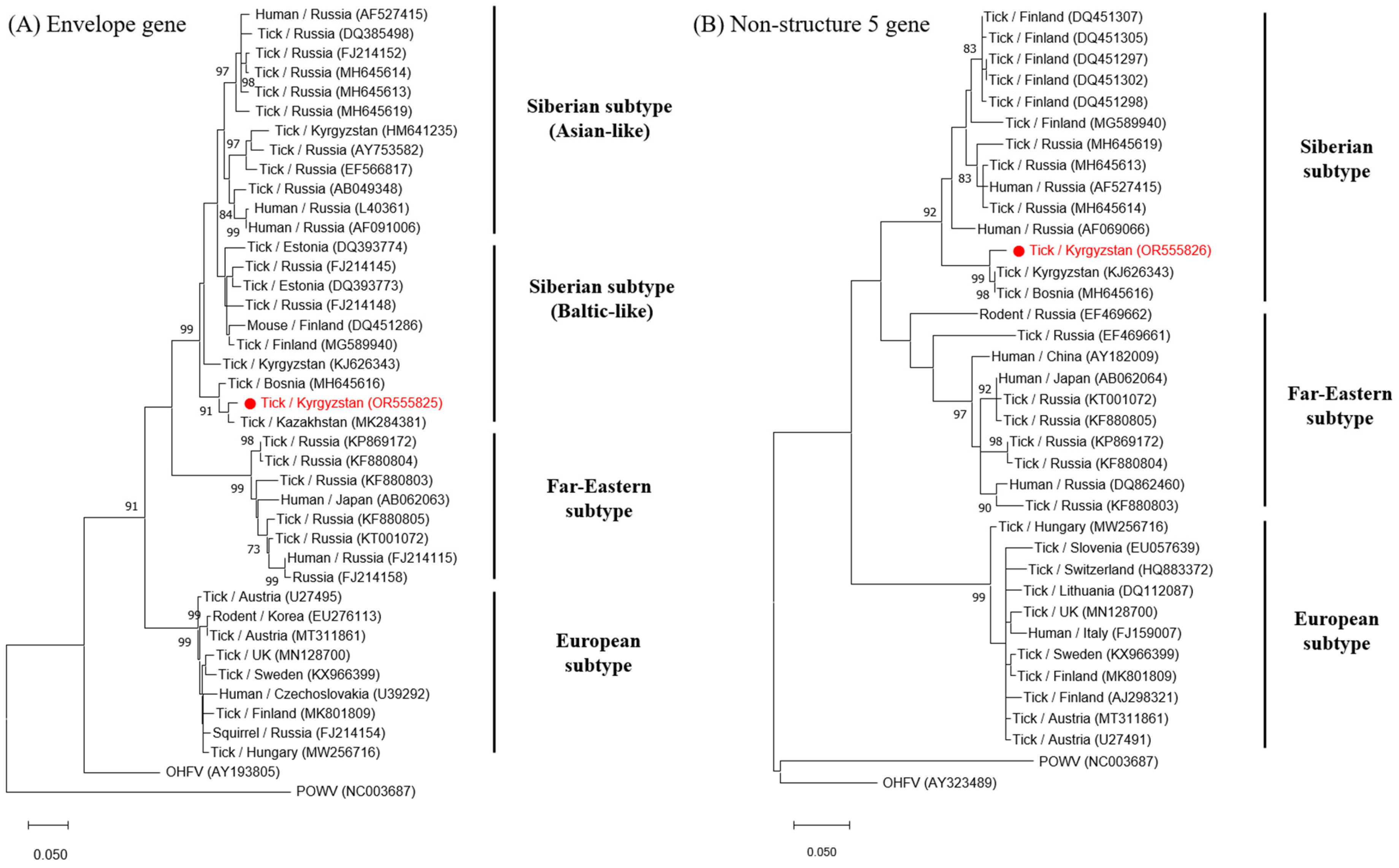
3.2. TBEV and CCHFV Detection
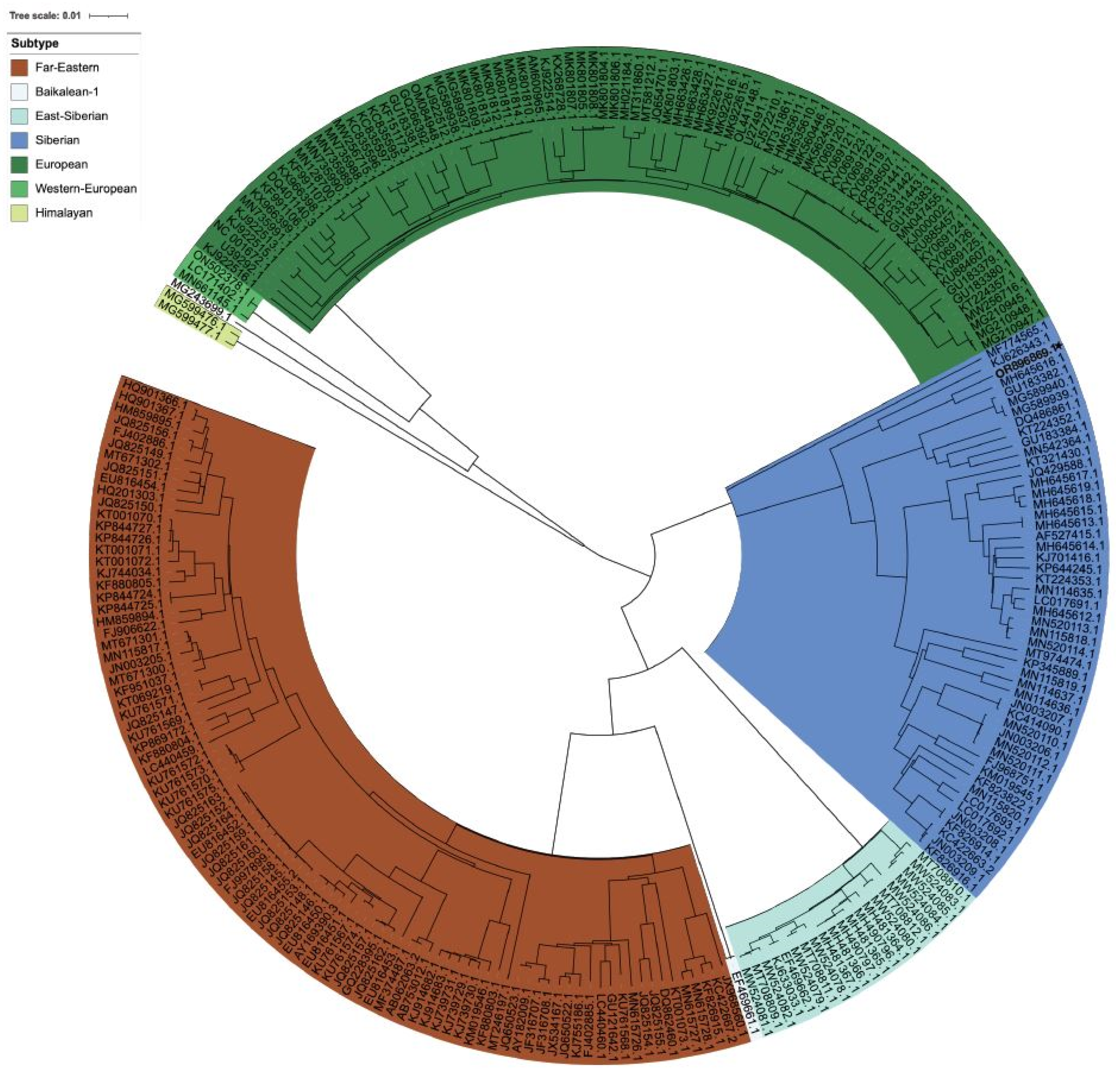
3.3. NGS Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madison-Antenucci, S.; Kramer, L.D.; Gebhardt, L.L.; Kauffman, E. Emerging tick-borne diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 00083-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, T.J.; Hahn, C.S.; Galler, R.; Rice, C.M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1990, 44, 649–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, G.; Gniel, D.; Petermann, R.; Pfeffer, M. Epidemiology and distribution of tick-borne encephalitis. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2012, 162, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.H.; Baek, J.H.; Durey, A.; Kwon, H.Y.; Chung, M.H.; Lee, J.S. Geographic distribution of Tick-borne encephalitis virus complex. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2020, 57, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süss, J. Tick-borne encephalitis 2010: Epidemiology, risk areas, and virus strains in Europe and Asia—An overview. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2011, 2, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovic, P.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsun, T.S.; Frolova, T.V.; Zhankov, A.I.; Armesto, M.; Turner, S.L.; Frolova, M.P.; Pogodina, V.V.; Lashkevich, V.A.; Gould, E.A. Characterization of a siberian virus isolated from a patient with progressive chronic tick-borne encephalitis. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shang, G.; Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. A new subtype of eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus discovered in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, S.Y.; Mukhacheva, T.A. Reconsidering the classification of tick-borne encephalitis virus within the Siberian subtype gives new insights into its evolutionary history. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.; Dobler, G. Emergence of zoonotic arboviruses by animal trade and migration. Parasit. Vectors 2010, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, K.L.; Johnson, N.; Phipps, L.P.; Stephenson, J.R.; Fooks, A.R.; Solomon, T. Tick-borne encephalitis virus—A review of an emerging zoonosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; de la Fuente, J. The ecology of ticks and epidemiology of tick-borne viral diseases. Antiviral. Res. 2014, 108, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, Z.; Ferenczi, E.; Szeles, K.; Stefanoff, P.; Gut, W.; Szomor, K.N.; Takacs, M.; Berencsi, G. Tick-borne encephalitis outbreak in Hungary due to consumption of raw goat milk. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzmann, H.; Aberle, S.W.; Stiasny, K.; Werner, P.; Mischak, A.; Zainer, B.; Netzer, M.; Koppi, S.; Bechter, E.; Heinz, F.X. Tick-borne encephalitis from eating goat cheese in a mountain region of Austria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1671–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y. Multiple transmissions of tick-borne encephalitis virus between Japan and Russia. Genes Genet. Syst. 2007, 82, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Waldenström, J.; Lundkvist, A.; Falk, K.I.; Garpmo, U.; Bergström, S.; Lindegren, G.; Sjöstedt, A.; Mejlon, H.; Fransson, T.; Haemig, P.D.; et al. Migrating birds and tickborne encephalitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tick-borne encephalitis. In ECDC. Annual Epidemiology Report for 2020; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/tick-borne-encephalitis-annual-epidemiological-report-2020 (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Deviatkin, A.A.; Kholodilov, I.S.; Vakulenko, Y.A.; Karganova, G.G.; Lukashev, A.N. Tick-borne encephalitis virus: An emerging ancient zoonosis? Viruses 2020, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.; Tukhanova, N.; Ndenkeh, J., Jr.; Shapiyeva, Z.; Yegemberdiyeva, R.; Yeraliyeva, L.; Nurmakhanov, T.; Froeschl, G.; Hoelscher, M.; Musralina, L.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus and West-Nile fever virus as causes of serous meningitis of unknown origin in Kazakhstan. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, J.; Yeh, K.B.; Dasgupta, D.; Shapieva, Z.; Omasheva, G.; Deryabin, P.; Nurmakhanov, T.; Ayazbayev, T.; Andryushchenko, A.; Zhunushov, A.; et al. Biosurveillance in Central Asia: Successes and challenges of tick-borne disease research in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, B.J.; Atkinson, B.; Czechowski, D.M.; Larsen, P.A.; Meeks, H.N.; Carrera, J.P.; Duplechin, R.M.; Hewson, R.; Junushov, A.T.; Gavrilova, O.N.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus, Kyrgyzstan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.G.; Noh, B.E.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, T.K.; Song, B.G.; Lee, H.I. Nationwide temporal and geographical distribution of tick populations and phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks in Korea, 2020. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguti, N.; Tipton, V.J.; Keegan, H.L.; Toshioka, S. Ticks of Japan, Korea, and the Ryukyu islands. Brigh. Young Univ. Sci. Bull. Biol. Ser. 1971, 15, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Vemaps. Available online: https://vemaps.com/search?q=kyrgyzstan (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Beati, L.; Keirans, J.E. Analysis of the systematic relationships among ticks of the genera Rhipicephalus and Boophilus (Acari: Ixodidae) based on mitochondrial 12S ribosomal DNA gene sequences and morphological characters. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, C.; Jia, G.; Lin, X. Development of a DNA barcoding system for the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 25, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternovoi, V.A.; Kurzhukov, G.P.; Sokolov, Y.V.; Ivanov, G.Y.; Ivanisenko, V.A.; Loktev, A.V.; Ryder, R.W.; Netesov, S.V.; Loktev, V.B. Tick-borne encephalitis with hemorrhagic syndrome, Novosibirsk region, Russia, 1999. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; Kunz, C.; Mandl, C.W.; Heinz, F.X. Identification of tick-borne encephalitis virus ribonucleic acid in tick suspensions and in clinical specimens by a reverse transcription-nested polymerase chain reaction assay. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1995, 4, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschera, L.S.; Wolfinger, M.T. Evolutionary traits of Tick-borne encephalitis virus: Pervasive non-coding RNA structure conservation and molecular epidemiology. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondaryuk, A.N.; Sidorova, E.A.; Adelshin, R.V.; Andaev, E.I.; Balakhonov, S.V. Reporting of New tick-borne encephalitis virus strains isolated in Eastern Siberia (Russia) in 1960–2011 and explaining them in an evolutionary context using Bayesian phylogenetic inference. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, M.; Kovalev, S.; Vasev, P.; Bolkov, M. (Eds.) TBEV analyzer: A platform for evolutionary analysis of tick-borne encephalitis virus. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Multi-Conference on Engineering, Computer and Information Sciences (SIBIRCON), Novosibirsk, Russia, 21–27 October 2019; IEEE Publications: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdiyeva, K.; Turebekov, N.; Yegemberdiyeva, R.; Dmitrovskiy, A.; Yeraliyeva, L.; Shapiyeva, Z.; Nurmakhanov, T.; Sansyzbayev, Y.; Froeschl, G.; Hoelscher, M.; et al. Vectors, molecular epidemiology and phylogeny of TBEV in Kazakhstan and central Asia. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y. Detection of the Siberian tick-borne encephalitis virus in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, northwestern China. Bing Du Xue Bao 2016, 32, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, G. A survey report on the natural foci of Russian spring-summer encephalitis in the mountainous areas of Tianshan and Altay mountains in Xinjiang. Di Fang Bing Tong Bao/Endem. Dis. Bull. 1991, 6, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, R.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Yin, X. Isolation of tick-borne encephalitis virus Far-eastern subtype and Siberian subtype in the China-Kazakhstan border area in Xinjiang. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2017, 12, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Tkachev, S.E.; Babkin, I.V.; Chicherina, G.S.; Kozlova, I.V.; Verkhozina, M.M.; Demina, T.V.; Lisak, O.V.; Doroshchenko, E.K.; Dzhioev, Y.P.; Suntsova, O.V.; et al. Genetic diversity and geographical distribution of the Siberian subtype of the tick-borne encephalitis virus. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorenko, V. The New Silk Road Initiatives in Central Asia; Rethink Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deniskova, T.; Dotsev, A.; Lushihina, E.; Shakhin, A.; Kunz, E.; Medugorac, I.; Reyer, H.; Wimmers, K.; Khayatzadeh, N.; Sölkner, J.; et al. Population structure and genetic diversity of sheep breeds in the Kyrgyzstan. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimon, R. Evolution of Land Use in Pastoral Culture in Central Asia with Special Reference to Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. In Rangeland Stewardship in Central Asia: Balancing Improved Livelihoods, Biodiversity Conservation and Land Protection; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, W.; Shnaider, S.; Abdykanova, A.; Fages, A.; Welker, F.; Irmer, F.