The Impact of the Definitions of Clinical Phases on the Profiles of Grey-Zone Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Enrollment
2.2. Classification of the Patients into Different Phases of Chronic HBV Infection
2.3. Characterization of the Grey-Zone Patients
2.4. Impact of Different ALT ULN Values on the Proportion of Patients in the Grey Zone
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
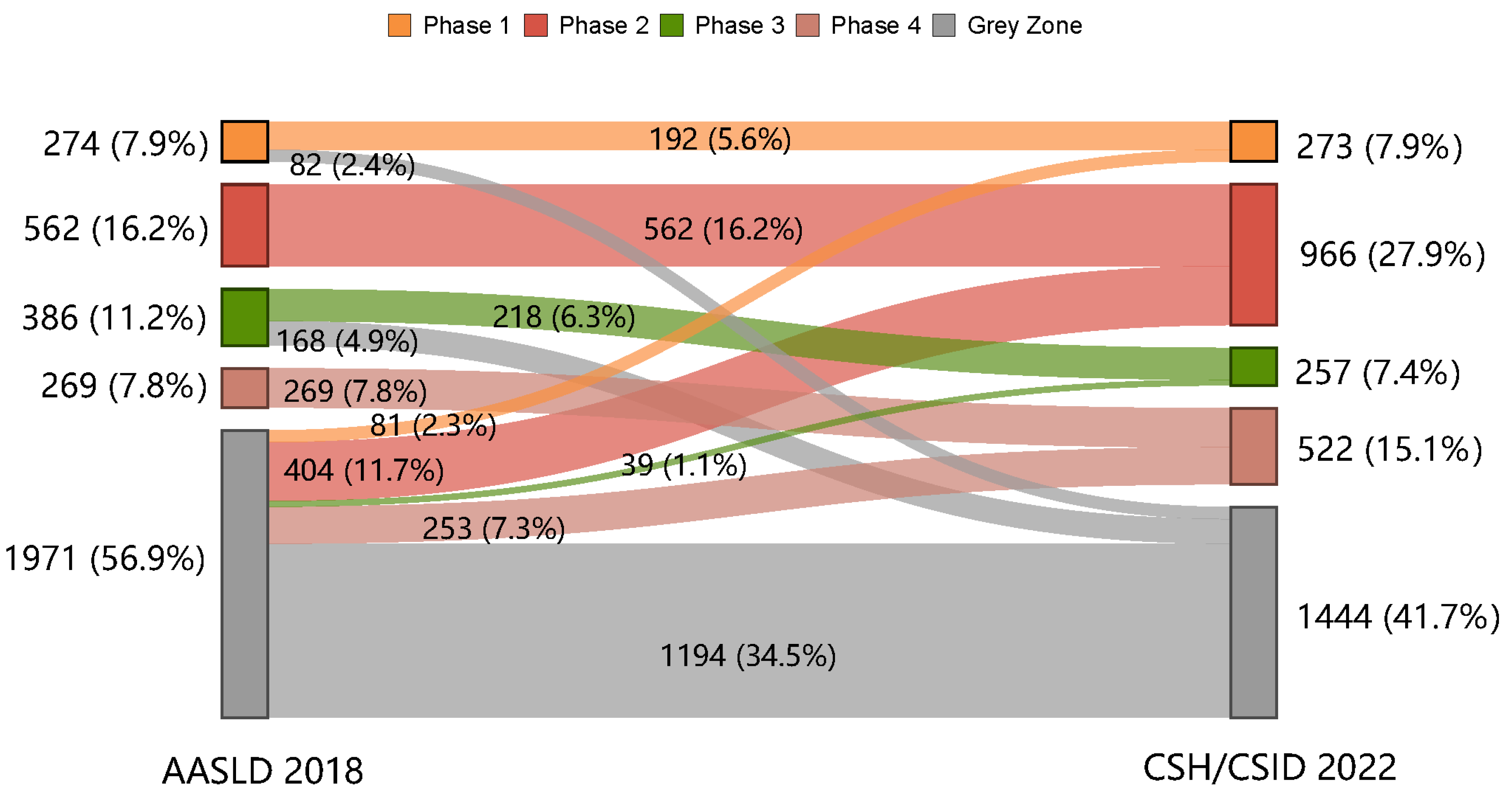
3.2. Proportion of the Patients in the Grey Zone as Per the AASLD 2018 and the CSH/CSID 2022
3.3. Characteristics of the Grey Zone Patients as Per the AASLD 2018 and the CSH/CSID 2022
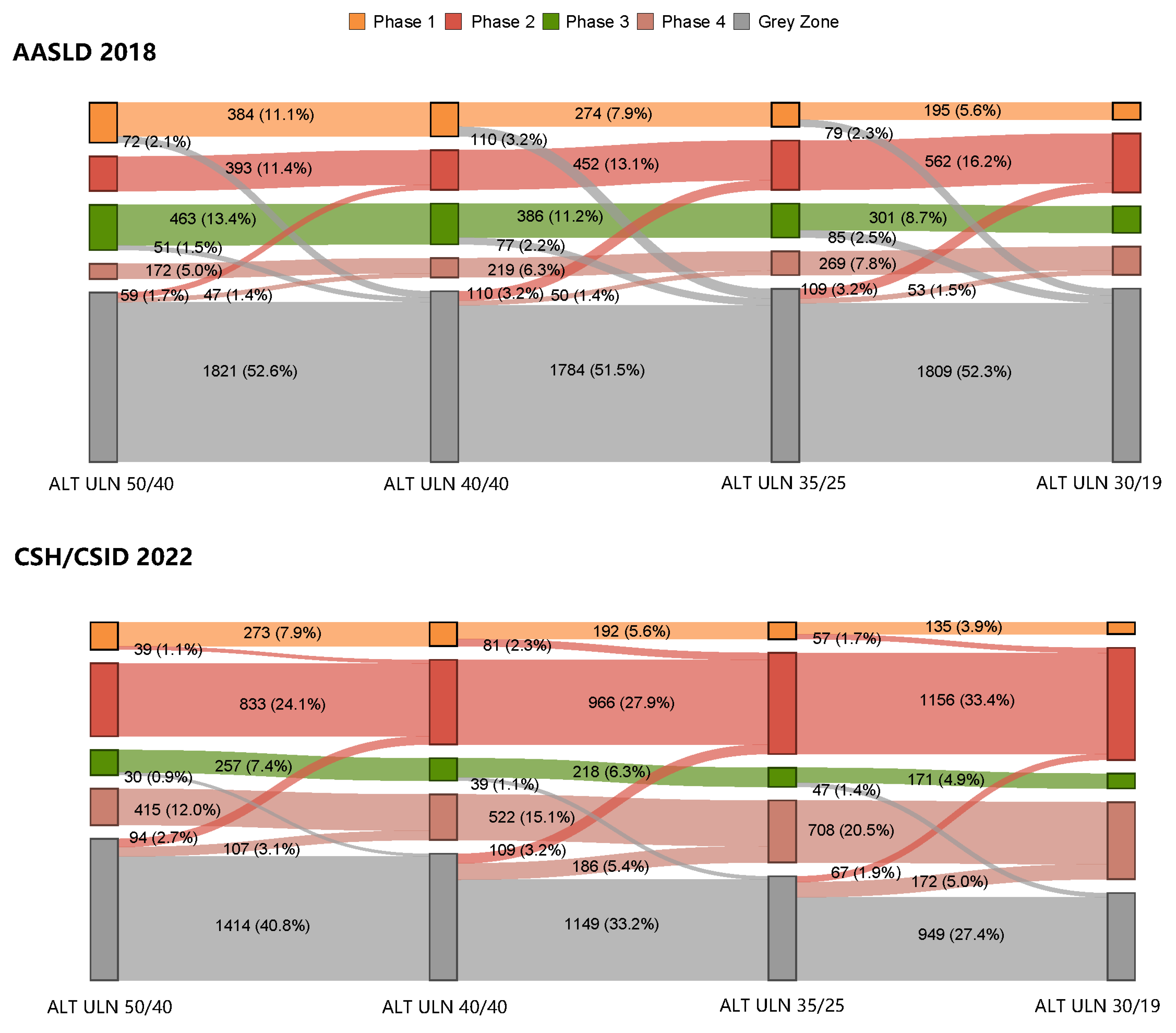
3.4. Changes in the Proportions in Grey Zone Patients with Varying ALT ULN Values as Per the AASLD 2018 and the CSH/CSID 2022
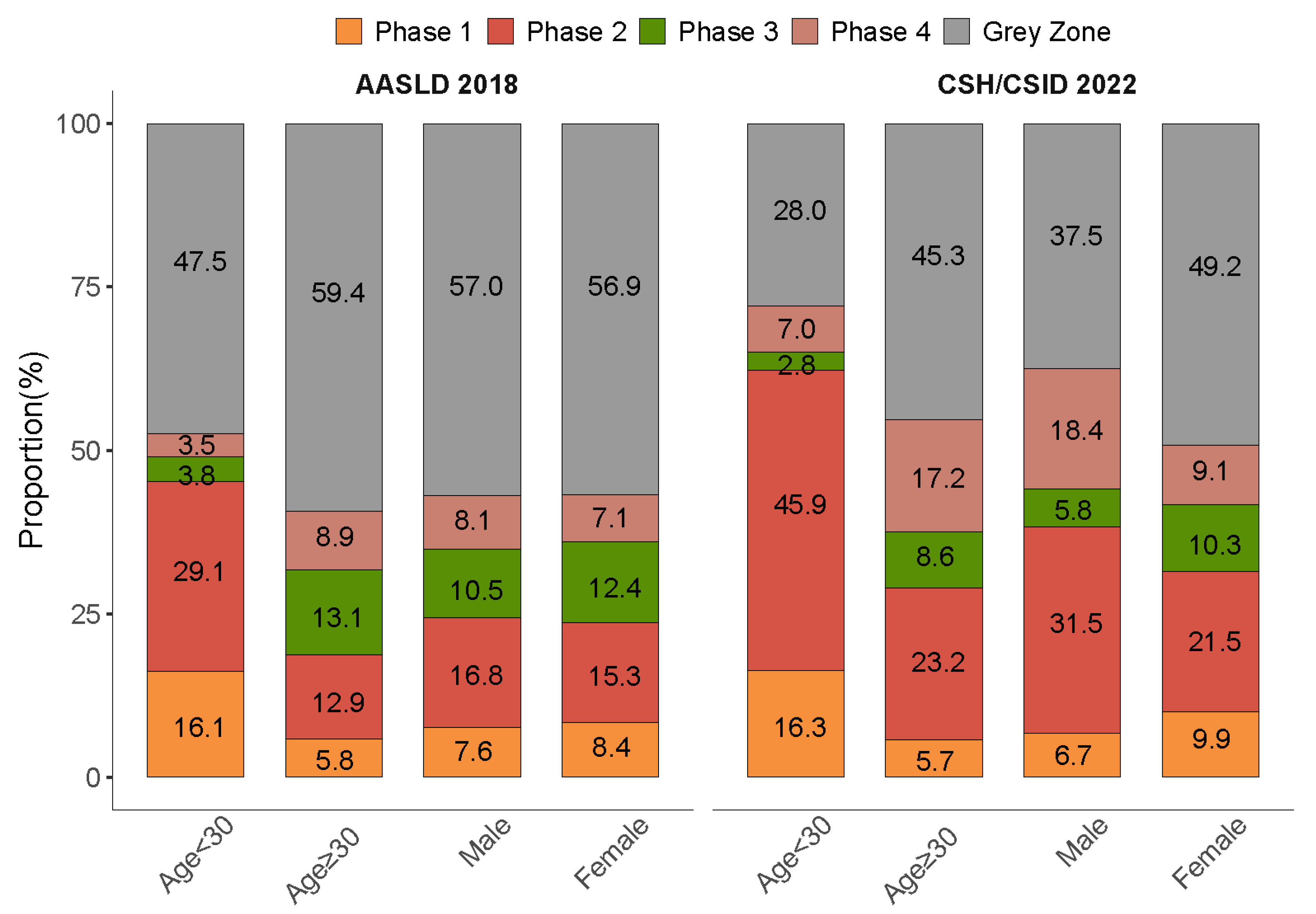
3.5. Subgroup Analyses by Age and Sex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Lau, G.K.; Abbas, Z.; Chan, H.L.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chien, R.N.; et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, E.L.; Jun, D.W. Precision medicine in the era of potent antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Society of Hepatology; Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases; Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2022). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2022, 30, 1309–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Society of Hepatology; Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases; Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2022). J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, K.; Ma, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Chen, X. Effect of the change in antiviral therapy indication on identifying significant liver injury among chronic hepatitis B virus infections in the grey zone. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1035923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Wei, W.; Kong, Y.; Niu, J.; Shang, J.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Tang, H.; Ding, H.; et al. China Registry of Hepatitis B (CR-HepB): Protocol and implementation of a nationwide hospital-based registry of hepatitis B. Scand. J. Public Health 2018, 48, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; You, H.; Niu, J.; Shang, J.