Structural Consequences of Antigenic Variants of Human A/H3N2 Influenza Viruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Structures of Cluster—Representative Strains
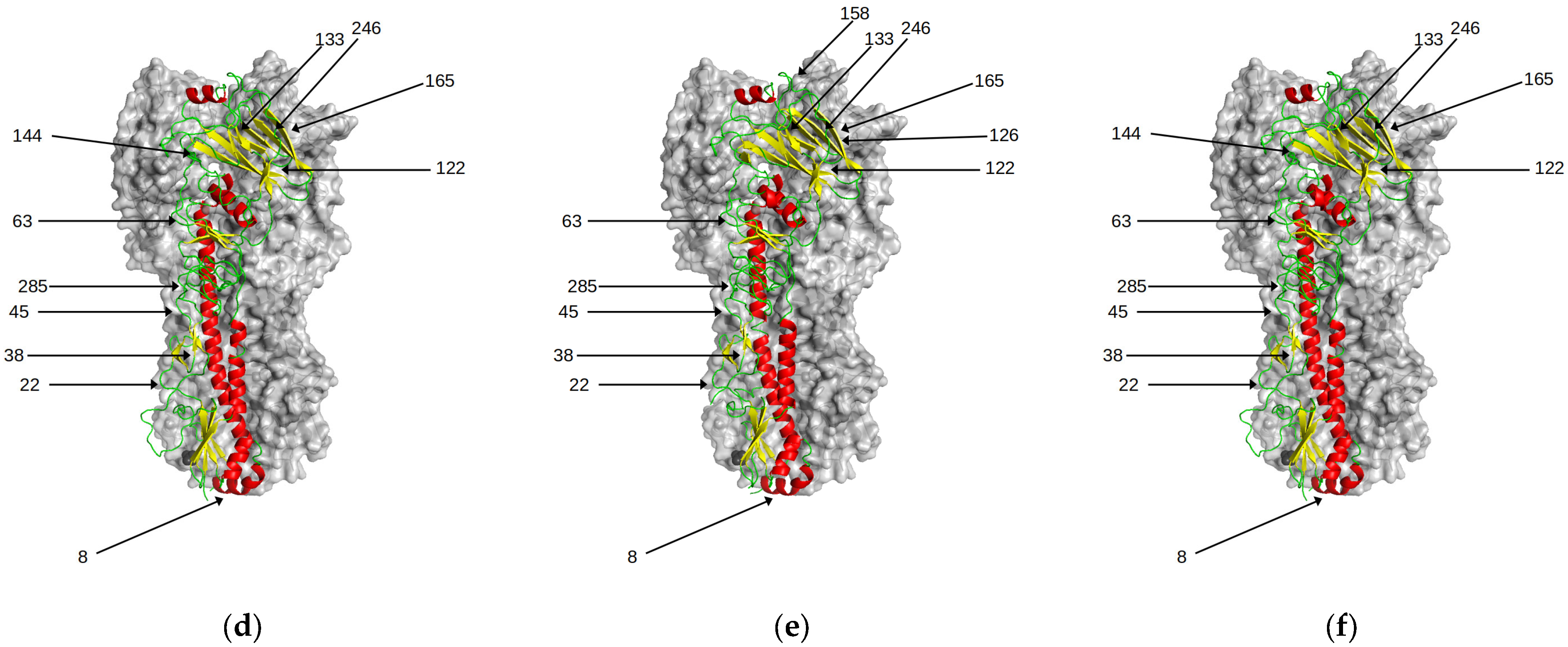
3. Results
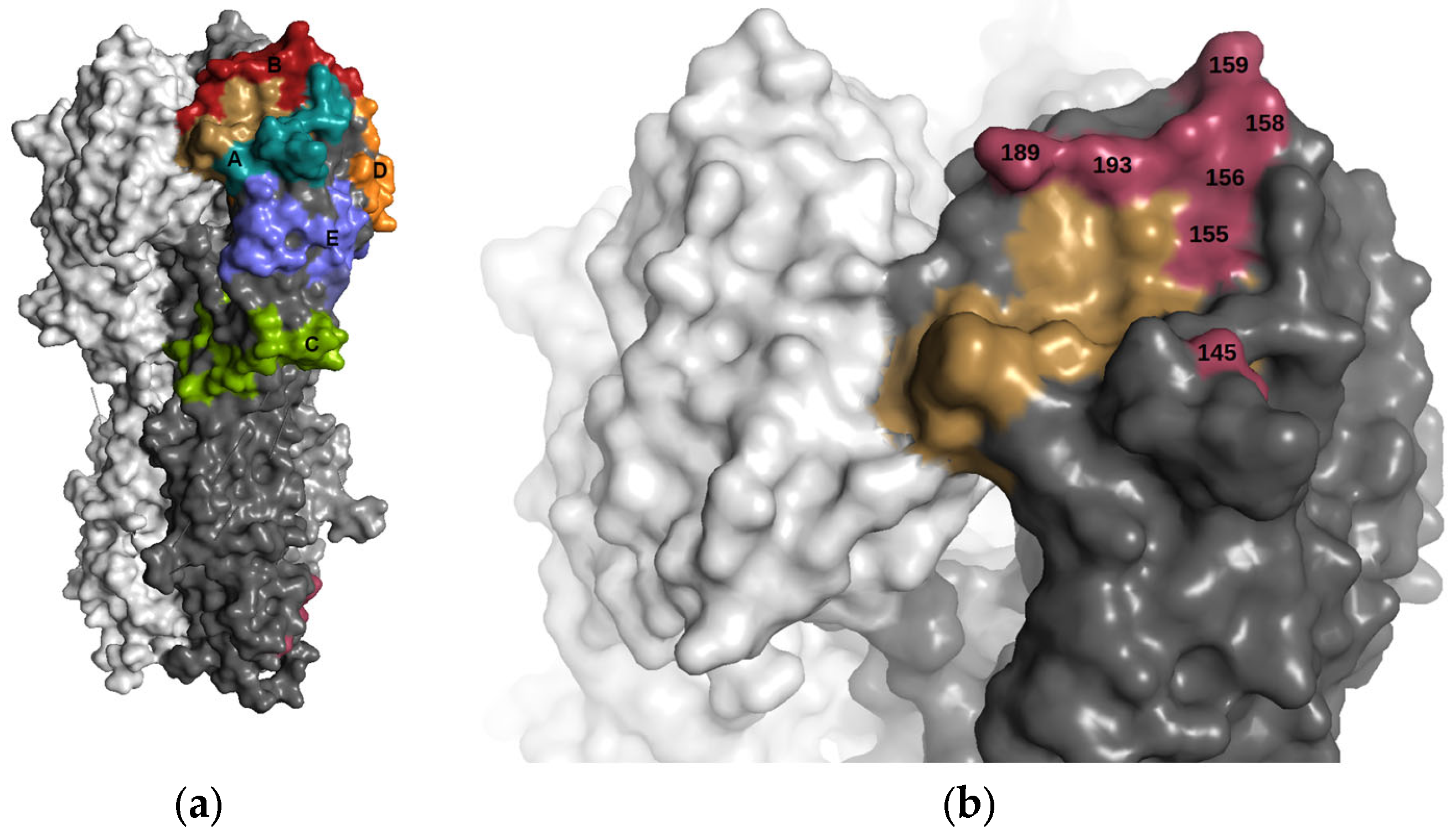
3.1. Antigenic Differences Explained by Changes in Biophysical Properties
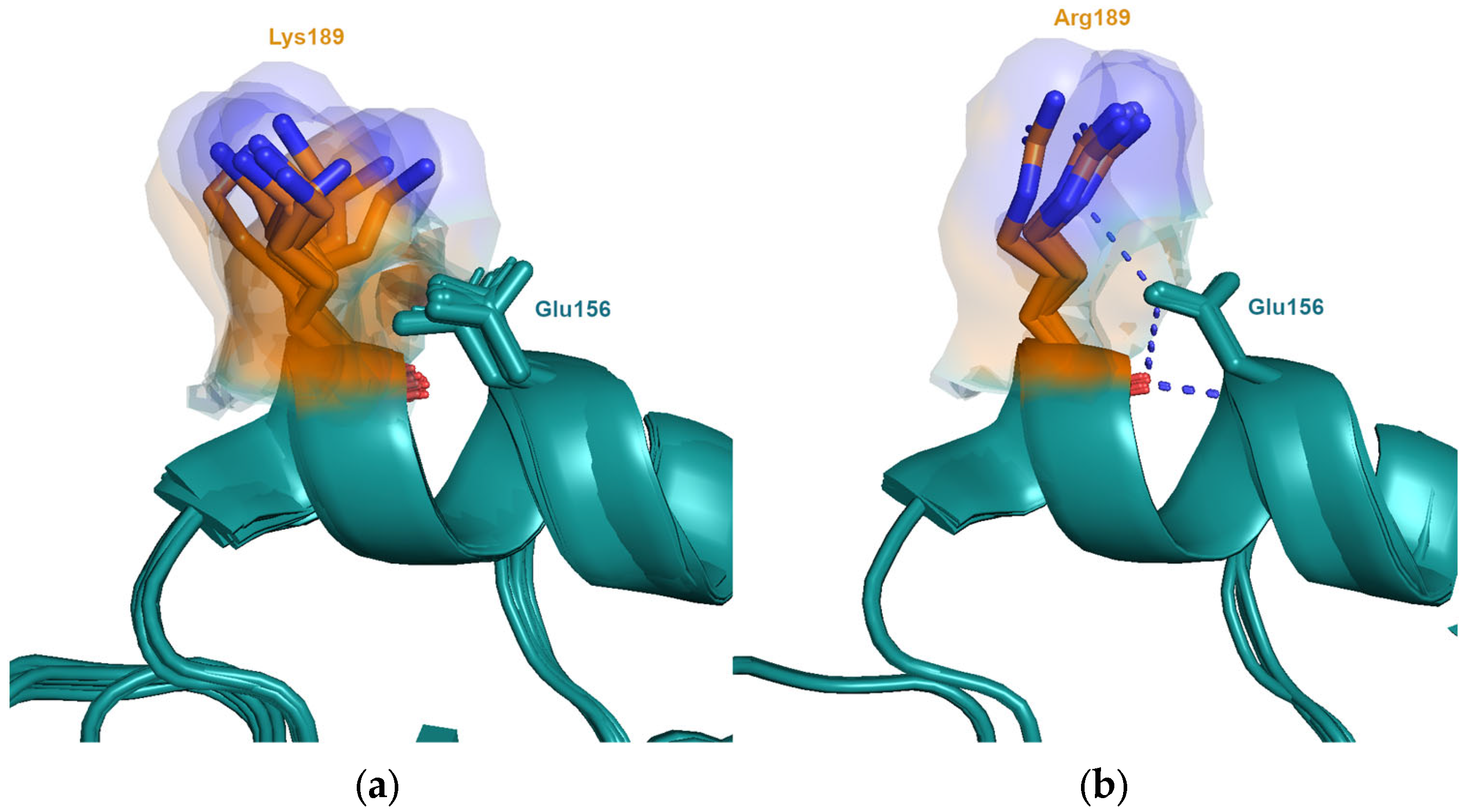
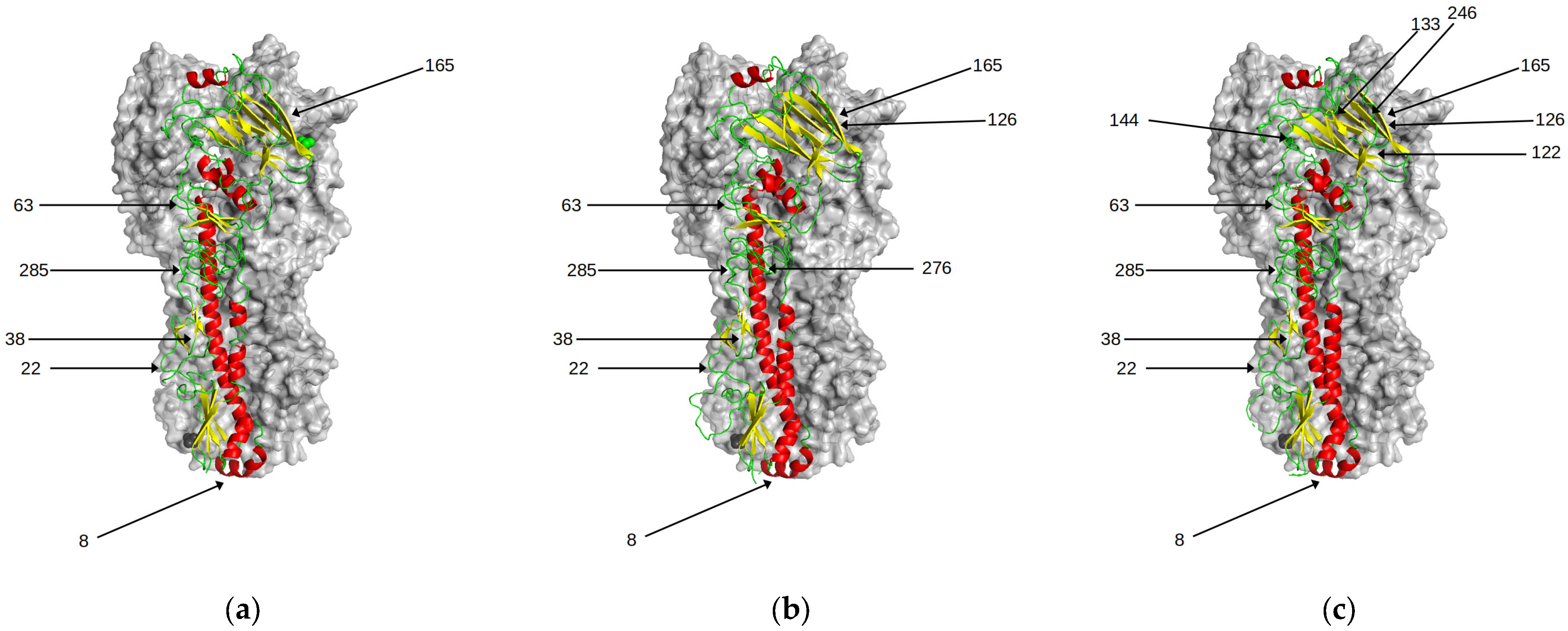
3.2. Magnitude of Antigenic Change: Neighbouring Interactions and Conformational Dynamics
3.3. Functional Equivalent Substitutions
3.4. Role of N-Linked Glycosylation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, I.; Cox, N.J. Structural basis of immune recognition of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1990, 8, 737–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, D.C.; Wilson, I.A.; Skehel, J.J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature 1981, 289, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Lapedes, A.S.; De Jong, J.C.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Mapping the Antigenic and Genetic Evolution of Influenza Virus. Science 2004, 305, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koel, B.F.; Burke, D.F.; Bestebroer, T.M.; van der Vliet, S.; Zondag, G.C.M.; Vervaet, G.; Skepner, E.; Lewis, N.S.; Spronken, M.I.J.; Russell, C.A.; et al. Substitutions Near the Receptor Binding Site Determine Major Antigenic Change During Influenza Virus Evolution. Science 2013, 342, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonville, J.M.; Fraaij, P.L.A.; de Mutsert, G.; Wilks, S.H.; van Beek, R.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Antigenic Maps of Influenza A(H3N2) Produced With Human Antisera Obtained After Primary Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 213, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, P.A.; Mishin, V.P.; Chesnokov, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; Mann, B.; Garten, R.; Barnes, J.; Hodges, E.; De La Cruz, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Insights into the antigenic advancement of influenza A(H3N2) viruses, 2011–2018. