Abstract
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a silent global health problem that can lead to suicide. MDD development is suggested to result from numerous risk factors, including genetic factors. A precise tool for MDD diagnosis is currently not available. Recently, inflammatory processes have been identified as being strongly involved in MDD development and the reactivation of human herpesvirus type 6 (HHV-6), upregulating cytokines such as TNF-α, which are associated with MDD. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the association of HHV-6 with genetic factors, especially TNF-α mutation, in MDD patients and their relatives compared to healthy controls. The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) was used to evaluate MDD status, and 471 oral buccal samples were investigated for HHV-6 infection and viral copy number by qPCR. TNF-α (-308G/A) gene mutation and the cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were analyzed by high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Whole-exome sequencing of buccal samples was performed to analyze for genetic factors. The results showed significantly higher HHV-6 positivities and viral loads in MDD patients (15/59 (25.67%) and 14,473 ± 16,948 copies/µL DNA) and their relatives (blood relatives 17/36 (47.22%) and 8146 ± 5656 copies/µL DNA); non-blood relatives 7/16 (43.75%) and 20,721 ± 12,458 copies/µL DNA) compared to the healthy population (51/360 (14.17%) and 6303 ± 5791 copies/µL DNA). The TNF-α (-308G/A) mutation showed no significant difference. Surprisingly, 12/26 (46.15%) participants with the TNF-α (-308G/A) mutation showed HHV-6 positivities at higher rates than those with wild-type TNF-α (-308G) (70/267 (26.22%)). HHV-6-positive participants with TNF-α (-308G/A) showed higher levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 than those of negative control. Exome analysis revealed that common mutations in immune genes were associated with depression. Therefore, this study unveiled the novel association of inflammatory gene TNF-α (-308G/A) mutations with HHV-6 reactivation, which could represent a combined risk factor for MDD. This result could induce further research on MDD development and clinical applications.
1. Introduction
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a silent global health problem that can result in suicide. According to the World Health Organization, 280 million people (approximately 3.8–13.0% [,,] of the global population) are afflicted with MDD [], and in Thailand, the MDD prevalence was 7.0–39.1%, which may relate to the lack of knowledge regarding depression and the absence of precise diagnostic tools for this condition [,,,,,,,,]. The Thai version of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) for MDD screening is the main tool available, which is a nine-item questionnaire based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV) criteria that are used for diagnosing major depressive episodes [,,,,,,,,]. However, accurate MDD diagnosis still requires a precise tool or gold standard biomarker.
Many risk factors are suggested to be associated with the development of MDD, and meta-analyses have identified several environmental risk factors including the loss of a spouse, physical abuse during childhood, obesity, the presence of 4–5 metabolic risk factors, sexual dysfunction, and work-related stress []. Other associated risk factors include high body mass index (BMI), smoking [], female sex [,], family and personal psychiatric history, family history of mental disorders, and alcohol consumption []. In addition, genetic risk factors [] such as genetic polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (-308G/A; rs1800629) [,,,,], interleukin (IL)-1β (rs1143627) [], IL-6 (174G/C; rs1800795) [], 5HTTP/SLC6A4 (rs25531), APOE, DRD4, GNB3, HTR1A, MTHFR, and SLC6A3 have been significantly associated with MDD [,]. Furthermore, numerous studies have found that families and twins had increased risks of MDD [,], whereby the heritability of MDD in twins is estimated at 38% [], and the odds ratio in first-degree relatives was determined to be 2.84 in a meta-analysis []. In contrast, a meta-analysis of genetic variation showed that the proportion of variance explained by genetic risk factors was extremely small (0.1–0.4%) [], possibly because other indirect or direct factors were involved that related to MDD in close relatives (but not twins), such as infectious particles; however, the reason for the differences in the results of these studies has yet to be determined.
Human herpesvirus type 6 (HHV-6) is a 160–162 kilobase (kb) double-stranded linear DNA virus that belongs to the family Herpesviridae and includes the HHV-6B and HHV-6A variants. Adults in developed countries show a greater than 95% seropositivity for HHV-6 [,,]. Latent infections of HHV-6 in astrocytoma cell lines have resulted in the production of IL-6 [], and a high level of IL-6 is associated with increased suicide risk. Antidepressant treatment has been shown to significantly decrease peripheral levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 [,], while IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10, IL-13, IL-18, and IL-12 are associated with MDD severity level []. In contrast, the levels of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-8, soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), IL-5, Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL-3), IL-17, and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β 1) were not considered significant in relation to MDD. Inflammatory processes involving cytokine production are reported to be associated with MDD, including neurotrophic viral infections, and since HHV-6 infection reflects an inflammatory response, it has an affiliation with MDD [,,,,,,]. Transmission of HHV-6 mainly occurs through saliva, nasal mucus, and the olfactory bulb which guides the axons of olfactory receptor neurons into the CNS in healthy populations. The genome of latent HHV-6 integrates into the telomeres of the host chromosome. Active infection of HHV-6 in MDD patients has been predominantly detected within the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum. A small protein encoded by an intermediate state transcript (SITH-1) is produced through the expression of an HHV-6 latency-associated gene, which induces depression symptoms. The corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) along with the urocortin, and REDD1 proteins are activated by HHV-6B latency in the hypothalamus [,,].
The “cytokine theory” of MDD explains the various behavioral, neuroendocrinal, and neurochemical changes involved in depression []. Although some studies have reported that peripheral cytokines do not cross the blood–brain barrier, molecular, cellular, and neural signals have been identified that activate brain inflammation []. However, immune cells have been recognized to infiltrate nervous tissue and cytokine signals can be transmitted to the nervous system. Moreover, the CNS (astrocytes, microglia, and in some cases, neurons) can generate cytokines and their receptors []. HHV-6 reactivates and persists in the host by avoiding immune surveillance through methods such as the immunosuppression of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, B cells, monocytes/macrophages, and NK cells []. HHV-6 increases specific pro-inflammatory gene expression and downregulates anti-inflammatory genes [,]. IFN-γ release was found to be inhibited by HHV-6 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) [,,]. In addition, HHV-6 induced TNF-α upregulation in PBMCs [] and differentiated U937 monocytoma cells []. Furthermore, the HHV-6 reactivation of CD4+ continuous JJHAN T cells increased TNF receptor 1 expression, resulting in the apoptosis of CD4+ lymphocytes from patients in vivo []. IL-10 and IL-14 were also found to be downregulated by HHV-6 infection in continuous T cells [,]. However, HHV-6 induced helper T cell (Th) differentiation from the Th1 to the Th2 type by upregulating IL-10 and downregulating IL-12 in PBMCs because of monocyte/macrophage-induced IL-10 expression []. IL-18 was increased in T cells infected with HHV-6 and the levels of IL-10 were reduced, whereas IL-12 production in stimulated macrophages was deficient after HHV-6 infection. HHV-6 has been reported to induce IL-6 both in vitro and in vivo, and upregulate the production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and IL-8 [,]. IL-6 levels approximating 0–175 pg/mL were detected in HHV-6-positive cells [] and were undetected in uninfected cells []. CD3 has been shown to be downregulated by HHV-6, resulting in reduced surface expression of the CD3/T cell receptor complex. Similarly, T cell proliferation was severely impaired after HHV-6 infection []. HHV-6 can frequently lead to acute inflammation, but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear [].
The presence of anti-HHV-6 IgG in serum can be detected with high sensitivity and specificity [], and reactivation can be identified in approximately 1.75–2% of patients 3 years of age or younger by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [,]. Using this method, the global spread of HHV-6 was determined as 28–78% [,]. Currently, sensitive methods for the detection of HHV-6 in saliva are available []. Buccal mucosa swabs and whole blood samples were used in the Japanese population to determine the HHV-6 copy number [,]. Nevertheless, depending on viral neurotropism, negative results in blood or saliva samples by serology or PCR cannot guarantee HHV-6 negativity in the brain []. HHV-6 might be a risk factor for MDD; therefore, an MDD diagnosis should not be based solely on a questionnaire. HHV-6 may be an additional factor to environmental risks that stimulates and increases the risk of recurrent inflammatory processes in MDD.