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, H.; Tang, H.; Ding, H.; et al. Baseline Characteristics and Treatment Patterns of the Patients Recruited to the China Registry of Hepatitis B. J Clin Transl Hepatol 2019, 7, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Chen, W.X.; Pan, B.S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.L.; Hao, X.K.; Huang, X.Z.; Zhang, C.B.; Peng, M.T.; Zhao, M.; et al. Establishment of reference intervals for commonly used clinical tests in Chinese population. Zhong Guo Wei Sheng Biao Zhun Guan Li 2013, 4, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Society of Hepatology; Chinese Medical Association. Expert opinion on expanding anti-HBV treatment for chronic hepatitis B. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2022, 30, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.H.; Hu, T.H.; Jia, J.; Kurosaki, M.; Lim, Y.S.; Lin, H.C.; Sinn, D.H.; Tanaka, Y.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yuen, M.F. East Asia expert opinion on treatment initiation for chronic hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, G.; Westby, M.; Bermingham, S.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.; Thomas, H. Diagnosis and management of chronic hepatitis B in children, young people, and adults: Summary of NICE guidance. BMJ 2013, 346, f3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Bzowej, N.H.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Murad, M.H. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016, 63, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Li, X.; Le, M.H.; Le, A.K.; Yeo, Y.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wong, C.; Wong, C.; et al. Natural History and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Untreated Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With Indeterminate Phase. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1803–1812.e1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradling, P.R.; Xing, J.; Rupp, L.B.; Moorman, A.C.; Gordon, S.C.; Teshale, E.T.; Lu, M.; Boscarino, J.A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Trinacty, C.M.; et al. Distribution of disease phase, treatment prescription and severe liver disease among 1598 patients with chronic hepatitis B in the Chronic Hepatitis Cohort Study, 2006-2013. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Xia, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Distribution and clinical characteristics of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the grey zone. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, R.; Zhan, J.; Jiang, S.; et al. Significant histological disease of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the grey zone. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 57, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendy, M.E.; Welzel, T.; Lesi, O.A.; Hainaut, P.; Hall, A.J.; Kuniholm, M.H.; McConkey, S.; Goedert, J.J.; Kaye, S.; Rowland-Jones, S.; et al. Hepatitis B viral load and risk for liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in The Gambia, West Africa. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, A.A.; Bzeizi, K.I.; Babatin, M.A.; AlSohaibani, F.; AlMana, H.; Alsaad, K.O.; AlGhamdi, H.; Al-Hamoudi, W.; AlSwat, K.; AlFaleh, F.Z.; et al. Predictors of significant fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients with low viremia. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, e50–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, N.; Sinn, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, I.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, W.; Gwak, G.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Non-invasive tests for liver disease severity and the hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients with low-level viremia. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J.; Kaufman, H.W.; Niles, J.K.; Kapoor, H.; Gish, R.G. Simplifying Treatment Criteria in Chronic Hepatitis B: Reducing Barriers to Elimination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e791–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.D.; Do, A.; Nguyen, N.H.; Kim, L.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Nguyen, H.A.; Nguyen, K.K.; Nguyen, M.; Huynh, A.; Nguyen, M.H. Long-term follow-up and suboptimal treatment rates of treatment-eligible chronic hepatitis B patients in diverse practice settings: A gap in linkage to care. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2015, 2, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Chi, X.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, H. High-normal alanine aminotransferase is an indicator for liver histopathology in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacci, M.; Lens, S.; Mariño, Z.; Londoño, M.C.; Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; Mas, A.; García-López, M.; Pérez-Del-Pulgar, S.