Asfarviruses and Closely Related Giant Viruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV)
2.1. History of Discovery
2.2. Structural Features
2.3. Phylogenetic and Genomic Features
2.4. Replication Cycle
2.5. Pathogenicity
3. Faustovirus
3.1. History of Discovery
3.2. Structural Features
3.3. Phylogenetic and Genomic Features
3.4. Replication Cycle
3.5. Pathogenicity
4. Kaumoebavirus
4.1. History of Discovery
4.2. Structural Features
4.3. Genomic and Phylogenetic Features
4.4. Replication Cycle
5. Pacmanvirus
5.1. History of Discovery
5.2. Structural Features
5.3. Genomic and Phylogenetic Features
5.4. Replication Cycle
6. Abalone Asfarvirus
7. Novel Viral Detection by Metagenome-Assembled Genomes (MAG)
8. Diversity in Asfarviridae and Relatives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- La Scola, B. A Giant Virus in Amoebae. Science 2003, 299, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Common Origin of Four Diverse Families of Large Eukaryotic DNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11720–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M.; Varsani, A.; Wolf, Y.I.; Yutin, N.; Zerbini, F.M.; Kuhn, J.H. Global Organization and Proposed Megataxonomy of the Virus World. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, e00061-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmini, J.; Woo, A.C.; Krupovic, M.; Forterre, P.; Gaia, M. Diversification of Giant and Large Eukaryotic DsDNA Viruses Predated the Origin of Modern Eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19585–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A. Marine Viruses—Major Players in the Global Ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardley, R.C.; Andrade, C.D.M.; Black, D.N.; de Castro Portugal, F.L.; Enjuanes, L.; Hess, W.R.; Mebus, C.; Ordas, A.; Rutili, D.; Sanchez Vizcaino, J.; et al. African Swine Fever Virus. Arch. Virol. 1983, 76, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchar, V.G.; Duffus, A.L.J. Molecular and Ecological Studies of a Virus Family (Iridoviridae) Infecting Invertebrates and Ectothermic Vertebrates. Viruses 2019, 11, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Arnault, J.-P.; Bou Khalil, J.Y.; Abrahão, J.; Tomei, E.; Vial, E.; Le Bideau, M.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Atypical Cowpox Virus Infection in Smallpox-Vaccinated Patient, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.E. On A Form of Swine Fever Occurring in British East Africa (Kenya Colony). J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 1921, 34, 159–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalobi, O.O.; Olugasa, B.O.; Oluwayelu, D.O.; Ijagbone, I.F.; Ayoade, G.O.; Agbede, S.A. Analysis and Evaluation of Mortality Losses of the 2001 African Swine Fever Outbreak, Ibadan, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2007, 39, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Toyoda, K.; Tomaru, Y.; Nakayama, N.; Shirai, Y.; Claverie, J.-M.; Nagasaki, K. Remarkable Sequence Similarity between the Dinoflagellate-Infecting Marine Girus and the Terrestrial Pathogen African Swine Fever Virus. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reteno, D.G.; Benamar, S.; Khalil, J.B.; Andreani, J.; Armstrong, N.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; Scola, B.L. Faustovirus, an Asfarvirus-Related New Lineage of Giant Viruses Infecting Amoebae. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajrai, L.H.; Benamar, S.; Azhar, E.I.; Robert, C.; Levasseur, A.