Investigations that highlight the correlation between the genetic markers of TNF-α gene variations, which are the most common genetic biomarkers, and MDD in the Thai population are currently scarce. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine the significance of TNF-α mutation in MDD and the association between HHV-6 reactivation and MDD in Thailand. The presence of HHV-6 DNA was detected using quantitative PCR (qPCR) with oral buccal cells from MDD patients, relatives of MDD patients, and a healthy population, and the HHV-6 viral load was determined. The TNF-α (-308G/A; rs1800629) mutation was identified by high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis, and the cytokine level of TNF-α with IL-6 and IL-10 was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Whole-exome sequencing (WES) was used to compare patients with MDD, relatives of patients with MDD, and healthy individuals to screen for genetic risk factors related to the Thai population.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens
Total of 471 oral buccal cell samples were collected from 360 healthy individuals, 59 MDD patients, 36 blood relatives of MDD patients, and 16 non-blood relatives of MDD patients (such as spouses or partners) for HHV-6 and TNF-α promoter (-308G/A; rs1800629) detection (Figure 1). The sample size was calculated as N = Z21−a P(1 − P)/d2 for an HHV-6 prevalence (P) of approximately 4–53.8 %, with Z = 1.96 for a 95 % confidence level and d = 0.05 [,]. The inclusion criteria used for patients who were diagnosed with MDD were the DMS-5 criteria from the Thai population between 2022–2023 for patients aged 18 to 90 years. The inclusion criterion for the healthy controls was the absence of a current or lifetime diagnosis of any psychiatric disorder. First-degree relatives with a history of suicide risk or depression diagnoses were excluded from participating as healthy controls. MDD patients were diagnosed by a certified hospital psychiatrist. This study evaluated the potential risk factors of MDD in families of MDD patients; therefore, the study was promoted using online social media among depression patients in Thailand. Oral buccal cell samples were collected using mail-in samples and medical certifications were used to confirm the MDD diagnosis with the PHQ-9. The results were interpreted as no depression (0–7), mild depression (8–12), moderate depression (13–17), and major depression (18 or greater). A PHQ-9 score of ≥9 was used to identify patients with depression, according to a previous study [,].
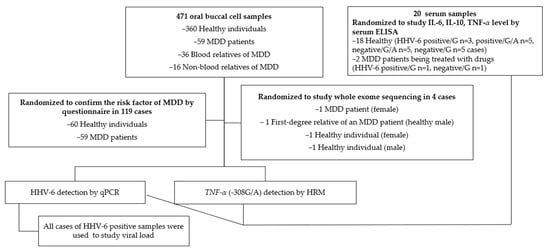
Figure 1.
Specimens.
A randomized sample matching the sex of 60 healthy individuals and 59 MDD patients was used to confirm the most common risk factors of MDD. Data were collected regarding sex, health status, and life history, BMI, exercise habits, alcohol consumption, second-hand smoke exposure, drinking water source, potable water purification, water type used for brushing teeth, and fresh fruit and vegetable consumption.
An ELISA was performed using 20 randomized undiluted serum samples, including those from healthy participants and MDD patients with known HHV-6/TNF-α promoter status.
Whole-exome sequencing of buccal samples was used to analyze the point mutation status of four randomized samples (an MDD patient and a healthy relative with a healthy subject).
This study was approved by the Committee on Human Research Ethics in Health Sciences and Science and Technology, University of Phayao, Thailand (UP-HEC 1.3/013/65). All procedures involving human participants performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki, the Belmont Report, the Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences guidelines, and the International Conference on Harmonization in Good Clinical Practice.
2.2. DNA Extraction
Oral buccal cells were collected by oral rinsing with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Samples were centrifuged at 4000× g for 5 min to remove the supernatant. DNA was extracted from the oral buccal cells using the Genomic DNA Isolation Kit (PDC11-0100; BIO-HELIX Co., Xindian District, New Taipei City, Taiwan, China) according to the methods of a previous study [].
2.3. HHV-6 DNA Detection by Quantitative PCR (qPCR) and Viral Load
HHV-6 DNA (U97 gene) was detected using qPCR with the forward primer 5′ GCTAGAACGTATTTGCTGCAGAACG 3′ and the reverse primer 5′ ATCCGAAACAACTGTCTGACTGGCA 3′, and a PCR product size of 259 base pairs (bp). An in-house plasmid containing the HHV-6 U97 gene (259 bp) was used as the positive control. The experiment was performed in duplicate. The PCR reaction was conducted using 5 × FiREPOL Eva Green qPCR Mix Plus (Solis Bio Dyne, Tartu, Estonia) according to the protocol of a previous study []. The B-globin gene was used as an internal control and was detected using the GH2O forward primer 5′ GAAGAGCCAAGGACAGGTAC 3′ and the PCO4 reverse primer 5′ CAACTTCATCCACGTTCACC 3′, with a PCR product size of 268 bp [].
The HHV-6 positive cases were confirmed for HHV-6 viral load in duplicate. The positive controls were diluted 10-fold in duplicate to create a standard curve. The number of copies was determined using the following formula:
where Z = amount of amplicon (ng), N = length of dsDNA amplicon, 660 g/mol = average mass of 1 bp dsDNA, 6.022 × 1023 = Avogadro’s constant, and 1 × 109 = conversion factor.
Number of copies =
(Z ng × 6.0221 × 1023 molecules/mole)/(N × 660 g/mole) × 1 × 109 ng/g
2.4. TNF-α Promoter (-308G/A; rs1800629) Detection by High-Resolution Melt (HRM) Analysis
TNF-α (-308G/A; rs1800629) was detected by HRM using the forward primer 5′CACAGACCTGGTCCCCAAAA 3′ and the reverse primer 5′ CATCCTCCCTGCTCCGATTC 3′, with a PCR product size of 136 bp. The experiment was performed in duplicate. The PCR reaction was performed using 5 × FiREPOL Eva Green HRM Mix Plus (Solis Bio Dyne, Tartu, Estonia) according to a previous study []. DNA samples known to have TNF-α with -308G/A and -308G were used as positive controls.
2.5. DNA Sequencing
Sanger sequencing was used to confirm the TNF-α promoter point mutation (-308G/A). The TNF-α primers identified in Section 2.4 were used as the forward and reward sequences for PCR DNA sequencing. The sequences were analyzed by comparison to reference sequences (>ref|NC_000006.12|:31,575,208–31,575,322 Homo sapiens chromosome 6, GRCh38.p13 Primary Assembly ACCTGGTCCCCAAAAGAAATGGAGGCAATAGGTTTTGAGGGGCATGGGGACGGGGTTCAGCCTCCAGGGTCCTACACACAAATCAGTCAGTGGCCCAGAAGACCCCCCTCGGAAT) from GenBank using Bioedit version 7.2 (a biological sequence alignment editor).
2.6. Screening Effect of HHV-6 Status and TNF-α Promoter (-308G/A) Mutation by ELISA
An ELISA was performed on 20 samples including healthy participants and MDD patients with known HHV-6 (positive or negative)/TNF-α promoter status (healthy: positive/G n = 3, positive/G/A n = 5, negative/G/A n = 5, negative/G n = 5; MDD patients treated with drugs: positive/G n = 1, negative/G n = 1). The serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) were measured using a human cytokine IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α ELISA kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and the methods of a previous study []. The experiment was performed in duplicate or triplicate.
