EBV and 1q Gains Affect Gene and miRNA Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BL Patient Samples and Cell Lines
2.2. Multicolor Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization and Probe Selection for Metaphase FISH Mapping of 1q Abnormalities
2.3. RNA Preparation, Reverse Transcription and Real-Time qPCR Analysis
2.4. Micro RNA Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EBV-Negative BL Accumulate 1q Gains
3.2. EBV and 1q Gains Affect the Expression of Genes Localized at 1q21.2–q22
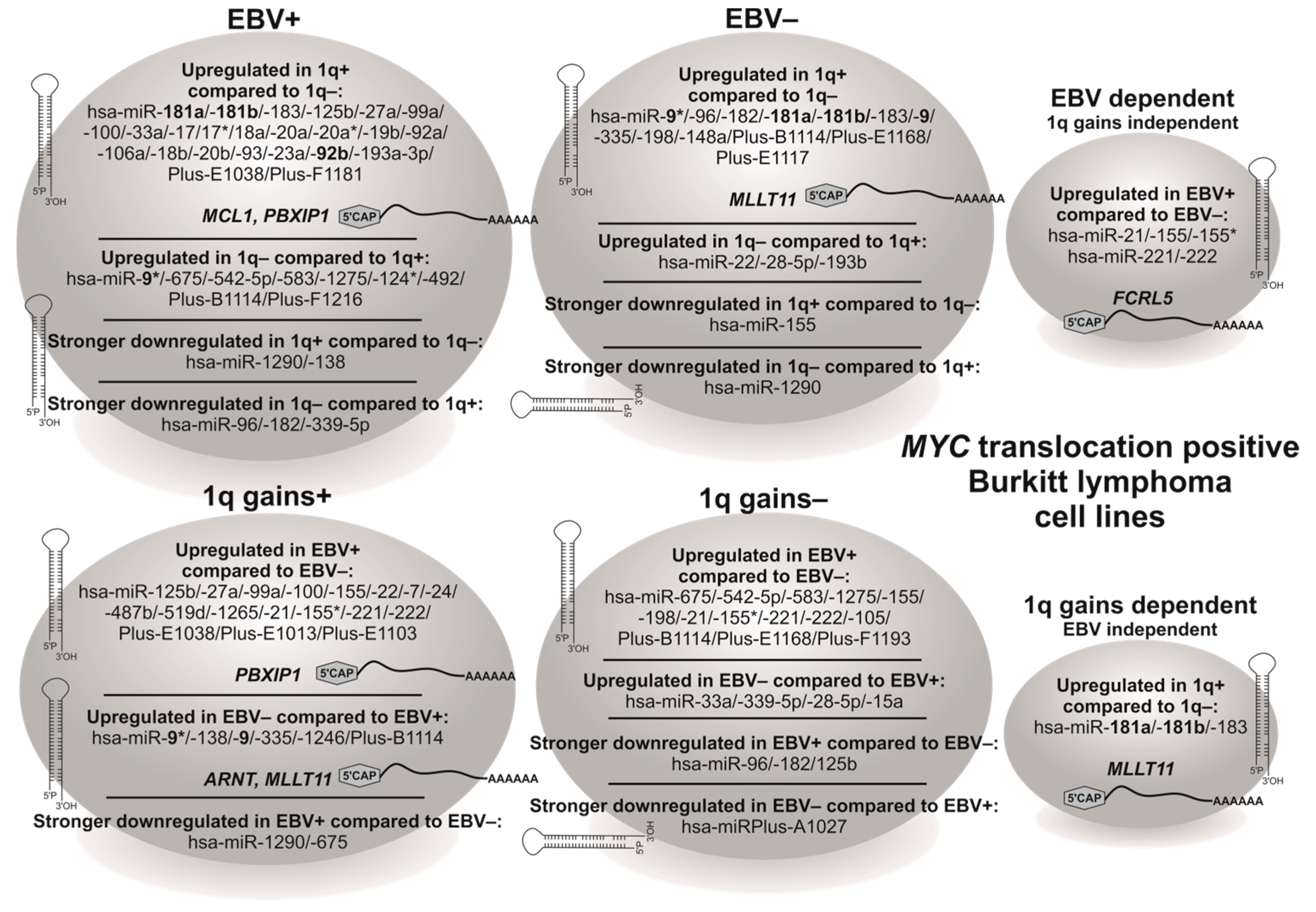
3.3. BL Cell Lines Show EBV- and 1q-Gains-Dependent Specific miRNA Expression Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johansson, B.; Brondum-Nielsen, K.; Billstrom, R.; Schiodt, I.; Mitelman, F. Translocations between the long arms of chromosomes 1 and 5 in hematologic malignancies are strongly associated with neoplasms of the myeloid lineages. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1997, 99, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoyama, T.; Nanjungud, G.; Chen, W.; Dyomin, V.G.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Chaganti, R.S. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of genomic instability at the 1q12-22 chromosomal site in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 35, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, J.R.; Tricot, G.; Lukacs, J.L.; Binz, R.L.; Tian, E.; Barlogie, B.; Shaughnessy, J., Jr. Genomic instability in multiple myeloma: Evidence for jumping segmental duplications of chromosome arm 1q. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 42, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, R.; Dilorenzo, S.; Lundin-Strom, K.B.; Olsson, L.; Biloglav, A.; Lilljebjorn, H.; Rissler, M.; Wahlberg, P.; Lundmark, A.; Castor, A.; et al. Mutation, methylation, and gene expression profiles in dup(1q)-positive pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offit, K.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Ladanyi, M.; Filippa, D.A.; Chaganti, R.S. Cytogenetic analysis of 434 consecutively ascertained specimens of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Correlations between recurrent aberrations, histology, and exposure to cytotoxic treatment. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1991, 3, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitelman, F.; Johansson, B.; Mertens, F. Mitelman Database of Chromosome Aberrations and Gene Fusions in Cancer (2022). Available online: https://mitelmandatabase.isb-cgc.org (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Vardiman, J.W. World Health Organization classification of tumours. In Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2001; pp. 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; Allday, M.J. The curious case of the tumour virus: 50 years of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla-Favera, R.; Bregni, M.; Erikson, J.; Patterson, D.; Gallo, R.C.; Croce, C.M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 7824–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, R.; Kirsch, I.; Morton, C.; Lenoir, G.; Swan, D.; Tronick, S.; Aaronson, S.; Leder, P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 7837–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaverria, I.; Zettl, A.; Bea, S.; Hartmann, E.M.; Dave, S.S.; Wright, G.W.; Boerma, E.J.; Kluin, P.M.; Ott, G.; Chan, W.C.; et al. Chromosomal alterations detected by comparative genomic hybridization in subgroups of gene expression-defined Burkitt’s lymphoma. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roug, A.S.; Wendtland, P.; Bendix, K.; Kjeldsen, E. Supernumerary isochromosome 1, idic(1)(p12), leading to tetrasomy 1q in Burkitt lymphoma. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 142, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, S.; Park, S.J.; Choi, J.R. Isochromosome 1q in childhood Burkitt lymphoma: The first reported case in Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukema, S.M.; Theil, L.; Rohde, M.; Bauer, B.; Bradtke, J.; Burkhardt, B.; Bonn, B.R.; Claviez, A.; Gattenlohner, S.; Makarova, O.; et al. Sequential karyotyping in Burkitt lymphoma reveals a linear clonal evolution with increase in karyotype complexity and a high frequency of recurrent secondary aberrations. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessenyei, B.; Ujfalusi, A.; Balogh, E.; Olah, E.; Szegedi, I.; Kiss, C. Jumping translocation of chromosome 1q associated with good clinical outcome in a case of Burkitt leukemia. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglass, E.C.; Magrath, I.T.; Lee, E.C.; Whang-Peng, J. Serial cytogenetic studies of nonendemic Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1980, 65, 891–895. [Google Scholar]
- Cigudosa, J.C.; Parsa, N.Z.; Louie, D.C.; Filippa, D.A.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Johansson, B.; Mitelman, F.; Chaganti, R.S. Cytogenetic analysis of 363 consecutively ascertained diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1999, 25, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.L.; Hernandez, J.M.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Flores, T.; Gonzalez, D.; Calasanz, M.J.; Martinez-Climent, J.A.; Piris, M.A.; Lopez-Capitan, C.; Gonzalez, M.B.; et al. Abnormalities on 1q and 7q are associated with poor outcome in sporadic Burkitt’s lymphoma. A cytogenetic and comparative genomic hybridization study. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lones, M.A.; Sanger, W.G.; Le Beau, M.M.; Heerema, N.A.; Sposto, R.; Perkins, S.L.; Buckley, J.; Kadin, M.E.; Kjeldsberg, C.R.; Meadows, A.; et al. Chromosome abnormalities may correlate with prognosis in Burkitt/Burkitt-like lymphomas of children and adolescents: A report from Children’s Cancer Group Study CCG-E08. J. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. 2004, 26, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onciu, M.; Schlette, E.; Zhou, Y.; Raimondi, S.C.; Giles, F.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Medeiros, L.J.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Pui, C.H.; Sandlund, J.T. Secondary chromosomal abnormalities predict outcome in pediatric and adult high-stage Burkitt lymphoma. Cancer 2006, 107, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, H.A.; Cairo, M.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Swansbury, J.; Auperin, A.; Launay, E.; Sanger, W.G.; Talley, P.; Perkins, S.L.; Raphael, M.; et al. Specific cytogenetic abnormalities are associated with a significantly inferior outcome in children and adolescents with mature B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Results of the FAB/LMB 96 international study. Leukemia 2009, 23, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, R.F.; Li, L.C.; Pookot, D.; Noonan, E.J.; Dahiya, R. MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, C.N.; Ito, K. A Macro View of MicroRNAs: The Discovery of MicroRNAs and Their Role in Hematopoiesis and Hematologic Disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 334, 99–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nature reviews. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar]