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Kaumoebavirus, a New Virus That Clusters with Faustoviruses and Asfarviridae. Viruses 2016, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Sevvana, M.; Benamar, S.; Pinto, F.D.; Bitam, I.; Colson, P.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.G.; Raoult, D.; et al. Pacmanvirus, a New Giant Icosahedral Virus at the Crossroads between Asfarviridae and Faustoviruses. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00212-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Takano, T.; Nishiki, I.; Fujiwara, A.; Kiryu, I.; Inada, M.; Sakai, T.; Terashima, S.; Matsuura, Y.; Isowa, K.; et al. A Novel Asfarvirus-like Virus Identified as a Potential Cause of Mass Mortality of Abalone. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denyer, M.S.; Wilkinson, P.J. African Swine Fever. In Encyclopedia of Immunology, 2nd ed.; Delves, P.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 54–56. ISBN 978-0-12-226765-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, L.K.; Nash, A.A.; Randall, R.E. Molecular Pathogenesis of Virus Infections; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0-521-83248-9. [Google Scholar]
- McVicar, J.W.; Mebus, C.A.; Becker, H.N.; Belden, R.C.; Gibbs, E.P. Induced African Swine Fever in Feral Pigs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1981, 179, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, E.P.; Butler, J.F. African Swine Fever—An Assessment of Risk for Florida. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1984, 184, 644–647. [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Nielsen, S.; Arias, M.L.; Panadero, J.; Escribano, J.M.; Gomez-Tejedor, C.; Perez Bonilla, Q.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M. Laboratory Diagnosis and Disease Occurrence in the Current African Swine Fever Eradication Program in Spain, 1989–1991. Prev. Vet. Med. 1993, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech-Nielsen, S.; Perez Bonilla, Q.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M. Benefit-Cost Analysis of the Current African Swine Fever Eradication Program in Spain and of an Accelerated Program. Prev. Vet. Med. 1993, 17, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costard, S.; Wieland, B.; de Glanville, W.; Jori, F.; Rowlands, R.; Vosloo, W.; Roger, F.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Dixon, L.K. African Swine Fever: How Can Global Spread Be Prevented? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2683–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda, C.; Salman, M.; Ruppanner, R. International Trade, Animal Health and Veterinary Epidemiology: Challenges and Opportunities. Prev. Vet. Med. 2001, 48, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, M.; Hartnett, E.; Cox, A.; Seaman, M. Quantitative Risk Assessment Case Study: Smuggled Meats as Disease Vectors. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2006, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgrove, G.S.; Haelterman, E.O.; Coggins, L. Pathogenesis of African Swine Fever in Young Pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1969, 30, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.; Plowright, W.; Pierce, M.A. The Epizootiology of African Swine Fever in Africa. Vet. Rec. 1969, 85, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomson, G.R.; Gainaru, M.D.; Van Dellen, A.F. Experimental Infection of Warthog (Phacochoerus Aethiopicus) with African Swine Fever Virus. (Infection experimental du Phacochere (Phacochoerus Aethiopicus) avec le virus de la fievre porcine Africaine). Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1980, 47, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Botija, C. Reservorios Del Virus de La Paste Porcina Africana. Investigation Del Virus de La PPA En Las Arthropodos Mediante La Prueba de La Hemadsocion. Bull. Off. Int. Epizootiol. 1963, 60, 895–899. [Google Scholar]
