Effect of IL-10 Deficiency on TGFβ Expression during Fatal Alphavirus Encephalomyelitis in C57Bl/6 Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Infection of Mice and Tissue Collection
2.2. mRNA and Protein Analyses
2.3. Mononuclear Cell Isolation
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
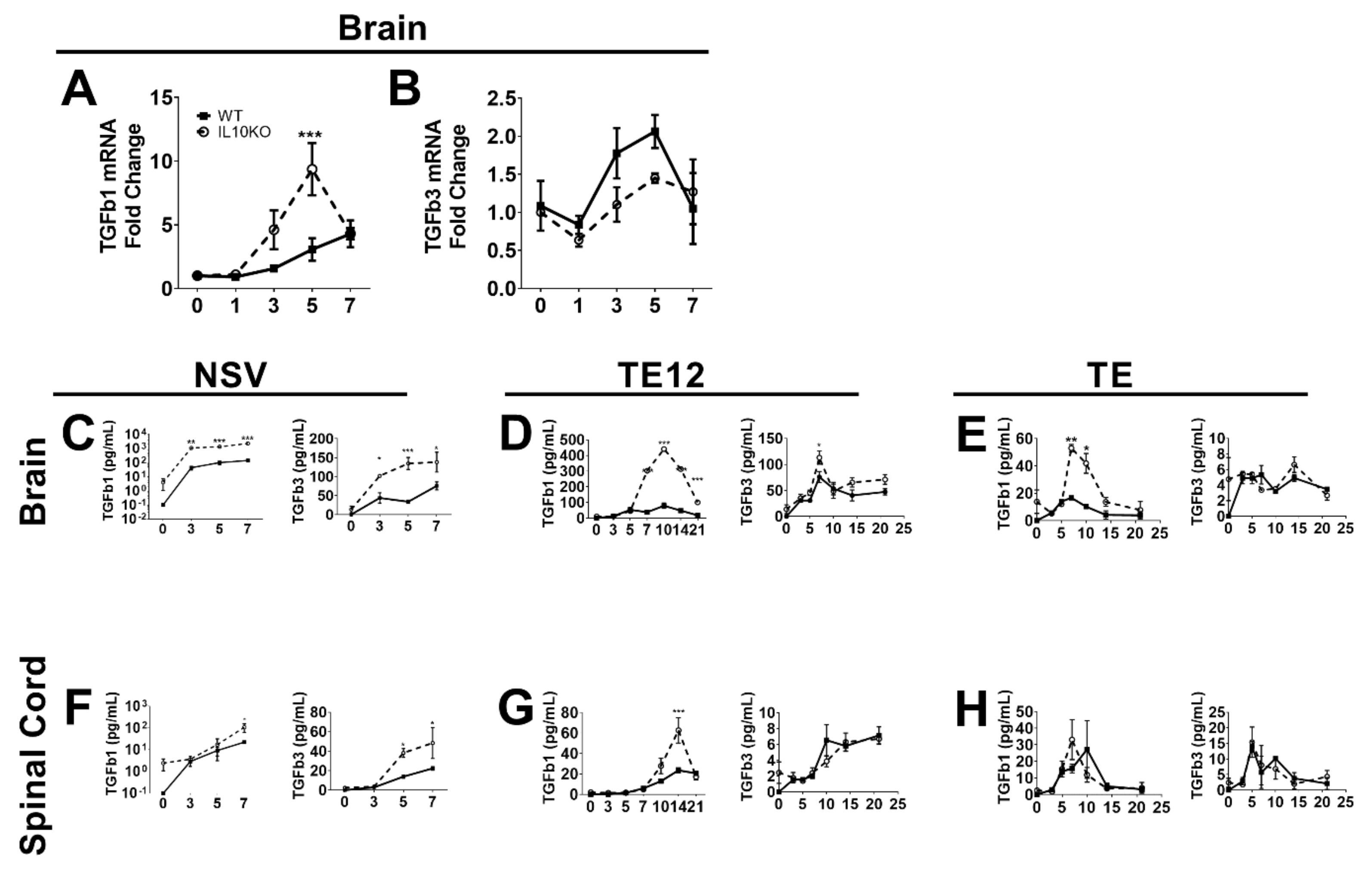
3.1. CNS Expression of TGFb after SINV Infection
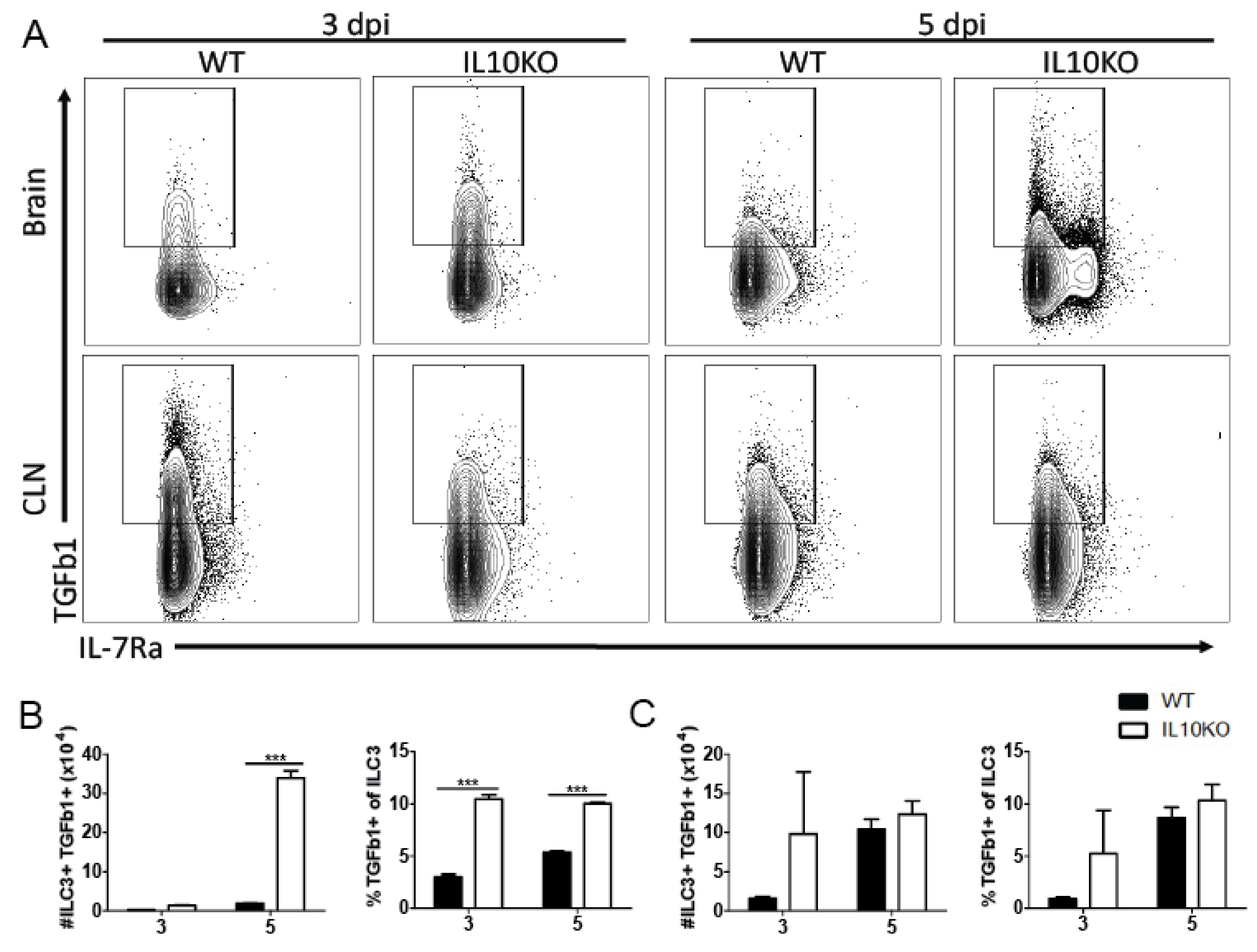
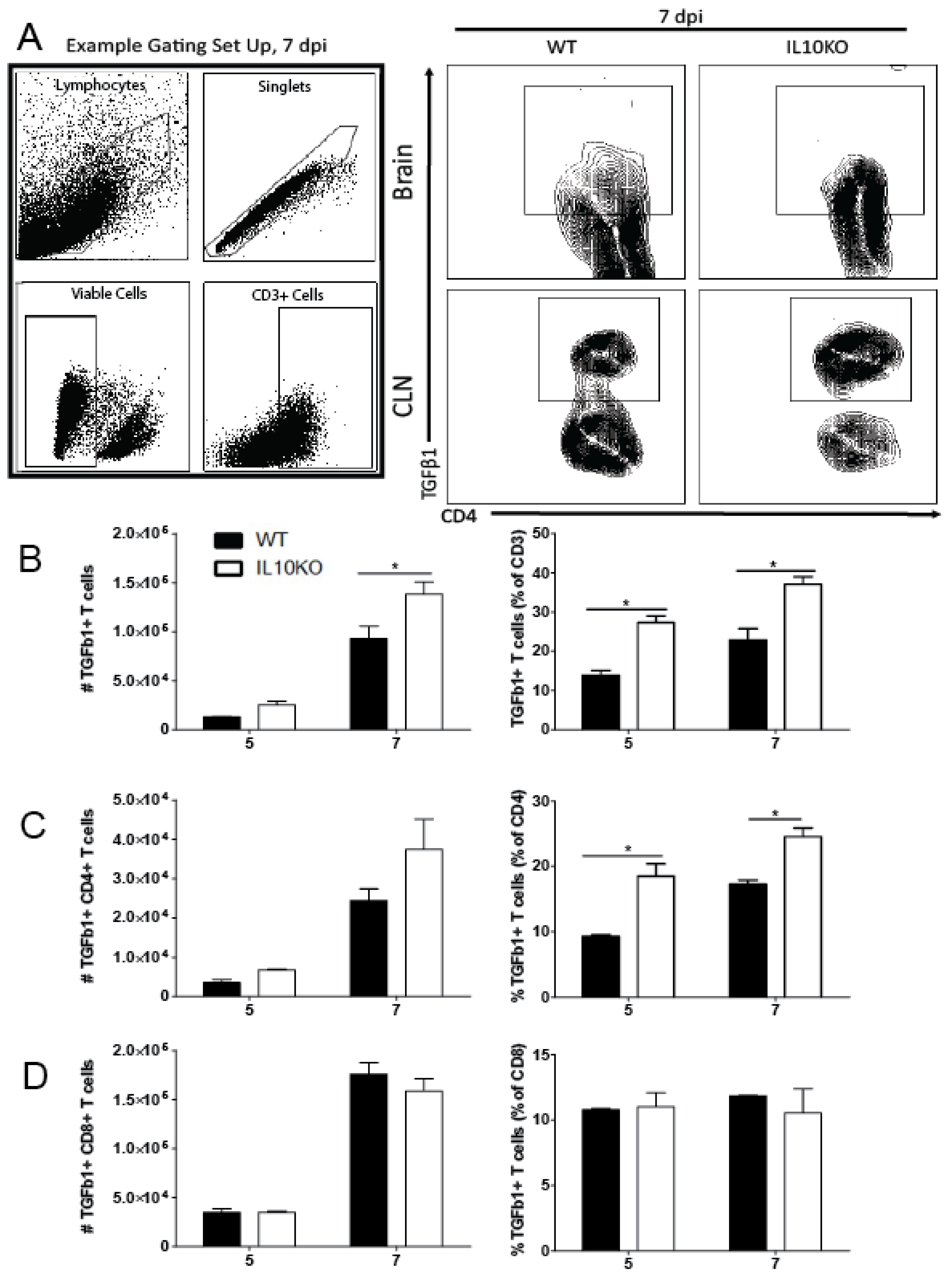
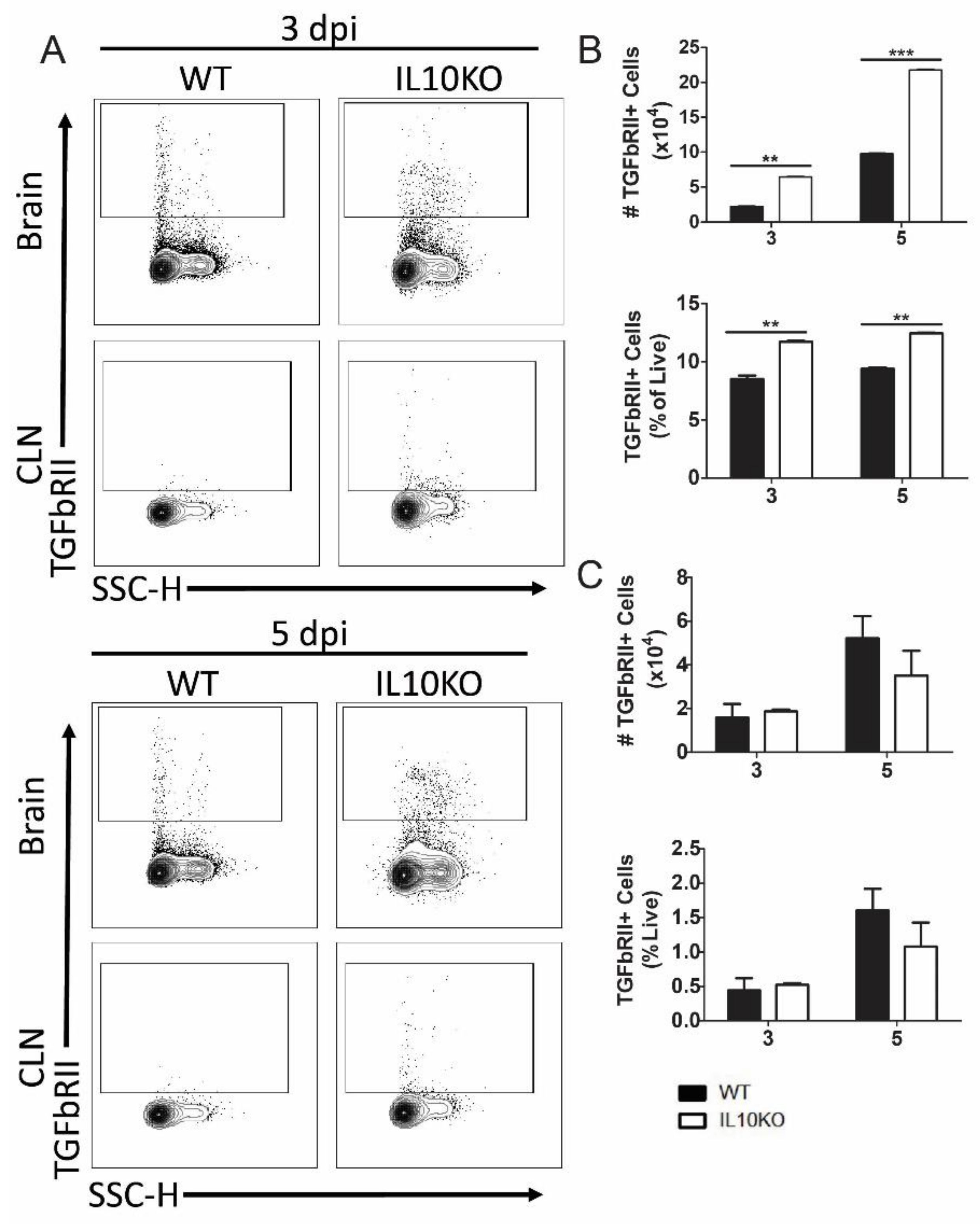
3.2. Cellular Sources of Increased TGFβ
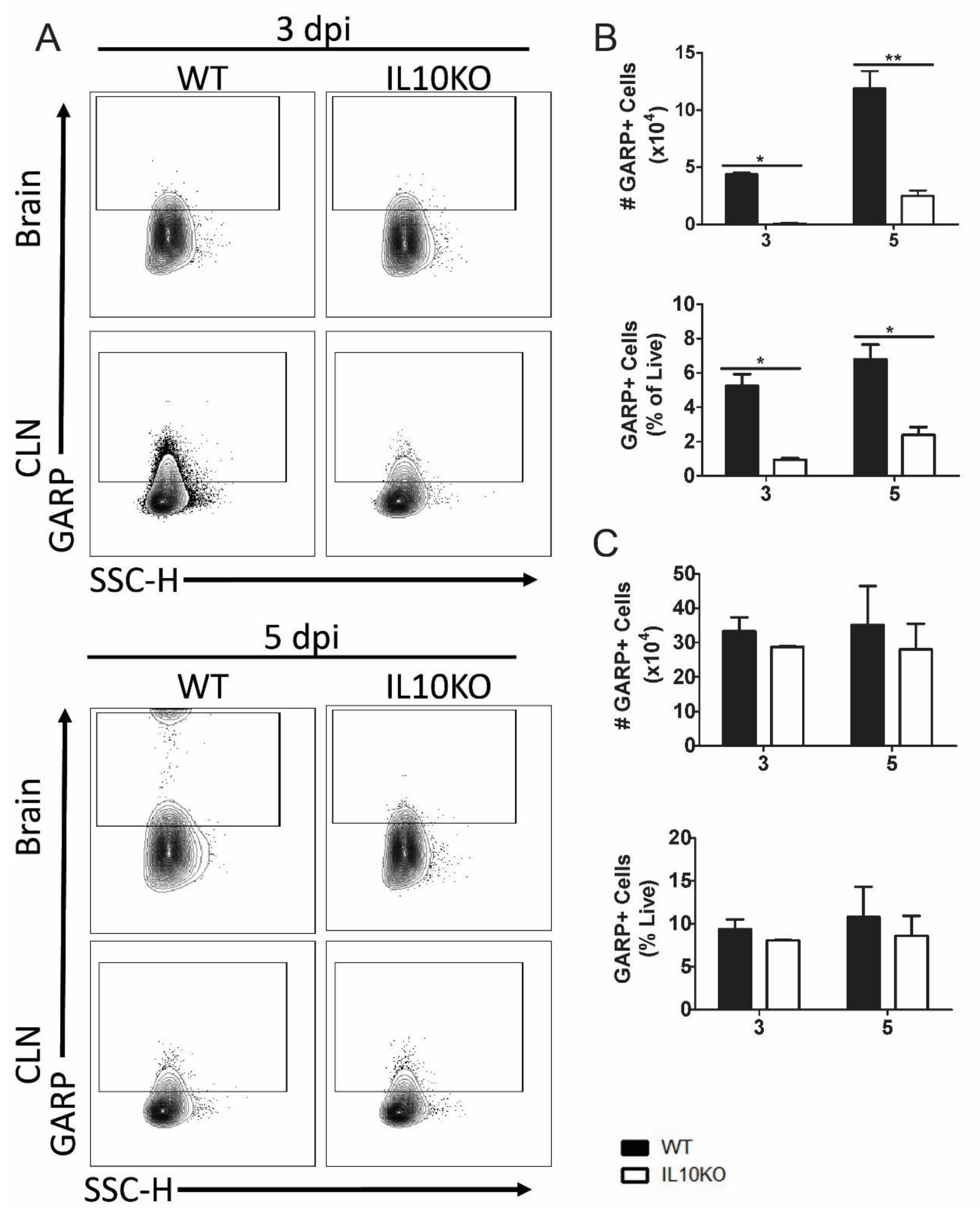
3.3. Changes in Lymphocyte Expression of Surface Proteins That Bind TGFβ
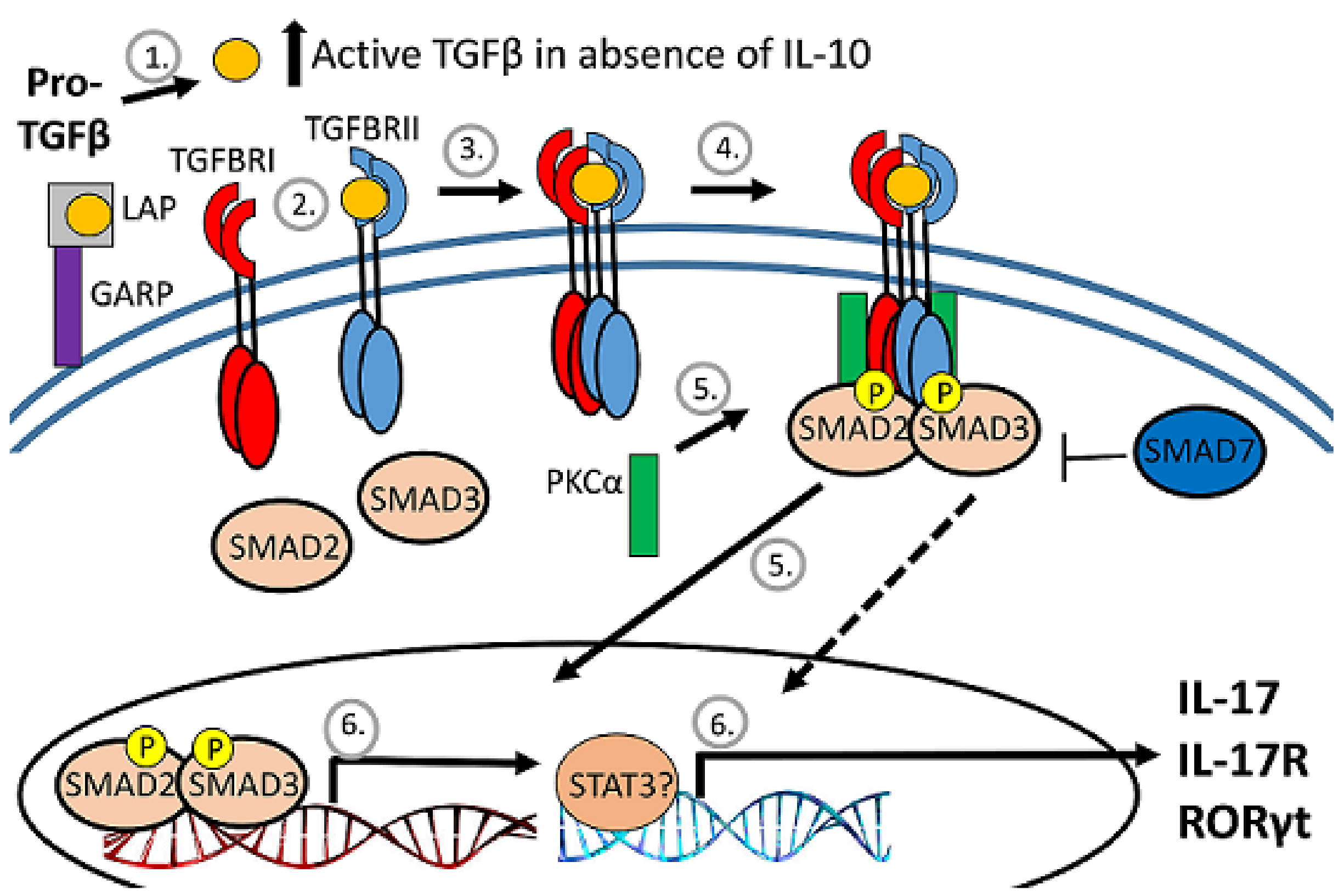
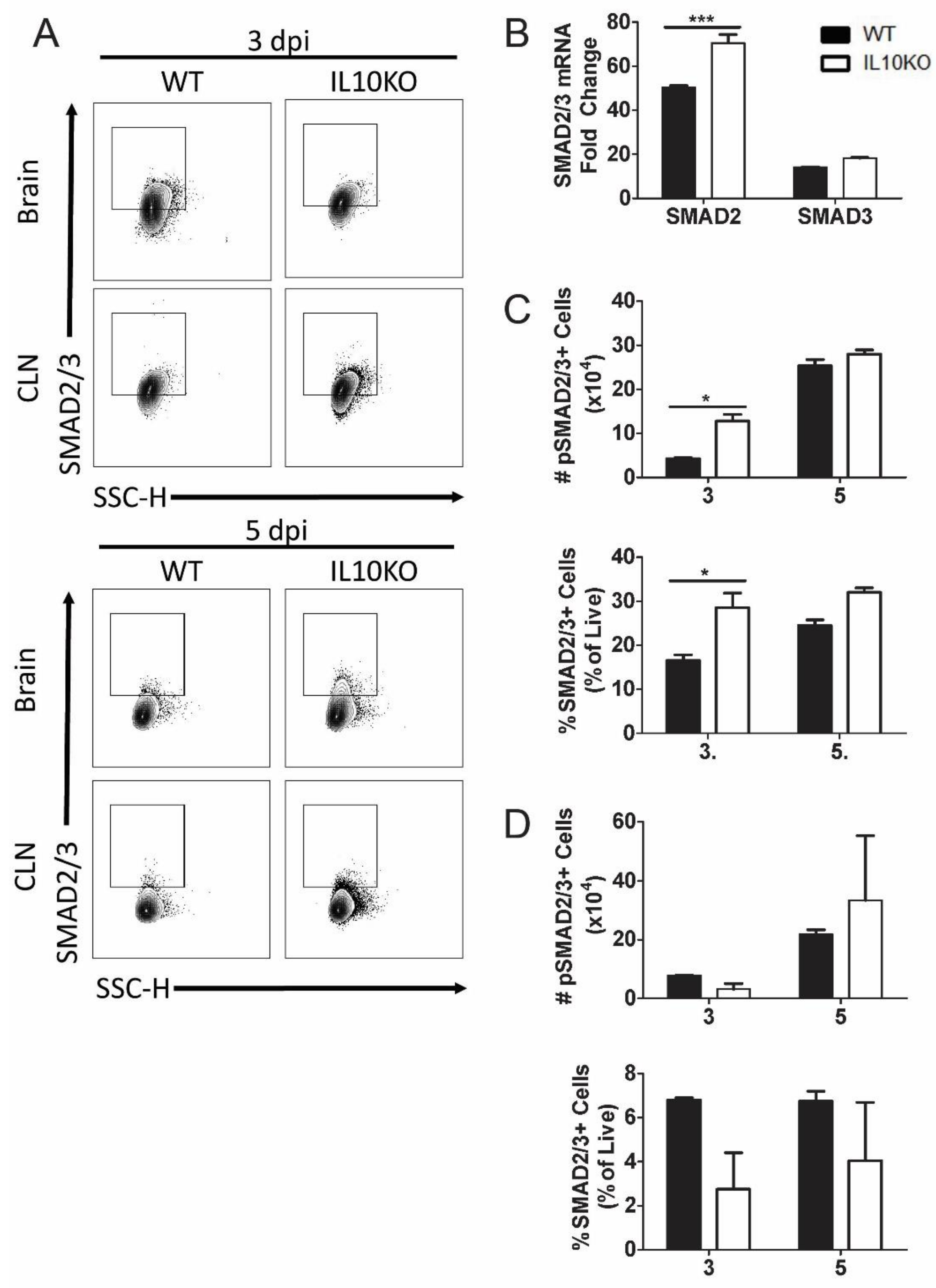
3.4. Effect of IL-10 Deficiency on Expression and Activation of Smad Transcription Factors
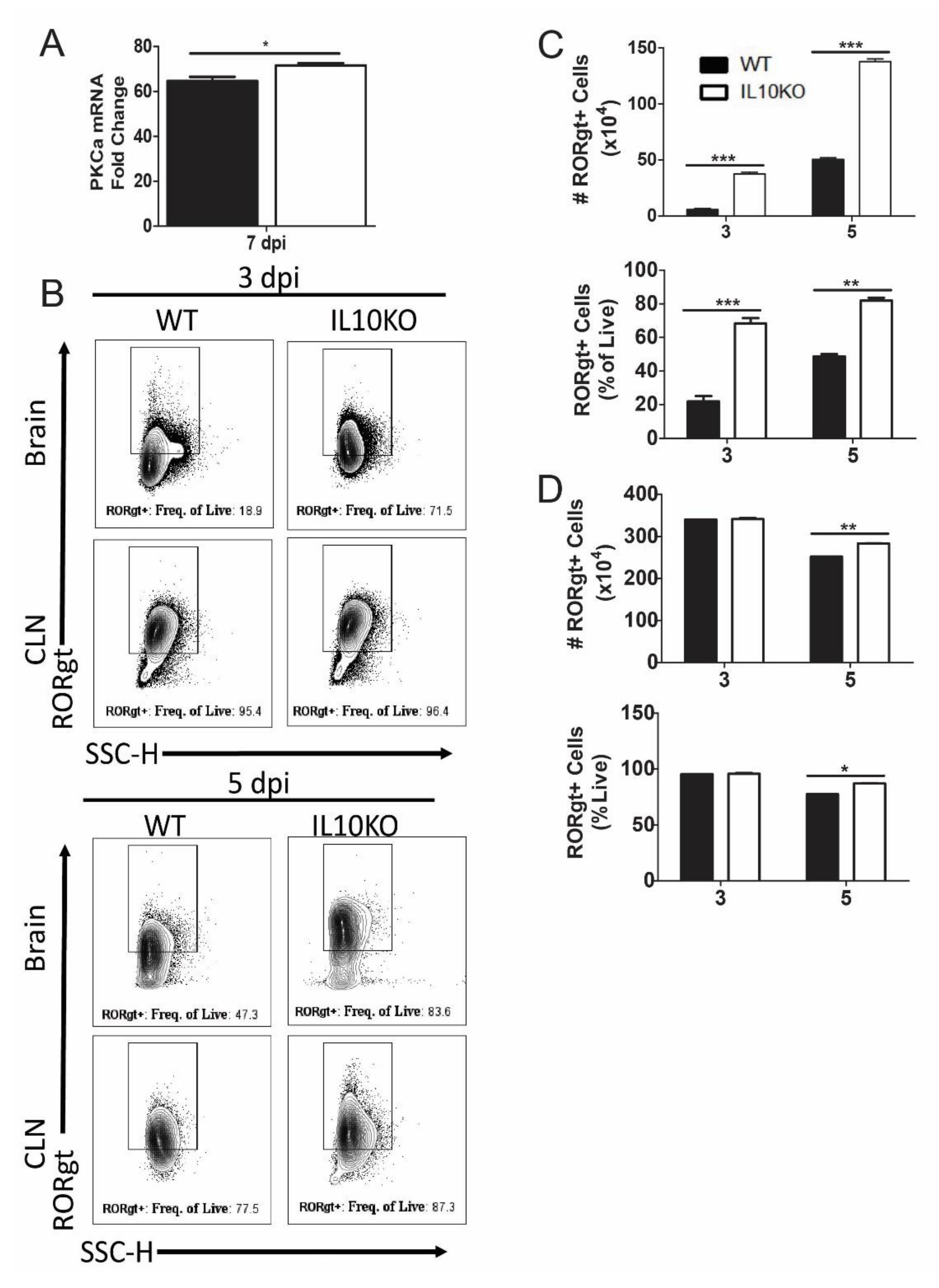
3.5. IL10 Deficiency and TGFβ Upregulation Associated with Expression of Pkca and RORgt
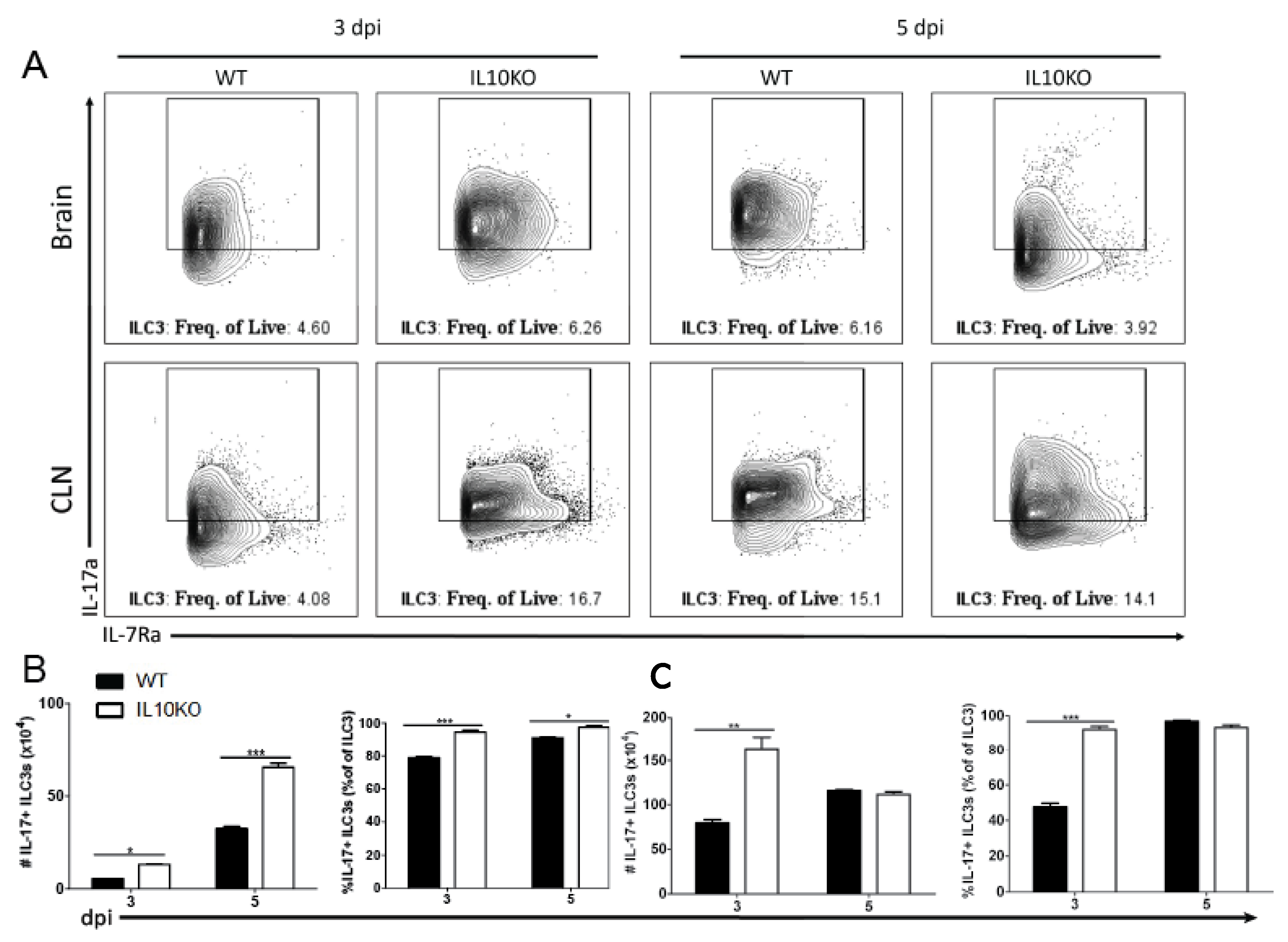
3.6. IL10 Deficiency and TGFβ Upregulation Associated with IL-17A-Producing ILC3s
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffin, D.E. Viral encephalomyelitis. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.E. Emergence and re-emergence of viral diseases of the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H. Medically important arboviruses of the United States and Canada. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 7, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.A.; Misasi, J.; Smole, S.; Feldman, H.A.; Cohen, A.B.; Santagata, S.; McManus, M.; Ahmed, A.A. Eastern equine encephalitis in children, Massachusetts and New Hampshire, USA, 1970–2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A.P.; Navarro-Lopez, R.; Ramirez-Aguilar, F.J.; Lopez-Gonzalez, I.; Leal, G.; Flores-Mayorga, J.M.; da Rosa, A.P.A.T.; Saxton-Shaw, K.D.; Singh, A.J.; Borland, E.M.; et al. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus activity in the Gulf Coast region of Mexico, 2003–2010. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Estrada-Franco, J.G.; Navarro-Lopez, R.; Ferro, C.; Haddow, A.D.; Weaver, S.C. Endemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in the Americas: Hidden under the dengue umbrella. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adouchief, S.; Smura, T.; Sane, J.; Vapalahti, O.; Kurkela, S. Sindbis virus as a human pathogen-epidemiology, clinical picture and pathogenesis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2016, 26, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.C.; Moench, T.R.; Trapp, B.D.; Griffin, D.E. Basis of neurovirulence in Sindbis virus encephalomyelitis of mice. Lab. Investig. Tech. Methods Pathol. 1988, 58, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.C.; Moench, T.R.; Griffin, D.E.; Johnson, R.T. The pathogenesis of spinal cord involvement in the encephalomyelitis of mice caused by neuroadapted Sindbis virus infection. Lab. Investig. Tech. Methods Pathol. 1987, 56, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Greene, I.P.; Coffey, L.L.; Medina, G.; Moncayo, A.C.; Anishchenko, M.; Ludwig, G.V.; Turell, M.J.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Lee, J.; et al. Endemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in northern Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Weaver, S.; Turell, M.J.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Rios, Z.; Huaman, A.; Klein, T.A.; Tesh, R.B.; Watts, D.M.; Olson, J.; et al. Endemic eastern equine encephalitis in the Amazon region of Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.E. Role of the immune response in age-dependent resistance of mice to encephalitis due to Sindbis virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 133, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, P.C.; Strauss, E.G.; Kuhn, R.J.; Strauss, J.H.; Griffin, D.E. Viral determinants of age-dependent virulence of Sindbis virus for mice. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4605–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, S.; Jackson, A.C.; Hahn, C.S.; Griffin, D.E.