- Calin, G.A.; Ferracin, M.; Cimmino, A.; Di Leva, G.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Iorio, M.V.; Visone, R.; Sever, N.I.; Fabbri, M.; et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lisio, L.; Martinez, N.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Piris-Villaespesa, M.; Sanchez-Beato, M.; Piris, M.A. The role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2012, 120, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lisio, L.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; Gómez-López, G.; Rodríguez, M.E.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Mollejo, M.; Menárguez, J.; Martínez, M.A.; Alves, F.J.; Pisano, D.G.; et al. MicroRNA signatures in B-cell lymphomas. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduor, C.I.; Kaymaz, Y.; Chelimo, K.; Otieno, J.A.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Moormann, A.M.; Bailey, J.A. Integrative microRNA and mRNA deep-sequencing expression profiling in endemic Burkitt lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaina, M.C.; Faccion, R.S.; Mazzoccoli, L.; Rezende, L.M.; Queiroga, E.; Bacchi, C.E.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Klumb, C.E. miR-17-92 cluster components analysis in Burkitt lymphoma: Overexpression of miR-17 is associated with poor prognosis. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murga Penas, E.M.; Schilling, G.; Behrmann, P.; Klokow, M.; Vettorazzi, E.; Bokemeyer, C.; Dierlamm, J. Comprehensive cytogenetic and molecular cytogenetic analysis of 44 Burkitt lymphoma cell lines: Secondary chromosomal changes characterization, karyotypic evolution, and comparison with primary samples. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan-Jordan, J.H.R.; Moore, S. (Eds.) ISCN 2020 An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (2020); Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sobol, H.; Benziane, A.; Kerangueven, F.; Yin, L.; Noguchi, T.; Pauly, S.; Eisinger, F.; Longy, M.; Romeo, G.; Lenoir, G.; et al. Genome-wide search for loss of heterozygosity in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 33, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, R.; Bernheim, A. [Is there a functional equivalence between abnormalities of the long arm of chromosome 1 and the presence of Epstein-Barr virus in continuous lines of Burkitt’s lymphoma?]. Comptes Rendus L’academie Sci. Ser. III Sci. Vie 1984, 298, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Zeller, K.I.; Dang, C.V.; Mendell, J.T. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005, 435, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsson, J.; Andersson, A.; Paulsson, K.; Heidenblad, M.; Isaksson, M.; Borg, A.; Heldrup, J.; Behrendtz, M.; Panagopoulos, I.; Fioretos, T.; et al. Tiling resolution array comparative genomic hybridization, expression and methylation analyses of dup(1q) in Burkitt lymphomas and pediatric high hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemias reveal clustered near-centromeric breakpoints and overexpression of genes in 1q22-32.3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar]
- Dierlamm, J.; Wlodarska, I.; Michaux, L.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Meeus, P.; Stul, M.; Criel, A.; Verhoef, G.; Thomas, J.; Delannoy, A.; et al. FISH identifies different types of duplications with 12q13-15 as the commonly involved segment in B-cell lymphoproliferative malignancies characterized by partial trisomy 12. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1997, 20, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busson-Le Coniat, M.; Salomon-Nguyen, F.; Dastugue, N.; Maarek, O.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M.; Mozziconacci, M.J.; Baranger, L.; Brizard, F.; Radford, I.; Jeanpierre, M.; et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of chromosome 1 abnormalities in hematopoietic disorders: Rearrangements of DNA satellite II and new recurrent translocations. Leukemia 1999, 13, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Le Baccon, P.; Leroux, D.; Dascalescu, C.; Duley, S.; Marais, D.; Esmenjaud, E.; Sotto, J.J.; Callanan, M. Novel evidence of a role for chromosome 1 pericentric heterochromatin in the pathogenesis of B-cell lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2001, 32, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestou, V.S.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Salski, C.; Connors, J.M.; Horsman, D.E. Uncovering novel inter- and intrachromosomal chromosome 1 aberrations in follicular lymphomas by using an innovative multicolor banding technique. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki-Celli, L.; Lefebvre, C.; Le Baccon, P.; Nadeau, G.; Bonnefoix, T.; Usson, Y.; Vourc’h, C.; Khochbin, S.; Leroux, D.; Callanan, M. Differences in nuclear positioning of 1q12 pericentric heterochromatin in normal and tumor B lymphocytes with 1q rearrangements. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 43, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrulis, E.D.; Neiman, A.M.; Zappulla, D.C.; Sternglanz, R. Perinuclear localization of chromatin facilitates transcriptional silencing. Nature 1998, 394, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, J.E.; Bailey, J.A.; Locke, D.P.; Eichler, E.E. Lessons from the human genome: Transitions between euchromatin and heterochromatin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürrbaum, M.; Storchová, Z. Effects of aneuploidy on gene expression: Implications for cancer. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toujani, S.; Dessen, P.; Ithzar, N.; Danglot, G.; Richon, C.; Vassetzky, Y.; Robert, T.; Lazar, V.; Bosq, J.; Da Costa, L.; et al. High resolution genome-wide analysis of chromosomal alterations in Burkitt’s lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholtysik, R.; Kreuz, M.; Klapper, W.; Burkhardt, B.; Feller, A.C.; Hummel, M.; Loeffler, M.; Rosolowski, M.; Schwaenen, C.; Spang, R.; et al. Detection of genomic aberrations in molecularly defined Burkitt’s lymphoma by array-based, high resolution, single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Haematologica 2010, 95, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullein, J.; Slabicki, M.; Rosolowski, M.; Jethwa, A.; Habringer, S.; Tomska, K.; Kurilov, R.; Lu, J.; Scheinost, S.; Wagener, R.; et al. MDM4 Is Targeted by 1q Gain and Drives Disease in Burkitt Lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3125–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, M.; Carrasco, D.E.; Zhang, Y.; Takada, K.; Gatt, M.E.; Dutta-Simmons, J.; Ikeda, H.; Diaz-Griffero, F.; Pena-Cruz, V.; Bertagnolli, M.; et al. BCL9 promotes tumor progression by conferring enhanced proliferative, metastatic, and angiogenic properties to cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7577–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, T.G.; Zalcberg, I.R.; Coignet, L.J.; Wlodarska, I.; Stul, M.; Jadayel, D.M.; Bastard, C.; Treleaven, J.G.; Catovsky, D.; Silva, M.L.; et al. Molecular cloning of translocation t(1;14)(q21;q32) defines a novel gene (BCL9) at chromosome 1q21. Blood 1998, 91, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, W.; Meshinchi, S.; Alonzo, T.A.; Stirewalt, D.L.; Gerbing, R.B.; Woods, W.G.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Radich, J.P. Elevated expression of the AF1q gene, an MLL fusion partner, is an independent adverse prognostic factor in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004, 104, 3058–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozopas, K.M.; Yang, T.; Buchan, H.L.; Zhou, P.; Craig, R.W. MCL1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3516–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho-Vega, J.H.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Admirand, J.H.; Oyarzo, M.; Ramalingam, P.; Paraguya, A.; McDonnell, T.J.; Amin, H.M.; Medeiros, L.J. MCL-1 expression in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, J.; O’Neill, J.W.; Dallman, C.L.; Mouzakiti, A.; Habens, F.; Brimmell, M.; Zhang, K.Y.; Craig, R.W.; Marcusson, E.G.; Johnson, P.W.; et al. Mcl-1 is required for Akata6 B-lymphoma cell survival and is converted to a cell death molecule by efficient caspase-mediated cleavage. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4818–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.L.; Grabow, S.; Glaser, S.P.; Fitzsimmons, L.; Aubrey, B.J.; Okamoto, T.; Valente, L.J.; Robati, M.; Tai, L.; Fairlie, W.D.; et al. Targeting of MCL-1 kills MYC-driven mouse and human lymphomas even when they bear mutations in p53. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Rowe, M.; Lundgren, E. Expression of the Epstein Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 causes a rapid and transient stimulation of the Bcl-2 homologue Mcl-1 levels in B-cell lines. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4610–4613. [Google Scholar]