2.7. Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES)
Whole-exome sequencing was used to analyze the point mutation status of samples from four participants: an MDD patient (female), the first-degree relative of an MDD patient (male; brother), a healthy female, and a healthy male aged between 21–30 years. DNA was extracted using previously described methods and instructions, and DNA was eluted using TE buffer. Whole-exome sequencing was conducted with no replications. DNA quality control, library preparation, library quality control, cluster generation, and sequencing were performed. The precision and stability of each experiment were necessary to ensure the reliability of the subsequent bioinformatics analysis. A qualifying DNA sample was fragmented using an ultra-sonicator and a resultant fragment was constructed into a high-throughput sequencing library through the steps of terminal repair, base A tail addition, adaptor ligation, purification and pre-amplification, quantitation, exon capture, and PCR enrichment. After the completion of library preparation, the size and concentration of each sample were determined, and a Qubit fluorometer was used for the accurate measurement of DNA concentration. The quality and concentration of the sequencing library were assessed.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using IBM SPSS software version 16, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Pearson’s chi-squared or Fisher’s exact test was used to compare the categorical variables between groups. An independent Student’s t-test or unpaired t-test was used to compare separate mean ± standard deviation (SD) sets. A one-way ANOVA, Median test, Mann–Whitney U-test, or Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare the mean/median ± SD or SEM of >3 groups.
3. Results
3.1. Risk Factor for MDD
Online samples were collected and confirmed as MDD based on medical certifications and the PHQ-9. A total of 60 healthy participants and 59 patients with depression were studied. Of the MDD patients, 89% reported mild-to-major depression based on the PHQ-9, while 93% of healthy participants disclosed no-to-mild depression.
Education, income, familial relationships, BMI, exercise, fermented food consumption, water type used for brushing teeth, and second-hand smoke exposure were associated with MDD (Table 1).

Table 1.
Risk factors for MDD.
3.2. HHV-6 Detection by qPCR
Oral buccal cells were collected from 471 donors from the Thai population and HHV-6 was detected using qPCR. The results showed a statistically significant difference in HHV-6 positivity between patients with depression (15/59 (25.67%)) and health participants (51/360 (14.17%)); p-value = 0.028 (odds ratio = 2.066, 95% CI = 1.071–3.983). The results are listed in Table 2, which also details the high prevalence of HHV-6-infected blood relatives and non-blood relatives of MDD patients.

Table 2.
Association of HHV-6 with MDD patients, relatives, and healthy participants.
This study determined the relationships among HHV-6 infection in MDD patients, blood relatives of MDD patients, and non-blood relatives of MDD patients, as shown in Figure 2.
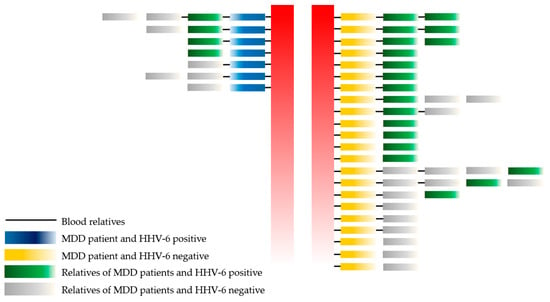
Figure 2.
The association of HHV-6 with MDD patients, blood relatives, and non-blood relatives. Remark: red color = separate between HHV-6 positive and negative in MDD group.
No statistically significant difference was observed between MDD patients, blood relatives of MDD patients (17/36 (47.20%)), and non-blood relatives of MDD patients (7/16 (43.75%); p-value = 0.076). Moreover, the healthy population included a lower number of HHV-6-positive cases than the healthy blood relatives and non-blood relatives of MDD patients (p-value = 0.000 and 0.001, respectively). Thus, a higher prevalence of HHV-6 infection was found among the family members (healthy) of MDD patients than the healthy control population.
Education, income, familial relationships, BMI, exercise, water type used for brushing teeth, and second-hand smoke exposure were associated in all MDD (59 cases) and MDD without HHV-6 cases. Only familial relationships and exercise were associated with MDD with HHV-6 positivity, as shown in Figure 3 and Supplementary Tables S1 and S2.
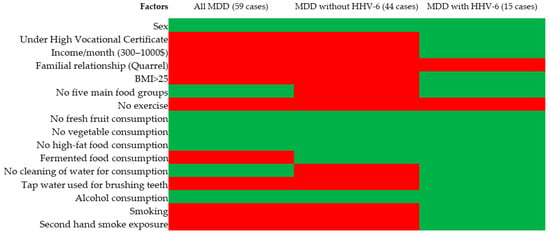
Figure 3.
Risk factors for MDD, MDD without HHV-6, MDD with HHV-6. Remark: red = statistically significant, green = not statistically significant when associated with MDD compared to healthy control.
Figure 4 shows the PHQ-9 level of the healthy individual controls and MDD patients in HHV-6 positive and negative cases. HHV-6 positive cases had a higher percentage of major depression based on the PHQ-9 level (highest severity level) than the HHV-6 negative level in MDD patients and healthy individual controls; however, the difference was not statistically significant. The result might be error because of PHQ-9 score ≥ 10 had a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 88% for major depression.
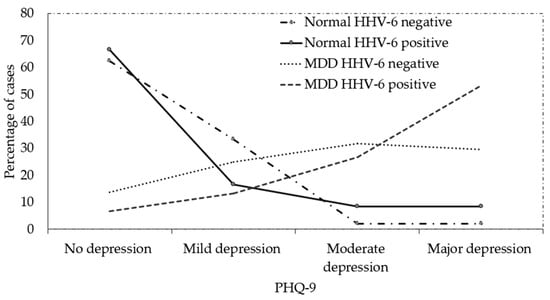
Figure 4.
PHQ-9 level of healthy individual control and MDD patients in HHV-6 positive and negative cases (percentage).
3.3. TNF-α (-308G/A; rs1800629) Promoter Detection by HRM Analysis
The TNF-α promoter (-308G/A) was detected using HRM. The results showed no statistically significant difference between the presence of G/A in depressed patients (3/39 (7.69%)) and that in the healthy population (15/220 (6.8%)); p-value = 0.843 (odds ratio = 1.139, 95% CI = 0.314–4.134). No statistically significant difference was observed between MDD patients and blood relatives (6/20 (30%)) and between MDD patients and non-blood relatives (2/14 (14.29%)) (p-value = 0.072). The results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The association of TNF-α promotor status with MDD patients, relatives, and the healthy population.
No statistically significant difference was observed between the healthy population and non-blood relatives of MDD patients (p-value = 0.279).
Surprisingly, a relationship was noted between the TNF-α (-308G/A; rs1800629) promoter mutation and HHV-6 infection (Figure 5).
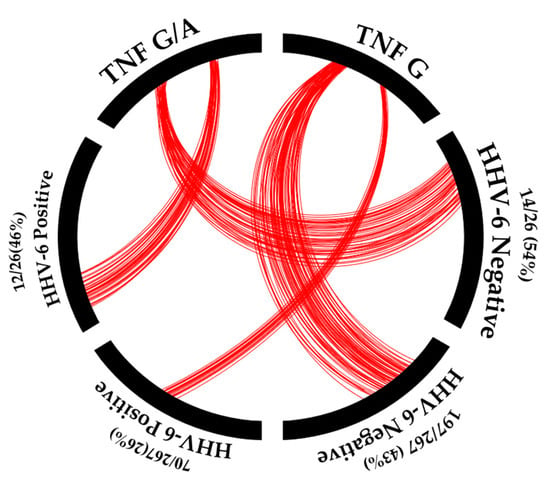
Figure 5.
The association of HHV-6 positivity with TNF-α promotor status. Remark: red = number of samples.
Individuals with the TNF-α (-308G/A) promoter mutation showed a higher frequency of HHV-6 infection (12/26 (46.15%)) than those with the wild-type TNF-α (-308G) (70/267 (26.22%)); p-value = 0.031 (odds ratio = 2.412, 95% CI = 1.065–5.465). Thus, the TNF-α (-308G/A) promoter mutation could affect HHV-6 infection. The prevalence of HHV-6 infection, the TNF-α (-308G/A) promotor mutation, and MDD patients in Asia are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Prevalence of HHV-6 infection, the TNF-α (-308G/A) promotor mutation, and MDD patients in Asia.
3.4. HHV-6 Viral Load
qPCR was used for viral load detection in the 90 HHV-6 positive cases. The results showed a statistically significantly higher load of HHV-6 in MDD patients (14,473 ± 16,948 copies/ng DNA) than in the healthy population (6303 ± 5791 copies/ng DNA); p-value = 0.044 (Figure 6).