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, B.S.; Parkhouse, K.; Ross, T.M.; Alby, K.; Hensley, S.E. Identification of hemagglutinin residues responsible for H3N2 antigenic drift during the 2014–2015 influenza season. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hatta, M.; Burke, D.F.; Ping, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ozawa, M.; Taft, A.S.; Das, S.C.; Hanson, A.P.; Song, J.; et al. Selection of antigenically advanced variants of seasonal influenza viruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koel, B.F.; Mögling, R.; Chutinimitkul, S.; Fraaij, P.L.; Burke, D.F.; van der Vliet, S.; de Wit, E.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; et al. Identification of Amino Acid Substitutions Supporting Antigenic Change of Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 Viruses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3763–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linster, M.; Schrauwen, E.J.A.; van der Vliet, S.; Burke, D.; Lexmond, P.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Smith, D.; Herfst, S.; Koel, B.F.; Fouchier, R.A.M. The Molecular Basis for Antigenic Drift of Human A/H2N2 Influenza Viruses. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koel, B.F.; van der Vliet, S.; Burke, D.F.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Bharoto, E.E.; Yasa, I.W.W.; Herliana, I. Antigenic variation of clade 2.1 H5N1 virus is determined by a few amino acid substitutions immediately adjacent to the receptor binding site. MBio 2014, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.S.; Daly, J.M.; Russell, C.A.; Horton, D.L.; Skepner, E.; Bryant, N.A.; Burke, D.F.; Rash, A.S.; Wood, J.L.N.; Chambers, T.M.; et al. Antigenic and Genetic Evolution of Equine Influenza A (H3N8) Virus from 1968 to 2007. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12742–12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.; Vincent, A.L.; Harland, M.L.; Alt, D.; Bayles, D.O.; Swenson, S.L.; Gramer, M.R.; Russell, C.; Smith, D.; Lager, K.M.; et al. Genetic and antigenic characterization of H1 influenza viruses from United States swine from 2008. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 92, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.S.; Anderson, T.K.; Kitikoon, P.; Skepner, E.; Burke, D.F.; Vincent, A.L. Substitutions near the Hemagglutinin Receptor-Binding Site Determine the Antigenic Evolution of Influenza A H3N2 Viruses in U.S. Swine. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4752–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doud, M.B.; Lee, J.M.; Bloom, J.D. How single mutations affect viral escape from broad and narrow antibodies to H1 influenza hemagglutinin. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using Modeller. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1.–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Lovell, S.C.; Burke, D.F.; Montalvao, R.W.; Blundell, T.L. Andante: Reducing side-chain rotamer search space during comparative modeling using environment-specific substitution probabilities. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, A.M.; Chothia, C. How different amino acid sequences determine similar protein structures: The structure and evolutionary dynamics of the globins. J. Mol. Biol. 1980, 136, 225–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.G.; Shirai, H.; Shi, J.; Nagendra, H.G.; Mueller, J.; Mizuguchi, K.; Miguel, R.N.; Lovell, S.C.; Innis, C.A.; Deane, C.M.; et al. Sequence-structure homology recognition by iterative alignment refinement and comparative modeling. Proteins 2001, 45, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Blundell, T.L. Structural and Functional Restraints on the Occurrence of Single Amino Acid Variations in Human Proteins. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.C.; Xie, J.; Zheng, T.; Nycholat, C.M.; Grande, G.; Paulson, J.C.; Lerner, R.A.; Wilson, I.A. Diversity of Functionally Permissive Sequences in the Receptor-Binding Site of Influenza Hemagglutinin. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 742–753.