- Plowright, W.; Parker, J.; Peirce, M.A. African Swine Fever Virus in Ticks (Ornithodoros Moubata, Murray) Collected from Animal Burrows in Tanzania. Nature 1969, 221, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Montoya, M.; Reis, A.L.; Dixon, L.K. African Swine Fever: A Re-Emerging Viral Disease Threatening the Global Pig Industry. Vet. J. 2018, 233, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallapaty, S. Spread of Deadly Pig Virus in China Hastens Vaccine Research. Nature 2019, 569, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowright, W. African Swine Fever. In Infectious Diseases in Livestock with Special Reference to Southern Africa; Coetzer, J.A.W., Thomson, G.R., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Penrith, M.; Thomson, G.; Bastos, A.; PHIRI, O.C.; Lubisi, B.; du Plessis, E.; Macome, F.; Pinto, F.; Botha, B.; Esterhuysen, J.J. An Investigation into Natural Resistance to African Swine Fever in Domestic Pigs from an Endemic Area of South Africa. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2004, 23, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mínguez, I.; Rueda, A.; Domínguez, J.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Double Labeling Immunohistological Study of African Swine Fever Virus Infected Spleen and Lymph Nodes. Vet. Pathol. 1988, 25, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Torres, C.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Gómez-del-Moral, M.; Alonso, F.; Escribano, J.M.; Ezquerra, A.; Domínguez, J. Expression of Porcine CD163 on Monocytes/Macrophages Correlates with Permissiveness to African Swine Fever Infection. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 2307–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.J.; Pegram, R.G.; Perry, B.D.; Lemche, J.; Schels, H.F. The distribution of African swine fever virus isolated from Ornithodoros moubata in Zambia. Epidemiol. Infect. 1988, 101, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciere, C. Peste Porcine Africaine. In Main Infectious and Parasitic Diseases of Livestock: Europe and Hot Regions; Lefèvre, P.-C., Blancou, J., Chermette, R., Eds.; CABI: Paris, France, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 735–746. [Google Scholar]
- Costard, S.; Mur, L.; Lubroth, J.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M.; Pfeiffer, D.U. Epidemiology of African Swine Fever Virus. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogin, A.; Gerasimov, V.; Malogolovkin, A.; Kolbasov, D. African Swine Fever in the North Caucasus Region and the Russian Federation in Years 2007–2012. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, Y.; Pérez-Núñez, D.; Richt, J.A. Chapter Three—African Swine Fever Virus Biology and Vaccine Approaches. In Advances in Virus Research; Kielian, M., Mettenleiter, T.C., Roossinck, M.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 100, pp. 41–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.-J. African Swine Fever: An Unprecedented Disaster and Challenge to China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, N.