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H. Molecular basis of Sindbis virus neurovirulence in mice. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, L.A.; Griffin, D.E. Pathogenesis of encephalitis induced in newborn mice by virulent and avirulent strains of Sindbis virus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.E.; Levine, B.; Tyor, W.R.; Tucker, P.C.; Hardwick, J.M. Age-dependent susceptibility to fatal encephalitis: Alphavirus infection of neurons. Arch. Virol. Suppl. 1994, 9, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Griffin, D.E. The role of CD8(+) T cells and major histocompatibility complex class I expression in the central nervous system of mice infected with neurovirulent Sindbis virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6117–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, J.F.; Griffin, D.E. Contribution of T cells to mortality in neurovirulent Sindbis virus encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 127, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, S.; Baxter, V.K.; Schultz, K.L.; Slusher, B.S.; Griffin, D.E. Protective effects of glutamine antagonist DON in mice with alphaviral encephalomyelitis. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9251–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, I.P.; Lee, E.Y.; Prow, N.; Ngwang, B.; Griffin, D.E. Protection from fatal viral encephalomyelitis: AMPA receptor antagonists have a direct effect on the inflammatory response to infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3575–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.O.; Flavell, R.A. Contextual regulation of inflammation: A duet by transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10. Immunity 2008, 28, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulcsar, K.A.; Baxter, V.K.; Greene, I.P.; Griffin, D.E. Interleukin 10 modulation of pathogenic Th17 cells during fatal alphavirus encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16053–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulcsar, K.A.; Griffin, D.E. T cell-derived interleukin-10 is an important regulator of the Th17 response during lethal alphavirus encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 295–296, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, A.; Samstein, R.M.; Treuting, P.; Liang, Y.; Pils, M.C.; Heinrich, J.