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karplus, P.A.; Schulz, G.E. Prediction of chain flexibility in proteins. Sci. Nat. 1985, 72, 212–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmanovich, R.; Kuttner, J.; Sobolev, V.; Edelman, M. Side-Chain Flexibility in Proteins Upon Ligand Binding PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Genetics. Proteins 2000, 39, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Bowden, T.A.; Wilson, I.A.; Crispin, M. Exploitation of glycosylation in enveloped virus pathobiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1480–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Decker, J.; Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Kappes, J.C.; Wu, X.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Salazar, M.G.; Kilby, J.M.; Saag, M.S.; et al. Antibody neutralization and escape by HIV-1. Nature 2003, 422, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doores, K.J. The HIV glycan shield as a target for broadly neutralizing antibodies. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 4679–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburne, B.P.; Hay, A.J.; Goldstein, R.A. Changing Selective Pressure during Antigenic Changes in Human Influenza H3. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, M.O.; Angel, M.; Košík, I.; Trovão, N.S.; Zost, S.J.; Gibbs, J.S.; Casalino, L.; Amaro, R.E.; Hensley, S.E.; Nelson, M.I.; et al. Human Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin Glycan Evolution Follows a Temporal Pattern to a Glycan Limit. Mbio 2019, 10, e00204-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.R.; Hensley, S.E.; David, A.; Schmidt, L.; Gibbs, J.S.; Puigbo, P.; Ince, W.L.; Bennink, J.R.; Yewdell, J.W. Fitness costs limit influenza A virus hemagglutinin glycosylation as an immune evasion strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1417–E1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zost, S.J.; Parkhouse, K.; Gumina, M.E.; Kim, K.; Perez, S.D.; Wilson, P.C.; Treanor, J.J.; Sant, A.J.; Cobey, S.; Hensley, S.E. Contemporary H3N2 influenza viruses have a glycosylation site that alters binding of antibodies elicited by egg-adapted vaccine strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12578–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cluster Name | Virus | PDB Entry | Resolution (Å) | Amino Acid Position | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 140 | 145 | 155 | 156 | 158 | 159 | 189 | 193 | ||||