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, F.; Chen, T.; Zhang, S.; Cao, P.; Li, X.; Tian, K.; et al. Emergence of African Swine Fever in China, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forth, J.H.; Tignon, M.; Cay, A.B.; Forth, L.F.; Höper, D.; Blome, S.; Beer, M. Comparative Analysis of Whole-Genome Sequence of African Swine Fever Virus Belgium 2018/1. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter-Louis, C.; Forth, J.H.; Probst, C.; Staubach, C.; Hlinak, A.; Rudovsky, A.; Holland, D.; Schlieben, P.; Göldner, M.; Schatz, J.; et al. Joining the Club: First Detection of African Swine Fever in Wild Boar in Germany. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). Immediate Notification Report; Report Ref OIE 7536; OIE: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Keeling, L.; Tunón, H.; Olmos Antillón, G.; Berg, C.; Jones, M.; Stuardo, L.; Swanson, J.; Wallenbeck, A.; Winckler, C.; Blokhuis, H. Animal Welfare and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momoyama, K.; Nakatsugawa, T.; Yurano, N. Mass Mortalities of Juvenile Abalones, Haliotis Spp., Caused by Amyotrophia. Fish Pathol. 1999, 34, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoyama, K. Experiments for Characterizing the Causative Agent of Amyotrophia in Juvenile Abalones Haliotis Spp. Fish Pathol. 2000, 35, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, R.; Agüero, M.; Almendral, J.M.; Viñuela, E. Variable and Constant Regions in African Swine Fever Virus DNA. Virology 1989, 168, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrascosa, J.L.; Carazo, J.M.; Carrascosa, A.L.; García, N.; Santisteban, A.; Viñuela, E. General Morphology and Capsid Fine Structure of African Swine Fever Virus Particles. Virology 1984, 132, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, R.J.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Nogal, M.L.; Yuste, L.; Enríquez, C.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Viñuela, E. Analysis of the Complete Nucleotide Sequence of African Swine Fever Virus. Virology 1995, 208, 249–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.K.; Twigg, S.R.F.; Baylis, S.A.; Vydelingum, S.; Bristow, C.; Hammond, J.M.; Smith, G.L.Y. Nucleotide Sequence of a 55 Kbp Region from the Right End of the Genome of a Pathogenic African Swine Fever Virus Isolate (Malawi LIL20/1). J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 1655–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Bu, Z.; Rao, Z. Architecture of African Swine Fever Virus and Implications for Viral Assembly. Science 2019, 366, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, G.; Charro, D.; Matamoros, T.; Dillard, R.S.; Abrescia, N.G.A. The Cryo-EM Structure of African Swine Fever Virus Unravels a Unique Architecture Comprising Two Icosahedral Protein Capsids and Two Lipoprotein Membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Bi, Y.; Sun, J.; Peng, R.; Song, H.; Zhu, D.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the African Swine Fever Virus. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 836–843.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, G.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Song, C.; Kayama, Y.; Mochizuki, T.; Murata, K.; Ogata, H.; Takemura, M. Medusavirus, a Novel Large DNA Virus Discovered from Hot Spring Water. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02130-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, A.; García-Castey, M.; Guerra, M.; Hernáez, B.; Martín, V.; Matamoros, T.; Andrés, G. African Swine Fever Virus Transmembrane Protein PEP84R Guides Core Assembly. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus: A Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.J.; Wardley, R.C. The Replication of African Swine Fever Virus in Pig Endothelial Cells. Br. Vet. J. 1978, 134, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Hervás, J.; Méndez, A.; Carrasco, L.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. Pathological Changes in the Renal Interstitial Capillaries of Pigs Inoculated with Two Different Strains of African Swine Fever Virus. J. Comp. Pathol. 1995, 112, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Hervás, J.; Mendéz, A.; Carrasco, L.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. A Pathological Study of the Perisinusoidal Unit of the Liver in Acute African Swine Fever. Res. Vet. Sci. 1995, 59, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Hervás, J.; Méndez, A.; Carrasco, L.; de las Mulas, J.M.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A.Y. Experimental African Swine Fever: Apoptosis of Lymphocytes and Virus Replication in Other Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; Chacón-M De Lara, F.; Martín De Las Mulas, J.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.; Hervás, J.; Wilkinson, P.; Sierra, M. Virus Association with Lymphocytes in Acute African Swine Fever. Vet. Res. 1996, 27, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcamí, A.; Carrascosa, A.L.; Viñuela, E. Interaction of African Swine Fever Virus with Macrophages. Virus Res. 1990, 17, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Galindo, I.; Hernáez, B.; Quetglas, J.I.; Dalmau-Mena, I.; Alonso, C. Endosomal Maturation, Rab7 GTPase and Phosphoinositides in African Swine Fever Virus Entry. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, B.; Alonso, C. Dynamin- and Clathrin-Dependent Endocytosis in African Swine Fever Virus Entry. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, I.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Hlavova, K.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Barrado-Gil, L.; Dominguez, J.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus Infects Macrophages, the Natural Host Cells, via Clathrin- and Cholesterol-Dependent Endocytosis. Virus Res. 2015, 200, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrado-Gil, L.; Galindo, I.; Martínez-Alonso, D.; Viedma, S.; Alonso, C. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Is Required for African Swine Fever Replication. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouvenet, N.; Monaghan, P.; Way, M.; Wileman, T. Transport of African Swine Fever Virus from Assembly Sites to the Plasma Membrane Is Dependent on Microtubules and Conventional Kinesin. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7990–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, P.S.; Kitching, R.P.; Wilkinson, P.J. Mechanical Transmission of Capripox Virus and African Swine Fever Virus by Stomoxys Calcitrans. Res. Vet. Sci. 1987, 43, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmquist, W.A.; Hay, D. Hemadsorption and Cytopathic Effect Produced by African Swine Fever Virus in Swine Bone Marrow and Buffy Coat Cultures. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1960, 21, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Oleaga-Pérez, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, R.; Encinas-Grandes, A. Distribution and Biology of Ornithodoros Erraticus in Parts of Spain Affected by African Swine Fever. Vet. Rec. 1990, 126, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boinas, F.S. Epidemiological Characterization of the Role of Ornithodoros Erraticus as a Reservoir of African Swine Fever in Portugal. Veterinária Técnica 1995, 5, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Mur, L.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L. An Update on the Epidemiology and Pathology of African Swine Fever. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M.L. African swine fever virus (asfarviridae). In Encyclopedia of Virology, 2nd ed.; Granoff, A., Webster, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 30–38. ISBN 978-0-12-227030-7. [Google Scholar]
