Viral Protein VP1 Virus-like Particles (VLP) of CVB4 Induces Protective Immunity against Lethal Challenges with Diabetogenic E2 and Wild Type JBV Strains in Mice Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses, Cells and Media
2.2. Design and Preparation of the VP1-VLP Vaccine
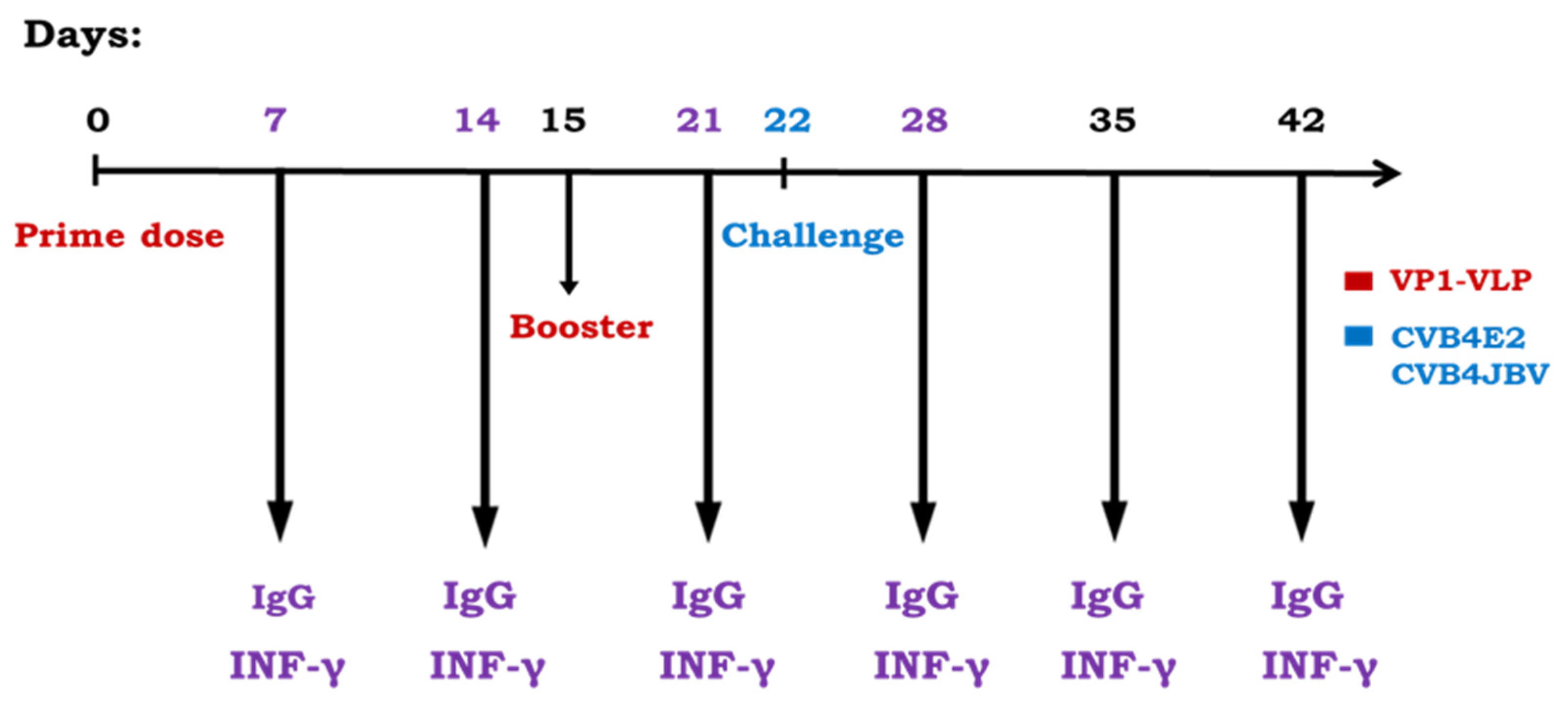
2.3. Mouse Immunization, Blood/Tissues Collection and Challenge Schedule
2.4. Micro-Neutralization Assay and Determination of Neutralizing Antibody Titers
2.5. VLP-VP1-Specific IgG Antibody Titers and IgG Subtypes Distribution
2.6. Cytokine Detection and Concentration Determination
2.7. Tissues Collection and Viral Titration
3. Results
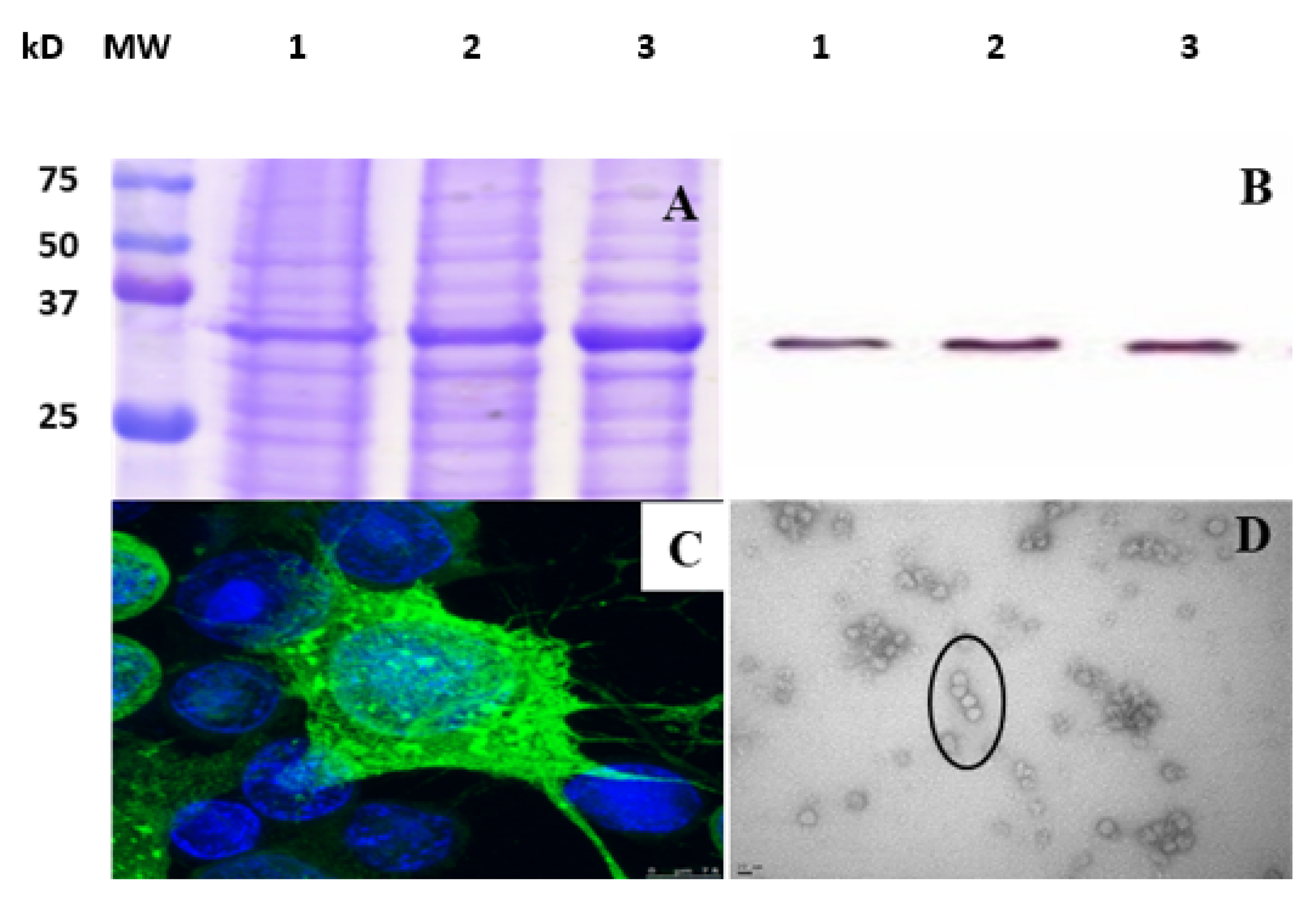
3.1. Construction and Characterization of VP1-VLP Vaccine
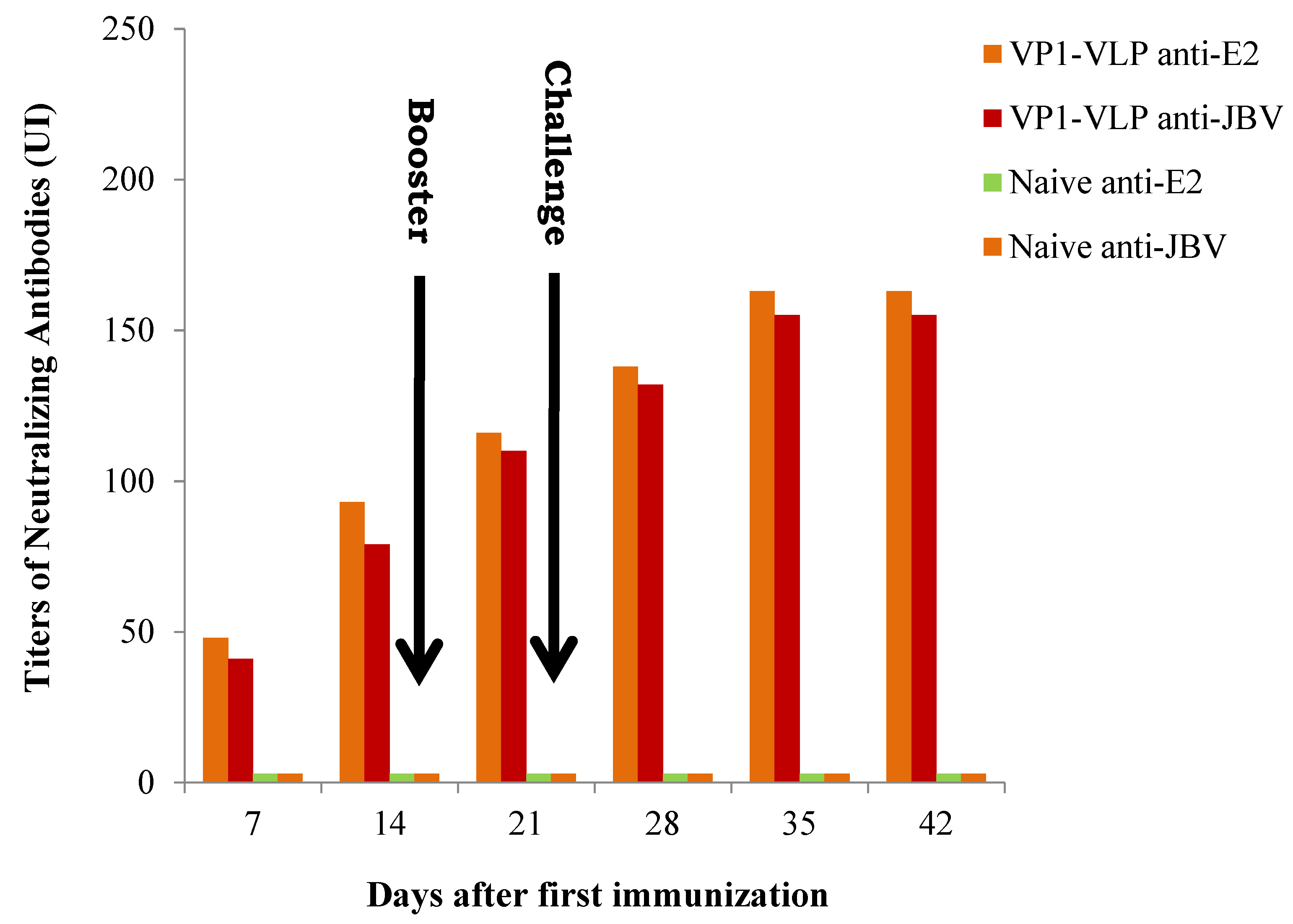
3.2. Specific Neutralizing Antibodies Anti-E2 and Anti-JBV Responses
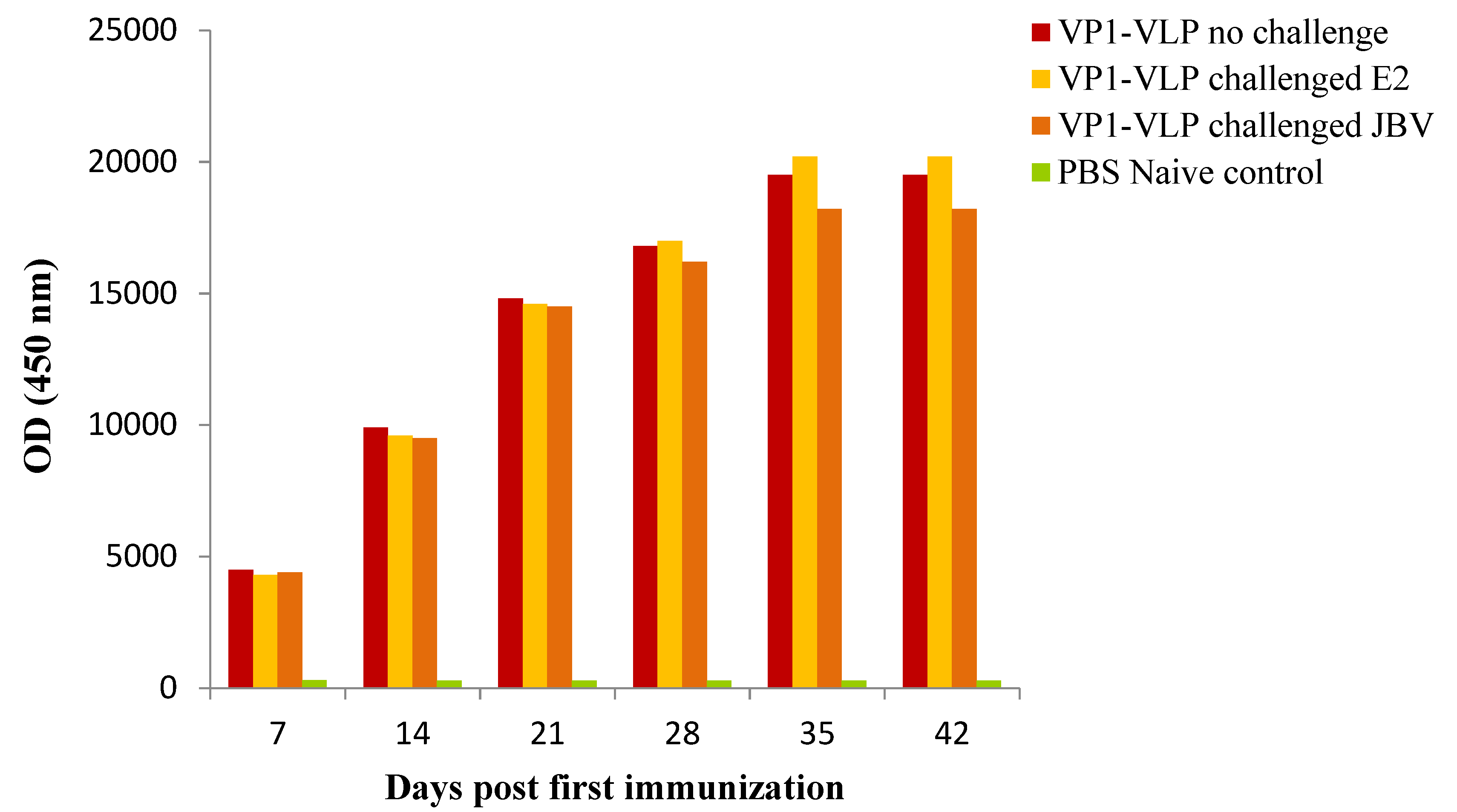
3.3. Serum IgG Antibodies Titers against VP1-VLP
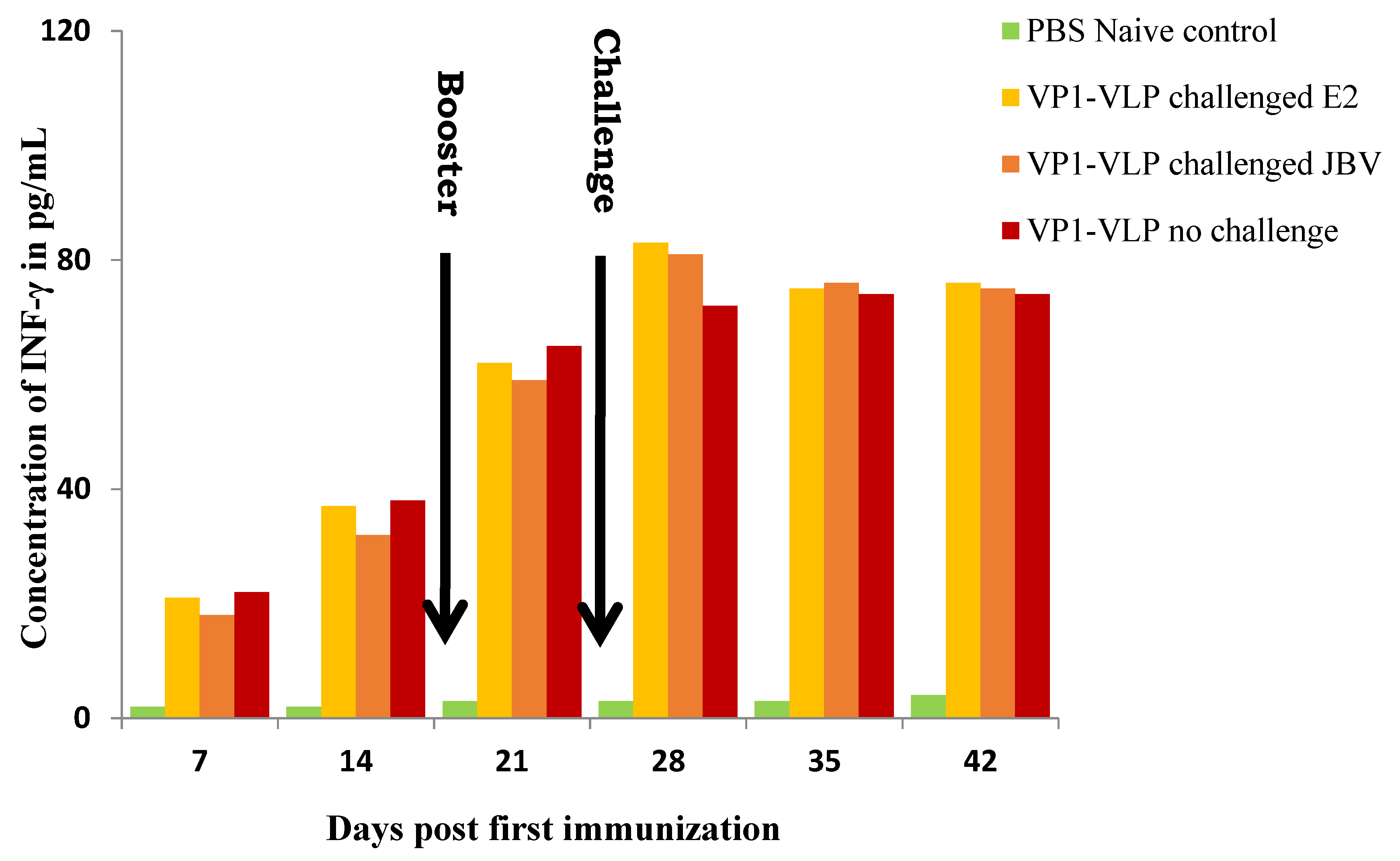
3.4. Cytokine Cellular Responses against VP1-VLP Vaccine
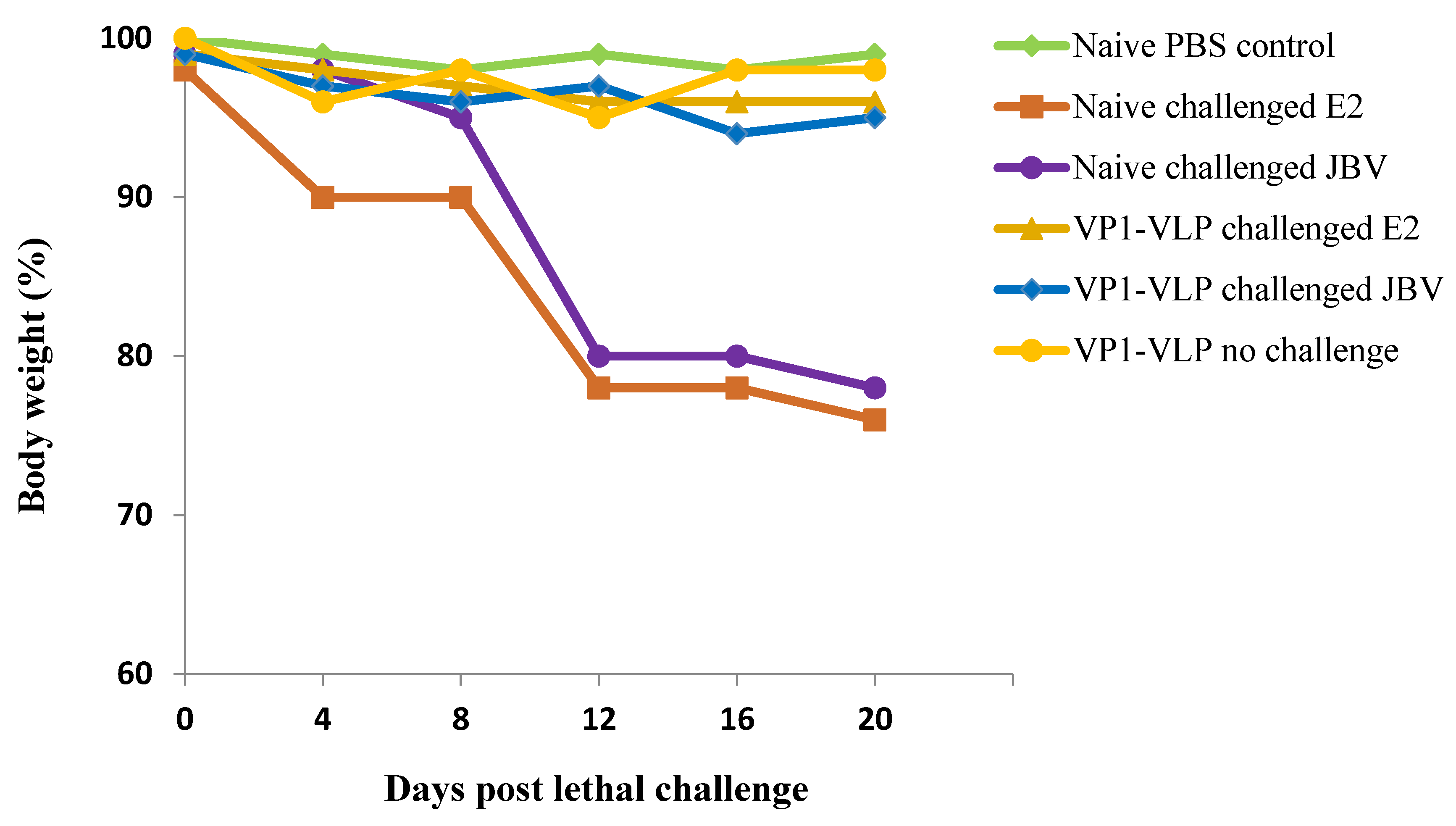
3.5. Mice Protection from E2 and JBV Lethal Challenges by VP1-VLP Immunization
