Mouse Adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Viral Infection Induces Neuroinflammation in Standard Laboratory Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and Ethics Statement
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Infection
2.3. Gene Expression
2.4. Histology
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 Immunofluorescence
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (MA10) Infection on Subgenomic N (Sgm-N) Viral Load in Laboratory Mice
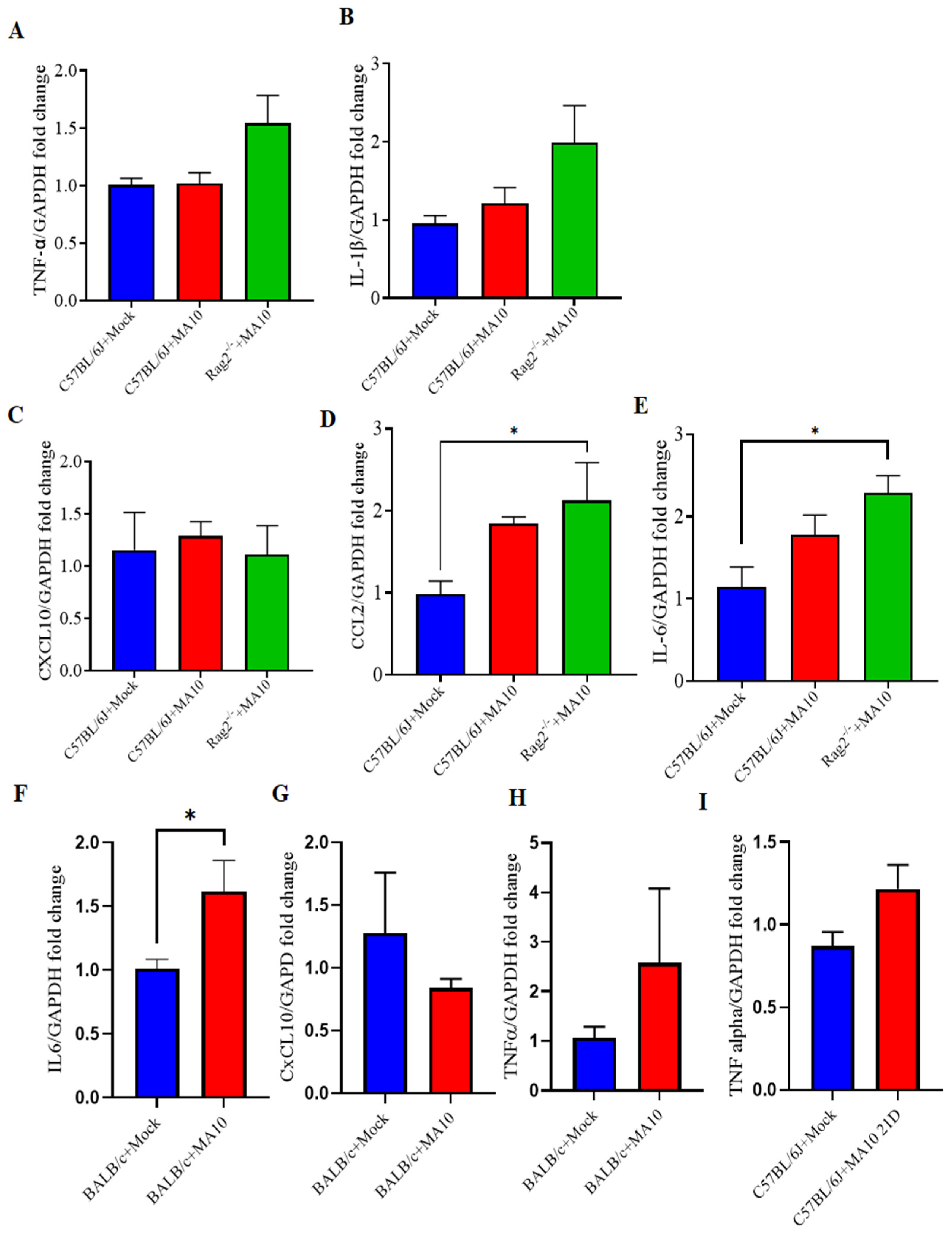
3.2. Cytokine and Chemokine Responses in the Brains of Mouse Adapted Strain of SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Infected Laboratory Mice
3.3. Claudin-5 mRNA Expression Is Decreased, and GFAP Expression Increased in the Brains of Mouse Adapted Strain of SARS-CoV2 (MA10) Infected Mice
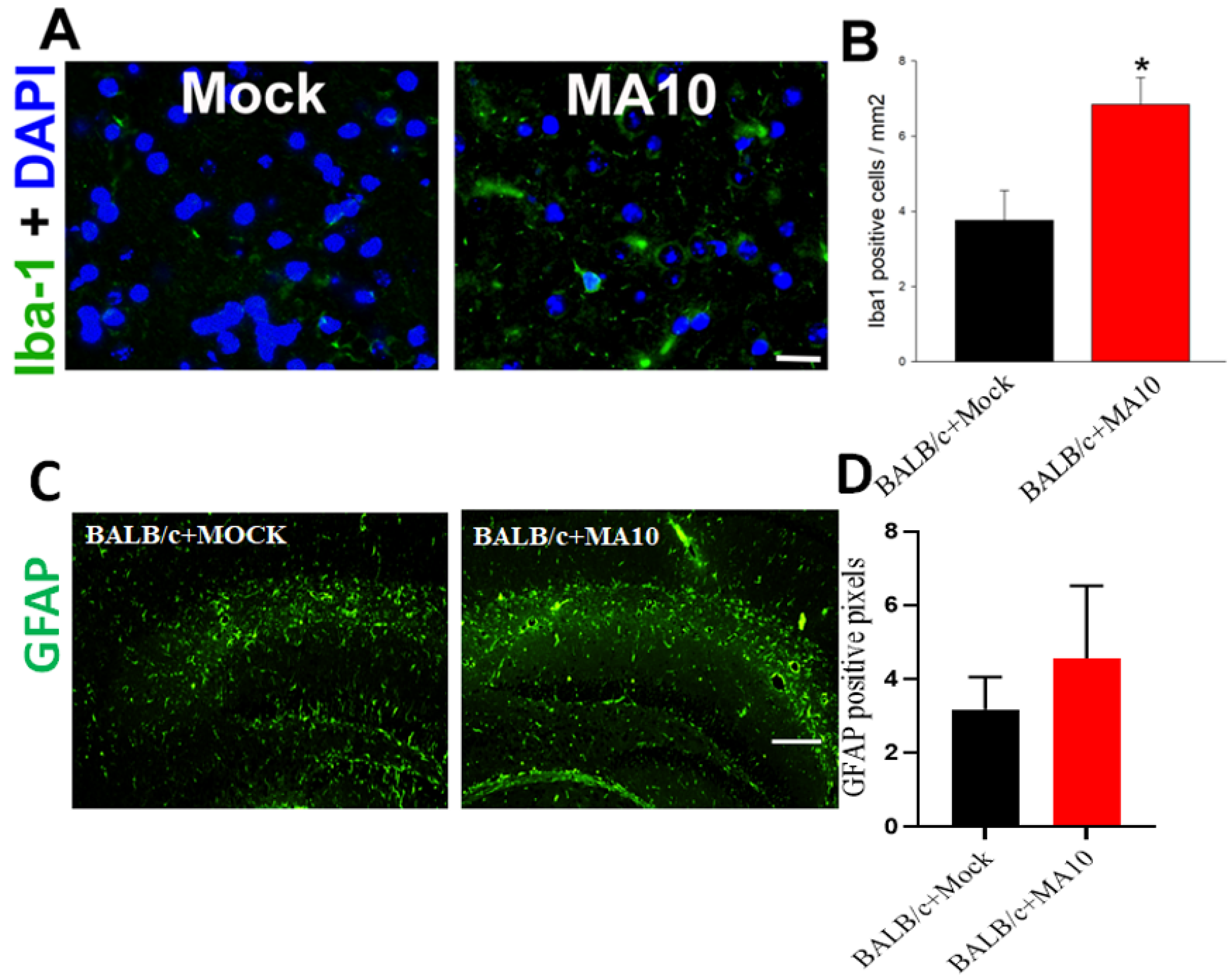
3.4. SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Infection Significantly Increases Iba-1 Positive Microglial Cells in Cortical Region of Brain of 1-Year Old Female BALB/c Mice
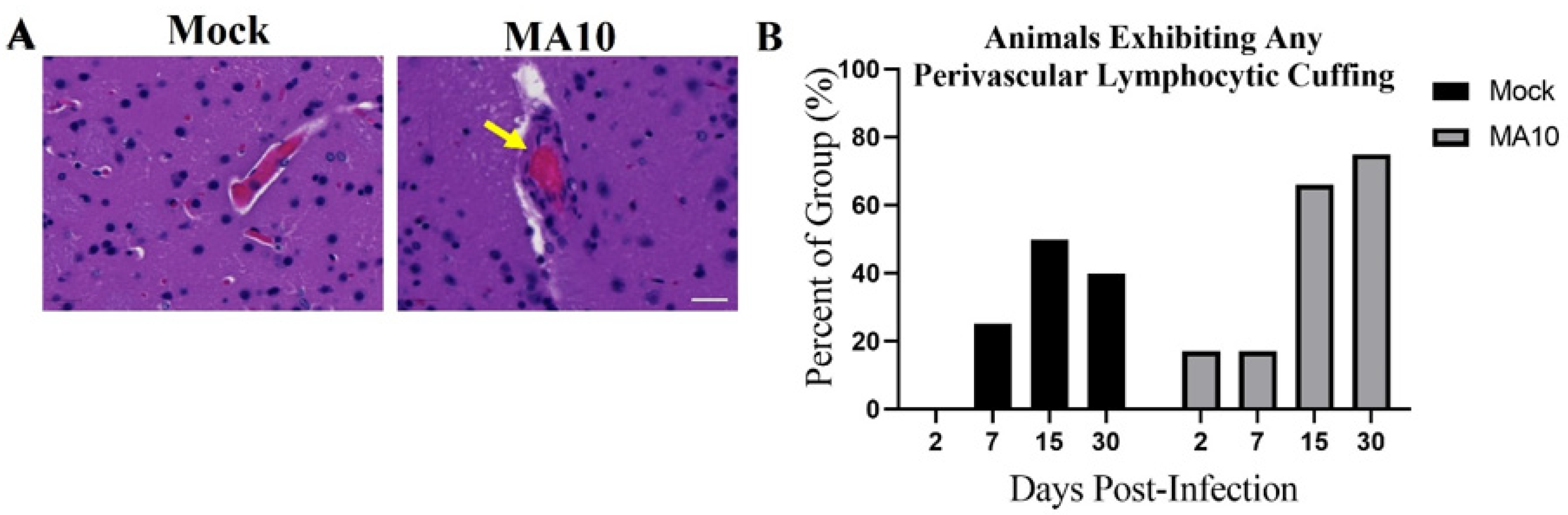
3.5. SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Infection Increases Perivascular Lymphocyte Cuffing in Brains of 1-Year-Old Female BALB/c
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amruta, N.; Chastain, W.H.; Paz, M.; Solch, R.J.; Murray-Brown, I.C.; Befeler, J.B.; Gressett, T.E.; Longo, M.T.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Bix, G. SARS-CoV-2 mediated neuroinflammation and the impact of COVID-19 in neurological disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Patidar, R.; Younis, K.; Desai, P.; Hosein, Z.; Padda, I.; Mangat, J.; Altaf, M. Comorbidity and its Impact on Patients with COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Soung, A.; Sissoko, C.; Nordvig, A.; Canoll, P.; Mariani, M.; Jiang, X.; Bricker, T.; Goldman, J.; Rosoklija, G.; et al. COVID-19 induces neuroinflammation and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Davis, P.B.; Gurney, M.E.; Xu, R. COVID-19 and dementia: Analyses of risk, disparity, and outcomes from electronic health records in the US. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, C. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Wong, A.H.M.; Rini, J.M.