COVID-19-Triggered Acute Liver Failure and Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
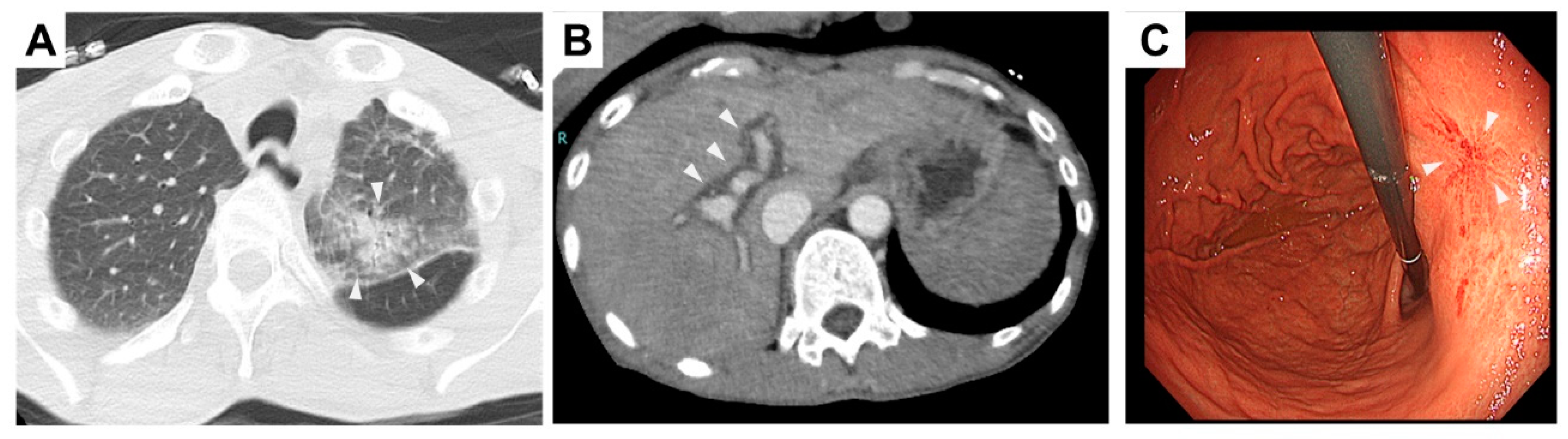
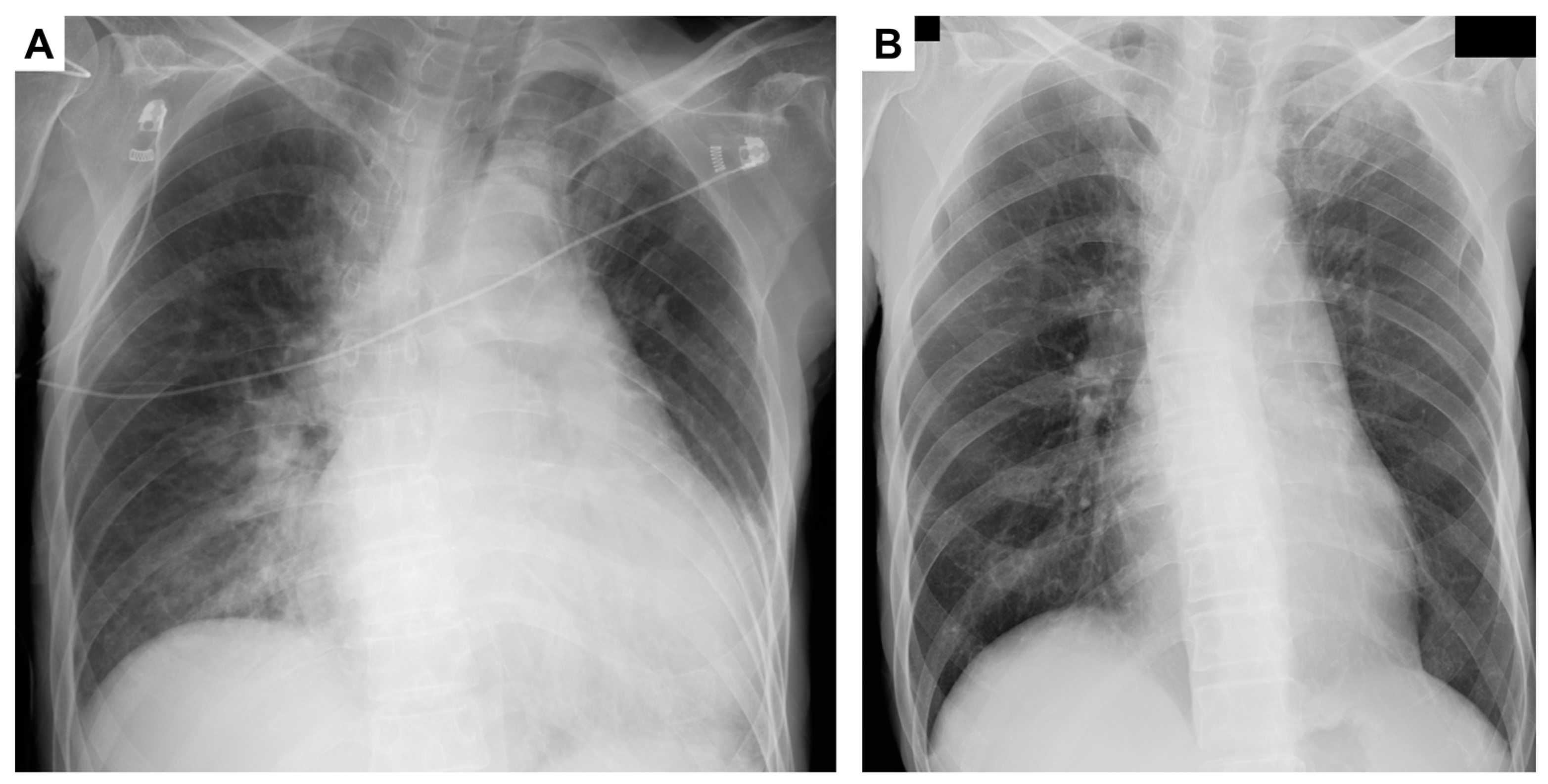
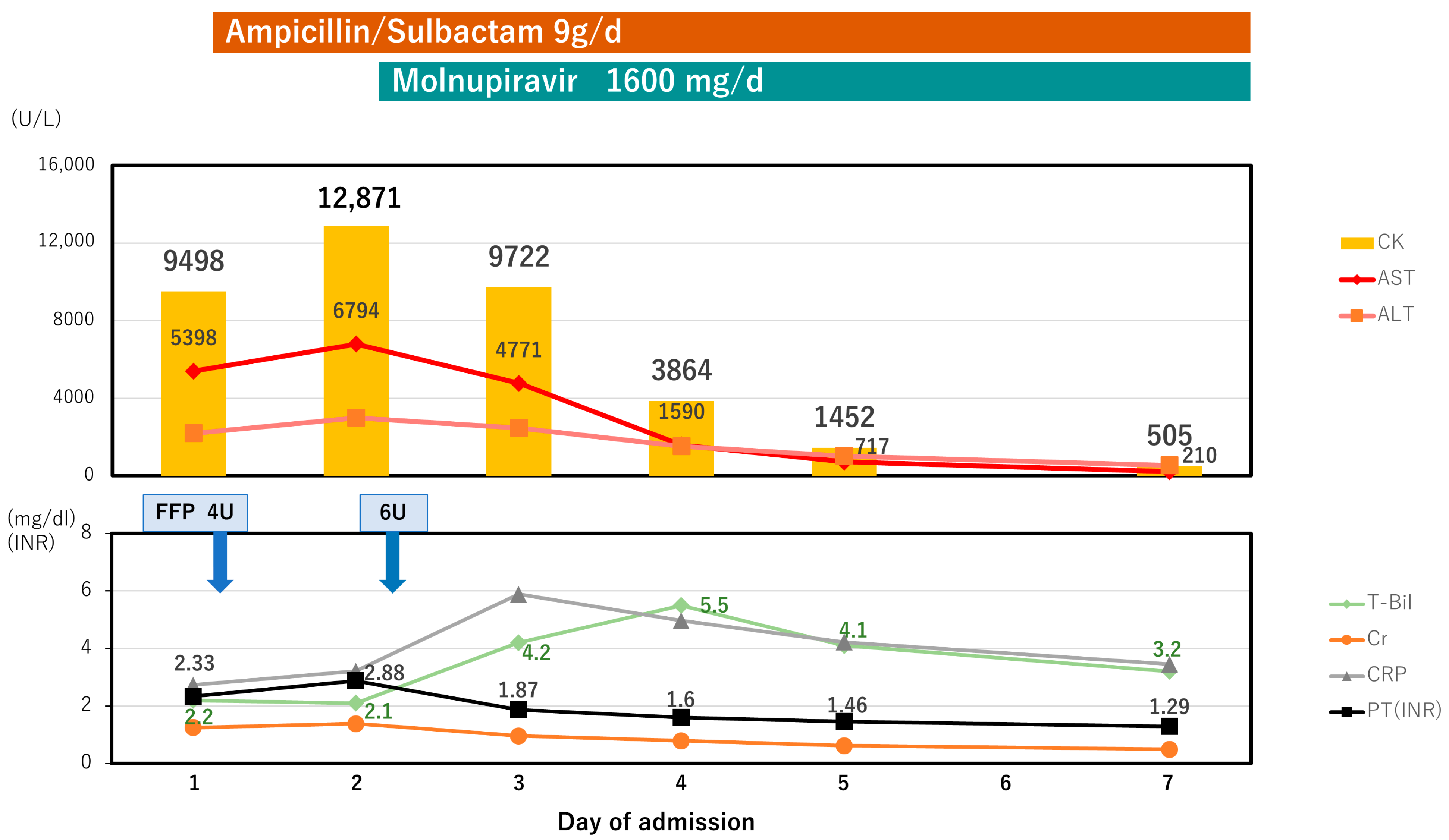
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard—WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Alzghoul, B.; Kalra, S.S. COVID-19 Infection and Severe Rhabdomyolysis. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2021, 34, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meegada, S.; Muppidi, V.; Wilkinson, D.C.; Siddamreddy, S.; Katta, S.K. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Induced Rhabdomyolysis. Cureus 2020, 12, e10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, M.; Kakleas, K.; Kimioni, V.; Georgiadi, D.; Spoulou, V.; Michos, A. Rhabdomyolysis and Coronavirus Disease-2019 in Children: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Investig. 2022, 6, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, S.G.; Nylen, E.S.; Khosla, R. Rhabdomyolysis in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Infection: Five Case Series. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2020, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, P.; Mechineni, A.; Maroules, M. Rhabdomyolysis in COVID-19: Report of Four Cases. Cureus 2020, 12, e10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, R.; Corcuera-Solano, I.; Dayan, E.; Jacobi, A.H.; Huang, M. Rhabdomyolysis as a Manifestation of a Severe Case of COVID-19: A Case Report. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-García, S.; Bernal, J.; Bachiller-Corral, J. Rhabdomyolysis as the Main Manifestation of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2174–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrubaye, R.; Choudhary, H. Severe Rhabdomyolysis in a 35-Year-Old Woman with COVID-19 Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e926733-1–e926733-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckholz, A.P.; Kaplan, A.; Rosenblatt, R.E.; Wan, D. Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Outcomes of 6 Patients With COVID-19 Infection and Rhabdomyolysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, J.G.; Pineda, A.E.; Minutti, P.A.; Sánchez, A.A. Case Report: Rhabdomyolysis in a Patient with COVID-19: A Proposed Diagnostic-Therapeutic Algorithm. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedid, N.R.; Udit, S.; Solhjou, Z.; Patanwala, M.Y.; Sheridan, A.M.; Barkoudah, E. COVID-19 and Rhabdomyolysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 3087–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byler, J.; Harrison, R.; Fell, L.L. Rhabdomyolysis Following Recovery from Severe COVID-19: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e931616-1–e931616-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, P.; Reid, R.R. Rhabdomyolysis Associated with COVID-19. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 102, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shanbhag, A.; Manaktala, P.S.; Rizvi, H.; Frey, K.; Narayanan, R. COVID-19 Presenting as Severe Rhabdomyolysis With Normal Renal Function. Cureus 2020, 12, e9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwanwongse, K.; Shabarek, N. Rhabdomyolysis as a Presentation of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease. Cureus 2020, 12, e7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Kanai, O.; Nanba, K.; Esaka, N.; Hata, H.; Seta, K.; Odagaki, T. Acute Rhabdomyolysis in a Young Woman with Moderate COVID-19. IDCases 2021, 25, e01212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxbro, K.; Kahlow, H.; Wulcan, H.; Fornarve, A. Rhabdomyolysis and Acute Kidney Injury in Severe COVID-19 Infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e237616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, B.B.; Ikitimur, H.; Yavuzer, S.; Islamoglu, M.S.; Cengiz, M. Case Report: A COVID-19 Patient Presenting with Mild Rhabdomyolysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, J.R.; Ali, S.S.; Nagra, D.; Adas, M.A.; Buazon, A.D.; Galloway, J.B.; Gordon, P.A. Skeletal muscles and COVID-19: A systematic review of rhabdomyolysis and myositis in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawor, M.; Sairam, S.; Rozewicz, R.; Viegas, S.; Comninos, A.N.; Abbara, A. Rhabdomyolysis after COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses 2022, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochida, S.; Takikawa, Y.; Nakayama, N.; Oketani, M.; Naiki, T.; Yamagishi, Y.; Ichida, T.; Tsubouchi, H. Diagnostic Criteria of Acute Liver Failure: A Report by the Intractable Hepato-Biliary Diseases Study Group of Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, W.H.; Yang, H.; Shah, K.H. Rhabdomyolysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2007, 2, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medetalibeyoglu, A.; Catma, Y.; Senkal, N.; Ormeci, A.; Cavus, B.; Kose, M.; Bayramlar, O.F.; Yildiz, G.; Akyuz, F.; Kaymakoglu, S.; et al. The Effect of Liver Test Abnormalities on the Prognosis of COVID-19. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Prichett, L.; Tao, X.