3.6. Pancreas Tissue Viral Titers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norris, J.M.; Dorman, J.S.; Rezers, M.; Porte, R.E. The epidemiology and genetics of insulindependent diabetes mellitus. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1987, 111, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karvonen, M.; Viik-Kajander, M.; Moltchanova, E.; Libman, I.; LaPorte, R.; Tuomilehto, J. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide. Diabetes Mondiale (DiaMond) project Group. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemola, P.; Kaijalainen, S.; Ylipaasto, P.; Roivainen, M. Diabetogenic effects of the most prevalent enteroviruses in Finnish sewage. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1150, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyôty, H. Enterovirus infections and type 1 diabetes. Ann. Med. 2002, 34, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehadeh, W.; Weill, J.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Alm, G.; Lefebvre, J.; Wattre, P.; Hober, D. Increased level of interferon-α in blood of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Relationship with coxsackievirus B infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyöty, H.; Hiltunen, M.; Knip, M.; Laakkonen, M.; Vähäsalo, P.; Karjalainen, J.; Koskela, P.; Roivainen, M.; Leinikki, P.; Hovi, T.; et al. A prospective study of the role of coxsackie B and other enterovirus infections in the pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetes 1995, 44, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roivainen, M.; Rasilainen, S.; Ylipaasto, P.; Nissinen, R.; Ustinov, J.; Bouwens, L.; Eizirik, D.L.; Hovi, T.; Otonkoski, T. Mechanisms of coxsackievirus-induced damage to human pancreatic beta-cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 432–440. [Google Scholar]
- Maghsoudi, N.; Khalilpour, A.; Kamali, M.; Zeinoddini, M. Cloning and expression of coxsakievirus B3 viral protein-1 in E. coli. Iran. Biomed. J. 2007, 11, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Berg, A.K.; Tuvemo, T.; Frisk, G. Enterovirus RNA is found in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a majority of type 1 diabetic children at onset. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Austin, M.; Onodera, T.; Notkins, A.L. Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis (virus-induced diabetes mellitus). N. Engl. J. Med. 1979, 300, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilot, F.; Chehadeh, W.; Charlet-Renard, C.; Martens, H.; Geenen, V.; Hober, D. Persistent infection of human thymic epithelial cells by coxsackievirus B4. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5260–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Abraham, A.A. Pancreatic isleitis with coxsackievirus B5 infection. Hum. Pathol. 1982, 13, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, F.; Censini, S.; van Halteren, A.G.; Marselli, L.; Masini, M.; Dionisi, S.; Mosca, F.; Boggi, U.; Muda, A.O.; Prato, S.D.; et al. CoxsackieB4 virus infection of beta cells and natural killer cellinsulitis in recent-onset type 1 diabetic patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5115–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikarinen, M.; Tauriainen, S.; Honkanen, T.; Vuori, K.; Karhunen, P.; Vasama-Nolvi, C.; Oikarinen, S.; Verbeke, C.; Blair, G.E.; Rantala, I.; et al. Analysis of pancreas tissue in a child positive for islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, V.M.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Laitinen, O.H.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.B.; Lin, A.; Diaz Lozano, I.M.; Mazur, M.A.; Marjomäki, V.; Loré, K.; Hyöty, H.; et al. A hexavalent coxsackievirus B vaccine is highly immunogenic and has a strong protective capacity in mice and nonhuman primates. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, V.M.; Butrym, M.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.B.; Hytönen, V.P.; Hyöty, H.; Flodström-Tullberg, M. Coxsackievirus B vaccines prevents infection-accelerated diabetes in NOD mice and have no disease-inducing effect. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankaniemi, M.M.; Baikoghli, M.A.; Stone, V.M.; Xing, L.; Väätäinen, O.; Soppela, S.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.; Saarinen, N.V.; Ou, T.; Anson, B.; et al. Structural insight into CVB3-VLP non-adjuvanted vaccine. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, A.; Zell, R.; Stelzner, A. DNA vaccine-mediated immune responses in Coxsackie virus B3-infected mice. Antivir. Res. 2001, 49, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.F.; Chang, M.H.; Chiang, B.L.; Jeng, S.T. Oral immunizationof mice using transgenic tomato fruit expressing VP1 protein from enterovirus 71. Vaccine 2006, 24, 2944–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj Hassine, I.; Gharbi, J.; Hamrita, B.; Almalki, M.