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Khan, N.; Douka, K.; Kolobova, K.; et al. Early pastoral economies along the Ancient Silk Road: Biomolecular evidence from the Alay Valley, Kyrgyzstan. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansford, K.M.; Pietzsch, M.E.; Cull, B.; Gillingham, E.L.; Medlock, J.M. Potential risk posed by the importation of ticks into the UK on animals: Records from the Tick Surveillance Scheme. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.F.; Pinter, A. Human parasitism by the exotic tick Dermacentor variabilis (Parasitiformes: Ixodida) in Brazil: Report of an imported case. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2022, 31, e017121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, P.; Grostieta, E.; Salceda-Sánchez, B.; Huerta-Jiménez, H.; Alcántara-Rodríguez, V.; Becker, I.; Sánchez-Montes, S. A story of a lone star tick: An imported case of Amblyomma americanum (Linnaeus, 1758) infected with Rickettsia amblyommatis that parasitized a US traveler returning to Mexico. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2023, 65, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant-Genevier, J.; Bumburidi, Y.; Kazazian, L.; Seffren, V.; Head, J.R.; Berezovskiy, D.; Zhakipbayeva, B.; Salyer, S.J.; Knust, B.; Klena, J.D.; et al. Prevalence of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus among livestock and ticks in Zhambyl Region, Kazakhstan, 2017. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 106, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultankulova, K.T.; Shynybekova, G.O.; Kozhabergenov, N.S.; Mukhami, N.N.; Chervyakova, O.V.; Burashev, Y.D.; Zakarya, K.D.; Nakhanov, A.K.; Barakbayev, K.B.; Orynbayev, M.B. The prevalence and genetic variants of the CCHF Virus circulating among ticks in the southern regions of Kazakhstan. Pathogens 2022, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Su, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Z.; et al. A new strain of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus isolated from Xinjiang, China. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moming, A.; Yue, X.; Shen, S.; Chang, C.; Wang, C.; Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in ticks from different ecosystems in Xinjiang, China. Virol. Sin. 2018, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, B.; Chamberlain, J.; Jameson, L.J.; Logue, C.H.; Lewis, J.; Belobrova, E.A.; Valikhodzhaeva, M.; Mullojonova, M.; Tishkova, F.H.; Hewson, R. Identification and analysis of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus from human sera in Tajikistan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e1031–e1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishkova, F.H.; Belobrova, E.A.; Valikhodzhaeva, M.; Atkinson, B.; Hewson, R.; Mullojonova, M. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Tajikistan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | PCR Condition | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COⅠ | LCO1490 | GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG | 95 °C, 5 min; 35 cycles (95 °C 1 min, 40 °C 1 min, 72 °C 30 s); 72 °C, 10 min | [26] |