- Kenney, J.L.; Guinness, M.E.; Curiel, T.; Lacy, J. Antisense to the epstein-barr virus (EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) suppresses LMP-1 and bcl-2 expression and promotes apoptosis in EBV-immortalized B cells. Blood 1998, 92, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, J.; Dement-Brown, J.; Maier, S.; Ise, T.; Kempkes, B.; Tolnay, M. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces FcRH5 expression through CBF1. Blood 2006, 107, 4433–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzivassiliou, G.; Miller, I.; Takizawa, J.; Palanisamy, N.; Rao, P.H.; Iida, S.; Tagawa, S.; Taniwaki, M.; Russo, J.; Neri, A.; et al. IRTA1 and IRTA2, novel immunoglobulin superfamily receptors expressed in B cells and involved in chromosome 1q21 abnormalities in B cell malignancy. Immunity 2001, 14, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Liu, A.H.; Li, G.M.; Wang, J.R. HPIP Silencing Prevents Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TGF-beta1 in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. 2016, 24, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Mi, D.; Ma, Z. HPIP silencing inhibits TGF-beta1-induced EMT in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vorrink, S.U.; Domann, F.E. Regulatory crosstalk and interference between the xenobiotic and hypoxia sensing pathways at the AhR-ARNT-HIF1alpha signaling node. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 218, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Ye, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. ARNT/HIF-1beta links high-risk 1q21 gain and microenvironmental hypoxia to drug resistance and poor prognosis in multiple myeloma. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 3899–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon-Nguyen, F.; Della-Valle, V.; Mauchauffe, M.; Busson-Le Coniat, M.; Ghysdael, J.; Berger, R.; Bernard, O.A. The t(1;12)(q21;p13) translocation of human acute myeloblastic leukemia results in a TEL-ARNT fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6757–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Khac, F.; Della Valle, V.; Lopez, R.G.; Ravet, E.; Mauchauffe, M.; Friedman, A.D.; Huang, L.E.; Fichelson, S.; Ghysdael, J.; Bernard, O.A. Functional analyses of the TEL-ARNT fusion protein underscores a role for oxygen tension in hematopoietic cellular differentiation. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4840–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilyansky, E.; Rigoutsos, I. The miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics, genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Yu, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Wentzel, E.A.; Arking, D.E.; West, K.M.; Dang, C.V.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Mendell, J.T. Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onnis, A.; De Falco, G.; Antonicelli, G.; Onorati, M.; Bellan, C.; Sherman, O.; Sayed, S.; Leoncini, L. Alteration of microRNAs regulated by c-Myc in Burkitt lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Sai, B.; Tang, J.; Luo, Z.; Shuai, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. miR-18a reactivates the Epstein-Barr virus through defective DNA damage response and promotes genomic instability in EBV-associated lymphomas. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Lwin, T.; Wright, G.; Moscinski, L.C.; Dalton, W.S.; Seto, E.; Wright, K.; Sotomayor, E.; et al. Myc represses miR-15a/miR-16-1 expression through recruitment of HDAC3 in mantle cell and other non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3002–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psathas, J.N.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A. MYC and the art of microRNA maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Setty, M.; Holmes, A.B.; Maute, R.L.; Leslie, C.S.; Mussolin, L.; Rosolen, A.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Basso, K. MicroRNA 28 controls cell proliferation and is down-regulated in B-cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8185–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilting, S.M.; Snijders, P.J.; Verlaat, W.; Jaspers, A.; van de Wiel, M.A.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Meijer, G.A.; Kenter, G.G.; Yi, Y.; le Sage, C.; et al. Altered microRNA expression associated with chromosomal changes contributes to cervical carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.X.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Fang, C.M. Unveiling the tumour-regulatory roles of miR-1275 in cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 230, 153745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galardi, S.; Mercatelli, N.; Giorda, E.; Massalini, S.; Frajese, G.V.; Ciafrè, S.A.; Farace, M.G. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23716–23724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazot, Q.; Paschos, K.; Skalska, L.; Kalchschmidt, J.S.; Parker, G.A.; Allday, M.J. Epstein-Barr Virus Proteins EBNA3A and EBNA3C Together Induce Expression of the Oncogenic MicroRNA Cluster miR-221/miR-222 and Ablate Expression of Its Target p57KIP2. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, T.A.; Evangelista, A.F.; Campos, A.H.; Poles, W.A.; Borges, N.M.; Camillo, C.M.; Soares, F.A.; Vassallo, J.; Paes, R.P.; Zerbini, M.C.; et al. A microRNA signature profile in EBV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11813–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosato, P.; Anastasiadou, E.; Garg, N.; Lenze, D.; Boccellato, F.; Vincenti, S.; Severa, M.; Coccia, E.M.; Bigi, R.; Cirone, M.; et al. Differential regulation of miR-21 and miR-146a by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA2. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibcus, J.H.; Tan, L.P.; Harms, G.; Schakel, R.N.; de Jong, D.; Blokzijl, T.; Möller, P.; Poppema, S.; Kroesen, B.J.; van den Berg, A. Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines are characterized by a specific miRNA expression profile. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussaief, L.; Fendri, A.; Chane-Woon-Ming, B.; Poirey, R.; Delecluse, H.J.; Joab, I.; Pfeffer, S. Modulation of MicroRNA Cluster miR-183-96-182 Expression by Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12178–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, C.; Lazzi, S.; Hummel, M.; Palummo, N.; de Santi, M.; Amato, T.; Nyagol, J.; Sabattini, E.; Lazure, T.; Pileri, S.A.; et al. Immunoglobulin gene analysis reveals 2 distinct cells of origin for EBV-positive and EBV-negative Burkitt lymphomas. Blood 2005, 106, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, T.; Abate, F.; Piccaluga, P.; Iacono, M.; Fallerini, C.; Renieri, A.; De Falco, G.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Mourmouras, V.; Ogwang, M.; et al. Clonality Analysis of Immunoglobulin Gene Rearrangement by Next-Generation Sequencing in Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma Suggests Antigen Drive Activation of BCR as Opposed to Sporadic Burkitt Lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierlamm, J.; Baens, M.; Stefanova-Ouzounova, M.; Hinz, K.; Wlodarska, I.; Maes, B.; Steyls, A.; Driessen, A.; Verhoef, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. Detection of t(11;18)(q21;q21) by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization using API2 and MLT specific probes. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2000, 96, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Hiller, B.; Bradtke, J.; Balz, H.; Rieder, H. CyDAS Online Analysis Site. Available online: http://www.cydas.org/OnlineAnalysis (accessed on 1 January 2010).