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Ben M’hadheb, M. Characterization of Coxsackievirus B4 virus-like particles VLP produced by the recombinant baculovirus-insect cell system expressing the major capsid protein. Mol. Bio. Rep. 2020, 47, 2835–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method for estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chan, W.; Ko, B.Y.; Van Lang, C.C.; Swartz, J.R. Assessing sequence plasticity of a virus-like nanoparticle by evolution toward a versatile scaffold for vaccines and drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12360–12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.C.; Yang, Y. Identifying and engineering promoters for high level and sustainable therapeutic recombinant protein production in cultured mammalian cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, J.N.; Schneider, C.; Schneider, D.S.; Baker, M.L. Going to bat(s) for studies of disease tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghi, N.; Howra, B.; Zakieh, S.H.; Camellia, K.; Abbas, H.; Andrew, J.E.; Gholamreza, A. Virus-like particles: Preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.L.; Mao, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhu, F.C.; Li, J.X.; Yao, X.; Gao, F.; Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.Z. Progress on the research and development of inactivated EV71 whole-virus vaccines. Hum. Vaccine Immunother. 2013, 9, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Parham, N.J.; Zhang, F.; Aasa-Chapman, M.; Gould, E.A.; Zhang, H. Vaccination with Coxsackievirus B3 virus-like particles elicits humoral immune response and protects mice against myocarditis. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2301–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yan, K.; Feng, Y.; Huang, X.; Ku, Z.; Cai, Y.; Liu, F.; Shi, J.; Huang, Z. A virus-like particle vaccine for Coxsackievirus A16 potently elicits neutralizing antibodies that protect mice against lethal challenge. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6642–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koho, T.; Koivunen, M.R.; Oikarinen, S.; Kummola, L.; Mäkinen, S.; Mähönen, A.J.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.; Marjomäki, V.; Kazmertsuk, A.; Junttila, I.; et al. Coxsackievirus B3 VLPs purified by ion exchange chromatography elicit strong immune responses in mice. Antivir. Res. 2014, 104, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gharbi, J.; Hadj Hassine, I.; Hassine, M.; Al-Malki, M.; Al-Yami, A.; Al-Bachir, A.; Ben M’hadheb, M. Viral Protein VP1 Virus-like Particles (VLP) of CVB4 Induces Protective Immunity against Lethal Challenges with Diabetogenic E2 and Wild Type JBV Strains in Mice Model. Viruses 2023, 15, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040878
Gharbi J, Hadj Hassine I, Hassine M, Al-Malki M, Al-Yami A, Al-Bachir A, Ben M’hadheb M. Viral Protein VP1 Virus-like Particles (VLP) of CVB4 Induces Protective Immunity against Lethal Challenges with Diabetogenic E2 and Wild Type JBV Strains in Mice Model. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040878
Chicago/Turabian StyleGharbi, Jawhar, Ikbel Hadj Hassine, Mouna Hassine, Mohammed Al-Malki, Ameera Al-Yami, Anwar Al-Bachir, and Manel Ben M’hadheb. 2023. "Viral Protein VP1 Virus-like Particles (VLP) of CVB4 Induces Protective Immunity against Lethal Challenges with Diabetogenic E2 and Wild Type JBV Strains in Mice Model" Viruses 15, no. 4: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040878
APA StyleGharbi, J., Hadj Hassine, I., Hassine, M., Al-Malki, M., Al-Yami, A., Al-Bachir, A., & Ben M’hadheb, M. (2023). Viral Protein VP1 Virus-like Particles (VLP) of CVB4 Induces Protective Immunity against Lethal Challenges with Diabetogenic E2 and Wild Type JBV Strains in Mice Model. Viruses, 15(4), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040878