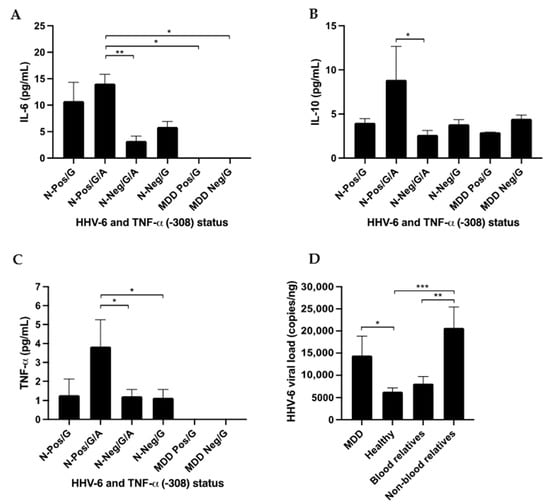
Figure 6.
The association of HHV-6 and TNF-α promotor status with cytokine expression measured using ELISA and HHV-6 viral load. N = normal healthy control. Healthy: positive/G, positive/G/A, negative/G/A, negative/G; and MDD patients being treated with drugs: positive/G, negative/G were available for ELISA analysis. (A) IL-6 cytokine level, (B) IL-10 cytokine level, (C) TNF-α cytokine level, and (D) HHV-6 viral load. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01 and *** p-value < 0.001.
MDD patients had HHV-6 viral loads similar to those of their non-blood relatives (20,721 ± 12,458 copies/ng DNA) and blood relatives (8146 ± 5656 copies/ng DNA; p-value 0.052). The healthy population had HHV-6 viral loads similar to those of blood relatives of MDD patients (p-value = 0.093). The viral load of HHV-6 was found to be higher among family members (healthy) of MDD patients than among healthy controls.
Based on the PHQ-9 level of the participants, the viral load was 2266 copies/ng DNA in those with no depression, 26,010 copies/ng DNA in participants with mild depression, 8557 copies/µL DNA in people with moderate depression, and 16,072 copies/µL DNA in those with major depression.
This study did not find a relationship between the TNF-α (-308G/A) promoter mutation and HHV-6 viral load. Samples with the TNF-α (-308G/A) promoter mutation had HHV-6 viral loads similar to those with the wild-type TNF-α (-308G) (8148 ± 5120 copies/ng DNA and 9842 ± 11,235 copies/ng DNA, respectively; p-value = 0.422).
3.5. ELISA
Twenty samples from normal and MDD patients with various HHV-6 (positive or negative)/TNF-α promoter statuses (healthy: positive/G n = 3, positive/G/A n = 5, negative/G/A n = 5, and negative/G n = 5; MDD patients being treated with drugs: positive/G n = 1 and negative/G n = 1) were available for the ELISA.
The results showed that the levels of IL-6, IL-10 were statistically significantly different (p-value = 0.002 and 0.013, respectively) when using the Median test.
The results showed that the levels of TNF-α was not statistically significantly different (p-value = 0.441) when using the Median test.
Surprising, the results showed that the levels of IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α were higher in healthy participants with HHV-6 positive/G/A status than in healthy participants with HHV-6 negative/G/A status (p-value = 0.004, 0.038, and 0.042, respectively, using the Kruskal–Wallis or unpaired t-test). The results are shown in Figure 6.
TNF-α mutations (-308G/A) are a risk factor of MDD and the results showed that the TNF-α mutation (-308G/A) induced high expression of TNF-α with the IL-6 and IL-10 signaling pathway in HHV-6 positive individuals.
HHV-6 might have affected the observed association with TNF-α gene variation in this study, considering its influence on TNF-α cytokine levels.
3.6. Whole-Exome Sequencing
The results of whole-exome sequencing showed the olfactory receptor family 8 subfamily G member 2 (OR8G2P; rs141204263) and olfactory receptor family 2 subfamily T member 4 (OR2T4) in MDD patients but not in healthy family members. Olfactory receptors are chemoreceptors expressed in the cell membranes of olfactory receptor neurons.
This study did not find genes commonly associated with MDD, such as serotonin, dopamine or SLC6A4, GNAZ, DRD2, MMP-1, SHANK3, VDR, GRIA1, ANKK1, TPH1, and RNF180 mutations in the MDD patients. Genes associated with depression or neuro-diseases were found in this study, such as ABCG1, ASMTL, CACNA1F, COX7A1, GRID2, HTR3E, and SHANK2 (Table 5).

Table 5.
Whole-exome sequencing comparison of mutations in MDD patients, their relatives, and healthy controls.
In addition, this study found gene mutations associated with the immune system, such as complement, interferon, interleukin, scavenger receptor, Toll-like receptor, TNF receptor, and CD molecule (Figure 7).
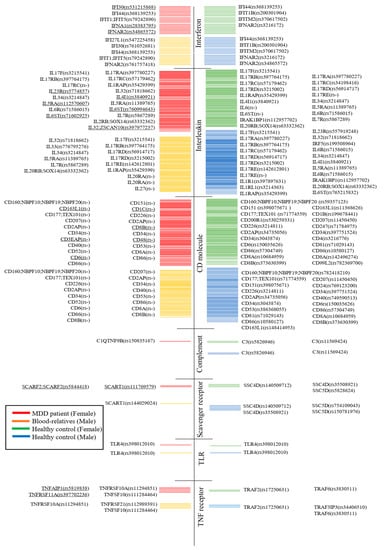
Figure 7.
Whole-exome sequencing comparison of mutations of MDD patients, their relatives, and healthy controls. Underlines indicate them only being detected in MDD patients.
4. Discussion
This study identified that HHV-6 has implications on the observed association between TNF-α gene variation and MDD. This influence on TNF-α mutation could have an impact on the immunological homeostasis of viral reactivation. Currently, information regarding the prevalence of the -308G/A allele in people with depression and its relationship with HHV-6 reactivation and viral load in terms of understanding MDD’s complex etiology is limited. Table 4 shows trend of HHV-6 prevalence and MDD in Asia (Supplementary Figure S1).
The detection of HHV-6 in patients diagnosed with encephalitis or meningitis using PCR strongly indicates that HHV-6 can affect central nervous system diseases [,]. An autopsy brain sample of a patient was positive for HHV-6 and showed a high viral load; however, a low level of HHV-6 infection was found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) []. In Japanese patients, HHV-6 infection is a common cause of acute sporadic encephalopathy but cannot be found in the CSF. These results indicate that HHV-6 encephalopathy is caused by an indirect mechanism []. Finally, although the biomarker might not consist of viral particles, the present study showed a new association of HHV-6 that could induce the severity of MDD, although, no statistical significant difference between HHV-6 positive cases with higher percentages at the PHQ-9 level (major depression) and HHV-6 negative cases were found. Increasing MDD sample sizes will be required to confirm the results of this experiment in further studies.
Genetic variations are risk factors for MDD, although meta-analyses of environmental risk factors have shown that the proportion of variance explained by genetic risk factors is extremely small (0.1–0.4%) []. A systematic review of TNF-α (-308G/A) showed both effects and an absence of effects in relation to MDD []. The present study suggested that TNF-α (-308G/A) was not significantly found in MDD and healthy individuals; however, the association between TNF-α (-308G/A) and HHV-6 reactivation was prevalent in MDD cases. A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 levels were associated with MDD []. IL-6 production is typically preceded by the release of TNF-α, triggering inflammation. The current study suggested that both TNF-α (-308G/A) and HHV-6 might affect TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 expression, influencing the severity and progression of depression via inflammatory processes. Only familial relationships and exercise were associated with MDD cases that were HHV-6 positive as opposed to MDD cases without HHV-6. Several meta-analyses found that exercise can decrease circulating inflammatory factors such as IL-6, IL-18, C-reactive protein (CRP), leptin, fibrinogen, and angiotensin II to create an anti-inflammatory environment [,]. HHV-6 cannot be eradicated throughout the lifetime of the host. However, exercise appears to reduce the effect of HHV-6 on inflammation. This result suggests that the mechanism of HHV-6 positivity that induces MDD might be different from that of uninfected MDD. Based on a meta-analysis, Köhler et al. [] found that family problems and exercise [,] were highly significantly associated with MDD.