- Coşkun, K.A.; Özçelik, S.; Tutar, L.; Elaldı, N.; Tutar, Y. Isolation and Identification of Free-Living Amoebae from Tap Water in Sivas, Turkey. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, e675145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnier, I.; Reteno, D.-G.I.; Saadi, H.; Boughalmi, M.; Gaia, M.; Slimani, M.; Ngounga, T.; Bekliz, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; et al. A Decade of Improvements in Mimiviridae and Marseilleviridae Isolation from Amoeba. Intervirology 2013, 56, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, R.S. Free-Living Amoebae Recovered from Human Stool Samples in Strongyloides Agar Culture. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, I.; Rodrigues, R.A.L.; Dornas, F.P.; Almeida, G.; Aquino, I.; Bonjardim, C.A.; Kroon, E.G.; La Scola, B.; Abrahão, J.S. Trapping the Enemy: Vermamoeba Vermiformis Circumvents Faustovirus Mariensis Dissemination by Enclosing Viral Progeny inside Cysts. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00312-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajrai, L.H.; Mougari, S.; Andreani, J.; Baptiste, E.; Delerce, J.; Raoult, D.; Azhar, E.I.; Scola, B.L.; Levasseur, A. Isolation of Yasminevirus, the First Member of Klosneuvirinae Isolated in Coculture with Vermamoeba Vermiformis, Demonstrates an Extended Arsenal of Translational Apparatus Components. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e01534-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, J.Y.B.; Andreani, J.; Raoult, D.; Scola, B.L. A Rapid Strategy for the Isolation of New Faustoviruses from Environmental Samples Using Vermamoeba vermiformis. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 112, e54104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahão, J.; Silva, L.; Silva, L.S.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Rodrigues, R.; Arantes, T.; Assis, F.; Boratto, P.; Andrade, M.; Kroon, E.G.; et al. Tailed Giant Tupanvirus Possesses the Most Complete Translational Apparatus of the Known Virosphere. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Baptiste, E.; Hasni, I.; Michelle, C.; Raoult, D.; Levasseur, A.; La Scola, B. Orpheovirus IHUMI-LCC2: A New Virus among the Giant Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif Louazani, A.; Andreani, J.; Ouarhache, M.; Aherfi, S.; Baptiste, E.; Levasseur, A.; La Scola, B. Genome Sequences of New Faustovirus Strains ST1 and LC9, Isolated from the South of France. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00613-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmam, S.; Monteil-Bouchard, S.; Sambou, M.; Aubadie-Ladrix, M.; Azza, S.; Decloquement, P.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Baudoin, J.-P.; Jardot, P.; Robert, C.; et al. Faustovirus-Like Asfarvirus in Hematophagous Biting Midges and Their Vertebrate Hosts. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, T.; Reteno, D.G.; Benamar, S.; Hollerbach, A.; Colson, P.; La Scola, B.