The Role of Epinephelus coioides DUSP5 in Regulating Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish, Cells, and Virus
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
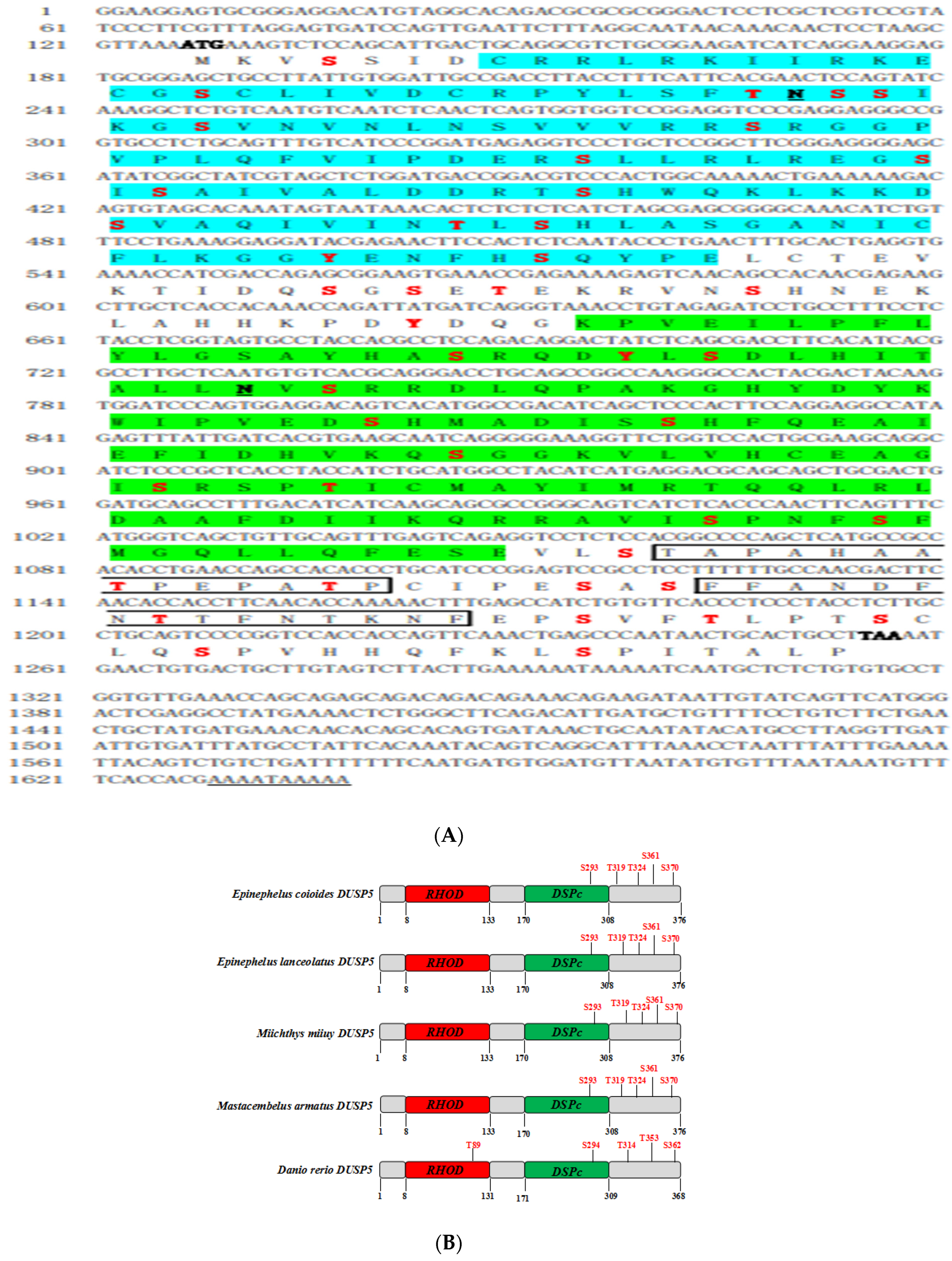
2.3. Identification of E. coioides DUSP5
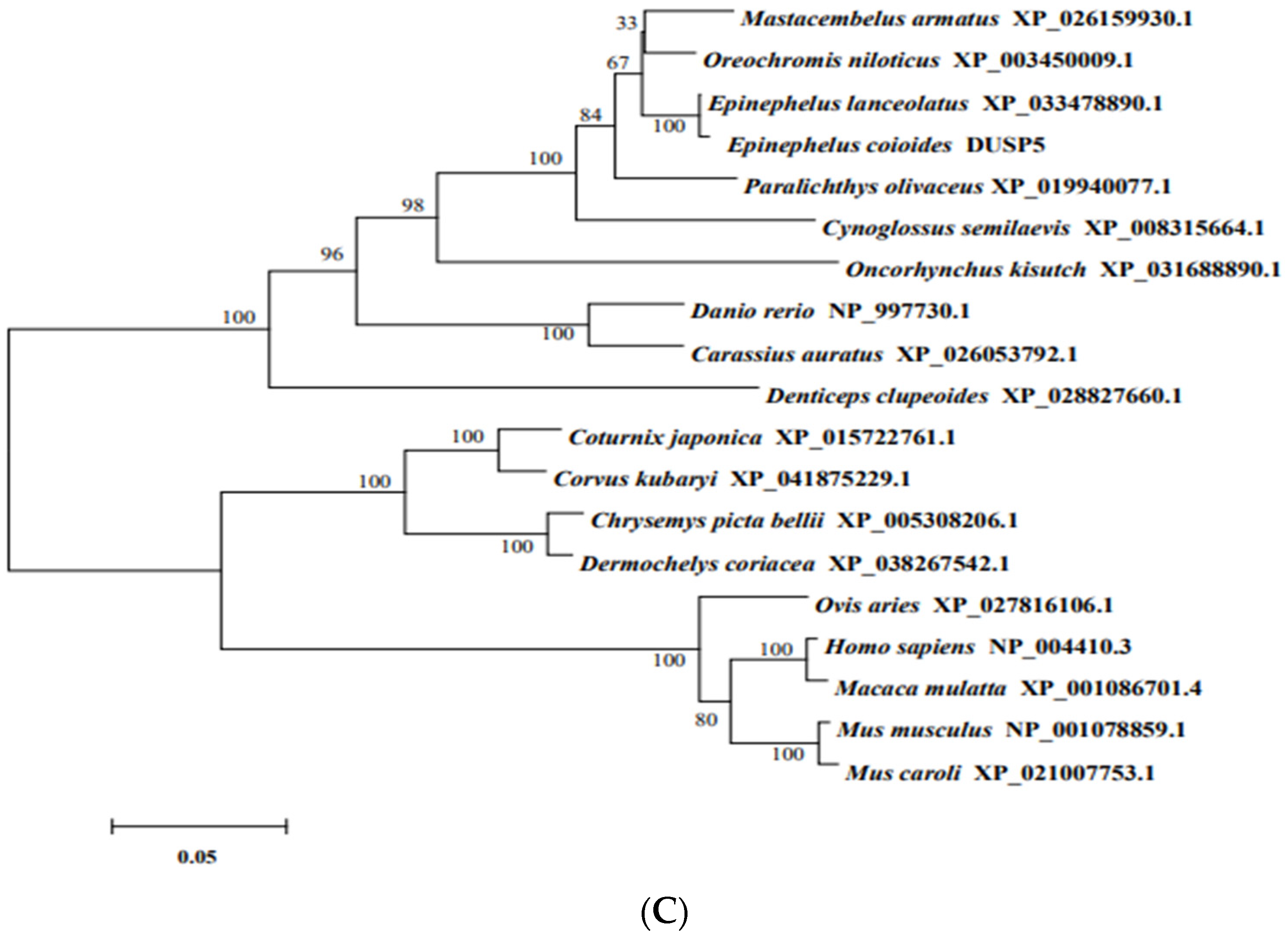
2.4. Biological Information
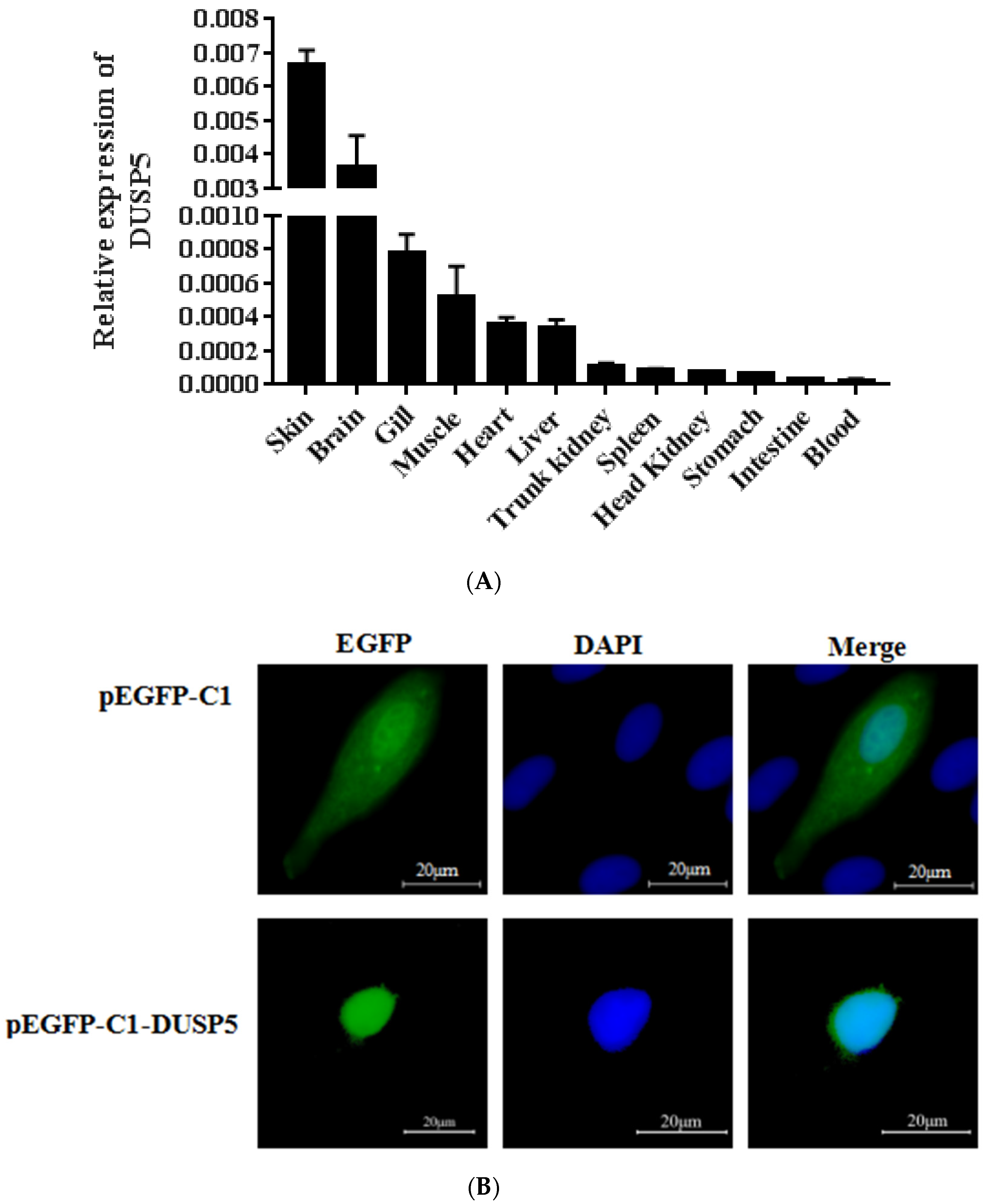
2.5. The Expression Patterns of E. coioides DUSP5
2.6. Subcellular Localization
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Virus Titer
2.9. Dual-Luciferase Reporter
2.10. Cell Apoptosis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Molecular Characterization of E. coioides DUSP5
3.2. Expression and Localization of E. coioides DUSP5
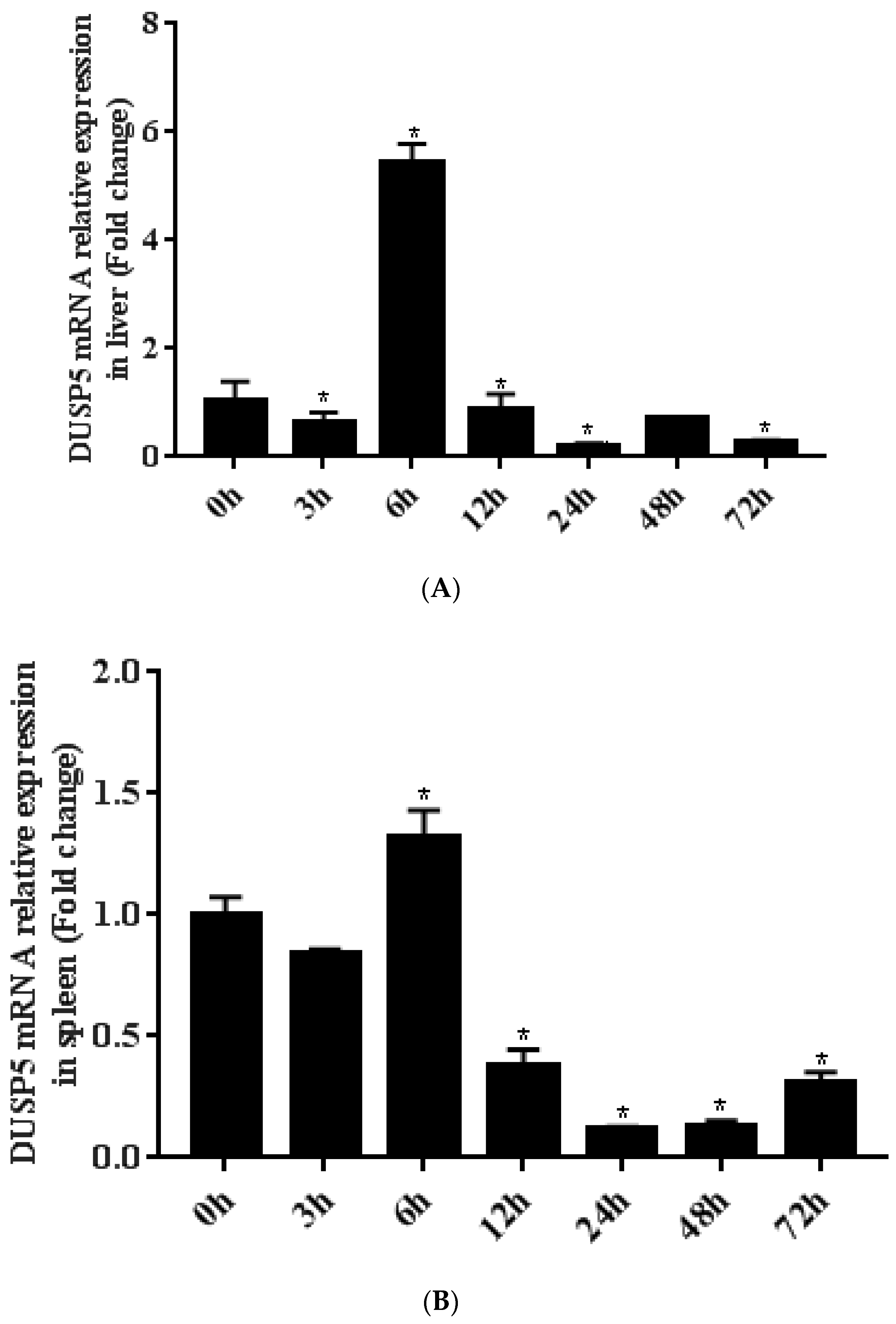
3.3. Differential Expression of E. coioides DUSP5 during SGIV Infection
3.4. Overexpression Efficiency of E. coioides DUSP5
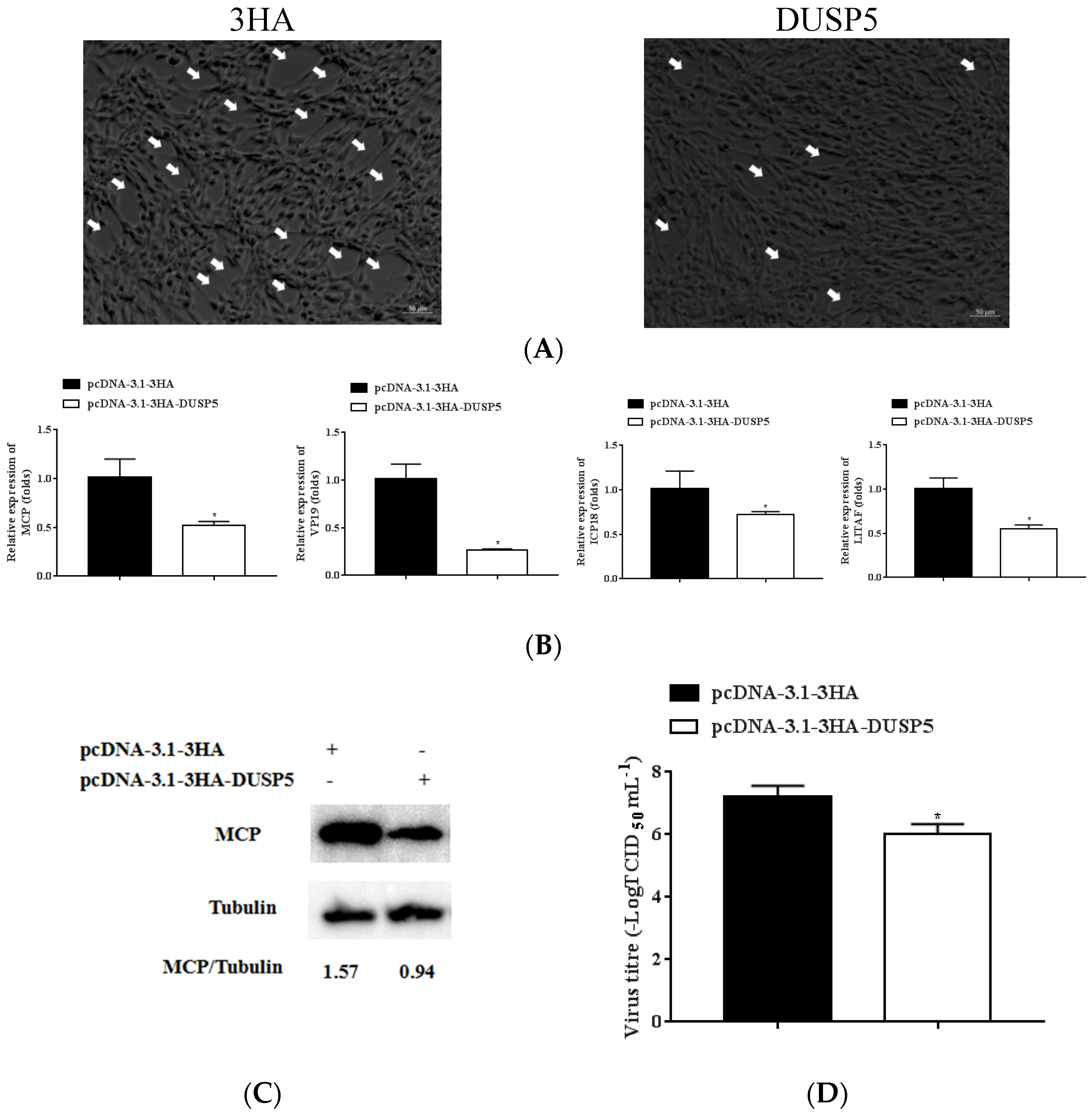
3.5. E. coioides DUSP5 Inhibits SGIV Replication
3.6. E. coioides DUSP5 Negatively Regulates Innate Immunity
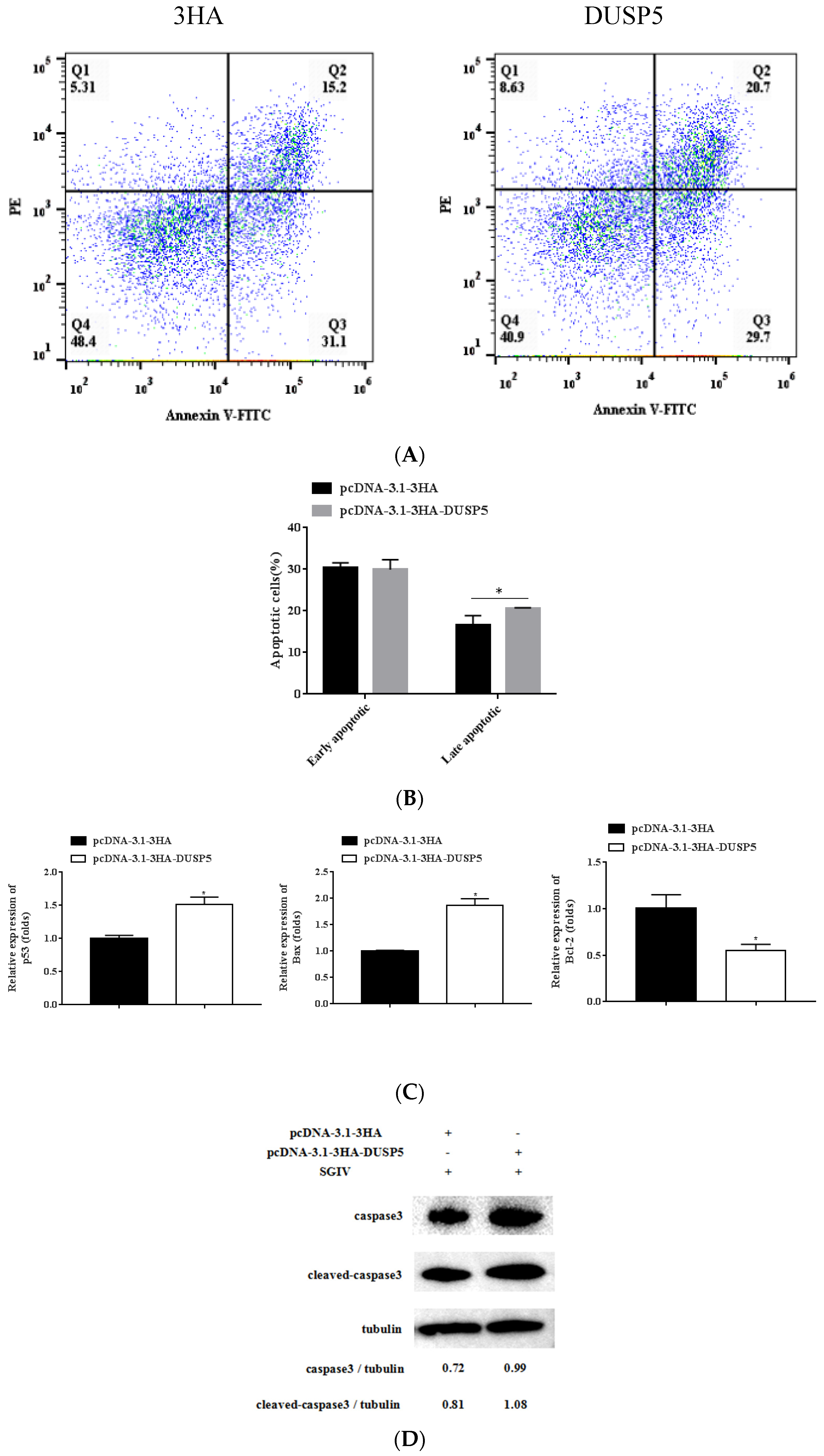
3.7. E. coioides DUSP5 Promotes SGIV-Induced Apoptosis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawan, A.; Al-Harthi, S.; Cadalbert, L.; McCluskey, A.G.; Shweash, M.G.; Grant, A.; Boyd, M.; Currie, S.; Plevin, R. Deletion of the dual specific phosphatase-4 (DUSP-4) gene reveals an essential non-redundant role for MAP kinase phosphatase-2 (MKP-2) in proliferation and cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12933–12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.M.; Lin, S.J.; Lin, J.H.; Lin, P.Y.; Teng, P.L.; Wu, H.E.; Yeh, T.