Inflammation is associated with MDD [] and a chronic inflammatory state involves increased activation of microglia, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. The persistent activation of microglia leads to the inefficient clearance of neurotoxic molecules, as well as neuron loss and a reduction in neurogenesis. Cytokines induce indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, an enzyme that reduces serotonin production [,], which causes decreased neurogenesis and a reduced number and size of glial cells in the hippocampus [,]. The presence of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α indicates resistance in the modulation of glucocorticoids, maintenance of the increased activity of the HPA axis [], and affectation of neurogenesis in the hippocampus due to the reduction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Increased levels of TNF-α were found in the dorsal–anterior cingulate cortex and the anterior insula of postmortem patients who presented with social rejection and increased anxiety []. Drugs that affect serotonin mechanisms could reduce inflammation and thereby reduce the effect of HHV-6. However, no mechanisms to remove HHV-6 from the brain, blood, or oral cells of infected patients have been identified. HHV-6 might affect the recurrence of MDD in patients after medication is stopped, due to stress or hypochondria because of a doubly activated inflammatory process.
Cytokine expression could be a potential biomarker of MDD. Antidepressant treatment significantly decreased the peripheral levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 [], and new evidence shows that anti-inflammatory drugs might be useful as antidepressants in MDD patients, such as in relation to IL-6 [].
Exome sequencing is a genomic technique for sequencing gene mutations. This study found gene mutations associated with immune system components such as complement, interferon, interleukin, scavenger receptor, Toll-like receptor, TNF receptor, and CD molecule in MDD patients. These results are similar to those of Ning et al. [], who determined that CD1C could be a useful biomarker for future studies in Thailand.
A limitation of this study was the low sample size of MDD patients and their relatives. Further studies should increase the sample size to improve the power of statistics. This study had bias as the mean ages in both groups were not a match and the result should be considered. The TNF-α mutation with cytokine level result showed a low power of statistical analysis. Therefore, to confirm this result, a larger group with the MDD TNF-α (-308G/A) mutation is required. No data are available on disease treatment or the exclusion of other chronic or acute inflammatory states. No conclusions can be drawn from the next-generation sequencing analysis since only four individuals were analyzed. However, a high prevalence of HHV-6 infection in the population and its ability to reactivate under any inflammatory or immunosuppressive conditions makes it difficult to discern whether an association between HHV-6 reactivation and a disease is causal or epiphenomenal and must be confirmed in the future.
5. Conclusions
Overall, this study revealed that HHV-6 infection is associated with MDD patients in the Thai population. TNF-α (-308G/A) gene mutations with HHV-6 positivity showed higher expression of TNF-α with the IL-6 and IL-10 signaling pathway than those with HHV-6 negativity. Novel insights derived from this study regarding TNF-α (-308G/A) mutations, HHV-6 and MDD could present a basis for future research and clinical applications. The relevance of investigating TNF-α gene variation and HHV-6 infection in the context of MDD could provide a better understanding of this association among the Thai population.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v15091898/s1. Supplementary Table S1: Risk factor of MDD (HHV-6 negative, 44 cases) and Supplementary Table S2 Risk factor of MDD (HHV-6 positive, 15 cases). Supplementary Figure S1: Prevalence of HHV-6 infection and MDD patients in Asia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai), C.P. and T.E.; methodology, S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai) and S.S.; investigation, S.S., S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai) and S.B. (Surachat Buddhisa); data curation, S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai); writing—original draft preparation, S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai) and S.S.; writing—review and editing, C.P., T.E., S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai), S.D. and S.J.; funding acquisition, S.B. (Sureewan Bumrungthai) and S.D.; method consultant, T.E., C.P., S.B. (Surachat Buddhisa), S.P. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Phayao (grant no. FF64-RIB005) and Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ubon Ratchathani University (grant no. ภส.อบ.0604.11-5/2566).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Committee on Human Research Ethics in Health Sciences and Science and Technology, University of Phayao, Thailand (UP-HEC 1.3/013/65). All procedures involving human participants performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki, the Belmont Report, the Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences guidelines, and the International Conference on Harmonization in Good Clinical Practice.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University for use of the qPCR machine.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx). Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/ (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Abdoli, N.; Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Jafarpour, S.; Solaymani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Shohaimi, S. The global prevalence of major depressive disorder (MDD) among the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumari, P.M.; Tangmunkongvorakul, A.; Srithanaviboonchai, K.; Techasrivichien, T.; Suguimoto, S.P.; Ono-Kihara, M.; Kihara, M. Grit is associated with lower level of depression and anxiety among university students in Chiang Mai, Thailand: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siripongpan, A.; Phattaramarut, K.; Namvichaisirikul, N.; Poochaya, S.; Horkaew, P. Prevalence of depression and stress among the first year students in Suranaree University of Technology, Thailand. Health Psychol. Res. 2022, 10, 35464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phomprasith, S.; Karawekpanyawong, N.; Pinyopornpanish, K.; Jiraporncharoen, W.; Maneeton, B.; Phinyo, P.; Lawanaskol, S. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression in Medical Students in a Northern Thailand University: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomchoei, C.; Apidechkul, T.; Keawdounglek, V.; Wongfu, C.; Khunthason, S.; Kullawong, N.; Tamornpark, R.; Upala, P.; Yeemard, F. Prevalence of and factors associated with depression among hill tribe individuals aged 30 years and over in Thailand. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singkhorn, O.; Apidechkul, T.; Pitchalard, K.; Moonpanane, K.; Hamtanon, P.; Sunsern, R.; Leaungsomnapa, Y.; Thepsaw, J. Prevalence of and factors associated with depression in the hill tribe population aged 40 years and older in northern Thailand. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 2021, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.N.N.; Moolphate, S.; Koyanagi, Y.; Angkurawaranon, C.; Supakankunti, S.; Yuasa, M.; Aung, M.N. Depression and Associated Factors among Community-Dwelling Thai Older Adults in Northern Thailand: The Relationship between History of Fall and Geriatric Depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangtongkum, S.; Sucharitakul, P.; Wongjaroen, S.; Maneechompoo, S. Prevalence of depression among a population aged over 45 years in Chiang Mai, Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2008, 91, 1812. [Google Scholar]
- Charoensakulchai, S.; Usawachoke, S.; Kongbangpor, W.; Thanavirun, P.; Mitsiriswat, A.; Pinijnai, O.; Kaensingh, S.; Chaiyakham, N.; Chamnanmont, C.; Ninnakala, N.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors influencing depression in older adults living in rural Thailand: A cross-sectional study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Evangelou, E.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Belbasis, L.; Bortolato, B.; Melo, M.C.; Coelho, C.A.; Fernandes, B.S.; et al. Mapping risk factors for depression across the lifespan: An umbrella review of evidence from meta-analyses and Mendelian randomization studies. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 103, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, G.S. Mechanisms and treatment of late-life depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2019, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, C.; Hodes, G.; Russo, S. Pathogenesis of depression: Insights from human and rodent studies. Neuroscience 2016, 321, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, M.M.; Bland, R.C.; Canino, G.J.; Faravelli, C.; Greenwald, S.; Hwu, H.-G.; Joyce, P.R.; Karam, E.G.; Lee, C.-K.; Lellouch, J.; et al. Cross-national epidemiology of major depression and bipolar disorder. JAMA 1996, 276, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawton, K.; Comabella, C.C.I.; Haw, C.; Saunders, K. Risk factors for suicide in individuals with depression: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 147, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, T.-Y.; Pae, C.-U.; Chae, J.-H.; Bahk, W.-M.; Kim, K.-S.; Serretti, A. Possible association between—G308A tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphism and major depressive disorder in the Korean population. Psychiatr. Genet. 2003, 13, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-M.; Stewart, R.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kang, H.