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Axonal Transport Enables Neuron-to-Neuron Propagation of Human Coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00404-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhardt, J.; Radke, J.; Dittmayer, C.; Franz, J.; Thomas, C.; Mothes, R.; Laue, M.; Schneider, J.; Brunink, S.; Greuel, S.; et al. Olfactory transmucosal SARS-CoV-2 invasion as a port of central nervous system entry in individuals with COVID-19. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleau, C.; Filliol, A.; Samson, M.; Lamontagne, L. Brain Invasion by Mouse Hepatitis Virus Depends on Impairment of Tight Junctions and Beta Interferon Production in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9896–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, M.; Bartok, E.; Zillinger, T.; Hartmann, G.; Behrendt, R. Animal models of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 for the development of prophylactic and therapeutic interventions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 228, 107931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.H.; Chen, Q.; Gu, H.J.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.X.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Zhang, N.N.; Li, X.F.; Xiong, R.; et al. A Mouse Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 124–133.e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, F.; Blair, R.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Mudd, J.; Currey, J.M.; Iwanaga, N.; He, J.; Mi, R.; et al. Endothelial cell infection and dysfunction, immune activation in severe COVID-19. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8076–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.H.; Lam, B.; Kung, Y.J.; Lin, J.; Liu, L.; Tsai, Y.C.; Ferrall, L.; Roden, R.B.S.; Wu, T.C.; Hung, C.F. A novel pseudovirus-based mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection to test COVID-19 interventions. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.O.; Case, J.B.; Winkler, E.S.; Thackray, L.B.; Kafai, N.M.; Bailey, A.L.; McCune, B.T.; Fox, J.M.; Chen, R.E.; Alsoussi, W.B.