-M.; Jack, R.S.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Brüning, J.C.; Müller, W.; et al. Interleukin-10 signaling in regulatory T cells is required for suppression of Th17 cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity 2011, 34, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.M.; Griffin, D.E. Interleukin-10 Modulation of Virus Clearance and Disease in Mice with Alphaviral Encephalomyelitis. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01517-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, K.N.; Blount, D.G.; Riley, E.M. IL-10: The master regulator of immunity to infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.P.; Sheikh, F.; Kotenko, S.V.; Dickensheets, H. The expanded family of class II cytokines that share the IL-10 receptor-2 (IL-10R2) chain. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Peng, X.; Insolera, R.; Fink, D.J.; Mata, M. IL-10 promotes neuronal survival following spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 220, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Derynck, R.; Miyazono, K. TGF-beta and the TGF-beta Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2016, 8, a021873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ten Dijke, P. Immunoregulation by members of the TGFbeta superfamily. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.O.; Wan, Y.Y.; Sanjabi, S.; Robertson, A.K.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 99–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, J.; Dong, X.; Shi, M.; Lu, C.; Springer, T.A. GARP regulates the bioavailability and activation of TGFbeta. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, A.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Mori, T. Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by TGF-beta. J. Biochem. 2010, 147, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.W.; Severin, M.E.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. TGF-beta regulation of encephalitogenic and regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbanks, G.A.; Streilein, J.W. Fluids from immune privileged sites endow macrophages with the capacity to induce antigen-specific immune deviation via a mechanism involving transforming growth factor-beta. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitkovic, L.; Maeda, S.; Sternberg, E. Anti-inflammatory cytokines: Expression and action in the brain. Neuroimmunomodulation 2001, 9, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.Q.; Andersson, J.; Wang, R.; Ramsey, H.; Unutmaz, D.; Shevach, E.M. GARP (LRRC32) is essential for the surface expression of latent TGF-beta on platelets and activated FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13445–13450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Schultz, K.L.; Griffin, D.E. Mice deficient in interferon-gamma or interferon-gamma receptor 1 have distinct inflammatory responses to acute viral encephalomyelitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thach, D.C.; Kimura, T.; Griffin, D.E. Differences between C57BL/6 and BALB/cBy mice in mortality and virus replication after intranasal infection with neuroadapted Sindbis virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6156–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, M.A.; Sheppard, D. TGF-beta activation and function in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 51–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockis, J.; Colau, D.; Coulie, P.G.; Lucas, S. Membrane protein GARP is a receptor for latent TGF-beta on the surface of activated human Treg. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Jin, H.; Li, H. GARP: A surface molecule of regulatory T cells that is involved in the regulatory function and TGF-beta releasing. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42826–42836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.M.; Petty, C.S.; Tompkins, M.B.; Fogle, J.E. CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells activated during feline immunodeficiency virus infection convert T helper cells into functional suppressors through a membrane-bound TGFbeta/GARP-mediated mechanism. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kozhaya, L.; Mercer, F.; Khaitan, A.; Fujii, H.; Unutmaz, D. Expression of GARP selectively identifies activated human FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13439–13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lopes, J.E.; Chong, M.M.; Ivanov, I.I.; Min, R.; Victora, G.D.; Shen, Y.; Du, J.; Rubtsov, Y.P.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature 2008, 453, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, N.; Kang, J. SMAD regulatory networks construct a balanced immune system. Immunology 2013, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyama, K.; Sekiya, T.; Inoue, N.; Tamiya, T.; Kashiwagi, I.; Kimura, A.; Morita, R.; Muto, G.; Shichita, T.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Transcription factor Smad-independent T helper 17 cell induction by transforming-growth factor-beta is mediated by suppression of eomesodermin. Immunity 2011, 34, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, M.; Hermann-Kleiter, N.; Hinterleitner, R.; Gruber, T.; Wachowicz, K.; Pfeifhofer-Obermair, C.; Fresser, F.; Leitges, M.; Soldani, C.; Viola, A.; et al. The kinase PKCalpha selectively upregulates interleukin-17A during Th17 cell immune responses. Immunity 2013, 38, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.K.; Brown, M.A. Group 3 innate lymphoid cells accumulate and exhibit disease-induced activation in the meninges in EAE. Cell Immunol. 2015, 297, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatori, H.; Kanno, Y.; Watford, W.T.; Tato, C.M.; Weiss, G.; Ivanov, I.I.; Littman, D.R.; O’Shea, J.J. Lymphoid tissue inducer-like cells are an innate source of IL-17 and IL-22. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiator, A.