-J.; Jang, J.-E.; Kim, S.-W.; Shin, I.-S.; Park, M.-H.; Yoon, J.-H.; Park, S.-W.; et al. A one year longitudinal study of cytokine genes and depression in breast cancer. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 148, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxenkrug, G.F. Genetic and hormonal regulation of tryptophan kynurenine metabolism: Implications for vascular cognitive impairment, major depressive disorder, and aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1122, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.M.; Koch, J.; Nowak, C.; Holdt, L.M.; Teupser, D.; Hegerl, U.; Himmerich, H. Ligands and receptors of the TNF superfamily are decreased in major depression and during early antidepressant therapy. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 119, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhang, H.; Baloch, Z. Pathogenetic and Therapeutic Applications of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wilkins, L.M.; Aziz, N.; Cannings, C.; Wyllie, D.H.; Bingle, C.; Rogus, J.; Beck, J.D.; Offenbacher, S.; Cork, M.J.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human interleukin-1B gene affect transcription according to haplotype context. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, D.; Faulds, G.; Jeffery, R.; Mohamed-Ali, V.; Yudkin, J.S.; Humphries, S.; Woo, P. The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, J.; Kendler, K.S. The genetics of major depression. Neuron 2014, 81, 484–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, J.B.; Slager, S.L.; McGrath, P.J.; Hamilton, S.P. Sequence analysis of the serotonin transporter and associations with antidepressant response. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 58, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohoff, F.W. Overview of the genetics of major depressive disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2010, 12, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S.; Gatz, M.; Gardner, C.O.; Pedersen, N.L.; Ohlsson, H.; Lichtenstein, P.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K.; Keverne, J.; Czamara, D.; et al. A Swedish national twin study of lifetime major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Neale, M.C.; Kendler, K.S.; Bauer, A.E.; Maegbaek, M.L.; Liu, X.; Wray, N.R.; Miller, W.C.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Munk-Olsen, T.; et al. Genetic epidemiology of major depression: Review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillargeon, J.; Piper, J.; Leach, C.T. Epidemiology of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) infection in pregnant and nonpregnant women. J. Clin. Virol. 2000, 16, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancharoen, C.; Mekmullica, J.; Bhattarakosol, P. Seroprevalence of anti-human herpes virus-6 IgG antibody in children of Bangkok, Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2001, 32, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, K.B.; Khairullah, N.S.; Hooi, P.S. Seroepidemiology of human herpesvirus 6 in a population seen in the University Hospital, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1996, 27, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Asano, Y.; Akimoto, S.; Ozaki, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Kurata, T.; Goshima, F.; Nishiyama, Y. Latent infection of human herpesvirus 6 in astrocytoma cell line and alteration of cytokine synthesis. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 66, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Stubbs, B.; Maes, M.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Morris, G.; Fernandes, B.S.; Brunoni, A.R.; et al. Peripheral Alterations in Cytokine and Chemokine Levels After Antidepressant Drug Treatment for Major Depressive Disorder: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 4195–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Walder, K.; Maes, M. The Putative Role of Viruses, Bacteria, and Chronic Fungal Biotoxin Exposure in the Genesis of Intractable Fatigue Accompanied by Cognitive and Physical Disability. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2550–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santpere, G.; Telford, M.; Andrés-Benito, P.; Navarro, A.; Ferrer, I. The Presence of Human Herpesvirus 6 in the Brain in Health and Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotheringham, J.; Williams, E.L.; Akhyani, N.; Jacobson, S. Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) induces dysregulation of glutamate uptake and transporter expression in astrocytes. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusty, B.K.; Gulve, N.; Govind, S.; Krueger, G.R.F.; Feichtinger, J.; Larcombe, L.; Aspinall, R.; Ablashi, D.V.; Toro, C.T. Active HHV-6 Infection of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells in Mood Disorders. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, C.T.; Eliassen, E.; Prusty, B.K. Does infection of cerebellar Purkinje neurons with human herpes virus 6A or 6B (HHV-6) increase the risk of developing mood disorders? Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Oka, N.; Takahashi, M.; Shimada, K.; Ishii, A.; Tatebayashi, Y.; Shigeta, M.; Yanagisawa, H.; Kondo, K. Human Herpesvirus 6B Greatly Increases Risk of Depression by Activating Hypothalamic-Pituitary -Adrenal Axis during Latent Phase of Infection. iScience 2020, 23, 101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.-M.; Ham, B.-J. How Inflammation Affects the Brain in Depression: A Review of Functional and Structural MRI Studies. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M. Major depression and activation of the inflammatory response system. Cytokines Stress Depress. 1999, 461, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeer, P.L.; McGeer, E.G. The inflammatory response system of brain: Implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Rev. 1995, 21, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Liberto, M.C.; Iannello, D.; Capozza, A.B.; Focà, A. Altered cytokine production after human herpes virus type 6 infection. New Microbiol. 1999, 22, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Rotola, A.; Caselli, E.; Rizzo, R. HHV-6A infection induces amyloid-beta expression and activation of microglial cells. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuta, H.; Nakane, A.; Lu, H.; Taguchi, Y.; Minagawa, T.; Matsumoto, S. Interferon induction by human herpesvirus 6 in human mononuclear cells. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 162, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Goodrich, J.M.; Yang, X. Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) regulates production of IL-10 and IL-12 in human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6)-infected monocyte/macrophage lineage. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 109, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, M.; Cheadle, C.; Soldan, S.S.; Cermelli, C.; Yamano, Y.; Akhyani, N.; Nagel, J.E.; Taub, D.D.; Becker, K.G.; Jacobson, S. Gene expression profile of herpesvirus-infected T cells obtained using immunomicroarrays: Induction of proinflammatory mechanisms. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11641–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, J.; Flamand, L.; D’Addario, M.; Hiscott, J.; Stefanescu, I.; Ablashi, D.V.; Gallo, R.C.; Menezes, J. Modulatory effects of Epstein-Barr, herpes simplex, and human herpes-6 viral infections and coinfections on cytokine synthesis: A comparative study. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Liberto, M.C.; Capozza, A.B.; Focà, A. Productive HHV-6 infection in differentiated U937 cells: Role of TNF alpha in regulation of HHV-6. New Microbiol. 1997, 20, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Duh, E.J.; Maury, W.J.; Folks, T.M.; Fauci, A.S.; Rabson, A.B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5974–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramian, E.; Furr, M.; Wu, J.T.; Ceballos, R.M. Differential Impacts of HHV-6A versus HHV-6B Infection in Differentiated Human Neural Stem Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, S.; Ito, Y.; Ohta, R.; Sofue, A.; Gotoh, K.; Morishima, T.; Kimura, H. Comparison of the levels of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) DNA and cytokines in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of children with HHV-6 encephalopathy. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, N.P.; Nattanmai, S.; Hull, R.; Fusco, H.; Dzigua, L.; Wang, H.; Dupuis, M. Detection and typing of human herpesvirus 6 by molecular methods in specimens from patients diagnosed with encephalitis or meningitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3972–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bolle, L.; Naesens, L.; De Clercq, E. Update on human herpesvirus 6 biology, clinical features, and therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.S.; Peiris, K.Y.; Yuen, R.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Lau, F.E.; Chen, S.K.; Lo, C.Y.; Chan, T.K.; Ng, M.H. Human herpesvirus-6 and human herpesvirus-7 infections in bone marrow transplant recipients. J. Med. Virol. 1997, 53, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungman, P.; Wang, F.Z.; Clark, D.A.; Emery, V.C.; Remberger, M.; Ringden, O.; Linde, A. High levels of human herpesvirus 6 DNA in peripheral blood leucocytes are correlated to platelet engraftment and disease in allogeneic stem cell transplant patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 774–781. [Google Scholar]
