Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Application to ELISA-Based Detection Methods with Broad Specificity by Combined Use of Detector Antibodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Virus Amplification
2.3. Synthesis, Construction, and Expression of Biotin Peptide-6 × His-Tagged Coronavirus N Proteins
2.4. Mouse Immunization
2.5. Production of a Mouse mAb against the SARS-CoV-2 N Protein
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. ELISA for Titration and Isotyping of the Anti-SARS-CoV-2 N Protein mAb
2.8. Measurement of mAb Binding Affinity by ELISA
2.9. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 N Protein in the Culture Supernatants of Infected Cells Using an ELISA
3. Results
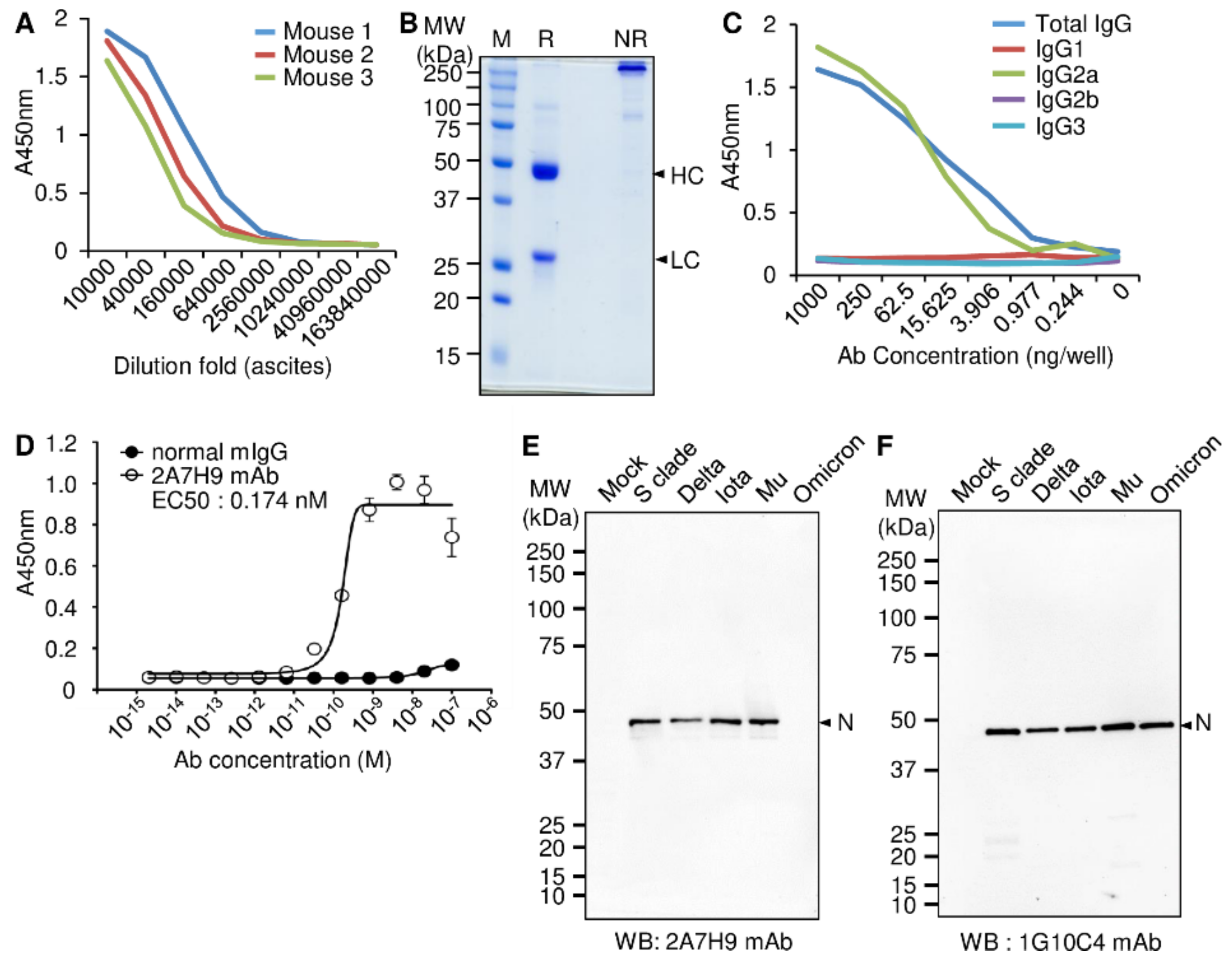
3.1. Production and Characterization of the Mouse mAb against the SARS-CoV-2 N Protein
3.2. Similarity of the Binding Affinity of the 2A7H9 and 1G10C4 mAbs to the SARS-CoV-2 N Protein
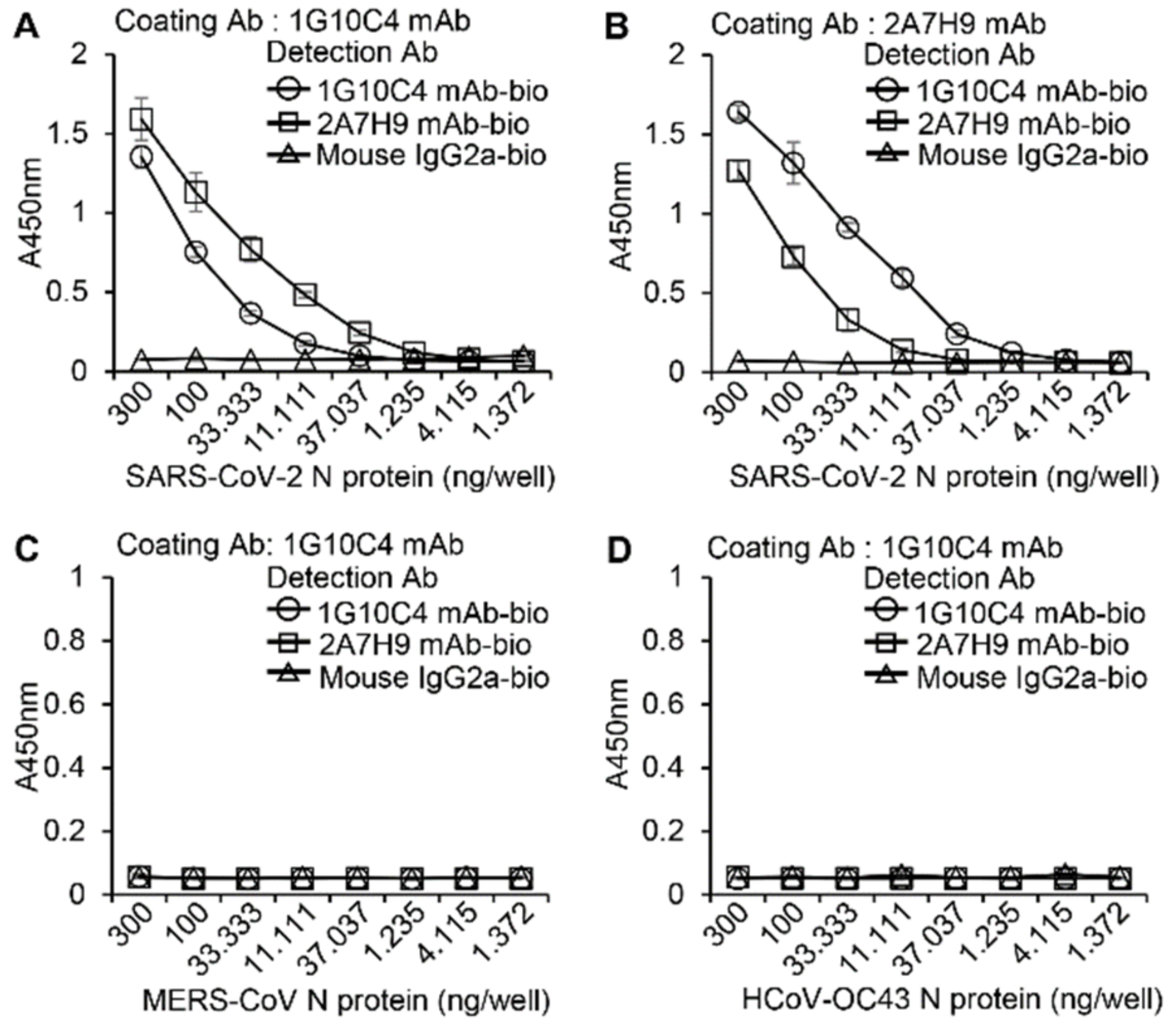
3.3. The 2A7H9 mAb Specifically Binds to the N Protein of SARS-CoV-2 but Not to That of MERS-CoV or HCoV-OC43
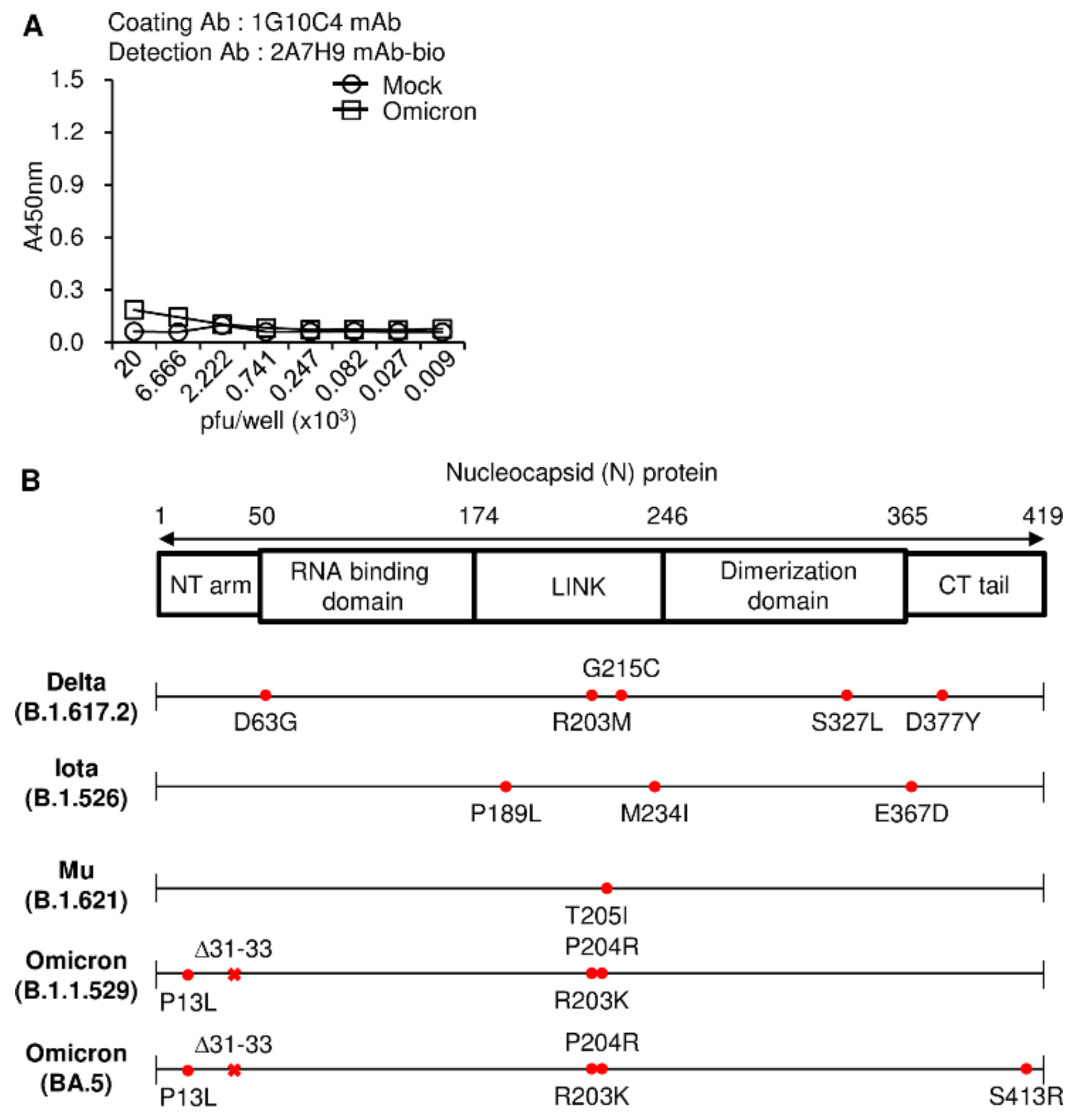
3.4. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 N Protein in the Lysates of SARS-CoV2 Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Berhanu, G.; Desalegn, C.; Kandi, V. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update. Cureus 2020, 12, e7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Lian, X.; Su, X.; Wu, W.; Marraro, G.A.; Zeng, Y. From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: A brief summary and comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three highly pathogenic human coronaviruses. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Mobarak, A.M.; Miguel, E.; Abaluck, J.; Ahuja, A.; Alsan, M.; Banerjee, A.; Breza, E.; Chandrasekhar, A.G.; Duflo, E.; Dzansi, J.; et al. End COVID-19 in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2022, 375, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.Y.; Cheung, P.P. Effectiveness of heterologous and homologous covid-19 vaccine regimens: Living systematic review with network meta-analysis. Br. Med. J. 2022, 377, e069989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic Dashboard. Available online: https://www.who.int/westernpacific/emergencies/covid-19/covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Farahani, M.; Niknam, Z.; Mohammadi Amirabad, L.; Amiri-Dashatan, N.; Koushki, M.; Nemati, M.; Danesh Pouya, F.