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of Faustovirus, a Large DsDNA Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6206–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamar, S.; Reteno, D.G.I.; Bandaly, V.; Labas, N.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Faustoviruses: Comparative Genomics of New Megavirales Family Members. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geballa-Koukoulas, K.; Boudjemaa, H.; Andreani, J.; Scola, B.; Blanc, G. Comparative Genomics Unveils Regionalized Evolution of the Faustovirus Genomes. Viruses 2020, 12, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, S.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Aylward, F.O. Comparative Genomics and Environmental Distribution of Large DsDNA Viruses in the Family Asfarviridae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 657471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherif Louazani, A.; Baptiste, E.; Levasseur, A.; Colson, P.; La Scola, B. Faustovirus E12 Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Complex Splicing in Capsid Gene. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Vega, I.; González, A.; Blasco, R.; Calvo, V.; Viñuela, E. Nucleotide Sequence and Variability of the Inverted Terminal Repetitions of African Swine Fever Virus DNA. Virology 1994, 201, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, P.; Zhang, Y.; Rohozinski, J.; Van Etten, J.L. The Termini of the Chlorella Virus PBCV-1 Genome Are Identical 2.2-Kbp Inverted Repeats. Virology 1991, 180, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B. Poxvirus DNA Replication. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a010199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.; Makhlouf, Z.; Khan, N.A. The Increasing Importance of Vermamoeba Vermiformis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2021, 68, e12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geballa-Koukoulas, K.; Andreani, J.; La Scola, B.; Blanc, G. The Kaumoebavirus LCC10 Genome Reveals a Unique Gene Strand Bias among “Extended Asfarviridae”. Viruses 2021, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.P.; de Aquino, I.L.M.; Luiz, A.P.M.F.; Abrahão, J.S. Putative Promoter Motif Analyses Reinforce the Evolutionary Relationships Among Faustoviruses, Kaumoebavirus, and Asfarvirus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, J.Y.B.; Robert, S.; Reteno, D.G.; Andreani, J.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. High-Throughput Isolation of Giant Viruses in Liquid Medium Using Automated Flow Cytometry and Fluorescence Staining. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, J.Y.B.; Langlois, T.; Andreani, J.; Sorraing, J.-M.; Raoult, D.; Camoin, L.; La Scola, B. Flow Cytometry Sorting to Separate Viable Giant Viruses from Amoeba Co-Culture Supernatants. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 6, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geballa-Koukoulas, K.; Abdi, S.; La Scola, B.; Blanc, G.; Andreani, J. Pacmanvirus S19, the Second Pacmanvirus Isolated from Sewage Waters in Oran, Algeria. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00693-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alempic, J.-M.; Lartigue, A.; Goncharov, A.E.; Grosse, G.; Strauss, J.; Tikhonov, A.N.; Fedorov, A.N.; Poirot, O.; Legendre, M.; Santini, S.; et al. An Update on Eukaryotic Viruses Revived from Ancient Permafrost. Viruses 2023, 15, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, T.; Kiryu, I.; Inada, M.; Takano, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Kamaishi, T. Susceptibility of Four Abalone Species, Haliotis Gigantea, Haliotis Discus Discus, Haliotis Discus Hannai and Haliotis Diversicolor, to Abalone Asfa-like Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.E.