Global Prevalence and Hemagglutinin Evolution of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2013 to 2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Compilation
2.2. Construction of the Phylogenetic Tree
2.3. The Estimation of the Time to the Most Recent Common Ancestor (tMRCA)
2.4. Prediction of N-Glycan Positions on the HA Protein of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses since 2019
2.5. Analysis of the Selection Pressure of H7N9 Viruses HA since 2019
3. Results
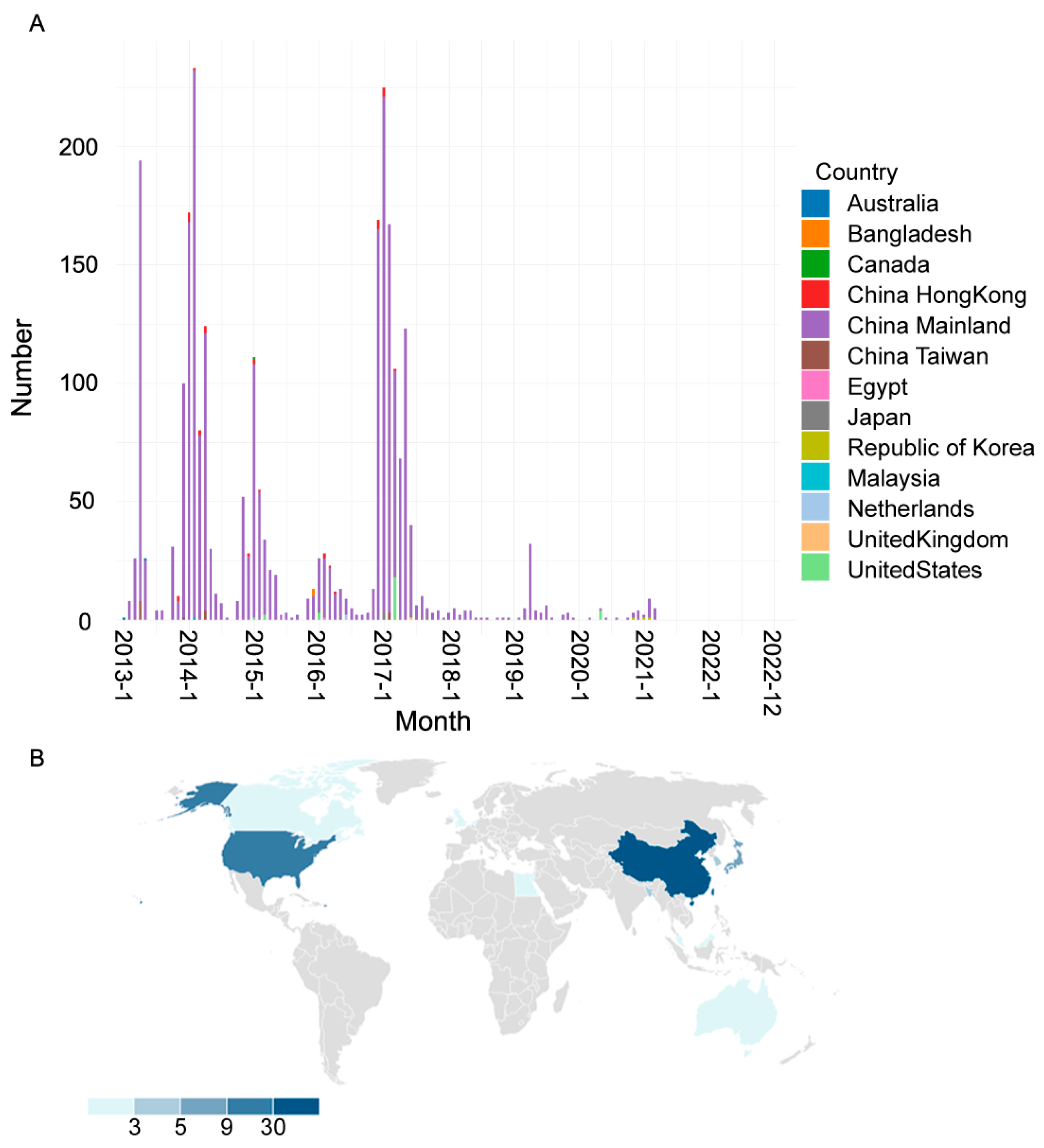
3.1. Global Prevalence of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of HA Genes of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses
3.3. Time to the Most Recent Common Ancestor (TMRCA)
3.4. Characteristics of Evolution, Prevalence and N-Glycans of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses after 2019
3.5. The Selection Pressure of H7N9 Viruses HA since 2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lam, T.T.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, B.; Duan, L.; Cheung, C.L.; Ma, C.; Lycett, S.J.; Leung, C.Y.; Chen, X.; et al. The Genesis and Source of the H7N9 Influenza Viruses Causing Human Infections in China. Nature 2013, 502, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cao, B.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, D.; Hu, W.; Chen, J.; Jie, Z.; Qiu, H.; Xu, K.; et al. Human Infection with a Novel Avian-Origin Influenza A (H7N9) Virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Jia, W.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Bi, Y.; Xie, S.; Li, B.; Hu, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, L.; et al. Emergence and Adaptation of a Novel Highly Pathogenic H7N9 Influenza Virus in Birds and Humans from a 2013 Human-Infecting Low-Pathogenic Ancestor. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00921-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, H. H7n9 Influenza Virus in China. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Pu, Z.; Luo, T.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Shen, X.; Irwin, D.M.; Murphy, R.W.; Liao, M.; Shen, Y. Evolutionary Dynamics of Avian Influenza N H7N9 Virus across Five Waves in Mainland China, 2013–2017. J. Infect. 2018, 77, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Gray, G.C.; Chen, J.M.; Ma, M.J. Will China’s H7n9 Control Strategy Continue to Be Effective? Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Deng, G.; Zeng, X.; Cui, P.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Pan, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; et al. Genetic and Biological Properties of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses Detected after Application of the H7N9 Poultry Vaccine in China. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xiang, G.; Zhu, W.; Lei, X.; Li, B.; Meng, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiao, H.