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Forns, X. Anti-viral therapy can be delayed or avoided in a significant proportion of HBeAg-negative Caucasian patients in the Grey Zone. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, W.; Chang, T.T.; Yang, H.I.; Peng, C.Y.; Su, C.W.; Su, T.H.; Hu, T.H.; Yu, M.L.; Yang, H.C.; Wu, J.C. Risk scores to predict HCC and the benefits of antiviral therapy for CHB patients in gray zone of treatment guidelines. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Liu, K.; Zhao, G.; Lou, S.; An, B.; Lin, L.; Ding, Y.; Bao, S.; Wang, H. A novel model based on qAnti-HBc and conventional biomarkers for identifying significant liver injury among CHB patients with ALT ≤ ULN. Antivir. Res. 2022, 202, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.J.; Tonthat, A.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Terrault, N.A. Aiming for Functional Cure With Established and Novel Therapies for Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.J.; Pan, C.Q.; Han, S.B.; Lu, D.S.; Raman, S.; Hu, K.Q.; Lim, J.K.; Hann, H.W.; Min, A.D. An expert consensus for the management of chronic hepatitis B in Asian Americans. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, A.L.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D.Z.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhao, H. Significant histological changes and satisfying antiviral efficacy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection patients with normal alanine aminotransferase. Antiviral therapy decision in chronic HBV patients with normal ALT. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2021, 45, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Yang, H.I.; Liu, J.; Batrla-Utermann, R.; Jen, C.L.; Iloeje, U.H.; Lu, S.N.; You, S.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Chen, C.J. Prediction models of long-term cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients: Risk scores integrating host and virus profiles. Hepatology 2013, 58, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, U.S.; Battisti, A.; Kennedy, P.T.F. Emerging tools in the changing landscape of chronic hepatitis B management. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Wong, N.K.