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Hamilton, J.P.; Mezey, E.; Strauss, A.T.; Kim, A.; Potter, J.J.; Chen, P.H.; et al. Abnormal Liver Chemistries as a Predictor of COVID-19 Severity and Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paštrovic, F.; Lucijanic, M.; Atic, A.; Stojic, J.; Barisic Jaman, M.; Tjesic Drinkovic, I.; Zelenika, M.; Milosevic, M.; Medic, B.; Loncar, J.; et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Impact of Deranged Liver Blood Tests in COVID-19: Experience from the Regional COVID-19 Center over the Cohort of 3812 Hospitalized Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, M.; Tang, Z.; Radcliffe, C.; Caruana, D.; Doilicho, N.; Ciarleglio, M.M.; Deng, Y.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Significant Liver Injury during Hospitalization for COVID-19 Is Not Associated with Liver Insufficiency or Death. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2182–2191.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotka, L.A.; Esteban, J.; Volk, M.L.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Rockey, D.C. Acute Liver Injury in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Huang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, G.; Gou, J.; Qu, J.; et al. COVID-19: Abnormal Liver Function Tests. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Bali, T.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Giannakodimos, A.; Gyftopoulos, A.; Georgilaki, V.; Gerogiannis, D.; Basoulis, D.; Eliadi, I.; Karamanakos, G.; et al. Prevalence of Abnormal Liver Biochemistry and Its Impact on COVID-19 Patients’ Outcomes: A Single-Center Greek Study. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2022, 35, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Hellmuth, J.C.; Scherer, C.; Muenchhoff, M.; Mayerle, J.; Gerbes, A.L. Liver Function Test Abnormalities at Hospital Admission Are Associated with Severe Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Prospective Cohort Study. Gut 2021, 70, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, S.; Teimouri, A. Severe Acute Hepatitis in a COVID-19 Patient: A Case Report. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, M.; Zago, T. Acute Hepatitis Caused by Asymptomatic COVID-19 Infection. J. Infect. 2021, 82, e25–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulou, V.; Bali, T.; Adamantou, M.; Asimakopoulou, S.; Makrodimitri, S.; Samara, S.; Triantafyllou, M.; Voutsinas, P.; Eliadi, I.; Karamanakos, G.; et al. Acute Hepatitis and Liver Injury in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 Infection. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaud, P.C.; Hermand, C.; Sobotka, J.; Raynal, P.A. Acute Icteric Hepatitis as the First Isolated Symptom of COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep 2021, 14, e242853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.N.; Sarı, S.F. A COVID-19 Patient Presenting With Acute Hepatitis. Eurasian J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 21, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melquist, S.; Estepp, K.; Aleksandrovich, Y.; Lee, A.; Beiseker, A.; Hamedani, F.S.; Bassett, J. COVID-19 Presenting as Fulminant Hepatic Failure: A Case Report. Medicine 2020, 99, e22818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurala, D.; Al Moussawi, H.; Philipose, J.; Abergel, J.R. Acute Liver Failure in a COVID-19 Patient without Any Preexisting Liver Disease. Cureus 2020, 12, e10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.; Mayerle, J.; Irlbeck, M.; Gerbes, A.L. Severe Liver Failure during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Gut 2020, 69, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Rapista, N.; Jean, L.-G. Corona virus disease-19-induced acute liver failure leading to severe metabolic acidosis. Chest 2020, 158, A1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, J.; Bawa, A.; Omer, H.; Ashraf, F.; Zulfiqar, P. COVID-19 Infection Presenting as an Isolated Severe Acute Liver Failure. Cureus 2022, 10, e24873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Krueger, N.; Mueller, M.A.; Drosten, C.; Poehlmann, S. The Novel Coronavirus 2019 (2019-NCoV) Uses the SARS-Coronavirus Receptor ACE2 and the Cellular Protease TMPRSS2 for Entry into Target Cells. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.H. Hypothesis: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Increase the Risk of Severe COVID-19. J. Travel Med. 2021, 27, taaa041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, N.; Chen, P.H. Hypoxic Hepatitis: A Review and Clinical Update. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, P.A.; Helmstetter, J.A.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Rhabdomyolysis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Ochsner J. 2015, 15, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Fadila, M.F.; Wool, K.J. Rhabdomyolysis Secondary to Influenza A Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 7, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, J.H. Virus-Associated Rhabdomyolysis in Children. Child. Kidney Dis. 2017, 21, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnstrom, M.; Ebied, A.M.; Khoury, A.P.; Reddy, R. Influenza-Induced Rhabdomyolysis. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 11, e226610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, A.; Naveen, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Gupta, L. COVID-19 and Myositis: What We Know So Far. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum-Cianflone, N.F. Nonbacterial Myositis. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2010, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.J.; van Goor, H. Tissue Distribution of ACE2 Protein, the Functional Receptor for SARS Coronavirus. A First Step in Understanding SARS Pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, V.K.; Garg, R.K.; Gupta, A.; Tejan, N. Neuromuscular Presentations in Patients with COVID-19. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3039–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines, Molnupiravir. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/antivirals-including-antibody-products/molnupiravir/ (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Teli, D.; Balar, P.; Patel, K.; Sharma, A.; Chavda, V.; Vora, L. Molnupiravir: A Versatile Prodrug against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Metabolites 2023, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CBC | Serology | ||||||
| WBC | 12.2 | (3.3–8.6) | ×103/µL | anti-EBV VCA IgG | 1:320 | (+) | |
| Neut | 91.4 | (38.5–80.5) | % | anti-EBV VCA IgM | <1:10 | (−) | |
| Lymph | 4.6 | (16.5–49.5) | % | anti-CMV IgG | 31.4 | (+) | |
| Mon | 4 | (2.0–10.0) | % | anti-CMV IgM | 0.32 | (−) | |
| Eos | 0 | (0.0–8.5) | % | anti-HSV IgG | 31.4 | (+) | |
| Bas | 0 | (0.0–2.5) | % | anti-HSV IgM | 0.32 | (−) | |
| RBC | 2.46 | (3.86–4.92) | ×104/mL | HBs Ag | (−) | ||
| Hb | 3.4 | (11.6–14.8) | g/dL | HBs Ab | (−) | ||
| Hct | 15.4 | (35.1–44.4) | % | HCV Ab | (−) | ||
| MCV | 62.6 | (83.6–98.2) | fL | IgM-HA Ab | <1:40 | ||
| MCH | 13.8 | (27.5–33.2) | % | IgA-HEV Ab | (−) | ||
| MCHC | 22.1 | (31.7–35.3) | % | ANA | <1:40 | ||
| Platelet | 18.9 | (15.8–34.8) | ×104/µL | AMA-M2 | <1.5 | (−) | |
| Biochemistry | Ig G | 1493 | (861–1747) | mg/dL | |||
| Total protein | 7.0 | (6.6–8.1) | g/dL | Ig G4 | 57 | (11–121) | mg/dL |
| Albumin | 3.9 | (4.1–5.1) | g/dL | Ig M | 37 | (50–269) | mg/dL |
| Total bilirubin | 2.2 | (0.4–1.5) | mg/dL | SARS-CoV-2 | (+) | ||
| Direct bilirubin | 0.9 | (≤0.4) | mg/dL | N (Ct) | 25.1 | ||
| AST | 5398 | (13–30) | U/L | N (copies) | 666,135.0 | ||
| ALT | 2197 | (7–23) | U/L | N2 (Ct) | 20.3 | ||
| ALP (IFCC) | 99 | (38–113) | U/L | N2 (copies) | 2,420,950.0 | ||
| GGT | 55 | (9–32) | U/L | Coagulation | |||