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. Innate lymphoid cells: New players in IL-17-mediated antifungal immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, J.; Steffen, J.F.; Muntau, B.; Gisbrecht, J.; Pörtner, K.; Herden, C.; Niller, H.H.; Bauswein, M.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Mehlhoop, U.; et al. Human Borna disease virus 1 encephalitis shows marked pro-inflammatory biomarker and tissue immunoactivation during the course of disease. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, I.; Libbey, J.E.; Fujinami, R.S. TGF-beta1 suppresses T cell infiltration and VP2 puff B mutation enhances apoptosis in acute polioencephalitis induced by Theiler’s virus. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 190, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.J.; Mott, K.R.; Wechsler, S.L.; Flavell, R.A.; Town, T.; Ghiasi, H. Adaptive and innate transforming growth factor beta signaling impact herpes simplex virus 1 latency and reactivation. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11448–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Beckham, J.D.; Tuttle, K.; Tyler, K.L. Reovirus activates transforming growth factor beta and bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathways in the central nervous system that contribute to neuronal survival following infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5035–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkel, M.; Mjosberg, J. Dysregulation of Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinstry, K.K.; Strutt, T.M.; Buck, A.; Curtis, J.D.; Dibble, J.P.; Huston, G.; Tighe, M.; Hamada, H.; Sell, S.; Dutton, R.W.; et al. IL-10 deficiency unleashes an influenza-specific Th17 response and enhances survival against high-dose challenge. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 7353–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, T.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.; Bettelli, E. Th17 cells: Effector T cells with inflammatory properties. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Gagliani, N.; Esplugues, E.; O’Connor, W.; Huber, F.J.; Chaudhry, A.; Kamanaka, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Booth, C.J.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. Th17 cells express interleukin-10 receptor and are controlled by Foxp3− and Foxp3+ regulatory CD4+ T cells in an interleukin-10-dependent manner. Immunity 2011, 34, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaka, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Katoh, I.; Takio, K.; Ikawa, Y. Induction of manganese-superoxide dismutase in MRC-5 cells persistently infected with an alphavirus, sindbis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 261, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Awasthi, A.; Yosef, N.; Xiao, S.; Peters, A.; Wu, C.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Kunder, S.; Hafler, D.A.; Sobel, R.A. Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic TH17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. Th17 cells, pathogenic or not? TGF-beta3 imposes the embargo. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, N.M.; Griffin, D.E. Effect of IL-10 Deficiency on TGFβ Expression during Fatal Alphavirus Encephalomyelitis in C57Bl/6 Mice. Viruses 2022, 14, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081791
Martin NM, Griffin DE. Effect of IL-10 Deficiency on TGFβ Expression during Fatal Alphavirus Encephalomyelitis in C57Bl/6 Mice. Viruses. 2022; 14(8):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081791
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Nina M., and Diane E. Griffin. 2022. "Effect of IL-10 Deficiency on TGFβ Expression during Fatal Alphavirus Encephalomyelitis in C57Bl/6 Mice" Viruses 14, no. 8: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081791
APA StyleMartin, N. M., & Griffin, D. E. (2022). Effect of IL-10 Deficiency on TGFβ Expression during Fatal Alphavirus Encephalomyelitis in C57Bl/6 Mice. Viruses, 14(8), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081791





