Phenotypic Characterization of Recombinant Marek’s Disease Virus in Live Birds Validates Polymorphisms Associated with Virulence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Mutagenesis of 686-BAC
2.3. Reconstitution of the 686 Mut Viruses
2.4. In Vivo Pathogenicity Study
2.5. Pathotyping Assay
2.6. Determination of Pathotype
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Modified Recombinant MDVs
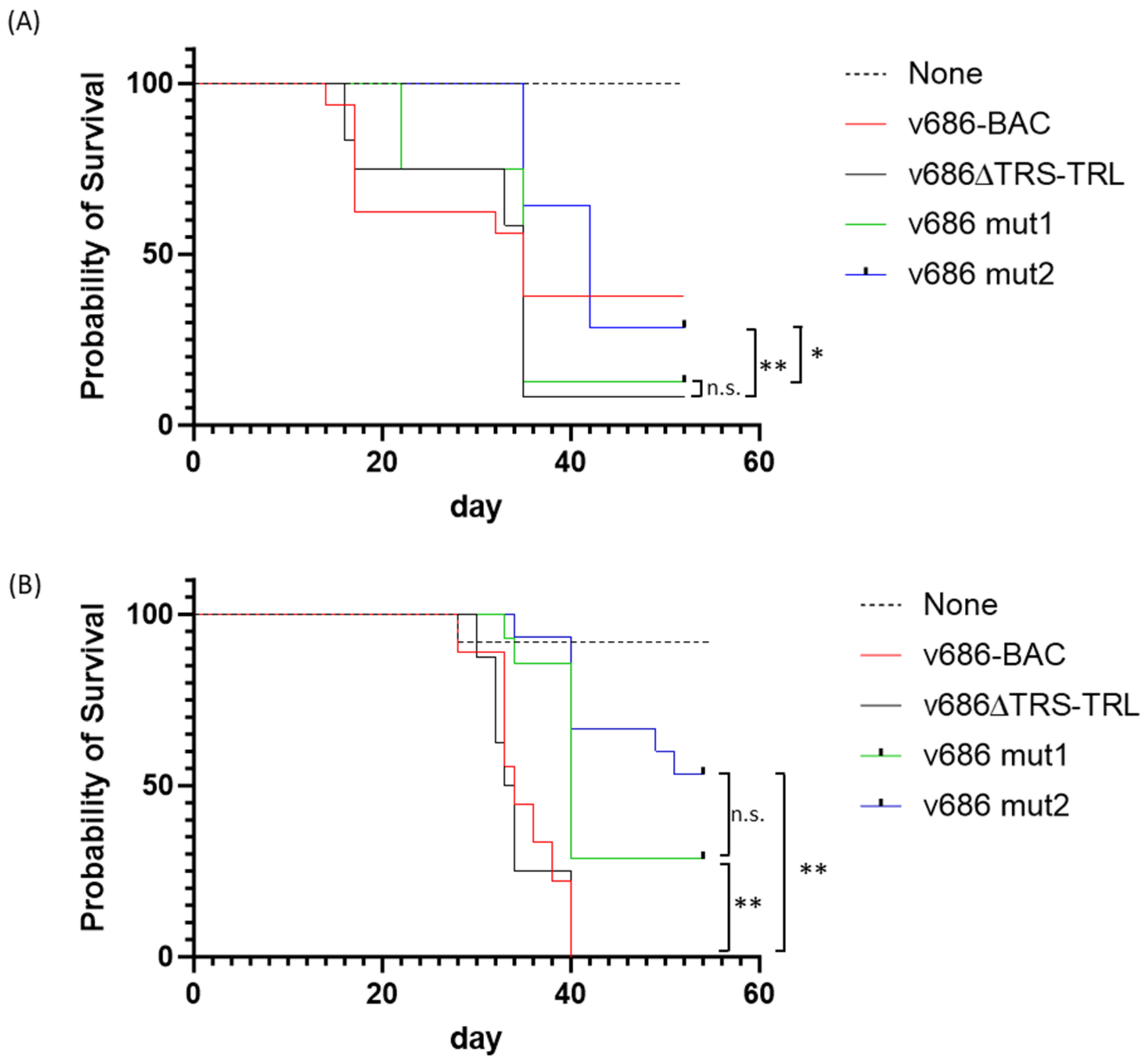
3.2. Pathogenicity Analysis of the Recombinant MDVs
3.3. Pathotype Analysis of the Recombinant MDVs
3.4. Graphical Display of the Recombinant MDV Pathotypes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schat, K.A.; Nair, V. Marek’s disease. In Diseases of Poultry, 13th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Suarez, D.L., Nair, V.L., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 515–552. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, P.M. The history and biology of Marek’s disease virus. In Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Hirai, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, C.; Fehler, F. Marek’s disease: A worldwide problem. In Marek’s Disease: An Evolving Problem; Davison, F., Nair, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, P.M.; Nair, V. The long view: 40 years of Marek’s disease research and Avian Pathology. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witter, R. Increased virulence of Marek’s disease virus field isolates. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witter, R.L. Control strategies for Marek’s disease: A perspective for the future. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, A.F.; Baigent, S.J.; Powers, C.; Kgosana, L.B.; Blackwell, L.; Smith, L.P.; Kennedy, D.A.; Walkden-Brown, S.W.; Nair, V.K. Imperfect Vaccination Can Enhance the Transmission of Highly Virulent Pathogens. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, I.M. Marek’s disease vaccines: A solution for today but a worry for tomorrow? Vaccine 2008, 26 (Suppl. S3), C31–C41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bublot, M.; Sharma, J.M. Vaccination against Marek’s disease. In Marek’s Disease: An Evolving Problem; Davison, F., Nair, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 168–185. [Google Scholar]
- Witter, R.L. The changing landscape of Marek’s disease. Avian Pathol. 1998, 27 (Suppl. S1), S46–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, R.L. Marek’s disease virus vaccines-past, present and future (chicken vs. virus—A battle of the centuries). In Current Progress on Marek’s Disease Research. Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Marek’s Disease; Schat, K.A., Morgan, R.M., Parcells, M.S., Spencer, J.L., Eds.; American Association of Avian Pathologists: Kennett Square, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, J.R.; Black Pyrkosz, A.; Steep, A.; Cheng, H.H. Identification of Marek’s disease virus genes associated with virulence of US strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnikova, E.; Norkina, S.; Vlasov, A.; Slobodchuk, A.; Lee, L.F.; Witter, R.L. Evaluation of Marek’s disease field isolates by the “best fit” pathotyping assay. Avian Pathol. 2007, 36, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, R.L.; Calnek, B.W.; Buscaglia, C.; Gimeno, I.M.; Schat, K.A. Classification of Marek’s disease viruses according to pathotype: Philosophy and methodology. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.; Brown, D.T. Growth and maintenance of chick embryo fibroblasts (CEF). Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2010, 17, 4I. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Spatz, S.J.; Dunn, J.R. Vaccinal efficacy of molecularly cloned Gallid alphaherpesvirus 3 strain 301B/1 against very virulent Marek’s disease virus challenge. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.M.; Sun, A.; Khan, O.A.; Lee, L.F.; Lupiani, B. Cloning of a very virulent plus, 686 strain of Marek’s disease virus as a bacterial artificial chromosome. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karstentischer, B.; von Einem, J.; Kaufer, B.; Osterrieder, N. Two-step red-mediated recombination for versatile high-efficiency markerless DNA manipulation in Escherichia coli. Biotechniques 2006, 40, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, R.L.; Kreager, K.S. Serotype 1 viruses modified by backpassage or insertional mutagenesis: Approaching the threshold of vaccine efficacy in Marek’s disease. Avian Dis. 2004, 48, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, A.; Venugopal, K. Molecular characteristics of very virulent European MDV isolates. Acta Virol. 1999, 43, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Shamblin, C.E.; Greene, N.; Arumugaswami, V.; Dienglewicz, R.L.; Parcells, M.S. Comparative analysis of Marek’s disease virus (MDV) glycoprotein-, lytic antigen pp38- and transformation antigen Meq-encoding genes: Association of meq mutations with MDVs of high virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatz, S.J.; Silva, R.F. Polymorphisms in the repeat long regions of oncogenic and attenuated pathotypes of Marek’s disease virus 1. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniakowski, G.; Samorek-Salamonowicz, E.; Kozdruń, W. Sequence analysis of meq oncogene among Polish strains of Marek’s disease. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 13, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wozniakowski, G.; Samorek-Salamonowicz, E. Molecular Evolution of Marek’s Disease Virus (MDV) Field Strains in a 40-Year Time Period. Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Deka, D. Sequence analysis of Meq oncogene among Indian isolates of Marek’s disease herpesvirus. Meta Gene 2016, 9, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.; Johnson Rajeswar, J.; Sukumar, K.; Harikrishnan, T.J.; Srinivasan, P. Complete nucleotide sequence analysis of the oncogene “Meq” from serotype 1 Marek’s disease virus isolates from India. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellatieff, H.A.; Abou Rawash, A.A.; Ellakany, H.F.; Goda, W.M.; Suzuki, T.; Yanai, T. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of a virulent Marek’s disease virus field strain in broiler chickens in Japan. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachheb, J.; Mastour, H.; Nsiri, J.; Kaboudi, K.; Choura, I.; Ammouna, F.; Amara, A.; Ghram, A. Newly detected mutations in the Meq oncogene and molecular pathotyping of very virulent Marek’s disease herpesvirus in Tunisia. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Machida, Y.; Isezaki, M.; Maekawa, N.; Okagawa, T.; Konnai, S.; Ohashi, K. Genetic characterization of a Marek’s disease virus strain isolated in Japan. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaki, T.R.; Priyanka, E.; Nishitha, Y.; Krishna, S.V.; Haunshi, S.; Subbiah, M. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of Marek’s disease virus virulence-associated genes from vaccinated flocks in southern India reveals circulation of virulent MDV genotype. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e244–e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, K.G.; Cooke, J.; Clarke, N.; Cheetham, B.F.; Hussain, Z.; Fakhrul Islam, A.F.; Tannock, G.A.; Walkden-Brown, S.W. Pathotyping of Australian isolates of Marek’s disease virus and association of pathogenicity with meq gene polymorphism. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimpert, J.; Groenke, N.; Jenckel, M.; He, S.; Kunec, D.; Szpara, M.L.; Spatz, S.J.; Osterrieder, N.; McMahon, D.P. A phylogenomic analysis of Marek’s disease virus reveals independent paths to virulence in Eurasia and North America. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J.R.; Reddy, S.M.; Niikura, M.; Nair, V.; Fulton, J.E.; Cheng, H.H. Evaluation and Identification of Marek’s Disease Virus BAC Clones as Standardized Reagents for Research. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupiani, B.; Lee, L.F.; Cui, X.; Gimeno, I.; Anderson, A.; Morgan, R.W.; Silva, R.F.; Witter, R.L.; Kung, H.J.; Reddy, S.M. Marek’s disease virus-encoded Meq gene is involved in transformation of lymphocytes but is dispensable for replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11815–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradie, A.M.; Bertzbach, L.D.; Bhandari, N.; Parcells, M.; Kaufer, B.B. A Common Live-Attenuated Avian Herpesvirus Vaccine Expresses a Very Potent Oncogene. mSphere 2019, 4, e00658-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conradie, A.M.; Bertzbach, L.D.; Trimpert, J.; Patria, J.N.; Murata, S.; Parcells, M.S.; Kaufer, B.B. Distinct polymorphisms in a single herpesvirus gene are capable of enhancing virulence and mediating vaccinal resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, P.F.; Izumiya, Y.; Lupiani, B.; Ajithdoss, D.K.; Gilad, O.; Lee, L.F.; Kung, H.J.; Reddy, S.M. Homodimerization of Marek’s disease virus-encoded Meq protein is not sufficient for transformation of lymphocytes in chickens. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, P.F.; Izumiya, Y.; Lupiani, B.; Ajithdoss, D.K.; Lee, L.F.; Kung, H.J.; Reddy, S.M. Both homo and heterodimers of Marek’s disease virus encoded Meq protein contribute to transformation of lymphocytes in chickens. Virology 2010, 399, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | vv+MDV | vMDV | Amino Acid Change | Protein Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL22 | C | A | R to M | 603 |
| UL36 | C | T | R to K | 35 |
| UL37 | A | G | V to A | 3 |
| UL41 | G | T | P to H | 136 |
| UL43 | A | G | I to V | 399 |
| R-LORF8 | T | C | M to V | 73 |
| R-LORF7 | C | T | R to C | 119 |
| R-LORF7 | A | C | Q to P | 153 |
| ICP4 | A | G | S to P | 181 |
| ORF | Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) * |
|---|---|---|