| LDH | 4636 | (124–222) | U/L | PT (%) | 26.2 | (70–130) | % |
| CK | 9498 | (41–153) | U/L | PT(INR) | 2.33 | (0.80–1.27) | |
| BUN | 31.3 | (8–20) | mg/dL | ||||
| Creatinine | 1.25 | (0.46–0.79) | mg/dL | ||||
| CRP | 2.73 | (<0.15) | mg/dL | Plasma myoglobin | 4366 | (≤154.9) | ng/mL |
| NH3 | 159 | (12–66) | µg/dL | Urine myoglobin | 73,900 | (≤2.0) | ng/mL |
| Case# | Age | Sex | Underlying Diseases | Highest AST (IU/L) | Highest ALT (IU/L) | T-bil (mg/dL) | PT-INR | CK | CRP (mg/dL) | Prognosis | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35 | F | SLE | 4202 (day 3) | 5524 (day 3) | 10.5 (day 3) | 4.9 | n/a | 6.68 | recovered | [39] |
| 2 | 80 | M | DM, HT, HLP, CAD, asthma, | >7000 * (day 5) | 3737 (day 5) | 8.4 (day 8) | 8.94 (day 8) | n/a | n/a | died (day 9) | [40] |
| 3 | 65 | M | HT | 746 (day 14) | 467 (day 14) | 22.2 (day 20) | 2–3 ** (day 20) | n/a | n/a | n/a | [41] |
| 4 | 53 | M | CM | 4735 (day 2) | 1988 (day 2) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | [42] |
| 5 | 49 | F | AD, HT, DA | 950 (day 1) | 1375 (day 1) | 21.2 (day 6) | 15.5 (day 4) | n/a | n/a | died (day 9) | [43] |
| 6 | 62 | M | PU, HF | 6798 (day 2) | 2987 (day 2) | 6.0 (day 19) | 2.88 (day 2) | 12,871 (day 2) | 5.89 | recovered | Presentcase |
| summary | Median 57.5 | 66.7% Male | Median 4469 | Median 2488 | Median 9.45 | Median 4.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuki, Y.; Sugihara, T.; Kihara, T.; Kawakami, T.; Kitaura, T.; Takata, T.; Nagahara, T.; Fujita, K.; Hirai, M.; Kato, M.; et al. COVID-19-Triggered Acute Liver Failure and Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses 2023, 15, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071445
Matsuki Y, Sugihara T, Kihara T, Kawakami T, Kitaura T, Takata T, Nagahara T, Fujita K, Hirai M, Kato M, et al. COVID-19-Triggered Acute Liver Failure and Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071445
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuki, Yukako, Takaaki Sugihara, Takuya Kihara, Tatsuru Kawakami, Tsuyoshi Kitaura, Tomoaki Takata, Takakazu Nagahara, Kai Fujita, Masayuki Hirai, Masaru Kato, and et al. 2023. "COVID-19-Triggered Acute Liver Failure and Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071445
APA StyleMatsuki, Y., Sugihara, T., Kihara, T., Kawakami, T., Kitaura, T., Takata, T., Nagahara, T., Fujita, K., Hirai, M., Kato, M., Kawaguchi, K., & Isomoto, H. (2023). COVID-19-Triggered Acute Liver Failure and Rhabdomyolysis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Viruses, 15(7), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071445