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Infection Model in Mice Demonstrates Protection by Neutralizing Antibodies. Cell 2020, 182, 744–753.e744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldera-Crespo, L.A.; Paidas, M.J.; Roy, S.; Schulman, C.I.; Kenyon, N.S.; Daunert, S.; Jayakumar, A.R. Experimental Models of COVID-19. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 792584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leist, S.R.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Schafer, A.; Tse, L.V.; Okuda, K.; Hou, Y.J.; West, A.; Edwards, C.E.; Sanders, W.; Fritch, E.J.; et al. A Mouse-Adapted SARS-CoV-2 Induces Acute Lung Injury and Mortality in Standard Laboratory Mice. Cell 2020, 183, 1070–1085.e1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.; He, L.; Fan, H.; Deng, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, Y.; et al. Adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 in BALB/c mice for testing vaccine efficacy. Science 2020, 369, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, Y.; Rathbun, G.; Lam, K.P.; Oltz, E.M.; Stewart, V.; Mendelsohn, M.; Charron, J.; Datta, M.; Young, F.; Stall, A.M.; et al. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell 1992, 68, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, J.M.; Rabito, F.; Maness, N.J.; Blair, R.V.; Rappaport, J.; Qin, X.; Kolls, J.K.; Srivastava, A.K. C57BL/6J Mice Are Not Suitable for Modeling Severe SARS-CoV-2 Beta and Gamma Variant Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amruta, N.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Murray-Brown, I.C.; Gressett, T.E.; Biose, I.J.; Chastain, W.H.; Befeler, J.B.; Bix, G. In Vivo protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection by ATN-161 in k18-hACE2 transgenic mice. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Blair, R.V.; Iwanaga, N.; Liu, F.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.E.; Qin, Z.; Midkiff, C.C.; Golden, N.A.; Doyle-Meyers, L.A.; Kabir, M.E.; et al. Lung Expression of Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Sensitizes the Mouse to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, C.D. The blessings and curses of C57BL/6 substrains in mouse genetic studies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1245, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Leist, S.R.; Schafer, A.; Edwards, C.E.; Martinez, D.R.; Montgomery, S.A.; West, A.