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, M.R.; Tsai, C.H. Dysregulation of Dual-Specificity Phosphatases by Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 and Its Impact on Lymphoblastoid Cell Line Survival. J. Virol. 2006, 94, e01837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hao, G.; Li, J.; Peng, W.; Geng, X.; Sun, J. Comparative analysis of dual specificity protein phosphatase genes 1, 2 and 5 in response to immune challenges in Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.F.; Chuang, H.C.; Tan, T.H. Regulation of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase (DUSP) Ubiquitination and Protein Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharska, A.; Rushworth, L.K.; Staples, C.; Morrice, N.A.; Keyse, S.M. Regulation of the inducible nuclear dual-specificity phosphatase DUSP5 by ERK MAPK. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffet, C.; Hecale-Perlemoine, K.; Bricaire, L.; Dumont, F.; Baudry, C.; Tissier, F.; Bertherat, J.; Cochand-Priollet, B.; Raffin-Sanson, M.L.; Cormier, F.; et al. DUSP5 and DUSP6, two ERK specific phosphatases, are markers of a higher MAPK signaling activation in BRAF mutated thyroid cancers. PLoS ONE. 2017, 12, e0184861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A. MAP kinases in the immune response. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers, G.T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.L.; Chen, J.P.; Mo, Z.Q.; Zheng, J.Y.; Lv, S.Y.; Li, P.H.; Wei, Y.S.; Liang, Y.L.; Wang, S.W.; Yang, M.; et al. A novel MKK gene (EcMKK6) in Epinephelus coioides: Identification, characterization and its response to Vibrio alginolyticus and SGIV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.; Hammer, M.; Mages, J. DUSP meet immunology: Dual specificity MAPK phosphatases in control of the inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7497–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushworth, L.K.; Kidger, A.M.; Delavaine, L.; Stewart, G.; Van Schelven, S.; Davidson, J.; Bryant, C.J.; Caddye, E.; East, P.; Caunt, C.J.; et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 5 regulates nuclear ERK activity and suppresses skin cancer by inhibiting mutant Harvey-Ras (HRasQ61L)-driven SerpinB2 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18267–18272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xue, D.; Song, F.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. DUSP5 (dual-specificity protein phosphatase 5) suppresses BCG-induced autophagy via ERK 1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 126, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Cho, Y.C.; Ju, A.; Lee, S.; Park, B.C.; Park, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Cho, S. Dual-specificity phosphatase 5 acts as an anti-inflammatory regulator by inhibiting the ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teferi, W.M.; Dodd, K.; Maranchuk, R.; Favis, N.; Evans, D.H. A whole-genome RNA interference screen for human cell factors affecting myxoma virus replication. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4623–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Chen, S.; Song, Y.; van der Veen, S.; Cheng, H. Human papillomavirus type 16 early protein E7 activates autophagy through inhibition of dual-specificity phosphatase 5. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1863098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Su, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.F.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Wei, J.G.; Huang, X.H.; Qin, Q.W.; et al. Molecular characterization and function analysis of Epinephelus coioides Hsp22 response to SGIV and Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Wang, L.Q.; He, J.Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Huang, W.; Wang, S.W.; Qin, Q.W.; Sun, H.Y. MicroRNA-124 Promotes Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Replication and Negatively Regulates Innate Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.W.; Lam, T.J.; Sin, Y.M.; Shen, H.; Chang, S.F.; Ngoh, G.H.; Chen, C.L. Electron microscopic observations of a marine fish iridovirus isolated from brown-spotted grouper, Epinephelus tauvina. J. Virol. Methods 2001, 98, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Cai, Y.J.; Zhu, X.L.; Yang, J.D.; Yang, S.Q.; Huang, W.; Wei, S.N.; Zhou, S.; Wei, J.G.; Qin, Q.W.; et al. Epinephelus coioides Hsp27 negatively regulates innate immune response and apoptosis induced by Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, E.; Borner, G.H.H. Spatial proteomics: A powerful discovery tool for cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Ouyang, Z.L.; Xu, L.; Yan, Y.; Cui, H.C.; Han, X.; Qin, Q.W. Singapore grouper iridovirus, a large DNA virus, induces nonapoptotic cell death by a cell type dependent fashion and evokes ERK signaling. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovanen, P.E.; Bernard, J.; Al-Shami, A.; Liu, C.; Bollenbacher-Reilley, J.; Young, C.; Pise-Masison, C.; Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J. T-cell development and function are modulated by dual specificity phosphatase DUSP5. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17362–17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.S.; Wennersten, S.A.; Demos-Davies, K.M.; Rubino, M.; Robinson, E.L.; Cavasin, M.A.; Stratton, M.S.; Kidger, A.M.; Hu, T.; Keyse, S.M.; et al. DUSP5-mediated inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation suppresses pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 321, H382–H389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.J.; Yang, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Choi, E.S.; Lim, C.S.; Lee, S.; Han, C.Y. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Increases DUSP5 Expression via PERK-CHOP Pathway, Leading to Hepatocyte Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.A.; Yeh, J.H.; Yan, D.; Xu, M.; Chan, A.C. Dusp5 negatively regulates IL-33-mediated eosinophil survival and function. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Xu, K.; Chen, Z.; Moqbel, S.A.A.; Ma, C.; Jiang, L.; Ran, J.; Wu, L.; et al. DUSP5 suppresses interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation and ameliorates osteoarthritis in rats. Aging 2020, 12, 26029–26046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibian, J.S.; Jefic, M.; Bagchi, R.A.; Lane, R.H.; McKnight, R.A.; McKinsey, T.A.; Morrison, R.F.; Ferguson, B.S. DUSP5 functions as a feedback regulator of TNFα-induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation and inflammatory gene expression in adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, F.; Saheb Sharif Askari, N.; Madkhana, B.; Alwaa, A.M.; Mahboub, B.; Zakeri, A.M.; Ratemi, E.; Hamoudi, R.; Hamid, Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Switches ‘on’ MAPK and NFκB Signaling via the Reduction of Nuclear DUSP1 and DUSP5 Expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 631879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, Y.; Hua, Z.C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistritto, G.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Ceci, C.; Garufi, A.; D’Orazi, G. Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging 2016, 8, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Su, Y.L.; Li, P.H.; He, J.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.W.; Huang, X.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Qin, Q.W. The Roles of Epinephelus coioides miR-122 in SGIV Infection and Replication. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TCuconati, A.; White, E. Viral homologs of BCL-2: Role of apoptosis in the regulation of virus infection. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, C.A.; Butrovich, K.D.; Lurain, N.S.; Corbeil, J.; Rooney, I.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J.; Ware, C.F. Cutting edge: A novel viral TNF receptor superfamily member in virulent strains of human cytomegalovirus. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6967–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Tan, P.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, A. microRNA-95 knockdown inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype in gastric cancer cells through MAPK pathway by upregulating DUSP5. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Jian, X.; Sun, B.Q.; Ge, X.S.; Huang, F.J.; Chen, Y.Q. LncRNA ROR1-AS1 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation by suppressing the expression of DUSP5/CDKN1A. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 4, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar]


| Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| DUSP5-ORF-F | ATGAAAGTCTCCAGCATTGAC |
| DUSP5-ORF-R | TTAAGGCAGTGCAGTTATTGG |
| DUSP5-RT-F | TCCTGAAAGGAGGATACGA |
| DUSP5-RT-R | TCACTTCCGCTCTGGTC |
| DUSP5-pcDNA3.1-F | GCATCAGCGGAAAAGATGAAAGTCTCCAGCATTGACTGC |
| DUSP5-pcDNA3.1-R | ACTGTGCTGGATATCTTAAGGCAGTGCAGTTATTGGGCT |
| DUSP5-pEGFP-F | TACAAGTCCGGACTCATGAAAGTCTCCAGCATTGACTGC |
| DUSP5-pEGFP-R | GGTGGATCCCGGGCCTTAAGGCAGTGCAGTTATTGGGCT |
| MCP-RT-F | GCACGCTTCTCTCACCTTCA |
| MCP-RT-R | AACGGCAACGGGAGCACTA |
| LITAF-RT-F | GATGCTGCCGTGTGAACTG |
| LITAF-RT-R | GCACATCCTTGGTGGTGTTG |
| ICP18-RT-F | ATCGGATCTACGTGGTTGG |
| ICP18-RT-R | CCGTCGTCGGTGTCTATTC |
| VP19-RT-F | TCCAAGGGAGAAACTGTAAG |
| VP19-RT-R | GGGGTAAGCGTGAAGACT |
| IL-6-RT-F | CTCTACACTCAACGCGTACATGC |
| IL-6-RT-R | TCATCTTCAAACTGCTTTTCGTG |
| IL-8-RT-F | GCCGTCAGTGAAGGGAGTCTAG |