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Rasmi, Y.; Tayebi, L. Molecular pathways involved in COVID-19 and potential pathway-based therapeutic targets. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Chemaitelly, H.; Butt, A.A.; National Study Group for COVID-19 Vaccination. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Gribben, C.; Bishop, J.; Hanlon, P.; Caldwell, D.; Wood, R.; Reid, M.; McMenamin, J.; Goldberg, D.; Stockton, D.; et al. Effect of Vaccination on Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Patel, K.J.; Ranjan, K. COVID-19: Unmasking Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Use of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detection Rapid Diagnostic Tests for COVID-19 Self-Testing. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Ag-RDTs-Self_testing-2022.1 (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Eshghifar, N.; Busheri, A.; Shrestha, R.; Beqaj, S. Evaluation of Analytical Performance of Seven Rapid Antigen Detection Kits for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raïch-Regué, D.; Muñoz-Basagoiti, J.; Perez-Zsolt, D.; Noguera-Julian, M.; Pradenas, E.; Riveira-Muñoz, E.; Giménez, N.; Carabaza, A.; Giménez, F.; Saludes, V.; et al. Performance of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Omicron and Other Variants of Concern. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 810576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, J.; Alston, J.J.; Incicco, J.J.; Singh, S.; Stuchell-Brereton, M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Vithani, N.; Griffith, D.; Wagoner, J.A.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Avti, P.; Shekhar, N.; Prajapat, M.; Sarma, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Kumar, S.; Kaur, H.; Prakash, A.; Medhi, B. Structural and conformational analysis of SARS CoV 2 N-CTD revealing monomeric and dimeric active sites during the RNA-binding and stabilization: Insights towards potential inhibitors for N-CTD. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zeng, R.; von Brunn, A.; Lei, J. Structural characterization of the C-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Mol. Biomed. 