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; et al. The Re-Emergence of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H7N9 Viruses in Humans in Mainland China, 2019. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.; Gilbert, M.; Cheng, M.C.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Joly, D. Historical Prevalence and Distribution of Avian Influenza Virus A(H7N9) among Wild Birds. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 19, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebarbenchon, C.; Pedersen, J.C.; Sreevatsan, S.; Ramey, A.M.; Dugan, V.G.; Halpin, R.A.; Ferro, P.J.; Lupiani, B.; Enomoto, S.; Poulson, R.L.; et al. H7N9 Influenza A Virus in Turkeys in Minnesota. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Torchetti, M.K.; Killian, M.L.; Berhane, Y.; Swayne, D.E. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Virus, Tennessee, USA, March 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1860–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belser, J.A.; Brock, N.; Sun, X.; Jones, J.; Zanders, N.; Hodges, E.; Pulit-Penaloza, J.A.; Wentworth, D.; Tumpey, T.M.; Davis, T.; et al. Mammalian Pathogenesis and Transmission of Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Viruses, Tennessee, USA, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.C.; Lee, M.S.; Ho, Y.H.; Chyi, W.L.; Wang, C.H. Avian Influenza Monitoring in Migrating Birds in Taiwan During 1998–2007. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Oem, J.-K. Genetic Characterization and Pathogenicity of H7N7 and H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses Isolated from South Korea. Viruses 2021, 13, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zeng, X.; Cui, P.; Yan, C.; Chen, H. Alarming Situation of Emerging H5 and H7 Avian Influenza and Effective Control Strategies. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2155072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Quirarte, H.O.; Lopez-Guerrero, D.V.; Gutierrez-Xicotencatl, L.; Esquivel-Guadarrama, F. Protective Antibodies against Influenza Proteins. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.A.; García-Sastre, A. Influenza A Viruses: New Research Developments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Nelson-Sathi, S.; Wang, Y.; Prasad, R.; Rayen, S.; Nandel, V.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Nair, R.; Dharmaseelan, S.; et al. Evolutionary, Genetic, Structural Characterization and Its Functional Implications for the Influenza A (H1N1) Infection Outbreak in India from 2009 to 2017. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Tan, T.J.C.; Wu, N.C.; Brooke, C.B. The Evolutionary Potential of Influenza a Virus Hemagglutinin Is Highly Constrained by Epistatic Interactions with Neuraminidase. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1363–1369.