| IL-8-RT-R | ATCGCAGTGGGAGTTTGCA |
| TNFα-RT-F | GTGTCCTGCTGTTTGCTTGGTA |
| TNFα-RT-R | CAGTGTCCGACTTGATTAGTGCTT |
| β-actin-RT-F | TACGAGCTGCCTGACGGACA |
| β-actin-RT-R | GGCTGTGATCTCCTTCTGCA |
| Bax-RT-F | TGTGCGACCCAAATACCAAGAGG |
| Bax-RT-R | AAGTAGAACAGTGCAACCACCCTGC |
| p53-RT-F | GGAGGAAAACAGCACCAAGACGC |
| p53-RT-R | CCACGAACATGCAGAACAAACACG |
| Bcl-2-RT-F | ATGAACAAAGAAGTAGATTGGGTCG |
| Bcl-2-RT-R | GTGAGATGAGTAAGGAAGGGATGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Cai, Y.; Huang, W.; Lin, Y.; Lei, Y.; Huang, C.; Cui, Z.; Qin, Q.; Sun, H. The Role of Epinephelus coioides DUSP5 in Regulating Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091807
He J, Cai Y, Huang W, Lin Y, Lei Y, Huang C, Cui Z, Qin Q, Sun H. The Role of Epinephelus coioides DUSP5 in Regulating Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Infection. Viruses. 2023; 15(9):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091807
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiayang, Yijie Cai, Wei Huang, Yunxiang Lin, Yurong Lei, Cuifen Huang, Zongbin Cui, Qiwei Qin, and Hongyan Sun. 2023. "The Role of Epinephelus coioides DUSP5 in Regulating Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Infection" Viruses 15, no. 9: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091807
APA StyleHe, J., Cai, Y., Huang, W., Lin, Y., Lei, Y., Huang, C., Cui, Z., Qin, Q., & Sun, H. (2023). The Role of Epinephelus coioides DUSP5 in Regulating Singapore Grouper Iridovirus Infection. Viruses, 15(9), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15091807