- Dierlamm, J.; Wlodarska, I.; Michaux, L.; La Starza, R.; Zeller, W.; Mecucci, C.; Van den Berghe, H. Successful use of the same slide for consecutive fluorescence in situ hybridization experiments. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1996, 16, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Alizadeh, S.; Jalili, A.; Shirzad, R.; Saki, N. The impact of Mir-9 regulation in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Oncol. Rev. 2018, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowek, K.; Wiemer, E.A.C.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M. The versatile nature of miR-9/9(*) in human cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20838–20854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Corrigan-Cummins, M.; Hudson, J.; Maric, I.; Simakova, O.; Neelapu, S.S.; Kwak, L.W.; Janik, J.E.; Gause, B.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. MicroRNA profiling of follicular lymphoma identifies microRNAs related to cell proliferation and tumor response. Haematologica 2012, 97, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ju, X.L.; Li, D.; Zhou, P.P.; Li, X.; Luo, R.H. miR-1290 promotes proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting FOXG1/SOCS3. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, S.; Ying, Y.; Zhou, R.; Mao, P. miR-196b/miR-1290 participate in the antitumor effect of resveratrol via regulation of IGFBP3 expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H. MALAT1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and enhances cytarabine chemosensitivity by upregulating miR-96 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yin, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. miR-96 acts as a tumor suppressor via targeting the BCR-ABL1 oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia blastic transformation. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 119, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, N.; Yasui, K.; Tomie, A.; Gen, Y.; Terasaki, K.; Kitaichi, T.; Soda, T.; Yamada, N.; Dohi, O.; Seko, Y.; et al. Oncogenic miR-96-5p inhibits apoptosis by targeting the caspase-9 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Sun, F.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. miR-96 promotes breast cancer metastasis by suppressing MTSS1. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3464–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Ushmorov, A.; Leithäuser, F.; Guan, H.; Steidl, C.; Färbinger, J.; Pelzer, C.; Vogel, M.J.; Maier, H.J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; et al. FOXO1 is a tumor suppressor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 119, 3503–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lv, G.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, B.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X. The Downregulation of MiR-182 Is Associated with the Growth and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells through the Regulation of TIAM1 Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, G.; Yin, J. MiR-182-5p regulates BCL2L12 and BCL2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia as a potential therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatopoulou, D.; Avgeris, M.; Marmarinos, A.; Xagorari, M.; Baka, M.; Doganis, D.; Kossiva, L.; Scorilas, A.; Gourgiotis, D. miR-125b predicts childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia poor response to BFM chemotherapy treatment. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liao, W.; Peng, H.; Luo, X.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L. miR-181a promotes G1/S transition and cell proliferation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia by targeting ATM. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Azzalin, G.; Gioiosa, S.; Carissimi, C.; Laudadio, I.; Fulci, V.; Macino, G. microRNA-181a enhances cell proliferation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by targeting EGR1. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichiorri, F.; Suh, S.S.; Ladetto, M.; Kuehl, M.; Palumbo, T.; Drandi, D.; Taccioli, C.; Zanesi, N.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; et al. MicroRNAs regulate critical genes associated with multiple myeloma pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Weng, X.D.; Liu, X.H.; Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Diao, C.H. miR-181a-5p is downregulated and inhibits proliferation and the cell cycle in prostate cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Cao, Y.; Dong, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Hua, X.; Ling, Y.; Xie, X.; Hu, S.; et al. The clinical characteristics and prognostic significance of AID, miR-181b, and miR-155 expression in adult patients with de novo B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visone, R.; Veronese, A.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Balatti, V.; Pearl, D.K.; Acunzo, M.; Volinia, S.; Taccioli, C.; Kipps, T.J.; Croce, C.M. miR-181b is a biomarker of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 118, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.G.; Ding, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, W.L.; Pan, L.L.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, X.N. FAMLF is a target of miR-181b in Burkitt lymphoma. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. De Pesqui. Medicas E Biol. 2017, 50, e5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zuo, D.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, X.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, R. MicroRNA-183 promotes cell proliferation via regulating programmed cell death 6 in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, L.; Boelle, P.Y.; Deswarte, C.; Spicuglia, S.; Benyoucef, A.; Calvo, J.; Uzan, B.; Belhocine, M.; Cieslak, A.; Landman-Parker, J.; et al. Homeobox protein TLX3 activates miR-125b expression to promote T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, X.Q.; Zhang, P.; Huang, L.B.; Zheng, Y.S.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.Q. MicroRNA patterns associated with clinical prognostic parameters and CNS relapse prediction in pediatric acute leukemia. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.J.; Luo, Z.; Volinia, S.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Kipps, T.J.; Croce, C.M. The down-regulation of miR-125b in chronic lymphocytic leukemias leads to metabolic adaptation of cells to a transformed state. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 120, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Caloro, G.A.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Crincoli, V.; Aiuto, R.; Coccia, E.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Circulating miR-21 as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.J.; Zhou, J.D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Ma, J.C.; Wen, X.M.; Yuan, Q.; Li, X.X.; Xu, Z.J.; Qian, J. H19 overexpression promotes leukemogenesis and predicts unfavorable prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Tan, Y.; Lian, G.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Huang, K.; Chen, Y. Bmi-1-induced miR-27a and miR-155 promote tumor metastasis and chemoresistance by targeting RKIP in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Lu, F.; Han, X.Y.; Ji, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, A.M.; Wang, H.C.; Ma, D.X.; Ji, C.Y. MiR-424 and miR-27a increase TRAIL sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia by targeting PLAG1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25276–25290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Scheibner, K.A.; Teaboldt, B.; Hauer, M.C.; Chen, X.; Cherukuri, S.; Guo, Y.; Kelley, S.M.; Liu, Z.; Baer, M.R.; Heimfeld, S.; et al. MiR-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in acute leukemia by regulating 14-3-3θ. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, J.K.; Erb, H.H.; Nappo, G.; Mann, V.M.; Simms, M.S.; Collins, A.T.; Visakorpi, T.; Maitland, N.J. Inhibition of the glucocorticoid receptor results in an enhanced miR-99a/100-mediated radiation response in stem-like cells from human prostate cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51965–51980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Zhang, X.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Shi, H.; Bai, J.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, T.; et al. Upregulation of miR-99a is associated with poor prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia and promotes myeloid leukemia cell expansion. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78095–78109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Luo, X.Q.; Han, B.W.; Duan, F.T.; Wei, P.P.; Chen, Y.Q. MicroRNA-100/99a, deregulated in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis by regulating the FKBP51 and IGF1R/mTOR signalling pathways. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arribas, A.J.; Gómez-Abad, C.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; Martinez, N.; Dilisio, L.; Casado, F.; Cruz, M.A.; Algara, P.; Piris, M.A.; Mollejo, M. Splenic marginal zone lymphoma: Comprehensive analysis of gene expression and miRNA profiling. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. U. S. Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc. 2013, 26, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, V.; Rusch, M.; Vartak, N.; Jüngst, C.; Schauss, A.; Waldmann, H.; Hedberg, C.; Pallasch, C.P.; Bastiaens, P.I.; Hallek, M.; et al. miRs-138 and -424 control palmitoylation-dependent CD95-mediated cell death by targeting acyl protein thioesterases 1 and 2 in CLL. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 125, 2948–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augello, C.; Gianelli, U.; Savi, F.; Moro, A.; Bonoldi, E.; Gambacorta, M.; Vaira, V.; Baldini, L.; Bosari, S. MicroRNA as potential biomarker in HCV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaar, Y.G.; Reeves, M.E. RASSF1C regulates miR-33a and EMT marker gene expression in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Gu, S.; Yuan, M.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J. MicroRNA-33a-5p overexpression sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to doxorubicin by inhibiting eIF5A2 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5986–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Qin, L. MicroRNA-339-5p inhibits cell proliferation of acute myeloid leukaemia by directly targeting SOX4. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5261–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.S.; Costa, E.S.M.; Coutinho, L.L.; Garcia Gomes, R.; Pedrosa, F.; Massaro, J.D.; Donadi, E.A.; Lucena-Silva, N. MicroRNA expression profiles discriminate childhood T- from B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashaei, E.; Pashaei, E.; Ahmady, M.; Ozen, M.; Aydin, N. Meta-analysis of miRNA expression profiles for prostate cancer recurrence following radical prostatectomy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.R.; Shi, M.X.; Zeng, Y. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells by sponging with micRNA-1275. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdogan, H.; Gur Dedeoglu, B.; Oztemur Islakoglu, Y.; Aydos, A.; Kose, S.; Atalay, A.; Yegin, Z.A.; Avcu, F.; Uckan Cetinkaya, D.; Ilhan, O. DICER1 gene and miRNA dysregulation in mesenchymal stem cells of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2017, 63, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, M.; Malinova, K.; Kotaskova, J.; Pavlova, S.; Tichy, B.; Malcikova, J.; Stano Kozubik, K.; Smardova, J.; Brychtova, Y.; Doubek, M.; et al. miR-34a, miR-29c and miR-17-5p are downregulated in CLL patients with TP53 abnormalities. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wake, L.; Liu, C.; Deffenbacher, K.; Lachel, C.M.; Wang, C.; Rohr, J.; et al. Global microRNA expression profiling uncovers molecular markers for classification and prognosis in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2015, 125, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, J.; Xie, W.; Ye, X. Profiling of microRNAs in AML cells following overexpression or silencing of the VEGF gene. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, F.; Zhang, J.; Josson, S.; St Clair, W.H.; St Clair, D.K. miR-17* suppresses tumorigenicity of prostate cancer by inhibiting mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Deng, J.; Sun, Z.M.; Pan, A.P.; Xiang, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Feng, M.; et al. Interference with the β-catenin gene in gastric cancer induces changes to the miRNA expression profile. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 6973–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.H.; Jin, M.; Wang, L.Q.; Xu, G.J.; Lin, Z.Y.; Yu, D.D.; Yang, S.L.; Ran, R.Z.; Wu, G.; Zhang, T. Long noncoding RNA TCL6 binds to miR-106a-5p to regulate hepatocellular carcinoma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6154–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Miao, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jia, L. MiR-106b and miR-93 regulate cell progression by suppression of PTEN via PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Sanchéz, M.A.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Fernández-Retana, J.; Arechaga-Ocampo, E.; Marchat, L.A.; Rodríguez-Cuevas, S.; Bautista-Piña, V.; Arellano-Anaya, Z.E.; Flores-Pérez, A.; Diaz-Chávez, J.; et al. microRNA-18b is upregulated in breast cancer and modulates genes involved in cell migration. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, S.G.; Kontos, C.K.; Tsiakanikas, P.; Stavroulaki, G.; Bouchla, A.; Vasilatou, D.; Bazani, E.; Lazarakou, A.; Scorilas, A.; Pappa, V. Elevated miR-20b-5p expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells: A novel, independent molecular biomarker of favorable prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2018, 70, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzl, S.; Geiger, O.; Kuepper, M.K.; Caraffini, V.; Seime, T.; Furlan, T.; Nussbaumer, E.; Wieser, R.; Pichler, M.; Scheideler, M.; et al. Increased Expression of miR-23a Mediates a Loss of Expression in the RAF Kinase Inhibitor Protein RKIP. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3644–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xishan, Z.; Xianjun, L.; Ziying, L.; Guangxin, C.; Gang, L. The malignancy suppression role of miR-23a by targeting the BCR/ABL oncogene in chromic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Zhan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Deoxycholic acid modulates the progression of gallbladder cancer through N6-methyladenosine-dependent microRNA maturation. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4983–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, L.Y.; Yang, R.H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, P.; Kong, L. Identification of reciprocal microRNA-mRNA pairs associated with metastatic potential disparities in human prostate cancer cells and signaling pathway analysis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 17779–17790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Byrd, J.C.; Grever, M.R.; Jacob, S.T.; Sif, S. Low levels of miR-92b/96 induce PRMT5 translation and H3R8/H4R3 methylation in mantle cell lymphoma. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3558–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Hu, J.; Ma, J.; Qi, X.; Zhou, H.; Miao, X.; Zheng, W.; Jia, L. MiR-193a-3p and miR-224 mediate renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase IV and the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; You, C.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Ba, Y. MiR-193a-3p is an Important Tumour Suppressor in Lung Cancer and Directly Targets KRAS. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 44, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Z. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 contributes to the progression and chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia by modulating Tspan3 through suppressing miR-193a-3p. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, G.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, S. MiR-124-5p inhibits the growth of high-grade gliomas through posttranscriptional regulation of LAMB1. Neuro-oncology 2014, 16, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Frowein, J.; Pagel, P.; Kappler, R.; von Schweinitz, D.; Roscher, A.; Schmid, I. MicroRNA-492 is processed from the keratin 19 gene and up-regulated in metastatic hepatoblastoma. Hepatology 2011, 53, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Lü, H.; Qu, H.; Xie, Q.; Sun, T.; Gan, O.; Hu, B. miR-492 Promotes Cancer Progression by Targeting GJB4 and Is a Novel Biomarker for Bladder Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11453–11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Z.; Di, M.; Fu, W.; Tang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lei, P.; Gu, X.; Liu, T.; Sun, M. Integrated Analysis Identifies a Nine-microRNA Signature Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabonne, D.; Benavente, Y.; Seifert, J.; Costas, L.; Armesto, M.; Arestin, M.; Besson, C.; Hosnijeh, F.S.; Duell, E.J.; Weiderpass, E.; et al. Serum levels of hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-miR-29a-3p, hsa-miR-150-5p, hsa-miR-155-5p and hsa-miR-223-3p and subsequent risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the EPIC study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokah, O.H.; Granot, G.; Ovcharenko, A.; Modai, S.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Toren, A.; Shomron, N.; Shpilberg, O. Downregulation of miR-31, miR-155, and miR-564 in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35501. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, E.; Staffas, A.; Röhner, L.; Krowiorz, K.; Heuser, M.; Döhner, K.; Bullinger, L.; Döhner, H.; Fogelstrand, L.; Rouhi, A.; et al. MicroRNA-155 is upregulated in MLL-rearranged AML but its absence does not affect leukemia development. Exp. Hematol. 2016, 44, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maadawy, E.A.; Elshal, M.F.; Bakry, R.M.; Moussa, M.M.; El-Naby, S.; Talaat, R.M. Regulation of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ cells in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Implication of cytokines and miRNAs. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 124, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrajoli, A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Ivan, C.; Shimizu, M.; Rabe, K.G.; Nouraee, N.; Ikuo, M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Lerner, S.; Rassenti, L.Z.; et al. Prognostic value of miR-155 in individuals with monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Bood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2013, 122, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulci, V.; Chiaretti, S.; Goldoni, M.; Azzalin, G.; Carucci, N.; Tavolaro, S.; Castellano, L.; Magrelli, A.; Citarella, F.; Messina, M.; et al. Quantitative technologies establish a novel microRNA profile of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Bood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2007, 109, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-155 promote the progression of Burkitt’s lymphoma by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borchert, G.M.; Holton, N.W.; Larson, E.D. Repression of human activation induced cytidine deaminase by miR-93 and miR-155. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluiver, J.; Haralambieva, E.; de Jong, D.; Blokzijl, T.; Jacobs, S.; Kroesen, B.J.; Poppema, S.; van den Berg, A. Lack of BIC and microRNA miR-155 expression in primary cases of Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006, 45, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Feng, W. High serum microRNA-335 level predicts aggressive tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Transl. Oncol. Off. Publ. Fed. Span. Oncol. Soc. Natl. Cancer Inst. Mex. 2015, 17, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchetti, D.; Lionetti, M.; Mosca, L.; Agnelli, L.; Andronache, A.; Fabris, S.; Deliliers, G.L.; Neri, A. An integrative genomic approach reveals coordinated expression of intronic miR-335, miR-342, and miR-561 with deregulated host genes in multiple myeloma. BMC Med. Genom. 2008, 1, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, L.M.; Wang, W.; Herman, S.E.; Saba, N.S.; Anastas, V.; Barber, E.; Corrigan-Cummins, M.; Farooqui, M.; Sun, C.; Sarasua, S.M.; et al. Ibrutinib downregulates a subset of miRNA leading to upregulation of tumor suppressors and inhibition of cell proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccomani, V.; Grassi, A.; Piovan, E.; Bongiovanni, D.; Di Martino, L.; Minuzzo, S.; Tosello, V.; Zanovello, P. miR-22-3p Negatively Affects Tumor Progression in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cells 2020, 9, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Zheng, G.; Cheng, S.; Xie, W.; Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Xie, B. Serum miR-22 is a novel prognostic marker for acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Miao, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Downregulation of microRNA-198 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in retinoblastoma by directly targeting PTEN. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Muller, C.; Li, D.; Bharadwaj, U.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Hodges, S.E.; Fisher, W.E.; Mo, Q.; Hung, M.C.; Yao, Q. A tumorigenic factor interactome connected through tumor suppressor microRNA-198 in human pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5901–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Xu, S. MicroRNA-198-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of non-small lung cancer cells by targeting fucosyltransferase 8. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.; Mijiti, M.; Du, G.; Li, Y.; Dangmurenjiafu, G. MiR-28-5p promotes human glioblastoma cell growth through inactivation of FOXO1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Gong, B.; Huang, H.; Xing, Y.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-28-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing AKT phosphorylation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9777–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomé-Izquierdo, N.; de Yébenes, V.G.; Álvarez-Prado, A.F.; Mur, S.M.; Lopez Del Olmo, J.A.; Roa, S.; Vazquez, J.; Ramiro, A.R. miR-28 regulates the germinal center reaction and blocks tumor growth in preclinical models of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Bood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2017, 129, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Preliminary study on the role of miR-148a and DNMT1 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2943–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Li, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X. Plasma-based microRNA signatures in early diagnosis of breast cancer. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayadia, R.; Krowiorz, K.; Haetscher, N.; Jammal, R.; Emmrich, S.; Obulkasim, A.; Fiedler, J.; Schwarzer, A.; Rouhi, A.; Heuser, M.; et al. Endogenous Tumor Suppressor microRNA-193b: Therapeutic and Prognostic Value in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Lentz, C.; Abi-Daoud, M.; Paré, G.C.; Yang, X.; Feilotter, H.E.; Tron, V.A. miR-193b Regulates Mcl-1 in Melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, M.; Bronger, H.; Buchner, T.; Kiechle, M.; Weichert, W.; Avril, S. MicroRNAs miR-7 and miR-340 predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 162, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Ni, L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Wu, X.; Ye, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Identification of miR-7 as an oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2013, 44, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, W.; Liu, J.; Lou, Y.; Xia, S. MiR-7 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Targeting the Oncogenes TAL1 in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820934130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.Q.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, Y.W.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, H.T. DNA-methylation-mediated silencing of miR-7-5p promotes gastric cancer stem cell invasion via increasing Smo and Hes1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 2643–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organista-Nava, J.; Gómez-Gómez, Y.; Illades-Aguiar, B.; Del Carmen Alarcón-Romero, L.; Saavedra-Herrera, M.V.; Rivera-Ramírez, A.B.; Garzón-Barrientos, V.H.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A. High miR-24 expression is associated with risk of relapse and poor survival in acute leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.F.; Wang, L.S.; Zhou, J.H. Long non-coding RNA CASC2 suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth and progression by regulating the miR-24/MUC6 axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Meng, K.; Sheng, G.; Yang, T. MicroRNA-24 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion and enhances chemosensitivity of human gastric cancer by targeting DND1. J. BUON Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2020, 25, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Ye, B.G.; Liu, J.Z.; Kong, D.L. miR-487b and TRAK2 that form an axis to regulate the aggressiveness of osteosarcoma, are potential therapeutic targets and prognostic biomarkers. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, Z.F.; Xi, W.J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.F.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, T.Z.; Jiang, Y.H.; et al. DNA methylation-regulated and tumor-suppressive roles of miR-487b in colorectal cancer via targeting MYC, SUZ12, and KRAS. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1694–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattolliat, C.H.; Thomas, L.; Ciafrè, S.A.; Meurice, G.; Le Teuff, G.; Job, B.; Richon, C.; Combaret, V.; Dessen, P.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; et al. Expression of miR-487b and miR-410 encoded by 14q32.31 locus is a prognostic marker in neuroblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.T.; Hong, J.B.; Sheen, Y.S.; Huang, H.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, J.S.; Liao, Y.H. miR-519d Promotes Melanoma Progression by Downregulating EphA4. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, C.; Yang, X. MiR-519d impedes cisplatin-resistance in breast cancer stem cells by down-regulating the expression of MCL-1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22003–22013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Xia, Y.; He, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Sun, G.; Xu, J.; et al. MIR-1265 regulates cellular proliferation and apoptosis by targeting calcium binding protein 39 in gastric cancer and, thereby, impairing oncogenic autophagy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 449, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, M.; Hu, F.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Z.; Guo, A.Y. Differential Co-expression and Regulatory Network Analysis Uncover the Relapse Factor and Mechanism of T Cell Acute Leukemia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.N.; Xu, J. Serum miR-1290 and miR-1246 as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Human Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H. MicroRNA-155-3p promotes glioma progression and temozolomide resistance by targeting Six1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5363–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhong, L.; Luo, H.; Wang, S. MicroRNA-155-3p promotes breast cancer progression through down-regulating CADM1. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7993–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Lei, B.; Qi, G.; Liang, X.; Tang, F.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; He, S. MicroRNA-155-3p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma formation by suppressing FBXW7 expression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2016, 35, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, R.L.; Wong, K.Y.; Kwong, Y.L.; Loong, F.; Leung, C.Y.; Chu, R.; Lam, W.W.; Hui, P.K.; Lai, R.; Chim, C.S. Methylation of miR-155-3p in mantle cell lymphoma and other non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9770–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gimenes-Teixeira, H.L.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Dos Santos, G.A.; Zanette, D.L.; Scheucher, P.S.; Oliveira, L.C.; Dalmazzo, L.F.; Silva-Júnior, W.A.; Falcão, R.P.; Rego, E.M. Increased expression of miR-221 is associated with shorter overall survival in T-cell acute lymphoid leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, G.; Augugliaro, L.; Salemi, D.; Agueli, C.; La Rosa, M.; Dagnino, L.; Civiletto, G.; Messana, F.; Marfia, A.; Bica, M.G.; et al. Differential expression of specific microRNA and their targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, S. Cervical Cancer Cells-Secreted Exosomal microRNA-221-3p Promotes Invasion, Migration and Angiogenesis of Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Cervical Cancer by Down-Regulating MAPK10 Expression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 10307–10319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felli, N.; Fontana, L.; Pelosi, E.; Botta, R.; Bonci, D.; Facchiano, F.; Liuzzi, F.; Lulli, V.; Morsilli, O.; Santoro, S.; et al. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18081–18086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenquelli, M.; Muzio, M.; Scielzo, C.; Fazi, C.; Scarfò, L.; Rossi, C.; Ferrari, G.; Ghia, P.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. MicroRNA and proliferation control in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Functional relationship between miR-221/222 cluster and p27. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2010, 115, 3949–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; An, Q.; Niu, B.; Lu, X.; Zhang, N.; Cao, X. Role of miR-221/222 in Tumor Development and the Underlying Mechanism. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 7252013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C. MicroRNA-105 plays an independent prognostic role in esophageal cancer and acts as an oncogene. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2020, 27, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.C.; Yu, G.Z.; Ji, Z.W.; Wang, X.Q.; Xia, L. MiR-105 inhibits gastric cancer cells metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting SOX9. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 6160–6169. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, F.; Hu, T.; Peng, W.; Gu, Q.; Sun, Y. The Diverse Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressor Roles of microRNA-105 in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekarsky, Y.; Croce, C.M. Role of miR-15/16 in CLL. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovat, F.; Nigita, G.; Distefano, R.; Nakamura, T.; Gasparini, P.; Tomasello, L.; Fadda, P.; Ibrahimova, N.; Catricalà, S.; Palamarchuk, A.; et al. Combined loss of function of two different loci of miR-15/16 drives the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12332–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
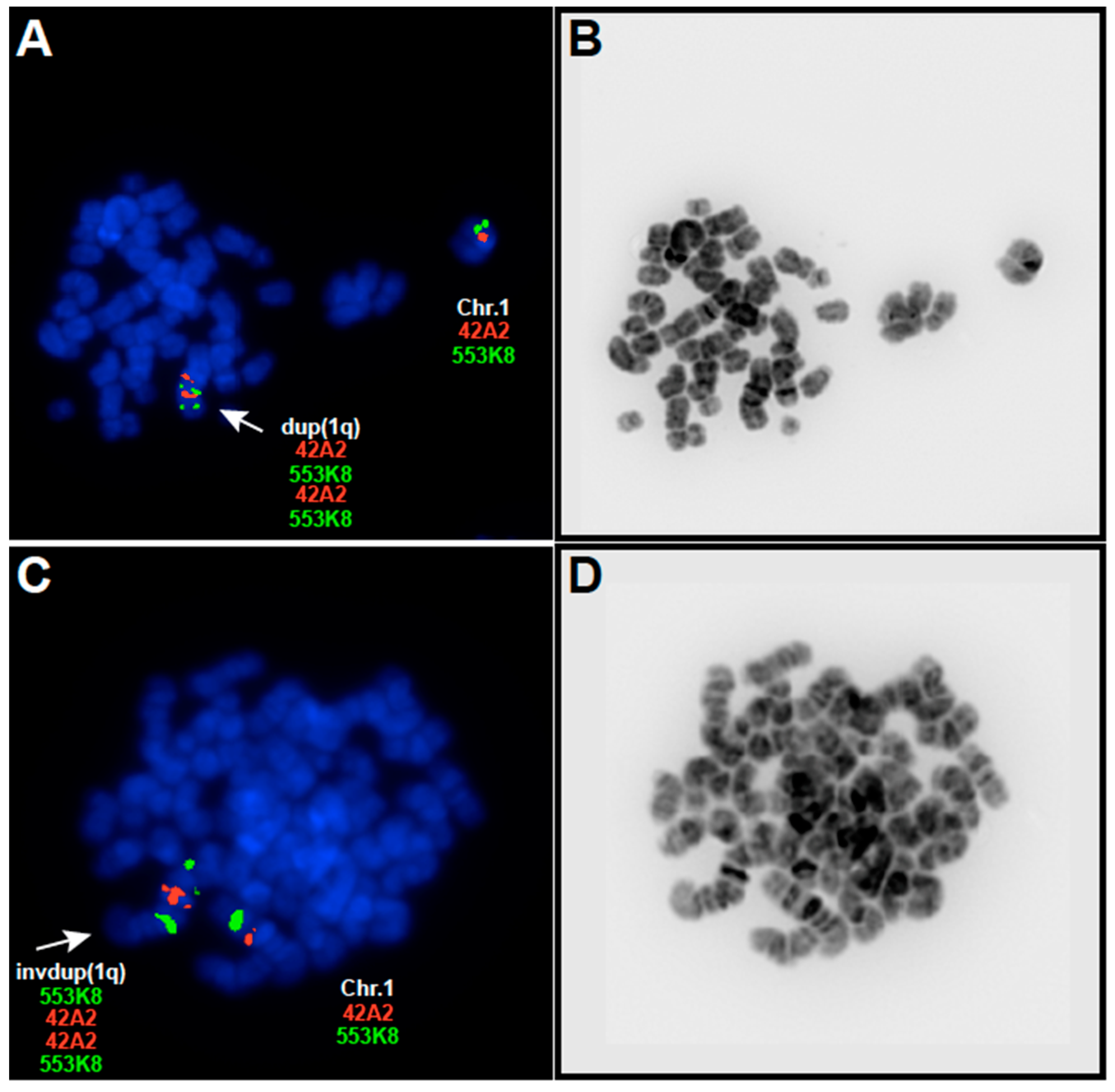
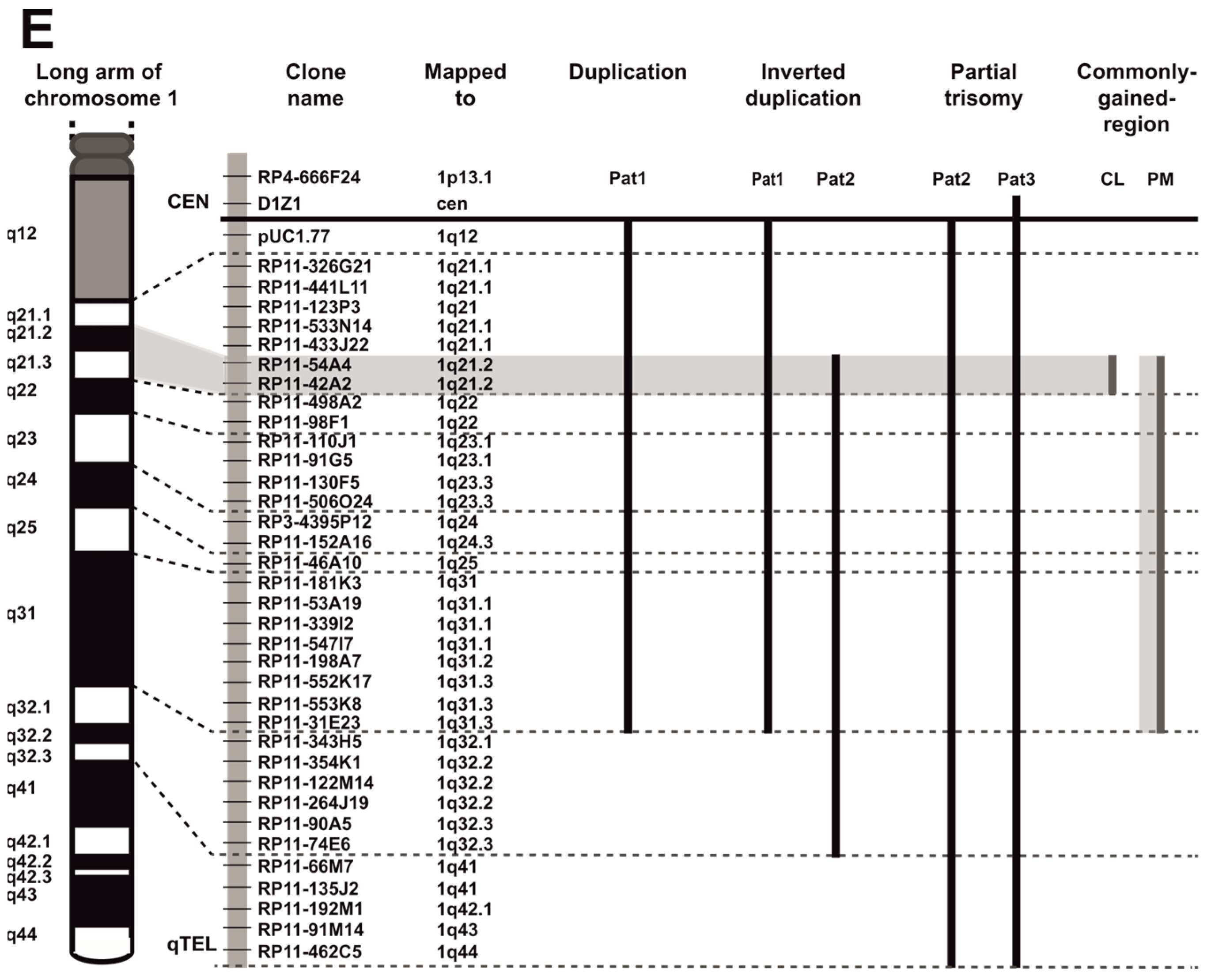



| Patient | G-Banding Karyotype | Partial mFISH Karyotype | Partial FISH Karyotype a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pat1 | 44-45,XY,dup(1)(q22q31),-3,-4, t(8;14)(q24;q32),del(11)(q23),+mar[cp25] | 45,XY,dup(1)(q22q31),t(8;14)(q24;q32) | I. dup(1)(q12q32.1)/ pUC1.77 to RP11-31E23 (PTPRC) II. dup(1)(q32.1q12)/ RP11-31E23 (PTPRC) to pUC1.77 |
| Pat2 | 45-47,XY,dup(1)(q21q44)[4], der(6)t(1;6)(q21;q27)[1],del(6)(q22q25)[1], der(7)t(1;7)(q21;p22)[3], t(8;14)(q24;q32)[cp9],+11 [cp9] | I.46,XY,der(7)t(1;7)(q;p),t(8;14)(q24;q32) II.43,XY,dup(1q),t(8;14)(q24;q32) | I. der(7)t(1;7)(q12;p22)/ pUC1.77 to 1qter II. dup(1)(q41q21.2)/ RP11-74E6 (PTPN14) to RP11-54A4 (MCL1) |
| Pat3 | 47,XX,+idic(1)(q10),t(8;14)(q24;q32), del(10)(p14),der(14)t(8;14)[10] | 47,XX,+idic(1)(q10),t(8;14)(q24;q32), der(14)t(8;14) | idic(1)(q10)/ centromere 1 to 1qter |
| No. | BL Cell Line a | EBV Status | 1q Gain Status | MYC Translocation | Sex | Age | Order No. | Purchased |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BL-28 | − | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 19 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 2 | BLUE-1 | − | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 29 | ACC 594 | DSMZ c |
| 3 | DG-75 | − | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 10 | ACC 83 | DSMZ c |
| 4 | Ramos | − | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 3 | ACC 603 | DSMZ c |
| 5 | BL-2 | − | par-tri; del | t(8;22)(q24;q11) | m | 7 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 6 | BL-92 | − | par-tri | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 14 | IARC1503 | IARC d |
| 7 | ST-486 | − | par-tri | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | n.a. | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 8 | BL-41 | − | inv-dup; par-tri | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 8 | ACC 160 | DSMZ c |
| 9 | CA-46 | − | inv-dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | n.a. | n.a. | ACC 73 | DSMZ c |
| 10 | CW698 | − | inv-dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | n.a. | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 11 | BL-30 | − | dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 19 | IARC116A | IARC d |
| 12 | BL-31 | − | dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 14 | IARC142A | IARC d |
| 13 | BL-70 | − | dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 16 | ACC 233 | DSMZ c |
| 14 | Loukes | − | dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | n.a. | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 15 | MN-60 | − | dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 20 | ACC 138 | DSMZ c |
| 16 | Tanoue | − | dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 11 | ACC 399 | DSMZ c |
| 17 | BL-49 | − | del | t(8;22)(q24;q11) | m | 3 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 18 | AG876 | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 8 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 19 | Akuba | + | − | t(8;22)(q24;q11) | n.a. | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 20 | BL-18 | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 3 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 21 | BL-60 | + | − | t(8;22)(q24;q11) | f | 4 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 22 | DAUDI | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 16 | ACC 78 | DSMZ c |
| 23 | DOHH-2 | + | − | t(8;14;18)(q24;q32;q21) | f | 9 | ACC 47 | DSMZ c |
| 24 | Jijoye M13 | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 7 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 25 | LY-91 | + | − | t(2;8)(p12;q24) | f | 7 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 26 | Naliaka | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | n.a. | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 27 | Rael | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | n.a. | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 28 | Raji | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 12 | ACC 319 | DSMZ c |
| 29 | Switzer | + | − | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | m | 16 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 30 | BL-16 | + | par-tri | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | f | 5 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 31 | JI | + | par-tri | t(2;8)(p12;q24) | f | 34 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 32 | LY-47 | + | par-tri | t(8;22)(q24;q11) | m | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 33 | Seraphina | + | par-tri | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | f | 7 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 34 | Silfere | + | par-tri | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | f | 6 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 35 | LY-66 | + | inv-dup | t(2;8)(p12;q24) | m | 13 | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
| 36 | NAMALWA | + | inv-dup | t(8;14)(q24;q32) | f | 3 | ACC 24 | DSMZ c |
| 37 | KK124 | + | dup; del | t(8;22)(q24;q11) | m | n.a. | − | Prof. G. Klein b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akyüz, N.; Janjetovic, S.; Ghandili, S.; Bokemeyer, C.; Dierlamm, J. EBV and 1q Gains Affect Gene and miRNA Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma. Viruses 2023, 15, 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091808
Akyüz N, Janjetovic S, Ghandili S, Bokemeyer C, Dierlamm J. EBV and 1q Gains Affect Gene and miRNA Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma. Viruses. 2023; 15(9):1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091808
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkyüz, Nuray, Snjezana Janjetovic, Susanne Ghandili, Carsten Bokemeyer, and Judith Dierlamm. 2023. "EBV and 1q Gains Affect Gene and miRNA Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma" Viruses 15, no. 9: 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091808
APA StyleAkyüz, N., Janjetovic, S., Ghandili, S., Bokemeyer, C., & Dierlamm, J. (2023). EBV and 1q Gains Affect Gene and miRNA Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma. Viruses, 15(9), 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091808