| UL22 | UL22mut.FP | ACAAGTCACAACTTCTGATGCATATATAGTCAACCTTCTCATCAATGGTGTTTTAAGCTTtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| UL22mut.RP | AGCAGAATTGGTAATCACCAAGCTTAAAACACCATTGATGAGAAGGTTGACTATATATGCgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| UL36 | UL36mut.FP | TTTCGATCAAGCGAACAGAGTCCAGACGTCGATTTATCTCTTAACACGTTCGCAGCTAGCtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| UL36mut.RP | CTACATCGAACGCACCCATGCTAGCTGCGAACGTGTTAAGAGATAAATCGACGTCTGGACgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| UL37 | UL37mut.FP | TCCAATAAAACTTTCAGTGGCCATATTTCATCGGTCGTTACGGCAGACATTATTCAGGCtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| UL37mut.RP | ACAGAGGGTTGGCGATAGTTGCCTGAATAATGTCTGCCGTAACGACCGATGAAATATGGCgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| UL41 | UL41mut.FP | TCAAACCTTTCGCTCCATCTACAAACCTTCTTCCCGGGGTGTTTCCTCTTACACCGCGCCtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| UL41mut.RP | GAAGTACGGATGTTGGAGAGGCGCGGTGTAAGAGGAAACACCCCGGGAAGAAGGTTTGTAgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| UL43 | UL43mut.FP | AATGCAAATAAGGGAATTAAACAATTAGCAGCTGCCTATGTAGTGAAATCTATACTGGGAtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| UL43mut.RP | GTAAACTAGTTATGATAAATCCCAGTATAGATTTCACTACATAGGCAGCTGCTAATTGTTgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| R-LORF8 | R-LORF8mut.FP | CTTCACAGGGGACATTCAAAACAAGCCCAGAGCCGTCACGTGGAACACGTCTCGAGTCGAtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| R-LORF8mut.RP | GCTTTCTTGAGGGGAGCGATCGACTCGAGACGTGTTCCACGTGACGGCTCTGGGCTTGTTgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| R-LORF7 | Meqmut.FP | CTAAGGACTGAGTGCACGTCCCTGCGTGTACAGTTGGCTTGTCATGAGCCAGTTTGCCCTtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| Meqmut.RP | CCGTTAGGGGTACCGCCATAGGGCAAACTGGCTCATGACAAGCCAACTGTACACGCAGGGgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| R-LORF7 | Meqmut2.FP | CGCACGATCCCGTTCCTGAACCTCCCATTTGCACTCCTCCACCTCCCTCACCGGATGAACtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| Meqmut2.RP | GAGCAATGTGGAGCGTTAGGTTCATCCGGTGAGGGAGGTGGAGGAGTGCAAATGGGAGGTgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc | |
| ICP4 | ICP4mut.FP | CCTCACCAAAATCGGCTGCCAGGATCTCCAGTAGAGGAGGACTGGATGTCCCGCCGCTTCtagggataacagggtaatcgattt |
| ICP4mut.RP | GACATCGAGTCCGCTTCCGGAAGCGGCGGGACATCCAGTCCTCCTCTACTGGAGATCCTGgccagtgttacaaccaattaacc |
| Gene | vv+MDV Allele | vMDV Allele | 686 | 686∆TRS-TRL | 686 mut1 | 686 mut2 | Average Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL22 | C | A | C | C | A | A | 126 |
| UL36 | C | T | C | C | T | T | 133 |
| UL37 | A | G | A | A | G | G | 131 |
| UL41 | G | T | G | G | T | T | 124 |
| UL43 * | G | T | G | G | T | T | 131 |
| UL43 | A | G | A | A | G | G | 133 |
| R-LORF8 | T | C | T | T | C | C | 174 |
| R-LORF7 | C | T | C | C | T | T | 186 |
| R-LORF7 | A | C | A | A | C | C | 157 |
| ICP4 | A | G | A | A | G | G | 97 |
| LORF2 * | A | G | A | G | A | A | 129 |
| Clinical Trial | Challenge Virus | Birds at Risk 1 | MD-Positive 2 | % MD | Differences 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | 15 | 0 | 0 | a |
| v686-BAC | 15 | 10 | 67 | b | |
| v686∆TRS-TRL | 12 | 11 | 92 | b | |
| v686 mut1 | 8 | 7 | 88 | b | |
| v686 mut2 | 14 | 12 | 86 | b | |
| 2 | None | 12 | 0 | 0 | a |
| v686-BAC | 9 | 9 | 100 | b | |
| v686∆TRS-TRL | 8 | 8 | 100 | b | |
| v686 mut1 | 14 | 11 | 79 | b | |
| v686 mut2 | 15 | 10 | 67 | b |
| Replicate | Group Vaccine/Challenge | Birds at Risk 1 | MD Positive 2 | % MD | Differences 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None/JM/102W | 16 | 15 | 94 | a |