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Koike, K.; et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Ning, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, S.; You, H.; et al. Impact of National Centralized Drug Procurement Policy on Antiviral Utilization and Expenditure for Hepatitis B in China. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | Grey Zone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terminology | |||||
| CSH/CSID 2022 | HBeAg-positive chronic HBV infection | HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B | HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection | HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B | Grey Zone/Indeterminate phase |
| AASLD 2018 | Immune tolerant | HBeAg-positive immune active | Inactive | HBeAg-negative immune active | |
| HBsAg | |||||
| CSH/CSID 2022 | >1 × 104 a | Detectable | <1 × 103 a | Detectable | |
| AASLD 2018 | Present for ≥ 6 months | ||||
| HBeAg | Positive | Positive | Negative | Negative | Patients who do not fit into any of the criteria of phases 1~4 were deemed grey zone. |
| HBV DNA, IU/mL | |||||
| CSH/CSID 2022 | >2 × 107 | Detectable | Undetectable | Detectable | |
| AASLD 2018 | >106 | >2 × 104 | <2 × 103 | ≥2 × 103 | |
| ALT, U/L | |||||
| CSH/CSID 2022 b | <1 × ULN | ≥1 × ULN | <1 × ULN | ≥1 × ULN | |
| AASLD 2018 c | <1 × ULN | ≥2 × ULN | <1 × ULN | ≥2 × ULN | |
| AASLD 2018 N = 1971 | CSH/CSID 2022 N = 1444 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 42.0 (32.9, 51.6) | 44.2 (35.0, 52.4) | 0.001 |
| % Male | 1267 (64.3) | 835 (57.8) | 0.000 |
| % HBeAg-positive | 966 (49.0) | 563 (39.0) | <0.0001 |
| PLT (×109/L) | 187.0 (141.0, 228.0) | 188.0 (145.0, 228.0) | 0.778 |
| ALT (U/L) | 37.0 (25.0, 50.0) | 26.0 (20.0, 35.0) | <0.0001 |
| AST (U/L) | 29.4 (23.4, 40.0) | 25.0 (21.0, 33.0) | <0.0001 |
| Alb (g/L) | 44.0 (40.5, 46.6) | 44.0 (40.8, 46.6) | 0.844 |
| TBil (μmol/L) | 15.1 (11.4, 21.2) | 14.6 (11.0, 20.4) | 0.059 |
| HBV DNA (log10 IU/mL) | 3.9 (2.9, 5.2) | 3.6 (2.0, 4.5) | <0.0001 |
| APRI | 0.4 (0.3, 0.7) | 0.3 (0.3, 0.5) | <0.0001 |
| % APRI ≥ 1.5 | 224 (11.4) | 114 (7.9) | 0.001 |
| FIB-4, Median | 1.1 (0.7, 2.1) | 1.2 (0.8, 2.0) | 0.218 |
| % FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 | 278 (14.1) | 188 (13.0) | 0.389 |