2020, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.N.; Chen, J.S.; Lin, S.M.; Hong, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Jeng, U.S.; Luo, S.Y.; Hou, M.H. Targeting the N-Terminus Domain of the Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Induces Abnormal Oligomerization via Allosteric Modulation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 871499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, B.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Pan, H.; Qiao, Y.; Suo, G.; Zhu, F. Development of Patient-Derived Human Monoclonal Antibodies Against Nucleocapsid Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Diagnosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 595970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Riedo, F.X.; Morishima, C.; Rawlings, S.; Smith, D.; Das, S.; Strich, J.R.; Chertow, D.S.; Davey, R.T., Jr.; Cohen, J.I. Detection of Nucleocapsid Antibody to SARS-CoV-2 is More Sensitive than Antibody to Spike Protein in COVID-19 Patients. J Infect Dis. 2020, 222, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, K.M.; Dowlatshahi, D.P.; Dai, J.; Becker, L.M.; Hensel, J.; Snowden, L.M.; Leveille, J.M.; Brunner, M.R.; Holden, K.W.; Hopkins, N.S. Heterogeneous antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain and nucleocapsid with implications for COVID-19 immunity. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Baek, K.; Kang, M.; Choi, J.K.; Maharjan, S.; Akauliya, M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Production of SARS-CoV-2 N Protein-Specific Monoclonal Antibody and Its Application in an ELISA-Based Detection System and Targeting the Interaction between the Spike C-Terminal Domain and N Protein. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 726231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Maharjan, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Park, J.A.; Park, B.K.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.J. MUC1-C influences cell survival in lung adenocarcinoma Calu-3 cells after SARS-CoV-2 infection. BMB Rep. 2021, 54, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.; Baek, K.; Bae, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, Y.; et al. MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 replication can be inhibited by targeting the interaction between the viral spike protein and the nucleocapsid protein. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3853–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, D.; Park, S.; Maharjan, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.K.; Akauliya, M.