| None/Md5 | 16 | 14 | 88 | a | |
| None/648A | 16 | 16 | 100 | a | |
| None/v686∆TRS-TRL | 15 | 15 | 100 | a | |
| None/v686 mut1 | 16 | 15 | 94 | a | |
| None/v686 mut2 | 16 | 16 | 100 | a | |
| HVT/JM/102W | 9 | 2 | 22 | a | |
| HVT/Md5 | 9 | 3 | 33 | b | |
| HVT/648A | 9 | 8 | 89 | b | |
| HVT/v686∆TRS-TRL | 10 | 6 | 60 | a,b | |
| HVT/v686 mut1 | 10 | 6 | 60 | a,b | |
| HVT/v686 mut2 | 9 | 4 | 44 | a,b | |
| HVT+SB1/JM/102W | 9 | 1 | 11 | a | |
| HVT+SB1/Md5 | 9 | 3 | 33 | a,b | |
| HVT+SB1/648A | 9 | 6 | 67 | b | |
| HVT+SB1/v686∆TRS-TRL | 10 | 7 | 70 | b | |
| HVT+SB1/v686 mut1 | 8 | 2 | 25 | a,c | |
| HVT+SB1/v686 mut2 | 6 | 3 | 50 | a,b | |
| 2 | None/JM/102W | 13 | 6 | 46 | a |
| None/Md5 | 13 | 13 | 100 | b | |
| None/648A | 11 | 11 | 100 | b | |
| None/v686∆TRS-TRL | 13 | 13 | 100 | b | |
| None/v686 mut1 | 13 | 9 | 69 | a,b | |
| None/v686 mut2 | 12 | 12 | 100 | b | |
| HVT/JM/102W | 16 | 0 | 0 | a | |
| HVT/Md5 | 15 | 1 | 7 | a | |
| HVT/648A | 15 | 10 | 67 | b | |
| HVT/v686∆TRS-TRL | 16 | 2 | 13 | a,b | |
| HVT/v686 mut1 | 16 | 4 | 25 | a,b | |
| HVT/v686 mut2 | 16 | 3 | 19 | a,b | |
| HVT+SB1/JM/102W | 16 | 0 | 0 | a | |
| HVT+SB1/Md5 | 15 | 3 | 20 | a | |
| HVT+SB1/648A | 16 | 4 | 25 | a | |
| HVT+SB1/v686∆TRS-TRL | 16 | 2 | 13 | a | |
| HVT+SB1/v686 mut1 | 16 | 3 | 19 | a | |
| HVT+SB1/v686 mut2 | 16 | 2 | 13 | a |
| Non-Vaccinated | Vaccinated | Virulence by Weighted Mean | Pathotype | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus | # of Birds | # of MD | % of MD | # of Birds Vaccinated | % of Total MD | ||||
| HVT | HVT+SB1 | HVT | HVT+SB1 | ||||||
| JM/102W | 29 | 21 | 72 | 25 | 25 | 8 | 4 | 5 | |
| Md5 | 29 | 27 | 93 | 24 | 24 | 17 | 25 | 22 | |
| 648A | 27 | 27 | 100 | 24 | 25 | 75 | 40 | 52 | |
| v686∆TRS-TRL | 28 | 28 | 100 | 26 | 26 | 31 | 35 | 33 | vv or vv plus |
| v686 mut1 | 29 | 24 | 83 | 26 | 24 | 38 | 21 | 27 | vv |
| v686 mut2 | 28 | 28 | 100 | 25 | 22 | 28 | 23 | 24 | vv |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Hearn, C.J.; Mays, J.; Velez-Irizarry, D.; Reddy, S.M.; Spatz, S.J.; Cheng, H.H.; Dunn, J.R. Phenotypic Characterization of Recombinant Marek’s Disease Virus in Live Birds Validates Polymorphisms Associated with Virulence. Viruses 2023, 15, 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112263
Kim T, Hearn CJ, Mays J, Velez-Irizarry D, Reddy SM, Spatz SJ, Cheng HH, Dunn JR. Phenotypic Characterization of Recombinant Marek’s Disease Virus in Live Birds Validates Polymorphisms Associated with Virulence. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112263
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taejoong, Cari J. Hearn, Jody Mays, Deborah Velez-Irizarry, Sanjay M. Reddy, Stephen J. Spatz, Hans H. Cheng, and John R. Dunn. 2023. "Phenotypic Characterization of Recombinant Marek’s Disease Virus in Live Birds Validates Polymorphisms Associated with Virulence" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112263
APA StyleKim, T., Hearn, C. J., Mays, J., Velez-Irizarry, D., Reddy, S. M., Spatz, S. J., Cheng, H. H., & Dunn, J. R. (2023). Phenotypic Characterization of Recombinant Marek’s Disease Virus in Live Birds Validates Polymorphisms Associated with Virulence. Viruses, 15(11), 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112263






