An Advanced Multiplex Real-Time Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Reliable Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Porcine Internal Positive Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.2. Construction of PEDV Reference Gene for mqRT-LAMP Assay
2.3. RT-PCR and qRT-PCR Assay
2.4. Primers and Assimilating Probes for PEDV N Gene and Internal Positive Control
2.5. Optimization of mqRT-LAMP Assay
2.6. Specificity and Sensitivity of mqRT-LAMP Assay
2.7. Precision of mqRT-LAMP
2.8. Clinical Evaluation of mqRT-LAMP
3. Results
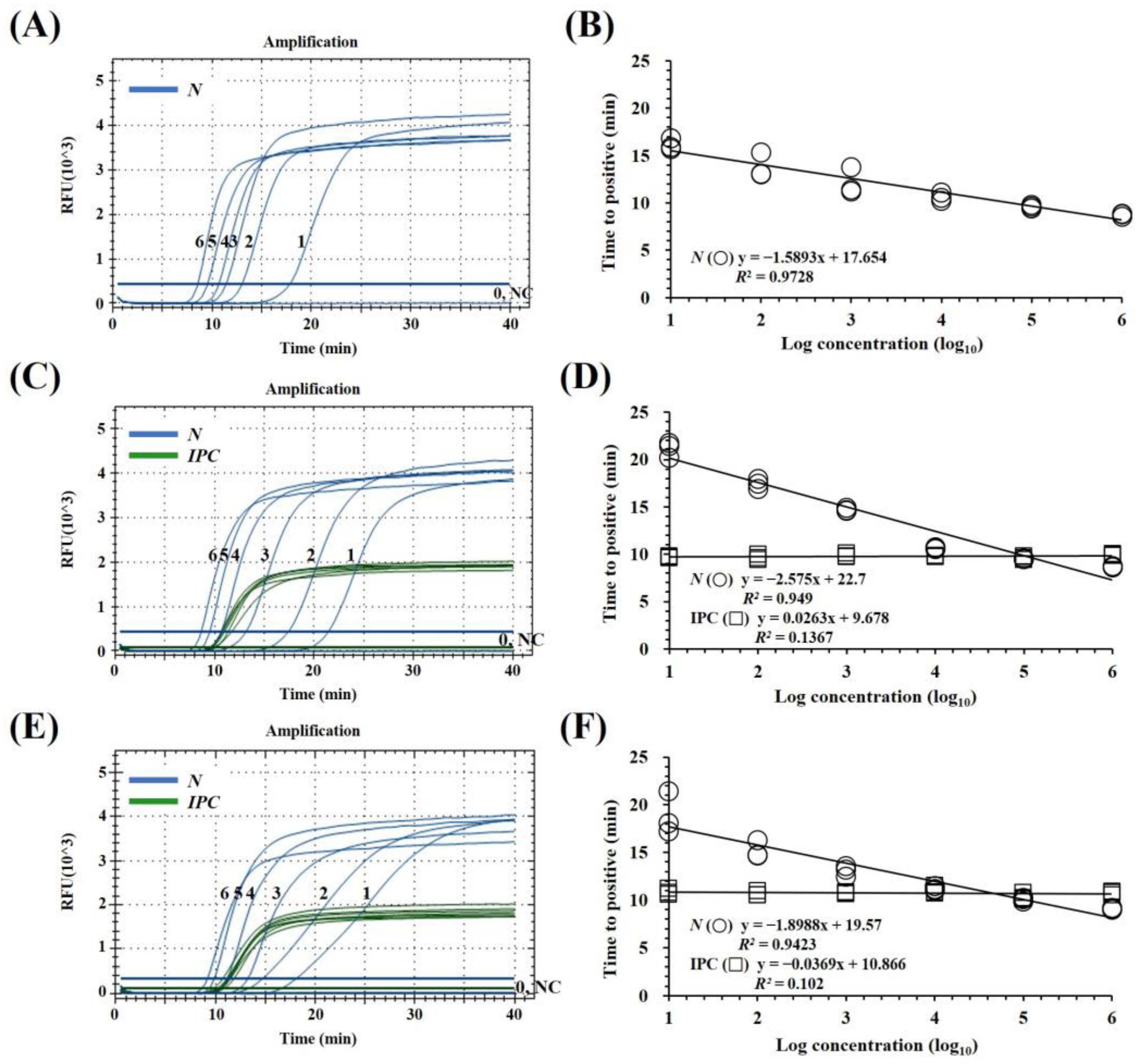
3.1. Optimization of the mqRT-LAMP Assay
3.2. Specificity of the mqRT-LAMP Assay
3.3. Sensitivity Comparison of mqRT-LAMP with RT-PCR and qRT-PCR Assay
3.4. Precision of mqRT-LAMP
3.5. Clinical Evaluation of mqRT-LAMP
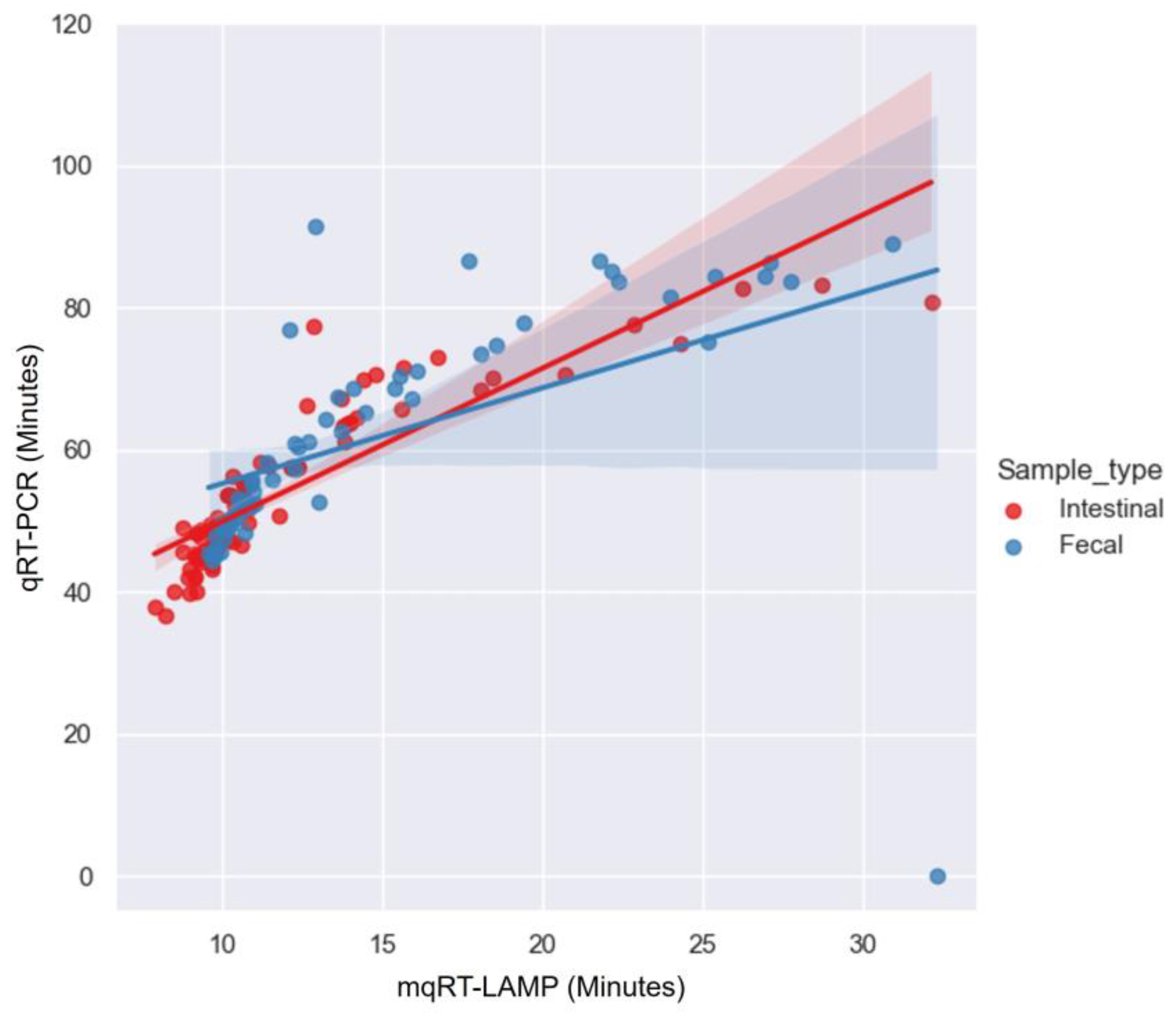
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Reaction Speed According to Clinical Evaluation Results of mqRT-LAMP and qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV): An update on etiology, transmission, pathogenesis, and prevention and control. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensaert, M.B.; Yeo, S.G. Porcine epidemic diarrhea. In Diseases of Swine, 9th ed.; Straw, B.E., Zimmerman, J.J., D’Allaire, S., Taylor, D.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: An emerging and re-emerging epizootic swine virus. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mole, B. Deadly pig virus slips through US borders. Nature 2013, 499, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, T.; Saif, L.J.; Marthaler, D.; Esseili, M.A.; Meulia, T.; Lin, C.M.; Vlasova, A.N.; Jung, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Cell culture isolation and sequence analysis of genetically diverse US porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains including a novel strain with a large deletion in the spike gene. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojkic, D.; Hazlett, M.; Fairles, J.; Marom, A.; Slavic, D.; Maxie, G.; Alexandersen, S.; Pasick, J.; Alsop, J.; Burlatschenko, S. The first case of porcine epidemic diarrhea in Canada. Can. Vet. J. 2015, 56, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, G.W.; Hoang, H.; Schwartz, K.J.; Burrough, E.R.; Sun, D.; Madson, D.; Cooper, V.L.; Pillatzki, A.; Gauger, P.; Schmitt, B.J.; et al. Emergence of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States: Clinical signs, lesions, and viral genomic sequences. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Marthaler, D.; Wang, Q.; Culhane, M.R.; Rossow, K.D.; Rovira, A.; Collins, J.; Saif, L.J. Distinct characteristics and complex evolution of PEDV strains, North America, May 2013–February 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C. Outbreak-related porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains similar to US strains, South Korea, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.N.; Chung, W.B.; Chang, S.W.; Wen, C.C.; Liu, H.; Chien, C.H.; Chiou, M.T. US-like strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus outbreaks in Taiwan, 2013–2014. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2014, 76, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diep, N.; Norimine, J.; Sueyoshi, M.; Lan, N.T.; Hirai, T.; Yamaguchi, R. US-like isolates of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus from Japanese outbreaks between 2013 and 2014. Springerplus 2015, 4, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antas, M.; Woźniakowski, G. Current status of porcine epidemic diarrhoea (PED) in European pigs. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.J.; Pyo, H.M.; Tark, D.S.; Song, J.Y.; Hyun, B.H. Multiplex real-time RT-PCR for the simultaneous detection and quantification of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 146, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Song, D.S.; Park, B.K. Differential detection of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus by duplex RT-PCR. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2001, 13, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.C.; Crawford, K.K.; Lager, K.M.; Kellner, S.G.; Brockmeier, S.L. Evaluation of two real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) to assess PEDV transmission in growing pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2016, 28, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.D.; Bai, J.; Jiang, P.; Tang, T.S.; Li, Y.; Tan, C.; Shi, X. Development of a multiplex TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR for discrimination of variant and classical porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 206, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, L.M.; Han, J.Q.; Sun, T.R.; Zhao, X.; Xu, R.T.; Song, Q.Y. A TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR to differentiate porcine epidemic diarrhea virus virulent strains from attenuated vaccine strains. Mol. Cell. Probes 2019, 45, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, R.; Kapoor, S.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, P. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA (LAMP): A new diagnostic tool lights the world of diagnosis of animal and human pathogens: A review. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 17, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.; Deng, J.; Wang, J.; Pei, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M.; Chen, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a vertical flow visualization strip. Mol. Cell. Probes 2015, 29, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.N.; Nguyen, V.D.; Yamazaki, W.; Okabayashi, T.; Mitoma, S.; Notsu, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yamaguchi, R.; Norimine, J.; Sekiguchi, S. Development of pooled testing system for porcine epidemic diarrhoea using real-time fluorescent reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, P. Development of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virus Genes 2011, 42, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.W.; Wu, S.Q.