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.J. Differential Signaling and Virus Production in Calu-3 Cells and Vero Cells upon SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.; Baek, K.; Kang, M.; An, S.; Gong, J.; Park, S.; Kandeel, M.; et al. Abiraterone Acetate Attenuates SARS-CoV-2 Replication by Interfering with the Structural Nucleocapsid Protein. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Maharjan, S.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Baek, K.; Kim, S.; Suh, J.G.; Lee, Y.; et al. Differential effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on stress granule formation in Vero and Calu-3 cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 997539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Park, S.; Kang, M.; Baek, K.; Choi, J.K.; Maharjan, S.; Akauliya, M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Targeting the Interaction Between Spike Protein and Nucleocapsid Protein for Suppression and Detection of Human Coronavirus OC43. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushell, K.M.; Söllner, C.; Schuster-Boeckler, B.; Bateman, A.; Wright, G.J. Large-scale screening for novel low-affinity extracellular protein interactions. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Kim, D.; Park, B.K.; Park, S.; Ha, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Gautam, A.; Kim, J.N.; Lee, S.I.; Park, H.B.; et al. Anti-metastatic effect of the TM4SF5-specific peptide vaccine and humanized monoclonal antibody on colon cancer in a mouse lung metastasis model. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79170–79186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kwon, S.; Rhee, J.W.; Kim, K.D.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, C.S.; Choi, M.J.; Suh, J.G.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, Y.; et al. Production of antibodies with peptide-CpG-DNA-liposome complex without carriers. BMC Immunol. 2011, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.N.; Park, S.; Maharjan, S.; Koh, H.; Moon, K.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.J. A Mucin1 C-terminal Subunit-directed Monoclonal Antibody Targets Overexpressed Mucin1 in Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2018, 8, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Lee, S.I.; Bae, J.Y.; Park, M.S.