| HCO2198 | TAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAAAAATCA | |||
| 12S rDNA | 12-SA1 | AAACTAGGATTAGATACCCTATTAT | 95 °C, 2 min; 28 cycles (95 °C 45 s, 52 °C 45 s, 72 °C 45 s); 72 °C, 10 min | [27] |
| 12-SB1 | AAGAGCGACGGGCGATGTGT | |||
| 16S rDNA | 16S-F | TTAAATTGCTGTRGTATT | 94 °C, 5 min; 5 cycles (94 °C 30 s, 49 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s); 5 cycles (94 °C 30 s, 47 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s); 5 cycles (94 °C 30 s, 45 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s); 25 cycles (94 °C 30 s, 43 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s); 68 °C, 5 min | [28] |
| 16S-R2 | CAACATCGAGGTCGCAAWCYA | |||
| E | TBE913F | TGCACACAYYTGGAAAACAGGGA | 94 °C, 5 min; 30 cycles (94 °C, 30 s; 52 °C, 30 s; 72 °C, 1 min); 72 °C, 5 min | [29] |
| TBE1738R | TGGCCACTTTTCAGGTGGTACTTGGTTCC | |||
| TBE1192F | CAGAGTGATCGAGGCTGGGGYAA | 94 °C, 2 min; 30 cycles (94 °C, 20 s; 62 °C, 10 s; 68 °C, 20 s); 70 °C, 5 min | ||
| TBE1669R | AACACTCCAGTCTGGTCTCCRAGGTTGTA | |||
| NS5 | FSM-1 | GAGGCTGAACAACTGCACG | 94 °C, 5 min; 35 cycles (96 °C 30 s, 40 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s); 72 °C, 5 min | [30] |
| FSM-2 | GAACACGTCCATTCCTGATCT | |||
| FSM-1i | ACGGAACGTGACAAGGCTAG | 94 °C, 5 min; 30 cycles (96 °C 30 s, 40 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s); 72 °C, 5 min | ||
| FSM-2i | GCTTGTTACCATCTTTGGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Choi, C.-H.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Aknazarov, B.; Nyrgaziev, R.; Atabekova, N.; Jetigenov, E.; Chung, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-I. Molecular Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus from Ticks Collected from Cattle in Kyrgyzstan, 2023. Viruses 2024, 16, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010107
Jung H, Choi C-H, Lee M, Kim S-Y, Aknazarov B, Nyrgaziev R, Atabekova N, Jetigenov E, Chung Y-S, Lee H-I. Molecular Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus from Ticks Collected from Cattle in Kyrgyzstan, 2023. Viruses. 2024; 16(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Haneul, Chi-Hwan Choi, Minji Lee, Seong-Yoon Kim, Bekbolsun Aknazarov, Rysbek Nyrgaziev, Nurzina Atabekova, Elmurat Jetigenov, Yoon-Seok Chung, and Hee-Il Lee. 2024. "Molecular Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus from Ticks Collected from Cattle in Kyrgyzstan, 2023" Viruses 16, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010107
APA StyleJung, H., Choi, C.-H., Lee, M., Kim, S.-Y., Aknazarov, B., Nyrgaziev, R., Atabekova, N., Jetigenov, E., Chung, Y.-S., & Lee, H.-I. (2024). Molecular Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus from Ticks Collected from Cattle in Kyrgyzstan, 2023. Viruses, 16(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010107