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Hou, Y.J.; Adams, L.E.; et al. A mouse-adapted model of SARS-CoV-2 to test COVID-19 countermeasures. Nature 2020, 586, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinnon, K.H.; Leist, S.R.; Okuda, K.; Dang, H.; Fritch, E.J.; Gully, K.L.; De la Cruz, G.; Evangelista, M.D.; Asakura, T.; Gilmore, R.C.; et al. A model of persistent post SARS-CoV-2 induced lung disease for target identification and testing of therapeutic strategies. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.W.; Roth, S.J.; Luther, E.; Rose, S.S.; Springer, T.A. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3652–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Rothan, H.A.; Natekar, J.P.; Stone, S.; Pathak, H.; Strate, P.G.; Arora, K.; Brinton, M.A.; Kumar, M. Neuroinvasion and Encephalitis Following Intranasal Inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 in K18-hACE2 Mice. Viruses 2021, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carossino, M.; Montanaro, P.; O’Connell, A.; Kenney, D.; Gertje, H.; Grosz, K.; Ericsson, M.; Huber, B.R.; Subramaniam, S.; Kirkland, T.A.; et al. Fatal neuroinvasion and SARS-CoV-2 tropism in K18-hACE2 mice is partially independent on hACE2 expression. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Zhang, C.; Israelow, B.; Lu-Culligan, A.; Prado, A.V.; Skriabine, S.; Lu, P.; Weizman, O.E.; Liu, F.; Dai, Y.; et al. Neuroinvasion of SARS-CoV-2 in human and mouse brain. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20202135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.; Jung, S.M.; Shih, S.R.; Kuo, T.T.; Shieh, W.J.; Zaki, S.; Lin, T.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Ning, H.C.; Yen, D.C. Acute encephalomyelitis during an outbreak of enterovirus type 71 infection in Taiwan: Report of an autopsy case with pathologic, immunofluorescence, and molecular studies. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, C.J.; Quinnell, M.; Lindsay, R.; DeLay, J.; Barker, I.K. Paraparesis in a polar bear (Ursus maritimus) associated with West Nile virus infection. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2009, 40, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Fan, D.; Chen, S.; Guan, Y.; Li, T.; An, J.; Luan, G. Detection of EBV and HHV6 in the Brain Tissue of Patients with Rasmussen’s Encephalitis. Virol. Sin. 2018, 33, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkai, I.; Mayer, M.G.; Hellmers, L.M.; Ning, B.; Huang, Z.; Monjure, C.J.; Coyne, C.; Silvestri, R.; Golden, N.; Hensley, K.; et al. Neuropathology and virus in brain of SARS-CoV-2 infected non-human primates. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufer, C.; Schreiber, C.S.; Hartke, A.S.; Denden, I.; Stanelle-Bertram, S.; Beck, S.; Kouassi, N.M.; Beythien, G.; Becker, K.; Schreiner, T.; et al. Microgliosis and neuronal proteinopathy in brain persist beyond viral clearance in SARS-CoV-2 hamster model. eBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amruta, N.; Ismael, S.; Leist, S.R.; Gressett, T.E.; Srivastava, A.; Dinnon, K.H., III; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Maness, N.J.; Qin, X.; Kolls, J.K.; et al. Mouse Adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Viral Infection Induces Neuroinflammation in Standard Laboratory Mice. Viruses 2023, 15, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010114
Amruta N, Ismael S, Leist SR, Gressett TE, Srivastava A, Dinnon KH III, Engler-Chiurazzi EB, Maness NJ, Qin X, Kolls JK, et al. Mouse Adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Viral Infection Induces Neuroinflammation in Standard Laboratory Mice. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmruta, Narayanappa, Saifudeen Ismael, Sarah R. Leist, Timothy E. Gressett, Akhilesh Srivastava, Kenneth H. Dinnon, III, Elizabeth B. Engler-Chiurazzi, Nicholas J. Maness, Xuebin Qin, Jay K. Kolls, and et al. 2023. "Mouse Adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Viral Infection Induces Neuroinflammation in Standard Laboratory Mice" Viruses 15, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010114
APA StyleAmruta, N., Ismael, S., Leist, S. R., Gressett, T. E., Srivastava, A., Dinnon, K. H., III, Engler-Chiurazzi, E. B., Maness, N. J., Qin, X., Kolls, J. K., Baric, R. S., & Bix, G. (2023). Mouse Adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA10) Viral Infection Induces Neuroinflammation in Standard Laboratory Mice. Viruses, 15(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010114