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, J.L.; Ge, J.; Chang, B.; Xu, T. Development of a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for visual detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2012, 11, 1897–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shi, L.; Lv, X.; Yao, W.; Cao, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, S. Development of a real-time reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kwon, N.Y.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.K.; Lee, C.; et al. A simple colorimetric detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay using hydroxynaphthol blue metal indicator. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 298, 114289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C., Jr. Simultaneous multiple target detection in real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biotechniques 2012, 53, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, R.; Jenkins, D. Real-time duplex applications of loop-mediated amplification (LAMP) by assimilating probes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4786–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Huang, S.; Liu, N.; Dong, D.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ma, W.; He, X.; Ao, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. Establishment of an accurate and fast detection method using molecular beacons in loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadkar, V.J.; Goldfarb, D.M.; Gantt, S.; Tilley, P.A. Real-time detection and monitoring of loop mediated amplification (LAMP) reaction using self-quenching and de-quenching fluorogenic probes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 8, 5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyan, D.C.; Swinson, K.L. A novel multiplex isothermal amplification method for rapid detection and identification of viruses. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, S.C.; Ramos, F.; Zé-Zé, L.; Alves, M.J.; Fagulha, T.; Duarte, M.; Henriques, M.; Luís, T.; Fevereiro, M. Simultaneous detection of West Nile and Japanese encephalitis virus RNA by duplex TaqMan RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, R.; Alvarez, A.M.; Su, W.W.; Jenkins, D.M. FRET-based assimilating probe for sequence-specific real-time monitoring of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Biol. Eng. Trans. 2011, 4, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Castaño, M.J.; Solera, J. Real-time PCR detection chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.M.; Kubota, R.