| HK68 | A/Aichi/2/1968 | 6e56 | 2.0 | Lys | Ser | Thr | Lys | Gly | Ser | Gln | Ser |
| A/HongKong/1/1968 | 4fnk | 1.90 | |||||||||
| A/Northern-Territory/60/1968 | 6bkm | 2.20 | |||||||||
| EN72 | A/Port-Chalmers/1/1973 | 4we5 | 2.10 | Lys | Ser | Tyr | Lys | Gly | Ser | Gln | Asn |
| VI75 | A/Victoria/3/1975 | 4gms | 2.95 | Lys | Ser | Tyr | Lys | Gly | Ser | Lys | Asn |
| TX77 | A/Texas/1/1977 | 6mxu | 1.85 | Lys | Asn | Tyr | Lys | Glu | Ser | Lys | Asn |
| BK79 | A/Netherlands/209/1980 | 6n08 | 1.92 | Lys | Asn | Tyr | Glu | Glu | Ser | Lys | Asn |
| A/Philipines/2/1982 | 6mym | 2.45 | |||||||||
| SI87 | A/Sichuan/2/1987 | 6p6p | 2.31 | Lys | Asn | His | Glu | Glu | Tyr * | Arg | Asn |
| BE89 | A/Netherlands/823/1992 | Model | n/a | Lys | Lys | His | Glu | Asp | Tyr | Arg | Ser |
| BE92 | A/Netherlands/179/1993 | Model | n/a | Lys | Asn | His | Lys | Glu | Tyr | Ser | Ser |
| WU95 | A/NetHiserlands/178/1995 | Model | n/a | Lys | Lys | His | Lys | Arg | Tyr | Ser | Ser |
| SY97 | A/Moscow/10/1999 | 6xpz | 3.45 | Lys | Lys | His | Gln | Lys † | Tyr † | Ser | Ser |
| FUO2 | A/Wyoming/3/2003 | 6bko | 1.65 | Lys | Lys | Thr | His | Lys | Tyr | Ser | Ser |
| CAL04 | A/Finland/486/2004 | 2yp2 | 1.90 | Lys | Asn | Thr | His | Lys | Phe | Asn | Ser |
| WI05 | A/Hong-Kong/4443/2005 | 2yp7 | 1.85 | Lys | Asn | Thr | His | Lys | Phe | Asn | Phe |
| BR07 | A/Brisbane/10/2007 | 6aop | 2.30 | Ile | Asn | Thr | His | Lys | Phe | Asn | Phe |
| VI09 | A/Victoria/361/2011 | 4we9 | 2.20 | Ile | Asn | Thr | His | Asn | Phe | Lys | Phe |
| 3C.1 | A/Texas/50/2012 | 5w08 | 2.60 | Ile | Asn | Thr | His | Asn | Phe | Lys | Phe |
| A/Singapore/H2011.447/2011 | 4o5n | 1.75 | |||||||||
| A/Alberta/26/2012 | 4we7 | 2.50 | |||||||||
| 3C.2A | A/Michigan/15/2014 | 6bkp | 2.05 | Ile | Ser | Thr | His | Asn | Tyr | Lys | Phe |
| 3C.3A | A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 | 6pdx | 3.99 | Ile ‡ | Ser | Thr | His | Asn | Ser | Lys | Phe |