| AASLD 2018 (N = 1971) | CSH/CSID 2022 (N = 1444) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age < 30 N = 338 n (%) | Age ≥ 30 N = 1633 n (%) | p Value | Male N = 1267 n (%) | Female N = 704 n (%) | p Value | Age < 30 N = 199 n (%) | Age ≥ 30 N = 1245 n (%) | p Value | Male N = 835 n (%) | Female N = 609 n (%) | p Value | |
| FIB-4 ≥ 3.25 | 10 (3.0) | 268 (16.4) | <0.001 | 190 (15.0) | 88 (12.5) | 0.145 | 7 (3.5) | 181 (14.5) | <0.001 | 125 (15.0) | 63 (10.3) | 0.012 |
| APRI ≥ 1.5 | 25 (7.4) | 199 (12.2) | 0.015 | 167 (13.2) | 57 (8.1) | 0.001 | 11 (5.5) | 103 (8.3) | 0.233 | 81 (9.7) | 33 (5.4) | 0.004 |
| ALT ≥ 40 U/L | 178 (52.7) | 697 (42.7) | 0.001 | 717 (54.6) | 158 (22.4) | <0.001 | 33 (16.6) | 185 (14.9) | 0.600 | 162 (19.4) | 56 (9.2) | <0.001 |
| PLT < 150 × 109/L | 65 (19.2) | 516 (31.6) | <0.001 | 406 (32.0) | 175 (24.9) | 0.001 | 38 (19.1) | 359 (28.8) | 0.006 | 253 (30.3) | 144 (23.7) | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Shan, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; You, H.; Jia, J.; Zhuang, H.; Kong, Y.; on behalf of the China Registry of Hepatitis B (CR-HepB) Group. The Impact of the Definitions of Clinical Phases on the Profiles of Grey-Zone Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051212
Xu X, Wang H, Shan S, Sun Y, Xu X, You H, Jia J, Zhuang H, Kong Y, on behalf of the China Registry of Hepatitis B (CR-HepB) Group. The Impact of the Definitions of Clinical Phases on the Profiles of Grey-Zone Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Viruses. 2023; 15(5):1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051212
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaoqian, Hao Wang, Shan Shan, Yameng Sun, Xiaoyuan Xu, Hong You, Jidong Jia, Hui Zhuang, Yuanyuan Kong, and on behalf of the China Registry of Hepatitis B (CR-HepB) Group. 2023. "The Impact of the Definitions of Clinical Phases on the Profiles of Grey-Zone Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection" Viruses 15, no. 5: 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051212
APA StyleXu, X., Wang, H., Shan, S., Sun, Y., Xu, X., You, H., Jia, J., Zhuang, H., Kong, Y., & on behalf of the China Registry of Hepatitis B (CR-HepB) Group. (2023). The Impact of the Definitions of Clinical Phases on the Profiles of Grey-Zone Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Viruses, 15(5), 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051212