- Zerr, D.M.; Huang, M.-L.; Corey, L.; Erickson, M.; Parker, H.L.; Frenkel, L.M. Sensitive method for detection of human herpesviruses 6 and 7 in saliva collected in field studies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1981–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kosugi, S.; Koide, R.; Kawamura, Y. Endogenization and excision of human herpesvirus 6 in human genomes. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantivanich, S.; Laohapand, P.; Thaweeboon, S.; Desakorn, V.; Wuthinuntiwong, P.; Chalermtaranukul, S.; Pansri, P.; Amarapal, P.; Balachandra, K.; Chantratita, W.; et al. Prevalence of cytomegalovirus, human herpesvirus-6, and Epstein-Barr virus in periodontitis patients and healthy subjects in the Thai population. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2004, 35, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thawaranantha, D.; Chimabutra, K.; Balachandra, K.; Warachit, P.; Pantuwatana, S.; Inagi, R.; Kurata, T.; Yamanishi, K. Prevalences of human herpesvirus 6 and human herpesvirus 7 in normal Thai population. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1999, 30, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Chantaratin, S.; Trimetha, K.; Werarak, P.; Lapphra, K.; Maleesatharn, A.; Rungmaitree, S.; Wittawatmongkol, O.; Phongsamart, W.; Kongstan, N.; Khumcha, B.; et al. Depression and Anxiety in Youth and Young Adults Living with HIV: Frequency and Associated Factors in Thai Setting. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care 2022, 21, 23259582221101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotrakul, M.; Sumrithe, S.; Saipanish, R. Reliability and validity of the Thai version of the PHQ-9. BMC Psychiatry 2008, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongpakdeesakul, S.; Ekalaksananan, T.; Pientong, C.; Iamchuen, N.; Buddhisa, S.; Mahingsa, K.; Pingyod, A.; Sangsrijun, W.; Passorn, S.; Chopjitt, P.; et al. Human Oncogenic Epstein–Barr Virus in Water and Human Blood Infection of Communities in Phayao Province, Thailand. Water 2023, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, M.A.M.; van Oeveren-Dybicz, A.; van den Bergh, F.A. Genotyping of HLA-B27 by real-time PCR without hybridization probes. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, M.-Y.; Shin, W.-S. Detection of human herpesvirus 6 variant A in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from multiple sclerosis patients. Eur. Neurol. 2000, 43, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Most Depressed Countries 2023—Wisevoter. Available online: https://wisevoter.com/country-rankings/most-depressed-countries/?fbclid=IwAR37FvIlUOM-XdUM4IT4hClUn3DtJzklYK4jEcE8ntzAhNBHMFMbowdWQH8 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Pengpid, S.; Peltzer, K.; Anantanasuwong, D. Prevalence and determinants of incident and persistent depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in Thailand: Prospective cohort study. BJPsych Open 2023, 9, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamdee, K.; Panadsako, N.; Mueangson, O.; Nuinoon, M.; Janwan, P.; Poonsawat, W.; Pongpanitanont, P.; Kitkumthorn, N.; Thongsroy, J.; Chunglok, W. Promoter polymorphism of TNF-α (rs1800629) is associated with ischemic stroke susceptibility in a southern Thai population. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karawekpanyawong, N.; Kaewkitikul, K.; Maneeton, B.; Maneeton, N.; Siriaree, S. The prevalence of depressive disorder and its association in Thai cervical cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchai, T.; Homchan, K.; Sopipong, W.; Chansaenroj, J.; Swangvaree, S.; Junyangdikul, P.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Lack of Associations between TNF-αPolymorphisms and Cervical Cancer in Thai women. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpakaran, N.; Wongpakaran, T. Prevalence of major depressive disorders and suicide in long-term care facilities: A report from northern Thailand. Psychogeriatrics 2012, 12, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Ohye, T.; Hattori, F.; Kozawa, K.; Ihira, M.; Yatsuya, H.; Nishizawa, H.; Kurahashi, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Inherited Chromosomally Integrated Human Herpesvirus 6 Is a Risk Factor for Spontaneous Abortion. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Hirota, T.; Tamari, M.; Ichikawa, K.; Takeda, K.; Arinami, T.; Shibasaki, M.; Noguchi, E. An association between asthma and TNF-308G/A polymorphism: Meta-analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 51, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Fujise, N.; Fukunaga, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ikeda, M. Comparisons of the prevalence of and risk factors for elderly depression between urban and rural populations in Japan. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2012, 24, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Hattori, F.; Kozawa, K.; Ihira, M.; Ohye, T.; Kurahashi, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 in the Japanese population. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamizono, S.; Yamada, K.; Seki, N.; Higuchi, T.; Kimura, A.; Nonaka, K.; Itoh, K. Susceptible locus for obese type 2 diabetes mellitus in the 5′-flanking region of the tumor necrosis factor-α gene. Tissue Antigens 2000, 55, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suto, M.; Isogai, E.; Mizutani, F.; Kakee, N.; Misago, C.; Takehara, K. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Postpartum Depression in Fathers: A Regional, Longitudinal Study in Japan. Res. Nurs. Health 2016, 39, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Miura, H.; Kozawa, K.; Yoshikawa, A.; Ikeda, N.; Yatsuya, H.; Yasuoka, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Inherited chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 and autoimmune connective tissue diseases. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 132, 104656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokushige, K.; Takakura, M.; Tsuchiya-Matsushita, N.; Taniai, M.; Hashimoto, E.; Shiratori, K. Influence of TNF gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with NASH and simple steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO World Mental Health Survey Consortium. Prevalence, severity, and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. JAMA 2004, 291, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Bromet, E.J. The epidemiology of depression across cultures. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2013, 34, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezhnyova, V.; Davidyuk, Y.; Mullakhmetova, A.; Markelova, M.; Zakharov, A.; Khaiboullina, S.; Martynova, E. Analysis of herpesvirus infection and genome single nucleotide polymorphism risk factors in multiple sclerosis, Volga federal district, Russia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1010605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churnosov, M.I.; Belousova, O.N.; Sirotina, S.S. Study of the associations between polymorphic markers rs1800629 TNFα, rs909253 Ltα, rs767455 TNFR1, rs1061624 TNFR2 and the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Mellitus 2017, 20, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakriev, S.; Kovalev, J.; Mozhaev, M. Prevalence of depression in a general hospital in Izhevsk, Russia. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2009, 63, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Zedan, H.T.; Aldewik, N.; Elkhider, A.; Hicazi, A.; Younes, N.; Ayoub, H.H.; Abu Raddad, L.; Yassine, H.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Human herpes simplex virus-6 (HHV-6) detection and seroprevalence among Qatari nationals and immigrants residing in Qatar. IJID Reg. 2022, 2, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algamdi, A.A.; Abdi, S.; Almutairi, R.M.; Sarwar, S.; Aldaghri, N.; Haq, S.H.; Alamro, A.; Muayqil, T.A. Clusterin, TNF-α, and IL-6 polymorphism and implications on Alzheimer’s disease risk determination in Saudi population. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, F.; Elshirbeny, M.; Hamad, A.; Kaddourah, A.; Ghonimi, T.; Ibrahim, R.; Fouda, T. Prevalence of Depression and Sleep Disorders in Patients on Dialysis: A Cross-Sectional Study in Qatar. Int. J. Nephrol. 2021, 2021, 5533416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, X.D.; Hoang, V.T.; Dang, T.T.D.; Vu, T.P.; To, M.M.; Tran, T.K.; Do, M.D.; Nguyen, D.C.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Colson, P.; et al. Aetiology of Acute Undifferentiated Fever Among Children Under the Age of Five in Vietnam: A Prospective Study. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, S.J.; Stephens, H.A.; Blackwell, J.M.; Duc, C.M.; Lanh, M.N.; Dudbridge, F.; Phuong, C.X.T.; Luxemburger, C.; Wain, J.; Ho, V.A.; et al. Genes of the class II and class III major histocompatibility complex are associated with typhoid fever in Vietnam. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Bui, L.; Nguyen, A.; Nguyen, B.; Tran, P.; Vu, P.; Dang, L. The prevalence of depression and associated risk factors among medical students: An untold story in Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rao, J. A multiplex real-time PCR quantitation of human herpesvirus-6, 7, 8 viruses: Application in blood transfusions. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, L.; Zhang, X. -308G/A polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) gene and metabolic syndrome susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, A.; Yin, J.; Waqas, A.; Bai, X.; Wang, D.; Rahman, A.; Li, X. Prevalence of perinatal depression and its determinants in Mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Wu, Y.; Cai, M.; Wu, X.; Shang, S. Subtype-specific, probe-based, real-time PCR for detection and typing of human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis from pediatric patients under the age of 2 years. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.T.C.; Lee, S.C.; Pu, Y.B.; Ng, M.C.Y.; So, W.; Thomas, N.; Chan, W.B.; Cockram, C.S.; Chan, J.C.N. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha promoter gene polymorphism at—308 (genotype AA) in Chinese subjects with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2003, 20, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.C.; Zhang, M.Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; He, Y.L.; Liu, Z.R.; Cheng, H.; Tsang, A.; Lee, S.; Kessler, R.C. Twelve-month prevalence, severity, and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in metropolitan China. Psychol Med. 2006, 36, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuh, A.A.; Chan, H.H.; Chiu, S.S.; Ng, H.Y.; Peiris, J.S. A prospective case control study of the association of Gianotti-Crosti syndrome with human herpesvirus 6 and human herpesvirus 7 infections. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2002, 19, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneghan, M.A.; Johnson, P.J.; Clare, M.; Ho, S.; Harrison, P.M.; Donaldson, P.T. Frequency and nature of cytokine gene polymorphisms in hepatocellular carcinoma in Hong Kong Chinese. Int. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2004, 34, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeno, T.; Kizawa, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Nakata, Y.; Sato, T. Depression among primary care patients with complaints of headache and general fatigue. Prim. Care Psychiatry 2002, 8, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktafiani, D.; Megasari, N.L.A.; Ana, E.F.; Nasronudin; Lusida, M.I.; Soetjipto. First Report on HHV-6 Infection Among HIV-Infected Individuals Residing in Surabaya, Indonesia. HIV/AIDS-Res. Palliat. Care 2020, 12, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiati, W.N.; Gani, A.Z.; Sulijaya, B.; Suhartono, W.A.; Auerkari, E.I. Relation of Susceptibility to Periodontitis and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha G-308A Polymorphism in Indonesian Males. J. Int. Dent. Med. Research 2020, 13, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Handajani, Y.S.; Schröder-Butterfill, E.; Hogervorst, E.; Turana, Y.; Hengky, A. Depression among Older Adults in Indonesia: Prevalence, Role of Chronic Conditions and Other Associated Factors. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2022, 18, e174501792207010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdinejad-Yazdi, M.; Sobhan, M.R.; Dastgheib, S.A.; Bahrami, R.; Shaker, S.H.; Mirjalili, H.; Sadeghizadeh-Yazdi, J.; Zare-Shehneh, M.; Neamatzadeh, H. A meta-analysis for association of TNF-α -308G>A polymorphism with susceptibility to Ankylosing Spondylitis. J. Orthop. 2021, 26, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S. The prevalence and correlates of depression in Korean adults with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 25, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Shim, J. Predictors of Depression among Individuals Receiving the Basic Livelihood Security Program Benefits in Korea: A Study Based on the Sixth and Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2018). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, L.; Piras, E.; Sullivan, K.; Gillen, S.; Bumbut, A.; Lin, C.-T.M.; Leibovitch, E.C.; Graves, J.S.; Waubant, E.L.; Chamberlain, J.M.; et al. Detection of HHV-6 and EBV and Cytokine Levels in Saliva from Children with Seizures: Results of a Multi-Center Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayal, A.D.; Sodimalla, K.V.; Chelerkar, V.; Deshpande, M. Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Primary Glaucoma in Western India. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 31, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanquan, C.; Yuqi, W.; Rui, S. Prevalence and gender disparity of those who screen positive for depression in China by the classification of the employer and industry: A cross-sectional, population-based study. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chiang, H.H.; Cho, Y.T.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, K.L.; Yang, C.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Chu, C.-Y. Human herpes virus reactivations and dynamic cytokine profiles in patients with cutaneous adverse drug reactions—A prospective comparative study. Allergy 2015, 70, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwu, H.-G.; Yeh, E.-K.; Chang, L.-Y. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in Taiwan defined by the Chinese Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1989, 79, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Arivananthan, M.; Chandrashekran, A.; Tan, B.S.; Hashim, B.Y. Human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) DNA and virus-encoded antigen in oral lesions. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 1997, 26, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojtaba, G. Association between TNF-a-308 G/A Polymorphism and Oral Cancer Risk among Malaysian Indian and Indigenous. Masters’s Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, G.G.; Ling, H.Y. Anxiety, Depression and quality of life of medical students in Malaysia. Med. J. Malays. 2019, 74, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Yu, T.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, F.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Feng, G.; et al. ABCB6, ABCB1 and ABCG1 genetic polymorphisms and antidepressant response of SSRIs in Chinese depressive patients. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałecki, P.; Talarowska, M.; Szemraj, J.; Zajączkowska, M. ASMT gene expression correlates with cognitive impairment in patients with recurrent depressive disorder. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Andrade, A.; Brennecke, A.; Mallat, S.; Brown, J.; Gomez-Rivadeneira, J.; Czepiel, N.; Londrigan, L. Genetic Associations between Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels and Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Bai, W.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kou, C.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q. Association of the CACNA2D2 gene with schizophrenia in Chinese Han population. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timón-Gómez, A.; Nývltová, E.; Abriata, L.A.; Vila, A.J.; Hosler, J.; Barrientos, A. Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis: Recent developments. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 76, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selimi, F.; Lohof, A.M.; Heitz, S.; Lalouette, A.; Jarvis, C.I.; Bailly, Y.; Mariani, J. Lurcher GRID2-induced death and depolarization can be dissociated in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron 2003, 37, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Li, T.; Cai, W.; Huang, D.; Ouyang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, K.; Ma, X. HTR3A and HTR3E gene polymorphisms and diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome risk: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100459–100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddato, G.; Fabbiani, A.; Scandurra, V.; Canitano, R.; Mencarelli, M.A.; Renieri, A.; Ariani, F. Identification of a Novel SHANK2 Pathogenic Variant in a Patient with a Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Genes 2022, 13, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Li, F.; Zhao, G.; Wei, Q.; Pan, F.; Evangelou, E. TPH2 gene polymorphisms and major depression--a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bozzola, E.; Krzysztofiak, A.; Bozzola, M.; Calcaterra, V.; Quondamcarlo, A.; Lancella, L.; Villani, A. HHV6 meningoencephalitis sequelae in previously healthy children. Infection 2012, 40, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, T.; Morikawa, T.; Kajita, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Kondo, K.; Maeda, K. Caregiver burden and fatigue in caregivers of people with dementia: Measuring human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and -7 DNA levels in saliva. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 66, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, A.; Ashdown-Franks, G.; Hendrikse, J.; Sabiston, C.M.; Stubbs, B. Physical activity and depression: Towards understanding the antidepressant mechanisms of physical activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujral, S.; Aizenstein, H.; Reynolds, C.F., III; Butters, M.A.; Erickson, K.I. Exercise effects on depression: Possible neural mechanisms. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2017, 49, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, N.A.L.; Del Ángel, D.S.; Brizuela, N.O.; Peraza, A.V.; Olguín, H.J.; Soto, M.P.; Guzmán, D.C. Inflammatory Process and Immune System in Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 25, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Won, E. The influence of stress on neuroinflammation and alterations in brain structure and function in major depressive disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 329, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, R.K.; Asghar, K.; Kanwal, S.; Zulqernain, A. Role of inflammatory cytokines in depression: Focus on interleukin-1β. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 6, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, P.; Bui, E.; Rogers, A.H.; Walton, Z.E.; Ross, R.; Zeng, M.; Nadal-Vicens, M.; Mischoulon, D.; Baker, A.W.; Keshaviah, A.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines in major depressive disorder: A case–control study. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2016, 51, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelace, M.D.; Varney, B.; Sundaram, G.; Lennon, M.J.; Lim, C.K.; Jacobs, K.; Guillemin, G.J.; Brew, B.J. Recent evidence for an expanded role of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in neurological diseases. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Deng, D. A novel 4 immune-related genes as diagnostic markers and correlated with immune infiltrates in major depressive disorder. BMC Immunol. 2022, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).