| Cluster | Cluster Transition | Citation | Mutation | Antigenic Distance | ΔCharge | ΔPolarity | ΔASA * | ΔLength | Size Category Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HK68 → EN72 | [4] | Thr155Tyr | 2.6 | 0 | −2.4 | +85 | +4.3 | Small → Large |
| 2 | EN72 → VI75 | [4] | Gln189Lys | 4.1 | +1 | +0.8 | +23 | +2.3 | Medium → Large |
| 3 | VI75 → TX77 * | [4] | Gly158Glu Asp193Asn | 0.6 | −1 | +3.3 | +138 | +4.1 | Very Small → Medium |
| 0.9 | 0 | −1.4 | −7 | −1 | Small → Small | ||||
| 4 | TX77 → BK79 | [4] | Lys156Glu | 1.2 | −2 | +1.0 | −29 | −3.3 | Large → Medium |
| 5 | BK79 → SI87 | [4] | Ser159Tyr | 1.6 | 0 | −3 | +107 | +4.3 | Small → Large |
| Tyr155His | 1.7 | 0 | −4.2 | −36 | −1.9 | Large → Medium | |||
| Lys189Arg | 3.1 | 0 | −0.8 | +29 | −0.3 | Large → Large | |||
| 6 | SI87 → BE89 * | [4] | Asn145Lys | 3.1 | +1 | −0.3 | +54 | +3.8 | Small → Large |
| 7 | SI87 → BE92 | [4] | Glu156Lys | 6.1 | +2 | −1.0 | +29 | +3.3 | Medium → Large |
| 8 | BE92 → WU95 | [4] | Asn145Lys | 2.2 | +1 | −0.3 | +54 | +3.8 | Small → Large |
| 9 | WU95 → SY97 | [4] | Lys156Gln | 2.2 | −1 | −0.8 | −23 | −2.3 | Large → Medium |
| Glu158Lys | 2.1 | +2 | −1.0 | +29 | +3.3 | Medium → Large | |||
| 10 | SY97 → FUO2 | [4] | Gln156His | 1.1 | 0 | −0.1 | +7 | −0.5 | Medium → Medium |
| 11 | FU02 → CAL04 | [5] | Lys145Asn † | 3 | −1 | +0.3 | −54 | −3.8 | Large → Small |
| 12 | CAL04 → WI05 | [5] | Ser193Phe † | 2.5 | 0 | −4.0 | +95 | +3.6 | Very Small → Large |
| 13 | WI05 → BR07 | [5] | Lys140Ile † | 2.5 | −1 | −6.1 | −27 | −2.8 | Large → Medium |
| 14 | BR07 → VI09 | [5] | Asn189Lys † | 3.2 | +1 | −0.3 | +54 | +3.8 | Small → Large |
| Lys158Asn † | −1 | +0.3 | −54 | −3.8 | Large → Small | ||||
| 15 | 3C.1 → 3C.2A | [8] | Lys160Thr (N-Gly158) | 2 | 0 | −2.7 | n/a | n/a | Large → Small |
| 16 | 3C.1 → 3C.3A | [8] | Phe159Ser | 6 | 0 | +4.0 | −95 | −3.6 | Large → Very Small |
| Virus | Genetic Clade | Position | 8 | 22 | 38 | 45 | 63 | 81 | 122 | 126 | 133 | 144 | 158 | 165 | 246 | 276 | 285 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Sites | |||||||||||||||||
| BI/16190/68 | HK68 | 6 | |||||||||||||||