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.J. Production of a Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the M Protein of MERS-CoV for Detection of MERS-CoV Using a Synthetic Peptide Epitope Formulated with a CpG-DNA-Liposome Complex. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancolella, M.; Colona, V.L.; Mehrian-Shai, R.; Watt, J.L.; Luzzatto, L.; Novelli, G.; Reichardt, J.K.V. COVID-19 2022 update: Transition of the pandemic to the endemic phase. Hum. Genom. 2022, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Chouhan, R.S.; Shahdeo, D.; Shrikrishna, N.S.; Kesarwani, V.; Horvat, M.; Gandhi, S. A Recent Update on Advanced Molecular Diagnostic Techniques for COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 32756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, M.J.; Parker, R.; Larremore, D.B. Rethinking Covid-19 Test Sensitivity—A Strategy for Containment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antigen-Detection in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Using Rapid Immunoassays: Interim guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/antigen-detection-in-the-diagnosis-of-sars-cov-2infection-using-rapid-immunoassays (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Llibre, J.M.; Videla, S.; Clotet, B.; Revollo, B. Screening for SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Before a Live Indoor Music Concert: An Observational Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1487–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubas-Atienzar, A.I.; Kontogianni, K.; Edwards, T.; Wooding, D.; Buist, K.; Thompson, C.R.; Williams, C.T.; Patterson, E.I.; Hughes, G.L.; Baldwin, L.; et al. Limit of detection in different matrices of 19 commercially available rapid antigen tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baro, B.; Rodo, P.; Ouchi, D.; Bordoy, A.E.; Saya Amaro, E.N.; Salsench, S.V.; Molinos, S.; Alemany, A.; Ubals, M.; Corbacho-Monné, M.; et al. Performance characteristics of five antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test (Ag-RDT) for SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic infection: A head-to-head benchmark comparison. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, A.U.; Bolukcu, S.; Ciragil, P.; Topkaya, A.E. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses after third CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccine following two-dose CoronaVac vaccine regimen. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, L.; Perchetti, G.A.; Phung, Q.; Lin, M.J.; Mills, M.G.; Roychoudhury, P.; Harmon, K.G.; Reed, J.C.; Greninger, A.L. A SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Variant that Affects Antigen Test Performance. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 141, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.G. Rapid Biosensor of SARS-CoV-2 Using Specific Monoclonal Antibodies Recognizing Conserved Nucleocapsid Protein Epitopes. Viruses 2022, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.M.; Ko, S.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Lin, H.T.; Wu, H.C. Monoclonal Antibodies against Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants for Detection of COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Ding, H.; Ding, J.; Xue, Y.; Lu, S.; Lv, H. Preparation of highly specific monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and the preliminary development of antigen detection test strips. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Baek, K.; Kim, M.; Kang, B.M.; Maharjan, S.; Park, S.; Choi, J.-K.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Application to ELISA-Based Detection Methods with Broad Specificity by Combined Use of Detector Antibodies. Viruses 2023, 15, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010028
Kim J, Kim D, Baek K, Kim M, Kang BM, Maharjan S, Park S, Choi J-K, Kim S, Kim YK, et al. Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Application to ELISA-Based Detection Methods with Broad Specificity by Combined Use of Detector Antibodies. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jinsoo, Dongbum Kim, Kyeongbin Baek, Minyoung Kim, Bo Min Kang, Sony Maharjan, Sangkyu Park, Jun-Kyu Choi, Suyeon Kim, Yong Kyun Kim, and et al. 2023. "Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Application to ELISA-Based Detection Methods with Broad Specificity by Combined Use of Detector Antibodies" Viruses 15, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010028
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, D., Baek, K., Kim, M., Kang, B. M., Maharjan, S., Park, S., Choi, J.-K., Kim, S., Kim, Y. K., Park, M.-S., Lee, Y., & Kwon, H.-J. (2023). Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Application to ELISA-Based Detection Methods with Broad Specificity by Combined Use of Detector Antibodies. Viruses, 15(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010028