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, M.; Lavie, A. Ph-Dependent Mechanisms of Influenza Infection Mediated by Hemagglutinin. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 777095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; McCauley, J. Gisaid: Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data–From Vision to Reality. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, R.A.; Chen, Z. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (2nd ed.). Meas. Interdiscip. Res. Perspect. 2019, 17, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Qiu, Y.; Pu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ge, X.Y. Bioaider: An Efficient Tool for Viral Genome Analysis and Its Application in Tracing SARS-CoV-2 Transmission. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. Mafft: A Novel Method for Rapid Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. Mega11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagulenko, P.; Puller, V.; Neher, R.A. Treetime: Maximum-Likelihood Phylodynamic Analysis. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vex042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Brunak, S. Prediction of Glycosylation across the Human Proteome and the Correlation to Protein Function. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 7, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Hou, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Tian, Z. Increased Genetic Variation of A(H3N2) Virus from Influenza Surveillance at the End of the 2016/2017 Season for Shanghai Port, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Zhu, L.J. Trackviewer: A Bioconductor Package for Interactive and Integrative Visualization of Multi-Omics Data. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.; Shank, S.D.; Spielman, S.J.; Li, M.; Muse, S.V.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2.0: A Modern Web Application for Characterizing Selective and Other Evolutionary Processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Frost, S.D.W. Estimating Selection Pressures on Alignments of Coding Sequences. In The Phylogenetic Handbook: A Practical Approach to Phylogenetic Analysis and Hypothesis Testing, 2nd ed.; Vandamme, A.-M., Salemi, M., Lemey, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 419–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D.W. Not So Different after All: A Comparison of Methods for Detecting Amino Acid Sites under Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Detecting Individual Sites Subject to Episodic Diversifying Selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Scheffler, K. Fubar: A Fast, Unconstrained Bayesian Approximation for Inferring Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.J.D.; Bahl, J.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Zhang, J.; Poon, L.L.M.; Chen, H.; Webster, R.G.