| BI/21793/72 | EN72 | 6 | |||||||||||||||
| VI/3/75 | VI75 | 7 | |||||||||||||||
| BI_2271_76 | TX77 | 7 | |||||||||||||||
| NL/233/82 | BK79 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Sichuan/2/87 | SI87 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
| NL/823/92 | BE89 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
| NL/179/93 | BE92 | 9 | |||||||||||||||
| NL/178/95 | WU95 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
| NL/301/99 | SY97 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| FU/411/02 | FU02 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Finland/486/2004 | CAL04 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/HongKong/4443/2005 | WI05 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Brisbane/10/2007 | BR07 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Victoria/361/2011 | VI09 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Texas/50/2012 | 3C.1 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 | 3C.2a1 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Switzerland/8060/2017 | 3C.2a2 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Cambodia/e0826360/2020 | 3C.2a1b.2a.1 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Darwin/9/2021 | 3C.2a1b.2a.2 | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 | 3C.3a | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| A/Kansas/14/2017 | 3C.3a | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burke, D.F. Structural Consequences of Antigenic Variants of Human A/H3N2 Influenza Viruses. Viruses 2023, 15, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041008
Burke DF. Structural Consequences of Antigenic Variants of Human A/H3N2 Influenza Viruses. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurke, David Francis. 2023. "Structural Consequences of Antigenic Variants of Human A/H3N2 Influenza Viruses" Viruses 15, no. 4: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041008
APA StyleBurke, D. F. (2023). Structural Consequences of Antigenic Variants of Human A/H3N2 Influenza Viruses. Viruses, 15(4), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15041008