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple Alignment of Conserved Genomic Sequence With Rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; Verneau, J.; Raoult, D.; Levasseur, A.; La Scola, B. Deciphering Viral Presences: Two Novel Partial Giant Viruses Detected in Marine Metagenome and in a Mine Drainage Metagenome. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, J.; La Scola, B. Metagenomic Binning Reconstruction Coupled with Automatic Pipeline Annotation and Giant Viruses: A Potential Source of Mistake in Annotations. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannat, S.; Pontarotti, P.; Colson, P.; Kuhn, M.-L.; Galiana, E.; La Scola, B.; Aherfi, S.; Panabières, F. Diverse Trajectories Drive the Expression of a Giant Virus in the Oomycete Plant Pathogen Phytophthora Parasitica. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Takahashi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Shimamura, S.; Takaki, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Toyoda, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Arimoto, A.; Ishii, H.; et al. Chloroplast Acquisition without the Gene Transfer in Kleptoplastic Sea Slugs, Plakobranchus ocellatus. eLife 2021, 10, e60176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
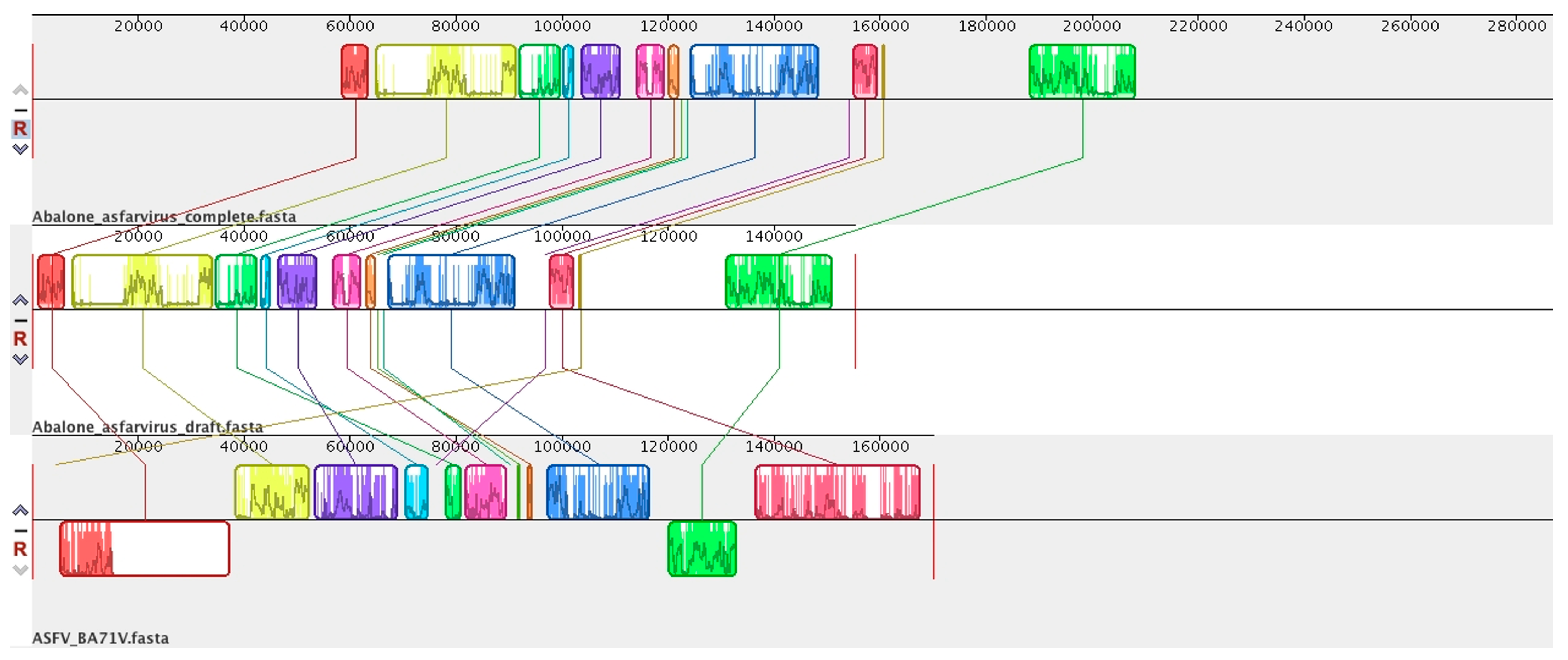
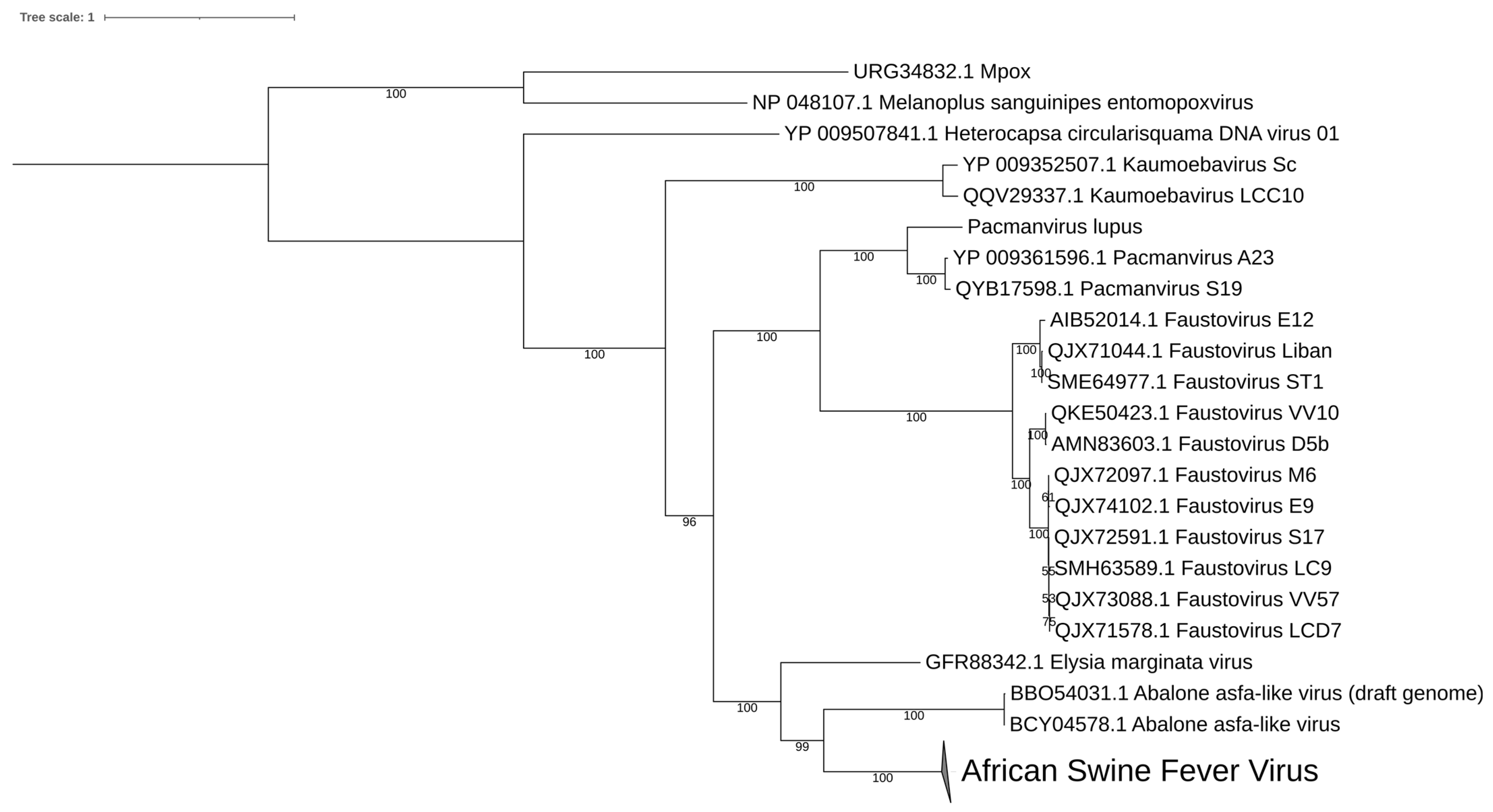
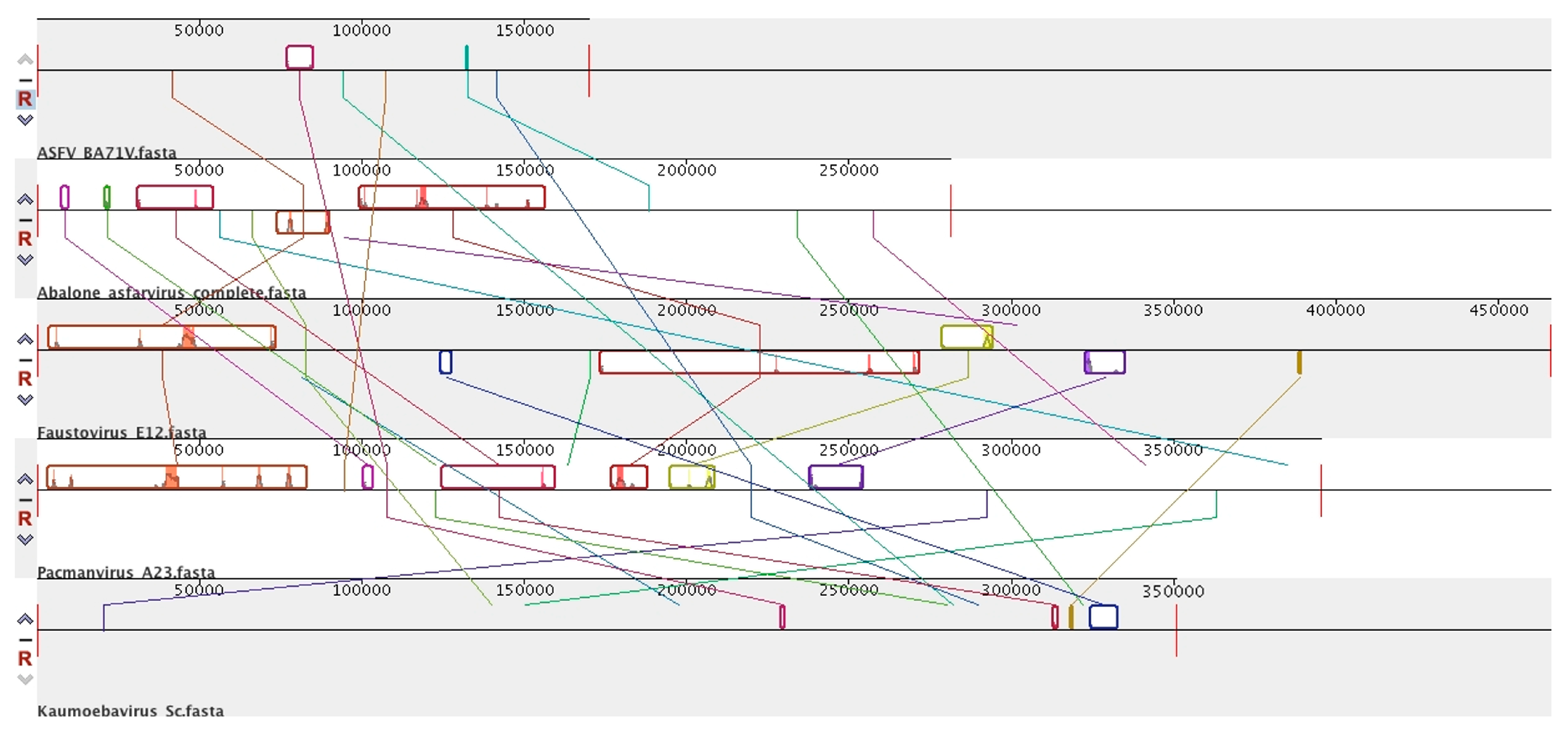
| Homologs/Virus | ASFV | Abalone Asfarvirus | Faustovirus | Pacmanvirus | Kaumoebavirus | Elysia Marginata | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer envelope | pEP402R | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| MCP chaperone | B602L | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Outer capsid | P72 capsid | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| M1249L(mCP) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| P49 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | |
| H240R | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | |
| Core proteic shell | pp220 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | yes |
| pp62 (pp60) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | yes | |
| pS273R | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | yes | |
| Inner envelope | E199L | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| p17 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | |
| p12 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | |
| E248R | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| pE84R | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | |
| Nucleoid | pK78R | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| pA104R | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hannat, S.; La Scola, B.; Andreani, J.; Aherfi, S. Asfarviruses and Closely Related Giant Viruses. Viruses 2023, 15, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041015
Hannat S, La Scola B, Andreani J, Aherfi S. Asfarviruses and Closely Related Giant Viruses. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041015
Chicago/Turabian StyleHannat, Sihem, Bernard La Scola, Julien Andreani, and Sarah Aherfi. 2023. "Asfarviruses and Closely Related Giant Viruses" Viruses 15, no. 4: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041015
APA StyleHannat, S., La Scola, B., Andreani, J., & Aherfi, S. (2023). Asfarviruses and Closely Related Giant Viruses. Viruses, 15(4), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041015