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Guan, Y. Dating the Emergence of Pandemic Influenza Viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11709–11712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlogeux, V.; Feng, L.; Tsang, T.K.; Jiang, H.; Fang, V.J.; Qin, Y.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Lau, E.H.Y.; et al. Evaluation of Animal-to-Human and Human-to-Human Transmission of Influenza A (H7N9) Virus in China, 2013–2015. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronski, D.M.; Chambers, C.; Gustafson, R.; Purych, D.B.; Tang, P.; Bastien, N.; Krajden, M.; Li, Y. Avian Influenza A(H7N9) Virus Infection in 2 Travelers Returning from China to Canada, January 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Gu, M.; Liu, D.; Cui, J.; Gao, G.F.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X. Epidemiology, Evolution, and Pathogenesis of H7N9 Influenza Viruses in Five Epidemic Waves since 2013 in China. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fen, J.; Liu, K.; Qin, T.; Chen, S.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. Characterization of an H7N9 Influenza Virus Isolated from Camels in Inner Mongolia, China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01798-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.C.; Wilson, I.A. Influenza Hemagglutinin Structures and Antibody Recognition. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a038778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, M.O.; Angel, M.; Košík, I.; Trovão, N.S.; Zost, S.J.; Gibbs, J.S.; Casalino, L.; Amaro, R.E.; Hensley, S.E.; Nelson, M.I.; et al. Human Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin Glycan Evolution Follows a Temporal Pattern to a Glycan Limit. mBio 2019, 10, e00204-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry Dunand, C.J.; Leon, P.E.; Huang, M.; Choi, A.; Chromikova, V.; Ho, I.Y.; Tan, G.S.; Cruz, J.; Hirsh, A.; Zheng, N.Y.; et al. Both Neutralizing and Non-Neutralizing Human H7N9 Influenza Vaccine-Induced Monoclonal Antibodies Confer Protection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jayaraman, A.; Maniprasad, P.; Raman, R.; Houser, K.V.; Pappas, C.; Zeng, H.; Sasisekharan, R.; Katz, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M. N-Linked Glycosylation of the Hemagglutinin Protein Influences Virulence and Antigenicity of the 1918 Pandemic and Seasonal H1N1 Influenza A Viruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8756–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.C.; Zost, S.J.; Thompson, A.J.; Oyen, D.; Nycholat, C.M.; McBride, R.; Paulson, J.C.; Hensley, S.E.; Wilson, I.A. A Structural Explanation for the Low Effectiveness of the Seasonal Influenza H3N2 Vaccine. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, M.A.; Zhang, R.; Walter, E.B.; Woods, C.W.; Ginsburg, G.S.; McClain, M.T.; Denny, T.N.; Chen, X.; Munshaw, S.; Marshall, D.J.; et al. H3n2 Influenza Infection Elicits More Cross-Reactive and Less Clonally Expanded Anti-Hemagglutinin Antibodies Than Influenza Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Carney, P.J.; Chang, J.C.; Guo, Z.; Stevens, J. Structural and Molecular Characterization of the Hemagglutinin from the Fifth-Epidemic-Wave A(H7N9) Influenza Viruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00375-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R.; Kurowski, B.; Johnson, A.E.; Hebert, D.N. N-Linked Glycans Direct the Cotranslational Folding Pathway of Influenza Hemagglutinin. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkoch, J.; Suwannakarn, K.; Payungporn, S.; Prachayangprecha, S.; Cheiocharnsin, T.; Linsuwanon, P.; Theamboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. Whole Genome Characterization, Phylogenetic and Genome Signature Analysis of Human Pandemic H1n1 Virus in Thailand, 2009–2012. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, U.; Chakrabarti, A.K.; Kanungo, S.; Dutta, S. Evolutionary Dynamics of Influenza A/H1N1 Virus Circulating in India from 2011 to 2021. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 110, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


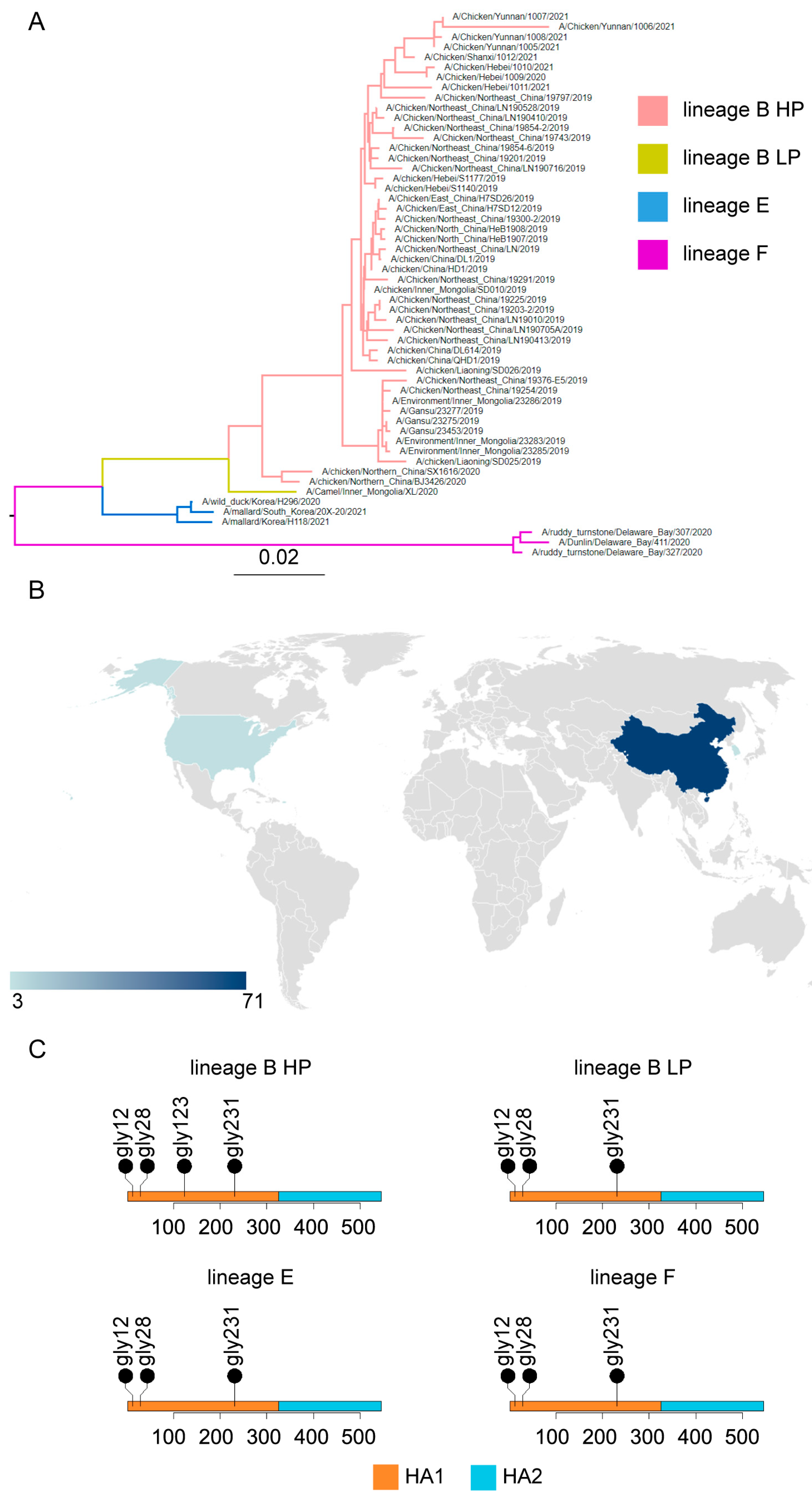

| Lineages | N-Glycan Positions on the HA Protein | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 28 | 123 | 231 | |
| Lineage B China HP | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Lineage B China LP | +++ | ++ | Null | ++ |
| Lineage E Korea | ++ | ++ | Null | ++ |
| Lineage F American | ++ | ++ | Null | ++ |
| Lineage | MEME | SLAC | Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| lineage B human | 0.306 | 0.325 | 0.316 |
| lineage B avian | 0.389 | 0.413 | 0.401 |
| lineage B environment | 0.490 | 0.507 | 0.499 |
| lineage E avian | 0.231 | 0.250 | 0.241 |
| lineage F avian | 0.216 | 0.230 | 0.223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zeng, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, G. Global Prevalence and Hemagglutinin Evolution of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2013 to 2022. Viruses 2023, 15, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112214
Liu Q, Zeng H, Wu X, Yang X, Wang G. Global Prevalence and Hemagglutinin Evolution of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2013 to 2022. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112214
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qianshuo, Haowen Zeng, Xinghui Wu, Xuelian Yang, and Guiqin Wang. 2023. "Global Prevalence and Hemagglutinin Evolution of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2013 to 2022" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112214
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zeng, H., Wu, X., Yang, X., & Wang, G. (2023). Global Prevalence and Hemagglutinin Evolution of H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2013 to 2022. Viruses, 15(11), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112214