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Higashiguchi, D. Handheld device for real-time, quantitative, LAMP-based detection of Salmonella enterica using assimilating probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen, L.D.; Neill, T.M.; Mahaffee, W.F. Development of a quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the field detection of Erysiphe necator. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiecien, R.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Blettner, M. Concordance analysis: Part 16 of a series on evaluation of scientific publications. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2011, 108, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi. Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liang, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, D.; He, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ni, J.; Zhao, K. Visual and rapid detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. Animals 2022, 12, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeders, S.; Huber, I.; Grohmann, L.; Berden, G.; Taverniers, I.; Mazzara, M.; Roosens, N.; Morisset, D. Guidelines for validation of qualitative real-time PCR methods. Trends. Food. Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.G.; Ku, B.K.; Nah, J.J.; Ryoo, S.; Wee, S.H.; Lee, C.; Lyoo, Y.S.; Park, C.K. Probe-based real-time reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RRT-LAMP) assay for rapid and specific detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kashina, A. Quantification of intracellular N-terminal β-actin arginylation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, F.; Quéguiner, S.; Gorin, S.; Deblanc, C.; Simon, G. Validation of commercial real-time RT-PCR kits for detection of influenza A viruses in porcine samples and differentiation of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus in pigs. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 171, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B. Development of a multiplex quantitative PCR for detecting porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, transmissible gastroenteritis virus, and porcine deltacoronavirus simultaneously in China. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Reilly, P.; Ryan, M.T.; Bahar, B.; Sweeney, T. The effects of laminarin derived from Laminaria digitata on measurements of gut health: Selected bacterial populations, intestinal fermentation, mucin gene expression and cytokine gene expression in the pig. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, T.; Pal, A.; Bag, P.K.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Nair, G.B.; Kurozano, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Shirai, H.; Takeda, T.; Uesaka, Y. Detection of cholera toxin gene in stool specimens by polymerase chain reaction: Comparison with bead enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and culture method for laboratory diagnosis of cholera. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 3068–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, R.; Matsui, S.M.; Baric, R.S.; Herrmann, J.E.; Blacklow, N.R.; Greenberg, H.B.; Sobsey, M.D. Detection of Norwalk virus in stool specimens by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and nonradioactive oligoprobes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, P.; Tangomo, M.; Hibbs, J.; Bonetti, E.J.; Boehme, C.C.; Notomi, T.; Perkins, M.D.; Schrenzel, J. Robustness of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction for diagnostic applications. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Kawana, T.; Fukushima, E.; Suzutani, T. Tolerance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to a culture medium and biological substances. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Assay | Primer and Probe | Sequence (5′-3′) | Target Gene | Genome Position a | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mqRT -LAMP | F3 | CTTCGAARGAACGTGACCT | PEDV N | 27,184–27,202 | [26] & this study |
| B3 | CAATGCTGCAACATTTGGT | 27,356–27,374 | |||
| LF | GCTATTTTCGCCCTTGGGA | 27,230–27,248 | |||
| LB | AGGTGTTGATGCSTCAGG | 27,314–27,331 | |||
| FIP (F1c + F2) | TGGGTCCGAAGCAAGCTG+ AGACATCCCAGAGTGGAGG | 27,253–27,270 + 27,206–27,224 | |||
| BIP (B1c + B2) | TTGGAGATGCGGAATTTGTCG+ AACTGGCGATCTGAGCATAG | 27,289–27,309 + 27,332–27,351 | |||
| PEDV-LF-F | FAM-ATAAGGTCCTCGCCGCTCAAGATAGGCAGA- GCTATTTTCGCCCTTGGGA | ||||
| Q | TCTGCCTATCTTGAGCGGCGAGGACCTTAT-BHQ1 | ||||
| EIPC-F3 | CATCCTGCGTCTGGACCT | Sus scrofa β-actin | 609–626 | This study | |
| EIPC-B3 | AGCTCTTCTCCAGGGAGG | 788–805 | |||
| EIPC-LF | CGCTCCGTCAGGATCTTCAT | 655–674 | |||
| EIPC-LB | CTACGTCGCCCTGGACTTC | 738–756 | |||
| EIPC-FIP (F1c + F2) | CCGTGGTGGTGAAGCTGTAGC+ GGACCTGACCGACTACCTC | 677–679 + 636–654 | |||
| EIPC-BIP (B1c + B2) | AGATCGTGCGGGACATCAAGG+ AGTGGCCATCTCCTGCTC | 707–727 + 757–774 | |||
| EIPC-LF-F | HEX-ATAAGGTCCTCGCCGCTCAAGATAGGCAGA- CGCTCCGTCAGGATCTTCAT | ||||
| Q | TCTGCCTATCTTGAGCGGCGAGGACCTTAT-BHQ1 | ||||
| RT- PCR | P1 | TTCCCAGCGTAGTTGAGATTG | PEDV N | 26,761–26,781 | [25] |
| P2 | CGAAGTGGCTCTGGATTTGTT | 27,168–27,188 | |||
| qRT- PCR | NF | CGCAAAGACTGAACCCACTAA | PEDV N | 26,684–26,704 | [13] modified |
| NR | TTGCCTCTGTTGTTACTTGGAGAT | 26,858–26,881 | |||
| NP-FAM | FAM–TGTTGCCATTRCCACGACTCCTGC–BHQ1 | 26,824–26,847 |
| Pathogen | Strain | Source a | Amplification of Target Gene (Tp) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDV N Gene (FAM) | EIPC b (HEX) | |||
| Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus | KNU141112-S DEL5/ORF3 | CVAS | 9.69 | − |
| Transmissible gastroenteritis virus | 175Lvac | APQA | − | 15.8 |
| Porcine delta coronavirus | KNU16-07 | IVBS | − | 16.6 |
| Porcine rotavirus | A1Va | IVBS | − | − |
| Porcine circovirus type 2 | PCK0201 | IVBS | − | 11.2 |
| Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus type 1 | Lelystad | APQA | − | − |
| Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus type 2 | LMY | APQA | − | − |
| Classical swine fever virus | LOM | APQA | − | 21.8 |
| Swine influenza virus | VDS1 | IVBS | − | − |
| Porcine parvovirus | NADL-2 | IVBS | − | 14 |
| Aujeszky’s disease virus | YS | IVBS | − | 12.7 |
| Non-infected pig fecal sample | − | IVBS | − | 13.7 |
| Non-infected pig intestinal sample | − | IVBS | − | 11.4 |
| PK-15 cell | − | IVBS | − | 10.9 |
| Vero cell | − | IVBS | − | − |
| Dilution (Copies/µL) | Intra-Assay Tp Value (min) | Inter-Assay Tp Value (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (106) | Medium (104) | Low (102) | High (106) | Medium (104) | Low (102) | |
| Mean | 8.73 | 10.47 | 15.04 | 9.09 | 11.20 | 17.45 |
| SD | 0.23 | 0.39 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.18 |
| CV (%) | 2.65 | 3.76 | 3.28 | 0.95 | 1.74 | 1.01 |
| Method | mqRT-LAMP Assay | Positive Rate | Overall Agreement (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative a | Total | ||||
| qRT-PCR | Positive | 142 | 0 | 142 | 76.8% | 99.5% |
| Negative | 1 | 42 | 43 | |||
| Total | 143 | 42 | 185 | |||
| RT-PCR | Positive | 129 | 0 | 129 | 69.7% | 92.4% |
| Negative | 14 | 42 | 56 | |||
| Total | 143 | 42 | 185 | |||
| Positive rate | 77.3% | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-R.; Kim, J.-M.; Baek, J.-S.; Park, J.; Kim, W.-I.; Ku, B.K.; Jeoung, H.-Y.; Lee, K.-K.; Park, C.-K. An Advanced Multiplex Real-Time Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Reliable Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Porcine Internal Positive Control. Viruses 2023, 15, 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112204
Kim H-R, Kim J-M, Baek J-S, Park J, Kim W-I, Ku BK, Jeoung H-Y, Lee K-K, Park C-K. An Advanced Multiplex Real-Time Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Reliable Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Porcine Internal Positive Control. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112204
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hye-Ryung, Jong-Min Kim, Ji-Su Baek, Jonghyun Park, Won-Il Kim, Bok Kyung Ku, Hye-Young Jeoung, Kyoung-Ki Lee, and Choi-Kyu Park. 2023. "An Advanced Multiplex Real-Time Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Reliable Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Porcine Internal Positive Control" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112204
APA StyleKim, H.-R., Kim, J.-M., Baek, J.-S., Park, J., Kim, W.-I., Ku, B. K., Jeoung, H.-Y., Lee, K.-K., & Park, C.-K. (2023). An Advanced Multiplex Real-Time Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Reliable Detection of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Porcine Internal Positive Control. Viruses, 15(11), 2204. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112204






